+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`fn`
+ |
+
+The function to run. The output must be a tf.nest of `Tensor`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`args`
+ |
+
+(Optional) Positional arguments to `fn`.
+ |
+
+|
+`kwargs`
+ |
+
+(Optional) Keyword arguments to `fn`.
+ |
+
+|
+`options`
+ |
+
+(Optional) An instance of tf.distribute.RunOptions specifying
+the options to run `fn`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+Merged return value of `fn` across replicas. The structure of the return
+value is the same as the return value from `fn`. Each element in the
+structure can either be tf.distribute.DistributedValues, `Tensor`
+objects, or `Tensor`s (for example, if running on a single replica).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+scope
+
+View source
+
+
+scope()
+
+
+Returns a context manager selecting this Strategy as current.
+
+Inside a `with strategy.scope():` code block, this thread
+will use a variable creator set by `strategy`, and will
+enter its "cross-replica context".
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A context manager.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+update_config_proto
+
+View source
+
+
+update_config_proto(
+ config_proto
+)
+
+
+Returns a copy of `config_proto` modified for use with this strategy.
+
+DEPRECATED: This method is not available in TF 2.x.
+
+The updated config has something needed to run a strategy, e.g.
+configuration to run collective ops, or device filters to improve
+distributed training performance.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`config_proto`
+ |
+
+a `tf.ConfigProto` object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The updated copy of the `config_proto`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distribute/experimental/TPUStrategy.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distribute/experimental/TPUStrategy.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..2955dd066b1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distribute/experimental/TPUStrategy.md
@@ -0,0 +1,941 @@
+description: TPU distribution strategy implementation.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.distribute.experimental.TPUStrategy
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+TPU distribution strategy implementation.
+
+Inherits From: [`Strategy`](../../../../../tf/compat/v1/distribute/Strategy.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.distribute.experimental.TPUStrategy(
+ tpu_cluster_resolver=None, steps_per_run=None, device_assignment=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`tpu_cluster_resolver`
+ |
+
+A tf.distribute.cluster_resolver.TPUClusterResolver,
+which provides information about the TPU cluster.
+ |
+
+|
+`steps_per_run`
+ |
+
+Number of steps to run on device before returning to the
+host. Note that this can have side-effects on performance, hooks,
+metrics, summaries etc.
+This parameter is only used when Distribution Strategy is used with
+estimator or keras.
+ |
+
+|
+`device_assignment`
+ |
+
+Optional tf.tpu.experimental.DeviceAssignment to
+specify the placement of replicas on the TPU cluster. Currently only
+supports the usecase of using a single core within a TPU cluster.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`extended`
+ |
+
+tf.distribute.StrategyExtended with additional methods.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_replicas_in_sync`
+ |
+
+Returns number of replicas over which gradients are aggregated.
+ |
+
+|
+`steps_per_run`
+ |
+
+DEPRECATED: use .extended.steps_per_run instead.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+experimental_distribute_dataset
+
+View source
+
+
+experimental_distribute_dataset(
+ dataset
+)
+
+
+Distributes a tf.data.Dataset instance provided via `dataset`.
+
+The returned distributed dataset can be iterated over similar to how
+regular datasets can.
+NOTE: Currently, the user cannot add any more transformations to a
+distributed dataset.
+
+The following is an example:
+
+```python
+strategy = tf.distribute.MirroredStrategy()
+
+# Create a dataset
+dataset = dataset_ops.Dataset.TFRecordDataset([
+ "/a/1.tfr", "/a/2.tfr", "/a/3.tfr", "/a/4.tfr"])
+
+# Distribute that dataset
+dist_dataset = strategy.experimental_distribute_dataset(dataset)
+
+# Iterate over the distributed dataset
+for x in dist_dataset:
+ # process dataset elements
+ strategy.run(train_step, args=(x,))
+```
+
+We will assume that the input dataset is batched by the
+global batch size. With this assumption, we will make a best effort to
+divide each batch across all the replicas (one or more workers).
+
+In a multi-worker setting, we will first attempt to distribute the dataset
+by attempting to detect whether the dataset is being created out of
+ReaderDatasets (e.g. TFRecordDataset, TextLineDataset, etc.) and if so,
+attempting to shard the input files. Note that there has to be at least one
+input file per worker. If you have less than one input file per worker, we
+suggest that you should disable distributing your dataset using the method
+below.
+
+If that attempt is unsuccessful (e.g. the dataset is created from a
+Dataset.range), we will shard the dataset evenly at the end by appending a
+`.shard` operation to the end of the processing pipeline. This will cause
+the entire preprocessing pipeline for all the data to be run on every
+worker, and each worker will do redundant work. We will print a warning
+if this method of sharding is selected.
+
+You can disable dataset sharding across workers using the
+`auto_shard_policy` option in tf.data.experimental.DistributeOptions.
+
+Within each worker, we will also split the data among all the worker
+devices (if more than one a present), and this will happen even if
+multi-worker sharding is disabled using the method above.
+
+If the above batch splitting and dataset sharding logic is undesirable,
+please use `experimental_distribute_datasets_from_function` instead, which
+does not do any automatic splitting or sharding.
+
+You can also use the `element_spec` property of the distributed dataset
+returned by this API to query the tf.TypeSpec of the elements returned
+by the iterator. This can be used to set the `input_signature` property
+of a tf.function.
+
+```python
+strategy = tf.distribute.MirroredStrategy()
+
+# Create a dataset
+dataset = dataset_ops.Dataset.TFRecordDataset([
+ "/a/1.tfr", "/a/2.tfr", "/a/3.tfr", "/a/4.tfr"])
+
+# Distribute that dataset
+dist_dataset = strategy.experimental_distribute_dataset(dataset)
+
+@tf.function(input_signature=[dist_dataset.element_spec])
+def train_step(inputs):
+ # train model with inputs
+ return
+
+# Iterate over the distributed dataset
+for x in dist_dataset:
+ # process dataset elements
+ strategy.run(train_step, args=(x,))
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`dataset`
+ |
+
+tf.data.Dataset that will be sharded across all replicas using
+the rules stated above.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+A "distributed `Dataset`", which acts like a tf.data.Dataset except
+it produces "per-replica" values.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+experimental_distribute_datasets_from_function
+
+View source
+
+
+experimental_distribute_datasets_from_function(
+ dataset_fn
+)
+
+
+Distributes tf.data.Dataset instances created by calls to `dataset_fn`.
+
+`dataset_fn` will be called once for each worker in the strategy. Each
+replica on that worker will dequeue one batch of inputs from the local
+`Dataset` (i.e. if a worker has two replicas, two batches will be dequeued
+from the `Dataset` every step).
+
+This method can be used for several purposes. For example, where
+`experimental_distribute_dataset` is unable to shard the input files, this
+method might be used to manually shard the dataset (avoiding the slow
+fallback behavior in `experimental_distribute_dataset`). In cases where the
+dataset is infinite, this sharding can be done by creating dataset replicas
+that differ only in their random seed.
+`experimental_distribute_dataset` may also sometimes fail to split the
+batch across replicas on a worker. In that case, this method can be used
+where that limitation does not exist.
+
+The `dataset_fn` should take an tf.distribute.InputContext instance where
+information about batching and input replication can be accessed:
+
+```
+def dataset_fn(input_context):
+ batch_size = input_context.get_per_replica_batch_size(global_batch_size)
+ d = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensors([[1.]]).repeat().batch(batch_size)
+ return d.shard(
+ input_context.num_input_pipelines, input_context.input_pipeline_id)
+
+inputs = strategy.experimental_distribute_datasets_from_function(dataset_fn)
+
+for batch in inputs:
+ replica_results = strategy.run(replica_fn, args=(batch,))
+```
+
+IMPORTANT: The tf.data.Dataset returned by `dataset_fn` should have a
+per-replica batch size, unlike `experimental_distribute_dataset`, which uses
+the global batch size. This may be computed using
+`input_context.get_per_replica_batch_size`.
+
+To query the tf.TypeSpec of the elements in the distributed dataset
+returned by this API, you need to use the `element_spec` property of the
+distributed iterator. This tf.TypeSpec can be used to set the
+`input_signature` property of a tf.function.
+
+```python
+# If you want to specify `input_signature` for a `tf.function` you must
+# first create the iterator.
+iterator = iter(inputs)
+
+@tf.function(input_signature=[iterator.element_spec])
+def replica_fn_with_signature(inputs):
+ # train the model with inputs
+ return
+
+for _ in range(steps):
+ strategy.run(replica_fn_with_signature,
+ args=(next(iterator),))
+```
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+A "distributed `Dataset`", which acts like a tf.data.Dataset except
+it produces "per-replica" values.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+experimental_local_results
+
+View source
+
+
+experimental_local_results(
+ value
+)
+
+
+Returns the list of all local per-replica values contained in `value`.
+
+Note: This only returns values on the worker initiated by this client.
+When using a tf.distribute.Strategy like
+tf.distribute.experimental.MultiWorkerMirroredStrategy, each worker
+will be its own client, and this function will only return values
+computed on that worker.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+A value returned by `experimental_run()`, `run()`,
+`extended.call_for_each_replica()`, or a variable created in `scope`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A tuple of values contained in `value`. If `value` represents a single
+value, this returns `(value,).`
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+experimental_make_numpy_dataset
+
+View source
+
+
+experimental_make_numpy_dataset(
+ numpy_input, session=None
+)
+
+
+Makes a tf.data.Dataset for input provided via a numpy array.
+
+This avoids adding `numpy_input` as a large constant in the graph,
+and copies the data to the machine or machines that will be processing
+the input.
+
+Note that you will likely need to use
+tf.distribute.Strategy.experimental_distribute_dataset
+with the returned dataset to further distribute it with the strategy.
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+```
+numpy_input = np.ones([10], dtype=np.float32)
+dataset = strategy.experimental_make_numpy_dataset(numpy_input)
+dist_dataset = strategy.experimental_distribute_dataset(dataset)
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`numpy_input`
+ |
+
+A nest of NumPy input arrays that will be converted into a
+dataset. Note that lists of Numpy arrays are stacked, as that is normal
+tf.data.Dataset behavior.
+ |
+
+|
+`session`
+ |
+
+(TensorFlow v1.x graph execution only) A session used for
+initialization.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+experimental_run
+
+View source
+
+
+experimental_run(
+ fn, input_iterator=None
+)
+
+
+Runs ops in `fn` on each replica, with inputs from `input_iterator`.
+
+DEPRECATED: This method is not available in TF 2.x. Please switch
+to using `run` instead.
+
+When eager execution is enabled, executes ops specified by `fn` on each
+replica. Otherwise, builds a graph to execute the ops on each replica.
+
+Each replica will take a single, different input from the inputs provided by
+one `get_next` call on the input iterator.
+
+`fn` may call tf.distribute.get_replica_context() to access members such
+as `replica_id_in_sync_group`.
+
+IMPORTANT: Depending on the tf.distribute.Strategy implementation being
+used, and whether eager execution is enabled, `fn` may be called one or more
+times (once for each replica).
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`fn`
+ |
+
+The function to run. The inputs to the function must match the outputs
+of `input_iterator.get_next()`. The output must be a tf.nest of
+`Tensor`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`input_iterator`
+ |
+
+(Optional) input iterator from which the inputs are taken.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Merged return value of `fn` across replicas. The structure of the return
+value is the same as the return value from `fn`. Each element in the
+structure can either be `PerReplica` (if the values are unsynchronized),
+`Mirrored` (if the values are kept in sync), or `Tensor` (if running on a
+single replica).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+make_dataset_iterator
+
+View source
+
+
+make_dataset_iterator(
+ dataset
+)
+
+
+Makes an iterator for input provided via `dataset`.
+
+DEPRECATED: This method is not available in TF 2.x.
+
+Data from the given dataset will be distributed evenly across all the
+compute replicas. We will assume that the input dataset is batched by the
+global batch size. With this assumption, we will make a best effort to
+divide each batch across all the replicas (one or more workers).
+If this effort fails, an error will be thrown, and the user should instead
+use `make_input_fn_iterator` which provides more control to the user, and
+does not try to divide a batch across replicas.
+
+The user could also use `make_input_fn_iterator` if they want to
+customize which input is fed to which replica/worker etc.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`dataset`
+ |
+
+tf.data.Dataset that will be distributed evenly across all
+replicas.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An `tf.distribute.InputIterator` which returns inputs for each step of the
+computation. User should call `initialize` on the returned iterator.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+View source
+
+
+make_input_fn_iterator(
+ input_fn, replication_mode=tf.distribute.InputReplicationMode.PER_WORKER
+)
+
+
+Returns an iterator split across replicas created from an input function.
+
+DEPRECATED: This method is not available in TF 2.x.
+
+The `input_fn` should take an tf.distribute.InputContext object where
+information about batching and input sharding can be accessed:
+
+```
+def input_fn(input_context):
+ batch_size = input_context.get_per_replica_batch_size(global_batch_size)
+ d = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensors([[1.]]).repeat().batch(batch_size)
+ return d.shard(input_context.num_input_pipelines,
+ input_context.input_pipeline_id)
+with strategy.scope():
+ iterator = strategy.make_input_fn_iterator(input_fn)
+ replica_results = strategy.experimental_run(replica_fn, iterator)
+```
+
+The tf.data.Dataset returned by `input_fn` should have a per-replica
+batch size, which may be computed using
+`input_context.get_per_replica_batch_size`.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An iterator object that should first be `.initialize()`-ed. It may then
+either be passed to `strategy.experimental_run()` or you can
+`iterator.get_next()` to get the next value to pass to
+`strategy.extended.call_for_each_replica()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+reduce
+
+View source
+
+
+reduce(
+ reduce_op, value, axis=None
+)
+
+
+Reduce `value` across replicas.
+
+Given a per-replica value returned by `run`, say a
+per-example loss, the batch will be divided across all the replicas. This
+function allows you to aggregate across replicas and optionally also across
+batch elements. For example, if you have a global batch size of 8 and 2
+replicas, values for examples `[0, 1, 2, 3]` will be on replica 0 and
+`[4, 5, 6, 7]` will be on replica 1. By default, `reduce` will just
+aggregate across replicas, returning `[0+4, 1+5, 2+6, 3+7]`. This is useful
+when each replica is computing a scalar or some other value that doesn't
+have a "batch" dimension (like a gradient). More often you will want to
+aggregate across the global batch, which you can get by specifying the batch
+dimension as the `axis`, typically `axis=0`. In this case it would return a
+scalar `0+1+2+3+4+5+6+7`.
+
+If there is a last partial batch, you will need to specify an axis so
+that the resulting shape is consistent across replicas. So if the last
+batch has size 6 and it is divided into [0, 1, 2, 3] and [4, 5], you
+would get a shape mismatch unless you specify `axis=0`. If you specify
+tf.distribute.ReduceOp.MEAN, using `axis=0` will use the correct
+denominator of 6. Contrast this with computing `reduce_mean` to get a
+scalar value on each replica and this function to average those means,
+which will weigh some values `1/8` and others `1/4`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`reduce_op`
+ |
+
+A tf.distribute.ReduceOp value specifying how values should
+be combined.
+ |
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+A "per replica" value, e.g. returned by `run` to
+be combined into a single tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`axis`
+ |
+
+Specifies the dimension to reduce along within each
+replica's tensor. Should typically be set to the batch dimension, or
+`None` to only reduce across replicas (e.g. if the tensor has no batch
+dimension).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+run
+
+View source
+
+
+run(
+ fn, args=(), kwargs=None, options=None
+)
+
+
+Run `fn` on each replica, with the given arguments.
+
+Executes ops specified by `fn` on each replica. If `args` or `kwargs` have
+"per-replica" values, such as those produced by a "distributed `Dataset`",
+when `fn` is executed on a particular replica, it will be executed with the
+component of those "per-replica" values that correspond to that replica.
+
+`fn` may call tf.distribute.get_replica_context() to access members such
+as `all_reduce`.
+
+All arguments in `args` or `kwargs` should either be nest of tensors or
+per-replica objects containing tensors or composite tensors.
+
+Users can pass strategy specific options to `options` argument. An example
+to enable bucketizing dynamic shapes in `TPUStrategy.run`
+is:
+```python
+
+resolver = tf.distribute.cluster_resolver.TPUClusterResolver(tpu='')
+tf.config.experimental_connect_to_cluster(resolver)
+tf.tpu.experimental.initialize_tpu_system(resolver)
+strategy = tf.distribute.experimental.TPUStrategy(tpu='')
+
+options = tf.distribute.RunOptions()
+options.experimental_bucketizing_dynamic_shape = True
+
+iterator = iter(inputs)
+
+@tf.function()
+def step_fn(inputs):
+ output = tf.reduce_sum(inputs)
+ return output
+
+ strategy.run(step_fn, args=(next(iterator),),
+ options=options)
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`fn`
+ |
+
+The function to run. The output must be a tf.nest of `Tensor`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`args`
+ |
+
+(Optional) Positional arguments to `fn`.
+ |
+
+|
+`kwargs`
+ |
+
+(Optional) Keyword arguments to `fn`.
+ |
+
+|
+`options`
+ |
+
+(Optional) An instance of tf.distribute.RunOptions specifying
+the options to run `fn`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Merged return value of `fn` across replicas. The structure of the return
+value is the same as the return value from `fn`. Each element in the
+structure can either be "per-replica" `Tensor` objects or `Tensor`s
+(for example, if running on a single replica).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+scope
+
+View source
+
+
+scope()
+
+
+Returns a context manager selecting this Strategy as current.
+
+Inside a `with strategy.scope():` code block, this thread
+will use a variable creator set by `strategy`, and will
+enter its "cross-replica context".
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A context manager.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+update_config_proto
+
+View source
+
+
+update_config_proto(
+ config_proto
+)
+
+
+Returns a copy of `config_proto` modified for use with this strategy.
+
+DEPRECATED: This method is not available in TF 2.x.
+
+The updated config has something needed to run a strategy, e.g.
+configuration to run collective ops, or device filters to improve
+distributed training performance.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`config_proto`
+ |
+
+a `tf.ConfigProto` object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The updated copy of the `config_proto`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distribute/get_loss_reduction.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distribute/get_loss_reduction.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..b4123996a21
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distribute/get_loss_reduction.md
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
+description: tf.distribute.ReduceOp corresponding to the last loss reduction.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.distribute.get_loss_reduction
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+tf.distribute.ReduceOp corresponding to the last loss reduction.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.distribute.get_loss_reduction()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This is used to decide whether loss should be scaled in optimizer (used only
+for estimator + v1 optimizer use case).
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..41fe91f055d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions.md
@@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
+description: Core module for TensorFlow distribution objects and helpers.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.distributions
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Core module for TensorFlow distribution objects and helpers.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class Bernoulli`](../../../tf/compat/v1/distributions/Bernoulli.md): Bernoulli distribution.
+
+[`class Beta`](../../../tf/compat/v1/distributions/Beta.md): Beta distribution.
+
+[`class Categorical`](../../../tf/compat/v1/distributions/Categorical.md): Categorical distribution.
+
+[`class Dirichlet`](../../../tf/compat/v1/distributions/Dirichlet.md): Dirichlet distribution.
+
+[`class DirichletMultinomial`](../../../tf/compat/v1/distributions/DirichletMultinomial.md): Dirichlet-Multinomial compound distribution.
+
+[`class Distribution`](../../../tf/compat/v1/distributions/Distribution.md): A generic probability distribution base class.
+
+[`class Exponential`](../../../tf/compat/v1/distributions/Exponential.md): Exponential distribution.
+
+[`class Gamma`](../../../tf/compat/v1/distributions/Gamma.md): Gamma distribution.
+
+[`class Laplace`](../../../tf/compat/v1/distributions/Laplace.md): The Laplace distribution with location `loc` and `scale` parameters.
+
+[`class Multinomial`](../../../tf/compat/v1/distributions/Multinomial.md): Multinomial distribution.
+
+[`class Normal`](../../../tf/compat/v1/distributions/Normal.md): The Normal distribution with location `loc` and `scale` parameters.
+
+[`class RegisterKL`](../../../tf/compat/v1/distributions/RegisterKL.md): Decorator to register a KL divergence implementation function.
+
+[`class ReparameterizationType`](../../../tf/compat/v1/distributions/ReparameterizationType.md): Instances of this class represent how sampling is reparameterized.
+
+[`class StudentT`](../../../tf/compat/v1/distributions/StudentT.md): Student's t-distribution.
+
+[`class Uniform`](../../../tf/compat/v1/distributions/Uniform.md): Uniform distribution with `low` and `high` parameters.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`kl_divergence(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/distributions/kl_divergence.md): Get the KL-divergence KL(distribution_a || distribution_b). (deprecated)
+
+## Other Members
+
+* `FULLY_REPARAMETERIZED`
+* `NOT_REPARAMETERIZED`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/Bernoulli.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/Bernoulli.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3a9957e6925
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/Bernoulli.md
@@ -0,0 +1,1458 @@
+description: Bernoulli distribution.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.distributions.Bernoulli
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Bernoulli distribution.
+
+Inherits From: [`Distribution`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/distributions/Distribution.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.distributions.Bernoulli(
+ logits=None, probs=None, dtype=tf.dtypes.int32, validate_args=(False),
+ allow_nan_stats=(True), name='Bernoulli'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The Bernoulli distribution with `probs` parameter, i.e., the probability of a
+`1` outcome (vs a `0` outcome).
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`logits`
+ |
+
+An N-D `Tensor` representing the log-odds of a `1` event. Each
+entry in the `Tensor` parametrizes an independent Bernoulli distribution
+where the probability of an event is sigmoid(logits). Only one of
+`logits` or `probs` should be passed in.
+ |
+
+|
+`probs`
+ |
+
+An N-D `Tensor` representing the probability of a `1`
+event. Each entry in the `Tensor` parameterizes an independent
+Bernoulli distribution. Only one of `logits` or `probs` should be passed
+in.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+The type of the event samples. Default: `int32`.
+ |
+
+|
+`validate_args`
+ |
+
+Python `bool`, default `False`. When `True` distribution
+parameters are checked for validity despite possibly degrading runtime
+performance. When `False` invalid inputs may silently render incorrect
+outputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`allow_nan_stats`
+ |
+
+Python `bool`, default `True`. When `True`,
+statistics (e.g., mean, mode, variance) use the value "`NaN`" to
+indicate the result is undefined. When `False`, an exception is raised
+if one or more of the statistic's batch members are undefined.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` name prefixed to Ops created by this class.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If p and logits are passed, or if neither are passed.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`allow_nan_stats`
+ |
+
+Python `bool` describing behavior when a stat is undefined.
+
+Stats return +/- infinity when it makes sense. E.g., the variance of a
+Cauchy distribution is infinity. However, sometimes the statistic is
+undefined, e.g., if a distribution's pdf does not achieve a maximum within
+the support of the distribution, the mode is undefined. If the mean is
+undefined, then by definition the variance is undefined. E.g. the mean for
+Student's T for df = 1 is undefined (no clear way to say it is either + or -
+infinity), so the variance = E[(X - mean)**2] is also undefined.
+ |
+
+|
+`batch_shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single event index as a `TensorShape`.
+
+May be partially defined or unknown.
+
+The batch dimensions are indexes into independent, non-identical
+parameterizations of this distribution.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+The `DType` of `Tensor`s handled by this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`event_shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single batch as a `TensorShape`.
+
+May be partially defined or unknown.
+ |
+
+|
+`logits`
+ |
+
+Log-odds of a `1` outcome (vs `0`).
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name prepended to all ops created by this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`parameters`
+ |
+
+Dictionary of parameters used to instantiate this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`probs`
+ |
+
+Probability of a `1` outcome (vs `0`).
+ |
+
+|
+`reparameterization_type`
+ |
+
+Describes how samples from the distribution are reparameterized.
+
+Currently this is one of the static instances
+`distributions.FULLY_REPARAMETERIZED`
+or `distributions.NOT_REPARAMETERIZED`.
+ |
+
+|
+`validate_args`
+ |
+
+Python `bool` indicating possibly expensive checks are enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+batch_shape_tensor
+
+View source
+
+
+batch_shape_tensor(
+ name='batch_shape_tensor'
+)
+
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single event index as a 1-D `Tensor`.
+
+The batch dimensions are indexes into independent, non-identical
+parameterizations of this distribution.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`batch_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+cdf
+
+View source
+
+
+cdf(
+ value, name='cdf'
+)
+
+
+Cumulative distribution function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the cumulative distribution function `cdf` is:
+
+```none
+cdf(x) := P[X <= x]
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cdf`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+copy
+
+View source
+
+
+copy(
+ **override_parameters_kwargs
+)
+
+
+Creates a deep copy of the distribution.
+
+Note: the copy distribution may continue to depend on the original
+initialization arguments.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`**override_parameters_kwargs`
+ |
+
+String/value dictionary of initialization
+arguments to override with new values.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`distribution`
+ |
+
+A new instance of `type(self)` initialized from the union
+of self.parameters and override_parameters_kwargs, i.e.,
+`dict(self.parameters, **override_parameters_kwargs)`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+covariance
+
+View source
+
+
+covariance(
+ name='covariance'
+)
+
+
+Covariance.
+
+Covariance is (possibly) defined only for non-scalar-event distributions.
+
+For example, for a length-`k`, vector-valued distribution, it is calculated
+as,
+
+```none
+Cov[i, j] = Covariance(X_i, X_j) = E[(X_i - E[X_i]) (X_j - E[X_j])]
+```
+
+where `Cov` is a (batch of) `k x k` matrix, `0 <= (i, j) < k`, and `E`
+denotes expectation.
+
+Alternatively, for non-vector, multivariate distributions (e.g.,
+matrix-valued, Wishart), `Covariance` shall return a (batch of) matrices
+under some vectorization of the events, i.e.,
+
+```none
+Cov[i, j] = Covariance(Vec(X)_i, Vec(X)_j) = [as above]
+```
+
+where `Cov` is a (batch of) `k' x k'` matrices,
+`0 <= (i, j) < k' = reduce_prod(event_shape)`, and `Vec` is some function
+mapping indices of this distribution's event dimensions to indices of a
+length-`k'` vector.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`covariance`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn, k', k']`
+where the first `n` dimensions are batch coordinates and
+`k' = reduce_prod(self.event_shape)`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+cross_entropy
+
+View source
+
+
+cross_entropy(
+ other, name='cross_entropy'
+)
+
+
+Computes the (Shannon) cross entropy.
+
+Denote this distribution (`self`) by `P` and the `other` distribution by
+`Q`. Assuming `P, Q` are absolutely continuous with respect to
+one another and permit densities `p(x) dr(x)` and `q(x) dr(x)`, (Shanon)
+cross entropy is defined as:
+
+```none
+H[P, Q] = E_p[-log q(X)] = -int_F p(x) log q(x) dr(x)
+```
+
+where `F` denotes the support of the random variable `X ~ P`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`other`
+ |
+
+`tfp.distributions.Distribution` instance.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cross_entropy`
+ |
+
+`self.dtype` `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn]`
+representing `n` different calculations of (Shanon) cross entropy.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+entropy
+
+View source
+
+
+entropy(
+ name='entropy'
+)
+
+
+Shannon entropy in nats.
+
+
+event_shape_tensor
+
+View source
+
+
+event_shape_tensor(
+ name='event_shape_tensor'
+)
+
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single batch as a 1-D int32 `Tensor`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`event_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+is_scalar_batch
+
+View source
+
+
+is_scalar_batch(
+ name='is_scalar_batch'
+)
+
+
+Indicates that `batch_shape == []`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`is_scalar_batch`
+ |
+
+`bool` scalar `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+is_scalar_event
+
+View source
+
+
+is_scalar_event(
+ name='is_scalar_event'
+)
+
+
+Indicates that `event_shape == []`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`is_scalar_event`
+ |
+
+`bool` scalar `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+kl_divergence
+
+View source
+
+
+kl_divergence(
+ other, name='kl_divergence'
+)
+
+
+Computes the Kullback--Leibler divergence.
+
+Denote this distribution (`self`) by `p` and the `other` distribution by
+`q`. Assuming `p, q` are absolutely continuous with respect to reference
+measure `r`, the KL divergence is defined as:
+
+```none
+KL[p, q] = E_p[log(p(X)/q(X))]
+ = -int_F p(x) log q(x) dr(x) + int_F p(x) log p(x) dr(x)
+ = H[p, q] - H[p]
+```
+
+where `F` denotes the support of the random variable `X ~ p`, `H[., .]`
+denotes (Shanon) cross entropy, and `H[.]` denotes (Shanon) entropy.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`other`
+ |
+
+`tfp.distributions.Distribution` instance.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`kl_divergence`
+ |
+
+`self.dtype` `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn]`
+representing `n` different calculations of the Kullback-Leibler
+divergence.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_cdf
+
+View source
+
+
+log_cdf(
+ value, name='log_cdf'
+)
+
+
+Log cumulative distribution function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the cumulative distribution function `cdf` is:
+
+```none
+log_cdf(x) := Log[ P[X <= x] ]
+```
+
+Often, a numerical approximation can be used for `log_cdf(x)` that yields
+a more accurate answer than simply taking the logarithm of the `cdf` when
+`x << -1`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`logcdf`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_prob
+
+View source
+
+
+log_prob(
+ value, name='log_prob'
+)
+
+
+Log probability density/mass function.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`log_prob`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_survival_function
+
+View source
+
+
+log_survival_function(
+ value, name='log_survival_function'
+)
+
+
+Log survival function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the survival function is defined:
+
+```none
+log_survival_function(x) = Log[ P[X > x] ]
+ = Log[ 1 - P[X <= x] ]
+ = Log[ 1 - cdf(x) ]
+```
+
+Typically, different numerical approximations can be used for the log
+survival function, which are more accurate than `1 - cdf(x)` when `x >> 1`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with values of type
+`self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+mean
+
+View source
+
+
+mean(
+ name='mean'
+)
+
+
+Mean.
+
+
+mode
+
+View source
+
+
+mode(
+ name='mode'
+)
+
+
+Mode.
+
+Additional documentation from `Bernoulli`:
+
+Returns `1` if `prob > 0.5` and `0` otherwise.
+
+param_shapes
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+param_shapes(
+ sample_shape, name='DistributionParamShapes'
+)
+
+
+Shapes of parameters given the desired shape of a call to `sample()`.
+
+This is a class method that describes what key/value arguments are required
+to instantiate the given `Distribution` so that a particular shape is
+returned for that instance's call to `sample()`.
+
+Subclasses should override class method `_param_shapes`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor` or python list/tuple. Desired shape of a call to
+`sample()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to prepend ops with.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`dict` of parameter name to `Tensor` shapes.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+param_static_shapes
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+param_static_shapes(
+ sample_shape
+)
+
+
+param_shapes with static (i.e. `TensorShape`) shapes.
+
+This is a class method that describes what key/value arguments are required
+to instantiate the given `Distribution` so that a particular shape is
+returned for that instance's call to `sample()`. Assumes that the sample's
+shape is known statically.
+
+Subclasses should override class method `_param_shapes` to return
+constant-valued tensors when constant values are fed.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+`TensorShape` or python list/tuple. Desired shape of a call
+to `sample()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`dict` of parameter name to `TensorShape`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `sample_shape` is a `TensorShape` and is not fully defined.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+prob
+
+View source
+
+
+prob(
+ value, name='prob'
+)
+
+
+Probability density/mass function.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`prob`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+quantile
+
+View source
+
+
+quantile(
+ value, name='quantile'
+)
+
+
+Quantile function. Aka "inverse cdf" or "percent point function".
+
+Given random variable `X` and `p in [0, 1]`, the `quantile` is:
+
+```none
+quantile(p) := x such that P[X <= x] == p
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`quantile`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+sample
+
+View source
+
+
+sample(
+ sample_shape=(), seed=None, name='sample'
+)
+
+
+Generate samples of the specified shape.
+
+Note that a call to `sample()` without arguments will generate a single
+sample.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+0D or 1D `int32` `Tensor`. Shape of the generated samples.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+Python integer seed for RNG
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`samples`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` with prepended dimensions `sample_shape`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+stddev
+
+View source
+
+
+stddev(
+ name='stddev'
+)
+
+
+Standard deviation.
+
+Standard deviation is defined as,
+
+```none
+stddev = E[(X - E[X])**2]**0.5
+```
+
+where `X` is the random variable associated with this distribution, `E`
+denotes expectation, and `stddev.shape = batch_shape + event_shape`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`stddev`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape identical to
+`batch_shape + event_shape`, i.e., the same shape as `self.mean()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+survival_function
+
+View source
+
+
+survival_function(
+ value, name='survival_function'
+)
+
+
+Survival function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the survival function is defined:
+
+```none
+survival_function(x) = P[X > x]
+ = 1 - P[X <= x]
+ = 1 - cdf(x).
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with values of type
+`self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+variance
+
+View source
+
+
+variance(
+ name='variance'
+)
+
+
+Variance.
+
+Variance is defined as,
+
+```none
+Var = E[(X - E[X])**2]
+```
+
+where `X` is the random variable associated with this distribution, `E`
+denotes expectation, and `Var.shape = batch_shape + event_shape`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`variance`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape identical to
+`batch_shape + event_shape`, i.e., the same shape as `self.mean()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/Beta.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/Beta.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..8b071bc086e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/Beta.md
@@ -0,0 +1,1567 @@
+description: Beta distribution.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.distributions.Beta
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Beta distribution.
+
+Inherits From: [`Distribution`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/distributions/Distribution.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.distributions.Beta(
+ concentration1=None, concentration0=None, validate_args=(False),
+ allow_nan_stats=(True), name='Beta'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The Beta distribution is defined over the `(0, 1)` interval using parameters
+`concentration1` (aka "alpha") and `concentration0` (aka "beta").
+
+#### Mathematical Details
+
+The probability density function (pdf) is,
+
+```none
+pdf(x; alpha, beta) = x**(alpha - 1) (1 - x)**(beta - 1) / Z
+Z = Gamma(alpha) Gamma(beta) / Gamma(alpha + beta)
+```
+
+where:
+
+* `concentration1 = alpha`,
+* `concentration0 = beta`,
+* `Z` is the normalization constant, and,
+* `Gamma` is the [gamma function](
+ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma_function).
+
+The concentration parameters represent mean total counts of a `1` or a `0`,
+i.e.,
+
+```none
+concentration1 = alpha = mean * total_concentration
+concentration0 = beta = (1. - mean) * total_concentration
+```
+
+where `mean` in `(0, 1)` and `total_concentration` is a positive real number
+representing a mean `total_count = concentration1 + concentration0`.
+
+Distribution parameters are automatically broadcast in all functions; see
+examples for details.
+
+Warning: The samples can be zero due to finite precision.
+This happens more often when some of the concentrations are very small.
+Make sure to round the samples to `np.finfo(dtype).tiny` before computing the
+density.
+
+Samples of this distribution are reparameterized (pathwise differentiable).
+The derivatives are computed using the approach described in
+(Figurnov et al., 2018).
+
+#### Examples
+
+```python
+import tensorflow_probability as tfp
+tfd = tfp.distributions
+
+# Create a batch of three Beta distributions.
+alpha = [1, 2, 3]
+beta = [1, 2, 3]
+dist = tfd.Beta(alpha, beta)
+
+dist.sample([4, 5]) # Shape [4, 5, 3]
+
+# `x` has three batch entries, each with two samples.
+x = [[.1, .4, .5],
+ [.2, .3, .5]]
+# Calculate the probability of each pair of samples under the corresponding
+# distribution in `dist`.
+dist.prob(x) # Shape [2, 3]
+```
+
+```python
+# Create batch_shape=[2, 3] via parameter broadcast:
+alpha = [[1.], [2]] # Shape [2, 1]
+beta = [3., 4, 5] # Shape [3]
+dist = tfd.Beta(alpha, beta)
+
+# alpha broadcast as: [[1., 1, 1,],
+# [2, 2, 2]]
+# beta broadcast as: [[3., 4, 5],
+# [3, 4, 5]]
+# batch_Shape [2, 3]
+dist.sample([4, 5]) # Shape [4, 5, 2, 3]
+
+x = [.2, .3, .5]
+# x will be broadcast as [[.2, .3, .5],
+# [.2, .3, .5]],
+# thus matching batch_shape [2, 3].
+dist.prob(x) # Shape [2, 3]
+```
+
+Compute the gradients of samples w.r.t. the parameters:
+
+```python
+alpha = tf.constant(1.0)
+beta = tf.constant(2.0)
+dist = tfd.Beta(alpha, beta)
+samples = dist.sample(5) # Shape [5]
+loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(samples)) # Arbitrary loss function
+# Unbiased stochastic gradients of the loss function
+grads = tf.gradients(loss, [alpha, beta])
+```
+
+#### References:
+
+Implicit Reparameterization Gradients:
+ [Figurnov et al., 2018]
+ (http://papers.nips.cc/paper/7326-implicit-reparameterization-gradients)
+ ([pdf]
+ (http://papers.nips.cc/paper/7326-implicit-reparameterization-gradients.pdf))
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`concentration1`
+ |
+
+Positive floating-point `Tensor` indicating mean
+number of successes; aka "alpha". Implies `self.dtype` and
+`self.batch_shape`, i.e.,
+`concentration1.shape = [N1, N2, ..., Nm] = self.batch_shape`.
+ |
+
+|
+`concentration0`
+ |
+
+Positive floating-point `Tensor` indicating mean
+number of failures; aka "beta". Otherwise has same semantics as
+`concentration1`.
+ |
+
+|
+`validate_args`
+ |
+
+Python `bool`, default `False`. When `True` distribution
+parameters are checked for validity despite possibly degrading runtime
+performance. When `False` invalid inputs may silently render incorrect
+outputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`allow_nan_stats`
+ |
+
+Python `bool`, default `True`. When `True`, statistics
+(e.g., mean, mode, variance) use the value "`NaN`" to indicate the
+result is undefined. When `False`, an exception is raised if one or
+more of the statistic's batch members are undefined.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` name prefixed to Ops created by this class.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`allow_nan_stats`
+ |
+
+Python `bool` describing behavior when a stat is undefined.
+
+Stats return +/- infinity when it makes sense. E.g., the variance of a
+Cauchy distribution is infinity. However, sometimes the statistic is
+undefined, e.g., if a distribution's pdf does not achieve a maximum within
+the support of the distribution, the mode is undefined. If the mean is
+undefined, then by definition the variance is undefined. E.g. the mean for
+Student's T for df = 1 is undefined (no clear way to say it is either + or -
+infinity), so the variance = E[(X - mean)**2] is also undefined.
+ |
+
+|
+`batch_shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single event index as a `TensorShape`.
+
+May be partially defined or unknown.
+
+The batch dimensions are indexes into independent, non-identical
+parameterizations of this distribution.
+ |
+
+|
+`concentration0`
+ |
+
+Concentration parameter associated with a `0` outcome.
+ |
+
+|
+`concentration1`
+ |
+
+Concentration parameter associated with a `1` outcome.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+The `DType` of `Tensor`s handled by this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`event_shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single batch as a `TensorShape`.
+
+May be partially defined or unknown.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name prepended to all ops created by this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`parameters`
+ |
+
+Dictionary of parameters used to instantiate this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`reparameterization_type`
+ |
+
+Describes how samples from the distribution are reparameterized.
+
+Currently this is one of the static instances
+`distributions.FULLY_REPARAMETERIZED`
+or `distributions.NOT_REPARAMETERIZED`.
+ |
+
+|
+`total_concentration`
+ |
+
+Sum of concentration parameters.
+ |
+
+|
+`validate_args`
+ |
+
+Python `bool` indicating possibly expensive checks are enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+batch_shape_tensor
+
+View source
+
+
+batch_shape_tensor(
+ name='batch_shape_tensor'
+)
+
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single event index as a 1-D `Tensor`.
+
+The batch dimensions are indexes into independent, non-identical
+parameterizations of this distribution.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`batch_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+cdf
+
+View source
+
+
+cdf(
+ value, name='cdf'
+)
+
+
+Cumulative distribution function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the cumulative distribution function `cdf` is:
+
+```none
+cdf(x) := P[X <= x]
+```
+
+
+Additional documentation from `Beta`:
+
+Note: `x` must have dtype `self.dtype` and be in
+`[0, 1].` It must have a shape compatible with `self.batch_shape()`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cdf`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+copy
+
+View source
+
+
+copy(
+ **override_parameters_kwargs
+)
+
+
+Creates a deep copy of the distribution.
+
+Note: the copy distribution may continue to depend on the original
+initialization arguments.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`**override_parameters_kwargs`
+ |
+
+String/value dictionary of initialization
+arguments to override with new values.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`distribution`
+ |
+
+A new instance of `type(self)` initialized from the union
+of self.parameters and override_parameters_kwargs, i.e.,
+`dict(self.parameters, **override_parameters_kwargs)`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+covariance
+
+View source
+
+
+covariance(
+ name='covariance'
+)
+
+
+Covariance.
+
+Covariance is (possibly) defined only for non-scalar-event distributions.
+
+For example, for a length-`k`, vector-valued distribution, it is calculated
+as,
+
+```none
+Cov[i, j] = Covariance(X_i, X_j) = E[(X_i - E[X_i]) (X_j - E[X_j])]
+```
+
+where `Cov` is a (batch of) `k x k` matrix, `0 <= (i, j) < k`, and `E`
+denotes expectation.
+
+Alternatively, for non-vector, multivariate distributions (e.g.,
+matrix-valued, Wishart), `Covariance` shall return a (batch of) matrices
+under some vectorization of the events, i.e.,
+
+```none
+Cov[i, j] = Covariance(Vec(X)_i, Vec(X)_j) = [as above]
+```
+
+where `Cov` is a (batch of) `k' x k'` matrices,
+`0 <= (i, j) < k' = reduce_prod(event_shape)`, and `Vec` is some function
+mapping indices of this distribution's event dimensions to indices of a
+length-`k'` vector.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`covariance`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn, k', k']`
+where the first `n` dimensions are batch coordinates and
+`k' = reduce_prod(self.event_shape)`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+cross_entropy
+
+View source
+
+
+cross_entropy(
+ other, name='cross_entropy'
+)
+
+
+Computes the (Shannon) cross entropy.
+
+Denote this distribution (`self`) by `P` and the `other` distribution by
+`Q`. Assuming `P, Q` are absolutely continuous with respect to
+one another and permit densities `p(x) dr(x)` and `q(x) dr(x)`, (Shanon)
+cross entropy is defined as:
+
+```none
+H[P, Q] = E_p[-log q(X)] = -int_F p(x) log q(x) dr(x)
+```
+
+where `F` denotes the support of the random variable `X ~ P`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`other`
+ |
+
+`tfp.distributions.Distribution` instance.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cross_entropy`
+ |
+
+`self.dtype` `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn]`
+representing `n` different calculations of (Shanon) cross entropy.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+entropy
+
+View source
+
+
+entropy(
+ name='entropy'
+)
+
+
+Shannon entropy in nats.
+
+
+event_shape_tensor
+
+View source
+
+
+event_shape_tensor(
+ name='event_shape_tensor'
+)
+
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single batch as a 1-D int32 `Tensor`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`event_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+is_scalar_batch
+
+View source
+
+
+is_scalar_batch(
+ name='is_scalar_batch'
+)
+
+
+Indicates that `batch_shape == []`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`is_scalar_batch`
+ |
+
+`bool` scalar `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+is_scalar_event
+
+View source
+
+
+is_scalar_event(
+ name='is_scalar_event'
+)
+
+
+Indicates that `event_shape == []`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`is_scalar_event`
+ |
+
+`bool` scalar `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+kl_divergence
+
+View source
+
+
+kl_divergence(
+ other, name='kl_divergence'
+)
+
+
+Computes the Kullback--Leibler divergence.
+
+Denote this distribution (`self`) by `p` and the `other` distribution by
+`q`. Assuming `p, q` are absolutely continuous with respect to reference
+measure `r`, the KL divergence is defined as:
+
+```none
+KL[p, q] = E_p[log(p(X)/q(X))]
+ = -int_F p(x) log q(x) dr(x) + int_F p(x) log p(x) dr(x)
+ = H[p, q] - H[p]
+```
+
+where `F` denotes the support of the random variable `X ~ p`, `H[., .]`
+denotes (Shanon) cross entropy, and `H[.]` denotes (Shanon) entropy.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`other`
+ |
+
+`tfp.distributions.Distribution` instance.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`kl_divergence`
+ |
+
+`self.dtype` `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn]`
+representing `n` different calculations of the Kullback-Leibler
+divergence.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_cdf
+
+View source
+
+
+log_cdf(
+ value, name='log_cdf'
+)
+
+
+Log cumulative distribution function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the cumulative distribution function `cdf` is:
+
+```none
+log_cdf(x) := Log[ P[X <= x] ]
+```
+
+Often, a numerical approximation can be used for `log_cdf(x)` that yields
+a more accurate answer than simply taking the logarithm of the `cdf` when
+`x << -1`.
+
+
+Additional documentation from `Beta`:
+
+Note: `x` must have dtype `self.dtype` and be in
+`[0, 1].` It must have a shape compatible with `self.batch_shape()`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`logcdf`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_prob
+
+View source
+
+
+log_prob(
+ value, name='log_prob'
+)
+
+
+Log probability density/mass function.
+
+
+Additional documentation from `Beta`:
+
+Note: `x` must have dtype `self.dtype` and be in
+`[0, 1].` It must have a shape compatible with `self.batch_shape()`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`log_prob`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_survival_function
+
+View source
+
+
+log_survival_function(
+ value, name='log_survival_function'
+)
+
+
+Log survival function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the survival function is defined:
+
+```none
+log_survival_function(x) = Log[ P[X > x] ]
+ = Log[ 1 - P[X <= x] ]
+ = Log[ 1 - cdf(x) ]
+```
+
+Typically, different numerical approximations can be used for the log
+survival function, which are more accurate than `1 - cdf(x)` when `x >> 1`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with values of type
+`self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+mean
+
+View source
+
+
+mean(
+ name='mean'
+)
+
+
+Mean.
+
+
+mode
+
+View source
+
+
+mode(
+ name='mode'
+)
+
+
+Mode.
+
+Additional documentation from `Beta`:
+
+Note: The mode is undefined when `concentration1 <= 1` or
+`concentration0 <= 1`. If `self.allow_nan_stats` is `True`, `NaN`
+is used for undefined modes. If `self.allow_nan_stats` is `False` an
+exception is raised when one or more modes are undefined.
+
+param_shapes
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+param_shapes(
+ sample_shape, name='DistributionParamShapes'
+)
+
+
+Shapes of parameters given the desired shape of a call to `sample()`.
+
+This is a class method that describes what key/value arguments are required
+to instantiate the given `Distribution` so that a particular shape is
+returned for that instance's call to `sample()`.
+
+Subclasses should override class method `_param_shapes`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor` or python list/tuple. Desired shape of a call to
+`sample()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to prepend ops with.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`dict` of parameter name to `Tensor` shapes.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+param_static_shapes
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+param_static_shapes(
+ sample_shape
+)
+
+
+param_shapes with static (i.e. `TensorShape`) shapes.
+
+This is a class method that describes what key/value arguments are required
+to instantiate the given `Distribution` so that a particular shape is
+returned for that instance's call to `sample()`. Assumes that the sample's
+shape is known statically.
+
+Subclasses should override class method `_param_shapes` to return
+constant-valued tensors when constant values are fed.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+`TensorShape` or python list/tuple. Desired shape of a call
+to `sample()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`dict` of parameter name to `TensorShape`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `sample_shape` is a `TensorShape` and is not fully defined.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+prob
+
+View source
+
+
+prob(
+ value, name='prob'
+)
+
+
+Probability density/mass function.
+
+
+Additional documentation from `Beta`:
+
+Note: `x` must have dtype `self.dtype` and be in
+`[0, 1].` It must have a shape compatible with `self.batch_shape()`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`prob`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+quantile
+
+View source
+
+
+quantile(
+ value, name='quantile'
+)
+
+
+Quantile function. Aka "inverse cdf" or "percent point function".
+
+Given random variable `X` and `p in [0, 1]`, the `quantile` is:
+
+```none
+quantile(p) := x such that P[X <= x] == p
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`quantile`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+sample
+
+View source
+
+
+sample(
+ sample_shape=(), seed=None, name='sample'
+)
+
+
+Generate samples of the specified shape.
+
+Note that a call to `sample()` without arguments will generate a single
+sample.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+0D or 1D `int32` `Tensor`. Shape of the generated samples.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+Python integer seed for RNG
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`samples`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` with prepended dimensions `sample_shape`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+stddev
+
+View source
+
+
+stddev(
+ name='stddev'
+)
+
+
+Standard deviation.
+
+Standard deviation is defined as,
+
+```none
+stddev = E[(X - E[X])**2]**0.5
+```
+
+where `X` is the random variable associated with this distribution, `E`
+denotes expectation, and `stddev.shape = batch_shape + event_shape`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`stddev`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape identical to
+`batch_shape + event_shape`, i.e., the same shape as `self.mean()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+survival_function
+
+View source
+
+
+survival_function(
+ value, name='survival_function'
+)
+
+
+Survival function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the survival function is defined:
+
+```none
+survival_function(x) = P[X > x]
+ = 1 - P[X <= x]
+ = 1 - cdf(x).
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with values of type
+`self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+variance
+
+View source
+
+
+variance(
+ name='variance'
+)
+
+
+Variance.
+
+Variance is defined as,
+
+```none
+Var = E[(X - E[X])**2]
+```
+
+where `X` is the random variable associated with this distribution, `E`
+denotes expectation, and `Var.shape = batch_shape + event_shape`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`variance`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape identical to
+`batch_shape + event_shape`, i.e., the same shape as `self.mean()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/Categorical.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/Categorical.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..2e62c299c7d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/Categorical.md
@@ -0,0 +1,1529 @@
+description: Categorical distribution.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.distributions.Categorical
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Categorical distribution.
+
+Inherits From: [`Distribution`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/distributions/Distribution.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.distributions.Categorical(
+ logits=None, probs=None, dtype=tf.dtypes.int32, validate_args=(False),
+ allow_nan_stats=(True), name='Categorical'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The Categorical distribution is parameterized by either probabilities or
+log-probabilities of a set of `K` classes. It is defined over the integers
+`{0, 1, ..., K}`.
+
+The Categorical distribution is closely related to the `OneHotCategorical` and
+`Multinomial` distributions. The Categorical distribution can be intuited as
+generating samples according to `argmax{ OneHotCategorical(probs) }` itself
+being identical to `argmax{ Multinomial(probs, total_count=1) }`.
+
+#### Mathematical Details
+
+The probability mass function (pmf) is,
+
+```none
+pmf(k; pi) = prod_j pi_j**[k == j]
+```
+
+#### Pitfalls
+
+The number of classes, `K`, must not exceed:
+- the largest integer representable by `self.dtype`, i.e.,
+ `2**(mantissa_bits+1)` (IEEE 754),
+- the maximum `Tensor` index, i.e., `2**31-1`.
+
+In other words,
+
+```python
+K <= min(2**31-1, {
+ tf.float16: 2**11,
+ tf.float32: 2**24,
+ tf.float64: 2**53 }[param.dtype])
+```
+
+Note: This condition is validated only when `self.validate_args = True`.
+
+#### Examples
+
+Creates a 3-class distribution with the 2nd class being most likely.
+
+```python
+dist = Categorical(probs=[0.1, 0.5, 0.4])
+n = 1e4
+empirical_prob = tf.cast(
+ tf.histogram_fixed_width(
+ dist.sample(int(n)),
+ [0., 2],
+ nbins=3),
+ dtype=tf.float32) / n
+# ==> array([ 0.1005, 0.5037, 0.3958], dtype=float32)
+```
+
+Creates a 3-class distribution with the 2nd class being most likely.
+Parameterized by [logits](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Logit) rather than
+probabilities.
+
+```python
+dist = Categorical(logits=np.log([0.1, 0.5, 0.4])
+n = 1e4
+empirical_prob = tf.cast(
+ tf.histogram_fixed_width(
+ dist.sample(int(n)),
+ [0., 2],
+ nbins=3),
+ dtype=tf.float32) / n
+# ==> array([0.1045, 0.5047, 0.3908], dtype=float32)
+```
+
+Creates a 3-class distribution with the 3rd class being most likely.
+The distribution functions can be evaluated on counts.
+
+```python
+# counts is a scalar.
+p = [0.1, 0.4, 0.5]
+dist = Categorical(probs=p)
+dist.prob(0) # Shape []
+
+# p will be broadcast to [[0.1, 0.4, 0.5], [0.1, 0.4, 0.5]] to match counts.
+counts = [1, 0]
+dist.prob(counts) # Shape [2]
+
+# p will be broadcast to shape [3, 5, 7, 3] to match counts.
+counts = [[...]] # Shape [5, 7, 3]
+dist.prob(counts) # Shape [5, 7, 3]
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`logits`
+ |
+
+An N-D `Tensor`, `N >= 1`, representing the log probabilities
+of a set of Categorical distributions. The first `N - 1` dimensions
+index into a batch of independent distributions and the last dimension
+represents a vector of logits for each class. Only one of `logits` or
+`probs` should be passed in.
+ |
+
+|
+`probs`
+ |
+
+An N-D `Tensor`, `N >= 1`, representing the probabilities
+of a set of Categorical distributions. The first `N - 1` dimensions
+index into a batch of independent distributions and the last dimension
+represents a vector of probabilities for each class. Only one of
+`logits` or `probs` should be passed in.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+The type of the event samples (default: int32).
+ |
+
+|
+`validate_args`
+ |
+
+Python `bool`, default `False`. When `True` distribution
+parameters are checked for validity despite possibly degrading runtime
+performance. When `False` invalid inputs may silently render incorrect
+outputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`allow_nan_stats`
+ |
+
+Python `bool`, default `True`. When `True`, statistics
+(e.g., mean, mode, variance) use the value "`NaN`" to indicate the
+result is undefined. When `False`, an exception is raised if one or
+more of the statistic's batch members are undefined.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` name prefixed to Ops created by this class.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`allow_nan_stats`
+ |
+
+Python `bool` describing behavior when a stat is undefined.
+
+Stats return +/- infinity when it makes sense. E.g., the variance of a
+Cauchy distribution is infinity. However, sometimes the statistic is
+undefined, e.g., if a distribution's pdf does not achieve a maximum within
+the support of the distribution, the mode is undefined. If the mean is
+undefined, then by definition the variance is undefined. E.g. the mean for
+Student's T for df = 1 is undefined (no clear way to say it is either + or -
+infinity), so the variance = E[(X - mean)**2] is also undefined.
+ |
+
+|
+`batch_shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single event index as a `TensorShape`.
+
+May be partially defined or unknown.
+
+The batch dimensions are indexes into independent, non-identical
+parameterizations of this distribution.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+The `DType` of `Tensor`s handled by this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`event_shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single batch as a `TensorShape`.
+
+May be partially defined or unknown.
+ |
+
+|
+`event_size`
+ |
+
+Scalar `int32` tensor: the number of classes.
+ |
+
+|
+`logits`
+ |
+
+Vector of coordinatewise logits.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name prepended to all ops created by this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`parameters`
+ |
+
+Dictionary of parameters used to instantiate this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`probs`
+ |
+
+Vector of coordinatewise probabilities.
+ |
+
+|
+`reparameterization_type`
+ |
+
+Describes how samples from the distribution are reparameterized.
+
+Currently this is one of the static instances
+`distributions.FULLY_REPARAMETERIZED`
+or `distributions.NOT_REPARAMETERIZED`.
+ |
+
+|
+`validate_args`
+ |
+
+Python `bool` indicating possibly expensive checks are enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+batch_shape_tensor
+
+View source
+
+
+batch_shape_tensor(
+ name='batch_shape_tensor'
+)
+
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single event index as a 1-D `Tensor`.
+
+The batch dimensions are indexes into independent, non-identical
+parameterizations of this distribution.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`batch_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+cdf
+
+View source
+
+
+cdf(
+ value, name='cdf'
+)
+
+
+Cumulative distribution function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the cumulative distribution function `cdf` is:
+
+```none
+cdf(x) := P[X <= x]
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cdf`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+copy
+
+View source
+
+
+copy(
+ **override_parameters_kwargs
+)
+
+
+Creates a deep copy of the distribution.
+
+Note: the copy distribution may continue to depend on the original
+initialization arguments.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`**override_parameters_kwargs`
+ |
+
+String/value dictionary of initialization
+arguments to override with new values.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`distribution`
+ |
+
+A new instance of `type(self)` initialized from the union
+of self.parameters and override_parameters_kwargs, i.e.,
+`dict(self.parameters, **override_parameters_kwargs)`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+covariance
+
+View source
+
+
+covariance(
+ name='covariance'
+)
+
+
+Covariance.
+
+Covariance is (possibly) defined only for non-scalar-event distributions.
+
+For example, for a length-`k`, vector-valued distribution, it is calculated
+as,
+
+```none
+Cov[i, j] = Covariance(X_i, X_j) = E[(X_i - E[X_i]) (X_j - E[X_j])]
+```
+
+where `Cov` is a (batch of) `k x k` matrix, `0 <= (i, j) < k`, and `E`
+denotes expectation.
+
+Alternatively, for non-vector, multivariate distributions (e.g.,
+matrix-valued, Wishart), `Covariance` shall return a (batch of) matrices
+under some vectorization of the events, i.e.,
+
+```none
+Cov[i, j] = Covariance(Vec(X)_i, Vec(X)_j) = [as above]
+```
+
+where `Cov` is a (batch of) `k' x k'` matrices,
+`0 <= (i, j) < k' = reduce_prod(event_shape)`, and `Vec` is some function
+mapping indices of this distribution's event dimensions to indices of a
+length-`k'` vector.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`covariance`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn, k', k']`
+where the first `n` dimensions are batch coordinates and
+`k' = reduce_prod(self.event_shape)`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+cross_entropy
+
+View source
+
+
+cross_entropy(
+ other, name='cross_entropy'
+)
+
+
+Computes the (Shannon) cross entropy.
+
+Denote this distribution (`self`) by `P` and the `other` distribution by
+`Q`. Assuming `P, Q` are absolutely continuous with respect to
+one another and permit densities `p(x) dr(x)` and `q(x) dr(x)`, (Shanon)
+cross entropy is defined as:
+
+```none
+H[P, Q] = E_p[-log q(X)] = -int_F p(x) log q(x) dr(x)
+```
+
+where `F` denotes the support of the random variable `X ~ P`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`other`
+ |
+
+`tfp.distributions.Distribution` instance.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cross_entropy`
+ |
+
+`self.dtype` `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn]`
+representing `n` different calculations of (Shanon) cross entropy.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+entropy
+
+View source
+
+
+entropy(
+ name='entropy'
+)
+
+
+Shannon entropy in nats.
+
+
+event_shape_tensor
+
+View source
+
+
+event_shape_tensor(
+ name='event_shape_tensor'
+)
+
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single batch as a 1-D int32 `Tensor`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`event_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+is_scalar_batch
+
+View source
+
+
+is_scalar_batch(
+ name='is_scalar_batch'
+)
+
+
+Indicates that `batch_shape == []`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`is_scalar_batch`
+ |
+
+`bool` scalar `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+is_scalar_event
+
+View source
+
+
+is_scalar_event(
+ name='is_scalar_event'
+)
+
+
+Indicates that `event_shape == []`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`is_scalar_event`
+ |
+
+`bool` scalar `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+kl_divergence
+
+View source
+
+
+kl_divergence(
+ other, name='kl_divergence'
+)
+
+
+Computes the Kullback--Leibler divergence.
+
+Denote this distribution (`self`) by `p` and the `other` distribution by
+`q`. Assuming `p, q` are absolutely continuous with respect to reference
+measure `r`, the KL divergence is defined as:
+
+```none
+KL[p, q] = E_p[log(p(X)/q(X))]
+ = -int_F p(x) log q(x) dr(x) + int_F p(x) log p(x) dr(x)
+ = H[p, q] - H[p]
+```
+
+where `F` denotes the support of the random variable `X ~ p`, `H[., .]`
+denotes (Shanon) cross entropy, and `H[.]` denotes (Shanon) entropy.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`other`
+ |
+
+`tfp.distributions.Distribution` instance.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`kl_divergence`
+ |
+
+`self.dtype` `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn]`
+representing `n` different calculations of the Kullback-Leibler
+divergence.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_cdf
+
+View source
+
+
+log_cdf(
+ value, name='log_cdf'
+)
+
+
+Log cumulative distribution function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the cumulative distribution function `cdf` is:
+
+```none
+log_cdf(x) := Log[ P[X <= x] ]
+```
+
+Often, a numerical approximation can be used for `log_cdf(x)` that yields
+a more accurate answer than simply taking the logarithm of the `cdf` when
+`x << -1`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`logcdf`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_prob
+
+View source
+
+
+log_prob(
+ value, name='log_prob'
+)
+
+
+Log probability density/mass function.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`log_prob`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_survival_function
+
+View source
+
+
+log_survival_function(
+ value, name='log_survival_function'
+)
+
+
+Log survival function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the survival function is defined:
+
+```none
+log_survival_function(x) = Log[ P[X > x] ]
+ = Log[ 1 - P[X <= x] ]
+ = Log[ 1 - cdf(x) ]
+```
+
+Typically, different numerical approximations can be used for the log
+survival function, which are more accurate than `1 - cdf(x)` when `x >> 1`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with values of type
+`self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+mean
+
+View source
+
+
+mean(
+ name='mean'
+)
+
+
+Mean.
+
+
+mode
+
+View source
+
+
+mode(
+ name='mode'
+)
+
+
+Mode.
+
+
+param_shapes
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+param_shapes(
+ sample_shape, name='DistributionParamShapes'
+)
+
+
+Shapes of parameters given the desired shape of a call to `sample()`.
+
+This is a class method that describes what key/value arguments are required
+to instantiate the given `Distribution` so that a particular shape is
+returned for that instance's call to `sample()`.
+
+Subclasses should override class method `_param_shapes`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor` or python list/tuple. Desired shape of a call to
+`sample()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to prepend ops with.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`dict` of parameter name to `Tensor` shapes.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+param_static_shapes
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+param_static_shapes(
+ sample_shape
+)
+
+
+param_shapes with static (i.e. `TensorShape`) shapes.
+
+This is a class method that describes what key/value arguments are required
+to instantiate the given `Distribution` so that a particular shape is
+returned for that instance's call to `sample()`. Assumes that the sample's
+shape is known statically.
+
+Subclasses should override class method `_param_shapes` to return
+constant-valued tensors when constant values are fed.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+`TensorShape` or python list/tuple. Desired shape of a call
+to `sample()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`dict` of parameter name to `TensorShape`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `sample_shape` is a `TensorShape` and is not fully defined.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+prob
+
+View source
+
+
+prob(
+ value, name='prob'
+)
+
+
+Probability density/mass function.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`prob`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+quantile
+
+View source
+
+
+quantile(
+ value, name='quantile'
+)
+
+
+Quantile function. Aka "inverse cdf" or "percent point function".
+
+Given random variable `X` and `p in [0, 1]`, the `quantile` is:
+
+```none
+quantile(p) := x such that P[X <= x] == p
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`quantile`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+sample
+
+View source
+
+
+sample(
+ sample_shape=(), seed=None, name='sample'
+)
+
+
+Generate samples of the specified shape.
+
+Note that a call to `sample()` without arguments will generate a single
+sample.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+0D or 1D `int32` `Tensor`. Shape of the generated samples.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+Python integer seed for RNG
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`samples`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` with prepended dimensions `sample_shape`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+stddev
+
+View source
+
+
+stddev(
+ name='stddev'
+)
+
+
+Standard deviation.
+
+Standard deviation is defined as,
+
+```none
+stddev = E[(X - E[X])**2]**0.5
+```
+
+where `X` is the random variable associated with this distribution, `E`
+denotes expectation, and `stddev.shape = batch_shape + event_shape`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`stddev`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape identical to
+`batch_shape + event_shape`, i.e., the same shape as `self.mean()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+survival_function
+
+View source
+
+
+survival_function(
+ value, name='survival_function'
+)
+
+
+Survival function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the survival function is defined:
+
+```none
+survival_function(x) = P[X > x]
+ = 1 - P[X <= x]
+ = 1 - cdf(x).
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with values of type
+`self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+variance
+
+View source
+
+
+variance(
+ name='variance'
+)
+
+
+Variance.
+
+Variance is defined as,
+
+```none
+Var = E[(X - E[X])**2]
+```
+
+where `X` is the random variable associated with this distribution, `E`
+denotes expectation, and `Var.shape = batch_shape + event_shape`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`variance`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape identical to
+`batch_shape + event_shape`, i.e., the same shape as `self.mean()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/Dirichlet.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/Dirichlet.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e94acc61e8e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/Dirichlet.md
@@ -0,0 +1,1552 @@
+description: Dirichlet distribution.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.distributions.Dirichlet
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Dirichlet distribution.
+
+Inherits From: [`Distribution`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/distributions/Distribution.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.distributions.Dirichlet(
+ concentration, validate_args=(False), allow_nan_stats=(True), name='Dirichlet'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The Dirichlet distribution is defined over the
+[`(k-1)`-simplex](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Simplex) using a positive,
+length-`k` vector `concentration` (`k > 1`). The Dirichlet is identically the
+Beta distribution when `k = 2`.
+
+#### Mathematical Details
+
+The Dirichlet is a distribution over the open `(k-1)`-simplex, i.e.,
+
+```none
+S^{k-1} = { (x_0, ..., x_{k-1}) in R^k : sum_j x_j = 1 and all_j x_j > 0 }.
+```
+
+The probability density function (pdf) is,
+
+```none
+pdf(x; alpha) = prod_j x_j**(alpha_j - 1) / Z
+Z = prod_j Gamma(alpha_j) / Gamma(sum_j alpha_j)
+```
+
+where:
+
+* `x in S^{k-1}`, i.e., the `(k-1)`-simplex,
+* `concentration = alpha = [alpha_0, ..., alpha_{k-1}]`, `alpha_j > 0`,
+* `Z` is the normalization constant aka the [multivariate beta function](
+ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beta_function#Multivariate_beta_function),
+ and,
+* `Gamma` is the [gamma function](
+ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma_function).
+
+The `concentration` represents mean total counts of class occurrence, i.e.,
+
+```none
+concentration = alpha = mean * total_concentration
+```
+
+where `mean` in `S^{k-1}` and `total_concentration` is a positive real number
+representing a mean total count.
+
+Distribution parameters are automatically broadcast in all functions; see
+examples for details.
+
+Warning: Some components of the samples can be zero due to finite precision.
+This happens more often when some of the concentrations are very small.
+Make sure to round the samples to `np.finfo(dtype).tiny` before computing the
+density.
+
+Samples of this distribution are reparameterized (pathwise differentiable).
+The derivatives are computed using the approach described in
+(Figurnov et al., 2018).
+
+#### Examples
+
+```python
+import tensorflow_probability as tfp
+tfd = tfp.distributions
+
+# Create a single trivariate Dirichlet, with the 3rd class being three times
+# more frequent than the first. I.e., batch_shape=[], event_shape=[3].
+alpha = [1., 2, 3]
+dist = tfd.Dirichlet(alpha)
+
+dist.sample([4, 5]) # shape: [4, 5, 3]
+
+# x has one sample, one batch, three classes:
+x = [.2, .3, .5] # shape: [3]
+dist.prob(x) # shape: []
+
+# x has two samples from one batch:
+x = [[.1, .4, .5],
+ [.2, .3, .5]]
+dist.prob(x) # shape: [2]
+
+# alpha will be broadcast to shape [5, 7, 3] to match x.
+x = [[...]] # shape: [5, 7, 3]
+dist.prob(x) # shape: [5, 7]
+```
+
+```python
+# Create batch_shape=[2], event_shape=[3]:
+alpha = [[1., 2, 3],
+ [4, 5, 6]] # shape: [2, 3]
+dist = tfd.Dirichlet(alpha)
+
+dist.sample([4, 5]) # shape: [4, 5, 2, 3]
+
+x = [.2, .3, .5]
+# x will be broadcast as [[.2, .3, .5],
+# [.2, .3, .5]],
+# thus matching batch_shape [2, 3].
+dist.prob(x) # shape: [2]
+```
+
+Compute the gradients of samples w.r.t. the parameters:
+
+```python
+alpha = tf.constant([1.0, 2.0, 3.0])
+dist = tfd.Dirichlet(alpha)
+samples = dist.sample(5) # Shape [5, 3]
+loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(samples)) # Arbitrary loss function
+# Unbiased stochastic gradients of the loss function
+grads = tf.gradients(loss, alpha)
+```
+
+#### References:
+
+Implicit Reparameterization Gradients:
+ [Figurnov et al., 2018]
+ (http://papers.nips.cc/paper/7326-implicit-reparameterization-gradients)
+ ([pdf]
+ (http://papers.nips.cc/paper/7326-implicit-reparameterization-gradients.pdf))
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`concentration`
+ |
+
+Positive floating-point `Tensor` indicating mean number
+of class occurrences; aka "alpha". Implies `self.dtype`, and
+`self.batch_shape`, `self.event_shape`, i.e., if
+`concentration.shape = [N1, N2, ..., Nm, k]` then
+`batch_shape = [N1, N2, ..., Nm]` and
+`event_shape = [k]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`validate_args`
+ |
+
+Python `bool`, default `False`. When `True` distribution
+parameters are checked for validity despite possibly degrading runtime
+performance. When `False` invalid inputs may silently render incorrect
+outputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`allow_nan_stats`
+ |
+
+Python `bool`, default `True`. When `True`, statistics
+(e.g., mean, mode, variance) use the value "`NaN`" to indicate the
+result is undefined. When `False`, an exception is raised if one or
+more of the statistic's batch members are undefined.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` name prefixed to Ops created by this class.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`allow_nan_stats`
+ |
+
+Python `bool` describing behavior when a stat is undefined.
+
+Stats return +/- infinity when it makes sense. E.g., the variance of a
+Cauchy distribution is infinity. However, sometimes the statistic is
+undefined, e.g., if a distribution's pdf does not achieve a maximum within
+the support of the distribution, the mode is undefined. If the mean is
+undefined, then by definition the variance is undefined. E.g. the mean for
+Student's T for df = 1 is undefined (no clear way to say it is either + or -
+infinity), so the variance = E[(X - mean)**2] is also undefined.
+ |
+
+|
+`batch_shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single event index as a `TensorShape`.
+
+May be partially defined or unknown.
+
+The batch dimensions are indexes into independent, non-identical
+parameterizations of this distribution.
+ |
+
+|
+`concentration`
+ |
+
+Concentration parameter; expected counts for that coordinate.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+The `DType` of `Tensor`s handled by this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`event_shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single batch as a `TensorShape`.
+
+May be partially defined or unknown.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name prepended to all ops created by this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`parameters`
+ |
+
+Dictionary of parameters used to instantiate this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`reparameterization_type`
+ |
+
+Describes how samples from the distribution are reparameterized.
+
+Currently this is one of the static instances
+`distributions.FULLY_REPARAMETERIZED`
+or `distributions.NOT_REPARAMETERIZED`.
+ |
+
+|
+`total_concentration`
+ |
+
+Sum of last dim of concentration parameter.
+ |
+
+|
+`validate_args`
+ |
+
+Python `bool` indicating possibly expensive checks are enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+batch_shape_tensor
+
+View source
+
+
+batch_shape_tensor(
+ name='batch_shape_tensor'
+)
+
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single event index as a 1-D `Tensor`.
+
+The batch dimensions are indexes into independent, non-identical
+parameterizations of this distribution.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`batch_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+cdf
+
+View source
+
+
+cdf(
+ value, name='cdf'
+)
+
+
+Cumulative distribution function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the cumulative distribution function `cdf` is:
+
+```none
+cdf(x) := P[X <= x]
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cdf`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+copy
+
+View source
+
+
+copy(
+ **override_parameters_kwargs
+)
+
+
+Creates a deep copy of the distribution.
+
+Note: the copy distribution may continue to depend on the original
+initialization arguments.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`**override_parameters_kwargs`
+ |
+
+String/value dictionary of initialization
+arguments to override with new values.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`distribution`
+ |
+
+A new instance of `type(self)` initialized from the union
+of self.parameters and override_parameters_kwargs, i.e.,
+`dict(self.parameters, **override_parameters_kwargs)`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+covariance
+
+View source
+
+
+covariance(
+ name='covariance'
+)
+
+
+Covariance.
+
+Covariance is (possibly) defined only for non-scalar-event distributions.
+
+For example, for a length-`k`, vector-valued distribution, it is calculated
+as,
+
+```none
+Cov[i, j] = Covariance(X_i, X_j) = E[(X_i - E[X_i]) (X_j - E[X_j])]
+```
+
+where `Cov` is a (batch of) `k x k` matrix, `0 <= (i, j) < k`, and `E`
+denotes expectation.
+
+Alternatively, for non-vector, multivariate distributions (e.g.,
+matrix-valued, Wishart), `Covariance` shall return a (batch of) matrices
+under some vectorization of the events, i.e.,
+
+```none
+Cov[i, j] = Covariance(Vec(X)_i, Vec(X)_j) = [as above]
+```
+
+where `Cov` is a (batch of) `k' x k'` matrices,
+`0 <= (i, j) < k' = reduce_prod(event_shape)`, and `Vec` is some function
+mapping indices of this distribution's event dimensions to indices of a
+length-`k'` vector.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`covariance`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn, k', k']`
+where the first `n` dimensions are batch coordinates and
+`k' = reduce_prod(self.event_shape)`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+cross_entropy
+
+View source
+
+
+cross_entropy(
+ other, name='cross_entropy'
+)
+
+
+Computes the (Shannon) cross entropy.
+
+Denote this distribution (`self`) by `P` and the `other` distribution by
+`Q`. Assuming `P, Q` are absolutely continuous with respect to
+one another and permit densities `p(x) dr(x)` and `q(x) dr(x)`, (Shanon)
+cross entropy is defined as:
+
+```none
+H[P, Q] = E_p[-log q(X)] = -int_F p(x) log q(x) dr(x)
+```
+
+where `F` denotes the support of the random variable `X ~ P`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`other`
+ |
+
+`tfp.distributions.Distribution` instance.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cross_entropy`
+ |
+
+`self.dtype` `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn]`
+representing `n` different calculations of (Shanon) cross entropy.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+entropy
+
+View source
+
+
+entropy(
+ name='entropy'
+)
+
+
+Shannon entropy in nats.
+
+
+event_shape_tensor
+
+View source
+
+
+event_shape_tensor(
+ name='event_shape_tensor'
+)
+
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single batch as a 1-D int32 `Tensor`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`event_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+is_scalar_batch
+
+View source
+
+
+is_scalar_batch(
+ name='is_scalar_batch'
+)
+
+
+Indicates that `batch_shape == []`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`is_scalar_batch`
+ |
+
+`bool` scalar `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+is_scalar_event
+
+View source
+
+
+is_scalar_event(
+ name='is_scalar_event'
+)
+
+
+Indicates that `event_shape == []`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`is_scalar_event`
+ |
+
+`bool` scalar `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+kl_divergence
+
+View source
+
+
+kl_divergence(
+ other, name='kl_divergence'
+)
+
+
+Computes the Kullback--Leibler divergence.
+
+Denote this distribution (`self`) by `p` and the `other` distribution by
+`q`. Assuming `p, q` are absolutely continuous with respect to reference
+measure `r`, the KL divergence is defined as:
+
+```none
+KL[p, q] = E_p[log(p(X)/q(X))]
+ = -int_F p(x) log q(x) dr(x) + int_F p(x) log p(x) dr(x)
+ = H[p, q] - H[p]
+```
+
+where `F` denotes the support of the random variable `X ~ p`, `H[., .]`
+denotes (Shanon) cross entropy, and `H[.]` denotes (Shanon) entropy.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`other`
+ |
+
+`tfp.distributions.Distribution` instance.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`kl_divergence`
+ |
+
+`self.dtype` `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn]`
+representing `n` different calculations of the Kullback-Leibler
+divergence.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_cdf
+
+View source
+
+
+log_cdf(
+ value, name='log_cdf'
+)
+
+
+Log cumulative distribution function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the cumulative distribution function `cdf` is:
+
+```none
+log_cdf(x) := Log[ P[X <= x] ]
+```
+
+Often, a numerical approximation can be used for `log_cdf(x)` that yields
+a more accurate answer than simply taking the logarithm of the `cdf` when
+`x << -1`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`logcdf`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_prob
+
+View source
+
+
+log_prob(
+ value, name='log_prob'
+)
+
+
+Log probability density/mass function.
+
+
+Additional documentation from `Dirichlet`:
+
+Note: `value` must be a non-negative tensor with
+dtype `self.dtype` and be in the `(self.event_shape() - 1)`-simplex, i.e.,
+`tf.reduce_sum(value, -1) = 1`. It must have a shape compatible with
+`self.batch_shape() + self.event_shape()`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`log_prob`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_survival_function
+
+View source
+
+
+log_survival_function(
+ value, name='log_survival_function'
+)
+
+
+Log survival function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the survival function is defined:
+
+```none
+log_survival_function(x) = Log[ P[X > x] ]
+ = Log[ 1 - P[X <= x] ]
+ = Log[ 1 - cdf(x) ]
+```
+
+Typically, different numerical approximations can be used for the log
+survival function, which are more accurate than `1 - cdf(x)` when `x >> 1`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with values of type
+`self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+mean
+
+View source
+
+
+mean(
+ name='mean'
+)
+
+
+Mean.
+
+
+mode
+
+View source
+
+
+mode(
+ name='mode'
+)
+
+
+Mode.
+
+Additional documentation from `Dirichlet`:
+
+Note: The mode is undefined when any `concentration <= 1`. If
+`self.allow_nan_stats` is `True`, `NaN` is used for undefined modes. If
+`self.allow_nan_stats` is `False` an exception is raised when one or more
+modes are undefined.
+
+param_shapes
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+param_shapes(
+ sample_shape, name='DistributionParamShapes'
+)
+
+
+Shapes of parameters given the desired shape of a call to `sample()`.
+
+This is a class method that describes what key/value arguments are required
+to instantiate the given `Distribution` so that a particular shape is
+returned for that instance's call to `sample()`.
+
+Subclasses should override class method `_param_shapes`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor` or python list/tuple. Desired shape of a call to
+`sample()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to prepend ops with.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`dict` of parameter name to `Tensor` shapes.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+param_static_shapes
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+param_static_shapes(
+ sample_shape
+)
+
+
+param_shapes with static (i.e. `TensorShape`) shapes.
+
+This is a class method that describes what key/value arguments are required
+to instantiate the given `Distribution` so that a particular shape is
+returned for that instance's call to `sample()`. Assumes that the sample's
+shape is known statically.
+
+Subclasses should override class method `_param_shapes` to return
+constant-valued tensors when constant values are fed.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+`TensorShape` or python list/tuple. Desired shape of a call
+to `sample()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`dict` of parameter name to `TensorShape`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `sample_shape` is a `TensorShape` and is not fully defined.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+prob
+
+View source
+
+
+prob(
+ value, name='prob'
+)
+
+
+Probability density/mass function.
+
+
+Additional documentation from `Dirichlet`:
+
+Note: `value` must be a non-negative tensor with
+dtype `self.dtype` and be in the `(self.event_shape() - 1)`-simplex, i.e.,
+`tf.reduce_sum(value, -1) = 1`. It must have a shape compatible with
+`self.batch_shape() + self.event_shape()`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`prob`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+quantile
+
+View source
+
+
+quantile(
+ value, name='quantile'
+)
+
+
+Quantile function. Aka "inverse cdf" or "percent point function".
+
+Given random variable `X` and `p in [0, 1]`, the `quantile` is:
+
+```none
+quantile(p) := x such that P[X <= x] == p
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`quantile`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+sample
+
+View source
+
+
+sample(
+ sample_shape=(), seed=None, name='sample'
+)
+
+
+Generate samples of the specified shape.
+
+Note that a call to `sample()` without arguments will generate a single
+sample.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+0D or 1D `int32` `Tensor`. Shape of the generated samples.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+Python integer seed for RNG
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`samples`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` with prepended dimensions `sample_shape`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+stddev
+
+View source
+
+
+stddev(
+ name='stddev'
+)
+
+
+Standard deviation.
+
+Standard deviation is defined as,
+
+```none
+stddev = E[(X - E[X])**2]**0.5
+```
+
+where `X` is the random variable associated with this distribution, `E`
+denotes expectation, and `stddev.shape = batch_shape + event_shape`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`stddev`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape identical to
+`batch_shape + event_shape`, i.e., the same shape as `self.mean()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+survival_function
+
+View source
+
+
+survival_function(
+ value, name='survival_function'
+)
+
+
+Survival function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the survival function is defined:
+
+```none
+survival_function(x) = P[X > x]
+ = 1 - P[X <= x]
+ = 1 - cdf(x).
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with values of type
+`self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+variance
+
+View source
+
+
+variance(
+ name='variance'
+)
+
+
+Variance.
+
+Variance is defined as,
+
+```none
+Var = E[(X - E[X])**2]
+```
+
+where `X` is the random variable associated with this distribution, `E`
+denotes expectation, and `Var.shape = batch_shape + event_shape`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`variance`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape identical to
+`batch_shape + event_shape`, i.e., the same shape as `self.mean()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/DirichletMultinomial.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/DirichletMultinomial.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..aa8c426de6b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/DirichletMultinomial.md
@@ -0,0 +1,1591 @@
+description: Dirichlet-Multinomial compound distribution.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.distributions.DirichletMultinomial
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Dirichlet-Multinomial compound distribution.
+
+Inherits From: [`Distribution`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/distributions/Distribution.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.distributions.DirichletMultinomial(
+ total_count, concentration, validate_args=(False), allow_nan_stats=(True),
+ name='DirichletMultinomial'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The Dirichlet-Multinomial distribution is parameterized by a (batch of)
+length-`K` `concentration` vectors (`K > 1`) and a `total_count` number of
+trials, i.e., the number of trials per draw from the DirichletMultinomial. It
+is defined over a (batch of) length-`K` vector `counts` such that
+`tf.reduce_sum(counts, -1) = total_count`. The Dirichlet-Multinomial is
+identically the Beta-Binomial distribution when `K = 2`.
+
+#### Mathematical Details
+
+The Dirichlet-Multinomial is a distribution over `K`-class counts, i.e., a
+length-`K` vector of non-negative integer `counts = n = [n_0, ..., n_{K-1}]`.
+
+The probability mass function (pmf) is,
+
+```none
+pmf(n; alpha, N) = Beta(alpha + n) / (prod_j n_j!) / Z
+Z = Beta(alpha) / N!
+```
+
+where:
+
+* `concentration = alpha = [alpha_0, ..., alpha_{K-1}]`, `alpha_j > 0`,
+* `total_count = N`, `N` a positive integer,
+* `N!` is `N` factorial, and,
+* `Beta(x) = prod_j Gamma(x_j) / Gamma(sum_j x_j)` is the
+ [multivariate beta function](
+ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beta_function#Multivariate_beta_function),
+ and,
+* `Gamma` is the [gamma function](
+ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma_function).
+
+Dirichlet-Multinomial is a [compound distribution](
+https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Compound_probability_distribution), i.e., its
+samples are generated as follows.
+
+ 1. Choose class probabilities:
+ `probs = [p_0,...,p_{K-1}] ~ Dir(concentration)`
+ 2. Draw integers:
+ `counts = [n_0,...,n_{K-1}] ~ Multinomial(total_count, probs)`
+
+The last `concentration` dimension parametrizes a single Dirichlet-Multinomial
+distribution. When calling distribution functions (e.g., `dist.prob(counts)`),
+`concentration`, `total_count` and `counts` are broadcast to the same shape.
+The last dimension of `counts` corresponds single Dirichlet-Multinomial
+distributions.
+
+Distribution parameters are automatically broadcast in all functions; see
+examples for details.
+
+#### Pitfalls
+
+The number of classes, `K`, must not exceed:
+- the largest integer representable by `self.dtype`, i.e.,
+ `2**(mantissa_bits+1)` (IEE754),
+- the maximum `Tensor` index, i.e., `2**31-1`.
+
+In other words,
+
+```python
+K <= min(2**31-1, {
+ tf.float16: 2**11,
+ tf.float32: 2**24,
+ tf.float64: 2**53 }[param.dtype])
+```
+
+Note: This condition is validated only when `self.validate_args = True`.
+
+#### Examples
+
+```python
+alpha = [1., 2., 3.]
+n = 2.
+dist = DirichletMultinomial(n, alpha)
+```
+
+Creates a 3-class distribution, with the 3rd class is most likely to be
+drawn.
+The distribution functions can be evaluated on counts.
+
+```python
+# counts same shape as alpha.
+counts = [0., 0., 2.]
+dist.prob(counts) # Shape []
+
+# alpha will be broadcast to [[1., 2., 3.], [1., 2., 3.]] to match counts.
+counts = [[1., 1., 0.], [1., 0., 1.]]
+dist.prob(counts) # Shape [2]
+
+# alpha will be broadcast to shape [5, 7, 3] to match counts.
+counts = [[...]] # Shape [5, 7, 3]
+dist.prob(counts) # Shape [5, 7]
+```
+
+Creates a 2-batch of 3-class distributions.
+
+```python
+alpha = [[1., 2., 3.], [4., 5., 6.]] # Shape [2, 3]
+n = [3., 3.]
+dist = DirichletMultinomial(n, alpha)
+
+# counts will be broadcast to [[2., 1., 0.], [2., 1., 0.]] to match alpha.
+counts = [2., 1., 0.]
+dist.prob(counts) # Shape [2]
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`total_count`
+ |
+
+Non-negative floating point tensor, whose dtype is the same
+as `concentration`. The shape is broadcastable to `[N1,..., Nm]` with
+`m >= 0`. Defines this as a batch of `N1 x ... x Nm` different
+Dirichlet multinomial distributions. Its components should be equal to
+integer values.
+ |
+
+|
+`concentration`
+ |
+
+Positive floating point tensor, whose dtype is the
+same as `n` with shape broadcastable to `[N1,..., Nm, K]` `m >= 0`.
+Defines this as a batch of `N1 x ... x Nm` different `K` class Dirichlet
+multinomial distributions.
+ |
+
+|
+`validate_args`
+ |
+
+Python `bool`, default `False`. When `True` distribution
+parameters are checked for validity despite possibly degrading runtime
+performance. When `False` invalid inputs may silently render incorrect
+outputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`allow_nan_stats`
+ |
+
+Python `bool`, default `True`. When `True`, statistics
+(e.g., mean, mode, variance) use the value "`NaN`" to indicate the
+result is undefined. When `False`, an exception is raised if one or
+more of the statistic's batch members are undefined.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` name prefixed to Ops created by this class.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`allow_nan_stats`
+ |
+
+Python `bool` describing behavior when a stat is undefined.
+
+Stats return +/- infinity when it makes sense. E.g., the variance of a
+Cauchy distribution is infinity. However, sometimes the statistic is
+undefined, e.g., if a distribution's pdf does not achieve a maximum within
+the support of the distribution, the mode is undefined. If the mean is
+undefined, then by definition the variance is undefined. E.g. the mean for
+Student's T for df = 1 is undefined (no clear way to say it is either + or -
+infinity), so the variance = E[(X - mean)**2] is also undefined.
+ |
+
+|
+`batch_shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single event index as a `TensorShape`.
+
+May be partially defined or unknown.
+
+The batch dimensions are indexes into independent, non-identical
+parameterizations of this distribution.
+ |
+
+|
+`concentration`
+ |
+
+Concentration parameter; expected prior counts for that coordinate.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+The `DType` of `Tensor`s handled by this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`event_shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single batch as a `TensorShape`.
+
+May be partially defined or unknown.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name prepended to all ops created by this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`parameters`
+ |
+
+Dictionary of parameters used to instantiate this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`reparameterization_type`
+ |
+
+Describes how samples from the distribution are reparameterized.
+
+Currently this is one of the static instances
+`distributions.FULLY_REPARAMETERIZED`
+or `distributions.NOT_REPARAMETERIZED`.
+ |
+
+|
+`total_concentration`
+ |
+
+Sum of last dim of concentration parameter.
+ |
+
+|
+`total_count`
+ |
+
+Number of trials used to construct a sample.
+ |
+
+|
+`validate_args`
+ |
+
+Python `bool` indicating possibly expensive checks are enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+batch_shape_tensor
+
+View source
+
+
+batch_shape_tensor(
+ name='batch_shape_tensor'
+)
+
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single event index as a 1-D `Tensor`.
+
+The batch dimensions are indexes into independent, non-identical
+parameterizations of this distribution.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`batch_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+cdf
+
+View source
+
+
+cdf(
+ value, name='cdf'
+)
+
+
+Cumulative distribution function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the cumulative distribution function `cdf` is:
+
+```none
+cdf(x) := P[X <= x]
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cdf`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+copy
+
+View source
+
+
+copy(
+ **override_parameters_kwargs
+)
+
+
+Creates a deep copy of the distribution.
+
+Note: the copy distribution may continue to depend on the original
+initialization arguments.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`**override_parameters_kwargs`
+ |
+
+String/value dictionary of initialization
+arguments to override with new values.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`distribution`
+ |
+
+A new instance of `type(self)` initialized from the union
+of self.parameters and override_parameters_kwargs, i.e.,
+`dict(self.parameters, **override_parameters_kwargs)`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+covariance
+
+View source
+
+
+covariance(
+ name='covariance'
+)
+
+
+Covariance.
+
+Covariance is (possibly) defined only for non-scalar-event distributions.
+
+For example, for a length-`k`, vector-valued distribution, it is calculated
+as,
+
+```none
+Cov[i, j] = Covariance(X_i, X_j) = E[(X_i - E[X_i]) (X_j - E[X_j])]
+```
+
+where `Cov` is a (batch of) `k x k` matrix, `0 <= (i, j) < k`, and `E`
+denotes expectation.
+
+Alternatively, for non-vector, multivariate distributions (e.g.,
+matrix-valued, Wishart), `Covariance` shall return a (batch of) matrices
+under some vectorization of the events, i.e.,
+
+```none
+Cov[i, j] = Covariance(Vec(X)_i, Vec(X)_j) = [as above]
+```
+
+where `Cov` is a (batch of) `k' x k'` matrices,
+`0 <= (i, j) < k' = reduce_prod(event_shape)`, and `Vec` is some function
+mapping indices of this distribution's event dimensions to indices of a
+length-`k'` vector.
+
+
+Additional documentation from `DirichletMultinomial`:
+
+The covariance for each batch member is defined as the following:
+
+```none
+Var(X_j) = n * alpha_j / alpha_0 * (1 - alpha_j / alpha_0) *
+(n + alpha_0) / (1 + alpha_0)
+```
+
+where `concentration = alpha` and
+`total_concentration = alpha_0 = sum_j alpha_j`.
+
+The covariance between elements in a batch is defined as:
+
+```none
+Cov(X_i, X_j) = -n * alpha_i * alpha_j / alpha_0 ** 2 *
+(n + alpha_0) / (1 + alpha_0)
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`covariance`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn, k', k']`
+where the first `n` dimensions are batch coordinates and
+`k' = reduce_prod(self.event_shape)`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+cross_entropy
+
+View source
+
+
+cross_entropy(
+ other, name='cross_entropy'
+)
+
+
+Computes the (Shannon) cross entropy.
+
+Denote this distribution (`self`) by `P` and the `other` distribution by
+`Q`. Assuming `P, Q` are absolutely continuous with respect to
+one another and permit densities `p(x) dr(x)` and `q(x) dr(x)`, (Shanon)
+cross entropy is defined as:
+
+```none
+H[P, Q] = E_p[-log q(X)] = -int_F p(x) log q(x) dr(x)
+```
+
+where `F` denotes the support of the random variable `X ~ P`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`other`
+ |
+
+`tfp.distributions.Distribution` instance.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cross_entropy`
+ |
+
+`self.dtype` `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn]`
+representing `n` different calculations of (Shanon) cross entropy.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+entropy
+
+View source
+
+
+entropy(
+ name='entropy'
+)
+
+
+Shannon entropy in nats.
+
+
+event_shape_tensor
+
+View source
+
+
+event_shape_tensor(
+ name='event_shape_tensor'
+)
+
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single batch as a 1-D int32 `Tensor`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`event_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+is_scalar_batch
+
+View source
+
+
+is_scalar_batch(
+ name='is_scalar_batch'
+)
+
+
+Indicates that `batch_shape == []`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`is_scalar_batch`
+ |
+
+`bool` scalar `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+is_scalar_event
+
+View source
+
+
+is_scalar_event(
+ name='is_scalar_event'
+)
+
+
+Indicates that `event_shape == []`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`is_scalar_event`
+ |
+
+`bool` scalar `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+kl_divergence
+
+View source
+
+
+kl_divergence(
+ other, name='kl_divergence'
+)
+
+
+Computes the Kullback--Leibler divergence.
+
+Denote this distribution (`self`) by `p` and the `other` distribution by
+`q`. Assuming `p, q` are absolutely continuous with respect to reference
+measure `r`, the KL divergence is defined as:
+
+```none
+KL[p, q] = E_p[log(p(X)/q(X))]
+ = -int_F p(x) log q(x) dr(x) + int_F p(x) log p(x) dr(x)
+ = H[p, q] - H[p]
+```
+
+where `F` denotes the support of the random variable `X ~ p`, `H[., .]`
+denotes (Shanon) cross entropy, and `H[.]` denotes (Shanon) entropy.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`other`
+ |
+
+`tfp.distributions.Distribution` instance.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`kl_divergence`
+ |
+
+`self.dtype` `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn]`
+representing `n` different calculations of the Kullback-Leibler
+divergence.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_cdf
+
+View source
+
+
+log_cdf(
+ value, name='log_cdf'
+)
+
+
+Log cumulative distribution function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the cumulative distribution function `cdf` is:
+
+```none
+log_cdf(x) := Log[ P[X <= x] ]
+```
+
+Often, a numerical approximation can be used for `log_cdf(x)` that yields
+a more accurate answer than simply taking the logarithm of the `cdf` when
+`x << -1`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`logcdf`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_prob
+
+View source
+
+
+log_prob(
+ value, name='log_prob'
+)
+
+
+Log probability density/mass function.
+
+
+Additional documentation from `DirichletMultinomial`:
+
+For each batch of counts,
+`value = [n_0, ..., n_{K-1}]`, `P[value]` is the probability that after
+sampling `self.total_count` draws from this Dirichlet-Multinomial distribution,
+the number of draws falling in class `j` is `n_j`. Since this definition is
+[exchangeable](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Exchangeable_random_variables);
+different sequences have the same counts so the probability includes a
+combinatorial coefficient.
+
+Note: `value` must be a non-negative tensor with dtype `self.dtype`, have no
+fractional components, and such that
+`tf.reduce_sum(value, -1) = self.total_count`. Its shape must be broadcastable
+with `self.concentration` and `self.total_count`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`log_prob`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_survival_function
+
+View source
+
+
+log_survival_function(
+ value, name='log_survival_function'
+)
+
+
+Log survival function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the survival function is defined:
+
+```none
+log_survival_function(x) = Log[ P[X > x] ]
+ = Log[ 1 - P[X <= x] ]
+ = Log[ 1 - cdf(x) ]
+```
+
+Typically, different numerical approximations can be used for the log
+survival function, which are more accurate than `1 - cdf(x)` when `x >> 1`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with values of type
+`self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+mean
+
+View source
+
+
+mean(
+ name='mean'
+)
+
+
+Mean.
+
+
+mode
+
+View source
+
+
+mode(
+ name='mode'
+)
+
+
+Mode.
+
+
+param_shapes
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+param_shapes(
+ sample_shape, name='DistributionParamShapes'
+)
+
+
+Shapes of parameters given the desired shape of a call to `sample()`.
+
+This is a class method that describes what key/value arguments are required
+to instantiate the given `Distribution` so that a particular shape is
+returned for that instance's call to `sample()`.
+
+Subclasses should override class method `_param_shapes`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor` or python list/tuple. Desired shape of a call to
+`sample()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to prepend ops with.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`dict` of parameter name to `Tensor` shapes.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+param_static_shapes
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+param_static_shapes(
+ sample_shape
+)
+
+
+param_shapes with static (i.e. `TensorShape`) shapes.
+
+This is a class method that describes what key/value arguments are required
+to instantiate the given `Distribution` so that a particular shape is
+returned for that instance's call to `sample()`. Assumes that the sample's
+shape is known statically.
+
+Subclasses should override class method `_param_shapes` to return
+constant-valued tensors when constant values are fed.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+`TensorShape` or python list/tuple. Desired shape of a call
+to `sample()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`dict` of parameter name to `TensorShape`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `sample_shape` is a `TensorShape` and is not fully defined.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+prob
+
+View source
+
+
+prob(
+ value, name='prob'
+)
+
+
+Probability density/mass function.
+
+
+Additional documentation from `DirichletMultinomial`:
+
+For each batch of counts,
+`value = [n_0, ..., n_{K-1}]`, `P[value]` is the probability that after
+sampling `self.total_count` draws from this Dirichlet-Multinomial distribution,
+the number of draws falling in class `j` is `n_j`. Since this definition is
+[exchangeable](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Exchangeable_random_variables);
+different sequences have the same counts so the probability includes a
+combinatorial coefficient.
+
+Note: `value` must be a non-negative tensor with dtype `self.dtype`, have no
+fractional components, and such that
+`tf.reduce_sum(value, -1) = self.total_count`. Its shape must be broadcastable
+with `self.concentration` and `self.total_count`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`prob`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+quantile
+
+View source
+
+
+quantile(
+ value, name='quantile'
+)
+
+
+Quantile function. Aka "inverse cdf" or "percent point function".
+
+Given random variable `X` and `p in [0, 1]`, the `quantile` is:
+
+```none
+quantile(p) := x such that P[X <= x] == p
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`quantile`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+sample
+
+View source
+
+
+sample(
+ sample_shape=(), seed=None, name='sample'
+)
+
+
+Generate samples of the specified shape.
+
+Note that a call to `sample()` without arguments will generate a single
+sample.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+0D or 1D `int32` `Tensor`. Shape of the generated samples.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+Python integer seed for RNG
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`samples`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` with prepended dimensions `sample_shape`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+stddev
+
+View source
+
+
+stddev(
+ name='stddev'
+)
+
+
+Standard deviation.
+
+Standard deviation is defined as,
+
+```none
+stddev = E[(X - E[X])**2]**0.5
+```
+
+where `X` is the random variable associated with this distribution, `E`
+denotes expectation, and `stddev.shape = batch_shape + event_shape`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`stddev`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape identical to
+`batch_shape + event_shape`, i.e., the same shape as `self.mean()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+survival_function
+
+View source
+
+
+survival_function(
+ value, name='survival_function'
+)
+
+
+Survival function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the survival function is defined:
+
+```none
+survival_function(x) = P[X > x]
+ = 1 - P[X <= x]
+ = 1 - cdf(x).
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with values of type
+`self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+variance
+
+View source
+
+
+variance(
+ name='variance'
+)
+
+
+Variance.
+
+Variance is defined as,
+
+```none
+Var = E[(X - E[X])**2]
+```
+
+where `X` is the random variable associated with this distribution, `E`
+denotes expectation, and `Var.shape = batch_shape + event_shape`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`variance`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape identical to
+`batch_shape + event_shape`, i.e., the same shape as `self.mean()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/Distribution.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/Distribution.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..2c882ac7128
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/Distribution.md
@@ -0,0 +1,1577 @@
+description: A generic probability distribution base class.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.distributions.Distribution
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A generic probability distribution base class.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.distributions.Distribution(
+ dtype, reparameterization_type, validate_args, allow_nan_stats, parameters=None,
+ graph_parents=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+`Distribution` is a base class for constructing and organizing properties
+(e.g., mean, variance) of random variables (e.g, Bernoulli, Gaussian).
+
+#### Subclassing
+
+Subclasses are expected to implement a leading-underscore version of the
+same-named function. The argument signature should be identical except for
+the omission of `name="..."`. For example, to enable `log_prob(value,
+name="log_prob")` a subclass should implement `_log_prob(value)`.
+
+Subclasses can append to public-level docstrings by providing
+docstrings for their method specializations. For example:
+
+```python
+@util.AppendDocstring("Some other details.")
+def _log_prob(self, value):
+ ...
+```
+
+would add the string "Some other details." to the `log_prob` function
+docstring. This is implemented as a simple decorator to avoid python
+linter complaining about missing Args/Returns/Raises sections in the
+partial docstrings.
+
+#### Broadcasting, batching, and shapes
+
+All distributions support batches of independent distributions of that type.
+The batch shape is determined by broadcasting together the parameters.
+
+The shape of arguments to `__init__`, `cdf`, `log_cdf`, `prob`, and
+`log_prob` reflect this broadcasting, as does the return value of `sample` and
+`sample_n`.
+
+`sample_n_shape = [n] + batch_shape + event_shape`, where `sample_n_shape` is
+the shape of the `Tensor` returned from `sample_n`, `n` is the number of
+samples, `batch_shape` defines how many independent distributions there are,
+and `event_shape` defines the shape of samples from each of those independent
+distributions. Samples are independent along the `batch_shape` dimensions, but
+not necessarily so along the `event_shape` dimensions (depending on the
+particulars of the underlying distribution).
+
+Using the `Uniform` distribution as an example:
+
+```python
+minval = 3.0
+maxval = [[4.0, 6.0],
+ [10.0, 12.0]]
+
+# Broadcasting:
+# This instance represents 4 Uniform distributions. Each has a lower bound at
+# 3.0 as the `minval` parameter was broadcasted to match `maxval`'s shape.
+u = Uniform(minval, maxval)
+
+# `event_shape` is `TensorShape([])`.
+event_shape = u.event_shape
+# `event_shape_t` is a `Tensor` which will evaluate to [].
+event_shape_t = u.event_shape_tensor()
+
+# Sampling returns a sample per distribution. `samples` has shape
+# [5, 2, 2], which is [n] + batch_shape + event_shape, where n=5,
+# batch_shape=[2, 2], and event_shape=[].
+samples = u.sample_n(5)
+
+# The broadcasting holds across methods. Here we use `cdf` as an example. The
+# same holds for `log_cdf` and the likelihood functions.
+
+# `cum_prob` has shape [2, 2] as the `value` argument was broadcasted to the
+# shape of the `Uniform` instance.
+cum_prob_broadcast = u.cdf(4.0)
+
+# `cum_prob`'s shape is [2, 2], one per distribution. No broadcasting
+# occurred.
+cum_prob_per_dist = u.cdf([[4.0, 5.0],
+ [6.0, 7.0]])
+
+# INVALID as the `value` argument is not broadcastable to the distribution's
+# shape.
+cum_prob_invalid = u.cdf([4.0, 5.0, 6.0])
+```
+
+#### Shapes
+
+There are three important concepts associated with TensorFlow Distributions
+shapes:
+- Event shape describes the shape of a single draw from the distribution;
+ it may be dependent across dimensions. For scalar distributions, the event
+ shape is `[]`. For a 5-dimensional MultivariateNormal, the event shape is
+ `[5]`.
+- Batch shape describes independent, not identically distributed draws, aka a
+ "collection" or "bunch" of distributions.
+- Sample shape describes independent, identically distributed draws of batches
+ from the distribution family.
+
+The event shape and the batch shape are properties of a Distribution object,
+whereas the sample shape is associated with a specific call to `sample` or
+`log_prob`.
+
+For detailed usage examples of TensorFlow Distributions shapes, see
+[this tutorial](
+https://github.com/tensorflow/probability/blob/master/tensorflow_probability/examples/jupyter_notebooks/Understanding_TensorFlow_Distributions_Shapes.ipynb)
+
+#### Parameter values leading to undefined statistics or distributions.
+
+Some distributions do not have well-defined statistics for all initialization
+parameter values. For example, the beta distribution is parameterized by
+positive real numbers `concentration1` and `concentration0`, and does not have
+well-defined mode if `concentration1 < 1` or `concentration0 < 1`.
+
+The user is given the option of raising an exception or returning `NaN`.
+
+```python
+a = tf.exp(tf.matmul(logits, weights_a))
+b = tf.exp(tf.matmul(logits, weights_b))
+
+# Will raise exception if ANY batch member has a < 1 or b < 1.
+dist = distributions.beta(a, b, allow_nan_stats=False)
+mode = dist.mode().eval()
+
+# Will return NaN for batch members with either a < 1 or b < 1.
+dist = distributions.beta(a, b, allow_nan_stats=True) # Default behavior
+mode = dist.mode().eval()
+```
+
+In all cases, an exception is raised if *invalid* parameters are passed, e.g.
+
+```python
+# Will raise an exception if any Op is run.
+negative_a = -1.0 * a # beta distribution by definition has a > 0.
+dist = distributions.beta(negative_a, b, allow_nan_stats=True)
+dist.mean().eval()
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+The type of the event samples. `None` implies no type-enforcement.
+ |
+
+|
+`reparameterization_type`
+ |
+
+Instance of `ReparameterizationType`.
+If `distributions.FULLY_REPARAMETERIZED`, this
+`Distribution` can be reparameterized in terms of some standard
+distribution with a function whose Jacobian is constant for the support
+of the standard distribution. If `distributions.NOT_REPARAMETERIZED`,
+then no such reparameterization is available.
+ |
+
+|
+`validate_args`
+ |
+
+Python `bool`, default `False`. When `True` distribution
+parameters are checked for validity despite possibly degrading runtime
+performance. When `False` invalid inputs may silently render incorrect
+outputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`allow_nan_stats`
+ |
+
+Python `bool`, default `True`. When `True`, statistics
+(e.g., mean, mode, variance) use the value "`NaN`" to indicate the
+result is undefined. When `False`, an exception is raised if one or
+more of the statistic's batch members are undefined.
+ |
+
+|
+`parameters`
+ |
+
+Python `dict` of parameters used to instantiate this
+`Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`graph_parents`
+ |
+
+Python `list` of graph prerequisites of this
+`Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` name prefixed to Ops created by this class. Default:
+subclass name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if any member of graph_parents is `None` or not a `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`allow_nan_stats`
+ |
+
+Python `bool` describing behavior when a stat is undefined.
+
+Stats return +/- infinity when it makes sense. E.g., the variance of a
+Cauchy distribution is infinity. However, sometimes the statistic is
+undefined, e.g., if a distribution's pdf does not achieve a maximum within
+the support of the distribution, the mode is undefined. If the mean is
+undefined, then by definition the variance is undefined. E.g. the mean for
+Student's T for df = 1 is undefined (no clear way to say it is either + or -
+infinity), so the variance = E[(X - mean)**2] is also undefined.
+ |
+
+|
+`batch_shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single event index as a `TensorShape`.
+
+May be partially defined or unknown.
+
+The batch dimensions are indexes into independent, non-identical
+parameterizations of this distribution.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+The `DType` of `Tensor`s handled by this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`event_shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single batch as a `TensorShape`.
+
+May be partially defined or unknown.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name prepended to all ops created by this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`parameters`
+ |
+
+Dictionary of parameters used to instantiate this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`reparameterization_type`
+ |
+
+Describes how samples from the distribution are reparameterized.
+
+Currently this is one of the static instances
+`distributions.FULLY_REPARAMETERIZED`
+or `distributions.NOT_REPARAMETERIZED`.
+ |
+
+|
+`validate_args`
+ |
+
+Python `bool` indicating possibly expensive checks are enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+batch_shape_tensor
+
+View source
+
+
+batch_shape_tensor(
+ name='batch_shape_tensor'
+)
+
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single event index as a 1-D `Tensor`.
+
+The batch dimensions are indexes into independent, non-identical
+parameterizations of this distribution.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`batch_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+cdf
+
+View source
+
+
+cdf(
+ value, name='cdf'
+)
+
+
+Cumulative distribution function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the cumulative distribution function `cdf` is:
+
+```none
+cdf(x) := P[X <= x]
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cdf`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+copy
+
+View source
+
+
+copy(
+ **override_parameters_kwargs
+)
+
+
+Creates a deep copy of the distribution.
+
+Note: the copy distribution may continue to depend on the original
+initialization arguments.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`**override_parameters_kwargs`
+ |
+
+String/value dictionary of initialization
+arguments to override with new values.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`distribution`
+ |
+
+A new instance of `type(self)` initialized from the union
+of self.parameters and override_parameters_kwargs, i.e.,
+`dict(self.parameters, **override_parameters_kwargs)`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+covariance
+
+View source
+
+
+covariance(
+ name='covariance'
+)
+
+
+Covariance.
+
+Covariance is (possibly) defined only for non-scalar-event distributions.
+
+For example, for a length-`k`, vector-valued distribution, it is calculated
+as,
+
+```none
+Cov[i, j] = Covariance(X_i, X_j) = E[(X_i - E[X_i]) (X_j - E[X_j])]
+```
+
+where `Cov` is a (batch of) `k x k` matrix, `0 <= (i, j) < k`, and `E`
+denotes expectation.
+
+Alternatively, for non-vector, multivariate distributions (e.g.,
+matrix-valued, Wishart), `Covariance` shall return a (batch of) matrices
+under some vectorization of the events, i.e.,
+
+```none
+Cov[i, j] = Covariance(Vec(X)_i, Vec(X)_j) = [as above]
+```
+
+where `Cov` is a (batch of) `k' x k'` matrices,
+`0 <= (i, j) < k' = reduce_prod(event_shape)`, and `Vec` is some function
+mapping indices of this distribution's event dimensions to indices of a
+length-`k'` vector.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`covariance`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn, k', k']`
+where the first `n` dimensions are batch coordinates and
+`k' = reduce_prod(self.event_shape)`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+cross_entropy
+
+View source
+
+
+cross_entropy(
+ other, name='cross_entropy'
+)
+
+
+Computes the (Shannon) cross entropy.
+
+Denote this distribution (`self`) by `P` and the `other` distribution by
+`Q`. Assuming `P, Q` are absolutely continuous with respect to
+one another and permit densities `p(x) dr(x)` and `q(x) dr(x)`, (Shanon)
+cross entropy is defined as:
+
+```none
+H[P, Q] = E_p[-log q(X)] = -int_F p(x) log q(x) dr(x)
+```
+
+where `F` denotes the support of the random variable `X ~ P`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`other`
+ |
+
+`tfp.distributions.Distribution` instance.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cross_entropy`
+ |
+
+`self.dtype` `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn]`
+representing `n` different calculations of (Shanon) cross entropy.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+entropy
+
+View source
+
+
+entropy(
+ name='entropy'
+)
+
+
+Shannon entropy in nats.
+
+
+event_shape_tensor
+
+View source
+
+
+event_shape_tensor(
+ name='event_shape_tensor'
+)
+
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single batch as a 1-D int32 `Tensor`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`event_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+is_scalar_batch
+
+View source
+
+
+is_scalar_batch(
+ name='is_scalar_batch'
+)
+
+
+Indicates that `batch_shape == []`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`is_scalar_batch`
+ |
+
+`bool` scalar `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+is_scalar_event
+
+View source
+
+
+is_scalar_event(
+ name='is_scalar_event'
+)
+
+
+Indicates that `event_shape == []`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`is_scalar_event`
+ |
+
+`bool` scalar `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+kl_divergence
+
+View source
+
+
+kl_divergence(
+ other, name='kl_divergence'
+)
+
+
+Computes the Kullback--Leibler divergence.
+
+Denote this distribution (`self`) by `p` and the `other` distribution by
+`q`. Assuming `p, q` are absolutely continuous with respect to reference
+measure `r`, the KL divergence is defined as:
+
+```none
+KL[p, q] = E_p[log(p(X)/q(X))]
+ = -int_F p(x) log q(x) dr(x) + int_F p(x) log p(x) dr(x)
+ = H[p, q] - H[p]
+```
+
+where `F` denotes the support of the random variable `X ~ p`, `H[., .]`
+denotes (Shanon) cross entropy, and `H[.]` denotes (Shanon) entropy.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`other`
+ |
+
+`tfp.distributions.Distribution` instance.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`kl_divergence`
+ |
+
+`self.dtype` `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn]`
+representing `n` different calculations of the Kullback-Leibler
+divergence.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_cdf
+
+View source
+
+
+log_cdf(
+ value, name='log_cdf'
+)
+
+
+Log cumulative distribution function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the cumulative distribution function `cdf` is:
+
+```none
+log_cdf(x) := Log[ P[X <= x] ]
+```
+
+Often, a numerical approximation can be used for `log_cdf(x)` that yields
+a more accurate answer than simply taking the logarithm of the `cdf` when
+`x << -1`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`logcdf`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_prob
+
+View source
+
+
+log_prob(
+ value, name='log_prob'
+)
+
+
+Log probability density/mass function.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`log_prob`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_survival_function
+
+View source
+
+
+log_survival_function(
+ value, name='log_survival_function'
+)
+
+
+Log survival function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the survival function is defined:
+
+```none
+log_survival_function(x) = Log[ P[X > x] ]
+ = Log[ 1 - P[X <= x] ]
+ = Log[ 1 - cdf(x) ]
+```
+
+Typically, different numerical approximations can be used for the log
+survival function, which are more accurate than `1 - cdf(x)` when `x >> 1`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with values of type
+`self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+mean
+
+View source
+
+
+mean(
+ name='mean'
+)
+
+
+Mean.
+
+
+mode
+
+View source
+
+
+mode(
+ name='mode'
+)
+
+
+Mode.
+
+
+param_shapes
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+param_shapes(
+ sample_shape, name='DistributionParamShapes'
+)
+
+
+Shapes of parameters given the desired shape of a call to `sample()`.
+
+This is a class method that describes what key/value arguments are required
+to instantiate the given `Distribution` so that a particular shape is
+returned for that instance's call to `sample()`.
+
+Subclasses should override class method `_param_shapes`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor` or python list/tuple. Desired shape of a call to
+`sample()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to prepend ops with.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`dict` of parameter name to `Tensor` shapes.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+param_static_shapes
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+param_static_shapes(
+ sample_shape
+)
+
+
+param_shapes with static (i.e. `TensorShape`) shapes.
+
+This is a class method that describes what key/value arguments are required
+to instantiate the given `Distribution` so that a particular shape is
+returned for that instance's call to `sample()`. Assumes that the sample's
+shape is known statically.
+
+Subclasses should override class method `_param_shapes` to return
+constant-valued tensors when constant values are fed.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+`TensorShape` or python list/tuple. Desired shape of a call
+to `sample()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`dict` of parameter name to `TensorShape`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `sample_shape` is a `TensorShape` and is not fully defined.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+prob
+
+View source
+
+
+prob(
+ value, name='prob'
+)
+
+
+Probability density/mass function.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`prob`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+quantile
+
+View source
+
+
+quantile(
+ value, name='quantile'
+)
+
+
+Quantile function. Aka "inverse cdf" or "percent point function".
+
+Given random variable `X` and `p in [0, 1]`, the `quantile` is:
+
+```none
+quantile(p) := x such that P[X <= x] == p
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`quantile`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+sample
+
+View source
+
+
+sample(
+ sample_shape=(), seed=None, name='sample'
+)
+
+
+Generate samples of the specified shape.
+
+Note that a call to `sample()` without arguments will generate a single
+sample.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+0D or 1D `int32` `Tensor`. Shape of the generated samples.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+Python integer seed for RNG
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`samples`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` with prepended dimensions `sample_shape`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+stddev
+
+View source
+
+
+stddev(
+ name='stddev'
+)
+
+
+Standard deviation.
+
+Standard deviation is defined as,
+
+```none
+stddev = E[(X - E[X])**2]**0.5
+```
+
+where `X` is the random variable associated with this distribution, `E`
+denotes expectation, and `stddev.shape = batch_shape + event_shape`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`stddev`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape identical to
+`batch_shape + event_shape`, i.e., the same shape as `self.mean()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+survival_function
+
+View source
+
+
+survival_function(
+ value, name='survival_function'
+)
+
+
+Survival function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the survival function is defined:
+
+```none
+survival_function(x) = P[X > x]
+ = 1 - P[X <= x]
+ = 1 - cdf(x).
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with values of type
+`self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+variance
+
+View source
+
+
+variance(
+ name='variance'
+)
+
+
+Variance.
+
+Variance is defined as,
+
+```none
+Var = E[(X - E[X])**2]
+```
+
+where `X` is the random variable associated with this distribution, `E`
+denotes expectation, and `Var.shape = batch_shape + event_shape`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`variance`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape identical to
+`batch_shape + event_shape`, i.e., the same shape as `self.mean()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/Exponential.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/Exponential.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3f8297f0c0c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/Exponential.md
@@ -0,0 +1,1448 @@
+description: Exponential distribution.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.distributions.Exponential
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Exponential distribution.
+
+Inherits From: [`Gamma`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/distributions/Gamma.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.distributions.Exponential(
+ rate, validate_args=(False), allow_nan_stats=(True), name='Exponential'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The Exponential distribution is parameterized by an event `rate` parameter.
+
+#### Mathematical Details
+
+The probability density function (pdf) is,
+
+```none
+pdf(x; lambda, x > 0) = exp(-lambda x) / Z
+Z = 1 / lambda
+```
+
+where `rate = lambda` and `Z` is the normalizaing constant.
+
+The Exponential distribution is a special case of the Gamma distribution,
+i.e.,
+
+```python
+Exponential(rate) = Gamma(concentration=1., rate)
+```
+
+The Exponential distribution uses a `rate` parameter, or "inverse scale",
+which can be intuited as,
+
+```none
+X ~ Exponential(rate=1)
+Y = X / rate
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`rate`
+ |
+
+Floating point tensor, equivalent to `1 / mean`. Must contain only
+positive values.
+ |
+
+|
+`validate_args`
+ |
+
+Python `bool`, default `False`. When `True` distribution
+parameters are checked for validity despite possibly degrading runtime
+performance. When `False` invalid inputs may silently render incorrect
+outputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`allow_nan_stats`
+ |
+
+Python `bool`, default `True`. When `True`, statistics
+(e.g., mean, mode, variance) use the value "`NaN`" to indicate the
+result is undefined. When `False`, an exception is raised if one or
+more of the statistic's batch members are undefined.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` name prefixed to Ops created by this class.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`allow_nan_stats`
+ |
+
+Python `bool` describing behavior when a stat is undefined.
+
+Stats return +/- infinity when it makes sense. E.g., the variance of a
+Cauchy distribution is infinity. However, sometimes the statistic is
+undefined, e.g., if a distribution's pdf does not achieve a maximum within
+the support of the distribution, the mode is undefined. If the mean is
+undefined, then by definition the variance is undefined. E.g. the mean for
+Student's T for df = 1 is undefined (no clear way to say it is either + or -
+infinity), so the variance = E[(X - mean)**2] is also undefined.
+ |
+
+|
+`batch_shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single event index as a `TensorShape`.
+
+May be partially defined or unknown.
+
+The batch dimensions are indexes into independent, non-identical
+parameterizations of this distribution.
+ |
+
+|
+`concentration`
+ |
+
+Concentration parameter.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+The `DType` of `Tensor`s handled by this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`event_shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single batch as a `TensorShape`.
+
+May be partially defined or unknown.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name prepended to all ops created by this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`parameters`
+ |
+
+Dictionary of parameters used to instantiate this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`rate`
+ |
+
+Rate parameter.
+ |
+
+|
+`reparameterization_type`
+ |
+
+Describes how samples from the distribution are reparameterized.
+
+Currently this is one of the static instances
+`distributions.FULLY_REPARAMETERIZED`
+or `distributions.NOT_REPARAMETERIZED`.
+ |
+
+|
+`validate_args`
+ |
+
+Python `bool` indicating possibly expensive checks are enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+batch_shape_tensor
+
+View source
+
+
+batch_shape_tensor(
+ name='batch_shape_tensor'
+)
+
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single event index as a 1-D `Tensor`.
+
+The batch dimensions are indexes into independent, non-identical
+parameterizations of this distribution.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`batch_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+cdf
+
+View source
+
+
+cdf(
+ value, name='cdf'
+)
+
+
+Cumulative distribution function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the cumulative distribution function `cdf` is:
+
+```none
+cdf(x) := P[X <= x]
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cdf`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+copy
+
+View source
+
+
+copy(
+ **override_parameters_kwargs
+)
+
+
+Creates a deep copy of the distribution.
+
+Note: the copy distribution may continue to depend on the original
+initialization arguments.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`**override_parameters_kwargs`
+ |
+
+String/value dictionary of initialization
+arguments to override with new values.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`distribution`
+ |
+
+A new instance of `type(self)` initialized from the union
+of self.parameters and override_parameters_kwargs, i.e.,
+`dict(self.parameters, **override_parameters_kwargs)`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+covariance
+
+View source
+
+
+covariance(
+ name='covariance'
+)
+
+
+Covariance.
+
+Covariance is (possibly) defined only for non-scalar-event distributions.
+
+For example, for a length-`k`, vector-valued distribution, it is calculated
+as,
+
+```none
+Cov[i, j] = Covariance(X_i, X_j) = E[(X_i - E[X_i]) (X_j - E[X_j])]
+```
+
+where `Cov` is a (batch of) `k x k` matrix, `0 <= (i, j) < k`, and `E`
+denotes expectation.
+
+Alternatively, for non-vector, multivariate distributions (e.g.,
+matrix-valued, Wishart), `Covariance` shall return a (batch of) matrices
+under some vectorization of the events, i.e.,
+
+```none
+Cov[i, j] = Covariance(Vec(X)_i, Vec(X)_j) = [as above]
+```
+
+where `Cov` is a (batch of) `k' x k'` matrices,
+`0 <= (i, j) < k' = reduce_prod(event_shape)`, and `Vec` is some function
+mapping indices of this distribution's event dimensions to indices of a
+length-`k'` vector.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`covariance`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn, k', k']`
+where the first `n` dimensions are batch coordinates and
+`k' = reduce_prod(self.event_shape)`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+cross_entropy
+
+View source
+
+
+cross_entropy(
+ other, name='cross_entropy'
+)
+
+
+Computes the (Shannon) cross entropy.
+
+Denote this distribution (`self`) by `P` and the `other` distribution by
+`Q`. Assuming `P, Q` are absolutely continuous with respect to
+one another and permit densities `p(x) dr(x)` and `q(x) dr(x)`, (Shanon)
+cross entropy is defined as:
+
+```none
+H[P, Q] = E_p[-log q(X)] = -int_F p(x) log q(x) dr(x)
+```
+
+where `F` denotes the support of the random variable `X ~ P`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`other`
+ |
+
+`tfp.distributions.Distribution` instance.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cross_entropy`
+ |
+
+`self.dtype` `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn]`
+representing `n` different calculations of (Shanon) cross entropy.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+entropy
+
+View source
+
+
+entropy(
+ name='entropy'
+)
+
+
+Shannon entropy in nats.
+
+
+event_shape_tensor
+
+View source
+
+
+event_shape_tensor(
+ name='event_shape_tensor'
+)
+
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single batch as a 1-D int32 `Tensor`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`event_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+is_scalar_batch
+
+View source
+
+
+is_scalar_batch(
+ name='is_scalar_batch'
+)
+
+
+Indicates that `batch_shape == []`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`is_scalar_batch`
+ |
+
+`bool` scalar `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+is_scalar_event
+
+View source
+
+
+is_scalar_event(
+ name='is_scalar_event'
+)
+
+
+Indicates that `event_shape == []`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`is_scalar_event`
+ |
+
+`bool` scalar `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+kl_divergence
+
+View source
+
+
+kl_divergence(
+ other, name='kl_divergence'
+)
+
+
+Computes the Kullback--Leibler divergence.
+
+Denote this distribution (`self`) by `p` and the `other` distribution by
+`q`. Assuming `p, q` are absolutely continuous with respect to reference
+measure `r`, the KL divergence is defined as:
+
+```none
+KL[p, q] = E_p[log(p(X)/q(X))]
+ = -int_F p(x) log q(x) dr(x) + int_F p(x) log p(x) dr(x)
+ = H[p, q] - H[p]
+```
+
+where `F` denotes the support of the random variable `X ~ p`, `H[., .]`
+denotes (Shanon) cross entropy, and `H[.]` denotes (Shanon) entropy.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`other`
+ |
+
+`tfp.distributions.Distribution` instance.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`kl_divergence`
+ |
+
+`self.dtype` `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn]`
+representing `n` different calculations of the Kullback-Leibler
+divergence.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_cdf
+
+View source
+
+
+log_cdf(
+ value, name='log_cdf'
+)
+
+
+Log cumulative distribution function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the cumulative distribution function `cdf` is:
+
+```none
+log_cdf(x) := Log[ P[X <= x] ]
+```
+
+Often, a numerical approximation can be used for `log_cdf(x)` that yields
+a more accurate answer than simply taking the logarithm of the `cdf` when
+`x << -1`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`logcdf`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_prob
+
+View source
+
+
+log_prob(
+ value, name='log_prob'
+)
+
+
+Log probability density/mass function.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`log_prob`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_survival_function
+
+View source
+
+
+log_survival_function(
+ value, name='log_survival_function'
+)
+
+
+Log survival function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the survival function is defined:
+
+```none
+log_survival_function(x) = Log[ P[X > x] ]
+ = Log[ 1 - P[X <= x] ]
+ = Log[ 1 - cdf(x) ]
+```
+
+Typically, different numerical approximations can be used for the log
+survival function, which are more accurate than `1 - cdf(x)` when `x >> 1`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with values of type
+`self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+mean
+
+View source
+
+
+mean(
+ name='mean'
+)
+
+
+Mean.
+
+
+mode
+
+View source
+
+
+mode(
+ name='mode'
+)
+
+
+Mode.
+
+Additional documentation from `Gamma`:
+
+The mode of a gamma distribution is `(shape - 1) / rate` when
+`shape > 1`, and `NaN` otherwise. If `self.allow_nan_stats` is `False`,
+an exception will be raised rather than returning `NaN`.
+
+param_shapes
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+param_shapes(
+ sample_shape, name='DistributionParamShapes'
+)
+
+
+Shapes of parameters given the desired shape of a call to `sample()`.
+
+This is a class method that describes what key/value arguments are required
+to instantiate the given `Distribution` so that a particular shape is
+returned for that instance's call to `sample()`.
+
+Subclasses should override class method `_param_shapes`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor` or python list/tuple. Desired shape of a call to
+`sample()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to prepend ops with.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`dict` of parameter name to `Tensor` shapes.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+param_static_shapes
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+param_static_shapes(
+ sample_shape
+)
+
+
+param_shapes with static (i.e. `TensorShape`) shapes.
+
+This is a class method that describes what key/value arguments are required
+to instantiate the given `Distribution` so that a particular shape is
+returned for that instance's call to `sample()`. Assumes that the sample's
+shape is known statically.
+
+Subclasses should override class method `_param_shapes` to return
+constant-valued tensors when constant values are fed.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+`TensorShape` or python list/tuple. Desired shape of a call
+to `sample()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`dict` of parameter name to `TensorShape`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `sample_shape` is a `TensorShape` and is not fully defined.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+prob
+
+View source
+
+
+prob(
+ value, name='prob'
+)
+
+
+Probability density/mass function.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`prob`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+quantile
+
+View source
+
+
+quantile(
+ value, name='quantile'
+)
+
+
+Quantile function. Aka "inverse cdf" or "percent point function".
+
+Given random variable `X` and `p in [0, 1]`, the `quantile` is:
+
+```none
+quantile(p) := x such that P[X <= x] == p
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`quantile`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+sample
+
+View source
+
+
+sample(
+ sample_shape=(), seed=None, name='sample'
+)
+
+
+Generate samples of the specified shape.
+
+Note that a call to `sample()` without arguments will generate a single
+sample.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+0D or 1D `int32` `Tensor`. Shape of the generated samples.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+Python integer seed for RNG
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`samples`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` with prepended dimensions `sample_shape`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+stddev
+
+View source
+
+
+stddev(
+ name='stddev'
+)
+
+
+Standard deviation.
+
+Standard deviation is defined as,
+
+```none
+stddev = E[(X - E[X])**2]**0.5
+```
+
+where `X` is the random variable associated with this distribution, `E`
+denotes expectation, and `stddev.shape = batch_shape + event_shape`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`stddev`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape identical to
+`batch_shape + event_shape`, i.e., the same shape as `self.mean()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+survival_function
+
+View source
+
+
+survival_function(
+ value, name='survival_function'
+)
+
+
+Survival function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the survival function is defined:
+
+```none
+survival_function(x) = P[X > x]
+ = 1 - P[X <= x]
+ = 1 - cdf(x).
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with values of type
+`self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+variance
+
+View source
+
+
+variance(
+ name='variance'
+)
+
+
+Variance.
+
+Variance is defined as,
+
+```none
+Var = E[(X - E[X])**2]
+```
+
+where `X` is the random variable associated with this distribution, `E`
+denotes expectation, and `Var.shape = batch_shape + event_shape`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`variance`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape identical to
+`batch_shape + event_shape`, i.e., the same shape as `self.mean()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/Gamma.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/Gamma.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..61210d71045
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/Gamma.md
@@ -0,0 +1,1524 @@
+description: Gamma distribution.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.distributions.Gamma
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Gamma distribution.
+
+Inherits From: [`Distribution`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/distributions/Distribution.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.distributions.Gamma(
+ concentration, rate, validate_args=(False), allow_nan_stats=(True), name='Gamma'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The Gamma distribution is defined over positive real numbers using
+parameters `concentration` (aka "alpha") and `rate` (aka "beta").
+
+#### Mathematical Details
+
+The probability density function (pdf) is,
+
+```none
+pdf(x; alpha, beta, x > 0) = x**(alpha - 1) exp(-x beta) / Z
+Z = Gamma(alpha) beta**(-alpha)
+```
+
+where:
+
+* `concentration = alpha`, `alpha > 0`,
+* `rate = beta`, `beta > 0`,
+* `Z` is the normalizing constant, and,
+* `Gamma` is the [gamma function](
+ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma_function).
+
+The cumulative density function (cdf) is,
+
+```none
+cdf(x; alpha, beta, x > 0) = GammaInc(alpha, beta x) / Gamma(alpha)
+```
+
+where `GammaInc` is the [lower incomplete Gamma function](
+https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Incomplete_gamma_function).
+
+The parameters can be intuited via their relationship to mean and stddev,
+
+```none
+concentration = alpha = (mean / stddev)**2
+rate = beta = mean / stddev**2 = concentration / mean
+```
+
+Distribution parameters are automatically broadcast in all functions; see
+examples for details.
+
+Warning: The samples of this distribution are always non-negative. However,
+the samples that are smaller than `np.finfo(dtype).tiny` are rounded
+to this value, so it appears more often than it should.
+This should only be noticeable when the `concentration` is very small, or the
+`rate` is very large. See note in tf.random.gamma docstring.
+
+Samples of this distribution are reparameterized (pathwise differentiable).
+The derivatives are computed using the approach described in
+(Figurnov et al., 2018).
+
+#### Examples
+
+```python
+import tensorflow_probability as tfp
+tfd = tfp.distributions
+
+dist = tfd.Gamma(concentration=3.0, rate=2.0)
+dist2 = tfd.Gamma(concentration=[3.0, 4.0], rate=[2.0, 3.0])
+```
+
+Compute the gradients of samples w.r.t. the parameters:
+
+```python
+concentration = tf.constant(3.0)
+rate = tf.constant(2.0)
+dist = tfd.Gamma(concentration, rate)
+samples = dist.sample(5) # Shape [5]
+loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(samples)) # Arbitrary loss function
+# Unbiased stochastic gradients of the loss function
+grads = tf.gradients(loss, [concentration, rate])
+```
+
+#### References:
+
+Implicit Reparameterization Gradients:
+ [Figurnov et al., 2018]
+ (http://papers.nips.cc/paper/7326-implicit-reparameterization-gradients)
+ ([pdf](http://papers.nips.cc/paper/7326-implicit-reparameterization-gradients.pdf))
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`concentration`
+ |
+
+Floating point tensor, the concentration params of the
+distribution(s). Must contain only positive values.
+ |
+
+|
+`rate`
+ |
+
+Floating point tensor, the inverse scale params of the
+distribution(s). Must contain only positive values.
+ |
+
+|
+`validate_args`
+ |
+
+Python `bool`, default `False`. When `True` distribution
+parameters are checked for validity despite possibly degrading runtime
+performance. When `False` invalid inputs may silently render incorrect
+outputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`allow_nan_stats`
+ |
+
+Python `bool`, default `True`. When `True`, statistics
+(e.g., mean, mode, variance) use the value "`NaN`" to indicate the
+result is undefined. When `False`, an exception is raised if one or
+more of the statistic's batch members are undefined.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` name prefixed to Ops created by this class.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+if `concentration` and `rate` are different dtypes.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`allow_nan_stats`
+ |
+
+Python `bool` describing behavior when a stat is undefined.
+
+Stats return +/- infinity when it makes sense. E.g., the variance of a
+Cauchy distribution is infinity. However, sometimes the statistic is
+undefined, e.g., if a distribution's pdf does not achieve a maximum within
+the support of the distribution, the mode is undefined. If the mean is
+undefined, then by definition the variance is undefined. E.g. the mean for
+Student's T for df = 1 is undefined (no clear way to say it is either + or -
+infinity), so the variance = E[(X - mean)**2] is also undefined.
+ |
+
+|
+`batch_shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single event index as a `TensorShape`.
+
+May be partially defined or unknown.
+
+The batch dimensions are indexes into independent, non-identical
+parameterizations of this distribution.
+ |
+
+|
+`concentration`
+ |
+
+Concentration parameter.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+The `DType` of `Tensor`s handled by this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`event_shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single batch as a `TensorShape`.
+
+May be partially defined or unknown.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name prepended to all ops created by this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`parameters`
+ |
+
+Dictionary of parameters used to instantiate this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`rate`
+ |
+
+Rate parameter.
+ |
+
+|
+`reparameterization_type`
+ |
+
+Describes how samples from the distribution are reparameterized.
+
+Currently this is one of the static instances
+`distributions.FULLY_REPARAMETERIZED`
+or `distributions.NOT_REPARAMETERIZED`.
+ |
+
+|
+`validate_args`
+ |
+
+Python `bool` indicating possibly expensive checks are enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+batch_shape_tensor
+
+View source
+
+
+batch_shape_tensor(
+ name='batch_shape_tensor'
+)
+
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single event index as a 1-D `Tensor`.
+
+The batch dimensions are indexes into independent, non-identical
+parameterizations of this distribution.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`batch_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+cdf
+
+View source
+
+
+cdf(
+ value, name='cdf'
+)
+
+
+Cumulative distribution function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the cumulative distribution function `cdf` is:
+
+```none
+cdf(x) := P[X <= x]
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cdf`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+copy
+
+View source
+
+
+copy(
+ **override_parameters_kwargs
+)
+
+
+Creates a deep copy of the distribution.
+
+Note: the copy distribution may continue to depend on the original
+initialization arguments.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`**override_parameters_kwargs`
+ |
+
+String/value dictionary of initialization
+arguments to override with new values.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`distribution`
+ |
+
+A new instance of `type(self)` initialized from the union
+of self.parameters and override_parameters_kwargs, i.e.,
+`dict(self.parameters, **override_parameters_kwargs)`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+covariance
+
+View source
+
+
+covariance(
+ name='covariance'
+)
+
+
+Covariance.
+
+Covariance is (possibly) defined only for non-scalar-event distributions.
+
+For example, for a length-`k`, vector-valued distribution, it is calculated
+as,
+
+```none
+Cov[i, j] = Covariance(X_i, X_j) = E[(X_i - E[X_i]) (X_j - E[X_j])]
+```
+
+where `Cov` is a (batch of) `k x k` matrix, `0 <= (i, j) < k`, and `E`
+denotes expectation.
+
+Alternatively, for non-vector, multivariate distributions (e.g.,
+matrix-valued, Wishart), `Covariance` shall return a (batch of) matrices
+under some vectorization of the events, i.e.,
+
+```none
+Cov[i, j] = Covariance(Vec(X)_i, Vec(X)_j) = [as above]
+```
+
+where `Cov` is a (batch of) `k' x k'` matrices,
+`0 <= (i, j) < k' = reduce_prod(event_shape)`, and `Vec` is some function
+mapping indices of this distribution's event dimensions to indices of a
+length-`k'` vector.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`covariance`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn, k', k']`
+where the first `n` dimensions are batch coordinates and
+`k' = reduce_prod(self.event_shape)`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+cross_entropy
+
+View source
+
+
+cross_entropy(
+ other, name='cross_entropy'
+)
+
+
+Computes the (Shannon) cross entropy.
+
+Denote this distribution (`self`) by `P` and the `other` distribution by
+`Q`. Assuming `P, Q` are absolutely continuous with respect to
+one another and permit densities `p(x) dr(x)` and `q(x) dr(x)`, (Shanon)
+cross entropy is defined as:
+
+```none
+H[P, Q] = E_p[-log q(X)] = -int_F p(x) log q(x) dr(x)
+```
+
+where `F` denotes the support of the random variable `X ~ P`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`other`
+ |
+
+`tfp.distributions.Distribution` instance.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cross_entropy`
+ |
+
+`self.dtype` `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn]`
+representing `n` different calculations of (Shanon) cross entropy.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+entropy
+
+View source
+
+
+entropy(
+ name='entropy'
+)
+
+
+Shannon entropy in nats.
+
+
+event_shape_tensor
+
+View source
+
+
+event_shape_tensor(
+ name='event_shape_tensor'
+)
+
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single batch as a 1-D int32 `Tensor`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`event_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+is_scalar_batch
+
+View source
+
+
+is_scalar_batch(
+ name='is_scalar_batch'
+)
+
+
+Indicates that `batch_shape == []`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`is_scalar_batch`
+ |
+
+`bool` scalar `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+is_scalar_event
+
+View source
+
+
+is_scalar_event(
+ name='is_scalar_event'
+)
+
+
+Indicates that `event_shape == []`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`is_scalar_event`
+ |
+
+`bool` scalar `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+kl_divergence
+
+View source
+
+
+kl_divergence(
+ other, name='kl_divergence'
+)
+
+
+Computes the Kullback--Leibler divergence.
+
+Denote this distribution (`self`) by `p` and the `other` distribution by
+`q`. Assuming `p, q` are absolutely continuous with respect to reference
+measure `r`, the KL divergence is defined as:
+
+```none
+KL[p, q] = E_p[log(p(X)/q(X))]
+ = -int_F p(x) log q(x) dr(x) + int_F p(x) log p(x) dr(x)
+ = H[p, q] - H[p]
+```
+
+where `F` denotes the support of the random variable `X ~ p`, `H[., .]`
+denotes (Shanon) cross entropy, and `H[.]` denotes (Shanon) entropy.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`other`
+ |
+
+`tfp.distributions.Distribution` instance.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`kl_divergence`
+ |
+
+`self.dtype` `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn]`
+representing `n` different calculations of the Kullback-Leibler
+divergence.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_cdf
+
+View source
+
+
+log_cdf(
+ value, name='log_cdf'
+)
+
+
+Log cumulative distribution function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the cumulative distribution function `cdf` is:
+
+```none
+log_cdf(x) := Log[ P[X <= x] ]
+```
+
+Often, a numerical approximation can be used for `log_cdf(x)` that yields
+a more accurate answer than simply taking the logarithm of the `cdf` when
+`x << -1`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`logcdf`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_prob
+
+View source
+
+
+log_prob(
+ value, name='log_prob'
+)
+
+
+Log probability density/mass function.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`log_prob`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_survival_function
+
+View source
+
+
+log_survival_function(
+ value, name='log_survival_function'
+)
+
+
+Log survival function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the survival function is defined:
+
+```none
+log_survival_function(x) = Log[ P[X > x] ]
+ = Log[ 1 - P[X <= x] ]
+ = Log[ 1 - cdf(x) ]
+```
+
+Typically, different numerical approximations can be used for the log
+survival function, which are more accurate than `1 - cdf(x)` when `x >> 1`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with values of type
+`self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+mean
+
+View source
+
+
+mean(
+ name='mean'
+)
+
+
+Mean.
+
+
+mode
+
+View source
+
+
+mode(
+ name='mode'
+)
+
+
+Mode.
+
+Additional documentation from `Gamma`:
+
+The mode of a gamma distribution is `(shape - 1) / rate` when
+`shape > 1`, and `NaN` otherwise. If `self.allow_nan_stats` is `False`,
+an exception will be raised rather than returning `NaN`.
+
+param_shapes
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+param_shapes(
+ sample_shape, name='DistributionParamShapes'
+)
+
+
+Shapes of parameters given the desired shape of a call to `sample()`.
+
+This is a class method that describes what key/value arguments are required
+to instantiate the given `Distribution` so that a particular shape is
+returned for that instance's call to `sample()`.
+
+Subclasses should override class method `_param_shapes`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor` or python list/tuple. Desired shape of a call to
+`sample()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to prepend ops with.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`dict` of parameter name to `Tensor` shapes.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+param_static_shapes
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+param_static_shapes(
+ sample_shape
+)
+
+
+param_shapes with static (i.e. `TensorShape`) shapes.
+
+This is a class method that describes what key/value arguments are required
+to instantiate the given `Distribution` so that a particular shape is
+returned for that instance's call to `sample()`. Assumes that the sample's
+shape is known statically.
+
+Subclasses should override class method `_param_shapes` to return
+constant-valued tensors when constant values are fed.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+`TensorShape` or python list/tuple. Desired shape of a call
+to `sample()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`dict` of parameter name to `TensorShape`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `sample_shape` is a `TensorShape` and is not fully defined.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+prob
+
+View source
+
+
+prob(
+ value, name='prob'
+)
+
+
+Probability density/mass function.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`prob`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+quantile
+
+View source
+
+
+quantile(
+ value, name='quantile'
+)
+
+
+Quantile function. Aka "inverse cdf" or "percent point function".
+
+Given random variable `X` and `p in [0, 1]`, the `quantile` is:
+
+```none
+quantile(p) := x such that P[X <= x] == p
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`quantile`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+sample
+
+View source
+
+
+sample(
+ sample_shape=(), seed=None, name='sample'
+)
+
+
+Generate samples of the specified shape.
+
+Note that a call to `sample()` without arguments will generate a single
+sample.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+0D or 1D `int32` `Tensor`. Shape of the generated samples.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+Python integer seed for RNG
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`samples`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` with prepended dimensions `sample_shape`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+stddev
+
+View source
+
+
+stddev(
+ name='stddev'
+)
+
+
+Standard deviation.
+
+Standard deviation is defined as,
+
+```none
+stddev = E[(X - E[X])**2]**0.5
+```
+
+where `X` is the random variable associated with this distribution, `E`
+denotes expectation, and `stddev.shape = batch_shape + event_shape`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`stddev`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape identical to
+`batch_shape + event_shape`, i.e., the same shape as `self.mean()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+survival_function
+
+View source
+
+
+survival_function(
+ value, name='survival_function'
+)
+
+
+Survival function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the survival function is defined:
+
+```none
+survival_function(x) = P[X > x]
+ = 1 - P[X <= x]
+ = 1 - cdf(x).
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with values of type
+`self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+variance
+
+View source
+
+
+variance(
+ name='variance'
+)
+
+
+Variance.
+
+Variance is defined as,
+
+```none
+Var = E[(X - E[X])**2]
+```
+
+where `X` is the random variable associated with this distribution, `E`
+denotes expectation, and `Var.shape = batch_shape + event_shape`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`variance`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape identical to
+`batch_shape + event_shape`, i.e., the same shape as `self.mean()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/Laplace.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/Laplace.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e20683c44af
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/Laplace.md
@@ -0,0 +1,1463 @@
+description: The Laplace distribution with location loc and scale parameters.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.distributions.Laplace
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The Laplace distribution with location `loc` and `scale` parameters.
+
+Inherits From: [`Distribution`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/distributions/Distribution.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.distributions.Laplace(
+ loc, scale, validate_args=(False), allow_nan_stats=(True), name='Laplace'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Mathematical details
+
+The probability density function (pdf) of this distribution is,
+
+```none
+pdf(x; mu, sigma) = exp(-|x - mu| / sigma) / Z
+Z = 2 sigma
+```
+
+where `loc = mu`, `scale = sigma`, and `Z` is the normalization constant.
+
+Note that the Laplace distribution can be thought of two exponential
+distributions spliced together "back-to-back."
+
+The Lpalce distribution is a member of the [location-scale family](
+https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Location-scale_family), i.e., it can be
+constructed as,
+
+```none
+X ~ Laplace(loc=0, scale=1)
+Y = loc + scale * X
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`loc`
+ |
+
+Floating point tensor which characterizes the location (center)
+of the distribution.
+ |
+
+|
+`scale`
+ |
+
+Positive floating point tensor which characterizes the spread of
+the distribution.
+ |
+
+|
+`validate_args`
+ |
+
+Python `bool`, default `False`. When `True` distribution
+parameters are checked for validity despite possibly degrading runtime
+performance. When `False` invalid inputs may silently render incorrect
+outputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`allow_nan_stats`
+ |
+
+Python `bool`, default `True`. When `True`,
+statistics (e.g., mean, mode, variance) use the value "`NaN`" to
+indicate the result is undefined. When `False`, an exception is raised
+if one or more of the statistic's batch members are undefined.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` name prefixed to Ops created by this class.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+if `loc` and `scale` are of different dtype.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`allow_nan_stats`
+ |
+
+Python `bool` describing behavior when a stat is undefined.
+
+Stats return +/- infinity when it makes sense. E.g., the variance of a
+Cauchy distribution is infinity. However, sometimes the statistic is
+undefined, e.g., if a distribution's pdf does not achieve a maximum within
+the support of the distribution, the mode is undefined. If the mean is
+undefined, then by definition the variance is undefined. E.g. the mean for
+Student's T for df = 1 is undefined (no clear way to say it is either + or -
+infinity), so the variance = E[(X - mean)**2] is also undefined.
+ |
+
+|
+`batch_shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single event index as a `TensorShape`.
+
+May be partially defined or unknown.
+
+The batch dimensions are indexes into independent, non-identical
+parameterizations of this distribution.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+The `DType` of `Tensor`s handled by this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`event_shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single batch as a `TensorShape`.
+
+May be partially defined or unknown.
+ |
+
+|
+`loc`
+ |
+
+Distribution parameter for the location.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name prepended to all ops created by this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`parameters`
+ |
+
+Dictionary of parameters used to instantiate this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`reparameterization_type`
+ |
+
+Describes how samples from the distribution are reparameterized.
+
+Currently this is one of the static instances
+`distributions.FULLY_REPARAMETERIZED`
+or `distributions.NOT_REPARAMETERIZED`.
+ |
+
+|
+`scale`
+ |
+
+Distribution parameter for scale.
+ |
+
+|
+`validate_args`
+ |
+
+Python `bool` indicating possibly expensive checks are enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+batch_shape_tensor
+
+View source
+
+
+batch_shape_tensor(
+ name='batch_shape_tensor'
+)
+
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single event index as a 1-D `Tensor`.
+
+The batch dimensions are indexes into independent, non-identical
+parameterizations of this distribution.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`batch_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+cdf
+
+View source
+
+
+cdf(
+ value, name='cdf'
+)
+
+
+Cumulative distribution function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the cumulative distribution function `cdf` is:
+
+```none
+cdf(x) := P[X <= x]
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cdf`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+copy
+
+View source
+
+
+copy(
+ **override_parameters_kwargs
+)
+
+
+Creates a deep copy of the distribution.
+
+Note: the copy distribution may continue to depend on the original
+initialization arguments.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`**override_parameters_kwargs`
+ |
+
+String/value dictionary of initialization
+arguments to override with new values.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`distribution`
+ |
+
+A new instance of `type(self)` initialized from the union
+of self.parameters and override_parameters_kwargs, i.e.,
+`dict(self.parameters, **override_parameters_kwargs)`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+covariance
+
+View source
+
+
+covariance(
+ name='covariance'
+)
+
+
+Covariance.
+
+Covariance is (possibly) defined only for non-scalar-event distributions.
+
+For example, for a length-`k`, vector-valued distribution, it is calculated
+as,
+
+```none
+Cov[i, j] = Covariance(X_i, X_j) = E[(X_i - E[X_i]) (X_j - E[X_j])]
+```
+
+where `Cov` is a (batch of) `k x k` matrix, `0 <= (i, j) < k`, and `E`
+denotes expectation.
+
+Alternatively, for non-vector, multivariate distributions (e.g.,
+matrix-valued, Wishart), `Covariance` shall return a (batch of) matrices
+under some vectorization of the events, i.e.,
+
+```none
+Cov[i, j] = Covariance(Vec(X)_i, Vec(X)_j) = [as above]
+```
+
+where `Cov` is a (batch of) `k' x k'` matrices,
+`0 <= (i, j) < k' = reduce_prod(event_shape)`, and `Vec` is some function
+mapping indices of this distribution's event dimensions to indices of a
+length-`k'` vector.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`covariance`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn, k', k']`
+where the first `n` dimensions are batch coordinates and
+`k' = reduce_prod(self.event_shape)`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+cross_entropy
+
+View source
+
+
+cross_entropy(
+ other, name='cross_entropy'
+)
+
+
+Computes the (Shannon) cross entropy.
+
+Denote this distribution (`self`) by `P` and the `other` distribution by
+`Q`. Assuming `P, Q` are absolutely continuous with respect to
+one another and permit densities `p(x) dr(x)` and `q(x) dr(x)`, (Shanon)
+cross entropy is defined as:
+
+```none
+H[P, Q] = E_p[-log q(X)] = -int_F p(x) log q(x) dr(x)
+```
+
+where `F` denotes the support of the random variable `X ~ P`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`other`
+ |
+
+`tfp.distributions.Distribution` instance.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cross_entropy`
+ |
+
+`self.dtype` `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn]`
+representing `n` different calculations of (Shanon) cross entropy.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+entropy
+
+View source
+
+
+entropy(
+ name='entropy'
+)
+
+
+Shannon entropy in nats.
+
+
+event_shape_tensor
+
+View source
+
+
+event_shape_tensor(
+ name='event_shape_tensor'
+)
+
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single batch as a 1-D int32 `Tensor`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`event_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+is_scalar_batch
+
+View source
+
+
+is_scalar_batch(
+ name='is_scalar_batch'
+)
+
+
+Indicates that `batch_shape == []`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`is_scalar_batch`
+ |
+
+`bool` scalar `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+is_scalar_event
+
+View source
+
+
+is_scalar_event(
+ name='is_scalar_event'
+)
+
+
+Indicates that `event_shape == []`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`is_scalar_event`
+ |
+
+`bool` scalar `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+kl_divergence
+
+View source
+
+
+kl_divergence(
+ other, name='kl_divergence'
+)
+
+
+Computes the Kullback--Leibler divergence.
+
+Denote this distribution (`self`) by `p` and the `other` distribution by
+`q`. Assuming `p, q` are absolutely continuous with respect to reference
+measure `r`, the KL divergence is defined as:
+
+```none
+KL[p, q] = E_p[log(p(X)/q(X))]
+ = -int_F p(x) log q(x) dr(x) + int_F p(x) log p(x) dr(x)
+ = H[p, q] - H[p]
+```
+
+where `F` denotes the support of the random variable `X ~ p`, `H[., .]`
+denotes (Shanon) cross entropy, and `H[.]` denotes (Shanon) entropy.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`other`
+ |
+
+`tfp.distributions.Distribution` instance.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`kl_divergence`
+ |
+
+`self.dtype` `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn]`
+representing `n` different calculations of the Kullback-Leibler
+divergence.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_cdf
+
+View source
+
+
+log_cdf(
+ value, name='log_cdf'
+)
+
+
+Log cumulative distribution function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the cumulative distribution function `cdf` is:
+
+```none
+log_cdf(x) := Log[ P[X <= x] ]
+```
+
+Often, a numerical approximation can be used for `log_cdf(x)` that yields
+a more accurate answer than simply taking the logarithm of the `cdf` when
+`x << -1`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`logcdf`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_prob
+
+View source
+
+
+log_prob(
+ value, name='log_prob'
+)
+
+
+Log probability density/mass function.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`log_prob`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_survival_function
+
+View source
+
+
+log_survival_function(
+ value, name='log_survival_function'
+)
+
+
+Log survival function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the survival function is defined:
+
+```none
+log_survival_function(x) = Log[ P[X > x] ]
+ = Log[ 1 - P[X <= x] ]
+ = Log[ 1 - cdf(x) ]
+```
+
+Typically, different numerical approximations can be used for the log
+survival function, which are more accurate than `1 - cdf(x)` when `x >> 1`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with values of type
+`self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+mean
+
+View source
+
+
+mean(
+ name='mean'
+)
+
+
+Mean.
+
+
+mode
+
+View source
+
+
+mode(
+ name='mode'
+)
+
+
+Mode.
+
+
+param_shapes
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+param_shapes(
+ sample_shape, name='DistributionParamShapes'
+)
+
+
+Shapes of parameters given the desired shape of a call to `sample()`.
+
+This is a class method that describes what key/value arguments are required
+to instantiate the given `Distribution` so that a particular shape is
+returned for that instance's call to `sample()`.
+
+Subclasses should override class method `_param_shapes`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor` or python list/tuple. Desired shape of a call to
+`sample()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to prepend ops with.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`dict` of parameter name to `Tensor` shapes.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+param_static_shapes
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+param_static_shapes(
+ sample_shape
+)
+
+
+param_shapes with static (i.e. `TensorShape`) shapes.
+
+This is a class method that describes what key/value arguments are required
+to instantiate the given `Distribution` so that a particular shape is
+returned for that instance's call to `sample()`. Assumes that the sample's
+shape is known statically.
+
+Subclasses should override class method `_param_shapes` to return
+constant-valued tensors when constant values are fed.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+`TensorShape` or python list/tuple. Desired shape of a call
+to `sample()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`dict` of parameter name to `TensorShape`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `sample_shape` is a `TensorShape` and is not fully defined.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+prob
+
+View source
+
+
+prob(
+ value, name='prob'
+)
+
+
+Probability density/mass function.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`prob`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+quantile
+
+View source
+
+
+quantile(
+ value, name='quantile'
+)
+
+
+Quantile function. Aka "inverse cdf" or "percent point function".
+
+Given random variable `X` and `p in [0, 1]`, the `quantile` is:
+
+```none
+quantile(p) := x such that P[X <= x] == p
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`quantile`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+sample
+
+View source
+
+
+sample(
+ sample_shape=(), seed=None, name='sample'
+)
+
+
+Generate samples of the specified shape.
+
+Note that a call to `sample()` without arguments will generate a single
+sample.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+0D or 1D `int32` `Tensor`. Shape of the generated samples.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+Python integer seed for RNG
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`samples`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` with prepended dimensions `sample_shape`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+stddev
+
+View source
+
+
+stddev(
+ name='stddev'
+)
+
+
+Standard deviation.
+
+Standard deviation is defined as,
+
+```none
+stddev = E[(X - E[X])**2]**0.5
+```
+
+where `X` is the random variable associated with this distribution, `E`
+denotes expectation, and `stddev.shape = batch_shape + event_shape`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`stddev`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape identical to
+`batch_shape + event_shape`, i.e., the same shape as `self.mean()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+survival_function
+
+View source
+
+
+survival_function(
+ value, name='survival_function'
+)
+
+
+Survival function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the survival function is defined:
+
+```none
+survival_function(x) = P[X > x]
+ = 1 - P[X <= x]
+ = 1 - cdf(x).
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with values of type
+`self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+variance
+
+View source
+
+
+variance(
+ name='variance'
+)
+
+
+Variance.
+
+Variance is defined as,
+
+```none
+Var = E[(X - E[X])**2]
+```
+
+where `X` is the random variable associated with this distribution, `E`
+denotes expectation, and `Var.shape = batch_shape + event_shape`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`variance`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape identical to
+`batch_shape + event_shape`, i.e., the same shape as `self.mean()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/Multinomial.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/Multinomial.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a70c45cf211
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/Multinomial.md
@@ -0,0 +1,1554 @@
+description: Multinomial distribution.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.distributions.Multinomial
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Multinomial distribution.
+
+Inherits From: [`Distribution`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/distributions/Distribution.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.distributions.Multinomial(
+ total_count, logits=None, probs=None, validate_args=(False),
+ allow_nan_stats=(True), name='Multinomial'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This Multinomial distribution is parameterized by `probs`, a (batch of)
+length-`K` `prob` (probability) vectors (`K > 1`) such that
+`tf.reduce_sum(probs, -1) = 1`, and a `total_count` number of trials, i.e.,
+the number of trials per draw from the Multinomial. It is defined over a
+(batch of) length-`K` vector `counts` such that
+`tf.reduce_sum(counts, -1) = total_count`. The Multinomial is identically the
+Binomial distribution when `K = 2`.
+
+#### Mathematical Details
+
+The Multinomial is a distribution over `K`-class counts, i.e., a length-`K`
+vector of non-negative integer `counts = n = [n_0, ..., n_{K-1}]`.
+
+The probability mass function (pmf) is,
+
+```none
+pmf(n; pi, N) = prod_j (pi_j)**n_j / Z
+Z = (prod_j n_j!) / N!
+```
+
+where:
+* `probs = pi = [pi_0, ..., pi_{K-1}]`, `pi_j > 0`, `sum_j pi_j = 1`,
+* `total_count = N`, `N` a positive integer,
+* `Z` is the normalization constant, and,
+* `N!` denotes `N` factorial.
+
+Distribution parameters are automatically broadcast in all functions; see
+examples for details.
+
+#### Pitfalls
+
+The number of classes, `K`, must not exceed:
+- the largest integer representable by `self.dtype`, i.e.,
+ `2**(mantissa_bits+1)` (IEE754),
+- the maximum `Tensor` index, i.e., `2**31-1`.
+
+In other words,
+
+```python
+K <= min(2**31-1, {
+ tf.float16: 2**11,
+ tf.float32: 2**24,
+ tf.float64: 2**53 }[param.dtype])
+```
+
+Note: This condition is validated only when `self.validate_args = True`.
+
+#### Examples
+
+Create a 3-class distribution, with the 3rd class is most likely to be drawn,
+using logits.
+
+```python
+logits = [-50., -43, 0]
+dist = Multinomial(total_count=4., logits=logits)
+```
+
+Create a 3-class distribution, with the 3rd class is most likely to be drawn.
+
+```python
+p = [.2, .3, .5]
+dist = Multinomial(total_count=4., probs=p)
+```
+
+The distribution functions can be evaluated on counts.
+
+```python
+# counts same shape as p.
+counts = [1., 0, 3]
+dist.prob(counts) # Shape []
+
+# p will be broadcast to [[.2, .3, .5], [.2, .3, .5]] to match counts.
+counts = [[1., 2, 1], [2, 2, 0]]
+dist.prob(counts) # Shape [2]
+
+# p will be broadcast to shape [5, 7, 3] to match counts.
+counts = [[...]] # Shape [5, 7, 3]
+dist.prob(counts) # Shape [5, 7]
+```
+
+Create a 2-batch of 3-class distributions.
+
+```python
+p = [[.1, .2, .7], [.3, .3, .4]] # Shape [2, 3]
+dist = Multinomial(total_count=[4., 5], probs=p)
+
+counts = [[2., 1, 1], [3, 1, 1]]
+dist.prob(counts) # Shape [2]
+
+dist.sample(5) # Shape [5, 2, 3]
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`total_count`
+ |
+
+Non-negative floating point tensor with shape broadcastable
+to `[N1,..., Nm]` with `m >= 0`. Defines this as a batch of
+`N1 x ... x Nm` different Multinomial distributions. Its components
+should be equal to integer values.
+ |
+
+|
+`logits`
+ |
+
+Floating point tensor representing unnormalized log-probabilities
+of a positive event with shape broadcastable to
+`[N1,..., Nm, K]` `m >= 0`, and the same dtype as `total_count`. Defines
+this as a batch of `N1 x ... x Nm` different `K` class Multinomial
+distributions. Only one of `logits` or `probs` should be passed in.
+ |
+
+|
+`probs`
+ |
+
+Positive floating point tensor with shape broadcastable to
+`[N1,..., Nm, K]` `m >= 0` and same dtype as `total_count`. Defines
+this as a batch of `N1 x ... x Nm` different `K` class Multinomial
+distributions. `probs`'s components in the last portion of its shape
+should sum to `1`. Only one of `logits` or `probs` should be passed in.
+ |
+
+|
+`validate_args`
+ |
+
+Python `bool`, default `False`. When `True` distribution
+parameters are checked for validity despite possibly degrading runtime
+performance. When `False` invalid inputs may silently render incorrect
+outputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`allow_nan_stats`
+ |
+
+Python `bool`, default `True`. When `True`, statistics
+(e.g., mean, mode, variance) use the value "`NaN`" to indicate the
+result is undefined. When `False`, an exception is raised if one or
+more of the statistic's batch members are undefined.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` name prefixed to Ops created by this class.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`allow_nan_stats`
+ |
+
+Python `bool` describing behavior when a stat is undefined.
+
+Stats return +/- infinity when it makes sense. E.g., the variance of a
+Cauchy distribution is infinity. However, sometimes the statistic is
+undefined, e.g., if a distribution's pdf does not achieve a maximum within
+the support of the distribution, the mode is undefined. If the mean is
+undefined, then by definition the variance is undefined. E.g. the mean for
+Student's T for df = 1 is undefined (no clear way to say it is either + or -
+infinity), so the variance = E[(X - mean)**2] is also undefined.
+ |
+
+|
+`batch_shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single event index as a `TensorShape`.
+
+May be partially defined or unknown.
+
+The batch dimensions are indexes into independent, non-identical
+parameterizations of this distribution.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+The `DType` of `Tensor`s handled by this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`event_shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single batch as a `TensorShape`.
+
+May be partially defined or unknown.
+ |
+
+|
+`logits`
+ |
+
+Vector of coordinatewise logits.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name prepended to all ops created by this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`parameters`
+ |
+
+Dictionary of parameters used to instantiate this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`probs`
+ |
+
+Probability of drawing a `1` in that coordinate.
+ |
+
+|
+`reparameterization_type`
+ |
+
+Describes how samples from the distribution are reparameterized.
+
+Currently this is one of the static instances
+`distributions.FULLY_REPARAMETERIZED`
+or `distributions.NOT_REPARAMETERIZED`.
+ |
+
+|
+`total_count`
+ |
+
+Number of trials used to construct a sample.
+ |
+
+|
+`validate_args`
+ |
+
+Python `bool` indicating possibly expensive checks are enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+batch_shape_tensor
+
+View source
+
+
+batch_shape_tensor(
+ name='batch_shape_tensor'
+)
+
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single event index as a 1-D `Tensor`.
+
+The batch dimensions are indexes into independent, non-identical
+parameterizations of this distribution.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`batch_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+cdf
+
+View source
+
+
+cdf(
+ value, name='cdf'
+)
+
+
+Cumulative distribution function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the cumulative distribution function `cdf` is:
+
+```none
+cdf(x) := P[X <= x]
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cdf`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+copy
+
+View source
+
+
+copy(
+ **override_parameters_kwargs
+)
+
+
+Creates a deep copy of the distribution.
+
+Note: the copy distribution may continue to depend on the original
+initialization arguments.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`**override_parameters_kwargs`
+ |
+
+String/value dictionary of initialization
+arguments to override with new values.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`distribution`
+ |
+
+A new instance of `type(self)` initialized from the union
+of self.parameters and override_parameters_kwargs, i.e.,
+`dict(self.parameters, **override_parameters_kwargs)`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+covariance
+
+View source
+
+
+covariance(
+ name='covariance'
+)
+
+
+Covariance.
+
+Covariance is (possibly) defined only for non-scalar-event distributions.
+
+For example, for a length-`k`, vector-valued distribution, it is calculated
+as,
+
+```none
+Cov[i, j] = Covariance(X_i, X_j) = E[(X_i - E[X_i]) (X_j - E[X_j])]
+```
+
+where `Cov` is a (batch of) `k x k` matrix, `0 <= (i, j) < k`, and `E`
+denotes expectation.
+
+Alternatively, for non-vector, multivariate distributions (e.g.,
+matrix-valued, Wishart), `Covariance` shall return a (batch of) matrices
+under some vectorization of the events, i.e.,
+
+```none
+Cov[i, j] = Covariance(Vec(X)_i, Vec(X)_j) = [as above]
+```
+
+where `Cov` is a (batch of) `k' x k'` matrices,
+`0 <= (i, j) < k' = reduce_prod(event_shape)`, and `Vec` is some function
+mapping indices of this distribution's event dimensions to indices of a
+length-`k'` vector.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`covariance`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn, k', k']`
+where the first `n` dimensions are batch coordinates and
+`k' = reduce_prod(self.event_shape)`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+cross_entropy
+
+View source
+
+
+cross_entropy(
+ other, name='cross_entropy'
+)
+
+
+Computes the (Shannon) cross entropy.
+
+Denote this distribution (`self`) by `P` and the `other` distribution by
+`Q`. Assuming `P, Q` are absolutely continuous with respect to
+one another and permit densities `p(x) dr(x)` and `q(x) dr(x)`, (Shanon)
+cross entropy is defined as:
+
+```none
+H[P, Q] = E_p[-log q(X)] = -int_F p(x) log q(x) dr(x)
+```
+
+where `F` denotes the support of the random variable `X ~ P`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`other`
+ |
+
+`tfp.distributions.Distribution` instance.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cross_entropy`
+ |
+
+`self.dtype` `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn]`
+representing `n` different calculations of (Shanon) cross entropy.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+entropy
+
+View source
+
+
+entropy(
+ name='entropy'
+)
+
+
+Shannon entropy in nats.
+
+
+event_shape_tensor
+
+View source
+
+
+event_shape_tensor(
+ name='event_shape_tensor'
+)
+
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single batch as a 1-D int32 `Tensor`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`event_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+is_scalar_batch
+
+View source
+
+
+is_scalar_batch(
+ name='is_scalar_batch'
+)
+
+
+Indicates that `batch_shape == []`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`is_scalar_batch`
+ |
+
+`bool` scalar `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+is_scalar_event
+
+View source
+
+
+is_scalar_event(
+ name='is_scalar_event'
+)
+
+
+Indicates that `event_shape == []`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`is_scalar_event`
+ |
+
+`bool` scalar `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+kl_divergence
+
+View source
+
+
+kl_divergence(
+ other, name='kl_divergence'
+)
+
+
+Computes the Kullback--Leibler divergence.
+
+Denote this distribution (`self`) by `p` and the `other` distribution by
+`q`. Assuming `p, q` are absolutely continuous with respect to reference
+measure `r`, the KL divergence is defined as:
+
+```none
+KL[p, q] = E_p[log(p(X)/q(X))]
+ = -int_F p(x) log q(x) dr(x) + int_F p(x) log p(x) dr(x)
+ = H[p, q] - H[p]
+```
+
+where `F` denotes the support of the random variable `X ~ p`, `H[., .]`
+denotes (Shanon) cross entropy, and `H[.]` denotes (Shanon) entropy.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`other`
+ |
+
+`tfp.distributions.Distribution` instance.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`kl_divergence`
+ |
+
+`self.dtype` `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn]`
+representing `n` different calculations of the Kullback-Leibler
+divergence.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_cdf
+
+View source
+
+
+log_cdf(
+ value, name='log_cdf'
+)
+
+
+Log cumulative distribution function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the cumulative distribution function `cdf` is:
+
+```none
+log_cdf(x) := Log[ P[X <= x] ]
+```
+
+Often, a numerical approximation can be used for `log_cdf(x)` that yields
+a more accurate answer than simply taking the logarithm of the `cdf` when
+`x << -1`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`logcdf`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_prob
+
+View source
+
+
+log_prob(
+ value, name='log_prob'
+)
+
+
+Log probability density/mass function.
+
+
+Additional documentation from `Multinomial`:
+
+For each batch of counts, `value = [n_0, ...
+,n_{k-1}]`, `P[value]` is the probability that after sampling `self.total_count`
+draws from this Multinomial distribution, the number of draws falling in class
+`j` is `n_j`. Since this definition is [exchangeable](
+https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Exchangeable_random_variables); different
+sequences have the same counts so the probability includes a combinatorial
+coefficient.
+
+Note: `value` must be a non-negative tensor with dtype `self.dtype`, have no
+fractional components, and such that
+`tf.reduce_sum(value, -1) = self.total_count`. Its shape must be broadcastable
+with `self.probs` and `self.total_count`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`log_prob`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_survival_function
+
+View source
+
+
+log_survival_function(
+ value, name='log_survival_function'
+)
+
+
+Log survival function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the survival function is defined:
+
+```none
+log_survival_function(x) = Log[ P[X > x] ]
+ = Log[ 1 - P[X <= x] ]
+ = Log[ 1 - cdf(x) ]
+```
+
+Typically, different numerical approximations can be used for the log
+survival function, which are more accurate than `1 - cdf(x)` when `x >> 1`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with values of type
+`self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+mean
+
+View source
+
+
+mean(
+ name='mean'
+)
+
+
+Mean.
+
+
+mode
+
+View source
+
+
+mode(
+ name='mode'
+)
+
+
+Mode.
+
+
+param_shapes
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+param_shapes(
+ sample_shape, name='DistributionParamShapes'
+)
+
+
+Shapes of parameters given the desired shape of a call to `sample()`.
+
+This is a class method that describes what key/value arguments are required
+to instantiate the given `Distribution` so that a particular shape is
+returned for that instance's call to `sample()`.
+
+Subclasses should override class method `_param_shapes`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor` or python list/tuple. Desired shape of a call to
+`sample()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to prepend ops with.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`dict` of parameter name to `Tensor` shapes.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+param_static_shapes
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+param_static_shapes(
+ sample_shape
+)
+
+
+param_shapes with static (i.e. `TensorShape`) shapes.
+
+This is a class method that describes what key/value arguments are required
+to instantiate the given `Distribution` so that a particular shape is
+returned for that instance's call to `sample()`. Assumes that the sample's
+shape is known statically.
+
+Subclasses should override class method `_param_shapes` to return
+constant-valued tensors when constant values are fed.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+`TensorShape` or python list/tuple. Desired shape of a call
+to `sample()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`dict` of parameter name to `TensorShape`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `sample_shape` is a `TensorShape` and is not fully defined.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+prob
+
+View source
+
+
+prob(
+ value, name='prob'
+)
+
+
+Probability density/mass function.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`prob`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+quantile
+
+View source
+
+
+quantile(
+ value, name='quantile'
+)
+
+
+Quantile function. Aka "inverse cdf" or "percent point function".
+
+Given random variable `X` and `p in [0, 1]`, the `quantile` is:
+
+```none
+quantile(p) := x such that P[X <= x] == p
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`quantile`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+sample
+
+View source
+
+
+sample(
+ sample_shape=(), seed=None, name='sample'
+)
+
+
+Generate samples of the specified shape.
+
+Note that a call to `sample()` without arguments will generate a single
+sample.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+0D or 1D `int32` `Tensor`. Shape of the generated samples.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+Python integer seed for RNG
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`samples`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` with prepended dimensions `sample_shape`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+stddev
+
+View source
+
+
+stddev(
+ name='stddev'
+)
+
+
+Standard deviation.
+
+Standard deviation is defined as,
+
+```none
+stddev = E[(X - E[X])**2]**0.5
+```
+
+where `X` is the random variable associated with this distribution, `E`
+denotes expectation, and `stddev.shape = batch_shape + event_shape`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`stddev`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape identical to
+`batch_shape + event_shape`, i.e., the same shape as `self.mean()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+survival_function
+
+View source
+
+
+survival_function(
+ value, name='survival_function'
+)
+
+
+Survival function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the survival function is defined:
+
+```none
+survival_function(x) = P[X > x]
+ = 1 - P[X <= x]
+ = 1 - cdf(x).
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with values of type
+`self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+variance
+
+View source
+
+
+variance(
+ name='variance'
+)
+
+
+Variance.
+
+Variance is defined as,
+
+```none
+Var = E[(X - E[X])**2]
+```
+
+where `X` is the random variable associated with this distribution, `E`
+denotes expectation, and `Var.shape = batch_shape + event_shape`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`variance`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape identical to
+`batch_shape + event_shape`, i.e., the same shape as `self.mean()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/Normal.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/Normal.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..13c4d9b701f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/Normal.md
@@ -0,0 +1,1498 @@
+description: The Normal distribution with location loc and scale parameters.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.distributions.Normal
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The Normal distribution with location `loc` and `scale` parameters.
+
+Inherits From: [`Distribution`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/distributions/Distribution.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.distributions.Normal(
+ loc, scale, validate_args=(False), allow_nan_stats=(True), name='Normal'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Mathematical details
+
+The probability density function (pdf) is,
+
+```none
+pdf(x; mu, sigma) = exp(-0.5 (x - mu)**2 / sigma**2) / Z
+Z = (2 pi sigma**2)**0.5
+```
+
+where `loc = mu` is the mean, `scale = sigma` is the std. deviation, and, `Z`
+is the normalization constant.
+
+The Normal distribution is a member of the [location-scale family](
+https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Location-scale_family), i.e., it can be
+constructed as,
+
+```none
+X ~ Normal(loc=0, scale=1)
+Y = loc + scale * X
+```
+
+#### Examples
+
+Examples of initialization of one or a batch of distributions.
+
+```python
+import tensorflow_probability as tfp
+tfd = tfp.distributions
+
+# Define a single scalar Normal distribution.
+dist = tfd.Normal(loc=0., scale=3.)
+
+# Evaluate the cdf at 1, returning a scalar.
+dist.cdf(1.)
+
+# Define a batch of two scalar valued Normals.
+# The first has mean 1 and standard deviation 11, the second 2 and 22.
+dist = tfd.Normal(loc=[1, 2.], scale=[11, 22.])
+
+# Evaluate the pdf of the first distribution on 0, and the second on 1.5,
+# returning a length two tensor.
+dist.prob([0, 1.5])
+
+# Get 3 samples, returning a 3 x 2 tensor.
+dist.sample([3])
+```
+
+Arguments are broadcast when possible.
+
+```python
+# Define a batch of two scalar valued Normals.
+# Both have mean 1, but different standard deviations.
+dist = tfd.Normal(loc=1., scale=[11, 22.])
+
+# Evaluate the pdf of both distributions on the same point, 3.0,
+# returning a length 2 tensor.
+dist.prob(3.0)
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`loc`
+ |
+
+Floating point tensor; the means of the distribution(s).
+ |
+
+|
+`scale`
+ |
+
+Floating point tensor; the stddevs of the distribution(s).
+Must contain only positive values.
+ |
+
+|
+`validate_args`
+ |
+
+Python `bool`, default `False`. When `True` distribution
+parameters are checked for validity despite possibly degrading runtime
+performance. When `False` invalid inputs may silently render incorrect
+outputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`allow_nan_stats`
+ |
+
+Python `bool`, default `True`. When `True`,
+statistics (e.g., mean, mode, variance) use the value "`NaN`" to
+indicate the result is undefined. When `False`, an exception is raised
+if one or more of the statistic's batch members are undefined.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` name prefixed to Ops created by this class.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+if `loc` and `scale` have different `dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`allow_nan_stats`
+ |
+
+Python `bool` describing behavior when a stat is undefined.
+
+Stats return +/- infinity when it makes sense. E.g., the variance of a
+Cauchy distribution is infinity. However, sometimes the statistic is
+undefined, e.g., if a distribution's pdf does not achieve a maximum within
+the support of the distribution, the mode is undefined. If the mean is
+undefined, then by definition the variance is undefined. E.g. the mean for
+Student's T for df = 1 is undefined (no clear way to say it is either + or -
+infinity), so the variance = E[(X - mean)**2] is also undefined.
+ |
+
+|
+`batch_shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single event index as a `TensorShape`.
+
+May be partially defined or unknown.
+
+The batch dimensions are indexes into independent, non-identical
+parameterizations of this distribution.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+The `DType` of `Tensor`s handled by this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`event_shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single batch as a `TensorShape`.
+
+May be partially defined or unknown.
+ |
+
+|
+`loc`
+ |
+
+Distribution parameter for the mean.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name prepended to all ops created by this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`parameters`
+ |
+
+Dictionary of parameters used to instantiate this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`reparameterization_type`
+ |
+
+Describes how samples from the distribution are reparameterized.
+
+Currently this is one of the static instances
+`distributions.FULLY_REPARAMETERIZED`
+or `distributions.NOT_REPARAMETERIZED`.
+ |
+
+|
+`scale`
+ |
+
+Distribution parameter for standard deviation.
+ |
+
+|
+`validate_args`
+ |
+
+Python `bool` indicating possibly expensive checks are enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+batch_shape_tensor
+
+View source
+
+
+batch_shape_tensor(
+ name='batch_shape_tensor'
+)
+
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single event index as a 1-D `Tensor`.
+
+The batch dimensions are indexes into independent, non-identical
+parameterizations of this distribution.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`batch_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+cdf
+
+View source
+
+
+cdf(
+ value, name='cdf'
+)
+
+
+Cumulative distribution function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the cumulative distribution function `cdf` is:
+
+```none
+cdf(x) := P[X <= x]
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cdf`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+copy
+
+View source
+
+
+copy(
+ **override_parameters_kwargs
+)
+
+
+Creates a deep copy of the distribution.
+
+Note: the copy distribution may continue to depend on the original
+initialization arguments.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`**override_parameters_kwargs`
+ |
+
+String/value dictionary of initialization
+arguments to override with new values.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`distribution`
+ |
+
+A new instance of `type(self)` initialized from the union
+of self.parameters and override_parameters_kwargs, i.e.,
+`dict(self.parameters, **override_parameters_kwargs)`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+covariance
+
+View source
+
+
+covariance(
+ name='covariance'
+)
+
+
+Covariance.
+
+Covariance is (possibly) defined only for non-scalar-event distributions.
+
+For example, for a length-`k`, vector-valued distribution, it is calculated
+as,
+
+```none
+Cov[i, j] = Covariance(X_i, X_j) = E[(X_i - E[X_i]) (X_j - E[X_j])]
+```
+
+where `Cov` is a (batch of) `k x k` matrix, `0 <= (i, j) < k`, and `E`
+denotes expectation.
+
+Alternatively, for non-vector, multivariate distributions (e.g.,
+matrix-valued, Wishart), `Covariance` shall return a (batch of) matrices
+under some vectorization of the events, i.e.,
+
+```none
+Cov[i, j] = Covariance(Vec(X)_i, Vec(X)_j) = [as above]
+```
+
+where `Cov` is a (batch of) `k' x k'` matrices,
+`0 <= (i, j) < k' = reduce_prod(event_shape)`, and `Vec` is some function
+mapping indices of this distribution's event dimensions to indices of a
+length-`k'` vector.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`covariance`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn, k', k']`
+where the first `n` dimensions are batch coordinates and
+`k' = reduce_prod(self.event_shape)`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+cross_entropy
+
+View source
+
+
+cross_entropy(
+ other, name='cross_entropy'
+)
+
+
+Computes the (Shannon) cross entropy.
+
+Denote this distribution (`self`) by `P` and the `other` distribution by
+`Q`. Assuming `P, Q` are absolutely continuous with respect to
+one another and permit densities `p(x) dr(x)` and `q(x) dr(x)`, (Shanon)
+cross entropy is defined as:
+
+```none
+H[P, Q] = E_p[-log q(X)] = -int_F p(x) log q(x) dr(x)
+```
+
+where `F` denotes the support of the random variable `X ~ P`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`other`
+ |
+
+`tfp.distributions.Distribution` instance.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cross_entropy`
+ |
+
+`self.dtype` `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn]`
+representing `n` different calculations of (Shanon) cross entropy.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+entropy
+
+View source
+
+
+entropy(
+ name='entropy'
+)
+
+
+Shannon entropy in nats.
+
+
+event_shape_tensor
+
+View source
+
+
+event_shape_tensor(
+ name='event_shape_tensor'
+)
+
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single batch as a 1-D int32 `Tensor`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`event_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+is_scalar_batch
+
+View source
+
+
+is_scalar_batch(
+ name='is_scalar_batch'
+)
+
+
+Indicates that `batch_shape == []`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`is_scalar_batch`
+ |
+
+`bool` scalar `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+is_scalar_event
+
+View source
+
+
+is_scalar_event(
+ name='is_scalar_event'
+)
+
+
+Indicates that `event_shape == []`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`is_scalar_event`
+ |
+
+`bool` scalar `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+kl_divergence
+
+View source
+
+
+kl_divergence(
+ other, name='kl_divergence'
+)
+
+
+Computes the Kullback--Leibler divergence.
+
+Denote this distribution (`self`) by `p` and the `other` distribution by
+`q`. Assuming `p, q` are absolutely continuous with respect to reference
+measure `r`, the KL divergence is defined as:
+
+```none
+KL[p, q] = E_p[log(p(X)/q(X))]
+ = -int_F p(x) log q(x) dr(x) + int_F p(x) log p(x) dr(x)
+ = H[p, q] - H[p]
+```
+
+where `F` denotes the support of the random variable `X ~ p`, `H[., .]`
+denotes (Shanon) cross entropy, and `H[.]` denotes (Shanon) entropy.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`other`
+ |
+
+`tfp.distributions.Distribution` instance.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`kl_divergence`
+ |
+
+`self.dtype` `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn]`
+representing `n` different calculations of the Kullback-Leibler
+divergence.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_cdf
+
+View source
+
+
+log_cdf(
+ value, name='log_cdf'
+)
+
+
+Log cumulative distribution function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the cumulative distribution function `cdf` is:
+
+```none
+log_cdf(x) := Log[ P[X <= x] ]
+```
+
+Often, a numerical approximation can be used for `log_cdf(x)` that yields
+a more accurate answer than simply taking the logarithm of the `cdf` when
+`x << -1`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`logcdf`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_prob
+
+View source
+
+
+log_prob(
+ value, name='log_prob'
+)
+
+
+Log probability density/mass function.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`log_prob`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_survival_function
+
+View source
+
+
+log_survival_function(
+ value, name='log_survival_function'
+)
+
+
+Log survival function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the survival function is defined:
+
+```none
+log_survival_function(x) = Log[ P[X > x] ]
+ = Log[ 1 - P[X <= x] ]
+ = Log[ 1 - cdf(x) ]
+```
+
+Typically, different numerical approximations can be used for the log
+survival function, which are more accurate than `1 - cdf(x)` when `x >> 1`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with values of type
+`self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+mean
+
+View source
+
+
+mean(
+ name='mean'
+)
+
+
+Mean.
+
+
+mode
+
+View source
+
+
+mode(
+ name='mode'
+)
+
+
+Mode.
+
+
+param_shapes
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+param_shapes(
+ sample_shape, name='DistributionParamShapes'
+)
+
+
+Shapes of parameters given the desired shape of a call to `sample()`.
+
+This is a class method that describes what key/value arguments are required
+to instantiate the given `Distribution` so that a particular shape is
+returned for that instance's call to `sample()`.
+
+Subclasses should override class method `_param_shapes`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor` or python list/tuple. Desired shape of a call to
+`sample()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to prepend ops with.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`dict` of parameter name to `Tensor` shapes.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+param_static_shapes
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+param_static_shapes(
+ sample_shape
+)
+
+
+param_shapes with static (i.e. `TensorShape`) shapes.
+
+This is a class method that describes what key/value arguments are required
+to instantiate the given `Distribution` so that a particular shape is
+returned for that instance's call to `sample()`. Assumes that the sample's
+shape is known statically.
+
+Subclasses should override class method `_param_shapes` to return
+constant-valued tensors when constant values are fed.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+`TensorShape` or python list/tuple. Desired shape of a call
+to `sample()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`dict` of parameter name to `TensorShape`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `sample_shape` is a `TensorShape` and is not fully defined.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+prob
+
+View source
+
+
+prob(
+ value, name='prob'
+)
+
+
+Probability density/mass function.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`prob`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+quantile
+
+View source
+
+
+quantile(
+ value, name='quantile'
+)
+
+
+Quantile function. Aka "inverse cdf" or "percent point function".
+
+Given random variable `X` and `p in [0, 1]`, the `quantile` is:
+
+```none
+quantile(p) := x such that P[X <= x] == p
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`quantile`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+sample
+
+View source
+
+
+sample(
+ sample_shape=(), seed=None, name='sample'
+)
+
+
+Generate samples of the specified shape.
+
+Note that a call to `sample()` without arguments will generate a single
+sample.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+0D or 1D `int32` `Tensor`. Shape of the generated samples.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+Python integer seed for RNG
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`samples`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` with prepended dimensions `sample_shape`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+stddev
+
+View source
+
+
+stddev(
+ name='stddev'
+)
+
+
+Standard deviation.
+
+Standard deviation is defined as,
+
+```none
+stddev = E[(X - E[X])**2]**0.5
+```
+
+where `X` is the random variable associated with this distribution, `E`
+denotes expectation, and `stddev.shape = batch_shape + event_shape`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`stddev`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape identical to
+`batch_shape + event_shape`, i.e., the same shape as `self.mean()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+survival_function
+
+View source
+
+
+survival_function(
+ value, name='survival_function'
+)
+
+
+Survival function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the survival function is defined:
+
+```none
+survival_function(x) = P[X > x]
+ = 1 - P[X <= x]
+ = 1 - cdf(x).
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with values of type
+`self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+variance
+
+View source
+
+
+variance(
+ name='variance'
+)
+
+
+Variance.
+
+Variance is defined as,
+
+```none
+Var = E[(X - E[X])**2]
+```
+
+where `X` is the random variable associated with this distribution, `E`
+denotes expectation, and `Var.shape = batch_shape + event_shape`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`variance`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape identical to
+`batch_shape + event_shape`, i.e., the same shape as `self.mean()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/RegisterKL.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/RegisterKL.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..335960d012a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/RegisterKL.md
@@ -0,0 +1,142 @@
+description: Decorator to register a KL divergence implementation function.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.distributions.RegisterKL
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Decorator to register a KL divergence implementation function.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.distributions.RegisterKL(
+ dist_cls_a, dist_cls_b
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Usage:
+
+
+
+@distributions.RegisterKL(distributions.Normal, distributions.Normal)
+def _kl_normal_mvn(norm_a, norm_b):
+ # Return KL(norm_a || norm_b)
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`dist_cls_a`
+ |
+
+the class of the first argument of the KL divergence.
+ |
+
+|
+`dist_cls_b`
+ |
+
+the class of the second argument of the KL divergence.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+__call__
+
+View source
+
+
+__call__(
+ kl_fn
+)
+
+
+Perform the KL registration.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`kl_fn`
+ |
+
+The function to use for the KL divergence.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+kl_fn
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+if kl_fn is not a callable.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if a KL divergence function has already been registered for
+the given argument classes.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/ReparameterizationType.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/ReparameterizationType.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..b286416368c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/ReparameterizationType.md
@@ -0,0 +1,99 @@
+description: Instances of this class represent how sampling is reparameterized.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.distributions.ReparameterizationType
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Instances of this class represent how sampling is reparameterized.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.distributions.ReparameterizationType(
+ rep_type
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Two static instances exist in the distributions library, signifying
+one of two possible properties for samples from a distribution:
+
+`FULLY_REPARAMETERIZED`: Samples from the distribution are fully
+ reparameterized, and straight-through gradients are supported.
+
+`NOT_REPARAMETERIZED`: Samples from the distribution are not fully
+ reparameterized, and straight-through gradients are either partially
+ unsupported or are not supported at all. In this case, for purposes of
+ e.g. RL or variational inference, it is generally safest to wrap the
+ sample results in a `stop_gradients` call and use policy
+ gradients / surrogate loss instead.
+
+## Methods
+
+__eq__
+
+View source
+
+
+__eq__(
+ other
+)
+
+
+Determine if this `ReparameterizationType` is equal to another.
+
+Since ReparameterizationType instances are constant static global
+instances, equality checks if two instances' id() values are equal.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`other`
+ |
+
+Object to compare against.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`self is other`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/StudentT.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/StudentT.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..79ab210fcd8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/StudentT.md
@@ -0,0 +1,1570 @@
+description: Student's t-distribution.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.distributions.StudentT
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Student's t-distribution.
+
+Inherits From: [`Distribution`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/distributions/Distribution.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.distributions.StudentT(
+ df, loc, scale, validate_args=(False), allow_nan_stats=(True), name='StudentT'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This distribution has parameters: degree of freedom `df`, location `loc`,
+and `scale`.
+
+#### Mathematical details
+
+The probability density function (pdf) is,
+
+```none
+pdf(x; df, mu, sigma) = (1 + y**2 / df)**(-0.5 (df + 1)) / Z
+where,
+y = (x - mu) / sigma
+Z = abs(sigma) sqrt(df pi) Gamma(0.5 df) / Gamma(0.5 (df + 1))
+```
+
+where:
+* `loc = mu`,
+* `scale = sigma`, and,
+* `Z` is the normalization constant, and,
+* `Gamma` is the [gamma function](
+ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma_function).
+
+The StudentT distribution is a member of the [location-scale family](
+https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Location-scale_family), i.e., it can be
+constructed as,
+
+```none
+X ~ StudentT(df, loc=0, scale=1)
+Y = loc + scale * X
+```
+
+Notice that `scale` has semantics more similar to standard deviation than
+variance. However it is not actually the std. deviation; the Student's
+t-distribution std. dev. is `scale sqrt(df / (df - 2))` when `df > 2`.
+
+Samples of this distribution are reparameterized (pathwise differentiable).
+The derivatives are computed using the approach described in
+(Figurnov et al., 2018).
+
+#### Examples
+
+Examples of initialization of one or a batch of distributions.
+
+```python
+import tensorflow_probability as tfp
+tfd = tfp.distributions
+
+# Define a single scalar Student t distribution.
+single_dist = tfd.StudentT(df=3)
+
+# Evaluate the pdf at 1, returning a scalar Tensor.
+single_dist.prob(1.)
+
+# Define a batch of two scalar valued Student t's.
+# The first has degrees of freedom 2, mean 1, and scale 11.
+# The second 3, 2 and 22.
+multi_dist = tfd.StudentT(df=[2, 3], loc=[1, 2.], scale=[11, 22.])
+
+# Evaluate the pdf of the first distribution on 0, and the second on 1.5,
+# returning a length two tensor.
+multi_dist.prob([0, 1.5])
+
+# Get 3 samples, returning a 3 x 2 tensor.
+multi_dist.sample(3)
+```
+
+Arguments are broadcast when possible.
+
+```python
+# Define a batch of two Student's t distributions.
+# Both have df 2 and mean 1, but different scales.
+dist = tfd.StudentT(df=2, loc=1, scale=[11, 22.])
+
+# Evaluate the pdf of both distributions on the same point, 3.0,
+# returning a length 2 tensor.
+dist.prob(3.0)
+```
+
+Compute the gradients of samples w.r.t. the parameters:
+
+```python
+df = tf.constant(2.0)
+loc = tf.constant(2.0)
+scale = tf.constant(11.0)
+dist = tfd.StudentT(df=df, loc=loc, scale=scale)
+samples = dist.sample(5) # Shape [5]
+loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(samples)) # Arbitrary loss function
+# Unbiased stochastic gradients of the loss function
+grads = tf.gradients(loss, [df, loc, scale])
+```
+
+#### References:
+
+Implicit Reparameterization Gradients:
+ [Figurnov et al., 2018]
+ (http://papers.nips.cc/paper/7326-implicit-reparameterization-gradients)
+ ([pdf](http://papers.nips.cc/paper/7326-implicit-reparameterization-gradients.pdf))
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`df`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor`. The degrees of freedom of the
+distribution(s). `df` must contain only positive values.
+ |
+
+|
+`loc`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor`. The mean(s) of the distribution(s).
+ |
+
+|
+`scale`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor`. The scaling factor(s) for the
+distribution(s). Note that `scale` is not technically the standard
+deviation of this distribution but has semantics more similar to
+standard deviation than variance.
+ |
+
+|
+`validate_args`
+ |
+
+Python `bool`, default `False`. When `True` distribution
+parameters are checked for validity despite possibly degrading runtime
+performance. When `False` invalid inputs may silently render incorrect
+outputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`allow_nan_stats`
+ |
+
+Python `bool`, default `True`. When `True`,
+statistics (e.g., mean, mode, variance) use the value "`NaN`" to
+indicate the result is undefined. When `False`, an exception is raised
+if one or more of the statistic's batch members are undefined.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` name prefixed to Ops created by this class.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+if loc and scale are different dtypes.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`allow_nan_stats`
+ |
+
+Python `bool` describing behavior when a stat is undefined.
+
+Stats return +/- infinity when it makes sense. E.g., the variance of a
+Cauchy distribution is infinity. However, sometimes the statistic is
+undefined, e.g., if a distribution's pdf does not achieve a maximum within
+the support of the distribution, the mode is undefined. If the mean is
+undefined, then by definition the variance is undefined. E.g. the mean for
+Student's T for df = 1 is undefined (no clear way to say it is either + or -
+infinity), so the variance = E[(X - mean)**2] is also undefined.
+ |
+
+|
+`batch_shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single event index as a `TensorShape`.
+
+May be partially defined or unknown.
+
+The batch dimensions are indexes into independent, non-identical
+parameterizations of this distribution.
+ |
+
+|
+`df`
+ |
+
+Degrees of freedom in these Student's t distribution(s).
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+The `DType` of `Tensor`s handled by this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`event_shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single batch as a `TensorShape`.
+
+May be partially defined or unknown.
+ |
+
+|
+`loc`
+ |
+
+Locations of these Student's t distribution(s).
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name prepended to all ops created by this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`parameters`
+ |
+
+Dictionary of parameters used to instantiate this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`reparameterization_type`
+ |
+
+Describes how samples from the distribution are reparameterized.
+
+Currently this is one of the static instances
+`distributions.FULLY_REPARAMETERIZED`
+or `distributions.NOT_REPARAMETERIZED`.
+ |
+
+|
+`scale`
+ |
+
+Scaling factors of these Student's t distribution(s).
+ |
+
+|
+`validate_args`
+ |
+
+Python `bool` indicating possibly expensive checks are enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+batch_shape_tensor
+
+View source
+
+
+batch_shape_tensor(
+ name='batch_shape_tensor'
+)
+
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single event index as a 1-D `Tensor`.
+
+The batch dimensions are indexes into independent, non-identical
+parameterizations of this distribution.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`batch_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+cdf
+
+View source
+
+
+cdf(
+ value, name='cdf'
+)
+
+
+Cumulative distribution function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the cumulative distribution function `cdf` is:
+
+```none
+cdf(x) := P[X <= x]
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cdf`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+copy
+
+View source
+
+
+copy(
+ **override_parameters_kwargs
+)
+
+
+Creates a deep copy of the distribution.
+
+Note: the copy distribution may continue to depend on the original
+initialization arguments.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`**override_parameters_kwargs`
+ |
+
+String/value dictionary of initialization
+arguments to override with new values.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`distribution`
+ |
+
+A new instance of `type(self)` initialized from the union
+of self.parameters and override_parameters_kwargs, i.e.,
+`dict(self.parameters, **override_parameters_kwargs)`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+covariance
+
+View source
+
+
+covariance(
+ name='covariance'
+)
+
+
+Covariance.
+
+Covariance is (possibly) defined only for non-scalar-event distributions.
+
+For example, for a length-`k`, vector-valued distribution, it is calculated
+as,
+
+```none
+Cov[i, j] = Covariance(X_i, X_j) = E[(X_i - E[X_i]) (X_j - E[X_j])]
+```
+
+where `Cov` is a (batch of) `k x k` matrix, `0 <= (i, j) < k`, and `E`
+denotes expectation.
+
+Alternatively, for non-vector, multivariate distributions (e.g.,
+matrix-valued, Wishart), `Covariance` shall return a (batch of) matrices
+under some vectorization of the events, i.e.,
+
+```none
+Cov[i, j] = Covariance(Vec(X)_i, Vec(X)_j) = [as above]
+```
+
+where `Cov` is a (batch of) `k' x k'` matrices,
+`0 <= (i, j) < k' = reduce_prod(event_shape)`, and `Vec` is some function
+mapping indices of this distribution's event dimensions to indices of a
+length-`k'` vector.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`covariance`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn, k', k']`
+where the first `n` dimensions are batch coordinates and
+`k' = reduce_prod(self.event_shape)`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+cross_entropy
+
+View source
+
+
+cross_entropy(
+ other, name='cross_entropy'
+)
+
+
+Computes the (Shannon) cross entropy.
+
+Denote this distribution (`self`) by `P` and the `other` distribution by
+`Q`. Assuming `P, Q` are absolutely continuous with respect to
+one another and permit densities `p(x) dr(x)` and `q(x) dr(x)`, (Shanon)
+cross entropy is defined as:
+
+```none
+H[P, Q] = E_p[-log q(X)] = -int_F p(x) log q(x) dr(x)
+```
+
+where `F` denotes the support of the random variable `X ~ P`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`other`
+ |
+
+`tfp.distributions.Distribution` instance.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cross_entropy`
+ |
+
+`self.dtype` `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn]`
+representing `n` different calculations of (Shanon) cross entropy.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+entropy
+
+View source
+
+
+entropy(
+ name='entropy'
+)
+
+
+Shannon entropy in nats.
+
+
+event_shape_tensor
+
+View source
+
+
+event_shape_tensor(
+ name='event_shape_tensor'
+)
+
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single batch as a 1-D int32 `Tensor`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`event_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+is_scalar_batch
+
+View source
+
+
+is_scalar_batch(
+ name='is_scalar_batch'
+)
+
+
+Indicates that `batch_shape == []`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`is_scalar_batch`
+ |
+
+`bool` scalar `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+is_scalar_event
+
+View source
+
+
+is_scalar_event(
+ name='is_scalar_event'
+)
+
+
+Indicates that `event_shape == []`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`is_scalar_event`
+ |
+
+`bool` scalar `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+kl_divergence
+
+View source
+
+
+kl_divergence(
+ other, name='kl_divergence'
+)
+
+
+Computes the Kullback--Leibler divergence.
+
+Denote this distribution (`self`) by `p` and the `other` distribution by
+`q`. Assuming `p, q` are absolutely continuous with respect to reference
+measure `r`, the KL divergence is defined as:
+
+```none
+KL[p, q] = E_p[log(p(X)/q(X))]
+ = -int_F p(x) log q(x) dr(x) + int_F p(x) log p(x) dr(x)
+ = H[p, q] - H[p]
+```
+
+where `F` denotes the support of the random variable `X ~ p`, `H[., .]`
+denotes (Shanon) cross entropy, and `H[.]` denotes (Shanon) entropy.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`other`
+ |
+
+`tfp.distributions.Distribution` instance.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`kl_divergence`
+ |
+
+`self.dtype` `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn]`
+representing `n` different calculations of the Kullback-Leibler
+divergence.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_cdf
+
+View source
+
+
+log_cdf(
+ value, name='log_cdf'
+)
+
+
+Log cumulative distribution function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the cumulative distribution function `cdf` is:
+
+```none
+log_cdf(x) := Log[ P[X <= x] ]
+```
+
+Often, a numerical approximation can be used for `log_cdf(x)` that yields
+a more accurate answer than simply taking the logarithm of the `cdf` when
+`x << -1`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`logcdf`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_prob
+
+View source
+
+
+log_prob(
+ value, name='log_prob'
+)
+
+
+Log probability density/mass function.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`log_prob`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_survival_function
+
+View source
+
+
+log_survival_function(
+ value, name='log_survival_function'
+)
+
+
+Log survival function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the survival function is defined:
+
+```none
+log_survival_function(x) = Log[ P[X > x] ]
+ = Log[ 1 - P[X <= x] ]
+ = Log[ 1 - cdf(x) ]
+```
+
+Typically, different numerical approximations can be used for the log
+survival function, which are more accurate than `1 - cdf(x)` when `x >> 1`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with values of type
+`self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+mean
+
+View source
+
+
+mean(
+ name='mean'
+)
+
+
+Mean.
+
+Additional documentation from `StudentT`:
+
+The mean of Student's T equals `loc` if `df > 1`, otherwise it is
+`NaN`. If `self.allow_nan_stats=True`, then an exception will be raised
+rather than returning `NaN`.
+
+mode
+
+View source
+
+
+mode(
+ name='mode'
+)
+
+
+Mode.
+
+
+param_shapes
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+param_shapes(
+ sample_shape, name='DistributionParamShapes'
+)
+
+
+Shapes of parameters given the desired shape of a call to `sample()`.
+
+This is a class method that describes what key/value arguments are required
+to instantiate the given `Distribution` so that a particular shape is
+returned for that instance's call to `sample()`.
+
+Subclasses should override class method `_param_shapes`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor` or python list/tuple. Desired shape of a call to
+`sample()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to prepend ops with.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`dict` of parameter name to `Tensor` shapes.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+param_static_shapes
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+param_static_shapes(
+ sample_shape
+)
+
+
+param_shapes with static (i.e. `TensorShape`) shapes.
+
+This is a class method that describes what key/value arguments are required
+to instantiate the given `Distribution` so that a particular shape is
+returned for that instance's call to `sample()`. Assumes that the sample's
+shape is known statically.
+
+Subclasses should override class method `_param_shapes` to return
+constant-valued tensors when constant values are fed.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+`TensorShape` or python list/tuple. Desired shape of a call
+to `sample()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`dict` of parameter name to `TensorShape`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `sample_shape` is a `TensorShape` and is not fully defined.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+prob
+
+View source
+
+
+prob(
+ value, name='prob'
+)
+
+
+Probability density/mass function.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`prob`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+quantile
+
+View source
+
+
+quantile(
+ value, name='quantile'
+)
+
+
+Quantile function. Aka "inverse cdf" or "percent point function".
+
+Given random variable `X` and `p in [0, 1]`, the `quantile` is:
+
+```none
+quantile(p) := x such that P[X <= x] == p
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`quantile`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+sample
+
+View source
+
+
+sample(
+ sample_shape=(), seed=None, name='sample'
+)
+
+
+Generate samples of the specified shape.
+
+Note that a call to `sample()` without arguments will generate a single
+sample.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+0D or 1D `int32` `Tensor`. Shape of the generated samples.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+Python integer seed for RNG
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`samples`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` with prepended dimensions `sample_shape`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+stddev
+
+View source
+
+
+stddev(
+ name='stddev'
+)
+
+
+Standard deviation.
+
+Standard deviation is defined as,
+
+```none
+stddev = E[(X - E[X])**2]**0.5
+```
+
+where `X` is the random variable associated with this distribution, `E`
+denotes expectation, and `stddev.shape = batch_shape + event_shape`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`stddev`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape identical to
+`batch_shape + event_shape`, i.e., the same shape as `self.mean()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+survival_function
+
+View source
+
+
+survival_function(
+ value, name='survival_function'
+)
+
+
+Survival function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the survival function is defined:
+
+```none
+survival_function(x) = P[X > x]
+ = 1 - P[X <= x]
+ = 1 - cdf(x).
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with values of type
+`self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+variance
+
+View source
+
+
+variance(
+ name='variance'
+)
+
+
+Variance.
+
+Variance is defined as,
+
+```none
+Var = E[(X - E[X])**2]
+```
+
+where `X` is the random variable associated with this distribution, `E`
+denotes expectation, and `Var.shape = batch_shape + event_shape`.
+
+
+Additional documentation from `StudentT`:
+
+The variance for Student's T equals
+
+```
+df / (df - 2), when df > 2
+infinity, when 1 < df <= 2
+NaN, when df <= 1
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`variance`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape identical to
+`batch_shape + event_shape`, i.e., the same shape as `self.mean()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/Uniform.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/Uniform.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3db63c17a78
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/Uniform.md
@@ -0,0 +1,1492 @@
+description: Uniform distribution with low and high parameters.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.distributions.Uniform
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Uniform distribution with `low` and `high` parameters.
+
+Inherits From: [`Distribution`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/distributions/Distribution.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.distributions.Uniform(
+ low=0.0, high=1.0, validate_args=(False), allow_nan_stats=(True), name='Uniform'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Mathematical Details
+
+The probability density function (pdf) is,
+
+```none
+pdf(x; a, b) = I[a <= x < b] / Z
+Z = b - a
+```
+
+where
+
+- `low = a`,
+- `high = b`,
+- `Z` is the normalizing constant, and
+- `I[predicate]` is the [indicator function](
+ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Indicator_function) for `predicate`.
+
+The parameters `low` and `high` must be shaped in a way that supports
+broadcasting (e.g., `high - low` is a valid operation).
+
+#### Examples
+
+```python
+# Without broadcasting:
+u1 = Uniform(low=3.0, high=4.0) # a single uniform distribution [3, 4]
+u2 = Uniform(low=[1.0, 2.0],
+ high=[3.0, 4.0]) # 2 distributions [1, 3], [2, 4]
+u3 = Uniform(low=[[1.0, 2.0],
+ [3.0, 4.0]],
+ high=[[1.5, 2.5],
+ [3.5, 4.5]]) # 4 distributions
+```
+
+```python
+# With broadcasting:
+u1 = Uniform(low=3.0, high=[5.0, 6.0, 7.0]) # 3 distributions
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`low`
+ |
+
+Floating point tensor, lower boundary of the output interval. Must
+have `low < high`.
+ |
+
+|
+`high`
+ |
+
+Floating point tensor, upper boundary of the output interval. Must
+have `low < high`.
+ |
+
+|
+`validate_args`
+ |
+
+Python `bool`, default `False`. When `True` distribution
+parameters are checked for validity despite possibly degrading runtime
+performance. When `False` invalid inputs may silently render incorrect
+outputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`allow_nan_stats`
+ |
+
+Python `bool`, default `True`. When `True`, statistics
+(e.g., mean, mode, variance) use the value "`NaN`" to indicate the
+result is undefined. When `False`, an exception is raised if one or
+more of the statistic's batch members are undefined.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` name prefixed to Ops created by this class.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`InvalidArgumentError`
+ |
+
+if `low >= high` and `validate_args=False`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`allow_nan_stats`
+ |
+
+Python `bool` describing behavior when a stat is undefined.
+
+Stats return +/- infinity when it makes sense. E.g., the variance of a
+Cauchy distribution is infinity. However, sometimes the statistic is
+undefined, e.g., if a distribution's pdf does not achieve a maximum within
+the support of the distribution, the mode is undefined. If the mean is
+undefined, then by definition the variance is undefined. E.g. the mean for
+Student's T for df = 1 is undefined (no clear way to say it is either + or -
+infinity), so the variance = E[(X - mean)**2] is also undefined.
+ |
+
+|
+`batch_shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single event index as a `TensorShape`.
+
+May be partially defined or unknown.
+
+The batch dimensions are indexes into independent, non-identical
+parameterizations of this distribution.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+The `DType` of `Tensor`s handled by this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`event_shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single batch as a `TensorShape`.
+
+May be partially defined or unknown.
+ |
+
+|
+`high`
+ |
+
+Upper boundary of the output interval.
+ |
+
+|
+`low`
+ |
+
+Lower boundary of the output interval.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name prepended to all ops created by this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`parameters`
+ |
+
+Dictionary of parameters used to instantiate this `Distribution`.
+ |
+
+|
+`reparameterization_type`
+ |
+
+Describes how samples from the distribution are reparameterized.
+
+Currently this is one of the static instances
+`distributions.FULLY_REPARAMETERIZED`
+or `distributions.NOT_REPARAMETERIZED`.
+ |
+
+|
+`validate_args`
+ |
+
+Python `bool` indicating possibly expensive checks are enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+batch_shape_tensor
+
+View source
+
+
+batch_shape_tensor(
+ name='batch_shape_tensor'
+)
+
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single event index as a 1-D `Tensor`.
+
+The batch dimensions are indexes into independent, non-identical
+parameterizations of this distribution.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`batch_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+cdf
+
+View source
+
+
+cdf(
+ value, name='cdf'
+)
+
+
+Cumulative distribution function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the cumulative distribution function `cdf` is:
+
+```none
+cdf(x) := P[X <= x]
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cdf`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+copy
+
+View source
+
+
+copy(
+ **override_parameters_kwargs
+)
+
+
+Creates a deep copy of the distribution.
+
+Note: the copy distribution may continue to depend on the original
+initialization arguments.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`**override_parameters_kwargs`
+ |
+
+String/value dictionary of initialization
+arguments to override with new values.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`distribution`
+ |
+
+A new instance of `type(self)` initialized from the union
+of self.parameters and override_parameters_kwargs, i.e.,
+`dict(self.parameters, **override_parameters_kwargs)`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+covariance
+
+View source
+
+
+covariance(
+ name='covariance'
+)
+
+
+Covariance.
+
+Covariance is (possibly) defined only for non-scalar-event distributions.
+
+For example, for a length-`k`, vector-valued distribution, it is calculated
+as,
+
+```none
+Cov[i, j] = Covariance(X_i, X_j) = E[(X_i - E[X_i]) (X_j - E[X_j])]
+```
+
+where `Cov` is a (batch of) `k x k` matrix, `0 <= (i, j) < k`, and `E`
+denotes expectation.
+
+Alternatively, for non-vector, multivariate distributions (e.g.,
+matrix-valued, Wishart), `Covariance` shall return a (batch of) matrices
+under some vectorization of the events, i.e.,
+
+```none
+Cov[i, j] = Covariance(Vec(X)_i, Vec(X)_j) = [as above]
+```
+
+where `Cov` is a (batch of) `k' x k'` matrices,
+`0 <= (i, j) < k' = reduce_prod(event_shape)`, and `Vec` is some function
+mapping indices of this distribution's event dimensions to indices of a
+length-`k'` vector.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`covariance`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn, k', k']`
+where the first `n` dimensions are batch coordinates and
+`k' = reduce_prod(self.event_shape)`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+cross_entropy
+
+View source
+
+
+cross_entropy(
+ other, name='cross_entropy'
+)
+
+
+Computes the (Shannon) cross entropy.
+
+Denote this distribution (`self`) by `P` and the `other` distribution by
+`Q`. Assuming `P, Q` are absolutely continuous with respect to
+one another and permit densities `p(x) dr(x)` and `q(x) dr(x)`, (Shanon)
+cross entropy is defined as:
+
+```none
+H[P, Q] = E_p[-log q(X)] = -int_F p(x) log q(x) dr(x)
+```
+
+where `F` denotes the support of the random variable `X ~ P`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`other`
+ |
+
+`tfp.distributions.Distribution` instance.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cross_entropy`
+ |
+
+`self.dtype` `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn]`
+representing `n` different calculations of (Shanon) cross entropy.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+entropy
+
+View source
+
+
+entropy(
+ name='entropy'
+)
+
+
+Shannon entropy in nats.
+
+
+event_shape_tensor
+
+View source
+
+
+event_shape_tensor(
+ name='event_shape_tensor'
+)
+
+
+Shape of a single sample from a single batch as a 1-D int32 `Tensor`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`event_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+is_scalar_batch
+
+View source
+
+
+is_scalar_batch(
+ name='is_scalar_batch'
+)
+
+
+Indicates that `batch_shape == []`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`is_scalar_batch`
+ |
+
+`bool` scalar `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+is_scalar_event
+
+View source
+
+
+is_scalar_event(
+ name='is_scalar_event'
+)
+
+
+Indicates that `event_shape == []`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`is_scalar_event`
+ |
+
+`bool` scalar `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+kl_divergence
+
+View source
+
+
+kl_divergence(
+ other, name='kl_divergence'
+)
+
+
+Computes the Kullback--Leibler divergence.
+
+Denote this distribution (`self`) by `p` and the `other` distribution by
+`q`. Assuming `p, q` are absolutely continuous with respect to reference
+measure `r`, the KL divergence is defined as:
+
+```none
+KL[p, q] = E_p[log(p(X)/q(X))]
+ = -int_F p(x) log q(x) dr(x) + int_F p(x) log p(x) dr(x)
+ = H[p, q] - H[p]
+```
+
+where `F` denotes the support of the random variable `X ~ p`, `H[., .]`
+denotes (Shanon) cross entropy, and `H[.]` denotes (Shanon) entropy.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`other`
+ |
+
+`tfp.distributions.Distribution` instance.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`kl_divergence`
+ |
+
+`self.dtype` `Tensor` with shape `[B1, ..., Bn]`
+representing `n` different calculations of the Kullback-Leibler
+divergence.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_cdf
+
+View source
+
+
+log_cdf(
+ value, name='log_cdf'
+)
+
+
+Log cumulative distribution function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the cumulative distribution function `cdf` is:
+
+```none
+log_cdf(x) := Log[ P[X <= x] ]
+```
+
+Often, a numerical approximation can be used for `log_cdf(x)` that yields
+a more accurate answer than simply taking the logarithm of the `cdf` when
+`x << -1`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`logcdf`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_prob
+
+View source
+
+
+log_prob(
+ value, name='log_prob'
+)
+
+
+Log probability density/mass function.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`log_prob`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+log_survival_function
+
+View source
+
+
+log_survival_function(
+ value, name='log_survival_function'
+)
+
+
+Log survival function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the survival function is defined:
+
+```none
+log_survival_function(x) = Log[ P[X > x] ]
+ = Log[ 1 - P[X <= x] ]
+ = Log[ 1 - cdf(x) ]
+```
+
+Typically, different numerical approximations can be used for the log
+survival function, which are more accurate than `1 - cdf(x)` when `x >> 1`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with values of type
+`self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+mean
+
+View source
+
+
+mean(
+ name='mean'
+)
+
+
+Mean.
+
+
+mode
+
+View source
+
+
+mode(
+ name='mode'
+)
+
+
+Mode.
+
+
+param_shapes
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+param_shapes(
+ sample_shape, name='DistributionParamShapes'
+)
+
+
+Shapes of parameters given the desired shape of a call to `sample()`.
+
+This is a class method that describes what key/value arguments are required
+to instantiate the given `Distribution` so that a particular shape is
+returned for that instance's call to `sample()`.
+
+Subclasses should override class method `_param_shapes`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+`Tensor` or python list/tuple. Desired shape of a call to
+`sample()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to prepend ops with.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`dict` of parameter name to `Tensor` shapes.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+param_static_shapes
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+param_static_shapes(
+ sample_shape
+)
+
+
+param_shapes with static (i.e. `TensorShape`) shapes.
+
+This is a class method that describes what key/value arguments are required
+to instantiate the given `Distribution` so that a particular shape is
+returned for that instance's call to `sample()`. Assumes that the sample's
+shape is known statically.
+
+Subclasses should override class method `_param_shapes` to return
+constant-valued tensors when constant values are fed.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+`TensorShape` or python list/tuple. Desired shape of a call
+to `sample()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`dict` of parameter name to `TensorShape`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `sample_shape` is a `TensorShape` and is not fully defined.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+prob
+
+View source
+
+
+prob(
+ value, name='prob'
+)
+
+
+Probability density/mass function.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`prob`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+quantile
+
+View source
+
+
+quantile(
+ value, name='quantile'
+)
+
+
+Quantile function. Aka "inverse cdf" or "percent point function".
+
+Given random variable `X` and `p in [0, 1]`, the `quantile` is:
+
+```none
+quantile(p) := x such that P[X <= x] == p
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`quantile`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with
+values of type `self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+range
+
+View source
+
+
+range(
+ name='range'
+)
+
+
+`high - low`.
+
+
+sample
+
+View source
+
+
+sample(
+ sample_shape=(), seed=None, name='sample'
+)
+
+
+Generate samples of the specified shape.
+
+Note that a call to `sample()` without arguments will generate a single
+sample.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sample_shape`
+ |
+
+0D or 1D `int32` `Tensor`. Shape of the generated samples.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+Python integer seed for RNG
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+name to give to the op.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`samples`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` with prepended dimensions `sample_shape`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+stddev
+
+View source
+
+
+stddev(
+ name='stddev'
+)
+
+
+Standard deviation.
+
+Standard deviation is defined as,
+
+```none
+stddev = E[(X - E[X])**2]**0.5
+```
+
+where `X` is the random variable associated with this distribution, `E`
+denotes expectation, and `stddev.shape = batch_shape + event_shape`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`stddev`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape identical to
+`batch_shape + event_shape`, i.e., the same shape as `self.mean()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+survival_function
+
+View source
+
+
+survival_function(
+ value, name='survival_function'
+)
+
+
+Survival function.
+
+Given random variable `X`, the survival function is defined:
+
+```none
+survival_function(x) = P[X > x]
+ = 1 - P[X <= x]
+ = 1 - cdf(x).
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`float` or `double` `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`Tensor` of shape `sample_shape(x) + self.batch_shape` with values of type
+`self.dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+variance
+
+View source
+
+
+variance(
+ name='variance'
+)
+
+
+Variance.
+
+Variance is defined as,
+
+```none
+Var = E[(X - E[X])**2]
+```
+
+where `X` is the random variable associated with this distribution, `E`
+denotes expectation, and `Var.shape = batch_shape + event_shape`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` prepended to names of ops created by this function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`variance`
+ |
+
+Floating-point `Tensor` with shape identical to
+`batch_shape + event_shape`, i.e., the same shape as `self.mean()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/kl_divergence.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/kl_divergence.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3d1dd250d45
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/distributions/kl_divergence.md
@@ -0,0 +1,124 @@
+description: Get the KL-divergence KL(distribution_a || distribution_b). (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.distributions.kl_divergence
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Get the KL-divergence KL(distribution_a || distribution_b). (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.distributions.kl_divergence(
+ distribution_a, distribution_b, allow_nan_stats=(True), name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed after 2019-01-01.
+Instructions for updating:
+The TensorFlow Distributions library has moved to TensorFlow Probability (https://github.com/tensorflow/probability). You should update all references to use `tfp.distributions` instead of `tf.distributions`.
+
+If there is no KL method registered specifically for `type(distribution_a)`
+and `type(distribution_b)`, then the class hierarchies of these types are
+searched.
+
+If one KL method is registered between any pairs of classes in these two
+parent hierarchies, it is used.
+
+If more than one such registered method exists, the method whose registered
+classes have the shortest sum MRO paths to the input types is used.
+
+If more than one such shortest path exists, the first method
+identified in the search is used (favoring a shorter MRO distance to
+`type(distribution_a)`).
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`distribution_a`
+ |
+
+The first distribution.
+ |
+
+|
+`distribution_b`
+ |
+
+The second distribution.
+ |
+
+|
+`allow_nan_stats`
+ |
+
+Python `bool`, default `True`. When `True`,
+statistics (e.g., mean, mode, variance) use the value "`NaN`" to
+indicate the result is undefined. When `False`, an exception is raised
+if one or more of the statistic's batch members are undefined.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Python `str` name prefixed to Ops created by this class.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A Tensor with the batchwise KL-divergence between `distribution_a`
+and `distribution_b`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`NotImplementedError`
+ |
+
+If no KL method is defined for distribution types
+of `distribution_a` and `distribution_b`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/dtypes.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/dtypes.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..7c8e8eeb992
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/dtypes.md
@@ -0,0 +1,91 @@
+description: Public API for tf.dtypes namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.dtypes
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.dtypes namespace.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class DType`](../../../tf/dtypes/DType.md): Represents the type of the elements in a `Tensor`.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`as_dtype(...)`](../../../tf/dtypes/as_dtype.md): Converts the given `type_value` to a `DType`.
+
+[`as_string(...)`](../../../tf/strings/as_string.md): Converts each entry in the given tensor to strings.
+
+[`cast(...)`](../../../tf/cast.md): Casts a tensor to a new type.
+
+[`complex(...)`](../../../tf/dtypes/complex.md): Converts two real numbers to a complex number.
+
+[`saturate_cast(...)`](../../../tf/dtypes/saturate_cast.md): Performs a safe saturating cast of `value` to `dtype`.
+
+## Other Members
+
+* `QUANTIZED_DTYPES`
+* `bfloat16`
+* `bool`
+* `complex128`
+* `complex64`
+* `double`
+* `float16`
+* `float32`
+* `float64`
+* `half`
+* `int16`
+* `int32`
+* `int64`
+* `int8`
+* `qint16`
+* `qint32`
+* `qint8`
+* `quint16`
+* `quint8`
+* `resource`
+* `string`
+* `uint16`
+* `uint32`
+* `uint64`
+* `uint8`
+* `variant`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/enable_control_flow_v2.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/enable_control_flow_v2.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..c0c622fcc7f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/enable_control_flow_v2.md
@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
+description: Use control flow v2.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.enable_control_flow_v2
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Use control flow v2.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.enable_control_flow_v2()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+control flow v2 (cfv2) is an improved version of control flow in TensorFlow
+with support for higher order derivatives. Enabling cfv2 will change the
+graph/function representation of control flow, e.g., tf.while_loop and
+tf.cond will generate functional `While` and `If` ops instead of low-level
+`Switch`, `Merge` etc. ops. Note: Importing and running graphs exported
+with old control flow will still be supported.
+
+Calling tf.enable_control_flow_v2() lets you opt-in to this TensorFlow 2.0
+feature.
+
+Note: v2 control flow is always enabled inside of tf.function. Calling this
+function is not required.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/enable_eager_execution.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/enable_eager_execution.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..08e4deffdfd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/enable_eager_execution.md
@@ -0,0 +1,132 @@
+description: Enables eager execution for the lifetime of this program.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.enable_eager_execution
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Enables eager execution for the lifetime of this program.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.enable_eager_execution(
+ config=None, device_policy=None, execution_mode=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Eager execution provides an imperative interface to TensorFlow. With eager
+execution enabled, TensorFlow functions execute operations immediately (as
+opposed to adding to a graph to be executed later in a tf.compat.v1.Session)
+and
+return concrete values (as opposed to symbolic references to a node in a
+computational graph).
+
+#### For example:
+
+
+
+```python
+tf.compat.v1.enable_eager_execution()
+
+# After eager execution is enabled, operations are executed as they are
+# defined and Tensor objects hold concrete values, which can be accessed as
+# numpy.ndarray`s through the numpy() method.
+assert tf.multiply(6, 7).numpy() == 42
+```
+
+Eager execution cannot be enabled after TensorFlow APIs have been used to
+create or execute graphs. It is typically recommended to invoke this function
+at program startup and not in a library (as most libraries should be usable
+both with and without eager execution).
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+(Optional.) A tf.compat.v1.ConfigProto to use to configure the
+environment in which operations are executed. Note that
+tf.compat.v1.ConfigProto is also used to configure graph execution (via
+tf.compat.v1.Session) and many options within tf.compat.v1.ConfigProto
+are not implemented (or are irrelevant) when eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+|
+`device_policy`
+ |
+
+(Optional.) Policy controlling how operations requiring
+inputs on a specific device (e.g., a GPU 0) handle inputs on a different
+device (e.g. GPU 1 or CPU). When set to None, an appropriate value will
+be picked automatically. The value picked may change between TensorFlow
+releases.
+Valid values:
+- tf.contrib.eager.DEVICE_PLACEMENT_EXPLICIT: raises an error if the
+placement is not correct.
+- tf.contrib.eager.DEVICE_PLACEMENT_WARN: copies the tensors which are not
+on the right device but logs a warning.
+- tf.contrib.eager.DEVICE_PLACEMENT_SILENT: silently copies the tensors.
+Note that this may hide performance problems as there is no notification
+provided when operations are blocked on the tensor being copied between
+devices.
+- tf.contrib.eager.DEVICE_PLACEMENT_SILENT_FOR_INT32: silently copies
+int32 tensors, raising errors on the other ones.
+ |
+
+|
+`execution_mode`
+ |
+
+(Optional.) Policy controlling how operations dispatched are
+actually executed. When set to None, an appropriate value will be picked
+automatically. The value picked may change between TensorFlow releases.
+Valid values:
+- tf.contrib.eager.SYNC: executes each operation synchronously.
+- tf.contrib.eager.ASYNC: executes each operation asynchronously. These
+operations may return "non-ready" handles.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If eager execution is enabled after creating/executing a
+TensorFlow graph, or if options provided conflict with a previous call
+to this function.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/enable_resource_variables.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/enable_resource_variables.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..f99b78a80c5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/enable_resource_variables.md
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
+description: Creates resource variables by default.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Creates resource variables by default.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.enable_resource_variables()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Resource variables are improved versions of TensorFlow variables with a
+well-defined memory model. Accessing a resource variable reads its value, and
+all ops which access a specific read value of the variable are guaranteed to
+see the same value for that tensor. Writes which happen after a read (by
+having a control or data dependency on the read) are guaranteed not to affect
+the value of the read tensor, and similarly writes which happen before a read
+are guaranteed to affect the value. No guarantees are made about unordered
+read/write pairs.
+
+Calling tf.enable_resource_variables() lets you opt-in to this TensorFlow 2.0
+feature.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/enable_tensor_equality.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/enable_tensor_equality.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..8d6132f6b97
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/enable_tensor_equality.md
@@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
+description: Compare Tensors with element-wise comparison and thus be unhashable.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.enable_tensor_equality
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Compare Tensors with element-wise comparison and thus be unhashable.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.enable_tensor_equality()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Comparing tensors with element-wise allows comparisons such as
+tf.Variable(1.0) == 1.0. Element-wise equality implies that tensors are
+unhashable. Thus tensors can no longer be directly used in sets or as a key in
+a dictionary.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/enable_v2_behavior.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/enable_v2_behavior.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..5771654a20f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/enable_v2_behavior.md
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
+description: Enables TensorFlow 2.x behaviors.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.enable_v2_behavior
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Enables TensorFlow 2.x behaviors.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.enable_v2_behavior()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This function can be called at the beginning of the program (before `Tensors`,
+`Graphs` or other structures have been created, and before devices have been
+initialized. It switches all global behaviors that are different between
+TensorFlow 1.x and 2.x to behave as intended for 2.x.
+
+This function is called in the main TensorFlow `__init__.py` file, user should
+not need to call it, except during complex migrations.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/enable_v2_tensorshape.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/enable_v2_tensorshape.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..1e3c97ba418
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/enable_v2_tensorshape.md
@@ -0,0 +1,76 @@
+description: In TensorFlow 2.0, iterating over a TensorShape instance returns values.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.enable_v2_tensorshape
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+In TensorFlow 2.0, iterating over a TensorShape instance returns values.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.enable_v2_tensorshape()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This enables the new behavior.
+
+Concretely, `tensor_shape[i]` returned a Dimension instance in V1, but
+it V2 it returns either an integer, or None.
+
+#### Examples:
+
+
+
+```
+#######################
+# If you had this in V1:
+value = tensor_shape[i].value
+
+# Do this in V2 instead:
+value = tensor_shape[i]
+
+#######################
+# If you had this in V1:
+for dim in tensor_shape:
+ value = dim.value
+ print(value)
+
+# Do this in V2 instead:
+for value in tensor_shape:
+ print(value)
+
+#######################
+# If you had this in V1:
+dim = tensor_shape[i]
+dim.assert_is_compatible_with(other_shape) # or using any other shape method
+
+# Do this in V2 instead:
+if tensor_shape.rank is None:
+ dim = Dimension(None)
+else:
+ dim = tensor_shape.dims[i]
+dim.assert_is_compatible_with(other_shape) # or using any other shape method
+
+# The V2 suggestion above is more explicit, which will save you from
+# the following trap (present in V1):
+# you might do in-place modifications to `dim` and expect them to be reflected
+# in `tensor_shape[i]`, but they would not be.
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/errors.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/errors.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..f1419a64622
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/errors.md
@@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
+description: Exception types for TensorFlow errors.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.errors
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Exception types for TensorFlow errors.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class AbortedError`](../../../tf/errors/AbortedError.md): The operation was aborted, typically due to a concurrent action.
+
+[`class AlreadyExistsError`](../../../tf/errors/AlreadyExistsError.md): Raised when an entity that we attempted to create already exists.
+
+[`class CancelledError`](../../../tf/errors/CancelledError.md): Raised when an operation or step is cancelled.
+
+[`class DataLossError`](../../../tf/errors/DataLossError.md): Raised when unrecoverable data loss or corruption is encountered.
+
+[`class DeadlineExceededError`](../../../tf/errors/DeadlineExceededError.md): Raised when a deadline expires before an operation could complete.
+
+[`class FailedPreconditionError`](../../../tf/errors/FailedPreconditionError.md): Operation was rejected because the system is not in a state to execute it.
+
+[`class InternalError`](../../../tf/errors/InternalError.md): Raised when the system experiences an internal error.
+
+[`class InvalidArgumentError`](../../../tf/errors/InvalidArgumentError.md): Raised when an operation receives an invalid argument.
+
+[`class NotFoundError`](../../../tf/errors/NotFoundError.md): Raised when a requested entity (e.g., a file or directory) was not found.
+
+[`class OpError`](../../../tf/errors/OpError.md): A generic error that is raised when TensorFlow execution fails.
+
+[`class OutOfRangeError`](../../../tf/errors/OutOfRangeError.md): Raised when an operation iterates past the valid input range.
+
+[`class PermissionDeniedError`](../../../tf/errors/PermissionDeniedError.md): Raised when the caller does not have permission to run an operation.
+
+[`class ResourceExhaustedError`](../../../tf/errors/ResourceExhaustedError.md): Some resource has been exhausted.
+
+[`class UnauthenticatedError`](../../../tf/errors/UnauthenticatedError.md): The request does not have valid authentication credentials.
+
+[`class UnavailableError`](../../../tf/errors/UnavailableError.md): Raised when the runtime is currently unavailable.
+
+[`class UnimplementedError`](../../../tf/errors/UnimplementedError.md): Raised when an operation has not been implemented.
+
+[`class UnknownError`](../../../tf/errors/UnknownError.md): Unknown error.
+
+[`class raise_exception_on_not_ok_status`](../../../tf/compat/v1/errors/raise_exception_on_not_ok_status.md): Context manager to check for C API status.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`error_code_from_exception_type(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/errors/error_code_from_exception_type.md)
+
+[`exception_type_from_error_code(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/errors/exception_type_from_error_code.md)
+
+## Other Members
+
+* `ABORTED = 10`
+* `ALREADY_EXISTS = 6`
+* `CANCELLED = 1`
+* `DATA_LOSS = 15`
+* `DEADLINE_EXCEEDED = 4`
+* `FAILED_PRECONDITION = 9`
+* `INTERNAL = 13`
+* `INVALID_ARGUMENT = 3`
+* `NOT_FOUND = 5`
+* `OK = 0`
+* `OUT_OF_RANGE = 11`
+* `PERMISSION_DENIED = 7`
+* `RESOURCE_EXHAUSTED = 8`
+* `UNAUTHENTICATED = 16`
+* `UNAVAILABLE = 14`
+* `UNIMPLEMENTED = 12`
+* `UNKNOWN = 2`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/errors/error_code_from_exception_type.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/errors/error_code_from_exception_type.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..f290e28394f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/errors/error_code_from_exception_type.md
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.errors.error_code_from_exception_type
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.errors.error_code_from_exception_type()
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/errors/exception_type_from_error_code.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/errors/exception_type_from_error_code.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e76852c75a5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/errors/exception_type_from_error_code.md
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.errors.exception_type_from_error_code
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.errors.exception_type_from_error_code(
+ error_code
+)
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/errors/raise_exception_on_not_ok_status.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/errors/raise_exception_on_not_ok_status.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3aebfec89c1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/errors/raise_exception_on_not_ok_status.md
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
+description: Context manager to check for C API status.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.errors.raise_exception_on_not_ok_status
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Context manager to check for C API status.
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+__enter__
+
+View source
+
+
+__enter__()
+
+
+
+
+
+__exit__
+
+View source
+
+
+__exit__(
+ type_arg, value_arg, traceback_arg
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..86b80a10f15
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator.md
@@ -0,0 +1,147 @@
+description: Estimator: High level tools for working with models.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.estimator
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Estimator: High level tools for working with models.
+
+
+
+## Modules
+
+[`experimental`](../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/experimental.md) module: Public API for tf.estimator.experimental namespace.
+
+[`export`](../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/export.md) module: All public utility methods for exporting Estimator to SavedModel.
+
+[`inputs`](../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/inputs.md) module: Utility methods to create simple input_fns.
+
+[`tpu`](../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/tpu.md) module: Public API for tf.estimator.tpu namespace.
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class BaselineClassifier`](../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/BaselineClassifier.md): A classifier that can establish a simple baseline.
+
+[`class BaselineEstimator`](../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/BaselineEstimator.md): An estimator that can establish a simple baseline.
+
+[`class BaselineRegressor`](../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/BaselineRegressor.md): A regressor that can establish a simple baseline.
+
+[`class BestExporter`](../../../tf/estimator/BestExporter.md): This class exports the serving graph and checkpoints of the best models.
+
+[`class BinaryClassHead`](../../../tf/estimator/BinaryClassHead.md): Creates a `Head` for single label binary classification.
+
+[`class BoostedTreesClassifier`](../../../tf/estimator/BoostedTreesClassifier.md): A Classifier for Tensorflow Boosted Trees models.
+
+[`class BoostedTreesEstimator`](../../../tf/estimator/BoostedTreesEstimator.md): An Estimator for Tensorflow Boosted Trees models.
+
+[`class BoostedTreesRegressor`](../../../tf/estimator/BoostedTreesRegressor.md): A Regressor for Tensorflow Boosted Trees models.
+
+[`class CheckpointSaverHook`](../../../tf/estimator/CheckpointSaverHook.md): Saves checkpoints every N steps or seconds.
+
+[`class CheckpointSaverListener`](../../../tf/estimator/CheckpointSaverListener.md): Interface for listeners that take action before or after checkpoint save.
+
+[`class DNNClassifier`](../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/DNNClassifier.md): A classifier for TensorFlow DNN models.
+
+[`class DNNEstimator`](../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/DNNEstimator.md): An estimator for TensorFlow DNN models with user-specified head.
+
+[`class DNNLinearCombinedClassifier`](../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/DNNLinearCombinedClassifier.md): An estimator for TensorFlow Linear and DNN joined classification models.
+
+[`class DNNLinearCombinedEstimator`](../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/DNNLinearCombinedEstimator.md): An estimator for TensorFlow Linear and DNN joined models with custom head.
+
+[`class DNNLinearCombinedRegressor`](../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/DNNLinearCombinedRegressor.md): An estimator for TensorFlow Linear and DNN joined models for regression.
+
+[`class DNNRegressor`](../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/DNNRegressor.md): A regressor for TensorFlow DNN models.
+
+[`class Estimator`](../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/Estimator.md): Estimator class to train and evaluate TensorFlow models.
+
+[`class EstimatorSpec`](../../../tf/estimator/EstimatorSpec.md): Ops and objects returned from a `model_fn` and passed to an `Estimator`.
+
+[`class EvalSpec`](../../../tf/estimator/EvalSpec.md): Configuration for the "eval" part for the `train_and_evaluate` call.
+
+[`class Exporter`](../../../tf/estimator/Exporter.md): A class representing a type of model export.
+
+[`class FeedFnHook`](../../../tf/estimator/FeedFnHook.md): Runs `feed_fn` and sets the `feed_dict` accordingly.
+
+[`class FinalExporter`](../../../tf/estimator/FinalExporter.md): This class exports the serving graph and checkpoints at the end.
+
+[`class FinalOpsHook`](../../../tf/estimator/FinalOpsHook.md): A hook which evaluates `Tensors` at the end of a session.
+
+[`class GlobalStepWaiterHook`](../../../tf/estimator/GlobalStepWaiterHook.md): Delays execution until global step reaches `wait_until_step`.
+
+[`class Head`](../../../tf/estimator/Head.md): Interface for the head/top of a model.
+
+[`class LatestExporter`](../../../tf/estimator/LatestExporter.md): This class regularly exports the serving graph and checkpoints.
+
+[`class LinearClassifier`](../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/LinearClassifier.md): Linear classifier model.
+
+[`class LinearEstimator`](../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/LinearEstimator.md): An estimator for TensorFlow linear models with user-specified head.
+
+[`class LinearRegressor`](../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/LinearRegressor.md): An estimator for TensorFlow Linear regression problems.
+
+[`class LoggingTensorHook`](../../../tf/estimator/LoggingTensorHook.md): Prints the given tensors every N local steps, every N seconds, or at end.
+
+[`class LogisticRegressionHead`](../../../tf/estimator/LogisticRegressionHead.md): Creates a `Head` for logistic regression.
+
+[`class ModeKeys`](../../../tf/estimator/ModeKeys.md): Standard names for Estimator model modes.
+
+[`class MultiClassHead`](../../../tf/estimator/MultiClassHead.md): Creates a `Head` for multi class classification.
+
+[`class MultiHead`](../../../tf/estimator/MultiHead.md): Creates a `Head` for multi-objective learning.
+
+[`class MultiLabelHead`](../../../tf/estimator/MultiLabelHead.md): Creates a `Head` for multi-label classification.
+
+[`class NanLossDuringTrainingError`](../../../tf/estimator/NanLossDuringTrainingError.md): Unspecified run-time error.
+
+[`class NanTensorHook`](../../../tf/estimator/NanTensorHook.md): Monitors the loss tensor and stops training if loss is NaN.
+
+[`class PoissonRegressionHead`](../../../tf/estimator/PoissonRegressionHead.md): Creates a `Head` for poisson regression using tf.nn.log_poisson_loss.
+
+[`class ProfilerHook`](../../../tf/estimator/ProfilerHook.md): Captures CPU/GPU profiling information every N steps or seconds.
+
+[`class RegressionHead`](../../../tf/estimator/RegressionHead.md): Creates a `Head` for regression using the `mean_squared_error` loss.
+
+[`class RunConfig`](../../../tf/estimator/RunConfig.md): This class specifies the configurations for an `Estimator` run.
+
+[`class SecondOrStepTimer`](../../../tf/estimator/SecondOrStepTimer.md): Timer that triggers at most once every N seconds or once every N steps.
+
+[`class SessionRunArgs`](../../../tf/estimator/SessionRunArgs.md): Represents arguments to be added to a `Session.run()` call.
+
+[`class SessionRunContext`](../../../tf/estimator/SessionRunContext.md): Provides information about the `session.run()` call being made.
+
+[`class SessionRunHook`](../../../tf/estimator/SessionRunHook.md): Hook to extend calls to MonitoredSession.run().
+
+[`class SessionRunValues`](../../../tf/estimator/SessionRunValues.md): Contains the results of `Session.run()`.
+
+[`class StepCounterHook`](../../../tf/estimator/StepCounterHook.md): Hook that counts steps per second.
+
+[`class StopAtStepHook`](../../../tf/estimator/StopAtStepHook.md): Hook that requests stop at a specified step.
+
+[`class SummarySaverHook`](../../../tf/estimator/SummarySaverHook.md): Saves summaries every N steps.
+
+[`class TrainSpec`](../../../tf/estimator/TrainSpec.md): Configuration for the "train" part for the `train_and_evaluate` call.
+
+[`class VocabInfo`](../../../tf/estimator/VocabInfo.md): Vocabulary information for warm-starting.
+
+[`class WarmStartSettings`](../../../tf/estimator/WarmStartSettings.md): Settings for warm-starting in `tf.estimator.Estimators`.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`add_metrics(...)`](../../../tf/estimator/add_metrics.md): Creates a new tf.estimator.Estimator which has given metrics.
+
+[`classifier_parse_example_spec(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/classifier_parse_example_spec.md): Generates parsing spec for tf.parse_example to be used with classifiers.
+
+[`regressor_parse_example_spec(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/regressor_parse_example_spec.md): Generates parsing spec for tf.parse_example to be used with regressors.
+
+[`train_and_evaluate(...)`](../../../tf/estimator/train_and_evaluate.md): Train and evaluate the `estimator`.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/BaselineClassifier.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/BaselineClassifier.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..7a275fb6372
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/BaselineClassifier.md
@@ -0,0 +1,1201 @@
+description: A classifier that can establish a simple baseline.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.estimator.BaselineClassifier
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A classifier that can establish a simple baseline.
+
+Inherits From: [`Estimator`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/Estimator.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.estimator.BaselineClassifier(
+ model_dir=None, n_classes=2, weight_column=None, label_vocabulary=None,
+ optimizer='Ftrl', config=None, loss_reduction=tf.compat.v1.losses.Reduction.SUM
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This classifier ignores feature values and will learn to predict the average
+value of each label. For single-label problems, this will predict the
+probability distribution of the classes as seen in the labels. For multi-label
+problems, this will predict the fraction of examples that are positive for
+each class.
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+
+# Build BaselineClassifier
+classifier = tf.estimator.BaselineClassifier(n_classes=3)
+
+# Input builders
+def input_fn_train:
+ # Returns tf.data.Dataset of (x, y) tuple where y represents label's class
+ # index.
+ pass
+
+def input_fn_eval:
+ # Returns tf.data.Dataset of (x, y) tuple where y represents label's class
+ # index.
+ pass
+
+# Fit model.
+classifier.train(input_fn=input_fn_train)
+
+# Evaluate cross entropy between the test and train labels.
+loss = classifier.evaluate(input_fn=input_fn_eval)["loss"]
+
+# predict outputs the probability distribution of the classes as seen in
+# training.
+predictions = classifier.predict(new_samples)
+
+```
+
+Input of `train` and `evaluate` should have following features,
+ otherwise there will be a `KeyError`:
+
+* if `weight_column` is not `None`, a feature with
+ `key=weight_column` whose value is a `Tensor`.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`model_fn`
+ |
+
+Model function. Follows the signature:
+* `features` -- This is the first item returned from the `input_fn`
+passed to `train`, `evaluate`, and `predict`. This should be a
+single tf.Tensor or `dict` of same.
+* `labels` -- This is the second item returned from the `input_fn`
+passed to `train`, `evaluate`, and `predict`. This should be a
+single tf.Tensor or `dict` of same (for multi-head models). If
+mode is tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT, `labels=None` will be
+passed. If the `model_fn`'s signature does not accept `mode`, the
+`model_fn` must still be able to handle `labels=None`.
+* `mode` -- Optional. Specifies if this is training, evaluation or
+prediction. See tf.estimator.ModeKeys.
+`params` -- Optional `dict` of hyperparameters. Will receive what is
+passed to Estimator in `params` parameter. This allows to configure
+Estimators from hyper parameter tuning.
+* `config` -- Optional `estimator.RunConfig` object. Will receive what
+is passed to Estimator as its `config` parameter, or a default
+value. Allows setting up things in your `model_fn` based on
+configuration such as `num_ps_replicas`, or `model_dir`.
+* Returns -- tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec
+ |
+
+|
+`model_dir`
+ |
+
+Directory to save model parameters, graph and etc. This can
+also be used to load checkpoints from the directory into an estimator to
+continue training a previously saved model. If `PathLike` object, the
+path will be resolved. If `None`, the model_dir in `config` will be used
+if set. If both are set, they must be same. If both are `None`, a
+temporary directory will be used.
+ |
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+`estimator.RunConfig` configuration object.
+ |
+
+|
+`params`
+ |
+
+`dict` of hyper parameters that will be passed into `model_fn`.
+Keys are names of parameters, values are basic python types.
+ |
+
+|
+`warm_start_from`
+ |
+
+Optional string filepath to a checkpoint or SavedModel to
+warm-start from, or a tf.estimator.WarmStartSettings object to fully
+configure warm-starting. If None, only TRAINABLE variables are
+warm-started. If the string filepath is provided instead of a
+tf.estimator.WarmStartSettings, then all variables are warm-started,
+and it is assumed that vocabularies and tf.Tensor names are unchanged.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+parameters of `model_fn` don't match `params`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if this is called via a subclass and if that class overrides
+a member of `Estimator`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+Estimators can be used while eager execution is enabled. Note that `input_fn`
+and all hooks are executed inside a graph context, so they have to be written
+to be compatible with graph mode. Note that `input_fn` code using tf.data
+generally works in both graph and eager modes.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`model_dir`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`model_fn`
+ |
+
+Returns the `model_fn` which is bound to `self.params`.
+ |
+
+|
+`params`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+eval_dir
+
+View source
+
+
+eval_dir(
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+Shows the directory name where evaluation metrics are dumped.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of the evaluation if user needs to run multiple evaluations on
+different data sets, such as on training data vs test data. Metrics for
+different evaluations are saved in separate folders, and appear
+separately in tensorboard.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A string which is the path of directory contains evaluation metrics.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+evaluate
+
+View source
+
+
+evaluate(
+ input_fn, steps=None, hooks=None, checkpoint_path=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+Evaluates the model given evaluation data `input_fn`.
+
+For each step, calls `input_fn`, which returns one batch of data.
+Evaluates until:
+- `steps` batches are processed, or
+- `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception (tf.errors.OutOfRangeError
+or
+`StopIteration`).
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that constructs the input data for evaluation. See
+[Premade Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The
+function should construct and return one of the following: * A
+tf.data.Dataset object: Outputs of `Dataset` object must be a tuple
+`(features, labels)` with same constraints as below. * A tuple
+`(features, labels)`: Where `features` is a tf.Tensor or a dictionary
+of string feature name to `Tensor` and `labels` is a `Tensor` or a
+dictionary of string label name to `Tensor`. Both `features` and
+`labels` are consumed by `model_fn`. They should satisfy the
+expectation of `model_fn` from inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`steps`
+ |
+
+Number of steps for which to evaluate model. If `None`, evaluates
+until `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the evaluation call.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+Path of a specific checkpoint to evaluate. If `None`, the
+latest checkpoint in `model_dir` is used. If there are no checkpoints
+in `model_dir`, evaluation is run with newly initialized `Variables`
+instead of ones restored from checkpoint.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of the evaluation if user needs to run multiple evaluations on
+different data sets, such as on training data vs test data. Metrics for
+different evaluations are saved in separate folders, and appear
+separately in tensorboard.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A dict containing the evaluation metrics specified in `model_fn` keyed by
+name, as well as an entry `global_step` which contains the value of the
+global step for which this evaluation was performed. For canned
+estimators, the dict contains the `loss` (mean loss per mini-batch) and
+the `average_loss` (mean loss per sample). Canned classifiers also return
+the `accuracy`. Canned regressors also return the `label/mean` and the
+`prediction/mean`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `steps <= 0`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+experimental_export_all_saved_models
+
+View source
+
+
+experimental_export_all_saved_models(
+ export_dir_base, input_receiver_fn_map, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None
+)
+
+
+Exports a `SavedModel` with `tf.MetaGraphDefs` for each requested mode.
+
+For each mode passed in via the `input_receiver_fn_map`,
+this method builds a new graph by calling the `input_receiver_fn` to obtain
+feature and label `Tensor`s. Next, this method calls the `Estimator`'s
+`model_fn` in the passed mode to generate the model graph based on
+those features and labels, and restores the given checkpoint
+(or, lacking that, the most recent checkpoint) into the graph.
+Only one of the modes is used for saving variables to the `SavedModel`
+(order of preference: tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN,
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys.EVAL, then
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT), such that up to three
+`tf.MetaGraphDefs` are saved with a single set of variables in a single
+`SavedModel` directory.
+
+For the variables and `tf.MetaGraphDefs`, a timestamped export directory
+below
+`export_dir_base`, and writes a `SavedModel` into it containing
+the `tf.MetaGraphDef` for the given mode and its associated signatures.
+
+For prediction, the exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef`
+for each element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`,
+named using the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+For training and evaluation, the `train_op` is stored in an extra
+collection,
+and loss, metrics, and predictions are included in a `SignatureDef` for the
+mode in question.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`input_receiver_fn_map`
+ |
+
+dict of tf.estimator.ModeKeys to
+`input_receiver_fn` mappings, where the `input_receiver_fn` is a
+function that takes no arguments and returns the appropriate subclass of
+`InputReceiver`.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if any `input_receiver_fn` is `None`, no `export_outputs`
+are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+export_saved_model
+
+View source
+
+
+export_saved_model(
+ export_dir_base, serving_input_receiver_fn, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None, experimental_mode=ModeKeys.PREDICT
+)
+
+
+Exports inference graph as a `SavedModel` into the given dir.
+
+For a detailed guide, see
+[Using SavedModel with
+Estimators](https://tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model#using_savedmodel_with_estimators).
+
+This method builds a new graph by first calling the
+`serving_input_receiver_fn` to obtain feature `Tensor`s, and then calling
+this `Estimator`'s `model_fn` to generate the model graph based on those
+features. It restores the given checkpoint (or, lacking that, the most
+recent checkpoint) into this graph in a fresh session. Finally it creates
+a timestamped export directory below the given `export_dir_base`, and writes
+a `SavedModel` into it containing a single `tf.MetaGraphDef` saved from this
+session.
+
+The exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef` for each
+element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`, named
+using
+the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+The experimental_mode parameter can be used to export a single
+train/eval/predict graph as a `SavedModel`.
+See `experimental_export_all_saved_models` for full docs.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`serving_input_receiver_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that takes no argument and returns a
+tf.estimator.export.ServingInputReceiver or
+tf.estimator.export.TensorServingInputReceiver.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+|
+`experimental_mode`
+ |
+
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys value indicating with mode will
+be exported. Note that this feature is experimental.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if no `serving_input_receiver_fn` is provided, no
+`export_outputs` are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+export_savedmodel
+
+View source
+
+
+export_savedmodel(
+ export_dir_base, serving_input_receiver_fn, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None, strip_default_attrs=(False)
+)
+
+
+Exports inference graph as a `SavedModel` into the given dir. (deprecated)
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+This function has been renamed, use `export_saved_model` instead.
+
+For a detailed guide, see
+[Using SavedModel with
+Estimators](https://tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model#using_savedmodel_with_estimators).
+
+This method builds a new graph by first calling the
+`serving_input_receiver_fn` to obtain feature `Tensor`s, and then calling
+this `Estimator`'s `model_fn` to generate the model graph based on those
+features. It restores the given checkpoint (or, lacking that, the most
+recent checkpoint) into this graph in a fresh session. Finally it creates
+a timestamped export directory below the given `export_dir_base`, and writes
+a `SavedModel` into it containing a single `tf.MetaGraphDef` saved from this
+session.
+
+The exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef` for each
+element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`, named
+using
+the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`serving_input_receiver_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that takes no argument and returns a
+tf.estimator.export.ServingInputReceiver or
+tf.estimator.export.TensorServingInputReceiver.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+|
+`strip_default_attrs`
+ |
+
+Boolean. If `True`, default-valued attributes will be
+removed from the `NodeDef`s. For a detailed guide, see [Stripping
+Default-Valued Attributes](
+https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/master/tensorflow/python/saved_model/README.md#stripping-default-valued-attributes).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if no `serving_input_receiver_fn` is provided, no
+`export_outputs` are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+get_variable_names
+
+View source
+
+
+get_variable_names()
+
+
+Returns list of all variable names in this model.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+List of names.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `Estimator` has not produced a checkpoint yet.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+get_variable_value
+
+View source
+
+
+get_variable_value(
+ name
+)
+
+
+Returns value of the variable given by name.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+string or a list of string, name of the tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Numpy array - value of the tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `Estimator` has not produced a checkpoint yet.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+latest_checkpoint
+
+View source
+
+
+latest_checkpoint()
+
+
+Finds the filename of the latest saved checkpoint file in `model_dir`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The full path to the latest checkpoint or `None` if no checkpoint was
+found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+predict
+
+View source
+
+
+predict(
+ input_fn, predict_keys=None, hooks=None, checkpoint_path=None,
+ yield_single_examples=(True)
+)
+
+
+Yields predictions for given features.
+
+Please note that interleaving two predict outputs does not work. See:
+[issue/20506](
+https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/issues/20506#issuecomment-422208517)
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that constructs the features. Prediction continues
+until `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception
+(tf.errors.OutOfRangeError or `StopIteration`). See [Premade
+Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The function should construct and return one of
+the following:
+* tf.data.Dataset object -- Outputs of `Dataset` object must have
+same constraints as below.
+* features -- A tf.Tensor or a dictionary of string feature name to
+`Tensor`. features are consumed by `model_fn`. They should satisfy
+the expectation of `model_fn` from inputs. * A tuple, in which case
+the first item is extracted as features.
+ |
+
+|
+`predict_keys`
+ |
+
+list of `str`, name of the keys to predict. It is used if
+the tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec.predictions is a `dict`. If
+`predict_keys` is used then rest of the predictions will be filtered
+from the dictionary. If `None`, returns all.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the prediction call.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+Path of a specific checkpoint to predict. If `None`, the
+latest checkpoint in `model_dir` is used. If there are no checkpoints
+in `model_dir`, prediction is run with newly initialized `Variables`
+instead of ones restored from checkpoint.
+ |
+
+|
+`yield_single_examples`
+ |
+
+If `False`, yields the whole batch as returned by
+the `model_fn` instead of decomposing the batch into individual
+elements. This is useful if `model_fn` returns some tensors whose first
+dimension is not equal to the batch size.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Yields:
+
+Evaluated values of `predictions` tensors.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If batch length of predictions is not the same and
+`yield_single_examples` is `True`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If there is a conflict between `predict_keys` and
+`predictions`. For example if `predict_keys` is not `None` but
+tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec.predictions is not a `dict`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+train
+
+View source
+
+
+train(
+ input_fn, hooks=None, steps=None, max_steps=None, saving_listeners=None
+)
+
+
+Trains a model given training data `input_fn`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that provides input data for training as minibatches.
+See [Premade Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The function should construct and return one of
+the following:
+* A tf.data.Dataset object: Outputs of `Dataset` object must be a
+tuple `(features, labels)` with same constraints as below.
+* A tuple `(features, labels)`: Where `features` is a tf.Tensor or a
+dictionary of string feature name to `Tensor` and `labels` is a
+`Tensor` or a dictionary of string label name to `Tensor`. Both
+`features` and `labels` are consumed by `model_fn`. They should
+satisfy the expectation of `model_fn` from inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the training loop.
+ |
+
+|
+`steps`
+ |
+
+Number of steps for which to train the model. If `None`, train
+forever or train until `input_fn` generates the `tf.errors.OutOfRange`
+error or `StopIteration` exception. `steps` works incrementally. If you
+call two times `train(steps=10)` then training occurs in total 20 steps.
+If `OutOfRange` or `StopIteration` occurs in the middle, training stops
+before 20 steps. If you don't want to have incremental behavior please
+set `max_steps` instead. If set, `max_steps` must be `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_steps`
+ |
+
+Number of total steps for which to train model. If `None`,
+train forever or train until `input_fn` generates the
+`tf.errors.OutOfRange` error or `StopIteration` exception. If set,
+`steps` must be `None`. If `OutOfRange` or `StopIteration` occurs in the
+middle, training stops before `max_steps` steps. Two calls to
+`train(steps=100)` means 200 training iterations. On the other hand, two
+calls to `train(max_steps=100)` means that the second call will not do
+any iteration since first call did all 100 steps.
+ |
+
+|
+`saving_listeners`
+ |
+
+list of `CheckpointSaverListener` objects. Used for
+callbacks that run immediately before or after checkpoint savings.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`self`, for chaining.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If both `steps` and `max_steps` are not `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If either `steps` or `max_steps <= 0`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/BaselineEstimator.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/BaselineEstimator.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..cc4e9715d21
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/BaselineEstimator.md
@@ -0,0 +1,1194 @@
+description: An estimator that can establish a simple baseline.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.estimator.BaselineEstimator
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+An estimator that can establish a simple baseline.
+
+Inherits From: [`Estimator`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/Estimator.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.estimator.BaselineEstimator(
+ head, model_dir=None, optimizer='Ftrl', config=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The estimator uses a user-specified head.
+
+This estimator ignores feature values and will learn to predict the average
+value of each label. E.g. for single-label classification problems, this will
+predict the probability distribution of the classes as seen in the labels.
+For multi-label classification problems, it will predict the ratio of examples
+that contain each class.
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+
+# Build baseline multi-label classifier.
+estimator = tf.estimator.BaselineEstimator(
+ head=tf.estimator.MultiLabelHead(n_classes=3))
+
+# Input builders
+def input_fn_train:
+ # Returns tf.data.Dataset of (x, y) tuple where y represents label's class
+ # index.
+ pass
+
+def input_fn_eval:
+ # Returns tf.data.Dataset of (x, y) tuple where y represents label's class
+ # index.
+ pass
+
+# Fit model.
+estimator.train(input_fn=input_fn_train)
+
+# Evaluates cross entropy between the test and train labels.
+loss = estimator.evaluate(input_fn=input_fn_eval)["loss"]
+
+# For each class, predicts the ratio of training examples that contain the
+# class.
+predictions = estimator.predict(new_samples)
+
+```
+
+Input of `train` and `evaluate` should have following features,
+ otherwise there will be a `KeyError`:
+
+* if `weight_column` is specified in the `head` constructor (and not None) for
+ the head passed to BaselineEstimator's constructor, a feature with
+ `key=weight_column` whose value is a `Tensor`.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`model_fn`
+ |
+
+Model function. Follows the signature:
+* `features` -- This is the first item returned from the `input_fn`
+passed to `train`, `evaluate`, and `predict`. This should be a
+single tf.Tensor or `dict` of same.
+* `labels` -- This is the second item returned from the `input_fn`
+passed to `train`, `evaluate`, and `predict`. This should be a
+single tf.Tensor or `dict` of same (for multi-head models). If
+mode is tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT, `labels=None` will be
+passed. If the `model_fn`'s signature does not accept `mode`, the
+`model_fn` must still be able to handle `labels=None`.
+* `mode` -- Optional. Specifies if this is training, evaluation or
+prediction. See tf.estimator.ModeKeys.
+`params` -- Optional `dict` of hyperparameters. Will receive what is
+passed to Estimator in `params` parameter. This allows to configure
+Estimators from hyper parameter tuning.
+* `config` -- Optional `estimator.RunConfig` object. Will receive what
+is passed to Estimator as its `config` parameter, or a default
+value. Allows setting up things in your `model_fn` based on
+configuration such as `num_ps_replicas`, or `model_dir`.
+* Returns -- tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec
+ |
+
+|
+`model_dir`
+ |
+
+Directory to save model parameters, graph and etc. This can
+also be used to load checkpoints from the directory into an estimator to
+continue training a previously saved model. If `PathLike` object, the
+path will be resolved. If `None`, the model_dir in `config` will be used
+if set. If both are set, they must be same. If both are `None`, a
+temporary directory will be used.
+ |
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+`estimator.RunConfig` configuration object.
+ |
+
+|
+`params`
+ |
+
+`dict` of hyper parameters that will be passed into `model_fn`.
+Keys are names of parameters, values are basic python types.
+ |
+
+|
+`warm_start_from`
+ |
+
+Optional string filepath to a checkpoint or SavedModel to
+warm-start from, or a tf.estimator.WarmStartSettings object to fully
+configure warm-starting. If None, only TRAINABLE variables are
+warm-started. If the string filepath is provided instead of a
+tf.estimator.WarmStartSettings, then all variables are warm-started,
+and it is assumed that vocabularies and tf.Tensor names are unchanged.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+parameters of `model_fn` don't match `params`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if this is called via a subclass and if that class overrides
+a member of `Estimator`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`model_dir`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`model_fn`
+ |
+
+Returns the `model_fn` which is bound to `self.params`.
+ |
+
+|
+`params`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+eval_dir
+
+View source
+
+
+eval_dir(
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+Shows the directory name where evaluation metrics are dumped.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of the evaluation if user needs to run multiple evaluations on
+different data sets, such as on training data vs test data. Metrics for
+different evaluations are saved in separate folders, and appear
+separately in tensorboard.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A string which is the path of directory contains evaluation metrics.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+evaluate
+
+View source
+
+
+evaluate(
+ input_fn, steps=None, hooks=None, checkpoint_path=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+Evaluates the model given evaluation data `input_fn`.
+
+For each step, calls `input_fn`, which returns one batch of data.
+Evaluates until:
+- `steps` batches are processed, or
+- `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception (tf.errors.OutOfRangeError
+or
+`StopIteration`).
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that constructs the input data for evaluation. See
+[Premade Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The
+function should construct and return one of the following: * A
+tf.data.Dataset object: Outputs of `Dataset` object must be a tuple
+`(features, labels)` with same constraints as below. * A tuple
+`(features, labels)`: Where `features` is a tf.Tensor or a dictionary
+of string feature name to `Tensor` and `labels` is a `Tensor` or a
+dictionary of string label name to `Tensor`. Both `features` and
+`labels` are consumed by `model_fn`. They should satisfy the
+expectation of `model_fn` from inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`steps`
+ |
+
+Number of steps for which to evaluate model. If `None`, evaluates
+until `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the evaluation call.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+Path of a specific checkpoint to evaluate. If `None`, the
+latest checkpoint in `model_dir` is used. If there are no checkpoints
+in `model_dir`, evaluation is run with newly initialized `Variables`
+instead of ones restored from checkpoint.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of the evaluation if user needs to run multiple evaluations on
+different data sets, such as on training data vs test data. Metrics for
+different evaluations are saved in separate folders, and appear
+separately in tensorboard.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A dict containing the evaluation metrics specified in `model_fn` keyed by
+name, as well as an entry `global_step` which contains the value of the
+global step for which this evaluation was performed. For canned
+estimators, the dict contains the `loss` (mean loss per mini-batch) and
+the `average_loss` (mean loss per sample). Canned classifiers also return
+the `accuracy`. Canned regressors also return the `label/mean` and the
+`prediction/mean`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `steps <= 0`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+experimental_export_all_saved_models
+
+View source
+
+
+experimental_export_all_saved_models(
+ export_dir_base, input_receiver_fn_map, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None
+)
+
+
+Exports a `SavedModel` with `tf.MetaGraphDefs` for each requested mode.
+
+For each mode passed in via the `input_receiver_fn_map`,
+this method builds a new graph by calling the `input_receiver_fn` to obtain
+feature and label `Tensor`s. Next, this method calls the `Estimator`'s
+`model_fn` in the passed mode to generate the model graph based on
+those features and labels, and restores the given checkpoint
+(or, lacking that, the most recent checkpoint) into the graph.
+Only one of the modes is used for saving variables to the `SavedModel`
+(order of preference: tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN,
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys.EVAL, then
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT), such that up to three
+`tf.MetaGraphDefs` are saved with a single set of variables in a single
+`SavedModel` directory.
+
+For the variables and `tf.MetaGraphDefs`, a timestamped export directory
+below
+`export_dir_base`, and writes a `SavedModel` into it containing
+the `tf.MetaGraphDef` for the given mode and its associated signatures.
+
+For prediction, the exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef`
+for each element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`,
+named using the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+For training and evaluation, the `train_op` is stored in an extra
+collection,
+and loss, metrics, and predictions are included in a `SignatureDef` for the
+mode in question.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`input_receiver_fn_map`
+ |
+
+dict of tf.estimator.ModeKeys to
+`input_receiver_fn` mappings, where the `input_receiver_fn` is a
+function that takes no arguments and returns the appropriate subclass of
+`InputReceiver`.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if any `input_receiver_fn` is `None`, no `export_outputs`
+are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+export_saved_model
+
+View source
+
+
+export_saved_model(
+ export_dir_base, serving_input_receiver_fn, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None, experimental_mode=ModeKeys.PREDICT
+)
+
+
+Exports inference graph as a `SavedModel` into the given dir.
+
+For a detailed guide, see
+[Using SavedModel with
+Estimators](https://tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model#using_savedmodel_with_estimators).
+
+This method builds a new graph by first calling the
+`serving_input_receiver_fn` to obtain feature `Tensor`s, and then calling
+this `Estimator`'s `model_fn` to generate the model graph based on those
+features. It restores the given checkpoint (or, lacking that, the most
+recent checkpoint) into this graph in a fresh session. Finally it creates
+a timestamped export directory below the given `export_dir_base`, and writes
+a `SavedModel` into it containing a single `tf.MetaGraphDef` saved from this
+session.
+
+The exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef` for each
+element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`, named
+using
+the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+The experimental_mode parameter can be used to export a single
+train/eval/predict graph as a `SavedModel`.
+See `experimental_export_all_saved_models` for full docs.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`serving_input_receiver_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that takes no argument and returns a
+tf.estimator.export.ServingInputReceiver or
+tf.estimator.export.TensorServingInputReceiver.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+|
+`experimental_mode`
+ |
+
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys value indicating with mode will
+be exported. Note that this feature is experimental.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if no `serving_input_receiver_fn` is provided, no
+`export_outputs` are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+export_savedmodel
+
+View source
+
+
+export_savedmodel(
+ export_dir_base, serving_input_receiver_fn, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None, strip_default_attrs=(False)
+)
+
+
+Exports inference graph as a `SavedModel` into the given dir. (deprecated)
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+This function has been renamed, use `export_saved_model` instead.
+
+For a detailed guide, see
+[Using SavedModel with
+Estimators](https://tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model#using_savedmodel_with_estimators).
+
+This method builds a new graph by first calling the
+`serving_input_receiver_fn` to obtain feature `Tensor`s, and then calling
+this `Estimator`'s `model_fn` to generate the model graph based on those
+features. It restores the given checkpoint (or, lacking that, the most
+recent checkpoint) into this graph in a fresh session. Finally it creates
+a timestamped export directory below the given `export_dir_base`, and writes
+a `SavedModel` into it containing a single `tf.MetaGraphDef` saved from this
+session.
+
+The exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef` for each
+element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`, named
+using
+the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`serving_input_receiver_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that takes no argument and returns a
+tf.estimator.export.ServingInputReceiver or
+tf.estimator.export.TensorServingInputReceiver.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+|
+`strip_default_attrs`
+ |
+
+Boolean. If `True`, default-valued attributes will be
+removed from the `NodeDef`s. For a detailed guide, see [Stripping
+Default-Valued Attributes](
+https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/master/tensorflow/python/saved_model/README.md#stripping-default-valued-attributes).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if no `serving_input_receiver_fn` is provided, no
+`export_outputs` are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+get_variable_names
+
+View source
+
+
+get_variable_names()
+
+
+Returns list of all variable names in this model.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+List of names.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `Estimator` has not produced a checkpoint yet.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+get_variable_value
+
+View source
+
+
+get_variable_value(
+ name
+)
+
+
+Returns value of the variable given by name.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+string or a list of string, name of the tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Numpy array - value of the tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `Estimator` has not produced a checkpoint yet.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+latest_checkpoint
+
+View source
+
+
+latest_checkpoint()
+
+
+Finds the filename of the latest saved checkpoint file in `model_dir`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The full path to the latest checkpoint or `None` if no checkpoint was
+found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+predict
+
+View source
+
+
+predict(
+ input_fn, predict_keys=None, hooks=None, checkpoint_path=None,
+ yield_single_examples=(True)
+)
+
+
+Yields predictions for given features.
+
+Please note that interleaving two predict outputs does not work. See:
+[issue/20506](
+https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/issues/20506#issuecomment-422208517)
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that constructs the features. Prediction continues
+until `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception
+(tf.errors.OutOfRangeError or `StopIteration`). See [Premade
+Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The function should construct and return one of
+the following:
+* tf.data.Dataset object -- Outputs of `Dataset` object must have
+same constraints as below.
+* features -- A tf.Tensor or a dictionary of string feature name to
+`Tensor`. features are consumed by `model_fn`. They should satisfy
+the expectation of `model_fn` from inputs. * A tuple, in which case
+the first item is extracted as features.
+ |
+
+|
+`predict_keys`
+ |
+
+list of `str`, name of the keys to predict. It is used if
+the tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec.predictions is a `dict`. If
+`predict_keys` is used then rest of the predictions will be filtered
+from the dictionary. If `None`, returns all.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the prediction call.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+Path of a specific checkpoint to predict. If `None`, the
+latest checkpoint in `model_dir` is used. If there are no checkpoints
+in `model_dir`, prediction is run with newly initialized `Variables`
+instead of ones restored from checkpoint.
+ |
+
+|
+`yield_single_examples`
+ |
+
+If `False`, yields the whole batch as returned by
+the `model_fn` instead of decomposing the batch into individual
+elements. This is useful if `model_fn` returns some tensors whose first
+dimension is not equal to the batch size.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Yields:
+
+Evaluated values of `predictions` tensors.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If batch length of predictions is not the same and
+`yield_single_examples` is `True`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If there is a conflict between `predict_keys` and
+`predictions`. For example if `predict_keys` is not `None` but
+tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec.predictions is not a `dict`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+train
+
+View source
+
+
+train(
+ input_fn, hooks=None, steps=None, max_steps=None, saving_listeners=None
+)
+
+
+Trains a model given training data `input_fn`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that provides input data for training as minibatches.
+See [Premade Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The function should construct and return one of
+the following:
+* A tf.data.Dataset object: Outputs of `Dataset` object must be a
+tuple `(features, labels)` with same constraints as below.
+* A tuple `(features, labels)`: Where `features` is a tf.Tensor or a
+dictionary of string feature name to `Tensor` and `labels` is a
+`Tensor` or a dictionary of string label name to `Tensor`. Both
+`features` and `labels` are consumed by `model_fn`. They should
+satisfy the expectation of `model_fn` from inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the training loop.
+ |
+
+|
+`steps`
+ |
+
+Number of steps for which to train the model. If `None`, train
+forever or train until `input_fn` generates the `tf.errors.OutOfRange`
+error or `StopIteration` exception. `steps` works incrementally. If you
+call two times `train(steps=10)` then training occurs in total 20 steps.
+If `OutOfRange` or `StopIteration` occurs in the middle, training stops
+before 20 steps. If you don't want to have incremental behavior please
+set `max_steps` instead. If set, `max_steps` must be `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_steps`
+ |
+
+Number of total steps for which to train model. If `None`,
+train forever or train until `input_fn` generates the
+`tf.errors.OutOfRange` error or `StopIteration` exception. If set,
+`steps` must be `None`. If `OutOfRange` or `StopIteration` occurs in the
+middle, training stops before `max_steps` steps. Two calls to
+`train(steps=100)` means 200 training iterations. On the other hand, two
+calls to `train(max_steps=100)` means that the second call will not do
+any iteration since first call did all 100 steps.
+ |
+
+|
+`saving_listeners`
+ |
+
+list of `CheckpointSaverListener` objects. Used for
+callbacks that run immediately before or after checkpoint savings.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`self`, for chaining.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If both `steps` and `max_steps` are not `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If either `steps` or `max_steps <= 0`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/BaselineRegressor.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/BaselineRegressor.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..0bc6598c5c4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/BaselineRegressor.md
@@ -0,0 +1,1196 @@
+description: A regressor that can establish a simple baseline.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.estimator.BaselineRegressor
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A regressor that can establish a simple baseline.
+
+Inherits From: [`Estimator`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/Estimator.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.estimator.BaselineRegressor(
+ model_dir=None, label_dimension=1, weight_column=None, optimizer='Ftrl',
+ config=None, loss_reduction=tf.compat.v1.losses.Reduction.SUM
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This regressor ignores feature values and will learn to predict the average
+value of each label.
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+
+# Build BaselineRegressor
+regressor = tf.estimator.BaselineRegressor()
+
+# Input builders
+def input_fn_train:
+ # Returns tf.data.Dataset of (x, y) tuple where y represents label's class
+ # index.
+ pass
+
+def input_fn_eval:
+ # Returns tf.data.Dataset of (x, y) tuple where y represents label's class
+ # index.
+ pass
+
+# Fit model.
+regressor.train(input_fn=input_fn_train)
+
+# Evaluate squared-loss between the test and train targets.
+loss = regressor.evaluate(input_fn=input_fn_eval)["loss"]
+
+# predict outputs the mean value seen during training.
+predictions = regressor.predict(new_samples)
+```
+
+Input of `train` and `evaluate` should have following features,
+ otherwise there will be a `KeyError`:
+
+* if `weight_column` is not `None`, a feature with
+ `key=weight_column` whose value is a `Tensor`.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`model_fn`
+ |
+
+Model function. Follows the signature:
+* `features` -- This is the first item returned from the `input_fn`
+passed to `train`, `evaluate`, and `predict`. This should be a
+single tf.Tensor or `dict` of same.
+* `labels` -- This is the second item returned from the `input_fn`
+passed to `train`, `evaluate`, and `predict`. This should be a
+single tf.Tensor or `dict` of same (for multi-head models). If
+mode is tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT, `labels=None` will be
+passed. If the `model_fn`'s signature does not accept `mode`, the
+`model_fn` must still be able to handle `labels=None`.
+* `mode` -- Optional. Specifies if this is training, evaluation or
+prediction. See tf.estimator.ModeKeys.
+`params` -- Optional `dict` of hyperparameters. Will receive what is
+passed to Estimator in `params` parameter. This allows to configure
+Estimators from hyper parameter tuning.
+* `config` -- Optional `estimator.RunConfig` object. Will receive what
+is passed to Estimator as its `config` parameter, or a default
+value. Allows setting up things in your `model_fn` based on
+configuration such as `num_ps_replicas`, or `model_dir`.
+* Returns -- tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec
+ |
+
+|
+`model_dir`
+ |
+
+Directory to save model parameters, graph and etc. This can
+also be used to load checkpoints from the directory into an estimator to
+continue training a previously saved model. If `PathLike` object, the
+path will be resolved. If `None`, the model_dir in `config` will be used
+if set. If both are set, they must be same. If both are `None`, a
+temporary directory will be used.
+ |
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+`estimator.RunConfig` configuration object.
+ |
+
+|
+`params`
+ |
+
+`dict` of hyper parameters that will be passed into `model_fn`.
+Keys are names of parameters, values are basic python types.
+ |
+
+|
+`warm_start_from`
+ |
+
+Optional string filepath to a checkpoint or SavedModel to
+warm-start from, or a tf.estimator.WarmStartSettings object to fully
+configure warm-starting. If None, only TRAINABLE variables are
+warm-started. If the string filepath is provided instead of a
+tf.estimator.WarmStartSettings, then all variables are warm-started,
+and it is assumed that vocabularies and tf.Tensor names are unchanged.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+parameters of `model_fn` don't match `params`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if this is called via a subclass and if that class overrides
+a member of `Estimator`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+Estimators can be used while eager execution is enabled. Note that `input_fn`
+and all hooks are executed inside a graph context, so they have to be written
+to be compatible with graph mode. Note that `input_fn` code using tf.data
+generally works in both graph and eager modes.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`model_dir`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`model_fn`
+ |
+
+Returns the `model_fn` which is bound to `self.params`.
+ |
+
+|
+`params`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+eval_dir
+
+View source
+
+
+eval_dir(
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+Shows the directory name where evaluation metrics are dumped.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of the evaluation if user needs to run multiple evaluations on
+different data sets, such as on training data vs test data. Metrics for
+different evaluations are saved in separate folders, and appear
+separately in tensorboard.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A string which is the path of directory contains evaluation metrics.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+evaluate
+
+View source
+
+
+evaluate(
+ input_fn, steps=None, hooks=None, checkpoint_path=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+Evaluates the model given evaluation data `input_fn`.
+
+For each step, calls `input_fn`, which returns one batch of data.
+Evaluates until:
+- `steps` batches are processed, or
+- `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception (tf.errors.OutOfRangeError
+or
+`StopIteration`).
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that constructs the input data for evaluation. See
+[Premade Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The
+function should construct and return one of the following: * A
+tf.data.Dataset object: Outputs of `Dataset` object must be a tuple
+`(features, labels)` with same constraints as below. * A tuple
+`(features, labels)`: Where `features` is a tf.Tensor or a dictionary
+of string feature name to `Tensor` and `labels` is a `Tensor` or a
+dictionary of string label name to `Tensor`. Both `features` and
+`labels` are consumed by `model_fn`. They should satisfy the
+expectation of `model_fn` from inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`steps`
+ |
+
+Number of steps for which to evaluate model. If `None`, evaluates
+until `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the evaluation call.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+Path of a specific checkpoint to evaluate. If `None`, the
+latest checkpoint in `model_dir` is used. If there are no checkpoints
+in `model_dir`, evaluation is run with newly initialized `Variables`
+instead of ones restored from checkpoint.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of the evaluation if user needs to run multiple evaluations on
+different data sets, such as on training data vs test data. Metrics for
+different evaluations are saved in separate folders, and appear
+separately in tensorboard.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A dict containing the evaluation metrics specified in `model_fn` keyed by
+name, as well as an entry `global_step` which contains the value of the
+global step for which this evaluation was performed. For canned
+estimators, the dict contains the `loss` (mean loss per mini-batch) and
+the `average_loss` (mean loss per sample). Canned classifiers also return
+the `accuracy`. Canned regressors also return the `label/mean` and the
+`prediction/mean`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `steps <= 0`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+experimental_export_all_saved_models
+
+View source
+
+
+experimental_export_all_saved_models(
+ export_dir_base, input_receiver_fn_map, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None
+)
+
+
+Exports a `SavedModel` with `tf.MetaGraphDefs` for each requested mode.
+
+For each mode passed in via the `input_receiver_fn_map`,
+this method builds a new graph by calling the `input_receiver_fn` to obtain
+feature and label `Tensor`s. Next, this method calls the `Estimator`'s
+`model_fn` in the passed mode to generate the model graph based on
+those features and labels, and restores the given checkpoint
+(or, lacking that, the most recent checkpoint) into the graph.
+Only one of the modes is used for saving variables to the `SavedModel`
+(order of preference: tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN,
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys.EVAL, then
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT), such that up to three
+`tf.MetaGraphDefs` are saved with a single set of variables in a single
+`SavedModel` directory.
+
+For the variables and `tf.MetaGraphDefs`, a timestamped export directory
+below
+`export_dir_base`, and writes a `SavedModel` into it containing
+the `tf.MetaGraphDef` for the given mode and its associated signatures.
+
+For prediction, the exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef`
+for each element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`,
+named using the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+For training and evaluation, the `train_op` is stored in an extra
+collection,
+and loss, metrics, and predictions are included in a `SignatureDef` for the
+mode in question.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`input_receiver_fn_map`
+ |
+
+dict of tf.estimator.ModeKeys to
+`input_receiver_fn` mappings, where the `input_receiver_fn` is a
+function that takes no arguments and returns the appropriate subclass of
+`InputReceiver`.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if any `input_receiver_fn` is `None`, no `export_outputs`
+are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+export_saved_model
+
+View source
+
+
+export_saved_model(
+ export_dir_base, serving_input_receiver_fn, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None, experimental_mode=ModeKeys.PREDICT
+)
+
+
+Exports inference graph as a `SavedModel` into the given dir.
+
+For a detailed guide, see
+[Using SavedModel with
+Estimators](https://tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model#using_savedmodel_with_estimators).
+
+This method builds a new graph by first calling the
+`serving_input_receiver_fn` to obtain feature `Tensor`s, and then calling
+this `Estimator`'s `model_fn` to generate the model graph based on those
+features. It restores the given checkpoint (or, lacking that, the most
+recent checkpoint) into this graph in a fresh session. Finally it creates
+a timestamped export directory below the given `export_dir_base`, and writes
+a `SavedModel` into it containing a single `tf.MetaGraphDef` saved from this
+session.
+
+The exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef` for each
+element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`, named
+using
+the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+The experimental_mode parameter can be used to export a single
+train/eval/predict graph as a `SavedModel`.
+See `experimental_export_all_saved_models` for full docs.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`serving_input_receiver_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that takes no argument and returns a
+tf.estimator.export.ServingInputReceiver or
+tf.estimator.export.TensorServingInputReceiver.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+|
+`experimental_mode`
+ |
+
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys value indicating with mode will
+be exported. Note that this feature is experimental.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if no `serving_input_receiver_fn` is provided, no
+`export_outputs` are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+export_savedmodel
+
+View source
+
+
+export_savedmodel(
+ export_dir_base, serving_input_receiver_fn, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None, strip_default_attrs=(False)
+)
+
+
+Exports inference graph as a `SavedModel` into the given dir. (deprecated)
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+This function has been renamed, use `export_saved_model` instead.
+
+For a detailed guide, see
+[Using SavedModel with
+Estimators](https://tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model#using_savedmodel_with_estimators).
+
+This method builds a new graph by first calling the
+`serving_input_receiver_fn` to obtain feature `Tensor`s, and then calling
+this `Estimator`'s `model_fn` to generate the model graph based on those
+features. It restores the given checkpoint (or, lacking that, the most
+recent checkpoint) into this graph in a fresh session. Finally it creates
+a timestamped export directory below the given `export_dir_base`, and writes
+a `SavedModel` into it containing a single `tf.MetaGraphDef` saved from this
+session.
+
+The exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef` for each
+element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`, named
+using
+the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`serving_input_receiver_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that takes no argument and returns a
+tf.estimator.export.ServingInputReceiver or
+tf.estimator.export.TensorServingInputReceiver.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+|
+`strip_default_attrs`
+ |
+
+Boolean. If `True`, default-valued attributes will be
+removed from the `NodeDef`s. For a detailed guide, see [Stripping
+Default-Valued Attributes](
+https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/master/tensorflow/python/saved_model/README.md#stripping-default-valued-attributes).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if no `serving_input_receiver_fn` is provided, no
+`export_outputs` are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+get_variable_names
+
+View source
+
+
+get_variable_names()
+
+
+Returns list of all variable names in this model.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+List of names.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `Estimator` has not produced a checkpoint yet.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+get_variable_value
+
+View source
+
+
+get_variable_value(
+ name
+)
+
+
+Returns value of the variable given by name.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+string or a list of string, name of the tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Numpy array - value of the tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `Estimator` has not produced a checkpoint yet.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+latest_checkpoint
+
+View source
+
+
+latest_checkpoint()
+
+
+Finds the filename of the latest saved checkpoint file in `model_dir`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The full path to the latest checkpoint or `None` if no checkpoint was
+found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+predict
+
+View source
+
+
+predict(
+ input_fn, predict_keys=None, hooks=None, checkpoint_path=None,
+ yield_single_examples=(True)
+)
+
+
+Yields predictions for given features.
+
+Please note that interleaving two predict outputs does not work. See:
+[issue/20506](
+https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/issues/20506#issuecomment-422208517)
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that constructs the features. Prediction continues
+until `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception
+(tf.errors.OutOfRangeError or `StopIteration`). See [Premade
+Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The function should construct and return one of
+the following:
+* tf.data.Dataset object -- Outputs of `Dataset` object must have
+same constraints as below.
+* features -- A tf.Tensor or a dictionary of string feature name to
+`Tensor`. features are consumed by `model_fn`. They should satisfy
+the expectation of `model_fn` from inputs. * A tuple, in which case
+the first item is extracted as features.
+ |
+
+|
+`predict_keys`
+ |
+
+list of `str`, name of the keys to predict. It is used if
+the tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec.predictions is a `dict`. If
+`predict_keys` is used then rest of the predictions will be filtered
+from the dictionary. If `None`, returns all.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the prediction call.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+Path of a specific checkpoint to predict. If `None`, the
+latest checkpoint in `model_dir` is used. If there are no checkpoints
+in `model_dir`, prediction is run with newly initialized `Variables`
+instead of ones restored from checkpoint.
+ |
+
+|
+`yield_single_examples`
+ |
+
+If `False`, yields the whole batch as returned by
+the `model_fn` instead of decomposing the batch into individual
+elements. This is useful if `model_fn` returns some tensors whose first
+dimension is not equal to the batch size.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Yields:
+
+Evaluated values of `predictions` tensors.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If batch length of predictions is not the same and
+`yield_single_examples` is `True`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If there is a conflict between `predict_keys` and
+`predictions`. For example if `predict_keys` is not `None` but
+tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec.predictions is not a `dict`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+train
+
+View source
+
+
+train(
+ input_fn, hooks=None, steps=None, max_steps=None, saving_listeners=None
+)
+
+
+Trains a model given training data `input_fn`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that provides input data for training as minibatches.
+See [Premade Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The function should construct and return one of
+the following:
+* A tf.data.Dataset object: Outputs of `Dataset` object must be a
+tuple `(features, labels)` with same constraints as below.
+* A tuple `(features, labels)`: Where `features` is a tf.Tensor or a
+dictionary of string feature name to `Tensor` and `labels` is a
+`Tensor` or a dictionary of string label name to `Tensor`. Both
+`features` and `labels` are consumed by `model_fn`. They should
+satisfy the expectation of `model_fn` from inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the training loop.
+ |
+
+|
+`steps`
+ |
+
+Number of steps for which to train the model. If `None`, train
+forever or train until `input_fn` generates the `tf.errors.OutOfRange`
+error or `StopIteration` exception. `steps` works incrementally. If you
+call two times `train(steps=10)` then training occurs in total 20 steps.
+If `OutOfRange` or `StopIteration` occurs in the middle, training stops
+before 20 steps. If you don't want to have incremental behavior please
+set `max_steps` instead. If set, `max_steps` must be `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_steps`
+ |
+
+Number of total steps for which to train model. If `None`,
+train forever or train until `input_fn` generates the
+`tf.errors.OutOfRange` error or `StopIteration` exception. If set,
+`steps` must be `None`. If `OutOfRange` or `StopIteration` occurs in the
+middle, training stops before `max_steps` steps. Two calls to
+`train(steps=100)` means 200 training iterations. On the other hand, two
+calls to `train(max_steps=100)` means that the second call will not do
+any iteration since first call did all 100 steps.
+ |
+
+|
+`saving_listeners`
+ |
+
+list of `CheckpointSaverListener` objects. Used for
+callbacks that run immediately before or after checkpoint savings.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`self`, for chaining.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If both `steps` and `max_steps` are not `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If either `steps` or `max_steps <= 0`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/DNNClassifier.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/DNNClassifier.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a8f39b53d92
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/DNNClassifier.md
@@ -0,0 +1,1237 @@
+description: A classifier for TensorFlow DNN models.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.estimator.DNNClassifier
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A classifier for TensorFlow DNN models.
+
+Inherits From: [`Estimator`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/Estimator.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.estimator.DNNClassifier(
+ hidden_units, feature_columns, model_dir=None, n_classes=2, weight_column=None,
+ label_vocabulary=None, optimizer='Adagrad', activation_fn=tf.nn.relu,
+ dropout=None, input_layer_partitioner=None, config=None, warm_start_from=None,
+ loss_reduction=tf.compat.v1.losses.Reduction.SUM, batch_norm=(False)
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+categorical_feature_a = categorical_column_with_hash_bucket(...)
+categorical_feature_b = categorical_column_with_hash_bucket(...)
+
+categorical_feature_a_emb = embedding_column(
+ categorical_column=categorical_feature_a, ...)
+categorical_feature_b_emb = embedding_column(
+ categorical_column=categorical_feature_b, ...)
+
+estimator = tf.estimator.DNNClassifier(
+ feature_columns=[categorical_feature_a_emb, categorical_feature_b_emb],
+ hidden_units=[1024, 512, 256])
+
+# Or estimator using the ProximalAdagradOptimizer optimizer with
+# regularization.
+estimator = tf.estimator.DNNClassifier(
+ feature_columns=[categorical_feature_a_emb, categorical_feature_b_emb],
+ hidden_units=[1024, 512, 256],
+ optimizer=tf.compat.v1.train.ProximalAdagradOptimizer(
+ learning_rate=0.1,
+ l1_regularization_strength=0.001
+ ))
+
+# Or estimator using an optimizer with a learning rate decay.
+estimator = tf.estimator.DNNClassifier(
+ feature_columns=[categorical_feature_a_emb, categorical_feature_b_emb],
+ hidden_units=[1024, 512, 256],
+ optimizer=lambda: tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(
+ learning_rate=tf.compat.v1.train.exponential_decay(
+ learning_rate=0.1,
+ global_step=tf.compat.v1.train.get_global_step(),
+ decay_steps=10000,
+ decay_rate=0.96))
+
+# Or estimator with warm-starting from a previous checkpoint.
+estimator = tf.estimator.DNNClassifier(
+ feature_columns=[categorical_feature_a_emb, categorical_feature_b_emb],
+ hidden_units=[1024, 512, 256],
+ warm_start_from="/path/to/checkpoint/dir")
+
+# Input builders
+def input_fn_train:
+ # Returns tf.data.Dataset of (x, y) tuple where y represents label's class
+ # index.
+ pass
+def input_fn_eval:
+ # Returns tf.data.Dataset of (x, y) tuple where y represents label's class
+ # index.
+ pass
+def input_fn_predict:
+ # Returns tf.data.Dataset of (x, None) tuple.
+ pass
+estimator.train(input_fn=input_fn_train)
+metrics = estimator.evaluate(input_fn=input_fn_eval)
+predictions = estimator.predict(input_fn=input_fn_predict)
+```
+
+Input of `train` and `evaluate` should have following features,
+otherwise there will be a `KeyError`:
+
+* if `weight_column` is not `None`, a feature with `key=weight_column` whose
+ value is a `Tensor`.
+* for each `column` in `feature_columns`:
+ - if `column` is a `CategoricalColumn`, a feature with `key=column.name`
+ whose `value` is a `SparseTensor`.
+ - if `column` is a `WeightedCategoricalColumn`, two features: the first
+ with `key` the id column name, the second with `key` the weight column
+ name. Both features' `value` must be a `SparseTensor`.
+ - if `column` is a `DenseColumn`, a feature with `key=column.name`
+ whose `value` is a `Tensor`.
+
+Loss is calculated by using softmax cross entropy.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`model_fn`
+ |
+
+Model function. Follows the signature:
+* `features` -- This is the first item returned from the `input_fn`
+passed to `train`, `evaluate`, and `predict`. This should be a
+single tf.Tensor or `dict` of same.
+* `labels` -- This is the second item returned from the `input_fn`
+passed to `train`, `evaluate`, and `predict`. This should be a
+single tf.Tensor or `dict` of same (for multi-head models). If
+mode is tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT, `labels=None` will be
+passed. If the `model_fn`'s signature does not accept `mode`, the
+`model_fn` must still be able to handle `labels=None`.
+* `mode` -- Optional. Specifies if this is training, evaluation or
+prediction. See tf.estimator.ModeKeys.
+`params` -- Optional `dict` of hyperparameters. Will receive what is
+passed to Estimator in `params` parameter. This allows to configure
+Estimators from hyper parameter tuning.
+* `config` -- Optional `estimator.RunConfig` object. Will receive what
+is passed to Estimator as its `config` parameter, or a default
+value. Allows setting up things in your `model_fn` based on
+configuration such as `num_ps_replicas`, or `model_dir`.
+* Returns -- tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec
+ |
+
+|
+`model_dir`
+ |
+
+Directory to save model parameters, graph and etc. This can
+also be used to load checkpoints from the directory into an estimator to
+continue training a previously saved model. If `PathLike` object, the
+path will be resolved. If `None`, the model_dir in `config` will be used
+if set. If both are set, they must be same. If both are `None`, a
+temporary directory will be used.
+ |
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+`estimator.RunConfig` configuration object.
+ |
+
+|
+`params`
+ |
+
+`dict` of hyper parameters that will be passed into `model_fn`.
+Keys are names of parameters, values are basic python types.
+ |
+
+|
+`warm_start_from`
+ |
+
+Optional string filepath to a checkpoint or SavedModel to
+warm-start from, or a tf.estimator.WarmStartSettings object to fully
+configure warm-starting. If None, only TRAINABLE variables are
+warm-started. If the string filepath is provided instead of a
+tf.estimator.WarmStartSettings, then all variables are warm-started,
+and it is assumed that vocabularies and tf.Tensor names are unchanged.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+parameters of `model_fn` don't match `params`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if this is called via a subclass and if that class overrides
+a member of `Estimator`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+Estimators can be used while eager execution is enabled. Note that `input_fn`
+and all hooks are executed inside a graph context, so they have to be written
+to be compatible with graph mode. Note that `input_fn` code using tf.data
+generally works in both graph and eager modes.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`model_dir`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`model_fn`
+ |
+
+Returns the `model_fn` which is bound to `self.params`.
+ |
+
+|
+`params`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+eval_dir
+
+View source
+
+
+eval_dir(
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+Shows the directory name where evaluation metrics are dumped.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of the evaluation if user needs to run multiple evaluations on
+different data sets, such as on training data vs test data. Metrics for
+different evaluations are saved in separate folders, and appear
+separately in tensorboard.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A string which is the path of directory contains evaluation metrics.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+evaluate
+
+View source
+
+
+evaluate(
+ input_fn, steps=None, hooks=None, checkpoint_path=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+Evaluates the model given evaluation data `input_fn`.
+
+For each step, calls `input_fn`, which returns one batch of data.
+Evaluates until:
+- `steps` batches are processed, or
+- `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception (tf.errors.OutOfRangeError
+or
+`StopIteration`).
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that constructs the input data for evaluation. See
+[Premade Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The
+function should construct and return one of the following: * A
+tf.data.Dataset object: Outputs of `Dataset` object must be a tuple
+`(features, labels)` with same constraints as below. * A tuple
+`(features, labels)`: Where `features` is a tf.Tensor or a dictionary
+of string feature name to `Tensor` and `labels` is a `Tensor` or a
+dictionary of string label name to `Tensor`. Both `features` and
+`labels` are consumed by `model_fn`. They should satisfy the
+expectation of `model_fn` from inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`steps`
+ |
+
+Number of steps for which to evaluate model. If `None`, evaluates
+until `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the evaluation call.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+Path of a specific checkpoint to evaluate. If `None`, the
+latest checkpoint in `model_dir` is used. If there are no checkpoints
+in `model_dir`, evaluation is run with newly initialized `Variables`
+instead of ones restored from checkpoint.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of the evaluation if user needs to run multiple evaluations on
+different data sets, such as on training data vs test data. Metrics for
+different evaluations are saved in separate folders, and appear
+separately in tensorboard.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A dict containing the evaluation metrics specified in `model_fn` keyed by
+name, as well as an entry `global_step` which contains the value of the
+global step for which this evaluation was performed. For canned
+estimators, the dict contains the `loss` (mean loss per mini-batch) and
+the `average_loss` (mean loss per sample). Canned classifiers also return
+the `accuracy`. Canned regressors also return the `label/mean` and the
+`prediction/mean`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `steps <= 0`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+experimental_export_all_saved_models
+
+View source
+
+
+experimental_export_all_saved_models(
+ export_dir_base, input_receiver_fn_map, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None
+)
+
+
+Exports a `SavedModel` with `tf.MetaGraphDefs` for each requested mode.
+
+For each mode passed in via the `input_receiver_fn_map`,
+this method builds a new graph by calling the `input_receiver_fn` to obtain
+feature and label `Tensor`s. Next, this method calls the `Estimator`'s
+`model_fn` in the passed mode to generate the model graph based on
+those features and labels, and restores the given checkpoint
+(or, lacking that, the most recent checkpoint) into the graph.
+Only one of the modes is used for saving variables to the `SavedModel`
+(order of preference: tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN,
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys.EVAL, then
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT), such that up to three
+`tf.MetaGraphDefs` are saved with a single set of variables in a single
+`SavedModel` directory.
+
+For the variables and `tf.MetaGraphDefs`, a timestamped export directory
+below
+`export_dir_base`, and writes a `SavedModel` into it containing
+the `tf.MetaGraphDef` for the given mode and its associated signatures.
+
+For prediction, the exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef`
+for each element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`,
+named using the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+For training and evaluation, the `train_op` is stored in an extra
+collection,
+and loss, metrics, and predictions are included in a `SignatureDef` for the
+mode in question.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`input_receiver_fn_map`
+ |
+
+dict of tf.estimator.ModeKeys to
+`input_receiver_fn` mappings, where the `input_receiver_fn` is a
+function that takes no arguments and returns the appropriate subclass of
+`InputReceiver`.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if any `input_receiver_fn` is `None`, no `export_outputs`
+are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+export_saved_model
+
+View source
+
+
+export_saved_model(
+ export_dir_base, serving_input_receiver_fn, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None, experimental_mode=ModeKeys.PREDICT
+)
+
+
+Exports inference graph as a `SavedModel` into the given dir.
+
+For a detailed guide, see
+[Using SavedModel with
+Estimators](https://tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model#using_savedmodel_with_estimators).
+
+This method builds a new graph by first calling the
+`serving_input_receiver_fn` to obtain feature `Tensor`s, and then calling
+this `Estimator`'s `model_fn` to generate the model graph based on those
+features. It restores the given checkpoint (or, lacking that, the most
+recent checkpoint) into this graph in a fresh session. Finally it creates
+a timestamped export directory below the given `export_dir_base`, and writes
+a `SavedModel` into it containing a single `tf.MetaGraphDef` saved from this
+session.
+
+The exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef` for each
+element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`, named
+using
+the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+The experimental_mode parameter can be used to export a single
+train/eval/predict graph as a `SavedModel`.
+See `experimental_export_all_saved_models` for full docs.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`serving_input_receiver_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that takes no argument and returns a
+tf.estimator.export.ServingInputReceiver or
+tf.estimator.export.TensorServingInputReceiver.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+|
+`experimental_mode`
+ |
+
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys value indicating with mode will
+be exported. Note that this feature is experimental.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if no `serving_input_receiver_fn` is provided, no
+`export_outputs` are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+export_savedmodel
+
+View source
+
+
+export_savedmodel(
+ export_dir_base, serving_input_receiver_fn, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None, strip_default_attrs=(False)
+)
+
+
+Exports inference graph as a `SavedModel` into the given dir. (deprecated)
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+This function has been renamed, use `export_saved_model` instead.
+
+For a detailed guide, see
+[Using SavedModel with
+Estimators](https://tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model#using_savedmodel_with_estimators).
+
+This method builds a new graph by first calling the
+`serving_input_receiver_fn` to obtain feature `Tensor`s, and then calling
+this `Estimator`'s `model_fn` to generate the model graph based on those
+features. It restores the given checkpoint (or, lacking that, the most
+recent checkpoint) into this graph in a fresh session. Finally it creates
+a timestamped export directory below the given `export_dir_base`, and writes
+a `SavedModel` into it containing a single `tf.MetaGraphDef` saved from this
+session.
+
+The exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef` for each
+element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`, named
+using
+the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`serving_input_receiver_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that takes no argument and returns a
+tf.estimator.export.ServingInputReceiver or
+tf.estimator.export.TensorServingInputReceiver.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+|
+`strip_default_attrs`
+ |
+
+Boolean. If `True`, default-valued attributes will be
+removed from the `NodeDef`s. For a detailed guide, see [Stripping
+Default-Valued Attributes](
+https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/master/tensorflow/python/saved_model/README.md#stripping-default-valued-attributes).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if no `serving_input_receiver_fn` is provided, no
+`export_outputs` are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+get_variable_names
+
+View source
+
+
+get_variable_names()
+
+
+Returns list of all variable names in this model.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+List of names.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `Estimator` has not produced a checkpoint yet.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+get_variable_value
+
+View source
+
+
+get_variable_value(
+ name
+)
+
+
+Returns value of the variable given by name.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+string or a list of string, name of the tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Numpy array - value of the tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `Estimator` has not produced a checkpoint yet.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+latest_checkpoint
+
+View source
+
+
+latest_checkpoint()
+
+
+Finds the filename of the latest saved checkpoint file in `model_dir`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The full path to the latest checkpoint or `None` if no checkpoint was
+found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+predict
+
+View source
+
+
+predict(
+ input_fn, predict_keys=None, hooks=None, checkpoint_path=None,
+ yield_single_examples=(True)
+)
+
+
+Yields predictions for given features.
+
+Please note that interleaving two predict outputs does not work. See:
+[issue/20506](
+https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/issues/20506#issuecomment-422208517)
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that constructs the features. Prediction continues
+until `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception
+(tf.errors.OutOfRangeError or `StopIteration`). See [Premade
+Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The function should construct and return one of
+the following:
+* tf.data.Dataset object -- Outputs of `Dataset` object must have
+same constraints as below.
+* features -- A tf.Tensor or a dictionary of string feature name to
+`Tensor`. features are consumed by `model_fn`. They should satisfy
+the expectation of `model_fn` from inputs. * A tuple, in which case
+the first item is extracted as features.
+ |
+
+|
+`predict_keys`
+ |
+
+list of `str`, name of the keys to predict. It is used if
+the tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec.predictions is a `dict`. If
+`predict_keys` is used then rest of the predictions will be filtered
+from the dictionary. If `None`, returns all.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the prediction call.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+Path of a specific checkpoint to predict. If `None`, the
+latest checkpoint in `model_dir` is used. If there are no checkpoints
+in `model_dir`, prediction is run with newly initialized `Variables`
+instead of ones restored from checkpoint.
+ |
+
+|
+`yield_single_examples`
+ |
+
+If `False`, yields the whole batch as returned by
+the `model_fn` instead of decomposing the batch into individual
+elements. This is useful if `model_fn` returns some tensors whose first
+dimension is not equal to the batch size.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Yields:
+
+Evaluated values of `predictions` tensors.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If batch length of predictions is not the same and
+`yield_single_examples` is `True`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If there is a conflict between `predict_keys` and
+`predictions`. For example if `predict_keys` is not `None` but
+tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec.predictions is not a `dict`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+train
+
+View source
+
+
+train(
+ input_fn, hooks=None, steps=None, max_steps=None, saving_listeners=None
+)
+
+
+Trains a model given training data `input_fn`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that provides input data for training as minibatches.
+See [Premade Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The function should construct and return one of
+the following:
+* A tf.data.Dataset object: Outputs of `Dataset` object must be a
+tuple `(features, labels)` with same constraints as below.
+* A tuple `(features, labels)`: Where `features` is a tf.Tensor or a
+dictionary of string feature name to `Tensor` and `labels` is a
+`Tensor` or a dictionary of string label name to `Tensor`. Both
+`features` and `labels` are consumed by `model_fn`. They should
+satisfy the expectation of `model_fn` from inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the training loop.
+ |
+
+|
+`steps`
+ |
+
+Number of steps for which to train the model. If `None`, train
+forever or train until `input_fn` generates the `tf.errors.OutOfRange`
+error or `StopIteration` exception. `steps` works incrementally. If you
+call two times `train(steps=10)` then training occurs in total 20 steps.
+If `OutOfRange` or `StopIteration` occurs in the middle, training stops
+before 20 steps. If you don't want to have incremental behavior please
+set `max_steps` instead. If set, `max_steps` must be `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_steps`
+ |
+
+Number of total steps for which to train model. If `None`,
+train forever or train until `input_fn` generates the
+`tf.errors.OutOfRange` error or `StopIteration` exception. If set,
+`steps` must be `None`. If `OutOfRange` or `StopIteration` occurs in the
+middle, training stops before `max_steps` steps. Two calls to
+`train(steps=100)` means 200 training iterations. On the other hand, two
+calls to `train(max_steps=100)` means that the second call will not do
+any iteration since first call did all 100 steps.
+ |
+
+|
+`saving_listeners`
+ |
+
+list of `CheckpointSaverListener` objects. Used for
+callbacks that run immediately before or after checkpoint savings.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`self`, for chaining.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If both `steps` and `max_steps` are not `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If either `steps` or `max_steps <= 0`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/DNNEstimator.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/DNNEstimator.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..1d80edd4dba
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/DNNEstimator.md
@@ -0,0 +1,1240 @@
+description: An estimator for TensorFlow DNN models with user-specified head.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.estimator.DNNEstimator
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+An estimator for TensorFlow DNN models with user-specified head.
+
+Inherits From: [`Estimator`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/Estimator.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.estimator.DNNEstimator(
+ head, hidden_units, feature_columns, model_dir=None, optimizer='Adagrad',
+ activation_fn=tf.nn.relu, dropout=None, input_layer_partitioner=None,
+ config=None, warm_start_from=None, batch_norm=(False)
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+sparse_feature_a = sparse_column_with_hash_bucket(...)
+sparse_feature_b = sparse_column_with_hash_bucket(...)
+
+sparse_feature_a_emb = embedding_column(sparse_id_column=sparse_feature_a,
+ ...)
+sparse_feature_b_emb = embedding_column(sparse_id_column=sparse_feature_b,
+ ...)
+
+estimator = tf.estimator.DNNEstimator(
+ head=tf.estimator.MultiLabelHead(n_classes=3),
+ feature_columns=[sparse_feature_a_emb, sparse_feature_b_emb],
+ hidden_units=[1024, 512, 256])
+
+# Or estimator using the ProximalAdagradOptimizer optimizer with
+# regularization.
+estimator = tf.estimator.DNNEstimator(
+ head=tf.estimator.MultiLabelHead(n_classes=3),
+ feature_columns=[sparse_feature_a_emb, sparse_feature_b_emb],
+ hidden_units=[1024, 512, 256],
+ optimizer=tf.compat.v1.train.ProximalAdagradOptimizer(
+ learning_rate=0.1,
+ l1_regularization_strength=0.001
+ ))
+
+# Or estimator using an optimizer with a learning rate decay.
+estimator = tf.estimator.DNNEstimator(
+ head=tf.estimator.MultiLabelHead(n_classes=3),
+ feature_columns=[sparse_feature_a_emb, sparse_feature_b_emb],
+ hidden_units=[1024, 512, 256],
+ optimizer=lambda: tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(
+ learning_rate=tf.compat.v1.train.exponential_decay(
+ learning_rate=0.1,
+ global_step=tf.compat.v1.train.get_global_step(),
+ decay_steps=10000,
+ decay_rate=0.96))
+
+# Or estimator with warm-starting from a previous checkpoint.
+estimator = tf.estimator.DNNEstimator(
+ head=tf.estimator.MultiLabelHead(n_classes=3),
+ feature_columns=[sparse_feature_a_emb, sparse_feature_b_emb],
+ hidden_units=[1024, 512, 256],
+ warm_start_from="/path/to/checkpoint/dir")
+
+# Input builders
+def input_fn_train:
+ # Returns tf.data.Dataset of (x, y) tuple where y represents label's class
+ # index.
+ pass
+def input_fn_eval:
+ # Returns tf.data.Dataset of (x, y) tuple where y represents label's class
+ # index.
+ pass
+def input_fn_predict:
+ # Returns tf.data.Dataset of (x, None) tuple.
+ pass
+estimator.train(input_fn=input_fn_train)
+metrics = estimator.evaluate(input_fn=input_fn_eval)
+predictions = estimator.predict(input_fn=input_fn_predict)
+```
+
+Input of `train` and `evaluate` should have following features,
+otherwise there will be a `KeyError`:
+
+* if `weight_column` is not `None`, a feature with `key=weight_column` whose
+ value is a `Tensor`.
+* for each `column` in `feature_columns`:
+ - if `column` is a `CategoricalColumn`, a feature with `key=column.name`
+ whose `value` is a `SparseTensor`.
+ - if `column` is a `WeightedCategoricalColumn`, two features: the first
+ with `key` the id column name, the second with `key` the weight column
+ name. Both features' `value` must be a `SparseTensor`.
+ - if `column` is a `DenseColumn`, a feature with `key=column.name`
+ whose `value` is a `Tensor`.
+
+Loss and predicted output are determined by the specified head.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`model_fn`
+ |
+
+Model function. Follows the signature:
+* `features` -- This is the first item returned from the `input_fn`
+passed to `train`, `evaluate`, and `predict`. This should be a
+single tf.Tensor or `dict` of same.
+* `labels` -- This is the second item returned from the `input_fn`
+passed to `train`, `evaluate`, and `predict`. This should be a
+single tf.Tensor or `dict` of same (for multi-head models). If
+mode is tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT, `labels=None` will be
+passed. If the `model_fn`'s signature does not accept `mode`, the
+`model_fn` must still be able to handle `labels=None`.
+* `mode` -- Optional. Specifies if this is training, evaluation or
+prediction. See tf.estimator.ModeKeys.
+`params` -- Optional `dict` of hyperparameters. Will receive what is
+passed to Estimator in `params` parameter. This allows to configure
+Estimators from hyper parameter tuning.
+* `config` -- Optional `estimator.RunConfig` object. Will receive what
+is passed to Estimator as its `config` parameter, or a default
+value. Allows setting up things in your `model_fn` based on
+configuration such as `num_ps_replicas`, or `model_dir`.
+* Returns -- tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec
+ |
+
+|
+`model_dir`
+ |
+
+Directory to save model parameters, graph and etc. This can
+also be used to load checkpoints from the directory into an estimator to
+continue training a previously saved model. If `PathLike` object, the
+path will be resolved. If `None`, the model_dir in `config` will be used
+if set. If both are set, they must be same. If both are `None`, a
+temporary directory will be used.
+ |
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+`estimator.RunConfig` configuration object.
+ |
+
+|
+`params`
+ |
+
+`dict` of hyper parameters that will be passed into `model_fn`.
+Keys are names of parameters, values are basic python types.
+ |
+
+|
+`warm_start_from`
+ |
+
+Optional string filepath to a checkpoint or SavedModel to
+warm-start from, or a tf.estimator.WarmStartSettings object to fully
+configure warm-starting. If None, only TRAINABLE variables are
+warm-started. If the string filepath is provided instead of a
+tf.estimator.WarmStartSettings, then all variables are warm-started,
+and it is assumed that vocabularies and tf.Tensor names are unchanged.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+parameters of `model_fn` don't match `params`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if this is called via a subclass and if that class overrides
+a member of `Estimator`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+Estimators can be used while eager execution is enabled. Note that `input_fn`
+and all hooks are executed inside a graph context, so they have to be written
+to be compatible with graph mode. Note that `input_fn` code using tf.data
+generally works in both graph and eager modes.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`model_dir`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`model_fn`
+ |
+
+Returns the `model_fn` which is bound to `self.params`.
+ |
+
+|
+`params`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+eval_dir
+
+View source
+
+
+eval_dir(
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+Shows the directory name where evaluation metrics are dumped.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of the evaluation if user needs to run multiple evaluations on
+different data sets, such as on training data vs test data. Metrics for
+different evaluations are saved in separate folders, and appear
+separately in tensorboard.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A string which is the path of directory contains evaluation metrics.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+evaluate
+
+View source
+
+
+evaluate(
+ input_fn, steps=None, hooks=None, checkpoint_path=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+Evaluates the model given evaluation data `input_fn`.
+
+For each step, calls `input_fn`, which returns one batch of data.
+Evaluates until:
+- `steps` batches are processed, or
+- `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception (tf.errors.OutOfRangeError
+or
+`StopIteration`).
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that constructs the input data for evaluation. See
+[Premade Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The
+function should construct and return one of the following: * A
+tf.data.Dataset object: Outputs of `Dataset` object must be a tuple
+`(features, labels)` with same constraints as below. * A tuple
+`(features, labels)`: Where `features` is a tf.Tensor or a dictionary
+of string feature name to `Tensor` and `labels` is a `Tensor` or a
+dictionary of string label name to `Tensor`. Both `features` and
+`labels` are consumed by `model_fn`. They should satisfy the
+expectation of `model_fn` from inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`steps`
+ |
+
+Number of steps for which to evaluate model. If `None`, evaluates
+until `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the evaluation call.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+Path of a specific checkpoint to evaluate. If `None`, the
+latest checkpoint in `model_dir` is used. If there are no checkpoints
+in `model_dir`, evaluation is run with newly initialized `Variables`
+instead of ones restored from checkpoint.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of the evaluation if user needs to run multiple evaluations on
+different data sets, such as on training data vs test data. Metrics for
+different evaluations are saved in separate folders, and appear
+separately in tensorboard.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A dict containing the evaluation metrics specified in `model_fn` keyed by
+name, as well as an entry `global_step` which contains the value of the
+global step for which this evaluation was performed. For canned
+estimators, the dict contains the `loss` (mean loss per mini-batch) and
+the `average_loss` (mean loss per sample). Canned classifiers also return
+the `accuracy`. Canned regressors also return the `label/mean` and the
+`prediction/mean`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `steps <= 0`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+experimental_export_all_saved_models
+
+View source
+
+
+experimental_export_all_saved_models(
+ export_dir_base, input_receiver_fn_map, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None
+)
+
+
+Exports a `SavedModel` with `tf.MetaGraphDefs` for each requested mode.
+
+For each mode passed in via the `input_receiver_fn_map`,
+this method builds a new graph by calling the `input_receiver_fn` to obtain
+feature and label `Tensor`s. Next, this method calls the `Estimator`'s
+`model_fn` in the passed mode to generate the model graph based on
+those features and labels, and restores the given checkpoint
+(or, lacking that, the most recent checkpoint) into the graph.
+Only one of the modes is used for saving variables to the `SavedModel`
+(order of preference: tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN,
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys.EVAL, then
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT), such that up to three
+`tf.MetaGraphDefs` are saved with a single set of variables in a single
+`SavedModel` directory.
+
+For the variables and `tf.MetaGraphDefs`, a timestamped export directory
+below
+`export_dir_base`, and writes a `SavedModel` into it containing
+the `tf.MetaGraphDef` for the given mode and its associated signatures.
+
+For prediction, the exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef`
+for each element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`,
+named using the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+For training and evaluation, the `train_op` is stored in an extra
+collection,
+and loss, metrics, and predictions are included in a `SignatureDef` for the
+mode in question.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`input_receiver_fn_map`
+ |
+
+dict of tf.estimator.ModeKeys to
+`input_receiver_fn` mappings, where the `input_receiver_fn` is a
+function that takes no arguments and returns the appropriate subclass of
+`InputReceiver`.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if any `input_receiver_fn` is `None`, no `export_outputs`
+are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+export_saved_model
+
+View source
+
+
+export_saved_model(
+ export_dir_base, serving_input_receiver_fn, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None, experimental_mode=ModeKeys.PREDICT
+)
+
+
+Exports inference graph as a `SavedModel` into the given dir.
+
+For a detailed guide, see
+[Using SavedModel with
+Estimators](https://tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model#using_savedmodel_with_estimators).
+
+This method builds a new graph by first calling the
+`serving_input_receiver_fn` to obtain feature `Tensor`s, and then calling
+this `Estimator`'s `model_fn` to generate the model graph based on those
+features. It restores the given checkpoint (or, lacking that, the most
+recent checkpoint) into this graph in a fresh session. Finally it creates
+a timestamped export directory below the given `export_dir_base`, and writes
+a `SavedModel` into it containing a single `tf.MetaGraphDef` saved from this
+session.
+
+The exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef` for each
+element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`, named
+using
+the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+The experimental_mode parameter can be used to export a single
+train/eval/predict graph as a `SavedModel`.
+See `experimental_export_all_saved_models` for full docs.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`serving_input_receiver_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that takes no argument and returns a
+tf.estimator.export.ServingInputReceiver or
+tf.estimator.export.TensorServingInputReceiver.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+|
+`experimental_mode`
+ |
+
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys value indicating with mode will
+be exported. Note that this feature is experimental.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if no `serving_input_receiver_fn` is provided, no
+`export_outputs` are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+export_savedmodel
+
+View source
+
+
+export_savedmodel(
+ export_dir_base, serving_input_receiver_fn, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None, strip_default_attrs=(False)
+)
+
+
+Exports inference graph as a `SavedModel` into the given dir. (deprecated)
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+This function has been renamed, use `export_saved_model` instead.
+
+For a detailed guide, see
+[Using SavedModel with
+Estimators](https://tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model#using_savedmodel_with_estimators).
+
+This method builds a new graph by first calling the
+`serving_input_receiver_fn` to obtain feature `Tensor`s, and then calling
+this `Estimator`'s `model_fn` to generate the model graph based on those
+features. It restores the given checkpoint (or, lacking that, the most
+recent checkpoint) into this graph in a fresh session. Finally it creates
+a timestamped export directory below the given `export_dir_base`, and writes
+a `SavedModel` into it containing a single `tf.MetaGraphDef` saved from this
+session.
+
+The exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef` for each
+element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`, named
+using
+the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`serving_input_receiver_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that takes no argument and returns a
+tf.estimator.export.ServingInputReceiver or
+tf.estimator.export.TensorServingInputReceiver.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+|
+`strip_default_attrs`
+ |
+
+Boolean. If `True`, default-valued attributes will be
+removed from the `NodeDef`s. For a detailed guide, see [Stripping
+Default-Valued Attributes](
+https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/master/tensorflow/python/saved_model/README.md#stripping-default-valued-attributes).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if no `serving_input_receiver_fn` is provided, no
+`export_outputs` are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+get_variable_names
+
+View source
+
+
+get_variable_names()
+
+
+Returns list of all variable names in this model.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+List of names.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `Estimator` has not produced a checkpoint yet.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+get_variable_value
+
+View source
+
+
+get_variable_value(
+ name
+)
+
+
+Returns value of the variable given by name.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+string or a list of string, name of the tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Numpy array - value of the tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `Estimator` has not produced a checkpoint yet.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+latest_checkpoint
+
+View source
+
+
+latest_checkpoint()
+
+
+Finds the filename of the latest saved checkpoint file in `model_dir`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The full path to the latest checkpoint or `None` if no checkpoint was
+found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+predict
+
+View source
+
+
+predict(
+ input_fn, predict_keys=None, hooks=None, checkpoint_path=None,
+ yield_single_examples=(True)
+)
+
+
+Yields predictions for given features.
+
+Please note that interleaving two predict outputs does not work. See:
+[issue/20506](
+https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/issues/20506#issuecomment-422208517)
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that constructs the features. Prediction continues
+until `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception
+(tf.errors.OutOfRangeError or `StopIteration`). See [Premade
+Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The function should construct and return one of
+the following:
+* tf.data.Dataset object -- Outputs of `Dataset` object must have
+same constraints as below.
+* features -- A tf.Tensor or a dictionary of string feature name to
+`Tensor`. features are consumed by `model_fn`. They should satisfy
+the expectation of `model_fn` from inputs. * A tuple, in which case
+the first item is extracted as features.
+ |
+
+|
+`predict_keys`
+ |
+
+list of `str`, name of the keys to predict. It is used if
+the tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec.predictions is a `dict`. If
+`predict_keys` is used then rest of the predictions will be filtered
+from the dictionary. If `None`, returns all.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the prediction call.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+Path of a specific checkpoint to predict. If `None`, the
+latest checkpoint in `model_dir` is used. If there are no checkpoints
+in `model_dir`, prediction is run with newly initialized `Variables`
+instead of ones restored from checkpoint.
+ |
+
+|
+`yield_single_examples`
+ |
+
+If `False`, yields the whole batch as returned by
+the `model_fn` instead of decomposing the batch into individual
+elements. This is useful if `model_fn` returns some tensors whose first
+dimension is not equal to the batch size.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Yields:
+
+Evaluated values of `predictions` tensors.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If batch length of predictions is not the same and
+`yield_single_examples` is `True`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If there is a conflict between `predict_keys` and
+`predictions`. For example if `predict_keys` is not `None` but
+tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec.predictions is not a `dict`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+train
+
+View source
+
+
+train(
+ input_fn, hooks=None, steps=None, max_steps=None, saving_listeners=None
+)
+
+
+Trains a model given training data `input_fn`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that provides input data for training as minibatches.
+See [Premade Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The function should construct and return one of
+the following:
+* A tf.data.Dataset object: Outputs of `Dataset` object must be a
+tuple `(features, labels)` with same constraints as below.
+* A tuple `(features, labels)`: Where `features` is a tf.Tensor or a
+dictionary of string feature name to `Tensor` and `labels` is a
+`Tensor` or a dictionary of string label name to `Tensor`. Both
+`features` and `labels` are consumed by `model_fn`. They should
+satisfy the expectation of `model_fn` from inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the training loop.
+ |
+
+|
+`steps`
+ |
+
+Number of steps for which to train the model. If `None`, train
+forever or train until `input_fn` generates the `tf.errors.OutOfRange`
+error or `StopIteration` exception. `steps` works incrementally. If you
+call two times `train(steps=10)` then training occurs in total 20 steps.
+If `OutOfRange` or `StopIteration` occurs in the middle, training stops
+before 20 steps. If you don't want to have incremental behavior please
+set `max_steps` instead. If set, `max_steps` must be `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_steps`
+ |
+
+Number of total steps for which to train model. If `None`,
+train forever or train until `input_fn` generates the
+`tf.errors.OutOfRange` error or `StopIteration` exception. If set,
+`steps` must be `None`. If `OutOfRange` or `StopIteration` occurs in the
+middle, training stops before `max_steps` steps. Two calls to
+`train(steps=100)` means 200 training iterations. On the other hand, two
+calls to `train(max_steps=100)` means that the second call will not do
+any iteration since first call did all 100 steps.
+ |
+
+|
+`saving_listeners`
+ |
+
+list of `CheckpointSaverListener` objects. Used for
+callbacks that run immediately before or after checkpoint savings.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`self`, for chaining.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If both `steps` and `max_steps` are not `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If either `steps` or `max_steps <= 0`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/DNNLinearCombinedClassifier.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/DNNLinearCombinedClassifier.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e52eb6a050c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/DNNLinearCombinedClassifier.md
@@ -0,0 +1,1236 @@
+description: An estimator for TensorFlow Linear and DNN joined classification models.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.estimator.DNNLinearCombinedClassifier
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+An estimator for TensorFlow Linear and DNN joined classification models.
+
+Inherits From: [`Estimator`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/Estimator.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.estimator.DNNLinearCombinedClassifier(
+ model_dir=None, linear_feature_columns=None, linear_optimizer='Ftrl',
+ dnn_feature_columns=None, dnn_optimizer='Adagrad', dnn_hidden_units=None,
+ dnn_activation_fn=tf.nn.relu, dnn_dropout=None, n_classes=2, weight_column=None,
+ label_vocabulary=None, input_layer_partitioner=None, config=None,
+ warm_start_from=None, loss_reduction=tf.compat.v1.losses.Reduction.SUM,
+ batch_norm=(False), linear_sparse_combiner='sum'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Note: This estimator is also known as wide-n-deep.
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+numeric_feature = numeric_column(...)
+categorical_column_a = categorical_column_with_hash_bucket(...)
+categorical_column_b = categorical_column_with_hash_bucket(...)
+
+categorical_feature_a_x_categorical_feature_b = crossed_column(...)
+categorical_feature_a_emb = embedding_column(
+ categorical_column=categorical_feature_a, ...)
+categorical_feature_b_emb = embedding_column(
+ categorical_id_column=categorical_feature_b, ...)
+
+estimator = tf.estimator.DNNLinearCombinedClassifier(
+ # wide settings
+ linear_feature_columns=[categorical_feature_a_x_categorical_feature_b],
+ linear_optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Ftrl(...),
+ # deep settings
+ dnn_feature_columns=[
+ categorical_feature_a_emb, categorical_feature_b_emb,
+ numeric_feature],
+ dnn_hidden_units=[1000, 500, 100],
+ dnn_optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adagrad(...),
+ # warm-start settings
+ warm_start_from="/path/to/checkpoint/dir")
+
+# To apply L1 and L2 regularization, you can set dnn_optimizer to:
+tf.compat.v1.train.ProximalAdagradOptimizer(
+ learning_rate=0.1,
+ l1_regularization_strength=0.001,
+ l2_regularization_strength=0.001)
+# To apply learning rate decay, you can set dnn_optimizer to a callable:
+lambda: tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(
+ learning_rate=tf.compat.v1.train.exponential_decay(
+ learning_rate=0.1,
+ global_step=tf.compat.v1.train.get_global_step(),
+ decay_steps=10000,
+ decay_rate=0.96)
+# It is the same for linear_optimizer.
+
+# Input builders
+def input_fn_train:
+ # Returns tf.data.Dataset of (x, y) tuple where y represents label's class
+ # index.
+ pass
+def input_fn_eval:
+ # Returns tf.data.Dataset of (x, y) tuple where y represents label's class
+ # index.
+ pass
+def input_fn_predict:
+ # Returns tf.data.Dataset of (x, None) tuple.
+ pass
+estimator.train(input_fn=input_fn_train, steps=100)
+metrics = estimator.evaluate(input_fn=input_fn_eval, steps=10)
+predictions = estimator.predict(input_fn=input_fn_predict)
+```
+
+Input of `train` and `evaluate` should have following features,
+otherwise there will be a `KeyError`:
+
+* for each `column` in `dnn_feature_columns` + `linear_feature_columns`:
+ - if `column` is a `CategoricalColumn`, a feature with `key=column.name`
+ whose `value` is a `SparseTensor`.
+ - if `column` is a `WeightedCategoricalColumn`, two features: the first
+ with `key` the id column name, the second with `key` the weight column
+ name. Both features' `value` must be a `SparseTensor`.
+ - if `column` is a `DenseColumn`, a feature with `key=column.name`
+ whose `value` is a `Tensor`.
+
+Loss is calculated by using softmax cross entropy.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`model_fn`
+ |
+
+Model function. Follows the signature:
+* `features` -- This is the first item returned from the `input_fn`
+passed to `train`, `evaluate`, and `predict`. This should be a
+single tf.Tensor or `dict` of same.
+* `labels` -- This is the second item returned from the `input_fn`
+passed to `train`, `evaluate`, and `predict`. This should be a
+single tf.Tensor or `dict` of same (for multi-head models). If
+mode is tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT, `labels=None` will be
+passed. If the `model_fn`'s signature does not accept `mode`, the
+`model_fn` must still be able to handle `labels=None`.
+* `mode` -- Optional. Specifies if this is training, evaluation or
+prediction. See tf.estimator.ModeKeys.
+`params` -- Optional `dict` of hyperparameters. Will receive what is
+passed to Estimator in `params` parameter. This allows to configure
+Estimators from hyper parameter tuning.
+* `config` -- Optional `estimator.RunConfig` object. Will receive what
+is passed to Estimator as its `config` parameter, or a default
+value. Allows setting up things in your `model_fn` based on
+configuration such as `num_ps_replicas`, or `model_dir`.
+* Returns -- tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec
+ |
+
+|
+`model_dir`
+ |
+
+Directory to save model parameters, graph and etc. This can
+also be used to load checkpoints from the directory into an estimator to
+continue training a previously saved model. If `PathLike` object, the
+path will be resolved. If `None`, the model_dir in `config` will be used
+if set. If both are set, they must be same. If both are `None`, a
+temporary directory will be used.
+ |
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+`estimator.RunConfig` configuration object.
+ |
+
+|
+`params`
+ |
+
+`dict` of hyper parameters that will be passed into `model_fn`.
+Keys are names of parameters, values are basic python types.
+ |
+
+|
+`warm_start_from`
+ |
+
+Optional string filepath to a checkpoint or SavedModel to
+warm-start from, or a tf.estimator.WarmStartSettings object to fully
+configure warm-starting. If None, only TRAINABLE variables are
+warm-started. If the string filepath is provided instead of a
+tf.estimator.WarmStartSettings, then all variables are warm-started,
+and it is assumed that vocabularies and tf.Tensor names are unchanged.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+parameters of `model_fn` don't match `params`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if this is called via a subclass and if that class overrides
+a member of `Estimator`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+Estimators can be used while eager execution is enabled. Note that `input_fn`
+and all hooks are executed inside a graph context, so they have to be written
+to be compatible with graph mode. Note that `input_fn` code using tf.data
+generally works in both graph and eager modes.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`model_dir`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`model_fn`
+ |
+
+Returns the `model_fn` which is bound to `self.params`.
+ |
+
+|
+`params`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+eval_dir
+
+View source
+
+
+eval_dir(
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+Shows the directory name where evaluation metrics are dumped.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of the evaluation if user needs to run multiple evaluations on
+different data sets, such as on training data vs test data. Metrics for
+different evaluations are saved in separate folders, and appear
+separately in tensorboard.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A string which is the path of directory contains evaluation metrics.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+evaluate
+
+View source
+
+
+evaluate(
+ input_fn, steps=None, hooks=None, checkpoint_path=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+Evaluates the model given evaluation data `input_fn`.
+
+For each step, calls `input_fn`, which returns one batch of data.
+Evaluates until:
+- `steps` batches are processed, or
+- `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception (tf.errors.OutOfRangeError
+or
+`StopIteration`).
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that constructs the input data for evaluation. See
+[Premade Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The
+function should construct and return one of the following: * A
+tf.data.Dataset object: Outputs of `Dataset` object must be a tuple
+`(features, labels)` with same constraints as below. * A tuple
+`(features, labels)`: Where `features` is a tf.Tensor or a dictionary
+of string feature name to `Tensor` and `labels` is a `Tensor` or a
+dictionary of string label name to `Tensor`. Both `features` and
+`labels` are consumed by `model_fn`. They should satisfy the
+expectation of `model_fn` from inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`steps`
+ |
+
+Number of steps for which to evaluate model. If `None`, evaluates
+until `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the evaluation call.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+Path of a specific checkpoint to evaluate. If `None`, the
+latest checkpoint in `model_dir` is used. If there are no checkpoints
+in `model_dir`, evaluation is run with newly initialized `Variables`
+instead of ones restored from checkpoint.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of the evaluation if user needs to run multiple evaluations on
+different data sets, such as on training data vs test data. Metrics for
+different evaluations are saved in separate folders, and appear
+separately in tensorboard.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A dict containing the evaluation metrics specified in `model_fn` keyed by
+name, as well as an entry `global_step` which contains the value of the
+global step for which this evaluation was performed. For canned
+estimators, the dict contains the `loss` (mean loss per mini-batch) and
+the `average_loss` (mean loss per sample). Canned classifiers also return
+the `accuracy`. Canned regressors also return the `label/mean` and the
+`prediction/mean`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `steps <= 0`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+experimental_export_all_saved_models
+
+View source
+
+
+experimental_export_all_saved_models(
+ export_dir_base, input_receiver_fn_map, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None
+)
+
+
+Exports a `SavedModel` with `tf.MetaGraphDefs` for each requested mode.
+
+For each mode passed in via the `input_receiver_fn_map`,
+this method builds a new graph by calling the `input_receiver_fn` to obtain
+feature and label `Tensor`s. Next, this method calls the `Estimator`'s
+`model_fn` in the passed mode to generate the model graph based on
+those features and labels, and restores the given checkpoint
+(or, lacking that, the most recent checkpoint) into the graph.
+Only one of the modes is used for saving variables to the `SavedModel`
+(order of preference: tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN,
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys.EVAL, then
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT), such that up to three
+`tf.MetaGraphDefs` are saved with a single set of variables in a single
+`SavedModel` directory.
+
+For the variables and `tf.MetaGraphDefs`, a timestamped export directory
+below
+`export_dir_base`, and writes a `SavedModel` into it containing
+the `tf.MetaGraphDef` for the given mode and its associated signatures.
+
+For prediction, the exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef`
+for each element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`,
+named using the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+For training and evaluation, the `train_op` is stored in an extra
+collection,
+and loss, metrics, and predictions are included in a `SignatureDef` for the
+mode in question.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`input_receiver_fn_map`
+ |
+
+dict of tf.estimator.ModeKeys to
+`input_receiver_fn` mappings, where the `input_receiver_fn` is a
+function that takes no arguments and returns the appropriate subclass of
+`InputReceiver`.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if any `input_receiver_fn` is `None`, no `export_outputs`
+are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+export_saved_model
+
+View source
+
+
+export_saved_model(
+ export_dir_base, serving_input_receiver_fn, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None, experimental_mode=ModeKeys.PREDICT
+)
+
+
+Exports inference graph as a `SavedModel` into the given dir.
+
+For a detailed guide, see
+[Using SavedModel with
+Estimators](https://tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model#using_savedmodel_with_estimators).
+
+This method builds a new graph by first calling the
+`serving_input_receiver_fn` to obtain feature `Tensor`s, and then calling
+this `Estimator`'s `model_fn` to generate the model graph based on those
+features. It restores the given checkpoint (or, lacking that, the most
+recent checkpoint) into this graph in a fresh session. Finally it creates
+a timestamped export directory below the given `export_dir_base`, and writes
+a `SavedModel` into it containing a single `tf.MetaGraphDef` saved from this
+session.
+
+The exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef` for each
+element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`, named
+using
+the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+The experimental_mode parameter can be used to export a single
+train/eval/predict graph as a `SavedModel`.
+See `experimental_export_all_saved_models` for full docs.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`serving_input_receiver_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that takes no argument and returns a
+tf.estimator.export.ServingInputReceiver or
+tf.estimator.export.TensorServingInputReceiver.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+|
+`experimental_mode`
+ |
+
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys value indicating with mode will
+be exported. Note that this feature is experimental.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if no `serving_input_receiver_fn` is provided, no
+`export_outputs` are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+export_savedmodel
+
+View source
+
+
+export_savedmodel(
+ export_dir_base, serving_input_receiver_fn, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None, strip_default_attrs=(False)
+)
+
+
+Exports inference graph as a `SavedModel` into the given dir. (deprecated)
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+This function has been renamed, use `export_saved_model` instead.
+
+For a detailed guide, see
+[Using SavedModel with
+Estimators](https://tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model#using_savedmodel_with_estimators).
+
+This method builds a new graph by first calling the
+`serving_input_receiver_fn` to obtain feature `Tensor`s, and then calling
+this `Estimator`'s `model_fn` to generate the model graph based on those
+features. It restores the given checkpoint (or, lacking that, the most
+recent checkpoint) into this graph in a fresh session. Finally it creates
+a timestamped export directory below the given `export_dir_base`, and writes
+a `SavedModel` into it containing a single `tf.MetaGraphDef` saved from this
+session.
+
+The exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef` for each
+element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`, named
+using
+the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`serving_input_receiver_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that takes no argument and returns a
+tf.estimator.export.ServingInputReceiver or
+tf.estimator.export.TensorServingInputReceiver.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+|
+`strip_default_attrs`
+ |
+
+Boolean. If `True`, default-valued attributes will be
+removed from the `NodeDef`s. For a detailed guide, see [Stripping
+Default-Valued Attributes](
+https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/master/tensorflow/python/saved_model/README.md#stripping-default-valued-attributes).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if no `serving_input_receiver_fn` is provided, no
+`export_outputs` are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+get_variable_names
+
+View source
+
+
+get_variable_names()
+
+
+Returns list of all variable names in this model.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+List of names.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `Estimator` has not produced a checkpoint yet.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+get_variable_value
+
+View source
+
+
+get_variable_value(
+ name
+)
+
+
+Returns value of the variable given by name.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+string or a list of string, name of the tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Numpy array - value of the tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `Estimator` has not produced a checkpoint yet.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+latest_checkpoint
+
+View source
+
+
+latest_checkpoint()
+
+
+Finds the filename of the latest saved checkpoint file in `model_dir`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The full path to the latest checkpoint or `None` if no checkpoint was
+found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+predict
+
+View source
+
+
+predict(
+ input_fn, predict_keys=None, hooks=None, checkpoint_path=None,
+ yield_single_examples=(True)
+)
+
+
+Yields predictions for given features.
+
+Please note that interleaving two predict outputs does not work. See:
+[issue/20506](
+https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/issues/20506#issuecomment-422208517)
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that constructs the features. Prediction continues
+until `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception
+(tf.errors.OutOfRangeError or `StopIteration`). See [Premade
+Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The function should construct and return one of
+the following:
+* tf.data.Dataset object -- Outputs of `Dataset` object must have
+same constraints as below.
+* features -- A tf.Tensor or a dictionary of string feature name to
+`Tensor`. features are consumed by `model_fn`. They should satisfy
+the expectation of `model_fn` from inputs. * A tuple, in which case
+the first item is extracted as features.
+ |
+
+|
+`predict_keys`
+ |
+
+list of `str`, name of the keys to predict. It is used if
+the tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec.predictions is a `dict`. If
+`predict_keys` is used then rest of the predictions will be filtered
+from the dictionary. If `None`, returns all.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the prediction call.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+Path of a specific checkpoint to predict. If `None`, the
+latest checkpoint in `model_dir` is used. If there are no checkpoints
+in `model_dir`, prediction is run with newly initialized `Variables`
+instead of ones restored from checkpoint.
+ |
+
+|
+`yield_single_examples`
+ |
+
+If `False`, yields the whole batch as returned by
+the `model_fn` instead of decomposing the batch into individual
+elements. This is useful if `model_fn` returns some tensors whose first
+dimension is not equal to the batch size.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Yields:
+
+Evaluated values of `predictions` tensors.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If batch length of predictions is not the same and
+`yield_single_examples` is `True`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If there is a conflict between `predict_keys` and
+`predictions`. For example if `predict_keys` is not `None` but
+tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec.predictions is not a `dict`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+train
+
+View source
+
+
+train(
+ input_fn, hooks=None, steps=None, max_steps=None, saving_listeners=None
+)
+
+
+Trains a model given training data `input_fn`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that provides input data for training as minibatches.
+See [Premade Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The function should construct and return one of
+the following:
+* A tf.data.Dataset object: Outputs of `Dataset` object must be a
+tuple `(features, labels)` with same constraints as below.
+* A tuple `(features, labels)`: Where `features` is a tf.Tensor or a
+dictionary of string feature name to `Tensor` and `labels` is a
+`Tensor` or a dictionary of string label name to `Tensor`. Both
+`features` and `labels` are consumed by `model_fn`. They should
+satisfy the expectation of `model_fn` from inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the training loop.
+ |
+
+|
+`steps`
+ |
+
+Number of steps for which to train the model. If `None`, train
+forever or train until `input_fn` generates the `tf.errors.OutOfRange`
+error or `StopIteration` exception. `steps` works incrementally. If you
+call two times `train(steps=10)` then training occurs in total 20 steps.
+If `OutOfRange` or `StopIteration` occurs in the middle, training stops
+before 20 steps. If you don't want to have incremental behavior please
+set `max_steps` instead. If set, `max_steps` must be `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_steps`
+ |
+
+Number of total steps for which to train model. If `None`,
+train forever or train until `input_fn` generates the
+`tf.errors.OutOfRange` error or `StopIteration` exception. If set,
+`steps` must be `None`. If `OutOfRange` or `StopIteration` occurs in the
+middle, training stops before `max_steps` steps. Two calls to
+`train(steps=100)` means 200 training iterations. On the other hand, two
+calls to `train(max_steps=100)` means that the second call will not do
+any iteration since first call did all 100 steps.
+ |
+
+|
+`saving_listeners`
+ |
+
+list of `CheckpointSaverListener` objects. Used for
+callbacks that run immediately before or after checkpoint savings.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`self`, for chaining.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If both `steps` and `max_steps` are not `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If either `steps` or `max_steps <= 0`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/DNNLinearCombinedEstimator.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/DNNLinearCombinedEstimator.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..b2a13d5741f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/DNNLinearCombinedEstimator.md
@@ -0,0 +1,1233 @@
+description: An estimator for TensorFlow Linear and DNN joined models with custom head.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.estimator.DNNLinearCombinedEstimator
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+An estimator for TensorFlow Linear and DNN joined models with custom head.
+
+Inherits From: [`Estimator`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/Estimator.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.estimator.DNNLinearCombinedEstimator(
+ head, model_dir=None, linear_feature_columns=None, linear_optimizer='Ftrl',
+ dnn_feature_columns=None, dnn_optimizer='Adagrad', dnn_hidden_units=None,
+ dnn_activation_fn=tf.nn.relu, dnn_dropout=None, input_layer_partitioner=None,
+ config=None, linear_sparse_combiner='sum'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Note: This estimator is also known as wide-n-deep.
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+numeric_feature = numeric_column(...)
+categorical_column_a = categorical_column_with_hash_bucket(...)
+categorical_column_b = categorical_column_with_hash_bucket(...)
+
+categorical_feature_a_x_categorical_feature_b = crossed_column(...)
+categorical_feature_a_emb = embedding_column(
+ categorical_column=categorical_feature_a, ...)
+categorical_feature_b_emb = embedding_column(
+ categorical_column=categorical_feature_b, ...)
+
+estimator = tf.estimator.DNNLinearCombinedEstimator(
+ head=tf.estimator.MultiLabelHead(n_classes=3),
+ # wide settings
+ linear_feature_columns=[categorical_feature_a_x_categorical_feature_b],
+ linear_optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Ftrl(...),
+ # deep settings
+ dnn_feature_columns=[
+ categorical_feature_a_emb, categorical_feature_b_emb,
+ numeric_feature],
+ dnn_hidden_units=[1000, 500, 100],
+ dnn_optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adagrad(...))
+
+# To apply L1 and L2 regularization, you can set dnn_optimizer to:
+tf.compat.v1.train.ProximalAdagradOptimizer(
+ learning_rate=0.1,
+ l1_regularization_strength=0.001,
+ l2_regularization_strength=0.001)
+# To apply learning rate decay, you can set dnn_optimizer to a callable:
+lambda: tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(
+ learning_rate=tf.compat.v1.train.exponential_decay(
+ learning_rate=0.1,
+ global_step=tf.compat.v1.train.get_global_step(),
+ decay_steps=10000,
+ decay_rate=0.96)
+# It is the same for linear_optimizer.
+
+# Input builders
+def input_fn_train:
+ # Returns tf.data.Dataset of (x, y) tuple where y represents label's class
+ # index.
+ pass
+def input_fn_eval:
+ # Returns tf.data.Dataset of (x, y) tuple where y represents label's class
+ # index.
+ pass
+def input_fn_predict:
+ # Returns tf.data.Dataset of (x, None) tuple.
+ pass
+estimator.train(input_fn=input_fn_train, steps=100)
+metrics = estimator.evaluate(input_fn=input_fn_eval, steps=10)
+predictions = estimator.predict(input_fn=input_fn_predict)
+```
+
+Input of `train` and `evaluate` should have following features,
+otherwise there will be a `KeyError`:
+
+* for each `column` in `dnn_feature_columns` + `linear_feature_columns`:
+ - if `column` is a `CategoricalColumn`, a feature with `key=column.name`
+ whose `value` is a `SparseTensor`.
+ - if `column` is a `WeightedCategoricalColumn`, two features: the first
+ with `key` the id column name, the second with `key` the weight column
+ name. Both features' `value` must be a `SparseTensor`.
+ - if `column` is a `DenseColumn`, a feature with `key=column.name`
+ whose `value` is a `Tensor`.
+
+Loss is calculated by using mean squared error.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`model_fn`
+ |
+
+Model function. Follows the signature:
+* `features` -- This is the first item returned from the `input_fn`
+passed to `train`, `evaluate`, and `predict`. This should be a
+single tf.Tensor or `dict` of same.
+* `labels` -- This is the second item returned from the `input_fn`
+passed to `train`, `evaluate`, and `predict`. This should be a
+single tf.Tensor or `dict` of same (for multi-head models). If
+mode is tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT, `labels=None` will be
+passed. If the `model_fn`'s signature does not accept `mode`, the
+`model_fn` must still be able to handle `labels=None`.
+* `mode` -- Optional. Specifies if this is training, evaluation or
+prediction. See tf.estimator.ModeKeys.
+`params` -- Optional `dict` of hyperparameters. Will receive what is
+passed to Estimator in `params` parameter. This allows to configure
+Estimators from hyper parameter tuning.
+* `config` -- Optional `estimator.RunConfig` object. Will receive what
+is passed to Estimator as its `config` parameter, or a default
+value. Allows setting up things in your `model_fn` based on
+configuration such as `num_ps_replicas`, or `model_dir`.
+* Returns -- tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec
+ |
+
+|
+`model_dir`
+ |
+
+Directory to save model parameters, graph and etc. This can
+also be used to load checkpoints from the directory into an estimator to
+continue training a previously saved model. If `PathLike` object, the
+path will be resolved. If `None`, the model_dir in `config` will be used
+if set. If both are set, they must be same. If both are `None`, a
+temporary directory will be used.
+ |
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+`estimator.RunConfig` configuration object.
+ |
+
+|
+`params`
+ |
+
+`dict` of hyper parameters that will be passed into `model_fn`.
+Keys are names of parameters, values are basic python types.
+ |
+
+|
+`warm_start_from`
+ |
+
+Optional string filepath to a checkpoint or SavedModel to
+warm-start from, or a tf.estimator.WarmStartSettings object to fully
+configure warm-starting. If None, only TRAINABLE variables are
+warm-started. If the string filepath is provided instead of a
+tf.estimator.WarmStartSettings, then all variables are warm-started,
+and it is assumed that vocabularies and tf.Tensor names are unchanged.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+parameters of `model_fn` don't match `params`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if this is called via a subclass and if that class overrides
+a member of `Estimator`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+Estimators can be used while eager execution is enabled. Note that `input_fn`
+and all hooks are executed inside a graph context, so they have to be written
+to be compatible with graph mode. Note that `input_fn` code using tf.data
+generally works in both graph and eager modes.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`model_dir`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`model_fn`
+ |
+
+Returns the `model_fn` which is bound to `self.params`.
+ |
+
+|
+`params`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+eval_dir
+
+View source
+
+
+eval_dir(
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+Shows the directory name where evaluation metrics are dumped.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of the evaluation if user needs to run multiple evaluations on
+different data sets, such as on training data vs test data. Metrics for
+different evaluations are saved in separate folders, and appear
+separately in tensorboard.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A string which is the path of directory contains evaluation metrics.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+evaluate
+
+View source
+
+
+evaluate(
+ input_fn, steps=None, hooks=None, checkpoint_path=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+Evaluates the model given evaluation data `input_fn`.
+
+For each step, calls `input_fn`, which returns one batch of data.
+Evaluates until:
+- `steps` batches are processed, or
+- `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception (tf.errors.OutOfRangeError
+or
+`StopIteration`).
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that constructs the input data for evaluation. See
+[Premade Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The
+function should construct and return one of the following: * A
+tf.data.Dataset object: Outputs of `Dataset` object must be a tuple
+`(features, labels)` with same constraints as below. * A tuple
+`(features, labels)`: Where `features` is a tf.Tensor or a dictionary
+of string feature name to `Tensor` and `labels` is a `Tensor` or a
+dictionary of string label name to `Tensor`. Both `features` and
+`labels` are consumed by `model_fn`. They should satisfy the
+expectation of `model_fn` from inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`steps`
+ |
+
+Number of steps for which to evaluate model. If `None`, evaluates
+until `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the evaluation call.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+Path of a specific checkpoint to evaluate. If `None`, the
+latest checkpoint in `model_dir` is used. If there are no checkpoints
+in `model_dir`, evaluation is run with newly initialized `Variables`
+instead of ones restored from checkpoint.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of the evaluation if user needs to run multiple evaluations on
+different data sets, such as on training data vs test data. Metrics for
+different evaluations are saved in separate folders, and appear
+separately in tensorboard.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A dict containing the evaluation metrics specified in `model_fn` keyed by
+name, as well as an entry `global_step` which contains the value of the
+global step for which this evaluation was performed. For canned
+estimators, the dict contains the `loss` (mean loss per mini-batch) and
+the `average_loss` (mean loss per sample). Canned classifiers also return
+the `accuracy`. Canned regressors also return the `label/mean` and the
+`prediction/mean`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `steps <= 0`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+experimental_export_all_saved_models
+
+View source
+
+
+experimental_export_all_saved_models(
+ export_dir_base, input_receiver_fn_map, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None
+)
+
+
+Exports a `SavedModel` with `tf.MetaGraphDefs` for each requested mode.
+
+For each mode passed in via the `input_receiver_fn_map`,
+this method builds a new graph by calling the `input_receiver_fn` to obtain
+feature and label `Tensor`s. Next, this method calls the `Estimator`'s
+`model_fn` in the passed mode to generate the model graph based on
+those features and labels, and restores the given checkpoint
+(or, lacking that, the most recent checkpoint) into the graph.
+Only one of the modes is used for saving variables to the `SavedModel`
+(order of preference: tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN,
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys.EVAL, then
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT), such that up to three
+`tf.MetaGraphDefs` are saved with a single set of variables in a single
+`SavedModel` directory.
+
+For the variables and `tf.MetaGraphDefs`, a timestamped export directory
+below
+`export_dir_base`, and writes a `SavedModel` into it containing
+the `tf.MetaGraphDef` for the given mode and its associated signatures.
+
+For prediction, the exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef`
+for each element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`,
+named using the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+For training and evaluation, the `train_op` is stored in an extra
+collection,
+and loss, metrics, and predictions are included in a `SignatureDef` for the
+mode in question.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`input_receiver_fn_map`
+ |
+
+dict of tf.estimator.ModeKeys to
+`input_receiver_fn` mappings, where the `input_receiver_fn` is a
+function that takes no arguments and returns the appropriate subclass of
+`InputReceiver`.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if any `input_receiver_fn` is `None`, no `export_outputs`
+are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+export_saved_model
+
+View source
+
+
+export_saved_model(
+ export_dir_base, serving_input_receiver_fn, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None, experimental_mode=ModeKeys.PREDICT
+)
+
+
+Exports inference graph as a `SavedModel` into the given dir.
+
+For a detailed guide, see
+[Using SavedModel with
+Estimators](https://tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model#using_savedmodel_with_estimators).
+
+This method builds a new graph by first calling the
+`serving_input_receiver_fn` to obtain feature `Tensor`s, and then calling
+this `Estimator`'s `model_fn` to generate the model graph based on those
+features. It restores the given checkpoint (or, lacking that, the most
+recent checkpoint) into this graph in a fresh session. Finally it creates
+a timestamped export directory below the given `export_dir_base`, and writes
+a `SavedModel` into it containing a single `tf.MetaGraphDef` saved from this
+session.
+
+The exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef` for each
+element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`, named
+using
+the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+The experimental_mode parameter can be used to export a single
+train/eval/predict graph as a `SavedModel`.
+See `experimental_export_all_saved_models` for full docs.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`serving_input_receiver_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that takes no argument and returns a
+tf.estimator.export.ServingInputReceiver or
+tf.estimator.export.TensorServingInputReceiver.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+|
+`experimental_mode`
+ |
+
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys value indicating with mode will
+be exported. Note that this feature is experimental.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if no `serving_input_receiver_fn` is provided, no
+`export_outputs` are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+export_savedmodel
+
+View source
+
+
+export_savedmodel(
+ export_dir_base, serving_input_receiver_fn, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None, strip_default_attrs=(False)
+)
+
+
+Exports inference graph as a `SavedModel` into the given dir. (deprecated)
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+This function has been renamed, use `export_saved_model` instead.
+
+For a detailed guide, see
+[Using SavedModel with
+Estimators](https://tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model#using_savedmodel_with_estimators).
+
+This method builds a new graph by first calling the
+`serving_input_receiver_fn` to obtain feature `Tensor`s, and then calling
+this `Estimator`'s `model_fn` to generate the model graph based on those
+features. It restores the given checkpoint (or, lacking that, the most
+recent checkpoint) into this graph in a fresh session. Finally it creates
+a timestamped export directory below the given `export_dir_base`, and writes
+a `SavedModel` into it containing a single `tf.MetaGraphDef` saved from this
+session.
+
+The exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef` for each
+element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`, named
+using
+the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`serving_input_receiver_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that takes no argument and returns a
+tf.estimator.export.ServingInputReceiver or
+tf.estimator.export.TensorServingInputReceiver.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+|
+`strip_default_attrs`
+ |
+
+Boolean. If `True`, default-valued attributes will be
+removed from the `NodeDef`s. For a detailed guide, see [Stripping
+Default-Valued Attributes](
+https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/master/tensorflow/python/saved_model/README.md#stripping-default-valued-attributes).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if no `serving_input_receiver_fn` is provided, no
+`export_outputs` are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+get_variable_names
+
+View source
+
+
+get_variable_names()
+
+
+Returns list of all variable names in this model.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+List of names.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `Estimator` has not produced a checkpoint yet.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+get_variable_value
+
+View source
+
+
+get_variable_value(
+ name
+)
+
+
+Returns value of the variable given by name.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+string or a list of string, name of the tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Numpy array - value of the tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `Estimator` has not produced a checkpoint yet.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+latest_checkpoint
+
+View source
+
+
+latest_checkpoint()
+
+
+Finds the filename of the latest saved checkpoint file in `model_dir`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The full path to the latest checkpoint or `None` if no checkpoint was
+found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+predict
+
+View source
+
+
+predict(
+ input_fn, predict_keys=None, hooks=None, checkpoint_path=None,
+ yield_single_examples=(True)
+)
+
+
+Yields predictions for given features.
+
+Please note that interleaving two predict outputs does not work. See:
+[issue/20506](
+https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/issues/20506#issuecomment-422208517)
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that constructs the features. Prediction continues
+until `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception
+(tf.errors.OutOfRangeError or `StopIteration`). See [Premade
+Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The function should construct and return one of
+the following:
+* tf.data.Dataset object -- Outputs of `Dataset` object must have
+same constraints as below.
+* features -- A tf.Tensor or a dictionary of string feature name to
+`Tensor`. features are consumed by `model_fn`. They should satisfy
+the expectation of `model_fn` from inputs. * A tuple, in which case
+the first item is extracted as features.
+ |
+
+|
+`predict_keys`
+ |
+
+list of `str`, name of the keys to predict. It is used if
+the tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec.predictions is a `dict`. If
+`predict_keys` is used then rest of the predictions will be filtered
+from the dictionary. If `None`, returns all.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the prediction call.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+Path of a specific checkpoint to predict. If `None`, the
+latest checkpoint in `model_dir` is used. If there are no checkpoints
+in `model_dir`, prediction is run with newly initialized `Variables`
+instead of ones restored from checkpoint.
+ |
+
+|
+`yield_single_examples`
+ |
+
+If `False`, yields the whole batch as returned by
+the `model_fn` instead of decomposing the batch into individual
+elements. This is useful if `model_fn` returns some tensors whose first
+dimension is not equal to the batch size.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Yields:
+
+Evaluated values of `predictions` tensors.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If batch length of predictions is not the same and
+`yield_single_examples` is `True`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If there is a conflict between `predict_keys` and
+`predictions`. For example if `predict_keys` is not `None` but
+tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec.predictions is not a `dict`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+train
+
+View source
+
+
+train(
+ input_fn, hooks=None, steps=None, max_steps=None, saving_listeners=None
+)
+
+
+Trains a model given training data `input_fn`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that provides input data for training as minibatches.
+See [Premade Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The function should construct and return one of
+the following:
+* A tf.data.Dataset object: Outputs of `Dataset` object must be a
+tuple `(features, labels)` with same constraints as below.
+* A tuple `(features, labels)`: Where `features` is a tf.Tensor or a
+dictionary of string feature name to `Tensor` and `labels` is a
+`Tensor` or a dictionary of string label name to `Tensor`. Both
+`features` and `labels` are consumed by `model_fn`. They should
+satisfy the expectation of `model_fn` from inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the training loop.
+ |
+
+|
+`steps`
+ |
+
+Number of steps for which to train the model. If `None`, train
+forever or train until `input_fn` generates the `tf.errors.OutOfRange`
+error or `StopIteration` exception. `steps` works incrementally. If you
+call two times `train(steps=10)` then training occurs in total 20 steps.
+If `OutOfRange` or `StopIteration` occurs in the middle, training stops
+before 20 steps. If you don't want to have incremental behavior please
+set `max_steps` instead. If set, `max_steps` must be `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_steps`
+ |
+
+Number of total steps for which to train model. If `None`,
+train forever or train until `input_fn` generates the
+`tf.errors.OutOfRange` error or `StopIteration` exception. If set,
+`steps` must be `None`. If `OutOfRange` or `StopIteration` occurs in the
+middle, training stops before `max_steps` steps. Two calls to
+`train(steps=100)` means 200 training iterations. On the other hand, two
+calls to `train(max_steps=100)` means that the second call will not do
+any iteration since first call did all 100 steps.
+ |
+
+|
+`saving_listeners`
+ |
+
+list of `CheckpointSaverListener` objects. Used for
+callbacks that run immediately before or after checkpoint savings.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`self`, for chaining.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If both `steps` and `max_steps` are not `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If either `steps` or `max_steps <= 0`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/DNNLinearCombinedRegressor.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/DNNLinearCombinedRegressor.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..369aa3408a8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/DNNLinearCombinedRegressor.md
@@ -0,0 +1,1236 @@
+description: An estimator for TensorFlow Linear and DNN joined models for regression.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.estimator.DNNLinearCombinedRegressor
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+An estimator for TensorFlow Linear and DNN joined models for regression.
+
+Inherits From: [`Estimator`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/Estimator.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.estimator.DNNLinearCombinedRegressor(
+ model_dir=None, linear_feature_columns=None, linear_optimizer='Ftrl',
+ dnn_feature_columns=None, dnn_optimizer='Adagrad', dnn_hidden_units=None,
+ dnn_activation_fn=tf.nn.relu, dnn_dropout=None, label_dimension=1,
+ weight_column=None, input_layer_partitioner=None, config=None,
+ warm_start_from=None, loss_reduction=tf.compat.v1.losses.Reduction.SUM,
+ batch_norm=(False), linear_sparse_combiner='sum'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Note: This estimator is also known as wide-n-deep.
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+numeric_feature = numeric_column(...)
+categorical_column_a = categorical_column_with_hash_bucket(...)
+categorical_column_b = categorical_column_with_hash_bucket(...)
+
+categorical_feature_a_x_categorical_feature_b = crossed_column(...)
+categorical_feature_a_emb = embedding_column(
+ categorical_column=categorical_feature_a, ...)
+categorical_feature_b_emb = embedding_column(
+ categorical_column=categorical_feature_b, ...)
+
+estimator = tf.estimator.DNNLinearCombinedRegressor(
+ # wide settings
+ linear_feature_columns=[categorical_feature_a_x_categorical_feature_b],
+ linear_optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Ftrl(...),
+ # deep settings
+ dnn_feature_columns=[
+ categorical_feature_a_emb, categorical_feature_b_emb,
+ numeric_feature],
+ dnn_hidden_units=[1000, 500, 100],
+ dnn_optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adagrad(...),
+ # warm-start settings
+ warm_start_from="/path/to/checkpoint/dir")
+
+# To apply L1 and L2 regularization, you can set dnn_optimizer to:
+tf.compat.v1.train.ProximalAdagradOptimizer(
+ learning_rate=0.1,
+ l1_regularization_strength=0.001,
+ l2_regularization_strength=0.001)
+# To apply learning rate decay, you can set dnn_optimizer to a callable:
+lambda: tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(
+ learning_rate=tf.compat.v1.train.exponential_decay(
+ learning_rate=0.1,
+ global_step=tf.compat.v1.train.get_global_step(),
+ decay_steps=10000,
+ decay_rate=0.96)
+# It is the same for linear_optimizer.
+
+# Input builders
+def input_fn_train:
+ # Returns tf.data.Dataset of (x, y) tuple where y represents label's class
+ # index.
+ pass
+def input_fn_eval:
+ # Returns tf.data.Dataset of (x, y) tuple where y represents label's class
+ # index.
+ pass
+def input_fn_predict:
+ # Returns tf.data.Dataset of (x, None) tuple.
+ pass
+estimator.train(input_fn=input_fn_train, steps=100)
+metrics = estimator.evaluate(input_fn=input_fn_eval, steps=10)
+predictions = estimator.predict(input_fn=input_fn_predict)
+```
+
+Input of `train` and `evaluate` should have following features,
+otherwise there will be a `KeyError`:
+
+* for each `column` in `dnn_feature_columns` + `linear_feature_columns`:
+ - if `column` is a `CategoricalColumn`, a feature with `key=column.name`
+ whose `value` is a `SparseTensor`.
+ - if `column` is a `WeightedCategoricalColumn`, two features: the first
+ with `key` the id column name, the second with `key` the weight column
+ name. Both features' `value` must be a `SparseTensor`.
+ - if `column` is a `DenseColumn`, a feature with `key=column.name`
+ whose `value` is a `Tensor`.
+
+Loss is calculated by using mean squared error.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`model_fn`
+ |
+
+Model function. Follows the signature:
+* `features` -- This is the first item returned from the `input_fn`
+passed to `train`, `evaluate`, and `predict`. This should be a
+single tf.Tensor or `dict` of same.
+* `labels` -- This is the second item returned from the `input_fn`
+passed to `train`, `evaluate`, and `predict`. This should be a
+single tf.Tensor or `dict` of same (for multi-head models). If
+mode is tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT, `labels=None` will be
+passed. If the `model_fn`'s signature does not accept `mode`, the
+`model_fn` must still be able to handle `labels=None`.
+* `mode` -- Optional. Specifies if this is training, evaluation or
+prediction. See tf.estimator.ModeKeys.
+`params` -- Optional `dict` of hyperparameters. Will receive what is
+passed to Estimator in `params` parameter. This allows to configure
+Estimators from hyper parameter tuning.
+* `config` -- Optional `estimator.RunConfig` object. Will receive what
+is passed to Estimator as its `config` parameter, or a default
+value. Allows setting up things in your `model_fn` based on
+configuration such as `num_ps_replicas`, or `model_dir`.
+* Returns -- tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec
+ |
+
+|
+`model_dir`
+ |
+
+Directory to save model parameters, graph and etc. This can
+also be used to load checkpoints from the directory into an estimator to
+continue training a previously saved model. If `PathLike` object, the
+path will be resolved. If `None`, the model_dir in `config` will be used
+if set. If both are set, they must be same. If both are `None`, a
+temporary directory will be used.
+ |
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+`estimator.RunConfig` configuration object.
+ |
+
+|
+`params`
+ |
+
+`dict` of hyper parameters that will be passed into `model_fn`.
+Keys are names of parameters, values are basic python types.
+ |
+
+|
+`warm_start_from`
+ |
+
+Optional string filepath to a checkpoint or SavedModel to
+warm-start from, or a tf.estimator.WarmStartSettings object to fully
+configure warm-starting. If None, only TRAINABLE variables are
+warm-started. If the string filepath is provided instead of a
+tf.estimator.WarmStartSettings, then all variables are warm-started,
+and it is assumed that vocabularies and tf.Tensor names are unchanged.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+parameters of `model_fn` don't match `params`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if this is called via a subclass and if that class overrides
+a member of `Estimator`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+Estimators can be used while eager execution is enabled. Note that `input_fn`
+and all hooks are executed inside a graph context, so they have to be written
+to be compatible with graph mode. Note that `input_fn` code using tf.data
+generally works in both graph and eager modes.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`model_dir`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`model_fn`
+ |
+
+Returns the `model_fn` which is bound to `self.params`.
+ |
+
+|
+`params`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+eval_dir
+
+View source
+
+
+eval_dir(
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+Shows the directory name where evaluation metrics are dumped.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of the evaluation if user needs to run multiple evaluations on
+different data sets, such as on training data vs test data. Metrics for
+different evaluations are saved in separate folders, and appear
+separately in tensorboard.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A string which is the path of directory contains evaluation metrics.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+evaluate
+
+View source
+
+
+evaluate(
+ input_fn, steps=None, hooks=None, checkpoint_path=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+Evaluates the model given evaluation data `input_fn`.
+
+For each step, calls `input_fn`, which returns one batch of data.
+Evaluates until:
+- `steps` batches are processed, or
+- `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception (tf.errors.OutOfRangeError
+or
+`StopIteration`).
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that constructs the input data for evaluation. See
+[Premade Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The
+function should construct and return one of the following: * A
+tf.data.Dataset object: Outputs of `Dataset` object must be a tuple
+`(features, labels)` with same constraints as below. * A tuple
+`(features, labels)`: Where `features` is a tf.Tensor or a dictionary
+of string feature name to `Tensor` and `labels` is a `Tensor` or a
+dictionary of string label name to `Tensor`. Both `features` and
+`labels` are consumed by `model_fn`. They should satisfy the
+expectation of `model_fn` from inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`steps`
+ |
+
+Number of steps for which to evaluate model. If `None`, evaluates
+until `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the evaluation call.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+Path of a specific checkpoint to evaluate. If `None`, the
+latest checkpoint in `model_dir` is used. If there are no checkpoints
+in `model_dir`, evaluation is run with newly initialized `Variables`
+instead of ones restored from checkpoint.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of the evaluation if user needs to run multiple evaluations on
+different data sets, such as on training data vs test data. Metrics for
+different evaluations are saved in separate folders, and appear
+separately in tensorboard.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A dict containing the evaluation metrics specified in `model_fn` keyed by
+name, as well as an entry `global_step` which contains the value of the
+global step for which this evaluation was performed. For canned
+estimators, the dict contains the `loss` (mean loss per mini-batch) and
+the `average_loss` (mean loss per sample). Canned classifiers also return
+the `accuracy`. Canned regressors also return the `label/mean` and the
+`prediction/mean`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `steps <= 0`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+experimental_export_all_saved_models
+
+View source
+
+
+experimental_export_all_saved_models(
+ export_dir_base, input_receiver_fn_map, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None
+)
+
+
+Exports a `SavedModel` with `tf.MetaGraphDefs` for each requested mode.
+
+For each mode passed in via the `input_receiver_fn_map`,
+this method builds a new graph by calling the `input_receiver_fn` to obtain
+feature and label `Tensor`s. Next, this method calls the `Estimator`'s
+`model_fn` in the passed mode to generate the model graph based on
+those features and labels, and restores the given checkpoint
+(or, lacking that, the most recent checkpoint) into the graph.
+Only one of the modes is used for saving variables to the `SavedModel`
+(order of preference: tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN,
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys.EVAL, then
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT), such that up to three
+`tf.MetaGraphDefs` are saved with a single set of variables in a single
+`SavedModel` directory.
+
+For the variables and `tf.MetaGraphDefs`, a timestamped export directory
+below
+`export_dir_base`, and writes a `SavedModel` into it containing
+the `tf.MetaGraphDef` for the given mode and its associated signatures.
+
+For prediction, the exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef`
+for each element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`,
+named using the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+For training and evaluation, the `train_op` is stored in an extra
+collection,
+and loss, metrics, and predictions are included in a `SignatureDef` for the
+mode in question.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`input_receiver_fn_map`
+ |
+
+dict of tf.estimator.ModeKeys to
+`input_receiver_fn` mappings, where the `input_receiver_fn` is a
+function that takes no arguments and returns the appropriate subclass of
+`InputReceiver`.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if any `input_receiver_fn` is `None`, no `export_outputs`
+are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+export_saved_model
+
+View source
+
+
+export_saved_model(
+ export_dir_base, serving_input_receiver_fn, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None, experimental_mode=ModeKeys.PREDICT
+)
+
+
+Exports inference graph as a `SavedModel` into the given dir.
+
+For a detailed guide, see
+[Using SavedModel with
+Estimators](https://tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model#using_savedmodel_with_estimators).
+
+This method builds a new graph by first calling the
+`serving_input_receiver_fn` to obtain feature `Tensor`s, and then calling
+this `Estimator`'s `model_fn` to generate the model graph based on those
+features. It restores the given checkpoint (or, lacking that, the most
+recent checkpoint) into this graph in a fresh session. Finally it creates
+a timestamped export directory below the given `export_dir_base`, and writes
+a `SavedModel` into it containing a single `tf.MetaGraphDef` saved from this
+session.
+
+The exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef` for each
+element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`, named
+using
+the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+The experimental_mode parameter can be used to export a single
+train/eval/predict graph as a `SavedModel`.
+See `experimental_export_all_saved_models` for full docs.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`serving_input_receiver_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that takes no argument and returns a
+tf.estimator.export.ServingInputReceiver or
+tf.estimator.export.TensorServingInputReceiver.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+|
+`experimental_mode`
+ |
+
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys value indicating with mode will
+be exported. Note that this feature is experimental.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if no `serving_input_receiver_fn` is provided, no
+`export_outputs` are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+export_savedmodel
+
+View source
+
+
+export_savedmodel(
+ export_dir_base, serving_input_receiver_fn, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None, strip_default_attrs=(False)
+)
+
+
+Exports inference graph as a `SavedModel` into the given dir. (deprecated)
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+This function has been renamed, use `export_saved_model` instead.
+
+For a detailed guide, see
+[Using SavedModel with
+Estimators](https://tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model#using_savedmodel_with_estimators).
+
+This method builds a new graph by first calling the
+`serving_input_receiver_fn` to obtain feature `Tensor`s, and then calling
+this `Estimator`'s `model_fn` to generate the model graph based on those
+features. It restores the given checkpoint (or, lacking that, the most
+recent checkpoint) into this graph in a fresh session. Finally it creates
+a timestamped export directory below the given `export_dir_base`, and writes
+a `SavedModel` into it containing a single `tf.MetaGraphDef` saved from this
+session.
+
+The exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef` for each
+element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`, named
+using
+the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`serving_input_receiver_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that takes no argument and returns a
+tf.estimator.export.ServingInputReceiver or
+tf.estimator.export.TensorServingInputReceiver.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+|
+`strip_default_attrs`
+ |
+
+Boolean. If `True`, default-valued attributes will be
+removed from the `NodeDef`s. For a detailed guide, see [Stripping
+Default-Valued Attributes](
+https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/master/tensorflow/python/saved_model/README.md#stripping-default-valued-attributes).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if no `serving_input_receiver_fn` is provided, no
+`export_outputs` are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+get_variable_names
+
+View source
+
+
+get_variable_names()
+
+
+Returns list of all variable names in this model.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+List of names.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `Estimator` has not produced a checkpoint yet.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+get_variable_value
+
+View source
+
+
+get_variable_value(
+ name
+)
+
+
+Returns value of the variable given by name.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+string or a list of string, name of the tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Numpy array - value of the tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `Estimator` has not produced a checkpoint yet.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+latest_checkpoint
+
+View source
+
+
+latest_checkpoint()
+
+
+Finds the filename of the latest saved checkpoint file in `model_dir`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The full path to the latest checkpoint or `None` if no checkpoint was
+found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+predict
+
+View source
+
+
+predict(
+ input_fn, predict_keys=None, hooks=None, checkpoint_path=None,
+ yield_single_examples=(True)
+)
+
+
+Yields predictions for given features.
+
+Please note that interleaving two predict outputs does not work. See:
+[issue/20506](
+https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/issues/20506#issuecomment-422208517)
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that constructs the features. Prediction continues
+until `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception
+(tf.errors.OutOfRangeError or `StopIteration`). See [Premade
+Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The function should construct and return one of
+the following:
+* tf.data.Dataset object -- Outputs of `Dataset` object must have
+same constraints as below.
+* features -- A tf.Tensor or a dictionary of string feature name to
+`Tensor`. features are consumed by `model_fn`. They should satisfy
+the expectation of `model_fn` from inputs. * A tuple, in which case
+the first item is extracted as features.
+ |
+
+|
+`predict_keys`
+ |
+
+list of `str`, name of the keys to predict. It is used if
+the tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec.predictions is a `dict`. If
+`predict_keys` is used then rest of the predictions will be filtered
+from the dictionary. If `None`, returns all.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the prediction call.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+Path of a specific checkpoint to predict. If `None`, the
+latest checkpoint in `model_dir` is used. If there are no checkpoints
+in `model_dir`, prediction is run with newly initialized `Variables`
+instead of ones restored from checkpoint.
+ |
+
+|
+`yield_single_examples`
+ |
+
+If `False`, yields the whole batch as returned by
+the `model_fn` instead of decomposing the batch into individual
+elements. This is useful if `model_fn` returns some tensors whose first
+dimension is not equal to the batch size.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Yields:
+
+Evaluated values of `predictions` tensors.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If batch length of predictions is not the same and
+`yield_single_examples` is `True`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If there is a conflict between `predict_keys` and
+`predictions`. For example if `predict_keys` is not `None` but
+tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec.predictions is not a `dict`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+train
+
+View source
+
+
+train(
+ input_fn, hooks=None, steps=None, max_steps=None, saving_listeners=None
+)
+
+
+Trains a model given training data `input_fn`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that provides input data for training as minibatches.
+See [Premade Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The function should construct and return one of
+the following:
+* A tf.data.Dataset object: Outputs of `Dataset` object must be a
+tuple `(features, labels)` with same constraints as below.
+* A tuple `(features, labels)`: Where `features` is a tf.Tensor or a
+dictionary of string feature name to `Tensor` and `labels` is a
+`Tensor` or a dictionary of string label name to `Tensor`. Both
+`features` and `labels` are consumed by `model_fn`. They should
+satisfy the expectation of `model_fn` from inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the training loop.
+ |
+
+|
+`steps`
+ |
+
+Number of steps for which to train the model. If `None`, train
+forever or train until `input_fn` generates the `tf.errors.OutOfRange`
+error or `StopIteration` exception. `steps` works incrementally. If you
+call two times `train(steps=10)` then training occurs in total 20 steps.
+If `OutOfRange` or `StopIteration` occurs in the middle, training stops
+before 20 steps. If you don't want to have incremental behavior please
+set `max_steps` instead. If set, `max_steps` must be `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_steps`
+ |
+
+Number of total steps for which to train model. If `None`,
+train forever or train until `input_fn` generates the
+`tf.errors.OutOfRange` error or `StopIteration` exception. If set,
+`steps` must be `None`. If `OutOfRange` or `StopIteration` occurs in the
+middle, training stops before `max_steps` steps. Two calls to
+`train(steps=100)` means 200 training iterations. On the other hand, two
+calls to `train(max_steps=100)` means that the second call will not do
+any iteration since first call did all 100 steps.
+ |
+
+|
+`saving_listeners`
+ |
+
+list of `CheckpointSaverListener` objects. Used for
+callbacks that run immediately before or after checkpoint savings.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`self`, for chaining.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If both `steps` and `max_steps` are not `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If either `steps` or `max_steps <= 0`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/DNNRegressor.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/DNNRegressor.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..42eb0ef27cd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/DNNRegressor.md
@@ -0,0 +1,1237 @@
+description: A regressor for TensorFlow DNN models.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.estimator.DNNRegressor
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A regressor for TensorFlow DNN models.
+
+Inherits From: [`Estimator`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/Estimator.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.estimator.DNNRegressor(
+ hidden_units, feature_columns, model_dir=None, label_dimension=1,
+ weight_column=None, optimizer='Adagrad', activation_fn=tf.nn.relu, dropout=None,
+ input_layer_partitioner=None, config=None, warm_start_from=None,
+ loss_reduction=tf.compat.v1.losses.Reduction.SUM, batch_norm=(False)
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+categorical_feature_a = categorical_column_with_hash_bucket(...)
+categorical_feature_b = categorical_column_with_hash_bucket(...)
+
+categorical_feature_a_emb = embedding_column(
+ categorical_column=categorical_feature_a, ...)
+categorical_feature_b_emb = embedding_column(
+ categorical_column=categorical_feature_b, ...)
+
+estimator = tf.estimator.DNNRegressor(
+ feature_columns=[categorical_feature_a_emb, categorical_feature_b_emb],
+ hidden_units=[1024, 512, 256])
+
+# Or estimator using the ProximalAdagradOptimizer optimizer with
+# regularization.
+estimator = tf.estimator.DNNRegressor(
+ feature_columns=[categorical_feature_a_emb, categorical_feature_b_emb],
+ hidden_units=[1024, 512, 256],
+ optimizer=tf.compat.v1.train.ProximalAdagradOptimizer(
+ learning_rate=0.1,
+ l1_regularization_strength=0.001
+ ))
+
+# Or estimator using an optimizer with a learning rate decay.
+estimator = tf.estimator.DNNRegressor(
+ feature_columns=[categorical_feature_a_emb, categorical_feature_b_emb],
+ hidden_units=[1024, 512, 256],
+ optimizer=lambda: tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(
+ learning_rate=tf.compat.v1.train.exponential_decay(
+ learning_rate=0.1,
+ global_step=tf.compat.v1.train.get_global_step(),
+ decay_steps=10000,
+ decay_rate=0.96))
+
+# Or estimator with warm-starting from a previous checkpoint.
+estimator = tf.estimator.DNNRegressor(
+ feature_columns=[categorical_feature_a_emb, categorical_feature_b_emb],
+ hidden_units=[1024, 512, 256],
+ warm_start_from="/path/to/checkpoint/dir")
+
+# Input builders
+def input_fn_train:
+ # Returns tf.data.Dataset of (x, y) tuple where y represents label's class
+ # index.
+ pass
+def input_fn_eval:
+ # Returns tf.data.Dataset of (x, y) tuple where y represents label's class
+ # index.
+ pass
+def input_fn_predict:
+ # Returns tf.data.Dataset of (x, None) tuple.
+ pass
+estimator.train(input_fn=input_fn_train)
+metrics = estimator.evaluate(input_fn=input_fn_eval)
+predictions = estimator.predict(input_fn=input_fn_predict)
+```
+
+Input of `train` and `evaluate` should have following features,
+otherwise there will be a `KeyError`:
+
+* if `weight_column` is not `None`, a feature with `key=weight_column` whose
+ value is a `Tensor`.
+* for each `column` in `feature_columns`:
+ - if `column` is a `CategoricalColumn`, a feature with `key=column.name`
+ whose `value` is a `SparseTensor`.
+ - if `column` is a `WeightedCategoricalColumn`, two features: the first
+ with `key` the id column name, the second with `key` the weight column
+ name. Both features' `value` must be a `SparseTensor`.
+ - if `column` is a `DenseColumn`, a feature with `key=column.name`
+ whose `value` is a `Tensor`.
+
+Loss is calculated by using mean squared error.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`model_fn`
+ |
+
+Model function. Follows the signature:
+* `features` -- This is the first item returned from the `input_fn`
+passed to `train`, `evaluate`, and `predict`. This should be a
+single tf.Tensor or `dict` of same.
+* `labels` -- This is the second item returned from the `input_fn`
+passed to `train`, `evaluate`, and `predict`. This should be a
+single tf.Tensor or `dict` of same (for multi-head models). If
+mode is tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT, `labels=None` will be
+passed. If the `model_fn`'s signature does not accept `mode`, the
+`model_fn` must still be able to handle `labels=None`.
+* `mode` -- Optional. Specifies if this is training, evaluation or
+prediction. See tf.estimator.ModeKeys.
+`params` -- Optional `dict` of hyperparameters. Will receive what is
+passed to Estimator in `params` parameter. This allows to configure
+Estimators from hyper parameter tuning.
+* `config` -- Optional `estimator.RunConfig` object. Will receive what
+is passed to Estimator as its `config` parameter, or a default
+value. Allows setting up things in your `model_fn` based on
+configuration such as `num_ps_replicas`, or `model_dir`.
+* Returns -- tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec
+ |
+
+|
+`model_dir`
+ |
+
+Directory to save model parameters, graph and etc. This can
+also be used to load checkpoints from the directory into an estimator to
+continue training a previously saved model. If `PathLike` object, the
+path will be resolved. If `None`, the model_dir in `config` will be used
+if set. If both are set, they must be same. If both are `None`, a
+temporary directory will be used.
+ |
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+`estimator.RunConfig` configuration object.
+ |
+
+|
+`params`
+ |
+
+`dict` of hyper parameters that will be passed into `model_fn`.
+Keys are names of parameters, values are basic python types.
+ |
+
+|
+`warm_start_from`
+ |
+
+Optional string filepath to a checkpoint or SavedModel to
+warm-start from, or a tf.estimator.WarmStartSettings object to fully
+configure warm-starting. If None, only TRAINABLE variables are
+warm-started. If the string filepath is provided instead of a
+tf.estimator.WarmStartSettings, then all variables are warm-started,
+and it is assumed that vocabularies and tf.Tensor names are unchanged.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+parameters of `model_fn` don't match `params`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if this is called via a subclass and if that class overrides
+a member of `Estimator`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+Estimators can be used while eager execution is enabled. Note that `input_fn`
+and all hooks are executed inside a graph context, so they have to be written
+to be compatible with graph mode. Note that `input_fn` code using tf.data
+generally works in both graph and eager modes.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`model_dir`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`model_fn`
+ |
+
+Returns the `model_fn` which is bound to `self.params`.
+ |
+
+|
+`params`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+eval_dir
+
+View source
+
+
+eval_dir(
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+Shows the directory name where evaluation metrics are dumped.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of the evaluation if user needs to run multiple evaluations on
+different data sets, such as on training data vs test data. Metrics for
+different evaluations are saved in separate folders, and appear
+separately in tensorboard.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A string which is the path of directory contains evaluation metrics.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+evaluate
+
+View source
+
+
+evaluate(
+ input_fn, steps=None, hooks=None, checkpoint_path=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+Evaluates the model given evaluation data `input_fn`.
+
+For each step, calls `input_fn`, which returns one batch of data.
+Evaluates until:
+- `steps` batches are processed, or
+- `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception (tf.errors.OutOfRangeError
+or
+`StopIteration`).
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that constructs the input data for evaluation. See
+[Premade Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The
+function should construct and return one of the following: * A
+tf.data.Dataset object: Outputs of `Dataset` object must be a tuple
+`(features, labels)` with same constraints as below. * A tuple
+`(features, labels)`: Where `features` is a tf.Tensor or a dictionary
+of string feature name to `Tensor` and `labels` is a `Tensor` or a
+dictionary of string label name to `Tensor`. Both `features` and
+`labels` are consumed by `model_fn`. They should satisfy the
+expectation of `model_fn` from inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`steps`
+ |
+
+Number of steps for which to evaluate model. If `None`, evaluates
+until `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the evaluation call.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+Path of a specific checkpoint to evaluate. If `None`, the
+latest checkpoint in `model_dir` is used. If there are no checkpoints
+in `model_dir`, evaluation is run with newly initialized `Variables`
+instead of ones restored from checkpoint.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of the evaluation if user needs to run multiple evaluations on
+different data sets, such as on training data vs test data. Metrics for
+different evaluations are saved in separate folders, and appear
+separately in tensorboard.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A dict containing the evaluation metrics specified in `model_fn` keyed by
+name, as well as an entry `global_step` which contains the value of the
+global step for which this evaluation was performed. For canned
+estimators, the dict contains the `loss` (mean loss per mini-batch) and
+the `average_loss` (mean loss per sample). Canned classifiers also return
+the `accuracy`. Canned regressors also return the `label/mean` and the
+`prediction/mean`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `steps <= 0`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+experimental_export_all_saved_models
+
+View source
+
+
+experimental_export_all_saved_models(
+ export_dir_base, input_receiver_fn_map, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None
+)
+
+
+Exports a `SavedModel` with `tf.MetaGraphDefs` for each requested mode.
+
+For each mode passed in via the `input_receiver_fn_map`,
+this method builds a new graph by calling the `input_receiver_fn` to obtain
+feature and label `Tensor`s. Next, this method calls the `Estimator`'s
+`model_fn` in the passed mode to generate the model graph based on
+those features and labels, and restores the given checkpoint
+(or, lacking that, the most recent checkpoint) into the graph.
+Only one of the modes is used for saving variables to the `SavedModel`
+(order of preference: tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN,
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys.EVAL, then
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT), such that up to three
+`tf.MetaGraphDefs` are saved with a single set of variables in a single
+`SavedModel` directory.
+
+For the variables and `tf.MetaGraphDefs`, a timestamped export directory
+below
+`export_dir_base`, and writes a `SavedModel` into it containing
+the `tf.MetaGraphDef` for the given mode and its associated signatures.
+
+For prediction, the exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef`
+for each element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`,
+named using the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+For training and evaluation, the `train_op` is stored in an extra
+collection,
+and loss, metrics, and predictions are included in a `SignatureDef` for the
+mode in question.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`input_receiver_fn_map`
+ |
+
+dict of tf.estimator.ModeKeys to
+`input_receiver_fn` mappings, where the `input_receiver_fn` is a
+function that takes no arguments and returns the appropriate subclass of
+`InputReceiver`.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if any `input_receiver_fn` is `None`, no `export_outputs`
+are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+export_saved_model
+
+View source
+
+
+export_saved_model(
+ export_dir_base, serving_input_receiver_fn, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None, experimental_mode=ModeKeys.PREDICT
+)
+
+
+Exports inference graph as a `SavedModel` into the given dir.
+
+For a detailed guide, see
+[Using SavedModel with
+Estimators](https://tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model#using_savedmodel_with_estimators).
+
+This method builds a new graph by first calling the
+`serving_input_receiver_fn` to obtain feature `Tensor`s, and then calling
+this `Estimator`'s `model_fn` to generate the model graph based on those
+features. It restores the given checkpoint (or, lacking that, the most
+recent checkpoint) into this graph in a fresh session. Finally it creates
+a timestamped export directory below the given `export_dir_base`, and writes
+a `SavedModel` into it containing a single `tf.MetaGraphDef` saved from this
+session.
+
+The exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef` for each
+element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`, named
+using
+the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+The experimental_mode parameter can be used to export a single
+train/eval/predict graph as a `SavedModel`.
+See `experimental_export_all_saved_models` for full docs.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`serving_input_receiver_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that takes no argument and returns a
+tf.estimator.export.ServingInputReceiver or
+tf.estimator.export.TensorServingInputReceiver.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+|
+`experimental_mode`
+ |
+
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys value indicating with mode will
+be exported. Note that this feature is experimental.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if no `serving_input_receiver_fn` is provided, no
+`export_outputs` are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+export_savedmodel
+
+View source
+
+
+export_savedmodel(
+ export_dir_base, serving_input_receiver_fn, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None, strip_default_attrs=(False)
+)
+
+
+Exports inference graph as a `SavedModel` into the given dir. (deprecated)
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+This function has been renamed, use `export_saved_model` instead.
+
+For a detailed guide, see
+[Using SavedModel with
+Estimators](https://tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model#using_savedmodel_with_estimators).
+
+This method builds a new graph by first calling the
+`serving_input_receiver_fn` to obtain feature `Tensor`s, and then calling
+this `Estimator`'s `model_fn` to generate the model graph based on those
+features. It restores the given checkpoint (or, lacking that, the most
+recent checkpoint) into this graph in a fresh session. Finally it creates
+a timestamped export directory below the given `export_dir_base`, and writes
+a `SavedModel` into it containing a single `tf.MetaGraphDef` saved from this
+session.
+
+The exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef` for each
+element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`, named
+using
+the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`serving_input_receiver_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that takes no argument and returns a
+tf.estimator.export.ServingInputReceiver or
+tf.estimator.export.TensorServingInputReceiver.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+|
+`strip_default_attrs`
+ |
+
+Boolean. If `True`, default-valued attributes will be
+removed from the `NodeDef`s. For a detailed guide, see [Stripping
+Default-Valued Attributes](
+https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/master/tensorflow/python/saved_model/README.md#stripping-default-valued-attributes).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if no `serving_input_receiver_fn` is provided, no
+`export_outputs` are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+get_variable_names
+
+View source
+
+
+get_variable_names()
+
+
+Returns list of all variable names in this model.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+List of names.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `Estimator` has not produced a checkpoint yet.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+get_variable_value
+
+View source
+
+
+get_variable_value(
+ name
+)
+
+
+Returns value of the variable given by name.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+string or a list of string, name of the tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Numpy array - value of the tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `Estimator` has not produced a checkpoint yet.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+latest_checkpoint
+
+View source
+
+
+latest_checkpoint()
+
+
+Finds the filename of the latest saved checkpoint file in `model_dir`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The full path to the latest checkpoint or `None` if no checkpoint was
+found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+predict
+
+View source
+
+
+predict(
+ input_fn, predict_keys=None, hooks=None, checkpoint_path=None,
+ yield_single_examples=(True)
+)
+
+
+Yields predictions for given features.
+
+Please note that interleaving two predict outputs does not work. See:
+[issue/20506](
+https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/issues/20506#issuecomment-422208517)
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that constructs the features. Prediction continues
+until `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception
+(tf.errors.OutOfRangeError or `StopIteration`). See [Premade
+Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The function should construct and return one of
+the following:
+* tf.data.Dataset object -- Outputs of `Dataset` object must have
+same constraints as below.
+* features -- A tf.Tensor or a dictionary of string feature name to
+`Tensor`. features are consumed by `model_fn`. They should satisfy
+the expectation of `model_fn` from inputs. * A tuple, in which case
+the first item is extracted as features.
+ |
+
+|
+`predict_keys`
+ |
+
+list of `str`, name of the keys to predict. It is used if
+the tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec.predictions is a `dict`. If
+`predict_keys` is used then rest of the predictions will be filtered
+from the dictionary. If `None`, returns all.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the prediction call.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+Path of a specific checkpoint to predict. If `None`, the
+latest checkpoint in `model_dir` is used. If there are no checkpoints
+in `model_dir`, prediction is run with newly initialized `Variables`
+instead of ones restored from checkpoint.
+ |
+
+|
+`yield_single_examples`
+ |
+
+If `False`, yields the whole batch as returned by
+the `model_fn` instead of decomposing the batch into individual
+elements. This is useful if `model_fn` returns some tensors whose first
+dimension is not equal to the batch size.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Yields:
+
+Evaluated values of `predictions` tensors.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If batch length of predictions is not the same and
+`yield_single_examples` is `True`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If there is a conflict between `predict_keys` and
+`predictions`. For example if `predict_keys` is not `None` but
+tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec.predictions is not a `dict`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+train
+
+View source
+
+
+train(
+ input_fn, hooks=None, steps=None, max_steps=None, saving_listeners=None
+)
+
+
+Trains a model given training data `input_fn`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that provides input data for training as minibatches.
+See [Premade Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The function should construct and return one of
+the following:
+* A tf.data.Dataset object: Outputs of `Dataset` object must be a
+tuple `(features, labels)` with same constraints as below.
+* A tuple `(features, labels)`: Where `features` is a tf.Tensor or a
+dictionary of string feature name to `Tensor` and `labels` is a
+`Tensor` or a dictionary of string label name to `Tensor`. Both
+`features` and `labels` are consumed by `model_fn`. They should
+satisfy the expectation of `model_fn` from inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the training loop.
+ |
+
+|
+`steps`
+ |
+
+Number of steps for which to train the model. If `None`, train
+forever or train until `input_fn` generates the `tf.errors.OutOfRange`
+error or `StopIteration` exception. `steps` works incrementally. If you
+call two times `train(steps=10)` then training occurs in total 20 steps.
+If `OutOfRange` or `StopIteration` occurs in the middle, training stops
+before 20 steps. If you don't want to have incremental behavior please
+set `max_steps` instead. If set, `max_steps` must be `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_steps`
+ |
+
+Number of total steps for which to train model. If `None`,
+train forever or train until `input_fn` generates the
+`tf.errors.OutOfRange` error or `StopIteration` exception. If set,
+`steps` must be `None`. If `OutOfRange` or `StopIteration` occurs in the
+middle, training stops before `max_steps` steps. Two calls to
+`train(steps=100)` means 200 training iterations. On the other hand, two
+calls to `train(max_steps=100)` means that the second call will not do
+any iteration since first call did all 100 steps.
+ |
+
+|
+`saving_listeners`
+ |
+
+list of `CheckpointSaverListener` objects. Used for
+callbacks that run immediately before or after checkpoint savings.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`self`, for chaining.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If both `steps` and `max_steps` are not `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If either `steps` or `max_steps <= 0`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/Estimator.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/Estimator.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..1a7e54d1ea5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/Estimator.md
@@ -0,0 +1,1199 @@
+description: Estimator class to train and evaluate TensorFlow models.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.estimator.Estimator
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Estimator class to train and evaluate TensorFlow models.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.estimator.Estimator(
+ model_fn, model_dir=None, config=None, params=None, warm_start_from=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The `Estimator` object wraps a model which is specified by a `model_fn`,
+which, given inputs and a number of other parameters, returns the ops
+necessary to perform training, evaluation, or predictions.
+
+All outputs (checkpoints, event files, etc.) are written to `model_dir`, or a
+subdirectory thereof. If `model_dir` is not set, a temporary directory is
+used.
+
+The `config` argument can be passed tf.estimator.RunConfig object containing
+information about the execution environment. It is passed on to the
+`model_fn`, if the `model_fn` has a parameter named "config" (and input
+functions in the same manner). If the `config` parameter is not passed, it is
+instantiated by the `Estimator`. Not passing config means that defaults useful
+for local execution are used. `Estimator` makes config available to the model
+(for instance, to allow specialization based on the number of workers
+available), and also uses some of its fields to control internals, especially
+regarding checkpointing.
+
+The `params` argument contains hyperparameters. It is passed to the
+`model_fn`, if the `model_fn` has a parameter named "params", and to the input
+functions in the same manner. `Estimator` only passes params along, it does
+not inspect it. The structure of `params` is therefore entirely up to the
+developer.
+
+None of `Estimator`'s methods can be overridden in subclasses (its
+constructor enforces this). Subclasses should use `model_fn` to configure
+the base class, and may add methods implementing specialized functionality.
+
+See [estimators](https://tensorflow.org/guide/estimators) for more
+ information.
+
+To warm-start an `Estimator`:
+
+```python
+estimator = tf.estimator.DNNClassifier(
+ feature_columns=[categorical_feature_a_emb, categorical_feature_b_emb],
+ hidden_units=[1024, 512, 256],
+ warm_start_from="/path/to/checkpoint/dir")
+```
+
+For more details on warm-start configuration, see
+tf.estimator.WarmStartSettings.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`model_fn`
+ |
+
+Model function. Follows the signature:
+* `features` -- This is the first item returned from the `input_fn`
+passed to `train`, `evaluate`, and `predict`. This should be a
+single tf.Tensor or `dict` of same.
+* `labels` -- This is the second item returned from the `input_fn`
+passed to `train`, `evaluate`, and `predict`. This should be a
+single tf.Tensor or `dict` of same (for multi-head models). If
+mode is tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT, `labels=None` will be
+passed. If the `model_fn`'s signature does not accept `mode`, the
+`model_fn` must still be able to handle `labels=None`.
+* `mode` -- Optional. Specifies if this is training, evaluation or
+prediction. See tf.estimator.ModeKeys.
+`params` -- Optional `dict` of hyperparameters. Will receive what is
+passed to Estimator in `params` parameter. This allows to configure
+Estimators from hyper parameter tuning.
+* `config` -- Optional `estimator.RunConfig` object. Will receive what
+is passed to Estimator as its `config` parameter, or a default
+value. Allows setting up things in your `model_fn` based on
+configuration such as `num_ps_replicas`, or `model_dir`.
+* Returns -- tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec
+ |
+
+|
+`model_dir`
+ |
+
+Directory to save model parameters, graph and etc. This can
+also be used to load checkpoints from the directory into an estimator to
+continue training a previously saved model. If `PathLike` object, the
+path will be resolved. If `None`, the model_dir in `config` will be used
+if set. If both are set, they must be same. If both are `None`, a
+temporary directory will be used.
+ |
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+`estimator.RunConfig` configuration object.
+ |
+
+|
+`params`
+ |
+
+`dict` of hyper parameters that will be passed into `model_fn`.
+Keys are names of parameters, values are basic python types.
+ |
+
+|
+`warm_start_from`
+ |
+
+Optional string filepath to a checkpoint or SavedModel to
+warm-start from, or a tf.estimator.WarmStartSettings object to fully
+configure warm-starting. If None, only TRAINABLE variables are
+warm-started. If the string filepath is provided instead of a
+tf.estimator.WarmStartSettings, then all variables are warm-started,
+and it is assumed that vocabularies and tf.Tensor names are unchanged.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+parameters of `model_fn` don't match `params`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if this is called via a subclass and if that class overrides
+a member of `Estimator`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+Calling methods of `Estimator` will work while eager execution is enabled.
+However, the `model_fn` and `input_fn` is not executed eagerly, `Estimator`
+will switch to graph mode before calling all user-provided functions (incl.
+hooks), so their code has to be compatible with graph mode execution. Note
+that `input_fn` code using tf.data generally works in both graph and eager
+modes.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`model_dir`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`model_fn`
+ |
+
+Returns the `model_fn` which is bound to `self.params`.
+ |
+
+|
+`params`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+eval_dir
+
+View source
+
+
+eval_dir(
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+Shows the directory name where evaluation metrics are dumped.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of the evaluation if user needs to run multiple evaluations on
+different data sets, such as on training data vs test data. Metrics for
+different evaluations are saved in separate folders, and appear
+separately in tensorboard.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A string which is the path of directory contains evaluation metrics.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+evaluate
+
+View source
+
+
+evaluate(
+ input_fn, steps=None, hooks=None, checkpoint_path=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+Evaluates the model given evaluation data `input_fn`.
+
+For each step, calls `input_fn`, which returns one batch of data.
+Evaluates until:
+- `steps` batches are processed, or
+- `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception (tf.errors.OutOfRangeError
+or
+`StopIteration`).
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that constructs the input data for evaluation. See
+[Premade Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The
+function should construct and return one of the following: * A
+tf.data.Dataset object: Outputs of `Dataset` object must be a tuple
+`(features, labels)` with same constraints as below. * A tuple
+`(features, labels)`: Where `features` is a tf.Tensor or a dictionary
+of string feature name to `Tensor` and `labels` is a `Tensor` or a
+dictionary of string label name to `Tensor`. Both `features` and
+`labels` are consumed by `model_fn`. They should satisfy the
+expectation of `model_fn` from inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`steps`
+ |
+
+Number of steps for which to evaluate model. If `None`, evaluates
+until `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the evaluation call.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+Path of a specific checkpoint to evaluate. If `None`, the
+latest checkpoint in `model_dir` is used. If there are no checkpoints
+in `model_dir`, evaluation is run with newly initialized `Variables`
+instead of ones restored from checkpoint.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of the evaluation if user needs to run multiple evaluations on
+different data sets, such as on training data vs test data. Metrics for
+different evaluations are saved in separate folders, and appear
+separately in tensorboard.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A dict containing the evaluation metrics specified in `model_fn` keyed by
+name, as well as an entry `global_step` which contains the value of the
+global step for which this evaluation was performed. For canned
+estimators, the dict contains the `loss` (mean loss per mini-batch) and
+the `average_loss` (mean loss per sample). Canned classifiers also return
+the `accuracy`. Canned regressors also return the `label/mean` and the
+`prediction/mean`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `steps <= 0`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+experimental_export_all_saved_models
+
+View source
+
+
+experimental_export_all_saved_models(
+ export_dir_base, input_receiver_fn_map, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None
+)
+
+
+Exports a `SavedModel` with `tf.MetaGraphDefs` for each requested mode.
+
+For each mode passed in via the `input_receiver_fn_map`,
+this method builds a new graph by calling the `input_receiver_fn` to obtain
+feature and label `Tensor`s. Next, this method calls the `Estimator`'s
+`model_fn` in the passed mode to generate the model graph based on
+those features and labels, and restores the given checkpoint
+(or, lacking that, the most recent checkpoint) into the graph.
+Only one of the modes is used for saving variables to the `SavedModel`
+(order of preference: tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN,
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys.EVAL, then
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT), such that up to three
+`tf.MetaGraphDefs` are saved with a single set of variables in a single
+`SavedModel` directory.
+
+For the variables and `tf.MetaGraphDefs`, a timestamped export directory
+below
+`export_dir_base`, and writes a `SavedModel` into it containing
+the `tf.MetaGraphDef` for the given mode and its associated signatures.
+
+For prediction, the exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef`
+for each element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`,
+named using the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+For training and evaluation, the `train_op` is stored in an extra
+collection,
+and loss, metrics, and predictions are included in a `SignatureDef` for the
+mode in question.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`input_receiver_fn_map`
+ |
+
+dict of tf.estimator.ModeKeys to
+`input_receiver_fn` mappings, where the `input_receiver_fn` is a
+function that takes no arguments and returns the appropriate subclass of
+`InputReceiver`.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if any `input_receiver_fn` is `None`, no `export_outputs`
+are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+export_saved_model
+
+View source
+
+
+export_saved_model(
+ export_dir_base, serving_input_receiver_fn, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None, experimental_mode=ModeKeys.PREDICT
+)
+
+
+Exports inference graph as a `SavedModel` into the given dir.
+
+For a detailed guide, see
+[Using SavedModel with
+Estimators](https://tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model#using_savedmodel_with_estimators).
+
+This method builds a new graph by first calling the
+`serving_input_receiver_fn` to obtain feature `Tensor`s, and then calling
+this `Estimator`'s `model_fn` to generate the model graph based on those
+features. It restores the given checkpoint (or, lacking that, the most
+recent checkpoint) into this graph in a fresh session. Finally it creates
+a timestamped export directory below the given `export_dir_base`, and writes
+a `SavedModel` into it containing a single `tf.MetaGraphDef` saved from this
+session.
+
+The exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef` for each
+element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`, named
+using
+the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+The experimental_mode parameter can be used to export a single
+train/eval/predict graph as a `SavedModel`.
+See `experimental_export_all_saved_models` for full docs.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`serving_input_receiver_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that takes no argument and returns a
+tf.estimator.export.ServingInputReceiver or
+tf.estimator.export.TensorServingInputReceiver.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+|
+`experimental_mode`
+ |
+
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys value indicating with mode will
+be exported. Note that this feature is experimental.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if no `serving_input_receiver_fn` is provided, no
+`export_outputs` are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+export_savedmodel
+
+View source
+
+
+export_savedmodel(
+ export_dir_base, serving_input_receiver_fn, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None, strip_default_attrs=(False)
+)
+
+
+Exports inference graph as a `SavedModel` into the given dir. (deprecated)
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+This function has been renamed, use `export_saved_model` instead.
+
+For a detailed guide, see
+[Using SavedModel with
+Estimators](https://tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model#using_savedmodel_with_estimators).
+
+This method builds a new graph by first calling the
+`serving_input_receiver_fn` to obtain feature `Tensor`s, and then calling
+this `Estimator`'s `model_fn` to generate the model graph based on those
+features. It restores the given checkpoint (or, lacking that, the most
+recent checkpoint) into this graph in a fresh session. Finally it creates
+a timestamped export directory below the given `export_dir_base`, and writes
+a `SavedModel` into it containing a single `tf.MetaGraphDef` saved from this
+session.
+
+The exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef` for each
+element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`, named
+using
+the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`serving_input_receiver_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that takes no argument and returns a
+tf.estimator.export.ServingInputReceiver or
+tf.estimator.export.TensorServingInputReceiver.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+|
+`strip_default_attrs`
+ |
+
+Boolean. If `True`, default-valued attributes will be
+removed from the `NodeDef`s. For a detailed guide, see [Stripping
+Default-Valued Attributes](
+https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/master/tensorflow/python/saved_model/README.md#stripping-default-valued-attributes).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if no `serving_input_receiver_fn` is provided, no
+`export_outputs` are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+get_variable_names
+
+View source
+
+
+get_variable_names()
+
+
+Returns list of all variable names in this model.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+List of names.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `Estimator` has not produced a checkpoint yet.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+get_variable_value
+
+View source
+
+
+get_variable_value(
+ name
+)
+
+
+Returns value of the variable given by name.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+string or a list of string, name of the tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Numpy array - value of the tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `Estimator` has not produced a checkpoint yet.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+latest_checkpoint
+
+View source
+
+
+latest_checkpoint()
+
+
+Finds the filename of the latest saved checkpoint file in `model_dir`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The full path to the latest checkpoint or `None` if no checkpoint was
+found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+predict
+
+View source
+
+
+predict(
+ input_fn, predict_keys=None, hooks=None, checkpoint_path=None,
+ yield_single_examples=(True)
+)
+
+
+Yields predictions for given features.
+
+Please note that interleaving two predict outputs does not work. See:
+[issue/20506](
+https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/issues/20506#issuecomment-422208517)
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that constructs the features. Prediction continues
+until `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception
+(tf.errors.OutOfRangeError or `StopIteration`). See [Premade
+Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The function should construct and return one of
+the following:
+* tf.data.Dataset object -- Outputs of `Dataset` object must have
+same constraints as below.
+* features -- A tf.Tensor or a dictionary of string feature name to
+`Tensor`. features are consumed by `model_fn`. They should satisfy
+the expectation of `model_fn` from inputs. * A tuple, in which case
+the first item is extracted as features.
+ |
+
+|
+`predict_keys`
+ |
+
+list of `str`, name of the keys to predict. It is used if
+the tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec.predictions is a `dict`. If
+`predict_keys` is used then rest of the predictions will be filtered
+from the dictionary. If `None`, returns all.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the prediction call.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+Path of a specific checkpoint to predict. If `None`, the
+latest checkpoint in `model_dir` is used. If there are no checkpoints
+in `model_dir`, prediction is run with newly initialized `Variables`
+instead of ones restored from checkpoint.
+ |
+
+|
+`yield_single_examples`
+ |
+
+If `False`, yields the whole batch as returned by
+the `model_fn` instead of decomposing the batch into individual
+elements. This is useful if `model_fn` returns some tensors whose first
+dimension is not equal to the batch size.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Yields:
+
+Evaluated values of `predictions` tensors.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If batch length of predictions is not the same and
+`yield_single_examples` is `True`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If there is a conflict between `predict_keys` and
+`predictions`. For example if `predict_keys` is not `None` but
+tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec.predictions is not a `dict`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+train
+
+View source
+
+
+train(
+ input_fn, hooks=None, steps=None, max_steps=None, saving_listeners=None
+)
+
+
+Trains a model given training data `input_fn`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that provides input data for training as minibatches.
+See [Premade Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The function should construct and return one of
+the following:
+* A tf.data.Dataset object: Outputs of `Dataset` object must be a
+tuple `(features, labels)` with same constraints as below.
+* A tuple `(features, labels)`: Where `features` is a tf.Tensor or a
+dictionary of string feature name to `Tensor` and `labels` is a
+`Tensor` or a dictionary of string label name to `Tensor`. Both
+`features` and `labels` are consumed by `model_fn`. They should
+satisfy the expectation of `model_fn` from inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the training loop.
+ |
+
+|
+`steps`
+ |
+
+Number of steps for which to train the model. If `None`, train
+forever or train until `input_fn` generates the `tf.errors.OutOfRange`
+error or `StopIteration` exception. `steps` works incrementally. If you
+call two times `train(steps=10)` then training occurs in total 20 steps.
+If `OutOfRange` or `StopIteration` occurs in the middle, training stops
+before 20 steps. If you don't want to have incremental behavior please
+set `max_steps` instead. If set, `max_steps` must be `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_steps`
+ |
+
+Number of total steps for which to train model. If `None`,
+train forever or train until `input_fn` generates the
+`tf.errors.OutOfRange` error or `StopIteration` exception. If set,
+`steps` must be `None`. If `OutOfRange` or `StopIteration` occurs in the
+middle, training stops before `max_steps` steps. Two calls to
+`train(steps=100)` means 200 training iterations. On the other hand, two
+calls to `train(max_steps=100)` means that the second call will not do
+any iteration since first call did all 100 steps.
+ |
+
+|
+`saving_listeners`
+ |
+
+list of `CheckpointSaverListener` objects. Used for
+callbacks that run immediately before or after checkpoint savings.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`self`, for chaining.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If both `steps` and `max_steps` are not `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If either `steps` or `max_steps <= 0`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/LinearClassifier.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/LinearClassifier.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..65cb199447c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/LinearClassifier.md
@@ -0,0 +1,1237 @@
+description: Linear classifier model.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.estimator.LinearClassifier
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Linear classifier model.
+
+Inherits From: [`Estimator`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/Estimator.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.estimator.LinearClassifier(
+ feature_columns, model_dir=None, n_classes=2, weight_column=None,
+ label_vocabulary=None, optimizer='Ftrl', config=None, partitioner=None,
+ warm_start_from=None, loss_reduction=tf.compat.v1.losses.Reduction.SUM,
+ sparse_combiner='sum'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Train a linear model to classify instances into one of multiple possible
+classes. When number of possible classes is 2, this is binary classification.
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+categorical_column_a = categorical_column_with_hash_bucket(...)
+categorical_column_b = categorical_column_with_hash_bucket(...)
+
+categorical_feature_a_x_categorical_feature_b = crossed_column(...)
+
+# Estimator using the default optimizer.
+estimator = tf.estimator.LinearClassifier(
+ feature_columns=[categorical_column_a,
+ categorical_feature_a_x_categorical_feature_b])
+
+# Or estimator using the FTRL optimizer with regularization.
+estimator = tf.estimator.LinearClassifier(
+ feature_columns=[categorical_column_a,
+ categorical_feature_a_x_categorical_feature_b],
+ optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Ftrl(
+ learning_rate=0.1,
+ l1_regularization_strength=0.001
+ ))
+
+# Or estimator using an optimizer with a learning rate decay.
+estimator = tf.estimator.LinearClassifier(
+ feature_columns=[categorical_column_a,
+ categorical_feature_a_x_categorical_feature_b],
+ optimizer=lambda: tf.keras.optimizers.Ftrl(
+ learning_rate=tf.exponential_decay(
+ learning_rate=0.1,
+ global_step=tf.get_global_step(),
+ decay_steps=10000,
+ decay_rate=0.96))
+
+# Or estimator with warm-starting from a previous checkpoint.
+estimator = tf.estimator.LinearClassifier(
+ feature_columns=[categorical_column_a,
+ categorical_feature_a_x_categorical_feature_b],
+ warm_start_from="/path/to/checkpoint/dir")
+
+
+# Input builders
+def input_fn_train:
+ # Returns tf.data.Dataset of (x, y) tuple where y represents label's class
+ # index.
+ pass
+def input_fn_eval:
+ # Returns tf.data.Dataset of (x, y) tuple where y represents label's class
+ # index.
+ pass
+def input_fn_predict:
+ # Returns tf.data.Dataset of (x, None) tuple.
+ pass
+estimator.train(input_fn=input_fn_train)
+metrics = estimator.evaluate(input_fn=input_fn_eval)
+predictions = estimator.predict(input_fn=input_fn_predict)
+```
+
+Input of `train` and `evaluate` should have following features,
+ otherwise there will be a `KeyError`:
+
+* if `weight_column` is not `None`, a feature with `key=weight_column` whose
+ value is a `Tensor`.
+* for each `column` in `feature_columns`:
+ - if `column` is a `SparseColumn`, a feature with `key=column.name`
+ whose `value` is a `SparseTensor`.
+ - if `column` is a `WeightedSparseColumn`, two features: the first with
+ `key` the id column name, the second with `key` the weight column name.
+ Both features' `value` must be a `SparseTensor`.
+ - if `column` is a `RealValuedColumn`, a feature with `key=column.name`
+ whose `value` is a `Tensor`.
+
+Loss is calculated by using softmax cross entropy.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`model_fn`
+ |
+
+Model function. Follows the signature:
+* `features` -- This is the first item returned from the `input_fn`
+passed to `train`, `evaluate`, and `predict`. This should be a
+single tf.Tensor or `dict` of same.
+* `labels` -- This is the second item returned from the `input_fn`
+passed to `train`, `evaluate`, and `predict`. This should be a
+single tf.Tensor or `dict` of same (for multi-head models). If
+mode is tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT, `labels=None` will be
+passed. If the `model_fn`'s signature does not accept `mode`, the
+`model_fn` must still be able to handle `labels=None`.
+* `mode` -- Optional. Specifies if this is training, evaluation or
+prediction. See tf.estimator.ModeKeys.
+`params` -- Optional `dict` of hyperparameters. Will receive what is
+passed to Estimator in `params` parameter. This allows to configure
+Estimators from hyper parameter tuning.
+* `config` -- Optional `estimator.RunConfig` object. Will receive what
+is passed to Estimator as its `config` parameter, or a default
+value. Allows setting up things in your `model_fn` based on
+configuration such as `num_ps_replicas`, or `model_dir`.
+* Returns -- tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec
+ |
+
+|
+`model_dir`
+ |
+
+Directory to save model parameters, graph and etc. This can
+also be used to load checkpoints from the directory into an estimator to
+continue training a previously saved model. If `PathLike` object, the
+path will be resolved. If `None`, the model_dir in `config` will be used
+if set. If both are set, they must be same. If both are `None`, a
+temporary directory will be used.
+ |
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+`estimator.RunConfig` configuration object.
+ |
+
+|
+`params`
+ |
+
+`dict` of hyper parameters that will be passed into `model_fn`.
+Keys are names of parameters, values are basic python types.
+ |
+
+|
+`warm_start_from`
+ |
+
+Optional string filepath to a checkpoint or SavedModel to
+warm-start from, or a tf.estimator.WarmStartSettings object to fully
+configure warm-starting. If None, only TRAINABLE variables are
+warm-started. If the string filepath is provided instead of a
+tf.estimator.WarmStartSettings, then all variables are warm-started,
+and it is assumed that vocabularies and tf.Tensor names are unchanged.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+parameters of `model_fn` don't match `params`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if this is called via a subclass and if that class overrides
+a member of `Estimator`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+Estimators can be used while eager execution is enabled. Note that `input_fn`
+and all hooks are executed inside a graph context, so they have to be written
+to be compatible with graph mode. Note that `input_fn` code using tf.data
+generally works in both graph and eager modes.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`model_dir`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`model_fn`
+ |
+
+Returns the `model_fn` which is bound to `self.params`.
+ |
+
+|
+`params`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+eval_dir
+
+View source
+
+
+eval_dir(
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+Shows the directory name where evaluation metrics are dumped.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of the evaluation if user needs to run multiple evaluations on
+different data sets, such as on training data vs test data. Metrics for
+different evaluations are saved in separate folders, and appear
+separately in tensorboard.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A string which is the path of directory contains evaluation metrics.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+evaluate
+
+View source
+
+
+evaluate(
+ input_fn, steps=None, hooks=None, checkpoint_path=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+Evaluates the model given evaluation data `input_fn`.
+
+For each step, calls `input_fn`, which returns one batch of data.
+Evaluates until:
+- `steps` batches are processed, or
+- `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception (tf.errors.OutOfRangeError
+or
+`StopIteration`).
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that constructs the input data for evaluation. See
+[Premade Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The
+function should construct and return one of the following: * A
+tf.data.Dataset object: Outputs of `Dataset` object must be a tuple
+`(features, labels)` with same constraints as below. * A tuple
+`(features, labels)`: Where `features` is a tf.Tensor or a dictionary
+of string feature name to `Tensor` and `labels` is a `Tensor` or a
+dictionary of string label name to `Tensor`. Both `features` and
+`labels` are consumed by `model_fn`. They should satisfy the
+expectation of `model_fn` from inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`steps`
+ |
+
+Number of steps for which to evaluate model. If `None`, evaluates
+until `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the evaluation call.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+Path of a specific checkpoint to evaluate. If `None`, the
+latest checkpoint in `model_dir` is used. If there are no checkpoints
+in `model_dir`, evaluation is run with newly initialized `Variables`
+instead of ones restored from checkpoint.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of the evaluation if user needs to run multiple evaluations on
+different data sets, such as on training data vs test data. Metrics for
+different evaluations are saved in separate folders, and appear
+separately in tensorboard.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A dict containing the evaluation metrics specified in `model_fn` keyed by
+name, as well as an entry `global_step` which contains the value of the
+global step for which this evaluation was performed. For canned
+estimators, the dict contains the `loss` (mean loss per mini-batch) and
+the `average_loss` (mean loss per sample). Canned classifiers also return
+the `accuracy`. Canned regressors also return the `label/mean` and the
+`prediction/mean`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `steps <= 0`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+experimental_export_all_saved_models
+
+View source
+
+
+experimental_export_all_saved_models(
+ export_dir_base, input_receiver_fn_map, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None
+)
+
+
+Exports a `SavedModel` with `tf.MetaGraphDefs` for each requested mode.
+
+For each mode passed in via the `input_receiver_fn_map`,
+this method builds a new graph by calling the `input_receiver_fn` to obtain
+feature and label `Tensor`s. Next, this method calls the `Estimator`'s
+`model_fn` in the passed mode to generate the model graph based on
+those features and labels, and restores the given checkpoint
+(or, lacking that, the most recent checkpoint) into the graph.
+Only one of the modes is used for saving variables to the `SavedModel`
+(order of preference: tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN,
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys.EVAL, then
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT), such that up to three
+`tf.MetaGraphDefs` are saved with a single set of variables in a single
+`SavedModel` directory.
+
+For the variables and `tf.MetaGraphDefs`, a timestamped export directory
+below
+`export_dir_base`, and writes a `SavedModel` into it containing
+the `tf.MetaGraphDef` for the given mode and its associated signatures.
+
+For prediction, the exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef`
+for each element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`,
+named using the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+For training and evaluation, the `train_op` is stored in an extra
+collection,
+and loss, metrics, and predictions are included in a `SignatureDef` for the
+mode in question.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`input_receiver_fn_map`
+ |
+
+dict of tf.estimator.ModeKeys to
+`input_receiver_fn` mappings, where the `input_receiver_fn` is a
+function that takes no arguments and returns the appropriate subclass of
+`InputReceiver`.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if any `input_receiver_fn` is `None`, no `export_outputs`
+are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+export_saved_model
+
+View source
+
+
+export_saved_model(
+ export_dir_base, serving_input_receiver_fn, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None, experimental_mode=ModeKeys.PREDICT
+)
+
+
+Exports inference graph as a `SavedModel` into the given dir.
+
+For a detailed guide, see
+[Using SavedModel with
+Estimators](https://tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model#using_savedmodel_with_estimators).
+
+This method builds a new graph by first calling the
+`serving_input_receiver_fn` to obtain feature `Tensor`s, and then calling
+this `Estimator`'s `model_fn` to generate the model graph based on those
+features. It restores the given checkpoint (or, lacking that, the most
+recent checkpoint) into this graph in a fresh session. Finally it creates
+a timestamped export directory below the given `export_dir_base`, and writes
+a `SavedModel` into it containing a single `tf.MetaGraphDef` saved from this
+session.
+
+The exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef` for each
+element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`, named
+using
+the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+The experimental_mode parameter can be used to export a single
+train/eval/predict graph as a `SavedModel`.
+See `experimental_export_all_saved_models` for full docs.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`serving_input_receiver_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that takes no argument and returns a
+tf.estimator.export.ServingInputReceiver or
+tf.estimator.export.TensorServingInputReceiver.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+|
+`experimental_mode`
+ |
+
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys value indicating with mode will
+be exported. Note that this feature is experimental.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if no `serving_input_receiver_fn` is provided, no
+`export_outputs` are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+export_savedmodel
+
+View source
+
+
+export_savedmodel(
+ export_dir_base, serving_input_receiver_fn, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None, strip_default_attrs=(False)
+)
+
+
+Exports inference graph as a `SavedModel` into the given dir. (deprecated)
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+This function has been renamed, use `export_saved_model` instead.
+
+For a detailed guide, see
+[Using SavedModel with
+Estimators](https://tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model#using_savedmodel_with_estimators).
+
+This method builds a new graph by first calling the
+`serving_input_receiver_fn` to obtain feature `Tensor`s, and then calling
+this `Estimator`'s `model_fn` to generate the model graph based on those
+features. It restores the given checkpoint (or, lacking that, the most
+recent checkpoint) into this graph in a fresh session. Finally it creates
+a timestamped export directory below the given `export_dir_base`, and writes
+a `SavedModel` into it containing a single `tf.MetaGraphDef` saved from this
+session.
+
+The exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef` for each
+element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`, named
+using
+the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`serving_input_receiver_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that takes no argument and returns a
+tf.estimator.export.ServingInputReceiver or
+tf.estimator.export.TensorServingInputReceiver.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+|
+`strip_default_attrs`
+ |
+
+Boolean. If `True`, default-valued attributes will be
+removed from the `NodeDef`s. For a detailed guide, see [Stripping
+Default-Valued Attributes](
+https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/master/tensorflow/python/saved_model/README.md#stripping-default-valued-attributes).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if no `serving_input_receiver_fn` is provided, no
+`export_outputs` are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+get_variable_names
+
+View source
+
+
+get_variable_names()
+
+
+Returns list of all variable names in this model.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+List of names.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `Estimator` has not produced a checkpoint yet.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+get_variable_value
+
+View source
+
+
+get_variable_value(
+ name
+)
+
+
+Returns value of the variable given by name.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+string or a list of string, name of the tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Numpy array - value of the tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `Estimator` has not produced a checkpoint yet.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+latest_checkpoint
+
+View source
+
+
+latest_checkpoint()
+
+
+Finds the filename of the latest saved checkpoint file in `model_dir`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The full path to the latest checkpoint or `None` if no checkpoint was
+found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+predict
+
+View source
+
+
+predict(
+ input_fn, predict_keys=None, hooks=None, checkpoint_path=None,
+ yield_single_examples=(True)
+)
+
+
+Yields predictions for given features.
+
+Please note that interleaving two predict outputs does not work. See:
+[issue/20506](
+https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/issues/20506#issuecomment-422208517)
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that constructs the features. Prediction continues
+until `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception
+(tf.errors.OutOfRangeError or `StopIteration`). See [Premade
+Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The function should construct and return one of
+the following:
+* tf.data.Dataset object -- Outputs of `Dataset` object must have
+same constraints as below.
+* features -- A tf.Tensor or a dictionary of string feature name to
+`Tensor`. features are consumed by `model_fn`. They should satisfy
+the expectation of `model_fn` from inputs. * A tuple, in which case
+the first item is extracted as features.
+ |
+
+|
+`predict_keys`
+ |
+
+list of `str`, name of the keys to predict. It is used if
+the tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec.predictions is a `dict`. If
+`predict_keys` is used then rest of the predictions will be filtered
+from the dictionary. If `None`, returns all.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the prediction call.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+Path of a specific checkpoint to predict. If `None`, the
+latest checkpoint in `model_dir` is used. If there are no checkpoints
+in `model_dir`, prediction is run with newly initialized `Variables`
+instead of ones restored from checkpoint.
+ |
+
+|
+`yield_single_examples`
+ |
+
+If `False`, yields the whole batch as returned by
+the `model_fn` instead of decomposing the batch into individual
+elements. This is useful if `model_fn` returns some tensors whose first
+dimension is not equal to the batch size.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Yields:
+
+Evaluated values of `predictions` tensors.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If batch length of predictions is not the same and
+`yield_single_examples` is `True`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If there is a conflict between `predict_keys` and
+`predictions`. For example if `predict_keys` is not `None` but
+tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec.predictions is not a `dict`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+train
+
+View source
+
+
+train(
+ input_fn, hooks=None, steps=None, max_steps=None, saving_listeners=None
+)
+
+
+Trains a model given training data `input_fn`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that provides input data for training as minibatches.
+See [Premade Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The function should construct and return one of
+the following:
+* A tf.data.Dataset object: Outputs of `Dataset` object must be a
+tuple `(features, labels)` with same constraints as below.
+* A tuple `(features, labels)`: Where `features` is a tf.Tensor or a
+dictionary of string feature name to `Tensor` and `labels` is a
+`Tensor` or a dictionary of string label name to `Tensor`. Both
+`features` and `labels` are consumed by `model_fn`. They should
+satisfy the expectation of `model_fn` from inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the training loop.
+ |
+
+|
+`steps`
+ |
+
+Number of steps for which to train the model. If `None`, train
+forever or train until `input_fn` generates the `tf.errors.OutOfRange`
+error or `StopIteration` exception. `steps` works incrementally. If you
+call two times `train(steps=10)` then training occurs in total 20 steps.
+If `OutOfRange` or `StopIteration` occurs in the middle, training stops
+before 20 steps. If you don't want to have incremental behavior please
+set `max_steps` instead. If set, `max_steps` must be `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_steps`
+ |
+
+Number of total steps for which to train model. If `None`,
+train forever or train until `input_fn` generates the
+`tf.errors.OutOfRange` error or `StopIteration` exception. If set,
+`steps` must be `None`. If `OutOfRange` or `StopIteration` occurs in the
+middle, training stops before `max_steps` steps. Two calls to
+`train(steps=100)` means 200 training iterations. On the other hand, two
+calls to `train(max_steps=100)` means that the second call will not do
+any iteration since first call did all 100 steps.
+ |
+
+|
+`saving_listeners`
+ |
+
+list of `CheckpointSaverListener` objects. Used for
+callbacks that run immediately before or after checkpoint savings.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`self`, for chaining.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If both `steps` and `max_steps` are not `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If either `steps` or `max_steps <= 0`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/LinearEstimator.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/LinearEstimator.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..b9251a32b4f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/LinearEstimator.md
@@ -0,0 +1,1198 @@
+description: An estimator for TensorFlow linear models with user-specified head.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.estimator.LinearEstimator
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+An estimator for TensorFlow linear models with user-specified head.
+
+Inherits From: [`Estimator`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/Estimator.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.estimator.LinearEstimator(
+ head, feature_columns, model_dir=None, optimizer='Ftrl', config=None,
+ partitioner=None, sparse_combiner='sum'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+categorical_column_a = categorical_column_with_hash_bucket(...)
+categorical_column_b = categorical_column_with_hash_bucket(...)
+
+categorical_feature_a_x_categorical_feature_b = crossed_column(...)
+
+# Estimator using the default optimizer.
+estimator = tf.estimator.LinearEstimator(
+ head=tf.estimator.MultiLabelHead(n_classes=3),
+ feature_columns=[categorical_column_a,
+ categorical_feature_a_x_categorical_feature_b])
+
+# Or estimator using an optimizer with a learning rate decay.
+estimator = tf.estimator.LinearEstimator(
+ head=tf.estimator.MultiLabelHead(n_classes=3),
+ feature_columns=[categorical_column_a,
+ categorical_feature_a_x_categorical_feature_b],
+ optimizer=lambda: tf.keras.optimizers.Ftrl(
+ learning_rate=tf.compat.v1.train.exponential_decay(
+ learning_rate=0.1,
+ global_step=tf.compat.v1.train.get_global_step(),
+ decay_steps=10000,
+ decay_rate=0.96))
+
+# Or estimator using the FTRL optimizer with regularization.
+estimator = tf.estimator.LinearEstimator(
+ head=tf.estimator.MultiLabelHead(n_classes=3),
+ feature_columns=[categorical_column_a,
+ categorical_feature_a_x_categorical_feature_b])
+ optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Ftrl(
+ learning_rate=0.1,
+ l1_regularization_strength=0.001
+ ))
+
+def input_fn_train:
+ # Returns tf.data.Dataset of (x, y) tuple where y represents label's class
+ # index.
+ pass
+def input_fn_eval:
+ # Returns tf.data.Dataset of (x, y) tuple where y represents label's class
+ # index.
+ pass
+def input_fn_predict:
+ # Returns tf.data.Dataset of (x, None) tuple.
+ pass
+estimator.train(input_fn=input_fn_train, steps=100)
+metrics = estimator.evaluate(input_fn=input_fn_eval, steps=10)
+predictions = estimator.predict(input_fn=input_fn_predict)
+```
+
+Input of `train` and `evaluate` should have following features,
+otherwise there will be a `KeyError`:
+
+* if `weight_column` is not `None`, a feature with `key=weight_column` whose
+ value is a `Tensor`.
+* for each `column` in `feature_columns`:
+ - if `column` is a `CategoricalColumn`, a feature with `key=column.name`
+ whose `value` is a `SparseTensor`.
+ - if `column` is a `WeightedCategoricalColumn`, two features: the first
+ with `key` the id column name, the second with `key` the weight column
+ name. Both features' `value` must be a `SparseTensor`.
+ - if `column` is a `DenseColumn`, a feature with `key=column.name`
+ whose `value` is a `Tensor`.
+
+Loss and predicted output are determined by the specified head.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`head`
+ |
+
+A `_Head` instance constructed with a method such as
+`tf.contrib.estimator.multi_label_head`.
+ |
+
+|
+`feature_columns`
+ |
+
+An iterable containing all the feature columns used by
+the model. All items in the set should be instances of classes derived
+from `FeatureColumn`.
+ |
+
+|
+`model_dir`
+ |
+
+Directory to save model parameters, graph and etc. This can
+also be used to load checkpoints from the directory into a estimator to
+continue training a previously saved model.
+ |
+
+|
+`optimizer`
+ |
+
+An instance of `tf.Optimizer` used to train the model. Can also
+be a string (one of 'Adagrad', 'Adam', 'Ftrl', 'RMSProp', 'SGD'), or
+callable. Defaults to FTRL optimizer.
+ |
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+`RunConfig` object to configure the runtime settings.
+ |
+
+|
+`partitioner`
+ |
+
+Optional. Partitioner for input layer.
+ |
+
+|
+`sparse_combiner`
+ |
+
+A string specifying how to reduce if a categorical column
+is multivalent. One of "mean", "sqrtn", and "sum" -- these are
+effectively different ways to do example-level normalization, which can
+be useful for bag-of-words features. for more details, see
+`tf.feature_column.linear_model`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+Estimators can be used while eager execution is enabled. Note that `input_fn`
+and all hooks are executed inside a graph context, so they have to be written
+to be compatible with graph mode. Note that `input_fn` code using tf.data
+generally works in both graph and eager modes.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`model_dir`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`model_fn`
+ |
+
+Returns the `model_fn` which is bound to `self.params`.
+ |
+
+|
+`params`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+eval_dir
+
+View source
+
+
+eval_dir(
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+Shows the directory name where evaluation metrics are dumped.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of the evaluation if user needs to run multiple evaluations on
+different data sets, such as on training data vs test data. Metrics for
+different evaluations are saved in separate folders, and appear
+separately in tensorboard.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A string which is the path of directory contains evaluation metrics.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+evaluate
+
+View source
+
+
+evaluate(
+ input_fn, steps=None, hooks=None, checkpoint_path=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+Evaluates the model given evaluation data `input_fn`.
+
+For each step, calls `input_fn`, which returns one batch of data.
+Evaluates until:
+- `steps` batches are processed, or
+- `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception (tf.errors.OutOfRangeError
+or
+`StopIteration`).
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that constructs the input data for evaluation. See
+[Premade Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The
+function should construct and return one of the following: * A
+tf.data.Dataset object: Outputs of `Dataset` object must be a tuple
+`(features, labels)` with same constraints as below. * A tuple
+`(features, labels)`: Where `features` is a tf.Tensor or a dictionary
+of string feature name to `Tensor` and `labels` is a `Tensor` or a
+dictionary of string label name to `Tensor`. Both `features` and
+`labels` are consumed by `model_fn`. They should satisfy the
+expectation of `model_fn` from inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`steps`
+ |
+
+Number of steps for which to evaluate model. If `None`, evaluates
+until `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the evaluation call.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+Path of a specific checkpoint to evaluate. If `None`, the
+latest checkpoint in `model_dir` is used. If there are no checkpoints
+in `model_dir`, evaluation is run with newly initialized `Variables`
+instead of ones restored from checkpoint.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of the evaluation if user needs to run multiple evaluations on
+different data sets, such as on training data vs test data. Metrics for
+different evaluations are saved in separate folders, and appear
+separately in tensorboard.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A dict containing the evaluation metrics specified in `model_fn` keyed by
+name, as well as an entry `global_step` which contains the value of the
+global step for which this evaluation was performed. For canned
+estimators, the dict contains the `loss` (mean loss per mini-batch) and
+the `average_loss` (mean loss per sample). Canned classifiers also return
+the `accuracy`. Canned regressors also return the `label/mean` and the
+`prediction/mean`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `steps <= 0`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+experimental_export_all_saved_models
+
+View source
+
+
+experimental_export_all_saved_models(
+ export_dir_base, input_receiver_fn_map, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None
+)
+
+
+Exports a `SavedModel` with `tf.MetaGraphDefs` for each requested mode.
+
+For each mode passed in via the `input_receiver_fn_map`,
+this method builds a new graph by calling the `input_receiver_fn` to obtain
+feature and label `Tensor`s. Next, this method calls the `Estimator`'s
+`model_fn` in the passed mode to generate the model graph based on
+those features and labels, and restores the given checkpoint
+(or, lacking that, the most recent checkpoint) into the graph.
+Only one of the modes is used for saving variables to the `SavedModel`
+(order of preference: tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN,
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys.EVAL, then
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT), such that up to three
+`tf.MetaGraphDefs` are saved with a single set of variables in a single
+`SavedModel` directory.
+
+For the variables and `tf.MetaGraphDefs`, a timestamped export directory
+below
+`export_dir_base`, and writes a `SavedModel` into it containing
+the `tf.MetaGraphDef` for the given mode and its associated signatures.
+
+For prediction, the exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef`
+for each element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`,
+named using the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+For training and evaluation, the `train_op` is stored in an extra
+collection,
+and loss, metrics, and predictions are included in a `SignatureDef` for the
+mode in question.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`input_receiver_fn_map`
+ |
+
+dict of tf.estimator.ModeKeys to
+`input_receiver_fn` mappings, where the `input_receiver_fn` is a
+function that takes no arguments and returns the appropriate subclass of
+`InputReceiver`.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if any `input_receiver_fn` is `None`, no `export_outputs`
+are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+export_saved_model
+
+View source
+
+
+export_saved_model(
+ export_dir_base, serving_input_receiver_fn, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None, experimental_mode=ModeKeys.PREDICT
+)
+
+
+Exports inference graph as a `SavedModel` into the given dir.
+
+For a detailed guide, see
+[Using SavedModel with
+Estimators](https://tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model#using_savedmodel_with_estimators).
+
+This method builds a new graph by first calling the
+`serving_input_receiver_fn` to obtain feature `Tensor`s, and then calling
+this `Estimator`'s `model_fn` to generate the model graph based on those
+features. It restores the given checkpoint (or, lacking that, the most
+recent checkpoint) into this graph in a fresh session. Finally it creates
+a timestamped export directory below the given `export_dir_base`, and writes
+a `SavedModel` into it containing a single `tf.MetaGraphDef` saved from this
+session.
+
+The exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef` for each
+element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`, named
+using
+the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+The experimental_mode parameter can be used to export a single
+train/eval/predict graph as a `SavedModel`.
+See `experimental_export_all_saved_models` for full docs.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`serving_input_receiver_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that takes no argument and returns a
+tf.estimator.export.ServingInputReceiver or
+tf.estimator.export.TensorServingInputReceiver.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+|
+`experimental_mode`
+ |
+
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys value indicating with mode will
+be exported. Note that this feature is experimental.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if no `serving_input_receiver_fn` is provided, no
+`export_outputs` are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+export_savedmodel
+
+View source
+
+
+export_savedmodel(
+ export_dir_base, serving_input_receiver_fn, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None, strip_default_attrs=(False)
+)
+
+
+Exports inference graph as a `SavedModel` into the given dir. (deprecated)
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+This function has been renamed, use `export_saved_model` instead.
+
+For a detailed guide, see
+[Using SavedModel with
+Estimators](https://tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model#using_savedmodel_with_estimators).
+
+This method builds a new graph by first calling the
+`serving_input_receiver_fn` to obtain feature `Tensor`s, and then calling
+this `Estimator`'s `model_fn` to generate the model graph based on those
+features. It restores the given checkpoint (or, lacking that, the most
+recent checkpoint) into this graph in a fresh session. Finally it creates
+a timestamped export directory below the given `export_dir_base`, and writes
+a `SavedModel` into it containing a single `tf.MetaGraphDef` saved from this
+session.
+
+The exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef` for each
+element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`, named
+using
+the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`serving_input_receiver_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that takes no argument and returns a
+tf.estimator.export.ServingInputReceiver or
+tf.estimator.export.TensorServingInputReceiver.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+|
+`strip_default_attrs`
+ |
+
+Boolean. If `True`, default-valued attributes will be
+removed from the `NodeDef`s. For a detailed guide, see [Stripping
+Default-Valued Attributes](
+https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/master/tensorflow/python/saved_model/README.md#stripping-default-valued-attributes).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if no `serving_input_receiver_fn` is provided, no
+`export_outputs` are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+get_variable_names
+
+View source
+
+
+get_variable_names()
+
+
+Returns list of all variable names in this model.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+List of names.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `Estimator` has not produced a checkpoint yet.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+get_variable_value
+
+View source
+
+
+get_variable_value(
+ name
+)
+
+
+Returns value of the variable given by name.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+string or a list of string, name of the tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Numpy array - value of the tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `Estimator` has not produced a checkpoint yet.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+latest_checkpoint
+
+View source
+
+
+latest_checkpoint()
+
+
+Finds the filename of the latest saved checkpoint file in `model_dir`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The full path to the latest checkpoint or `None` if no checkpoint was
+found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+predict
+
+View source
+
+
+predict(
+ input_fn, predict_keys=None, hooks=None, checkpoint_path=None,
+ yield_single_examples=(True)
+)
+
+
+Yields predictions for given features.
+
+Please note that interleaving two predict outputs does not work. See:
+[issue/20506](
+https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/issues/20506#issuecomment-422208517)
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that constructs the features. Prediction continues
+until `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception
+(tf.errors.OutOfRangeError or `StopIteration`). See [Premade
+Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The function should construct and return one of
+the following:
+* tf.data.Dataset object -- Outputs of `Dataset` object must have
+same constraints as below.
+* features -- A tf.Tensor or a dictionary of string feature name to
+`Tensor`. features are consumed by `model_fn`. They should satisfy
+the expectation of `model_fn` from inputs. * A tuple, in which case
+the first item is extracted as features.
+ |
+
+|
+`predict_keys`
+ |
+
+list of `str`, name of the keys to predict. It is used if
+the tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec.predictions is a `dict`. If
+`predict_keys` is used then rest of the predictions will be filtered
+from the dictionary. If `None`, returns all.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the prediction call.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+Path of a specific checkpoint to predict. If `None`, the
+latest checkpoint in `model_dir` is used. If there are no checkpoints
+in `model_dir`, prediction is run with newly initialized `Variables`
+instead of ones restored from checkpoint.
+ |
+
+|
+`yield_single_examples`
+ |
+
+If `False`, yields the whole batch as returned by
+the `model_fn` instead of decomposing the batch into individual
+elements. This is useful if `model_fn` returns some tensors whose first
+dimension is not equal to the batch size.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Yields:
+
+Evaluated values of `predictions` tensors.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If batch length of predictions is not the same and
+`yield_single_examples` is `True`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If there is a conflict between `predict_keys` and
+`predictions`. For example if `predict_keys` is not `None` but
+tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec.predictions is not a `dict`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+train
+
+View source
+
+
+train(
+ input_fn, hooks=None, steps=None, max_steps=None, saving_listeners=None
+)
+
+
+Trains a model given training data `input_fn`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that provides input data for training as minibatches.
+See [Premade Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The function should construct and return one of
+the following:
+* A tf.data.Dataset object: Outputs of `Dataset` object must be a
+tuple `(features, labels)` with same constraints as below.
+* A tuple `(features, labels)`: Where `features` is a tf.Tensor or a
+dictionary of string feature name to `Tensor` and `labels` is a
+`Tensor` or a dictionary of string label name to `Tensor`. Both
+`features` and `labels` are consumed by `model_fn`. They should
+satisfy the expectation of `model_fn` from inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the training loop.
+ |
+
+|
+`steps`
+ |
+
+Number of steps for which to train the model. If `None`, train
+forever or train until `input_fn` generates the `tf.errors.OutOfRange`
+error or `StopIteration` exception. `steps` works incrementally. If you
+call two times `train(steps=10)` then training occurs in total 20 steps.
+If `OutOfRange` or `StopIteration` occurs in the middle, training stops
+before 20 steps. If you don't want to have incremental behavior please
+set `max_steps` instead. If set, `max_steps` must be `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_steps`
+ |
+
+Number of total steps for which to train model. If `None`,
+train forever or train until `input_fn` generates the
+`tf.errors.OutOfRange` error or `StopIteration` exception. If set,
+`steps` must be `None`. If `OutOfRange` or `StopIteration` occurs in the
+middle, training stops before `max_steps` steps. Two calls to
+`train(steps=100)` means 200 training iterations. On the other hand, two
+calls to `train(max_steps=100)` means that the second call will not do
+any iteration since first call did all 100 steps.
+ |
+
+|
+`saving_listeners`
+ |
+
+list of `CheckpointSaverListener` objects. Used for
+callbacks that run immediately before or after checkpoint savings.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`self`, for chaining.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If both `steps` and `max_steps` are not `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If either `steps` or `max_steps <= 0`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/LinearRegressor.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/LinearRegressor.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..bfb418fb2eb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/LinearRegressor.md
@@ -0,0 +1,1236 @@
+description: An estimator for TensorFlow Linear regression problems.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.estimator.LinearRegressor
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+An estimator for TensorFlow Linear regression problems.
+
+Inherits From: [`Estimator`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/Estimator.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.estimator.LinearRegressor(
+ feature_columns, model_dir=None, label_dimension=1, weight_column=None,
+ optimizer='Ftrl', config=None, partitioner=None, warm_start_from=None,
+ loss_reduction=tf.compat.v1.losses.Reduction.SUM, sparse_combiner='sum'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Train a linear regression model to predict label value given observation of
+feature values.
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+categorical_column_a = categorical_column_with_hash_bucket(...)
+categorical_column_b = categorical_column_with_hash_bucket(...)
+
+categorical_feature_a_x_categorical_feature_b = crossed_column(...)
+
+# Estimator using the default optimizer.
+estimator = tf.estimator.LinearRegressor(
+ feature_columns=[categorical_column_a,
+ categorical_feature_a_x_categorical_feature_b])
+
+# Or estimator using the FTRL optimizer with regularization.
+estimator = tf.estimator.LinearRegressor(
+ feature_columns=[categorical_column_a,
+ categorical_feature_a_x_categorical_feature_b],
+ optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Ftrl(
+ learning_rate=0.1,
+ l1_regularization_strength=0.001
+ ))
+
+# Or estimator using an optimizer with a learning rate decay.
+estimator = tf.estimator.LinearRegressor(
+ feature_columns=[categorical_column_a,
+ categorical_feature_a_x_categorical_feature_b],
+ optimizer=lambda: tf.keras.optimizers.Ftrl(
+ learning_rate=tf.compat.v1.train.exponential_decay(
+ learning_rate=0.1,
+ global_step=tf.compat.v1.train.get_global_step(),
+ decay_steps=10000,
+ decay_rate=0.96))
+
+# Or estimator with warm-starting from a previous checkpoint.
+estimator = tf.estimator.LinearRegressor(
+ feature_columns=[categorical_column_a,
+ categorical_feature_a_x_categorical_feature_b],
+ warm_start_from="/path/to/checkpoint/dir")
+
+
+# Input builders
+def input_fn_train:
+ # Returns tf.data.Dataset of (x, y) tuple where y represents label's class
+ # index.
+ pass
+def input_fn_eval:
+ # Returns tf.data.Dataset of (x, y) tuple where y represents label's class
+ # index.
+ pass
+def input_fn_predict:
+ # Returns tf.data.Dataset of (x, None) tuple.
+ pass
+estimator.train(input_fn=input_fn_train)
+metrics = estimator.evaluate(input_fn=input_fn_eval)
+predictions = estimator.predict(input_fn=input_fn_predict)
+```
+
+Input of `train` and `evaluate` should have following features,
+ otherwise there will be a KeyError:
+
+* if `weight_column` is not `None`, a feature with `key=weight_column` whose
+ value is a `Tensor`.
+* for each `column` in `feature_columns`:
+ - if `column` is a `SparseColumn`, a feature with `key=column.name`
+ whose `value` is a `SparseTensor`.
+ - if `column` is a `WeightedSparseColumn`, two features: the first with
+ `key` the id column name, the second with `key` the weight column name.
+ Both features' `value` must be a `SparseTensor`.
+ - if `column` is a `RealValuedColumn`, a feature with `key=column.name`
+ whose `value` is a `Tensor`.
+
+Loss is calculated by using mean squared error.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`model_fn`
+ |
+
+Model function. Follows the signature:
+* `features` -- This is the first item returned from the `input_fn`
+passed to `train`, `evaluate`, and `predict`. This should be a
+single tf.Tensor or `dict` of same.
+* `labels` -- This is the second item returned from the `input_fn`
+passed to `train`, `evaluate`, and `predict`. This should be a
+single tf.Tensor or `dict` of same (for multi-head models). If
+mode is tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT, `labels=None` will be
+passed. If the `model_fn`'s signature does not accept `mode`, the
+`model_fn` must still be able to handle `labels=None`.
+* `mode` -- Optional. Specifies if this is training, evaluation or
+prediction. See tf.estimator.ModeKeys.
+`params` -- Optional `dict` of hyperparameters. Will receive what is
+passed to Estimator in `params` parameter. This allows to configure
+Estimators from hyper parameter tuning.
+* `config` -- Optional `estimator.RunConfig` object. Will receive what
+is passed to Estimator as its `config` parameter, or a default
+value. Allows setting up things in your `model_fn` based on
+configuration such as `num_ps_replicas`, or `model_dir`.
+* Returns -- tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec
+ |
+
+|
+`model_dir`
+ |
+
+Directory to save model parameters, graph and etc. This can
+also be used to load checkpoints from the directory into an estimator to
+continue training a previously saved model. If `PathLike` object, the
+path will be resolved. If `None`, the model_dir in `config` will be used
+if set. If both are set, they must be same. If both are `None`, a
+temporary directory will be used.
+ |
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+`estimator.RunConfig` configuration object.
+ |
+
+|
+`params`
+ |
+
+`dict` of hyper parameters that will be passed into `model_fn`.
+Keys are names of parameters, values are basic python types.
+ |
+
+|
+`warm_start_from`
+ |
+
+Optional string filepath to a checkpoint or SavedModel to
+warm-start from, or a tf.estimator.WarmStartSettings object to fully
+configure warm-starting. If None, only TRAINABLE variables are
+warm-started. If the string filepath is provided instead of a
+tf.estimator.WarmStartSettings, then all variables are warm-started,
+and it is assumed that vocabularies and tf.Tensor names are unchanged.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+parameters of `model_fn` don't match `params`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if this is called via a subclass and if that class overrides
+a member of `Estimator`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+Estimators can be used while eager execution is enabled. Note that `input_fn`
+and all hooks are executed inside a graph context, so they have to be written
+to be compatible with graph mode. Note that `input_fn` code using tf.data
+generally works in both graph and eager modes.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`model_dir`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`model_fn`
+ |
+
+Returns the `model_fn` which is bound to `self.params`.
+ |
+
+|
+`params`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+eval_dir
+
+View source
+
+
+eval_dir(
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+Shows the directory name where evaluation metrics are dumped.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of the evaluation if user needs to run multiple evaluations on
+different data sets, such as on training data vs test data. Metrics for
+different evaluations are saved in separate folders, and appear
+separately in tensorboard.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A string which is the path of directory contains evaluation metrics.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+evaluate
+
+View source
+
+
+evaluate(
+ input_fn, steps=None, hooks=None, checkpoint_path=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+Evaluates the model given evaluation data `input_fn`.
+
+For each step, calls `input_fn`, which returns one batch of data.
+Evaluates until:
+- `steps` batches are processed, or
+- `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception (tf.errors.OutOfRangeError
+or
+`StopIteration`).
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that constructs the input data for evaluation. See
+[Premade Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The
+function should construct and return one of the following: * A
+tf.data.Dataset object: Outputs of `Dataset` object must be a tuple
+`(features, labels)` with same constraints as below. * A tuple
+`(features, labels)`: Where `features` is a tf.Tensor or a dictionary
+of string feature name to `Tensor` and `labels` is a `Tensor` or a
+dictionary of string label name to `Tensor`. Both `features` and
+`labels` are consumed by `model_fn`. They should satisfy the
+expectation of `model_fn` from inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`steps`
+ |
+
+Number of steps for which to evaluate model. If `None`, evaluates
+until `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the evaluation call.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+Path of a specific checkpoint to evaluate. If `None`, the
+latest checkpoint in `model_dir` is used. If there are no checkpoints
+in `model_dir`, evaluation is run with newly initialized `Variables`
+instead of ones restored from checkpoint.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of the evaluation if user needs to run multiple evaluations on
+different data sets, such as on training data vs test data. Metrics for
+different evaluations are saved in separate folders, and appear
+separately in tensorboard.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A dict containing the evaluation metrics specified in `model_fn` keyed by
+name, as well as an entry `global_step` which contains the value of the
+global step for which this evaluation was performed. For canned
+estimators, the dict contains the `loss` (mean loss per mini-batch) and
+the `average_loss` (mean loss per sample). Canned classifiers also return
+the `accuracy`. Canned regressors also return the `label/mean` and the
+`prediction/mean`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `steps <= 0`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+experimental_export_all_saved_models
+
+View source
+
+
+experimental_export_all_saved_models(
+ export_dir_base, input_receiver_fn_map, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None
+)
+
+
+Exports a `SavedModel` with `tf.MetaGraphDefs` for each requested mode.
+
+For each mode passed in via the `input_receiver_fn_map`,
+this method builds a new graph by calling the `input_receiver_fn` to obtain
+feature and label `Tensor`s. Next, this method calls the `Estimator`'s
+`model_fn` in the passed mode to generate the model graph based on
+those features and labels, and restores the given checkpoint
+(or, lacking that, the most recent checkpoint) into the graph.
+Only one of the modes is used for saving variables to the `SavedModel`
+(order of preference: tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN,
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys.EVAL, then
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT), such that up to three
+`tf.MetaGraphDefs` are saved with a single set of variables in a single
+`SavedModel` directory.
+
+For the variables and `tf.MetaGraphDefs`, a timestamped export directory
+below
+`export_dir_base`, and writes a `SavedModel` into it containing
+the `tf.MetaGraphDef` for the given mode and its associated signatures.
+
+For prediction, the exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef`
+for each element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`,
+named using the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+For training and evaluation, the `train_op` is stored in an extra
+collection,
+and loss, metrics, and predictions are included in a `SignatureDef` for the
+mode in question.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`input_receiver_fn_map`
+ |
+
+dict of tf.estimator.ModeKeys to
+`input_receiver_fn` mappings, where the `input_receiver_fn` is a
+function that takes no arguments and returns the appropriate subclass of
+`InputReceiver`.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if any `input_receiver_fn` is `None`, no `export_outputs`
+are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+export_saved_model
+
+View source
+
+
+export_saved_model(
+ export_dir_base, serving_input_receiver_fn, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None, experimental_mode=ModeKeys.PREDICT
+)
+
+
+Exports inference graph as a `SavedModel` into the given dir.
+
+For a detailed guide, see
+[Using SavedModel with
+Estimators](https://tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model#using_savedmodel_with_estimators).
+
+This method builds a new graph by first calling the
+`serving_input_receiver_fn` to obtain feature `Tensor`s, and then calling
+this `Estimator`'s `model_fn` to generate the model graph based on those
+features. It restores the given checkpoint (or, lacking that, the most
+recent checkpoint) into this graph in a fresh session. Finally it creates
+a timestamped export directory below the given `export_dir_base`, and writes
+a `SavedModel` into it containing a single `tf.MetaGraphDef` saved from this
+session.
+
+The exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef` for each
+element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`, named
+using
+the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+The experimental_mode parameter can be used to export a single
+train/eval/predict graph as a `SavedModel`.
+See `experimental_export_all_saved_models` for full docs.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`serving_input_receiver_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that takes no argument and returns a
+tf.estimator.export.ServingInputReceiver or
+tf.estimator.export.TensorServingInputReceiver.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+|
+`experimental_mode`
+ |
+
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys value indicating with mode will
+be exported. Note that this feature is experimental.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if no `serving_input_receiver_fn` is provided, no
+`export_outputs` are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+export_savedmodel
+
+View source
+
+
+export_savedmodel(
+ export_dir_base, serving_input_receiver_fn, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None, strip_default_attrs=(False)
+)
+
+
+Exports inference graph as a `SavedModel` into the given dir. (deprecated)
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+This function has been renamed, use `export_saved_model` instead.
+
+For a detailed guide, see
+[Using SavedModel with
+Estimators](https://tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model#using_savedmodel_with_estimators).
+
+This method builds a new graph by first calling the
+`serving_input_receiver_fn` to obtain feature `Tensor`s, and then calling
+this `Estimator`'s `model_fn` to generate the model graph based on those
+features. It restores the given checkpoint (or, lacking that, the most
+recent checkpoint) into this graph in a fresh session. Finally it creates
+a timestamped export directory below the given `export_dir_base`, and writes
+a `SavedModel` into it containing a single `tf.MetaGraphDef` saved from this
+session.
+
+The exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef` for each
+element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`, named
+using
+the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`serving_input_receiver_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that takes no argument and returns a
+tf.estimator.export.ServingInputReceiver or
+tf.estimator.export.TensorServingInputReceiver.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+|
+`strip_default_attrs`
+ |
+
+Boolean. If `True`, default-valued attributes will be
+removed from the `NodeDef`s. For a detailed guide, see [Stripping
+Default-Valued Attributes](
+https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/master/tensorflow/python/saved_model/README.md#stripping-default-valued-attributes).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if no `serving_input_receiver_fn` is provided, no
+`export_outputs` are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+get_variable_names
+
+View source
+
+
+get_variable_names()
+
+
+Returns list of all variable names in this model.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+List of names.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `Estimator` has not produced a checkpoint yet.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+get_variable_value
+
+View source
+
+
+get_variable_value(
+ name
+)
+
+
+Returns value of the variable given by name.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+string or a list of string, name of the tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Numpy array - value of the tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `Estimator` has not produced a checkpoint yet.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+latest_checkpoint
+
+View source
+
+
+latest_checkpoint()
+
+
+Finds the filename of the latest saved checkpoint file in `model_dir`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The full path to the latest checkpoint or `None` if no checkpoint was
+found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+predict
+
+View source
+
+
+predict(
+ input_fn, predict_keys=None, hooks=None, checkpoint_path=None,
+ yield_single_examples=(True)
+)
+
+
+Yields predictions for given features.
+
+Please note that interleaving two predict outputs does not work. See:
+[issue/20506](
+https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/issues/20506#issuecomment-422208517)
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that constructs the features. Prediction continues
+until `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception
+(tf.errors.OutOfRangeError or `StopIteration`). See [Premade
+Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The function should construct and return one of
+the following:
+* tf.data.Dataset object -- Outputs of `Dataset` object must have
+same constraints as below.
+* features -- A tf.Tensor or a dictionary of string feature name to
+`Tensor`. features are consumed by `model_fn`. They should satisfy
+the expectation of `model_fn` from inputs. * A tuple, in which case
+the first item is extracted as features.
+ |
+
+|
+`predict_keys`
+ |
+
+list of `str`, name of the keys to predict. It is used if
+the tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec.predictions is a `dict`. If
+`predict_keys` is used then rest of the predictions will be filtered
+from the dictionary. If `None`, returns all.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the prediction call.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+Path of a specific checkpoint to predict. If `None`, the
+latest checkpoint in `model_dir` is used. If there are no checkpoints
+in `model_dir`, prediction is run with newly initialized `Variables`
+instead of ones restored from checkpoint.
+ |
+
+|
+`yield_single_examples`
+ |
+
+If `False`, yields the whole batch as returned by
+the `model_fn` instead of decomposing the batch into individual
+elements. This is useful if `model_fn` returns some tensors whose first
+dimension is not equal to the batch size.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Yields:
+
+Evaluated values of `predictions` tensors.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If batch length of predictions is not the same and
+`yield_single_examples` is `True`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If there is a conflict between `predict_keys` and
+`predictions`. For example if `predict_keys` is not `None` but
+tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec.predictions is not a `dict`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+train
+
+View source
+
+
+train(
+ input_fn, hooks=None, steps=None, max_steps=None, saving_listeners=None
+)
+
+
+Trains a model given training data `input_fn`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that provides input data for training as minibatches.
+See [Premade Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The function should construct and return one of
+the following:
+* A tf.data.Dataset object: Outputs of `Dataset` object must be a
+tuple `(features, labels)` with same constraints as below.
+* A tuple `(features, labels)`: Where `features` is a tf.Tensor or a
+dictionary of string feature name to `Tensor` and `labels` is a
+`Tensor` or a dictionary of string label name to `Tensor`. Both
+`features` and `labels` are consumed by `model_fn`. They should
+satisfy the expectation of `model_fn` from inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the training loop.
+ |
+
+|
+`steps`
+ |
+
+Number of steps for which to train the model. If `None`, train
+forever or train until `input_fn` generates the `tf.errors.OutOfRange`
+error or `StopIteration` exception. `steps` works incrementally. If you
+call two times `train(steps=10)` then training occurs in total 20 steps.
+If `OutOfRange` or `StopIteration` occurs in the middle, training stops
+before 20 steps. If you don't want to have incremental behavior please
+set `max_steps` instead. If set, `max_steps` must be `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_steps`
+ |
+
+Number of total steps for which to train model. If `None`,
+train forever or train until `input_fn` generates the
+`tf.errors.OutOfRange` error or `StopIteration` exception. If set,
+`steps` must be `None`. If `OutOfRange` or `StopIteration` occurs in the
+middle, training stops before `max_steps` steps. Two calls to
+`train(steps=100)` means 200 training iterations. On the other hand, two
+calls to `train(max_steps=100)` means that the second call will not do
+any iteration since first call did all 100 steps.
+ |
+
+|
+`saving_listeners`
+ |
+
+list of `CheckpointSaverListener` objects. Used for
+callbacks that run immediately before or after checkpoint savings.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`self`, for chaining.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If both `steps` and `max_steps` are not `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If either `steps` or `max_steps <= 0`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/classifier_parse_example_spec.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/classifier_parse_example_spec.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a1251e13aed
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/classifier_parse_example_spec.md
@@ -0,0 +1,223 @@
+description: Generates parsing spec for tf.parse_example to be used with classifiers.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.estimator.classifier_parse_example_spec
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Generates parsing spec for tf.parse_example to be used with classifiers.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.estimator.classifier_parse_example_spec(
+ feature_columns, label_key, label_dtype=tf.dtypes.int64, label_default=None,
+ weight_column=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+If users keep data in tf.Example format, they need to call tf.parse_example
+with a proper feature spec. There are two main things that this utility helps:
+
+* Users need to combine parsing spec of features with labels and weights
+ (if any) since they are all parsed from same tf.Example instance. This
+ utility combines these specs.
+* It is difficult to map expected label by a classifier such as
+ `DNNClassifier` to corresponding tf.parse_example spec. This utility encodes
+ it by getting related information from users (key, dtype).
+
+Example output of parsing spec:
+
+```python
+# Define features and transformations
+feature_b = tf.feature_column.numeric_column(...)
+feature_c_bucketized = tf.feature_column.bucketized_column(
+ tf.feature_column.numeric_column("feature_c"), ...)
+feature_a_x_feature_c = tf.feature_column.crossed_column(
+ columns=["feature_a", feature_c_bucketized], ...)
+
+feature_columns = [feature_b, feature_c_bucketized, feature_a_x_feature_c]
+parsing_spec = tf.estimator.classifier_parse_example_spec(
+ feature_columns, label_key='my-label', label_dtype=tf.string)
+
+# For the above example, classifier_parse_example_spec would return the dict:
+assert parsing_spec == {
+ "feature_a": parsing_ops.VarLenFeature(tf.string),
+ "feature_b": parsing_ops.FixedLenFeature([1], dtype=tf.float32),
+ "feature_c": parsing_ops.FixedLenFeature([1], dtype=tf.float32)
+ "my-label" : parsing_ops.FixedLenFeature([1], dtype=tf.string)
+}
+```
+
+Example usage with a classifier:
+
+```python
+feature_columns = # define features via tf.feature_column
+estimator = DNNClassifier(
+ n_classes=1000,
+ feature_columns=feature_columns,
+ weight_column='example-weight',
+ label_vocabulary=['photos', 'keep', ...],
+ hidden_units=[256, 64, 16])
+# This label configuration tells the classifier the following:
+# * weights are retrieved with key 'example-weight'
+# * label is string and can be one of the following ['photos', 'keep', ...]
+# * integer id for label 'photos' is 0, 'keep' is 1, ...
+
+
+# Input builders
+def input_fn_train(): # Returns a tuple of features and labels.
+ features = tf.contrib.learn.read_keyed_batch_features(
+ file_pattern=train_files,
+ batch_size=batch_size,
+ # creates parsing configuration for tf.parse_example
+ features=tf.estimator.classifier_parse_example_spec(
+ feature_columns,
+ label_key='my-label',
+ label_dtype=tf.string,
+ weight_column='example-weight'),
+ reader=tf.RecordIOReader)
+ labels = features.pop('my-label')
+ return features, labels
+
+estimator.train(input_fn=input_fn_train)
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`feature_columns`
+ |
+
+An iterable containing all feature columns. All items
+should be instances of classes derived from `FeatureColumn`.
+ |
+
+|
+`label_key`
+ |
+
+A string identifying the label. It means tf.Example stores labels
+with this key.
+ |
+
+|
+`label_dtype`
+ |
+
+A `tf.dtype` identifies the type of labels. By default it is
+tf.int64. If user defines a `label_vocabulary`, this should be set as
+tf.string. tf.float32 labels are only supported for binary
+classification.
+ |
+
+|
+`label_default`
+ |
+
+used as label if label_key does not exist in given
+tf.Example. An example usage: let's say `label_key` is 'clicked' and
+tf.Example contains clicked data only for positive examples in following
+format `key:clicked, value:1`. This means that if there is no data with
+key 'clicked' it should count as negative example by setting
+`label_deafault=0`. Type of this value should be compatible with
+`label_dtype`.
+ |
+
+|
+`weight_column`
+ |
+
+A string or a `NumericColumn` created by
+tf.feature_column.numeric_column defining feature column representing
+weights. It is used to down weight or boost examples during training. It
+will be multiplied by the loss of the example. If it is a string, it is
+used as a key to fetch weight tensor from the `features`. If it is a
+`NumericColumn`, raw tensor is fetched by key `weight_column.key`, then
+weight_column.normalizer_fn is applied on it to get weight tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A dict mapping each feature key to a `FixedLenFeature` or `VarLenFeature`
+value.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If label is used in `feature_columns`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If weight_column is used in `feature_columns`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If any of the given `feature_columns` is not a `_FeatureColumn`
+instance.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `weight_column` is not a `NumericColumn` instance.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if label_key is None.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/experimental.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/experimental.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..35116699fb6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/experimental.md
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
+description: Public API for tf.estimator.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.estimator.experimental
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.estimator.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class InMemoryEvaluatorHook`](../../../../tf/estimator/experimental/InMemoryEvaluatorHook.md): Hook to run evaluation in training without a checkpoint.
+
+[`class KMeans`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/experimental/KMeans.md): An Estimator for K-Means clustering.
+
+[`class LinearSDCA`](../../../../tf/estimator/experimental/LinearSDCA.md): Stochastic Dual Coordinate Ascent helper for linear estimators.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`build_raw_supervised_input_receiver_fn(...)`](../../../../tf/estimator/experimental/build_raw_supervised_input_receiver_fn.md): Build a supervised_input_receiver_fn for raw features and labels.
+
+[`call_logit_fn(...)`](../../../../tf/estimator/experimental/call_logit_fn.md): Calls logit_fn (experimental).
+
+[`dnn_logit_fn_builder(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/experimental/dnn_logit_fn_builder.md): Function builder for a dnn logit_fn.
+
+[`linear_logit_fn_builder(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/experimental/linear_logit_fn_builder.md): Function builder for a linear logit_fn.
+
+[`make_early_stopping_hook(...)`](../../../../tf/estimator/experimental/make_early_stopping_hook.md): Creates early-stopping hook.
+
+[`make_stop_at_checkpoint_step_hook(...)`](../../../../tf/estimator/experimental/make_stop_at_checkpoint_step_hook.md): Creates a proper StopAtCheckpointStepHook based on chief status.
+
+[`stop_if_higher_hook(...)`](../../../../tf/estimator/experimental/stop_if_higher_hook.md): Creates hook to stop if the given metric is higher than the threshold.
+
+[`stop_if_lower_hook(...)`](../../../../tf/estimator/experimental/stop_if_lower_hook.md): Creates hook to stop if the given metric is lower than the threshold.
+
+[`stop_if_no_decrease_hook(...)`](../../../../tf/estimator/experimental/stop_if_no_decrease_hook.md): Creates hook to stop if metric does not decrease within given max steps.
+
+[`stop_if_no_increase_hook(...)`](../../../../tf/estimator/experimental/stop_if_no_increase_hook.md): Creates hook to stop if metric does not increase within given max steps.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/experimental/KMeans.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/experimental/KMeans.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..5006140c4ad
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/experimental/KMeans.md
@@ -0,0 +1,1393 @@
+description: An Estimator for K-Means clustering.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.estimator.experimental.KMeans
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+An Estimator for K-Means clustering.
+
+Inherits From: [`Estimator`](../../../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/Estimator.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.estimator.experimental.KMeans(
+ num_clusters, model_dir=None, initial_clusters=RANDOM_INIT,
+ distance_metric=SQUARED_EUCLIDEAN_DISTANCE, seed=None, use_mini_batch=(True),
+ mini_batch_steps_per_iteration=1, kmeans_plus_plus_num_retries=2,
+ relative_tolerance=None, config=None, feature_columns=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+```
+import numpy as np
+import tensorflow as tf
+
+num_points = 100
+dimensions = 2
+points = np.random.uniform(0, 1000, [num_points, dimensions])
+
+def input_fn():
+ return tf.compat.v1.train.limit_epochs(
+ tf.convert_to_tensor(points, dtype=tf.float32), num_epochs=1)
+
+num_clusters = 5
+kmeans = tf.compat.v1.estimator.experimental.KMeans(
+ num_clusters=num_clusters, use_mini_batch=False)
+
+# train
+num_iterations = 10
+previous_centers = None
+for _ in xrange(num_iterations):
+ kmeans.train(input_fn)
+ cluster_centers = kmeans.cluster_centers()
+ if previous_centers is not None:
+ print 'delta:', cluster_centers - previous_centers
+ previous_centers = cluster_centers
+ print 'score:', kmeans.score(input_fn)
+print 'cluster centers:', cluster_centers
+
+# map the input points to their clusters
+cluster_indices = list(kmeans.predict_cluster_index(input_fn))
+for i, point in enumerate(points):
+ cluster_index = cluster_indices[i]
+ center = cluster_centers[cluster_index]
+ print 'point:', point, 'is in cluster', cluster_index, 'centered at', center
+```
+
+The `SavedModel` saved by the `export_saved_model` method does not include the
+cluster centers. However, the cluster centers may be retrieved by the
+latest checkpoint saved during training. Specifically,
+```
+kmeans.cluster_centers()
+```
+is equivalent to
+```
+tf.train.load_variable(
+ kmeans.model_dir, KMeansClustering.CLUSTER_CENTERS_VAR_NAME)
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`num_clusters`
+ |
+
+An integer tensor specifying the number of clusters. This
+argument is ignored if `initial_clusters` is a tensor or numpy array.
+ |
+
+|
+`model_dir`
+ |
+
+The directory to save the model results and log files.
+ |
+
+|
+`initial_clusters`
+ |
+
+Specifies how the initial cluster centers are chosen.
+One of the following: * a tensor or numpy array with the initial cluster
+centers. * a callable `f(inputs, k)` that selects and returns up to
+`k` centers from an input batch. `f` is free to return any number of
+centers from `0` to `k`. It will be invoked on successive input
+batches as necessary until all `num_clusters` centers are chosen.
+* `KMeansClustering.RANDOM_INIT`: Choose centers randomly from an input
+batch. If the batch size is less than `num_clusters` then the entire
+batch is chosen to be initial cluster centers and the remaining
+centers are chosen from successive input batches.
+* `KMeansClustering.KMEANS_PLUS_PLUS_INIT`: Use kmeans++ to choose
+centers from the first input batch. If the batch size is less than
+`num_clusters`, a TensorFlow runtime error occurs.
+ |
+
+|
+`distance_metric`
+ |
+
+The distance metric used for clustering. One of:
+* `KMeansClustering.SQUARED_EUCLIDEAN_DISTANCE`: Euclidean distance
+between vectors `u` and `v` is defined as \\(||u - v||_2\\) which is
+the square root of the sum of the absolute squares of the elements'
+difference.
+* `KMeansClustering.COSINE_DISTANCE`: Cosine distance between vectors
+`u` and `v` is defined as \\(1 - (u . v) / (||u||_2 ||v||_2)\\).
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+Python integer. Seed for PRNG used to initialize centers.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_mini_batch`
+ |
+
+A boolean specifying whether to use the mini-batch k-means
+algorithm. See explanation above.
+ |
+
+|
+`mini_batch_steps_per_iteration`
+ |
+
+The number of steps after which the
+updated cluster centers are synced back to a master copy. Used only if
+`use_mini_batch=True`. See explanation above.
+ |
+
+|
+`kmeans_plus_plus_num_retries`
+ |
+
+For each point that is sampled during
+kmeans++ initialization, this parameter specifies the number of
+additional points to draw from the current distribution before selecting
+the best. If a negative value is specified, a heuristic is used to
+sample `O(log(num_to_sample))` additional points. Used only if
+`initial_clusters=KMeansClustering.KMEANS_PLUS_PLUS_INIT`.
+ |
+
+|
+`relative_tolerance`
+ |
+
+A relative tolerance of change in the loss between
+iterations. Stops learning if the loss changes less than this amount.
+This may not work correctly if `use_mini_batch=True`.
+ |
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+See tf.estimator.Estimator.
+ |
+
+|
+`feature_columns`
+ |
+
+An optionable iterable containing all the feature columns
+used by the model. All items in the set should be feature column
+instances that can be passed to `tf.feature_column.input_layer`. If this
+is None, all features will be used.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+An invalid argument was passed to `initial_clusters` or
+`distance_metric`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`model_dir`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`model_fn`
+ |
+
+Returns the `model_fn` which is bound to `self.params`.
+ |
+
+|
+`params`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+cluster_centers
+
+View source
+
+
+cluster_centers()
+
+
+Returns the cluster centers.
+
+
+eval_dir
+
+View source
+
+
+eval_dir(
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+Shows the directory name where evaluation metrics are dumped.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of the evaluation if user needs to run multiple evaluations on
+different data sets, such as on training data vs test data. Metrics for
+different evaluations are saved in separate folders, and appear
+separately in tensorboard.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A string which is the path of directory contains evaluation metrics.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+evaluate
+
+View source
+
+
+evaluate(
+ input_fn, steps=None, hooks=None, checkpoint_path=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+Evaluates the model given evaluation data `input_fn`.
+
+For each step, calls `input_fn`, which returns one batch of data.
+Evaluates until:
+- `steps` batches are processed, or
+- `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception (tf.errors.OutOfRangeError
+or
+`StopIteration`).
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that constructs the input data for evaluation. See
+[Premade Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The
+function should construct and return one of the following: * A
+tf.data.Dataset object: Outputs of `Dataset` object must be a tuple
+`(features, labels)` with same constraints as below. * A tuple
+`(features, labels)`: Where `features` is a tf.Tensor or a dictionary
+of string feature name to `Tensor` and `labels` is a `Tensor` or a
+dictionary of string label name to `Tensor`. Both `features` and
+`labels` are consumed by `model_fn`. They should satisfy the
+expectation of `model_fn` from inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`steps`
+ |
+
+Number of steps for which to evaluate model. If `None`, evaluates
+until `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the evaluation call.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+Path of a specific checkpoint to evaluate. If `None`, the
+latest checkpoint in `model_dir` is used. If there are no checkpoints
+in `model_dir`, evaluation is run with newly initialized `Variables`
+instead of ones restored from checkpoint.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of the evaluation if user needs to run multiple evaluations on
+different data sets, such as on training data vs test data. Metrics for
+different evaluations are saved in separate folders, and appear
+separately in tensorboard.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A dict containing the evaluation metrics specified in `model_fn` keyed by
+name, as well as an entry `global_step` which contains the value of the
+global step for which this evaluation was performed. For canned
+estimators, the dict contains the `loss` (mean loss per mini-batch) and
+the `average_loss` (mean loss per sample). Canned classifiers also return
+the `accuracy`. Canned regressors also return the `label/mean` and the
+`prediction/mean`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `steps <= 0`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+experimental_export_all_saved_models
+
+View source
+
+
+experimental_export_all_saved_models(
+ export_dir_base, input_receiver_fn_map, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None
+)
+
+
+Exports a `SavedModel` with `tf.MetaGraphDefs` for each requested mode.
+
+For each mode passed in via the `input_receiver_fn_map`,
+this method builds a new graph by calling the `input_receiver_fn` to obtain
+feature and label `Tensor`s. Next, this method calls the `Estimator`'s
+`model_fn` in the passed mode to generate the model graph based on
+those features and labels, and restores the given checkpoint
+(or, lacking that, the most recent checkpoint) into the graph.
+Only one of the modes is used for saving variables to the `SavedModel`
+(order of preference: tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN,
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys.EVAL, then
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT), such that up to three
+`tf.MetaGraphDefs` are saved with a single set of variables in a single
+`SavedModel` directory.
+
+For the variables and `tf.MetaGraphDefs`, a timestamped export directory
+below
+`export_dir_base`, and writes a `SavedModel` into it containing
+the `tf.MetaGraphDef` for the given mode and its associated signatures.
+
+For prediction, the exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef`
+for each element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`,
+named using the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+For training and evaluation, the `train_op` is stored in an extra
+collection,
+and loss, metrics, and predictions are included in a `SignatureDef` for the
+mode in question.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`input_receiver_fn_map`
+ |
+
+dict of tf.estimator.ModeKeys to
+`input_receiver_fn` mappings, where the `input_receiver_fn` is a
+function that takes no arguments and returns the appropriate subclass of
+`InputReceiver`.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if any `input_receiver_fn` is `None`, no `export_outputs`
+are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+export_saved_model
+
+View source
+
+
+export_saved_model(
+ export_dir_base, serving_input_receiver_fn, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None, experimental_mode=ModeKeys.PREDICT
+)
+
+
+Exports inference graph as a `SavedModel` into the given dir.
+
+For a detailed guide, see
+[Using SavedModel with
+Estimators](https://tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model#using_savedmodel_with_estimators).
+
+This method builds a new graph by first calling the
+`serving_input_receiver_fn` to obtain feature `Tensor`s, and then calling
+this `Estimator`'s `model_fn` to generate the model graph based on those
+features. It restores the given checkpoint (or, lacking that, the most
+recent checkpoint) into this graph in a fresh session. Finally it creates
+a timestamped export directory below the given `export_dir_base`, and writes
+a `SavedModel` into it containing a single `tf.MetaGraphDef` saved from this
+session.
+
+The exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef` for each
+element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`, named
+using
+the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+The experimental_mode parameter can be used to export a single
+train/eval/predict graph as a `SavedModel`.
+See `experimental_export_all_saved_models` for full docs.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`serving_input_receiver_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that takes no argument and returns a
+tf.estimator.export.ServingInputReceiver or
+tf.estimator.export.TensorServingInputReceiver.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+|
+`experimental_mode`
+ |
+
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys value indicating with mode will
+be exported. Note that this feature is experimental.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if no `serving_input_receiver_fn` is provided, no
+`export_outputs` are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+export_savedmodel
+
+View source
+
+
+export_savedmodel(
+ export_dir_base, serving_input_receiver_fn, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None, strip_default_attrs=(False)
+)
+
+
+Exports inference graph as a `SavedModel` into the given dir. (deprecated)
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+This function has been renamed, use `export_saved_model` instead.
+
+For a detailed guide, see
+[Using SavedModel with
+Estimators](https://tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model#using_savedmodel_with_estimators).
+
+This method builds a new graph by first calling the
+`serving_input_receiver_fn` to obtain feature `Tensor`s, and then calling
+this `Estimator`'s `model_fn` to generate the model graph based on those
+features. It restores the given checkpoint (or, lacking that, the most
+recent checkpoint) into this graph in a fresh session. Finally it creates
+a timestamped export directory below the given `export_dir_base`, and writes
+a `SavedModel` into it containing a single `tf.MetaGraphDef` saved from this
+session.
+
+The exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef` for each
+element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`, named
+using
+the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`serving_input_receiver_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that takes no argument and returns a
+tf.estimator.export.ServingInputReceiver or
+tf.estimator.export.TensorServingInputReceiver.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+|
+`strip_default_attrs`
+ |
+
+Boolean. If `True`, default-valued attributes will be
+removed from the `NodeDef`s. For a detailed guide, see [Stripping
+Default-Valued Attributes](
+https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/master/tensorflow/python/saved_model/README.md#stripping-default-valued-attributes).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if no `serving_input_receiver_fn` is provided, no
+`export_outputs` are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+get_variable_names
+
+View source
+
+
+get_variable_names()
+
+
+Returns list of all variable names in this model.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+List of names.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `Estimator` has not produced a checkpoint yet.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+get_variable_value
+
+View source
+
+
+get_variable_value(
+ name
+)
+
+
+Returns value of the variable given by name.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+string or a list of string, name of the tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Numpy array - value of the tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `Estimator` has not produced a checkpoint yet.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+latest_checkpoint
+
+View source
+
+
+latest_checkpoint()
+
+
+Finds the filename of the latest saved checkpoint file in `model_dir`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The full path to the latest checkpoint or `None` if no checkpoint was
+found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+predict
+
+View source
+
+
+predict(
+ input_fn, predict_keys=None, hooks=None, checkpoint_path=None,
+ yield_single_examples=(True)
+)
+
+
+Yields predictions for given features.
+
+Please note that interleaving two predict outputs does not work. See:
+[issue/20506](
+https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/issues/20506#issuecomment-422208517)
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that constructs the features. Prediction continues
+until `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception
+(tf.errors.OutOfRangeError or `StopIteration`). See [Premade
+Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The function should construct and return one of
+the following:
+* tf.data.Dataset object -- Outputs of `Dataset` object must have
+same constraints as below.
+* features -- A tf.Tensor or a dictionary of string feature name to
+`Tensor`. features are consumed by `model_fn`. They should satisfy
+the expectation of `model_fn` from inputs. * A tuple, in which case
+the first item is extracted as features.
+ |
+
+|
+`predict_keys`
+ |
+
+list of `str`, name of the keys to predict. It is used if
+the tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec.predictions is a `dict`. If
+`predict_keys` is used then rest of the predictions will be filtered
+from the dictionary. If `None`, returns all.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the prediction call.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+Path of a specific checkpoint to predict. If `None`, the
+latest checkpoint in `model_dir` is used. If there are no checkpoints
+in `model_dir`, prediction is run with newly initialized `Variables`
+instead of ones restored from checkpoint.
+ |
+
+|
+`yield_single_examples`
+ |
+
+If `False`, yields the whole batch as returned by
+the `model_fn` instead of decomposing the batch into individual
+elements. This is useful if `model_fn` returns some tensors whose first
+dimension is not equal to the batch size.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Yields:
+
+Evaluated values of `predictions` tensors.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If batch length of predictions is not the same and
+`yield_single_examples` is `True`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If there is a conflict between `predict_keys` and
+`predictions`. For example if `predict_keys` is not `None` but
+tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec.predictions is not a `dict`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+predict_cluster_index
+
+View source
+
+
+predict_cluster_index(
+ input_fn
+)
+
+
+Finds the index of the closest cluster center to each input point.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Yields:
+
+The index of the closest cluster center for each input point.
+
+
+score
+
+View source
+
+
+score(
+ input_fn
+)
+
+
+Returns the sum of squared distances to nearest clusters.
+
+Note that this function is different from the corresponding one in sklearn
+which returns the negative sum.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The sum of the squared distance from each point in the first batch of
+inputs to its nearest cluster center.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+train
+
+View source
+
+
+train(
+ input_fn, hooks=None, steps=None, max_steps=None, saving_listeners=None
+)
+
+
+Trains a model given training data `input_fn`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that provides input data for training as minibatches.
+See [Premade Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The function should construct and return one of
+the following:
+* A tf.data.Dataset object: Outputs of `Dataset` object must be a
+tuple `(features, labels)` with same constraints as below.
+* A tuple `(features, labels)`: Where `features` is a tf.Tensor or a
+dictionary of string feature name to `Tensor` and `labels` is a
+`Tensor` or a dictionary of string label name to `Tensor`. Both
+`features` and `labels` are consumed by `model_fn`. They should
+satisfy the expectation of `model_fn` from inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the training loop.
+ |
+
+|
+`steps`
+ |
+
+Number of steps for which to train the model. If `None`, train
+forever or train until `input_fn` generates the `tf.errors.OutOfRange`
+error or `StopIteration` exception. `steps` works incrementally. If you
+call two times `train(steps=10)` then training occurs in total 20 steps.
+If `OutOfRange` or `StopIteration` occurs in the middle, training stops
+before 20 steps. If you don't want to have incremental behavior please
+set `max_steps` instead. If set, `max_steps` must be `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_steps`
+ |
+
+Number of total steps for which to train model. If `None`,
+train forever or train until `input_fn` generates the
+`tf.errors.OutOfRange` error or `StopIteration` exception. If set,
+`steps` must be `None`. If `OutOfRange` or `StopIteration` occurs in the
+middle, training stops before `max_steps` steps. Two calls to
+`train(steps=100)` means 200 training iterations. On the other hand, two
+calls to `train(max_steps=100)` means that the second call will not do
+any iteration since first call did all 100 steps.
+ |
+
+|
+`saving_listeners`
+ |
+
+list of `CheckpointSaverListener` objects. Used for
+callbacks that run immediately before or after checkpoint savings.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`self`, for chaining.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If both `steps` and `max_steps` are not `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If either `steps` or `max_steps <= 0`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+View source
+
+
+transform(
+ input_fn
+)
+
+
+Transforms each input point to its distances to all cluster centers.
+
+Note that if `distance_metric=KMeansClustering.SQUARED_EUCLIDEAN_DISTANCE`,
+this
+function returns the squared Euclidean distance while the corresponding
+sklearn function returns the Euclidean distance.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Yields:
+
+The distances from each input point to each cluster center.
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `ALL_DISTANCES = 'all_distances'`
+* `CLUSTER_CENTERS_VAR_NAME = 'clusters'`
+* `CLUSTER_INDEX = 'cluster_index'`
+* `COSINE_DISTANCE = 'cosine'`
+* `KMEANS_PLUS_PLUS_INIT = 'kmeans_plus_plus'`
+* `RANDOM_INIT = 'random'`
+* `SCORE = 'score'`
+* `SQUARED_EUCLIDEAN_DISTANCE = 'squared_euclidean'`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/experimental/dnn_logit_fn_builder.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/experimental/dnn_logit_fn_builder.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e3d4ec0c094
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/experimental/dnn_logit_fn_builder.md
@@ -0,0 +1,126 @@
+description: Function builder for a dnn logit_fn.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.estimator.experimental.dnn_logit_fn_builder
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Function builder for a dnn logit_fn.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.estimator.experimental.dnn_logit_fn_builder(
+ units, hidden_units, feature_columns, activation_fn, dropout,
+ input_layer_partitioner, batch_norm
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`units`
+ |
+
+An int indicating the dimension of the logit layer. In the MultiHead
+case, this should be the sum of all component Heads' logit dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`hidden_units`
+ |
+
+Iterable of integer number of hidden units per layer.
+ |
+
+|
+`feature_columns`
+ |
+
+Iterable of `feature_column._FeatureColumn` model inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`activation_fn`
+ |
+
+Activation function applied to each layer.
+ |
+
+|
+`dropout`
+ |
+
+When not `None`, the probability we will drop out a given
+coordinate.
+ |
+
+|
+`input_layer_partitioner`
+ |
+
+Partitioner for input layer.
+ |
+
+|
+`batch_norm`
+ |
+
+Whether to use batch normalization after each hidden layer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A logit_fn (see below).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If units is not an int.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/experimental/linear_logit_fn_builder.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/experimental/linear_logit_fn_builder.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3338b75e4ed
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/experimental/linear_logit_fn_builder.md
@@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
+description: Function builder for a linear logit_fn.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.estimator.experimental.linear_logit_fn_builder
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Function builder for a linear logit_fn.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.estimator.experimental.linear_logit_fn_builder(
+ units, feature_columns, sparse_combiner='sum'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`units`
+ |
+
+An int indicating the dimension of the logit layer.
+ |
+
+|
+`feature_columns`
+ |
+
+An iterable containing all the feature columns used by the
+model.
+ |
+
+|
+`sparse_combiner`
+ |
+
+A string specifying how to reduce if a categorical column
+is multivalent. One of "mean", "sqrtn", and "sum".
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A logit_fn (see below).
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/export.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/export.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..d7c1ba82ec2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/export.md
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
+description: All public utility methods for exporting Estimator to SavedModel.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.estimator.export
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+All public utility methods for exporting Estimator to SavedModel.
+
+
+This file includes functions and constants from core (model_utils) and export.py
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class ClassificationOutput`](../../../../tf/estimator/export/ClassificationOutput.md): Represents the output of a classification head.
+
+[`class ExportOutput`](../../../../tf/estimator/export/ExportOutput.md): Represents an output of a model that can be served.
+
+[`class PredictOutput`](../../../../tf/estimator/export/PredictOutput.md): Represents the output of a generic prediction head.
+
+[`class RegressionOutput`](../../../../tf/estimator/export/RegressionOutput.md): Represents the output of a regression head.
+
+[`class ServingInputReceiver`](../../../../tf/estimator/export/ServingInputReceiver.md): A return type for a serving_input_receiver_fn.
+
+[`class TensorServingInputReceiver`](../../../../tf/estimator/export/TensorServingInputReceiver.md): A return type for a serving_input_receiver_fn.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`build_parsing_serving_input_receiver_fn(...)`](../../../../tf/estimator/export/build_parsing_serving_input_receiver_fn.md): Build a serving_input_receiver_fn expecting fed tf.Examples.
+
+[`build_raw_serving_input_receiver_fn(...)`](../../../../tf/estimator/export/build_raw_serving_input_receiver_fn.md): Build a serving_input_receiver_fn expecting feature Tensors.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/inputs.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/inputs.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..d950fdb60be
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/inputs.md
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
+description: Utility methods to create simple input_fns.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.estimator.inputs
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Utility methods to create simple input_fns.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`numpy_input_fn(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/inputs/numpy_input_fn.md): Returns input function that would feed dict of numpy arrays into the model.
+
+[`pandas_input_fn(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/inputs/pandas_input_fn.md): Returns input function that would feed Pandas DataFrame into the model.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/inputs/numpy_input_fn.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/inputs/numpy_input_fn.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..88fa87bd527
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/inputs/numpy_input_fn.md
@@ -0,0 +1,176 @@
+description: Returns input function that would feed dict of numpy arrays into the model.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.estimator.inputs.numpy_input_fn
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns input function that would feed dict of numpy arrays into the model.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.estimator.inputs.numpy_input_fn(
+ x, y=None, batch_size=128, num_epochs=1, shuffle=None, queue_capacity=1000,
+ num_threads=1
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This returns a function outputting `features` and `targets` based on the dict
+of numpy arrays. The dict `features` has the same keys as the `x`. The dict
+`targets` has the same keys as the `y` if `y` is a dict.
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+age = np.arange(4) * 1.0
+height = np.arange(32, 36)
+x = {'age': age, 'height': height}
+y = np.arange(-32, -28)
+
+with tf.Session() as session:
+ input_fn = numpy_io.numpy_input_fn(
+ x, y, batch_size=2, shuffle=False, num_epochs=1)
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`x`
+ |
+
+numpy array object or dict of numpy array objects. If an array, the array
+will be treated as a single feature.
+ |
+
+|
+`y`
+ |
+
+numpy array object or dict of numpy array object. `None` if absent.
+ |
+
+|
+`batch_size`
+ |
+
+Integer, size of batches to return.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_epochs`
+ |
+
+Integer, number of epochs to iterate over data. If `None` will
+run forever.
+ |
+
+|
+`shuffle`
+ |
+
+Boolean, if True shuffles the queue. Avoid shuffle at prediction
+time.
+ |
+
+|
+`queue_capacity`
+ |
+
+Integer, size of queue to accumulate.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_threads`
+ |
+
+Integer, number of threads used for reading and enqueueing. In
+order to have predicted and repeatable order of reading and enqueueing,
+such as in prediction and evaluation mode, `num_threads` should be 1.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Function, that has signature of ()->(dict of `features`, `targets`)
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if the shape of `y` mismatches the shape of values in `x` (i.e.,
+values in `x` have same shape).
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if duplicate keys are in both `x` and `y` when `y` is a dict.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if x or y is an empty dict.
+ |
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+`x` is not a dict or array.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if 'shuffle' is not provided or a bool.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/inputs/pandas_input_fn.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/inputs/pandas_input_fn.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..1dd9fbe682a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/inputs/pandas_input_fn.md
@@ -0,0 +1,145 @@
+description: Returns input function that would feed Pandas DataFrame into the model.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.estimator.inputs.pandas_input_fn
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns input function that would feed Pandas DataFrame into the model.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.estimator.inputs.pandas_input_fn(
+ x, y=None, batch_size=128, num_epochs=1, shuffle=None, queue_capacity=1000,
+ num_threads=1, target_column='target'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Note: `y`'s index must match `x`'s index.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`x`
+ |
+
+pandas `DataFrame` object.
+ |
+
+|
+`y`
+ |
+
+pandas `Series` object or `DataFrame`. `None` if absent.
+ |
+
+|
+`batch_size`
+ |
+
+int, size of batches to return.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_epochs`
+ |
+
+int, number of epochs to iterate over data. If not `None`, read
+attempts that would exceed this value will raise `OutOfRangeError`.
+ |
+
+|
+`shuffle`
+ |
+
+bool, whether to read the records in random order.
+ |
+
+|
+`queue_capacity`
+ |
+
+int, size of the read queue. If `None`, it will be set
+roughly to the size of `x`.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_threads`
+ |
+
+Integer, number of threads used for reading and enqueueing. In
+order to have predicted and repeatable order of reading and enqueueing,
+such as in prediction and evaluation mode, `num_threads` should be 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`target_column`
+ |
+
+str, name to give the target column `y`. This parameter is
+not used when `y` is a `DataFrame`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Function, that has signature of ()->(dict of `features`, `target`)
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `x` already contains a column with the same name as `y`, or
+if the indexes of `x` and `y` don't match.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if 'shuffle' is not provided or a bool.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/regressor_parse_example_spec.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/regressor_parse_example_spec.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3025f2d5aad
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/regressor_parse_example_spec.md
@@ -0,0 +1,224 @@
+description: Generates parsing spec for tf.parse_example to be used with regressors.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.estimator.regressor_parse_example_spec
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Generates parsing spec for tf.parse_example to be used with regressors.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.estimator.regressor_parse_example_spec(
+ feature_columns, label_key, label_dtype=tf.dtypes.float32, label_default=None,
+ label_dimension=1, weight_column=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+If users keep data in tf.Example format, they need to call tf.parse_example
+with a proper feature spec. There are two main things that this utility helps:
+
+* Users need to combine parsing spec of features with labels and weights
+ (if any) since they are all parsed from same tf.Example instance. This
+ utility combines these specs.
+* It is difficult to map expected label by a regressor such as `DNNRegressor`
+ to corresponding tf.parse_example spec. This utility encodes it by getting
+ related information from users (key, dtype).
+
+Example output of parsing spec:
+
+```python
+# Define features and transformations
+feature_b = tf.feature_column.numeric_column(...)
+feature_c_bucketized = tf.feature_column.bucketized_column(
+ tf.feature_column.numeric_column("feature_c"), ...)
+feature_a_x_feature_c = tf.feature_column.crossed_column(
+ columns=["feature_a", feature_c_bucketized], ...)
+
+feature_columns = [feature_b, feature_c_bucketized, feature_a_x_feature_c]
+parsing_spec = tf.estimator.regressor_parse_example_spec(
+ feature_columns, label_key='my-label')
+
+# For the above example, regressor_parse_example_spec would return the dict:
+assert parsing_spec == {
+ "feature_a": parsing_ops.VarLenFeature(tf.string),
+ "feature_b": parsing_ops.FixedLenFeature([1], dtype=tf.float32),
+ "feature_c": parsing_ops.FixedLenFeature([1], dtype=tf.float32)
+ "my-label" : parsing_ops.FixedLenFeature([1], dtype=tf.float32)
+}
+```
+
+Example usage with a regressor:
+
+```python
+feature_columns = # define features via tf.feature_column
+estimator = DNNRegressor(
+ hidden_units=[256, 64, 16],
+ feature_columns=feature_columns,
+ weight_column='example-weight',
+ label_dimension=3)
+# This label configuration tells the regressor the following:
+# * weights are retrieved with key 'example-weight'
+# * label is a 3 dimension tensor with float32 dtype.
+
+
+# Input builders
+def input_fn_train(): # Returns a tuple of features and labels.
+ features = tf.contrib.learn.read_keyed_batch_features(
+ file_pattern=train_files,
+ batch_size=batch_size,
+ # creates parsing configuration for tf.parse_example
+ features=tf.estimator.classifier_parse_example_spec(
+ feature_columns,
+ label_key='my-label',
+ label_dimension=3,
+ weight_column='example-weight'),
+ reader=tf.RecordIOReader)
+ labels = features.pop('my-label')
+ return features, labels
+
+estimator.train(input_fn=input_fn_train)
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`feature_columns`
+ |
+
+An iterable containing all feature columns. All items
+should be instances of classes derived from `_FeatureColumn`.
+ |
+
+|
+`label_key`
+ |
+
+A string identifying the label. It means tf.Example stores labels
+with this key.
+ |
+
+|
+`label_dtype`
+ |
+
+A `tf.dtype` identifies the type of labels. By default it is
+tf.float32.
+ |
+
+|
+`label_default`
+ |
+
+used as label if label_key does not exist in given
+tf.Example. By default default_value is none, which means
+`tf.parse_example` will error out if there is any missing label.
+ |
+
+|
+`label_dimension`
+ |
+
+Number of regression targets per example. This is the size
+of the last dimension of the labels and logits `Tensor` objects
+(typically, these have shape `[batch_size, label_dimension]`).
+ |
+
+|
+`weight_column`
+ |
+
+A string or a `NumericColumn` created by
+tf.feature_column.numeric_column defining feature column representing
+weights. It is used to down weight or boost examples during training. It
+will be multiplied by the loss of the example. If it is a string, it is
+used as a key to fetch weight tensor from the `features`. If it is a
+`NumericColumn`, raw tensor is fetched by key `weight_column.key`, then
+weight_column.normalizer_fn is applied on it to get weight tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A dict mapping each feature key to a `FixedLenFeature` or `VarLenFeature`
+value.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If label is used in `feature_columns`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If weight_column is used in `feature_columns`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If any of the given `feature_columns` is not a `_FeatureColumn`
+instance.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `weight_column` is not a `NumericColumn` instance.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if label_key is None.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/tpu.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/tpu.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..341a8e0a47e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/tpu.md
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
+description: Public API for tf.estimator.tpu namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.estimator.tpu
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.estimator.tpu namespace.
+
+
+
+## Modules
+
+[`experimental`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/tpu/experimental.md) module: Public API for tf.estimator.tpu.experimental namespace.
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class InputPipelineConfig`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/tpu/InputPipelineConfig.md): Please see the definition of these values in TPUConfig.
+
+[`class RunConfig`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/tpu/RunConfig.md): RunConfig with TPU support.
+
+[`class TPUConfig`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/tpu/TPUConfig.md): TPU related configuration required by `TPUEstimator`.
+
+[`class TPUEstimator`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/tpu/TPUEstimator.md): Estimator with TPU support.
+
+[`class TPUEstimatorSpec`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/tpu/TPUEstimatorSpec.md): Ops and objects returned from a `model_fn` and passed to `TPUEstimator`.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/tpu/InputPipelineConfig.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/tpu/InputPipelineConfig.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..6de8af40f97
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/tpu/InputPipelineConfig.md
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
+description: Please see the definition of these values in TPUConfig.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.estimator.tpu.InputPipelineConfig
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Please see the definition of these values in TPUConfig.
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `BROADCAST = 4`
+* `PER_HOST_V1 = 2`
+* `PER_HOST_V2 = 3`
+* `PER_SHARD_V1 = 1`
+* `SLICED = 5`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/tpu/RunConfig.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/tpu/RunConfig.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..239b6e17ac6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/tpu/RunConfig.md
@@ -0,0 +1,426 @@
+description: RunConfig with TPU support.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.estimator.tpu.RunConfig
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+RunConfig with TPU support.
+
+Inherits From: [`RunConfig`](../../../../../tf/estimator/RunConfig.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.estimator.tpu.RunConfig(
+ tpu_config=None, evaluation_master=None, master=None, cluster=None, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`tpu_config`
+ |
+
+the TPUConfig that specifies TPU-specific configuration.
+ |
+
+|
+`evaluation_master`
+ |
+
+a string. The address of the master to use for eval.
+Defaults to master if not set.
+ |
+
+|
+`master`
+ |
+
+a string. The address of the master to use for training.
+ |
+
+|
+`cluster`
+ |
+
+a ClusterResolver
+ |
+
+|
+`**kwargs`
+ |
+
+keyword config parameters.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if cluster is not None and the provided session_config has a
+cluster_def already.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cluster`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`cluster_spec`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`device_fn`
+ |
+
+Returns the device_fn.
+
+If device_fn is not `None`, it overrides the default
+device function used in `Estimator`.
+Otherwise the default one is used.
+ |
+
+|
+`eval_distribute`
+ |
+
+Optional tf.distribute.Strategy for evaluation.
+ |
+
+|
+`evaluation_master`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`experimental_max_worker_delay_secs`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`global_id_in_cluster`
+ |
+
+The global id in the training cluster.
+
+All global ids in the training cluster are assigned from an increasing
+sequence of consecutive integers. The first id is 0.
+
+Note: Task id (the property field `task_id`) is tracking the index of the
+node among all nodes with the SAME task type. For example, given the cluster
+definition as follows:
+
+```
+cluster = {'chief': ['host0:2222'],
+'ps': ['host1:2222', 'host2:2222'],
+'worker': ['host3:2222', 'host4:2222', 'host5:2222']}
+```
+
+Nodes with task type `worker` can have id 0, 1, 2. Nodes with task type
+`ps` can have id, 0, 1. So, `task_id` is not unique, but the pair
+(`task_type`, `task_id`) can uniquely determine a node in the cluster.
+
+Global id, i.e., this field, is tracking the index of the node among ALL
+nodes in the cluster. It is uniquely assigned. For example, for the cluster
+spec given above, the global ids are assigned as:
+```
+task_type | task_id | global_id
+--------------------------------
+chief | 0 | 0
+worker | 0 | 1
+worker | 1 | 2
+worker | 2 | 3
+ps | 0 | 4
+ps | 1 | 5
+```
+ |
+
+|
+`is_chief`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`keep_checkpoint_every_n_hours`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`keep_checkpoint_max`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`log_step_count_steps`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`master`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`model_dir`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`num_ps_replicas`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`num_worker_replicas`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`protocol`
+ |
+
+Returns the optional protocol value.
+ |
+
+|
+`save_checkpoints_secs`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`save_checkpoints_steps`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`save_summary_steps`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`service`
+ |
+
+Returns the platform defined (in TF_CONFIG) service dict.
+ |
+
+|
+`session_config`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`session_creation_timeout_secs`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`task_id`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`task_type`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`tf_random_seed`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`tpu_config`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`train_distribute`
+ |
+
+Optional tf.distribute.Strategy for training.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+replace
+
+View source
+
+
+replace(
+ **kwargs
+)
+
+
+Returns a new instance of `RunConfig` replacing specified properties.
+
+Only the properties in the following list are allowed to be replaced:
+
+ - `model_dir`,
+ - `tf_random_seed`,
+ - `save_summary_steps`,
+ - `save_checkpoints_steps`,
+ - `save_checkpoints_secs`,
+ - `session_config`,
+ - `keep_checkpoint_max`,
+ - `keep_checkpoint_every_n_hours`,
+ - `log_step_count_steps`,
+ - `train_distribute`,
+ - `device_fn`,
+ - `protocol`.
+ - `eval_distribute`,
+ - `experimental_distribute`,
+ - `experimental_max_worker_delay_secs`,
+
+In addition, either `save_checkpoints_steps` or `save_checkpoints_secs`
+can be set (should not be both).
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`**kwargs`
+ |
+
+keyword named properties with new values.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If any property name in `kwargs` does not exist or is not
+allowed to be replaced, or both `save_checkpoints_steps` and
+`save_checkpoints_secs` are set.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+a new instance of `RunConfig`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/tpu/TPUConfig.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/tpu/TPUConfig.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e539b78eb2e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/tpu/TPUConfig.md
@@ -0,0 +1,277 @@
+description: TPU related configuration required by TPUEstimator.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.estimator.tpu.TPUConfig
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+TPU related configuration required by `TPUEstimator`.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.estimator.tpu.TPUConfig(
+ iterations_per_loop=2, num_shards=None, num_cores_per_replica=None,
+ per_host_input_for_training=(True), tpu_job_name=None,
+ initial_infeed_sleep_secs=None, input_partition_dims=None,
+ eval_training_input_configuration=InputPipelineConfig.PER_HOST_V1,
+ experimental_host_call_every_n_steps=1
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`iterations_per_loop`
+ |
+
+This is the number of train steps running in TPU system
+before returning to CPU host for each `Session.run`. This means global
+step is increased `iterations_per_loop` times in one `Session.run`. It is
+recommended to be set as number of global steps for next checkpoint. Note
+that in evaluation don't use this value, instead we run total eval `steps`
+on TPU for a single `Session.run`.
+[Experimental]: `iterations_per_loop` can be specified as a time interval.
+To specify N seconds in one `Session.run`, one can specify it as `Ns`
+and substitute the N with the N with the number of desired seconds.
+Alternatively, the unit of time can also be specified in minutes or
+hours, e.g. `3600s` or `60m` or `1h`.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_shards`
+ |
+
+(Deprecated, ignored by TPUEstimator). The number of model
+replicas in the system. For non-model-parallelism case, this number equals
+the total number of TPU cores. For model-parallelism, the total number of
+TPU cores equals num_cores_per_replica * num_shards.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_cores_per_replica`
+ |
+
+Defaults to `None`, which disables model parallelism.
+An integer which describes the number of TPU cores per model replica. This
+is required by model-parallelism which enables partitioning the model to
+multiple cores. Currently num_cores_per_replica must be 1, 2, 4, or 8.
+ |
+
+|
+`per_host_input_for_training`
+ |
+
+If `True`, for `PER_HOST_V1`, the `input_fn` is
+invoked once on each host, and the number of hosts must be smaller or
+equal to the number of replicas. For PER_HOST_V2, the `input_fn` is
+invoked once for each host (if the number of hosts is less than the number
+of replicas) or replica (if the number of replicas is less than the number
+of hosts. With the per-core input pipeline configuration, it is invoked
+once for each core. With a global batch size `train_batch_size` in
+`TPUEstimator` constructor, the batch size for each shard is
+`train_batch_size` // #hosts in the `True` or `PER_HOST_V1` mode. In
+`PER_HOST_V2` mode, it is `train_batch_size` // #cores. In `BROADCAST`
+mode, `input_fn` is only invoked once on host 0 and the tensors are
+broadcasted to all other replicas. The batch size equals to
+`train_batch_size`. With the per-core input pipeline configuration, the
+shard batch size is also `train_batch_size` // #cores.
+Note: per_host_input_for_training==PER_SHARD_V1 only supports mode.TRAIN.
+ |
+
+|
+`tpu_job_name`
+ |
+
+The name of the TPU job. Typically, this name is auto-inferred
+within TPUEstimator, however when using ClusterSpec propagation in more
+esoteric cluster configurations, you may need to specify the job name as a
+string.
+ |
+
+|
+`initial_infeed_sleep_secs`
+ |
+
+The number of seconds the infeed thread should
+wait before enqueueing the first batch. This helps avoid timeouts for
+models that require a long compilation time.
+ |
+
+|
+`input_partition_dims`
+ |
+
+A nested list to describe the partition dims for all
+the tensors from input_fn(). The structure of input_partition_dims must
+match the structure of `features` and `labels` from input_fn(). The total
+number of partitions must match
+`num_cores_per_replica`. For example, if input_fn() returns two tensors:
+images with shape [N, H, W, C] and labels [N]. input_partition_dims =
+[[1, 2, 2, 1], None] will split the images to 4 pieces and feed into 4
+TPU cores. labels tensor are directly broadcasted to all the TPU cores
+since the partition dims is `None`.
+Current limitations: This feature is only supported with the PER_HOST_V2
+input mode.
+ |
+
+|
+`eval_training_input_configuration`
+ |
+
+If `SLICED`, `input_fn` is only invoked
+once on host 0 and the tensors are broadcasted to all other replicas.
+Unlike per_host_input_for_training=BROADCAST, each replica will only get a
+slice of the data instead of a whole copy. If `PER_HOST_V1`, the behaviour
+is determined by per_host_input_for_training.
+ |
+
+|
+`experimental_host_call_every_n_steps`
+ |
+
+Within a training loop, this argument
+sets how often host calls are performed during training. Host calls will
+be evaluated every n steps within a training loop where n is the value of
+this argument.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `num_cores_per_replica` is not 1, 2, 4, 8, ..., 128.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`iterations_per_loop`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`num_shards`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`num_cores_per_replica`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`per_host_input_for_training`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`tpu_job_name`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`initial_infeed_sleep_secs`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`input_partition_dims`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`eval_training_input_configuration`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`experimental_host_call_every_n_steps`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `eval_training_input_configuration`
+* `experimental_host_call_every_n_steps`
+* `initial_infeed_sleep_secs`
+* `input_partition_dims`
+* `iterations_per_loop`
+* `num_cores_per_replica`
+* `num_shards`
+* `per_host_input_for_training`
+* `tpu_job_name`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/tpu/TPUEstimator.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/tpu/TPUEstimator.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a5328fa494b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/tpu/TPUEstimator.md
@@ -0,0 +1,1464 @@
+description: Estimator with TPU support.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.estimator.tpu.TPUEstimator
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Estimator with TPU support.
+
+Inherits From: [`Estimator`](../../../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/Estimator.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.estimator.tpu.TPUEstimator(
+ model_fn=None, model_dir=None, config=None, params=None, use_tpu=(True),
+ train_batch_size=None, eval_batch_size=None, predict_batch_size=None,
+ batch_axis=None, eval_on_tpu=(True), export_to_tpu=(True), export_to_cpu=(True),
+ warm_start_from=None, embedding_config_spec=None,
+ export_saved_model_api_version=ExportSavedModelApiVersion.V1
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+TPUEstimator also supports training on CPU and GPU. You don't need to define
+a separate tf.estimator.Estimator.
+
+TPUEstimator handles many of the details of running on TPU devices, such as
+replicating inputs and models for each core, and returning to host
+periodically to run hooks.
+
+TPUEstimator transforms a global batch size in params to a per-shard batch
+size when calling the `input_fn` and `model_fn`. Users should specify
+global batch size in constructor, and then get the batch size for each shard
+in `input_fn` and `model_fn` by `params['batch_size']`.
+
+- For training, `model_fn` gets per-core batch size; `input_fn` may get
+ per-core or per-host batch size depending on `per_host_input_for_training`
+ in `TPUConfig` (See docstring for TPUConfig for details).
+
+- For evaluation and prediction, `model_fn` gets per-core batch size and
+ `input_fn` get per-host batch size.
+
+Evaluation
+==========
+
+`model_fn` should return `TPUEstimatorSpec`, which expects the `eval_metrics`
+for TPU evaluation. If eval_on_tpu is False, the evaluation will execute on
+CPU or GPU; in this case the following discussion on TPU evaluation does not
+apply.
+
+`TPUEstimatorSpec.eval_metrics` is a tuple of `metric_fn` and `tensors`, where
+`tensors` could be a list of any nested structure of `Tensor`s (See
+`TPUEstimatorSpec` for details). `metric_fn` takes the `tensors` and returns
+a dict from metric string name to the result of calling a metric function,
+namely a `(metric_tensor, update_op)` tuple.
+
+One can set `use_tpu` to `False` for testing. All training, evaluation, and
+predict will be executed on CPU. `input_fn` and `model_fn` will receive
+`train_batch_size` or `eval_batch_size` unmodified as `params['batch_size']`.
+
+#### Current limitations:
+
+
+--------------------
+
+1. TPU evaluation only works on a single host (one TPU worker) except
+ BROADCAST mode.
+
+2. `input_fn` for evaluation should **NOT** raise an end-of-input exception
+ (`OutOfRangeError` or `StopIteration`). And all evaluation steps and all
+ batches should have the same size.
+
+Example (MNIST):
+----------------
+
+```
+# The metric Fn which runs on CPU.
+def metric_fn(labels, logits):
+ predictions = tf.argmax(logits, 1)
+ return {
+ 'accuracy': tf.compat.v1.metrics.precision(
+ labels=labels, predictions=predictions),
+ }
+
+# Your model Fn which runs on TPU (eval_metrics is list in this example)
+def model_fn(features, labels, mode, config, params):
+ ...
+ logits = ...
+
+ if mode = tf.estimator.ModeKeys.EVAL:
+ return tpu_estimator.TPUEstimatorSpec(
+ mode=mode,
+ loss=loss,
+ eval_metrics=(metric_fn, [labels, logits]))
+
+# or specify the eval_metrics tensors as dict.
+def model_fn(features, labels, mode, config, params):
+ ...
+ final_layer_output = ...
+
+ if mode = tf.estimator.ModeKeys.EVAL:
+ return tpu_estimator.TPUEstimatorSpec(
+ mode=mode,
+ loss=loss,
+ eval_metrics=(metric_fn, {
+ 'labels': labels,
+ 'logits': final_layer_output,
+ }))
+```
+
+Prediction
+==========
+
+Prediction on TPU is an experimental feature to support large batch inference.
+It is not designed for latency-critical system. In addition, due to some
+usability issues, for prediction with small dataset, CPU `.predict`, i.e.,
+creating a new `TPUEstimator` instance with `use_tpu=False`, might be more
+convenient.
+
+Note: In contrast to TPU training/evaluation, the `input_fn` for prediction
+*should* raise an end-of-input exception (`OutOfRangeError` or
+`StopIteration`), which serves as the stopping signal to `TPUEstimator`. To be
+precise, the ops created by `input_fn` produce one batch of the data.
+The `predict()` API processes one batch at a time. When reaching the end of
+the data source, an end-of-input exception should be raised by one of these
+operations. The user usually does not need to do this manually. As long as the
+dataset is not repeated forever, the tf.data API will raise an end-of-input
+exception automatically after the last batch has been produced.
+
+Note: Estimator.predict returns a Python generator. Please consume all the
+data from the generator so that TPUEstimator can shutdown the TPU system
+properly for user.
+
+#### Current limitations:
+
+
+--------------------
+1. TPU prediction only works on a single host (one TPU worker).
+
+2. `input_fn` must return a `Dataset` instance rather than `features`. In
+fact, .train() and .evaluate() also support Dataset as return value.
+
+Example (MNIST):
+----------------
+```
+height = 32
+width = 32
+total_examples = 100
+
+def predict_input_fn(params):
+ batch_size = params['batch_size']
+
+ images = tf.random.uniform(
+ [total_examples, height, width, 3], minval=-1, maxval=1)
+
+ dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(images)
+ dataset = dataset.map(lambda images: {'image': images})
+
+ dataset = dataset.batch(batch_size)
+ return dataset
+
+def model_fn(features, labels, params, mode):
+ # Generate predictions, called 'output', from features['image']
+
+ if mode == tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT:
+ return tf.contrib.tpu.TPUEstimatorSpec(
+ mode=mode,
+ predictions={
+ 'predictions': output,
+ 'is_padding': features['is_padding']
+ })
+
+tpu_est = TPUEstimator(
+ model_fn=model_fn,
+ ...,
+ predict_batch_size=16)
+
+# Fully consume the generator so that TPUEstimator can shutdown the TPU
+# system.
+for item in tpu_est.predict(input_fn=input_fn):
+ # Filter out item if the `is_padding` is 1.
+ # Process the 'predictions'
+```
+
+Exporting
+=========
+
+`export_saved_model` exports 2 metagraphs, one with `saved_model.SERVING`, and
+another with `saved_model.SERVING` and `saved_model.TPU` tags. At serving
+time, these tags are used to select the appropriate metagraph to load.
+
+Before running the graph on TPU, the TPU system needs to be initialized. If
+TensorFlow Serving model-server is used, this is done automatically. If not,
+please use `session.run(tpu.initialize_system())`.
+
+There are two versions of the API: ExportSavedModelApiVersion.V1 and V2.
+
+In V1, the exported CPU graph is `model_fn` as it is. The exported TPU graph
+wraps `tpu.rewrite()` and `TPUPartitionedCallOp` around `model_fn` so
+`model_fn` is on TPU by default. To place ops on CPU,
+`tpu.outside_compilation(host_call, logits)` can be used.
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+----------------
+
+```
+def model_fn(features, labels, mode, config, params):
+ ...
+ logits = ...
+ export_outputs = {
+ 'logits': export_output_lib.PredictOutput(
+ {'logits': logits})
+ }
+
+ def host_call(logits):
+ class_ids = math_ops.argmax(logits)
+ classes = string_ops.as_string(class_ids)
+ export_outputs['classes'] =
+ export_output_lib.ClassificationOutput(classes=classes)
+
+ tpu.outside_compilation(host_call, logits)
+
+ ...
+```
+
+In V2, `export_saved_model()` sets up `params['use_tpu']` flag to let the user
+know if the code is exporting to TPU (or not). When `params['use_tpu']` is
+`True`, users need to call `tpu.rewrite()`, `TPUPartitionedCallOp` and/or
+`batch_function()`. Alternatively use `inference_on_tpu()` which is a
+convenience wrapper of the three.
+
+```
+ def model_fn(features, labels, mode, config, params):
+ ...
+ # This could be some pre-processing on CPU like calls to input layer with
+ # embedding columns.
+ x2 = features['x'] * 2
+
+ def computation(input_tensor):
+ return layers.dense(
+ input_tensor, 1, kernel_initializer=init_ops.zeros_initializer())
+
+ inputs = [x2]
+ if params['use_tpu']:
+ predictions = array_ops.identity(
+ tpu_estimator.inference_on_tpu(computation, inputs,
+ num_batch_threads=1, max_batch_size=2, batch_timeout_micros=100),
+ name='predictions')
+ else:
+ predictions = array_ops.identity(
+ computation(*inputs), name='predictions')
+ key = signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY
+ export_outputs = {
+ key: export_lib.PredictOutput({'prediction': predictions})
+ }
+ ...
+```
+
+TIP: V2 is recommended as it is more flexible (eg: batching, etc).
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`model_fn`
+ |
+
+Model function as required by `Estimator` which returns
+EstimatorSpec or TPUEstimatorSpec. `training_hooks`, 'evaluation_hooks',
+and `prediction_hooks` must not capure any TPU Tensor inside the
+model_fn.
+ |
+
+|
+`model_dir`
+ |
+
+Directory to save model parameters, graph and etc. This can
+also be used to load checkpoints from the directory into a estimator to
+continue training a previously saved model. If `None`, the model_dir in
+`config` will be used if set. If both are set, they must be same. If
+both are `None`, a temporary directory will be used.
+ |
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+An `tpu_config.RunConfig` configuration object. Cannot be `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`params`
+ |
+
+An optional `dict` of hyper parameters that will be passed into
+`input_fn` and `model_fn`. Keys are names of parameters, values are
+basic python types. There are reserved keys for `TPUEstimator`,
+including 'batch_size'.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_tpu`
+ |
+
+A bool indicating whether TPU support is enabled. Currently, -
+TPU training and evaluation respect this bit, but eval_on_tpu can
+override execution of eval. See below.
+ |
+
+|
+`train_batch_size`
+ |
+
+An int representing the global training batch size.
+TPUEstimator transforms this global batch size to a per-shard batch
+size, as params['batch_size'], when calling `input_fn` and `model_fn`.
+Cannot be `None` if `use_tpu` is `True`. Must be divisible by total
+number of replicas.
+ |
+
+|
+`eval_batch_size`
+ |
+
+An int representing evaluation batch size. Must be
+divisible by total number of replicas.
+ |
+
+|
+`predict_batch_size`
+ |
+
+An int representing the prediction batch size. Must be
+divisible by total number of replicas.
+ |
+
+|
+`batch_axis`
+ |
+
+A python tuple of int values describing how each tensor
+produced by the Estimator `input_fn` should be split across the TPU
+compute shards. For example, if your input_fn produced (images, labels)
+where the images tensor is in `HWCN` format, your shard dimensions would
+be [3, 0], where 3 corresponds to the `N` dimension of your images
+Tensor, and 0 corresponds to the dimension along which to split the
+labels to match up with the corresponding images. If None is supplied,
+and per_host_input_for_training is True, batches will be sharded based
+on the major dimension. If tpu_config.per_host_input_for_training is
+False or `PER_HOST_V2`, batch_axis is ignored.
+ |
+
+|
+`eval_on_tpu`
+ |
+
+If False, evaluation runs on CPU or GPU. In this case, the
+model_fn must return `EstimatorSpec` when called with `mode` as `EVAL`.
+ |
+
+|
+`export_to_tpu`
+ |
+
+If True, `export_saved_model()` exports a metagraph for
+serving on TPU. Note that unsupported export modes such as EVAL will be
+ignored. For those modes, only a CPU model will be exported. Currently,
+export_to_tpu only supports PREDICT.
+ |
+
+|
+`export_to_cpu`
+ |
+
+If True, `export_saved_model()` exports a metagraph for
+serving on CPU.
+ |
+
+|
+`warm_start_from`
+ |
+
+Optional string filepath to a checkpoint or SavedModel to
+warm-start from, or a tf.estimator.WarmStartSettings object to fully
+configure warm-starting. If the string filepath is provided instead of
+a `WarmStartSettings`, then all variables are warm-started, and it is
+assumed that vocabularies and Tensor names are unchanged.
+ |
+
+|
+`embedding_config_spec`
+ |
+
+Optional EmbeddingConfigSpec instance to support
+using TPU embedding.
+ |
+
+|
+`export_saved_model_api_version`
+ |
+
+ExportSavedModelApiVersion, V1 or V2. With
+V1, `export_saved_model()` adds rewrite() and TPUPartitionedCallOp() for
+user; while in v2, user is expected to add rewrite(),
+TPUPartitionedCallOp() etc in their model_fn. A helper function
+`inference_on_tpu` is provided for V2. brn_tpu_estimator.py includes
+examples for both versions i.e. TPUEstimatorExportTest and
+TPUEstimatorExportV2Test.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+`params` has reserved keys already.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`model_dir`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`model_fn`
+ |
+
+Returns the `model_fn` which is bound to `self.params`.
+ |
+
+|
+`params`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+eval_dir
+
+View source
+
+
+eval_dir(
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+Shows the directory name where evaluation metrics are dumped.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of the evaluation if user needs to run multiple evaluations on
+different data sets, such as on training data vs test data. Metrics for
+different evaluations are saved in separate folders, and appear
+separately in tensorboard.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A string which is the path of directory contains evaluation metrics.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+evaluate
+
+View source
+
+
+evaluate(
+ input_fn, steps=None, hooks=None, checkpoint_path=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+Evaluates the model given evaluation data `input_fn`.
+
+For each step, calls `input_fn`, which returns one batch of data.
+Evaluates until:
+- `steps` batches are processed, or
+- `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception (tf.errors.OutOfRangeError
+or
+`StopIteration`).
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that constructs the input data for evaluation. See
+[Premade Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The
+function should construct and return one of the following: * A
+tf.data.Dataset object: Outputs of `Dataset` object must be a tuple
+`(features, labels)` with same constraints as below. * A tuple
+`(features, labels)`: Where `features` is a tf.Tensor or a dictionary
+of string feature name to `Tensor` and `labels` is a `Tensor` or a
+dictionary of string label name to `Tensor`. Both `features` and
+`labels` are consumed by `model_fn`. They should satisfy the
+expectation of `model_fn` from inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`steps`
+ |
+
+Number of steps for which to evaluate model. If `None`, evaluates
+until `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the evaluation call.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+Path of a specific checkpoint to evaluate. If `None`, the
+latest checkpoint in `model_dir` is used. If there are no checkpoints
+in `model_dir`, evaluation is run with newly initialized `Variables`
+instead of ones restored from checkpoint.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of the evaluation if user needs to run multiple evaluations on
+different data sets, such as on training data vs test data. Metrics for
+different evaluations are saved in separate folders, and appear
+separately in tensorboard.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A dict containing the evaluation metrics specified in `model_fn` keyed by
+name, as well as an entry `global_step` which contains the value of the
+global step for which this evaluation was performed. For canned
+estimators, the dict contains the `loss` (mean loss per mini-batch) and
+the `average_loss` (mean loss per sample). Canned classifiers also return
+the `accuracy`. Canned regressors also return the `label/mean` and the
+`prediction/mean`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `steps <= 0`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+experimental_export_all_saved_models
+
+View source
+
+
+experimental_export_all_saved_models(
+ export_dir_base, input_receiver_fn_map, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None
+)
+
+
+Exports a `SavedModel` with `tf.MetaGraphDefs` for each requested mode.
+
+For each mode passed in via the `input_receiver_fn_map`,
+this method builds a new graph by calling the `input_receiver_fn` to obtain
+feature and label `Tensor`s. Next, this method calls the `Estimator`'s
+`model_fn` in the passed mode to generate the model graph based on
+those features and labels, and restores the given checkpoint
+(or, lacking that, the most recent checkpoint) into the graph.
+Only one of the modes is used for saving variables to the `SavedModel`
+(order of preference: tf.estimator.ModeKeys.TRAIN,
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys.EVAL, then
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys.PREDICT), such that up to three
+`tf.MetaGraphDefs` are saved with a single set of variables in a single
+`SavedModel` directory.
+
+For the variables and `tf.MetaGraphDefs`, a timestamped export directory
+below
+`export_dir_base`, and writes a `SavedModel` into it containing
+the `tf.MetaGraphDef` for the given mode and its associated signatures.
+
+For prediction, the exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef`
+for each element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`,
+named using the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+For training and evaluation, the `train_op` is stored in an extra
+collection,
+and loss, metrics, and predictions are included in a `SignatureDef` for the
+mode in question.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`input_receiver_fn_map`
+ |
+
+dict of tf.estimator.ModeKeys to
+`input_receiver_fn` mappings, where the `input_receiver_fn` is a
+function that takes no arguments and returns the appropriate subclass of
+`InputReceiver`.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if any `input_receiver_fn` is `None`, no `export_outputs`
+are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+export_saved_model
+
+View source
+
+
+export_saved_model(
+ export_dir_base, serving_input_receiver_fn, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None, experimental_mode=ModeKeys.PREDICT
+)
+
+
+Exports inference graph as a `SavedModel` into the given dir.
+
+For a detailed guide, see
+[Using SavedModel with
+Estimators](https://tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model#using_savedmodel_with_estimators).
+
+This method builds a new graph by first calling the
+`serving_input_receiver_fn` to obtain feature `Tensor`s, and then calling
+this `Estimator`'s `model_fn` to generate the model graph based on those
+features. It restores the given checkpoint (or, lacking that, the most
+recent checkpoint) into this graph in a fresh session. Finally it creates
+a timestamped export directory below the given `export_dir_base`, and writes
+a `SavedModel` into it containing a single `tf.MetaGraphDef` saved from this
+session.
+
+The exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef` for each
+element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`, named
+using
+the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+The experimental_mode parameter can be used to export a single
+train/eval/predict graph as a `SavedModel`.
+See `experimental_export_all_saved_models` for full docs.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`serving_input_receiver_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that takes no argument and returns a
+tf.estimator.export.ServingInputReceiver or
+tf.estimator.export.TensorServingInputReceiver.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+|
+`experimental_mode`
+ |
+
+tf.estimator.ModeKeys value indicating with mode will
+be exported. Note that this feature is experimental.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if no `serving_input_receiver_fn` is provided, no
+`export_outputs` are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+export_savedmodel
+
+View source
+
+
+export_savedmodel(
+ export_dir_base, serving_input_receiver_fn, assets_extra=None, as_text=(False),
+ checkpoint_path=None, strip_default_attrs=(False)
+)
+
+
+Exports inference graph as a `SavedModel` into the given dir. (deprecated)
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+This function has been renamed, use `export_saved_model` instead.
+
+For a detailed guide, see
+[Using SavedModel with
+Estimators](https://tensorflow.org/guide/saved_model#using_savedmodel_with_estimators).
+
+This method builds a new graph by first calling the
+`serving_input_receiver_fn` to obtain feature `Tensor`s, and then calling
+this `Estimator`'s `model_fn` to generate the model graph based on those
+features. It restores the given checkpoint (or, lacking that, the most
+recent checkpoint) into this graph in a fresh session. Finally it creates
+a timestamped export directory below the given `export_dir_base`, and writes
+a `SavedModel` into it containing a single `tf.MetaGraphDef` saved from this
+session.
+
+The exported `MetaGraphDef` will provide one `SignatureDef` for each
+element of the `export_outputs` dict returned from the `model_fn`, named
+using
+the same keys. One of these keys is always
+`tf.saved_model.signature_constants.DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY`,
+indicating which
+signature will be served when a serving request does not specify one.
+For each signature, the outputs are provided by the corresponding
+tf.estimator.export.ExportOutputs, and the inputs are always the input
+receivers provided by
+the `serving_input_receiver_fn`.
+
+Extra assets may be written into the `SavedModel` via the `assets_extra`
+argument. This should be a dict, where each key gives a destination path
+(including the filename) relative to the assets.extra directory. The
+corresponding value gives the full path of the source file to be copied.
+For example, the simple case of copying a single file without renaming it
+is specified as `{'my_asset_file.txt': '/path/to/my_asset_file.txt'}`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir_base`
+ |
+
+A string containing a directory in which to create
+timestamped subdirectories containing exported `SavedModel`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`serving_input_receiver_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that takes no argument and returns a
+tf.estimator.export.ServingInputReceiver or
+tf.estimator.export.TensorServingInputReceiver.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_extra`
+ |
+
+A dict specifying how to populate the assets.extra directory
+within the exported `SavedModel`, or `None` if no extra assets are
+needed.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+whether to write the `SavedModel` proto in text format.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint path to export. If `None` (the default),
+the most recent checkpoint found within the model directory is chosen.
+ |
+
+|
+`strip_default_attrs`
+ |
+
+Boolean. If `True`, default-valued attributes will be
+removed from the `NodeDef`s. For a detailed guide, see [Stripping
+Default-Valued Attributes](
+https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/master/tensorflow/python/saved_model/README.md#stripping-default-valued-attributes).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the exported directory as a bytes object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if no `serving_input_receiver_fn` is provided, no
+`export_outputs` are provided, or no checkpoint can be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+get_variable_names
+
+View source
+
+
+get_variable_names()
+
+
+Returns list of all variable names in this model.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+List of names.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `Estimator` has not produced a checkpoint yet.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+get_variable_value
+
+View source
+
+
+get_variable_value(
+ name
+)
+
+
+Returns value of the variable given by name.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+string or a list of string, name of the tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Numpy array - value of the tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `Estimator` has not produced a checkpoint yet.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+latest_checkpoint
+
+View source
+
+
+latest_checkpoint()
+
+
+Finds the filename of the latest saved checkpoint file in `model_dir`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The full path to the latest checkpoint or `None` if no checkpoint was
+found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+predict
+
+View source
+
+
+predict(
+ input_fn, predict_keys=None, hooks=None, checkpoint_path=None,
+ yield_single_examples=(True)
+)
+
+
+Yields predictions for given features.
+
+Please note that interleaving two predict outputs does not work. See:
+[issue/20506](
+https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/issues/20506#issuecomment-422208517)
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that constructs the features. Prediction continues
+until `input_fn` raises an end-of-input exception
+(tf.errors.OutOfRangeError or `StopIteration`). See [Premade
+Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The function should construct and return one of
+the following:
+* tf.data.Dataset object -- Outputs of `Dataset` object must have
+same constraints as below.
+* features -- A tf.Tensor or a dictionary of string feature name to
+`Tensor`. features are consumed by `model_fn`. They should satisfy
+the expectation of `model_fn` from inputs. * A tuple, in which case
+the first item is extracted as features.
+ |
+
+|
+`predict_keys`
+ |
+
+list of `str`, name of the keys to predict. It is used if
+the tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec.predictions is a `dict`. If
+`predict_keys` is used then rest of the predictions will be filtered
+from the dictionary. If `None`, returns all.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the prediction call.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+Path of a specific checkpoint to predict. If `None`, the
+latest checkpoint in `model_dir` is used. If there are no checkpoints
+in `model_dir`, prediction is run with newly initialized `Variables`
+instead of ones restored from checkpoint.
+ |
+
+|
+`yield_single_examples`
+ |
+
+If `False`, yields the whole batch as returned by
+the `model_fn` instead of decomposing the batch into individual
+elements. This is useful if `model_fn` returns some tensors whose first
+dimension is not equal to the batch size.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Yields:
+
+Evaluated values of `predictions` tensors.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If batch length of predictions is not the same and
+`yield_single_examples` is `True`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If there is a conflict between `predict_keys` and
+`predictions`. For example if `predict_keys` is not `None` but
+tf.estimator.EstimatorSpec.predictions is not a `dict`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+train
+
+View source
+
+
+train(
+ input_fn, hooks=None, steps=None, max_steps=None, saving_listeners=None
+)
+
+
+Trains a model given training data `input_fn`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that provides input data for training as minibatches.
+See [Premade Estimators](
+https://tensorflow.org/guide/premade_estimators#create_input_functions)
+for more information. The function should construct and return one of
+the following:
+* A tf.data.Dataset object: Outputs of `Dataset` object must be a
+tuple `(features, labels)` with same constraints as below.
+* A tuple `(features, labels)`: Where `features` is a tf.Tensor or a
+dictionary of string feature name to `Tensor` and `labels` is a
+`Tensor` or a dictionary of string label name to `Tensor`. Both
+`features` and `labels` are consumed by `model_fn`. They should
+satisfy the expectation of `model_fn` from inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+List of `tf.train.SessionRunHook` subclass instances. Used for
+callbacks inside the training loop.
+ |
+
+|
+`steps`
+ |
+
+Number of steps for which to train the model. If `None`, train
+forever or train until `input_fn` generates the `tf.errors.OutOfRange`
+error or `StopIteration` exception. `steps` works incrementally. If you
+call two times `train(steps=10)` then training occurs in total 20 steps.
+If `OutOfRange` or `StopIteration` occurs in the middle, training stops
+before 20 steps. If you don't want to have incremental behavior please
+set `max_steps` instead. If set, `max_steps` must be `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_steps`
+ |
+
+Number of total steps for which to train model. If `None`,
+train forever or train until `input_fn` generates the
+`tf.errors.OutOfRange` error or `StopIteration` exception. If set,
+`steps` must be `None`. If `OutOfRange` or `StopIteration` occurs in the
+middle, training stops before `max_steps` steps. Two calls to
+`train(steps=100)` means 200 training iterations. On the other hand, two
+calls to `train(max_steps=100)` means that the second call will not do
+any iteration since first call did all 100 steps.
+ |
+
+|
+`saving_listeners`
+ |
+
+list of `CheckpointSaverListener` objects. Used for
+callbacks that run immediately before or after checkpoint savings.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`self`, for chaining.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If both `steps` and `max_steps` are not `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If either `steps` or `max_steps <= 0`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/tpu/TPUEstimatorSpec.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/tpu/TPUEstimatorSpec.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..f35b26f83df
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/tpu/TPUEstimatorSpec.md
@@ -0,0 +1,198 @@
+description: Ops and objects returned from a model_fn and passed to TPUEstimator.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.estimator.tpu.TPUEstimatorSpec
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Ops and objects returned from a `model_fn` and passed to `TPUEstimator`.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.estimator.tpu.TPUEstimatorSpec(
+ mode, predictions=None, loss=None, train_op=None, eval_metrics=None,
+ export_outputs=None, scaffold_fn=None, host_call=None, training_hooks=None,
+ evaluation_hooks=None, prediction_hooks=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+See `EstimatorSpec` for `mode`, `predictions`, `loss`, `train_op`, and
+`export_outputs`.
+
+For evaluation, `eval_metrics `is a tuple of `metric_fn` and `tensors`, where
+`metric_fn` runs on CPU to generate metrics and `tensors` represents the
+`Tensor`s transferred from TPU system to CPU host and passed to `metric_fn`.
+To be precise, TPU evaluation expects a slightly different signature from the
+tf.estimator.Estimator. While `EstimatorSpec.eval_metric_ops` expects a
+dict, `TPUEstimatorSpec.eval_metrics` is a tuple of `metric_fn` and `tensors`.
+The `tensors` could be a list of `Tensor`s or dict of names to `Tensor`s. The
+`tensors` usually specify the model logits, which are transferred back from
+TPU system to CPU host. All tensors must have be batch-major, i.e., the batch
+size is the first dimension. Once all tensors are available at CPU host from
+all shards, they are concatenated (on CPU) and passed as positional arguments
+to the `metric_fn` if `tensors` is list or keyword arguments if `tensors` is
+a dict. `metric_fn` takes the `tensors` and returns a dict from metric string
+name to the result of calling a metric function, namely a `(metric_tensor,
+update_op)` tuple. See `TPUEstimator` for MNIST example how to specify the
+`eval_metrics`.
+
+`scaffold_fn` is a function running on CPU to generate the `Scaffold`. This
+function should not capture any Tensors in `model_fn`.
+
+`host_call` is a tuple of a `function` and a list or dictionary of `tensors`
+to pass to that function and returns a list of Tensors. `host_call` currently
+works for train() and evaluate(). The Tensors returned by the function is
+executed on the CPU on every step, so there is communication overhead when
+sending tensors from TPU to CPU. To reduce the overhead, try reducing the
+size of the tensors. The `tensors` are concatenated along their major (batch)
+dimension, and so must be >= rank 1. The `host_call` is useful for writing
+summaries with `tf.contrib.summary.create_file_writer`.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`mode`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`loss`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`train_op`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`eval_metrics`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`export_outputs`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`scaffold_fn`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`host_call`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`training_hooks`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`evaluation_hooks`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`prediction_hooks`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+as_estimator_spec
+
+View source
+
+
+as_estimator_spec()
+
+
+Creates an equivalent `EstimatorSpec` used by CPU train/eval.
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `eval_metrics`
+* `evaluation_hooks`
+* `export_outputs`
+* `host_call`
+* `loss`
+* `mode`
+* `prediction_hooks`
+* `predictions`
+* `scaffold_fn`
+* `train_op`
+* `training_hooks`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/tpu/experimental.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/tpu/experimental.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..1c6bd95c5e8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/tpu/experimental.md
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+description: Public API for tf.estimator.tpu.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.estimator.tpu.experimental
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.estimator.tpu.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class EmbeddingConfigSpec`](../../../../../tf/compat/v1/estimator/tpu/experimental/EmbeddingConfigSpec.md): Class to keep track of the specification for TPU embeddings.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/tpu/experimental/EmbeddingConfigSpec.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/tpu/experimental/EmbeddingConfigSpec.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a2be676b8a4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/estimator/tpu/experimental/EmbeddingConfigSpec.md
@@ -0,0 +1,274 @@
+description: Class to keep track of the specification for TPU embeddings.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.estimator.tpu.experimental.EmbeddingConfigSpec
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Class to keep track of the specification for TPU embeddings.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.estimator.tpu.experimental.EmbeddingConfigSpec(
+ feature_columns=None, optimization_parameters=None, clipping_limit=None,
+ pipeline_execution_with_tensor_core=(False),
+ experimental_gradient_multiplier_fn=None, feature_to_config_dict=None,
+ table_to_config_dict=None, partition_strategy='div'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Pass this class to `tf.estimator.tpu.TPUEstimator` via the
+`embedding_config_spec` parameter. At minimum you need to specify
+`feature_columns` and `optimization_parameters`. The feature columns passed
+should be created with some combination of
+`tf.tpu.experimental.embedding_column` and
+`tf.tpu.experimental.shared_embedding_columns`.
+
+TPU embeddings do not support arbitrary Tensorflow optimizers and the
+main optimizer you use for your model will be ignored for the embedding table
+variables. Instead TPU embeddigns support a fixed set of predefined optimizers
+that you can select from and set the parameters of. These include adagrad,
+adam and stochastic gradient descent. Each supported optimizer has a
+`Parameters` class in the tf.tpu.experimental namespace.
+
+```
+column_a = tf.feature_column.categorical_column_with_identity(...)
+column_b = tf.feature_column.categorical_column_with_identity(...)
+column_c = tf.feature_column.categorical_column_with_identity(...)
+tpu_shared_columns = tf.tpu.experimental.shared_embedding_columns(
+ [column_a, column_b], 10)
+tpu_non_shared_column = tf.tpu.experimental.embedding_column(
+ column_c, 10)
+tpu_columns = [tpu_non_shared_column] + tpu_shared_columns
+...
+def model_fn(features):
+ dense_features = tf.keras.layers.DenseFeature(tpu_columns)
+ embedded_feature = dense_features(features)
+ ...
+
+estimator = tf.estimator.tpu.TPUEstimator(
+ model_fn=model_fn,
+ ...
+ embedding_config_spec=tf.estimator.tpu.experimental.EmbeddingConfigSpec(
+ column=tpu_columns,
+ optimization_parameters=(
+ tf.estimator.tpu.experimental.AdagradParameters(0.1))))
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`feature_columns`
+ |
+
+All embedding `FeatureColumn`s used by model.
+ |
+
+|
+`optimization_parameters`
+ |
+
+An instance of `AdagradParameters`,
+`AdamParameters` or `StochasticGradientDescentParameters`. This
+optimizer will be applied to all embedding variables specified by
+`feature_columns`.
+ |
+
+|
+`clipping_limit`
+ |
+
+(Optional) Clipping limit (absolute value).
+ |
+
+|
+`pipeline_execution_with_tensor_core`
+ |
+
+setting this to `True` makes training
+faster, but trained model will be different if step N and step N+1
+involve the same set of embedding IDs. Please see
+`tpu_embedding_configuration.proto` for details.
+ |
+
+|
+`experimental_gradient_multiplier_fn`
+ |
+
+(Optional) A Fn taking global step as
+input returning the current multiplier for all embedding gradients.
+ |
+
+|
+`feature_to_config_dict`
+ |
+
+A dictionary mapping features names to instances
+of the class `FeatureConfig`. Either features_columns or the pair of
+`feature_to_config_dict` and `table_to_config_dict` must be specified.
+ |
+
+|
+`table_to_config_dict`
+ |
+
+A dictionary mapping features names to instances of
+the class `TableConfig`. Either features_columns or the pair of
+`feature_to_config_dict` and `table_to_config_dict` must be specified.
+ |
+
+|
+`partition_strategy`
+ |
+
+A string, determining how tensors are sharded to the
+tpu hosts. See tf.nn.safe_embedding_lookup_sparse for more details.
+Allowed value are `"div"` and `"mod"'. If `"mod"` is used, evaluation
+and exporting the model to CPU will not work as expected.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the feature_columns are not specified.
+ |
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If the feature columns are not of ths correct type (one of
+_SUPPORTED_FEATURE_COLUMNS, _TPU_EMBEDDING_COLUMN_CLASSES OR
+_EMBEDDING_COLUMN_CLASSES).
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `optimization_parameters` is not one of the required types.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`feature_columns`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`optimization_parameters`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`clipping_limit`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`pipeline_execution_with_tensor_core`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`experimental_gradient_multiplier_fn`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`feature_to_config_dict`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`table_to_config_dict`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`partition_strategy`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `clipping_limit`
+* `experimental_gradient_multiplier_fn`
+* `feature_columns`
+* `feature_to_config_dict`
+* `optimization_parameters`
+* `partition_strategy`
+* `pipeline_execution_with_tensor_core`
+* `table_to_config_dict`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/executing_eagerly.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/executing_eagerly.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..2b4be2caf92
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/executing_eagerly.md
@@ -0,0 +1,109 @@
+description: Checks whether the current thread has eager execution enabled.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.executing_eagerly
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Checks whether the current thread has eager execution enabled.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.executing_eagerly()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Eager execution is typically enabled via
+tf.compat.v1.enable_eager_execution, but may also be enabled within the
+context of a Python function via tf.contrib.eager.py_func.
+
+When eager execution is enabled, returns `True` in most cases. However,
+this API might return `False` in the following use cases.
+
+* Executing inside tf.function, unless under tf.init_scope or
+ tf.config.experimental_run_functions_eagerly(True) is previously called.
+* Executing inside a transformation function for `tf.dataset`.
+* tf.compat.v1.disable_eager_execution() is called.
+
+```
+>>> tf.compat.v1.enable_eager_execution()
+```
+
+#### General case:
+
+
+
+```
+>>> print(tf.executing_eagerly())
+True
+```
+
+Inside tf.function:
+
+```
+>>> @tf.function
+... def fn():
+... with tf.init_scope():
+... print(tf.executing_eagerly())
+... print(tf.executing_eagerly())
+>>> fn()
+True
+False
+```
+
+Inside tf.function
+after tf.config.experimental_run_functions_eagerly(True) is called:
+
+```
+>>> tf.config.experimental_run_functions_eagerly(True)
+>>> @tf.function
+... def fn():
+... with tf.init_scope():
+... print(tf.executing_eagerly())
+... print(tf.executing_eagerly())
+>>> fn()
+True
+True
+>>> tf.config.experimental_run_functions_eagerly(False)
+```
+
+Inside a transformation function for `tf.dataset`:
+
+```
+>>> def data_fn(x):
+... print(tf.executing_eagerly())
+... return x
+>>> dataset = tf.data.Dataset.range(100)
+>>> dataset = dataset.map(data_fn)
+False
+```
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`True` if the current thread has eager execution enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/executing_eagerly_outside_functions.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/executing_eagerly_outside_functions.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..f8866844dbf
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/executing_eagerly_outside_functions.md
@@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
+description: Returns True if executing eagerly, even if inside a graph function.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.executing_eagerly_outside_functions
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns True if executing eagerly, even if inside a graph function.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.executing_eagerly_outside_functions()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This function will check the outermost context for the program and see if
+it is in eager mode. It is useful comparing to tf.executing_eagerly(),
+which checks the current context and will return `False` within a
+tf.function body. It can be used to build library that behave differently
+in eager runtime and v1 session runtime (deprecated).
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```
+>>> tf.compat.v1.enable_eager_execution()
+>>> @tf.function
+... def func():
+... # A function constructs TensorFlow graphs, it does not execute eagerly,
+... # but the outer most context is still eager.
+... assert not tf.executing_eagerly()
+... return tf.compat.v1.executing_eagerly_outside_functions()
+>>> func()
+
+```
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+boolean, whether the outermost context is in eager mode.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/expand_dims.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/expand_dims.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..5689ee112b6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/expand_dims.md
@@ -0,0 +1,140 @@
+description: Inserts a dimension of 1 into a tensor's shape. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.expand_dims
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Inserts a dimension of 1 into a tensor's shape. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.expand_dims(
+ input, axis=None, name=None, dim=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: SOME ARGUMENTS ARE DEPRECATED: `(dim)`. They will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use the `axis` argument instead
+
+Given a tensor `input`, this operation inserts a dimension of 1 at the
+dimension index `axis` of `input`'s shape. The dimension index `axis` starts
+at zero; if you specify a negative number for `axis` it is counted backward
+from the end.
+
+This operation is useful if you want to add a batch dimension to a single
+element. For example, if you have a single image of shape `[height, width,
+channels]`, you can make it a batch of 1 image with `expand_dims(image, 0)`,
+which will make the shape `[1, height, width, channels]`.
+
+#### Other examples:
+
+
+
+```python
+# 't' is a tensor of shape [2]
+tf.shape(tf.expand_dims(t, 0)) # [1, 2]
+tf.shape(tf.expand_dims(t, 1)) # [2, 1]
+tf.shape(tf.expand_dims(t, -1)) # [2, 1]
+
+# 't2' is a tensor of shape [2, 3, 5]
+tf.shape(tf.expand_dims(t2, 0)) # [1, 2, 3, 5]
+tf.shape(tf.expand_dims(t2, 2)) # [2, 3, 1, 5]
+tf.shape(tf.expand_dims(t2, 3)) # [2, 3, 5, 1]
+```
+
+This operation requires that:
+
+`-1-input.dims() <= dim <= input.dims()`
+
+This operation is related to `squeeze()`, which removes dimensions of
+size 1.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`axis`
+ |
+
+0-D (scalar). Specifies the dimension index at which to expand the
+shape of `input`. Must be in the range `[-rank(input) - 1, rank(input)]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+The name of the output `Tensor` (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`dim`
+ |
+
+0-D (scalar). Equivalent to `axis`, to be deprecated.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` with the same data as `input`, but its shape has an additional
+dimension of size 1 added.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if either both or neither of `dim` and `axis` are specified.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/experimental.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/experimental.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..00d2befba2e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/experimental.md
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+description: Public API for tf.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.experimental
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`async_clear_error(...)`](../../../tf/experimental/async_clear_error.md): Clear pending operations and error statuses in async execution.
+
+[`async_scope(...)`](../../../tf/experimental/async_scope.md): Context manager for grouping async operations.
+
+[`function_executor_type(...)`](../../../tf/experimental/function_executor_type.md): Context manager for setting the executor of eager defined functions.
+
+[`output_all_intermediates(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/experimental/output_all_intermediates.md): Whether to output all intermediates from functional control flow ops.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/experimental/output_all_intermediates.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/experimental/output_all_intermediates.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..40e418a91cf
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/experimental/output_all_intermediates.md
@@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
+description: Whether to output all intermediates from functional control flow ops.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.experimental.output_all_intermediates
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Whether to output all intermediates from functional control flow ops.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.experimental.output_all_intermediates(
+ state
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The "default" behavior to is to output all intermediates when using v2 control
+flow inside Keras models in graph mode (possibly inside Estimators). This is
+needed to support taking gradients of v2 control flow. In graph mode, Keras
+can sometimes freeze the forward graph before the gradient computation which
+does not work for v2 control flow since it requires updating the forward ops
+to output the needed intermediates. We work around this by proactively
+outputting the needed intermediates when building the forward pass itself.
+Ideally any such extra tensors should be pruned out at runtime. However, if
+for any reason this doesn't work for you or if you have an inference-only
+model you can turn this behavior off using
+tf.compat.v1.experimental.output_all_intermediates(False).
+
+If with the default behavior you are still seeing errors of the form
+"Connecting to invalid output X of source node Y which has Z outputs" try
+setting tf.compat.v1.experimental.output_all_intermediates(True) and
+please file an issue at https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/issues.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`state`
+ |
+
+True, False or None. None restores the default behavior.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/extract_image_patches.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/extract_image_patches.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e927776732a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/extract_image_patches.md
@@ -0,0 +1,122 @@
+description: Extract patches from images and put them in the "depth" output dimension.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.extract_image_patches
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Extract `patches` from `images` and put them in the "depth" output dimension.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.image.extract_image_patches`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.extract_image_patches(
+ images, ksizes=None, strides=None, rates=None, padding=None, name=None,
+ sizes=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`images`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `bfloat16`, `half`, `float32`, `float64`, `int8`, `int16`, `int32`, `int64`, `uint8`, `uint16`, `uint32`, `uint64`, `complex64`, `complex128`, `bool`.
+4-D Tensor with shape `[batch, in_rows, in_cols, depth]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ksizes`
+ |
+
+A list of `ints` that has length `>= 4`.
+The size of the sliding window for each dimension of `images`.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+A list of `ints` that has length `>= 4`.
+How far the centers of two consecutive patches are in
+the images. Must be: `[1, stride_rows, stride_cols, 1]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`rates`
+ |
+
+A list of `ints` that has length `>= 4`.
+Must be: `[1, rate_rows, rate_cols, 1]`. This is the
+input stride, specifying how far two consecutive patch samples are in the
+input. Equivalent to extracting patches with
+`patch_sizes_eff = patch_sizes + (patch_sizes - 1) * (rates - 1)`, followed by
+subsampling them spatially by a factor of `rates`. This is equivalent to
+`rate` in dilated (a.k.a. Atrous) convolutions.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+A `string` from: `"SAME", "VALID"`.
+The type of padding algorithm to use.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `images`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/feature_column.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/feature_column.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..8ed121c7c74
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/feature_column.md
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
+description: Public API for tf.feature_column namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.feature_column
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.feature_column namespace.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`bucketized_column(...)`](../../../tf/feature_column/bucketized_column.md): Represents discretized dense input bucketed by `boundaries`.
+
+[`categorical_column_with_hash_bucket(...)`](../../../tf/feature_column/categorical_column_with_hash_bucket.md): Represents sparse feature where ids are set by hashing.
+
+[`categorical_column_with_identity(...)`](../../../tf/feature_column/categorical_column_with_identity.md): A `CategoricalColumn` that returns identity values.
+
+[`categorical_column_with_vocabulary_file(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/feature_column/categorical_column_with_vocabulary_file.md): A `CategoricalColumn` with a vocabulary file.
+
+[`categorical_column_with_vocabulary_list(...)`](../../../tf/feature_column/categorical_column_with_vocabulary_list.md): A `CategoricalColumn` with in-memory vocabulary.
+
+[`crossed_column(...)`](../../../tf/feature_column/crossed_column.md): Returns a column for performing crosses of categorical features.
+
+[`embedding_column(...)`](../../../tf/feature_column/embedding_column.md): `DenseColumn` that converts from sparse, categorical input.
+
+[`indicator_column(...)`](../../../tf/feature_column/indicator_column.md): Represents multi-hot representation of given categorical column.
+
+[`input_layer(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/feature_column/input_layer.md): Returns a dense `Tensor` as input layer based on given `feature_columns`.
+
+[`linear_model(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/feature_column/linear_model.md): Returns a linear prediction `Tensor` based on given `feature_columns`.
+
+[`make_parse_example_spec(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/feature_column/make_parse_example_spec.md): Creates parsing spec dictionary from input feature_columns.
+
+[`numeric_column(...)`](../../../tf/feature_column/numeric_column.md): Represents real valued or numerical features.
+
+[`sequence_categorical_column_with_hash_bucket(...)`](../../../tf/feature_column/sequence_categorical_column_with_hash_bucket.md): A sequence of categorical terms where ids are set by hashing.
+
+[`sequence_categorical_column_with_identity(...)`](../../../tf/feature_column/sequence_categorical_column_with_identity.md): Returns a feature column that represents sequences of integers.
+
+[`sequence_categorical_column_with_vocabulary_file(...)`](../../../tf/feature_column/sequence_categorical_column_with_vocabulary_file.md): A sequence of categorical terms where ids use a vocabulary file.
+
+[`sequence_categorical_column_with_vocabulary_list(...)`](../../../tf/feature_column/sequence_categorical_column_with_vocabulary_list.md): A sequence of categorical terms where ids use an in-memory list.
+
+[`sequence_numeric_column(...)`](../../../tf/feature_column/sequence_numeric_column.md): Returns a feature column that represents sequences of numeric data.
+
+[`shared_embedding_columns(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/feature_column/shared_embedding_columns.md): List of dense columns that convert from sparse, categorical input.
+
+[`weighted_categorical_column(...)`](../../../tf/feature_column/weighted_categorical_column.md): Applies weight values to a `CategoricalColumn`.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/feature_column/categorical_column_with_vocabulary_file.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/feature_column/categorical_column_with_vocabulary_file.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..7f014cf5f6f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/feature_column/categorical_column_with_vocabulary_file.md
@@ -0,0 +1,202 @@
+description: A CategoricalColumn with a vocabulary file.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.feature_column.categorical_column_with_vocabulary_file
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A `CategoricalColumn` with a vocabulary file.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.feature_column.categorical_column_with_vocabulary_file(
+ key, vocabulary_file, vocabulary_size=None, num_oov_buckets=0,
+ default_value=None, dtype=tf.dtypes.string
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Use this when your inputs are in string or integer format, and you have a
+vocabulary file that maps each value to an integer ID. By default,
+out-of-vocabulary values are ignored. Use either (but not both) of
+`num_oov_buckets` and `default_value` to specify how to include
+out-of-vocabulary values.
+
+For input dictionary `features`, `features[key]` is either `Tensor` or
+`SparseTensor`. If `Tensor`, missing values can be represented by `-1` for int
+and `''` for string, which will be dropped by this feature column.
+
+Example with `num_oov_buckets`:
+File '/us/states.txt' contains 50 lines, each with a 2-character U.S. state
+abbreviation. All inputs with values in that file are assigned an ID 0-49,
+corresponding to its line number. All other values are hashed and assigned an
+ID 50-54.
+
+```python
+states = categorical_column_with_vocabulary_file(
+ key='states', vocabulary_file='/us/states.txt', vocabulary_size=50,
+ num_oov_buckets=5)
+columns = [states, ...]
+features = tf.io.parse_example(..., features=make_parse_example_spec(columns))
+linear_prediction = linear_model(features, columns)
+```
+
+Example with `default_value`:
+File '/us/states.txt' contains 51 lines - the first line is 'XX', and the
+other 50 each have a 2-character U.S. state abbreviation. Both a literal 'XX'
+in input, and other values missing from the file, will be assigned ID 0. All
+others are assigned the corresponding line number 1-50.
+
+```python
+states = categorical_column_with_vocabulary_file(
+ key='states', vocabulary_file='/us/states.txt', vocabulary_size=51,
+ default_value=0)
+columns = [states, ...]
+features = tf.io.parse_example(..., features=make_parse_example_spec(columns))
+linear_prediction, _, _ = linear_model(features, columns)
+```
+
+And to make an embedding with either:
+
+```python
+columns = [embedding_column(states, 3),...]
+features = tf.io.parse_example(..., features=make_parse_example_spec(columns))
+dense_tensor = input_layer(features, columns)
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`key`
+ |
+
+A unique string identifying the input feature. It is used as the
+column name and the dictionary key for feature parsing configs, feature
+`Tensor` objects, and feature columns.
+ |
+
+|
+`vocabulary_file`
+ |
+
+The vocabulary file name.
+ |
+
+|
+`vocabulary_size`
+ |
+
+Number of the elements in the vocabulary. This must be no
+greater than length of `vocabulary_file`, if less than length, later
+values are ignored. If None, it is set to the length of `vocabulary_file`.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_oov_buckets`
+ |
+
+Non-negative integer, the number of out-of-vocabulary
+buckets. All out-of-vocabulary inputs will be assigned IDs in the range
+`[vocabulary_size, vocabulary_size+num_oov_buckets)` based on a hash of
+the input value. A positive `num_oov_buckets` can not be specified with
+`default_value`.
+ |
+
+|
+`default_value`
+ |
+
+The integer ID value to return for out-of-vocabulary feature
+values, defaults to `-1`. This can not be specified with a positive
+`num_oov_buckets`.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+The type of features. Only string and integer types are supported.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `CategoricalColumn` with a vocabulary file.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+`vocabulary_file` is missing or cannot be opened.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+`vocabulary_size` is missing or < 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+`num_oov_buckets` is a negative integer.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+`num_oov_buckets` and `default_value` are both specified.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+`dtype` is neither string nor integer.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/feature_column/input_layer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/feature_column/input_layer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..59911664a3d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/feature_column/input_layer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,158 @@
+description: Returns a dense Tensor as input layer based on given feature_columns.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.feature_column.input_layer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns a dense `Tensor` as input layer based on given `feature_columns`.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.feature_column.input_layer(
+ features, feature_columns, weight_collections=None, trainable=(True),
+ cols_to_vars=None, cols_to_output_tensors=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Generally a single example in training data is described with FeatureColumns.
+At the first layer of the model, this column oriented data should be converted
+to a single `Tensor`.
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+price = numeric_column('price')
+keywords_embedded = embedding_column(
+ categorical_column_with_hash_bucket("keywords", 10K), dimensions=16)
+columns = [price, keywords_embedded, ...]
+features = tf.io.parse_example(..., features=make_parse_example_spec(columns))
+dense_tensor = input_layer(features, columns)
+for units in [128, 64, 32]:
+ dense_tensor = tf.compat.v1.layers.dense(dense_tensor, units, tf.nn.relu)
+prediction = tf.compat.v1.layers.dense(dense_tensor, 1)
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`features`
+ |
+
+A mapping from key to tensors. `_FeatureColumn`s look up via these
+keys. For example `numeric_column('price')` will look at 'price' key in
+this dict. Values can be a `SparseTensor` or a `Tensor` depends on
+corresponding `_FeatureColumn`.
+ |
+
+|
+`feature_columns`
+ |
+
+An iterable containing the FeatureColumns to use as inputs
+to your model. All items should be instances of classes derived from
+`_DenseColumn` such as `numeric_column`, `embedding_column`,
+`bucketized_column`, `indicator_column`. If you have categorical features,
+you can wrap them with an `embedding_column` or `indicator_column`.
+ |
+
+|
+`weight_collections`
+ |
+
+A list of collection names to which the Variable will be
+added. Note that variables will also be added to collections
+`tf.GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES` and `ops.GraphKeys.MODEL_VARIABLES`.
+ |
+
+|
+`trainable`
+ |
+
+If `True` also add the variable to the graph collection
+`GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES` (see tf.Variable).
+ |
+
+|
+`cols_to_vars`
+ |
+
+If not `None`, must be a dictionary that will be filled with a
+mapping from `_FeatureColumn` to list of `Variable`s. For example, after
+the call, we might have cols_to_vars =
+{_EmbeddingColumn(
+categorical_column=_HashedCategoricalColumn(
+key='sparse_feature', hash_bucket_size=5, dtype=tf.string),
+dimension=10): [
+ |
+|
+`cols_to_output_tensors`
+ |
+
+If not `None`, must be a dictionary that will be
+filled with a mapping from '_FeatureColumn' to the associated
+output `Tensor`s.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` which represents input layer of a model. Its shape
+is (batch_size, first_layer_dimension) and its dtype is `float32`.
+first_layer_dimension is determined based on given `feature_columns`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if an item in `feature_columns` is not a `_DenseColumn`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/feature_column/linear_model.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/feature_column/linear_model.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..16d9b05d3f4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/feature_column/linear_model.md
@@ -0,0 +1,223 @@
+description: Returns a linear prediction Tensor based on given feature_columns.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.feature_column.linear_model
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns a linear prediction `Tensor` based on given `feature_columns`.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.feature_column.linear_model(
+ features, feature_columns, units=1, sparse_combiner='sum',
+ weight_collections=None, trainable=(True), cols_to_vars=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This function generates a weighted sum based on output dimension `units`.
+Weighted sum refers to logits in classification problems. It refers to the
+prediction itself for linear regression problems.
+
+Note on supported columns: `linear_model` treats categorical columns as
+`indicator_column`s. To be specific, assume the input as `SparseTensor` looks
+like:
+
+```python
+ shape = [2, 2]
+ {
+ [0, 0]: "a"
+ [1, 0]: "b"
+ [1, 1]: "c"
+ }
+```
+`linear_model` assigns weights for the presence of "a", "b", "c' implicitly,
+just like `indicator_column`, while `input_layer` explicitly requires wrapping
+each of categorical columns with an `embedding_column` or an
+`indicator_column`.
+
+#### Example of usage:
+
+
+
+```python
+price = numeric_column('price')
+price_buckets = bucketized_column(price, boundaries=[0., 10., 100., 1000.])
+keywords = categorical_column_with_hash_bucket("keywords", 10K)
+keywords_price = crossed_column('keywords', price_buckets, ...)
+columns = [price_buckets, keywords, keywords_price ...]
+features = tf.io.parse_example(..., features=make_parse_example_spec(columns))
+prediction = linear_model(features, columns)
+```
+
+The `sparse_combiner` argument works as follows
+For example, for two features represented as the categorical columns:
+
+```python
+ # Feature 1
+
+ shape = [2, 2]
+ {
+ [0, 0]: "a"
+ [0, 1]: "b"
+ [1, 0]: "c"
+ }
+
+ # Feature 2
+
+ shape = [2, 3]
+ {
+ [0, 0]: "d"
+ [1, 0]: "e"
+ [1, 1]: "f"
+ [1, 2]: "f"
+ }
+```
+
+with `sparse_combiner` as "mean", the linear model outputs consequently
+are:
+
+```
+ y_0 = 1.0 / 2.0 * ( w_a + w_b ) + w_d + b
+ y_1 = w_c + 1.0 / 3.0 * ( w_e + 2.0 * w_f ) + b
+```
+
+where `y_i` is the output, `b` is the bias, and `w_x` is the weight
+assigned to the presence of `x` in the input features.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`features`
+ |
+
+A mapping from key to tensors. `_FeatureColumn`s look up via these
+keys. For example `numeric_column('price')` will look at 'price' key in
+this dict. Values are `Tensor` or `SparseTensor` depending on
+corresponding `_FeatureColumn`.
+ |
+
+|
+`feature_columns`
+ |
+
+An iterable containing the FeatureColumns to use as inputs
+to your model. All items should be instances of classes derived from
+`_FeatureColumn`s.
+ |
+
+|
+`units`
+ |
+
+An integer, dimensionality of the output space. Default value is 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`sparse_combiner`
+ |
+
+A string specifying how to reduce if a categorical column
+is multivalent. Except `numeric_column`, almost all columns passed to
+`linear_model` are considered as categorical columns. It combines each
+categorical column independently. Currently "mean", "sqrtn" and "sum" are
+supported, with "sum" the default for linear model. "sqrtn" often achieves
+good accuracy, in particular with bag-of-words columns.
+* "sum": do not normalize features in the column
+* "mean": do l1 normalization on features in the column
+* "sqrtn": do l2 normalization on features in the column
+ |
+
+|
+`weight_collections`
+ |
+
+A list of collection names to which the Variable will be
+added. Note that, variables will also be added to collections
+`tf.GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES` and `ops.GraphKeys.MODEL_VARIABLES`.
+ |
+
+|
+`trainable`
+ |
+
+If `True` also add the variable to the graph collection
+`GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES` (see tf.Variable).
+ |
+
+|
+`cols_to_vars`
+ |
+
+If not `None`, must be a dictionary that will be filled with a
+mapping from `_FeatureColumn` to associated list of `Variable`s. For
+example, after the call, we might have cols_to_vars = {
+_NumericColumn(
+key='numeric_feature1', shape=(1,):
+[],
+'bias': [],
+_NumericColumn(
+key='numeric_feature2', shape=(2,)):
+[]}
+If a column creates no variables, its value will be an empty list. Note
+that cols_to_vars will also contain a string key 'bias' that maps to a
+list of Variables.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` which represents predictions/logits of a linear model. Its shape
+is (batch_size, units) and its dtype is `float32`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if an item in `feature_columns` is neither a `_DenseColumn`
+nor `_CategoricalColumn`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/feature_column/make_parse_example_spec.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/feature_column/make_parse_example_spec.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e84b38ad8cc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/feature_column/make_parse_example_spec.md
@@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
+description: Creates parsing spec dictionary from input feature_columns.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.feature_column.make_parse_example_spec
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Creates parsing spec dictionary from input feature_columns.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.feature_column.make_parse_example_spec(
+ feature_columns
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The returned dictionary can be used as arg 'features' in
+tf.io.parse_example.
+
+#### Typical usage example:
+
+
+
+```python
+# Define features and transformations
+feature_a = categorical_column_with_vocabulary_file(...)
+feature_b = numeric_column(...)
+feature_c_bucketized = bucketized_column(numeric_column("feature_c"), ...)
+feature_a_x_feature_c = crossed_column(
+ columns=["feature_a", feature_c_bucketized], ...)
+
+feature_columns = set(
+ [feature_b, feature_c_bucketized, feature_a_x_feature_c])
+features = tf.io.parse_example(
+ serialized=serialized_examples,
+ features=make_parse_example_spec(feature_columns))
+```
+
+For the above example, make_parse_example_spec would return the dict:
+
+```python
+{
+ "feature_a": parsing_ops.VarLenFeature(tf.string),
+ "feature_b": parsing_ops.FixedLenFeature([1], dtype=tf.float32),
+ "feature_c": parsing_ops.FixedLenFeature([1], dtype=tf.float32)
+}
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`feature_columns`
+ |
+
+An iterable containing all feature columns. All items
+should be instances of classes derived from `_FeatureColumn`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A dict mapping each feature key to a `FixedLenFeature` or `VarLenFeature`
+value.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If any of the given `feature_columns` is not a `_FeatureColumn`
+instance.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/feature_column/shared_embedding_columns.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/feature_column/shared_embedding_columns.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3e36066a871
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/feature_column/shared_embedding_columns.md
@@ -0,0 +1,253 @@
+description: List of dense columns that convert from sparse, categorical input.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.feature_column.shared_embedding_columns
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+List of dense columns that convert from sparse, categorical input.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.feature_column.shared_embedding_columns(
+ categorical_columns, dimension, combiner='mean', initializer=None,
+ shared_embedding_collection_name=None, ckpt_to_load_from=None,
+ tensor_name_in_ckpt=None, max_norm=None, trainable=(True),
+ use_safe_embedding_lookup=(True)
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This is similar to `embedding_column`, except that it produces a list of
+embedding columns that share the same embedding weights.
+
+Use this when your inputs are sparse and of the same type (e.g. watched and
+impression video IDs that share the same vocabulary), and you want to convert
+them to a dense representation (e.g., to feed to a DNN).
+
+Inputs must be a list of categorical columns created by any of the
+`categorical_column_*` function. They must all be of the same type and have
+the same arguments except `key`. E.g. they can be
+categorical_column_with_vocabulary_file with the same vocabulary_file. Some or
+all columns could also be weighted_categorical_column.
+
+Here is an example embedding of two features for a DNNClassifier model:
+
+```python
+watched_video_id = categorical_column_with_vocabulary_file(
+ 'watched_video_id', video_vocabulary_file, video_vocabulary_size)
+impression_video_id = categorical_column_with_vocabulary_file(
+ 'impression_video_id', video_vocabulary_file, video_vocabulary_size)
+columns = shared_embedding_columns(
+ [watched_video_id, impression_video_id], dimension=10)
+
+estimator = tf.estimator.DNNClassifier(feature_columns=columns, ...)
+
+label_column = ...
+def input_fn():
+ features = tf.io.parse_example(
+ ..., features=make_parse_example_spec(columns + [label_column]))
+ labels = features.pop(label_column.name)
+ return features, labels
+
+estimator.train(input_fn=input_fn, steps=100)
+```
+
+Here is an example using `shared_embedding_columns` with model_fn:
+
+```python
+def model_fn(features, ...):
+ watched_video_id = categorical_column_with_vocabulary_file(
+ 'watched_video_id', video_vocabulary_file, video_vocabulary_size)
+ impression_video_id = categorical_column_with_vocabulary_file(
+ 'impression_video_id', video_vocabulary_file, video_vocabulary_size)
+ columns = shared_embedding_columns(
+ [watched_video_id, impression_video_id], dimension=10)
+ dense_tensor = input_layer(features, columns)
+ # Form DNN layers, calculate loss, and return EstimatorSpec.
+ ...
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`categorical_columns`
+ |
+
+List of categorical columns created by a
+`categorical_column_with_*` function. These columns produce the sparse IDs
+that are inputs to the embedding lookup. All columns must be of the same
+type and have the same arguments except `key`. E.g. they can be
+categorical_column_with_vocabulary_file with the same vocabulary_file.
+Some or all columns could also be weighted_categorical_column.
+ |
+
+|
+`dimension`
+ |
+
+An integer specifying dimension of the embedding, must be > 0.
+ |
+
+|
+`combiner`
+ |
+
+A string specifying how to reduce if there are multiple entries in
+a single row. Currently 'mean', 'sqrtn' and 'sum' are supported, with
+'mean' the default. 'sqrtn' often achieves good accuracy, in particular
+with bag-of-words columns. Each of this can be thought as example level
+normalizations on the column. For more information, see
+`tf.embedding_lookup_sparse`.
+ |
+
+|
+`initializer`
+ |
+
+A variable initializer function to be used in embedding
+variable initialization. If not specified, defaults to
+`truncated_normal_initializer` with mean `0.0` and
+standard deviation `1/sqrt(dimension)`.
+ |
+
+|
+`shared_embedding_collection_name`
+ |
+
+Optional name of the collection where
+shared embedding weights are added. If not given, a reasonable name will
+be chosen based on the names of `categorical_columns`. This is also used
+in `variable_scope` when creating shared embedding weights.
+ |
+
+|
+`ckpt_to_load_from`
+ |
+
+String representing checkpoint name/pattern from which to
+restore column weights. Required if `tensor_name_in_ckpt` is not `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`tensor_name_in_ckpt`
+ |
+
+Name of the `Tensor` in `ckpt_to_load_from` from which
+to restore the column weights. Required if `ckpt_to_load_from` is not
+`None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_norm`
+ |
+
+If not `None`, each embedding is clipped if its l2-norm is larger
+than this value, before combining.
+ |
+
+|
+`trainable`
+ |
+
+Whether or not the embedding is trainable. Default is True.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_safe_embedding_lookup`
+ |
+
+If true, uses safe_embedding_lookup_sparse
+instead of embedding_lookup_sparse. safe_embedding_lookup_sparse ensures
+there are no empty rows and all weights and ids are positive at the
+expense of extra compute cost. This only applies to rank 2 (NxM) shaped
+input tensors. Defaults to true, consider turning off if the above checks
+are not needed. Note that having empty rows will not trigger any error
+though the output result might be 0 or omitted.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of dense columns that converts from sparse input. The order of
+results follows the ordering of `categorical_columns`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `dimension` not > 0.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if any of the given `categorical_columns` is of different type
+or has different arguments than the others.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if exactly one of `ckpt_to_load_from` and `tensor_name_in_ckpt`
+is specified.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `initializer` is specified and is not callable.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+if eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/fixed_size_partitioner.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/fixed_size_partitioner.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..08b5dd5e338
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/fixed_size_partitioner.md
@@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
+description: Partitioner to specify a fixed number of shards along given axis.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.fixed_size_partitioner
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Partitioner to specify a fixed number of shards along given axis.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.fixed_size_partitioner(
+ num_shards, axis=0
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`num_shards`
+ |
+
+`int`, number of shards to partition variable.
+ |
+
+|
+`axis`
+ |
+
+`int`, axis to partition on.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A partition function usable as the `partitioner` argument to
+`variable_scope` and `get_variable`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..416bddafd82
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags.md
@@ -0,0 +1,167 @@
+description: Import router for absl.flags. See https://github.com/abseil/abseil-py.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.flags
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Import router for absl.flags. See https://github.com/abseil/abseil-py.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags`
+
+
+
+
+
+## Modules
+
+[`tf_decorator`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator.md) module: Base TFDecorator class and utility functions for working with decorators.
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class ArgumentParser`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/ArgumentParser.md): Base class used to parse and convert arguments.
+
+[`class ArgumentSerializer`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/ArgumentSerializer.md): Base class for generating string representations of a flag value.
+
+[`class BaseListParser`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/BaseListParser.md): Base class for a parser of lists of strings.
+
+[`class BooleanFlag`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/BooleanFlag.md): Basic boolean flag.
+
+[`class BooleanParser`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/BooleanParser.md): Parser of boolean values.
+
+[`class CantOpenFlagFileError`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/CantOpenFlagFileError.md): Raised when flagfile fails to open.
+
+[`class CsvListSerializer`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/CsvListSerializer.md): Base class for generating string representations of a flag value.
+
+[`class DuplicateFlagError`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/DuplicateFlagError.md): Raised if there is a flag naming conflict.
+
+[`class EnumClassFlag`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/EnumClassFlag.md): Basic enum flag; its value is an enum class's member.
+
+[`class EnumClassParser`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/EnumClassParser.md): Parser of an Enum class member.
+
+[`class EnumFlag`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/EnumFlag.md): Basic enum flag; its value can be any string from list of enum_values.
+
+[`class EnumParser`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/EnumParser.md): Parser of a string enum value (a string value from a given set).
+
+[`class Error`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/Error.md): The base class for all flags errors.
+
+[`class Flag`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/Flag.md): Information about a command-line flag.
+
+[`class FlagNameConflictsWithMethodError`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/FlagNameConflictsWithMethodError.md): Raised when a flag name conflicts with FlagValues methods.
+
+[`class FlagValues`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/FlagValues.md): Registry of 'Flag' objects.
+
+[`class FloatParser`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/FloatParser.md): Parser of floating point values.
+
+[`class IllegalFlagValueError`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/IllegalFlagValueError.md): Raised when the flag command line argument is illegal.
+
+[`class IntegerParser`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/IntegerParser.md): Parser of an integer value.
+
+[`class ListParser`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/ListParser.md): Parser for a comma-separated list of strings.
+
+[`class ListSerializer`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/ListSerializer.md): Base class for generating string representations of a flag value.
+
+[`class MultiEnumClassFlag`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/MultiEnumClassFlag.md): A multi_enum_class flag.
+
+[`class MultiFlag`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/MultiFlag.md): A flag that can appear multiple time on the command-line.
+
+[`class UnparsedFlagAccessError`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/UnparsedFlagAccessError.md): Raised when accessing the flag value from unparsed FlagValues.
+
+[`class UnrecognizedFlagError`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/UnrecognizedFlagError.md): Raised when a flag is unrecognized.
+
+[`class ValidationError`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/ValidationError.md): Raised when flag validator constraint is not satisfied.
+
+[`class WhitespaceSeparatedListParser`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/WhitespaceSeparatedListParser.md): Parser for a whitespace-separated list of strings.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`DEFINE(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE.md): Registers a generic Flag object.
+
+[`DEFINE_alias(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_alias.md): Defines an alias flag for an existing one.
+
+[`DEFINE_bool(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_bool.md): Registers a boolean flag.
+
+[`DEFINE_boolean(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_bool.md): Registers a boolean flag.
+
+[`DEFINE_enum(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_enum.md): Registers a flag whose value can be any string from enum_values.
+
+[`DEFINE_enum_class(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_enum_class.md): Registers a flag whose value can be the name of enum members.
+
+[`DEFINE_flag(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_flag.md): Registers a 'Flag' object with a 'FlagValues' object.
+
+[`DEFINE_float(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_float.md): Registers a flag whose value must be a float.
+
+[`DEFINE_integer(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_integer.md): Registers a flag whose value must be an integer.
+
+[`DEFINE_list(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_list.md): Registers a flag whose value is a comma-separated list of strings.
+
+[`DEFINE_multi(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_multi.md): Registers a generic MultiFlag that parses its args with a given parser.
+
+[`DEFINE_multi_enum(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_multi_enum.md): Registers a flag whose value can be a list strings from enum_values.
+
+[`DEFINE_multi_enum_class(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_multi_enum_class.md): Registers a flag whose value can be a list of enum members.
+
+[`DEFINE_multi_float(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_multi_float.md): Registers a flag whose value can be a list of arbitrary floats.
+
+[`DEFINE_multi_integer(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_multi_integer.md): Registers a flag whose value can be a list of arbitrary integers.
+
+[`DEFINE_multi_string(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_multi_string.md): Registers a flag whose value can be a list of any strings.
+
+[`DEFINE_spaceseplist(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_spaceseplist.md): Registers a flag whose value is a whitespace-separated list of strings.
+
+[`DEFINE_string(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_string.md): Registers a flag whose value can be any string.
+
+[`FLAGS(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/FLAGS.md): Registry of 'Flag' objects.
+
+[`adopt_module_key_flags(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/adopt_module_key_flags.md): Declares that all flags key to a module are key to the current module.
+
+[`declare_key_flag(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/declare_key_flag.md): Declares one flag as key to the current module.
+
+[`disclaim_key_flags(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/disclaim_key_flags.md): Declares that the current module will not define any more key flags.
+
+[`doc_to_help(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/doc_to_help.md): Takes a __doc__ string and reformats it as help.
+
+[`flag_dict_to_args(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/flag_dict_to_args.md): Convert a dict of values into process call parameters.
+
+[`get_help_width(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/get_help_width.md): Returns the integer width of help lines that is used in TextWrap.
+
+[`mark_bool_flags_as_mutual_exclusive(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/mark_bool_flags_as_mutual_exclusive.md): Ensures that only one flag among flag_names is True.
+
+[`mark_flag_as_required(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/mark_flag_as_required.md): Ensures that flag is not None during program execution.
+
+[`mark_flags_as_mutual_exclusive(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/mark_flags_as_mutual_exclusive.md): Ensures that only one flag among flag_names is not None.
+
+[`mark_flags_as_required(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/mark_flags_as_required.md): Ensures that flags are not None during program execution.
+
+[`multi_flags_validator(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/multi_flags_validator.md): A function decorator for defining a multi-flag validator.
+
+[`register_multi_flags_validator(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/register_multi_flags_validator.md): Adds a constraint to multiple flags.
+
+[`register_validator(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/register_validator.md): Adds a constraint, which will be enforced during program execution.
+
+[`text_wrap(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/text_wrap.md): Wraps a given text to a maximum line length and returns it.
+
+[`validator(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/validator.md): A function decorator for defining a flag validator.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/ArgumentParser.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/ArgumentParser.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..6f6a24ae835
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/ArgumentParser.md
@@ -0,0 +1,130 @@
+description: Base class used to parse and convert arguments.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.ArgumentParser
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Base class used to parse and convert arguments.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.ArgumentParser`
+
+
+
+
+
+The parse() method checks to make sure that the string argument is a
+legal value and convert it to a native type. If the value cannot be
+converted, it should throw a 'ValueError' exception with a human
+readable explanation of why the value is illegal.
+
+Subclasses should also define a syntactic_help string which may be
+presented to the user to describe the form of the legal values.
+
+Argument parser classes must be stateless, since instances are cached
+and shared between flags. Initializer arguments are allowed, but all
+member variables must be derived from initializer arguments only.
+
+## Methods
+
+flag_type
+
+
+flag_type()
+
+
+Returns a string representing the type of the flag.
+
+
+parse
+
+
+parse(
+ argument
+)
+
+
+Parses the string argument and returns the native value.
+
+By default it returns its argument unmodified.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`argument`
+ |
+
+string argument passed in the commandline.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+Raised when it fails to parse the argument.
+ |
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+Raised when the argument has the wrong type.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The parsed value in native type.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `syntactic_help = ''`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/ArgumentSerializer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/ArgumentSerializer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..16be9e3902e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/ArgumentSerializer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
+description: Base class for generating string representations of a flag value.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.ArgumentSerializer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Base class for generating string representations of a flag value.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.ArgumentSerializer`
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+serialize
+
+
+serialize(
+ value
+)
+
+
+Returns a serialized string of the value.
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/BaseListParser.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/BaseListParser.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..1c226914119
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/BaseListParser.md
@@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
+description: Base class for a parser of lists of strings.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.BaseListParser
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Base class for a parser of lists of strings.
+
+Inherits From: [`ArgumentParser`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/ArgumentParser.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.BaseListParser`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.BaseListParser(
+ token=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+To extend, inherit from this class; from the subclass __init__, call
+
+ BaseListParser.__init__(self, token, name)
+
+where token is a character used to tokenize, and name is a description
+of the separator.
+
+## Methods
+
+flag_type
+
+
+flag_type()
+
+
+See base class.
+
+
+parse
+
+
+parse(
+ argument
+)
+
+
+See base class.
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `syntactic_help = ''`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/BooleanFlag.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/BooleanFlag.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..fa997dd466e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/BooleanFlag.md
@@ -0,0 +1,197 @@
+description: Basic boolean flag.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.BooleanFlag
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Basic boolean flag.
+
+Inherits From: [`Flag`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/Flag.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.BooleanFlag`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.BooleanFlag(
+ name, default, help, short_name=None, **args
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Boolean flags do not take any arguments, and their value is either
+True (1) or False (0). The false value is specified on the command
+line by prepending the word 'no' to either the long or the short flag
+name.
+
+For example, if a Boolean flag was created whose long name was
+'update' and whose short name was 'x', then this flag could be
+explicitly unset through either --noupdate or --nox.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+flag_type
+
+
+flag_type()
+
+
+Returns a str that describes the type of the flag.
+
+NOTE: we use strings, and not the types.*Type constants because
+our flags can have more exotic types, e.g., 'comma separated list
+of strings', 'whitespace separated list of strings', etc.
+
+parse
+
+
+parse(
+ argument
+)
+
+
+Parses string and sets flag value.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`argument`
+ |
+
+str or the correct flag value type, argument to be parsed.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+serialize
+
+
+serialize()
+
+
+Serializes the flag.
+
+
+unparse
+
+
+unparse()
+
+
+
+
+
+__eq__
+
+
+__eq__(
+ other
+)
+
+
+Return self==value.
+
+
+__ge__
+
+
+__ge__(
+ other, NotImplemented=NotImplemented
+)
+
+
+Return a >= b. Computed by @total_ordering from (not a < b).
+
+
+__gt__
+
+
+__gt__(
+ other, NotImplemented=NotImplemented
+)
+
+
+Return a > b. Computed by @total_ordering from (not a < b) and (a != b).
+
+
+__le__
+
+
+__le__(
+ other, NotImplemented=NotImplemented
+)
+
+
+Return a <= b. Computed by @total_ordering from (a < b) or (a == b).
+
+
+__lt__
+
+
+__lt__(
+ other
+)
+
+
+Return self
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.BooleanParser
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Parser of boolean values.
+
+Inherits From: [`ArgumentParser`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/ArgumentParser.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.BooleanParser`
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+flag_type
+
+
+flag_type()
+
+
+See base class.
+
+
+parse
+
+
+parse(
+ argument
+)
+
+
+See base class.
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `syntactic_help = ''`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/CantOpenFlagFileError.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/CantOpenFlagFileError.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..866d350a194
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/CantOpenFlagFileError.md
@@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
+description: Raised when flagfile fails to open.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.CantOpenFlagFileError
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raised when flagfile fails to open.
+
+Inherits From: [`Error`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/Error.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.CantOpenFlagFileError`
+
+
+
+
+
+E.g. the file doesn't exist, or has wrong permissions.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/CsvListSerializer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/CsvListSerializer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..6c215f18005
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/CsvListSerializer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+description: Base class for generating string representations of a flag value.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.CsvListSerializer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Base class for generating string representations of a flag value.
+
+Inherits From: [`ArgumentSerializer`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/ArgumentSerializer.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.CsvListSerializer`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.CsvListSerializer(
+ list_sep
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+serialize
+
+
+serialize(
+ value
+)
+
+
+Serializes a list as a CSV string or unicode.
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..99d43058b6c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE.md
@@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
+description: Registers a generic Flag object.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.DEFINE
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Registers a generic Flag object.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.DEFINE`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.DEFINE(
+ parser, name, default, help, flag_values=_flagvalues.FLAGS, serializer=None,
+ module_name=None, **args
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+NOTE: in the docstrings of all DEFINE* functions, "registers" is short
+for "creates a new flag and registers it".
+
+Auxiliary function: clients should use the specialized DEFINE_
+function instead.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`parser`
+ |
+
+ArgumentParser, used to parse the flag arguments.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+str, the flag name.
+ |
+
+|
+`default`
+ |
+
+The default value of the flag.
+ |
+
+|
+`help`
+ |
+
+str, the help message.
+ |
+
+|
+`flag_values`
+ |
+
+FlagValues, the FlagValues instance with which the flag will
+be registered. This should almost never need to be overridden.
+ |
+
+|
+`serializer`
+ |
+
+ArgumentSerializer, the flag serializer instance.
+ |
+
+|
+`module_name`
+ |
+
+str, the name of the Python module declaring this flag.
+If not provided, it will be computed using the stack trace of this call.
+ |
+
+|
+`**args`
+ |
+
+dict, the extra keyword args that are passed to Flag __init__.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_alias.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_alias.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..da3d0252084
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_alias.md
@@ -0,0 +1,96 @@
+description: Defines an alias flag for an existing one.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.DEFINE_alias
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Defines an alias flag for an existing one.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.DEFINE_alias`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.DEFINE_alias(
+ name, original_name, flag_values=_flagvalues.FLAGS, module_name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+str, the flag name.
+ |
+
+|
+`original_name`
+ |
+
+str, the original flag name.
+ |
+
+|
+`flag_values`
+ |
+
+FlagValues, the FlagValues instance with which the flag will
+be registered. This should almost never need to be overridden.
+ |
+
+|
+`module_name`
+ |
+
+A string, the name of the module that defines this flag.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`flags.FlagError`
+ |
+
+UnrecognizedFlagError: if the referenced flag doesn't exist.
+DuplicateFlagError: if the alias name has been used by some existing flag.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_bool.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_bool.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..df111257b28
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_bool.md
@@ -0,0 +1,100 @@
+description: Registers a boolean flag.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.DEFINE_bool
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Registers a boolean flag.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.DEFINE_bool`, `tf.compat.v1.app.flags.DEFINE_boolean`, `tf.compat.v1.flags.DEFINE_boolean`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.DEFINE_bool(
+ name, default, help, flag_values=_flagvalues.FLAGS, module_name=None, **args
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Such a boolean flag does not take an argument. If a user wants to
+specify a false value explicitly, the long option beginning with 'no'
+must be used: i.e. --noflag
+
+This flag will have a value of None, True or False. None is possible
+if default=None and the user does not specify the flag on the command
+line.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+str, the flag name.
+ |
+
+|
+`default`
+ |
+
+bool|str|None, the default value of the flag.
+ |
+
+|
+`help`
+ |
+
+str, the help message.
+ |
+
+|
+`flag_values`
+ |
+
+FlagValues, the FlagValues instance with which the flag will
+be registered. This should almost never need to be overridden.
+ |
+
+|
+`module_name`
+ |
+
+str, the name of the Python module declaring this flag.
+If not provided, it will be computed using the stack trace of this call.
+ |
+
+|
+`**args`
+ |
+
+dict, the extra keyword args that are passed to Flag __init__.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_enum.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_enum.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..ebb7e453677
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_enum.md
@@ -0,0 +1,104 @@
+description: Registers a flag whose value can be any string from enum_values.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.DEFINE_enum
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Registers a flag whose value can be any string from enum_values.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.DEFINE_enum`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.DEFINE_enum(
+ name, default, enum_values, help, flag_values=_flagvalues.FLAGS,
+ module_name=None, **args
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Instead of a string enum, prefer `DEFINE_enum_class`, which allows
+defining enums from an `enum.Enum` class.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+str, the flag name.
+ |
+
+|
+`default`
+ |
+
+str|None, the default value of the flag.
+ |
+
+|
+`enum_values`
+ |
+
+[str], a non-empty list of strings with the possible values for
+the flag.
+ |
+
+|
+`help`
+ |
+
+str, the help message.
+ |
+
+|
+`flag_values`
+ |
+
+FlagValues, the FlagValues instance with which the flag will
+be registered. This should almost never need to be overridden.
+ |
+
+|
+`module_name`
+ |
+
+str, the name of the Python module declaring this flag.
+If not provided, it will be computed using the stack trace of this call.
+ |
+
+|
+`**args`
+ |
+
+dict, the extra keyword args that are passed to Flag __init__.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_enum_class.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_enum_class.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..fd056829f65
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_enum_class.md
@@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
+description: Registers a flag whose value can be the name of enum members.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.DEFINE_enum_class
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Registers a flag whose value can be the name of enum members.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.DEFINE_enum_class`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.DEFINE_enum_class(
+ name, default, enum_class, help, flag_values=_flagvalues.FLAGS,
+ module_name=None, **args
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+str, the flag name.
+ |
+
+|
+`default`
+ |
+
+Enum|str|None, the default value of the flag.
+ |
+
+|
+`enum_class`
+ |
+
+class, the Enum class with all the possible values for the flag.
+ |
+
+|
+`help`
+ |
+
+str, the help message.
+ |
+
+|
+`flag_values`
+ |
+
+FlagValues, the FlagValues instance with which the flag will
+be registered. This should almost never need to be overridden.
+ |
+
+|
+`module_name`
+ |
+
+str, the name of the Python module declaring this flag.
+If not provided, it will be computed using the stack trace of this call.
+ |
+
+|
+`**args`
+ |
+
+dict, the extra keyword args that are passed to Flag __init__.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_flag.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_flag.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..c4830a06366
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_flag.md
@@ -0,0 +1,78 @@
+description: Registers a 'Flag' object with a 'FlagValues' object.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.DEFINE_flag
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Registers a 'Flag' object with a 'FlagValues' object.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.DEFINE_flag`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.DEFINE_flag(
+ flag, flag_values=_flagvalues.FLAGS, module_name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+By default, the global FLAGS 'FlagValue' object is used.
+
+Typical users will use one of the more specialized DEFINE_xxx
+functions, such as DEFINE_string or DEFINE_integer. But developers
+who need to create Flag objects themselves should use this function
+to register their flags.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`flag`
+ |
+
+Flag, a flag that is key to the module.
+ |
+
+|
+`flag_values`
+ |
+
+FlagValues, the FlagValues instance with which the flag will
+be registered. This should almost never need to be overridden.
+ |
+
+|
+`module_name`
+ |
+
+str, the name of the Python module declaring this flag.
+If not provided, it will be computed using the stack trace of this call.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_float.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_float.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..301b4304917
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_float.md
@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
+description: Registers a flag whose value must be a float.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.DEFINE_float
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Registers a flag whose value must be a float.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.DEFINE_float`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.DEFINE_float(
+ name, default, help, lower_bound=None, upper_bound=None,
+ flag_values=_flagvalues.FLAGS, **args
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+If lower_bound or upper_bound are set, then this flag must be
+within the given range.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+str, the flag name.
+ |
+
+|
+`default`
+ |
+
+float|str|None, the default value of the flag.
+ |
+
+|
+`help`
+ |
+
+str, the help message.
+ |
+
+|
+`lower_bound`
+ |
+
+float, min value of the flag.
+ |
+
+|
+`upper_bound`
+ |
+
+float, max value of the flag.
+ |
+
+|
+`flag_values`
+ |
+
+FlagValues, the FlagValues instance with which the flag will
+be registered. This should almost never need to be overridden.
+ |
+
+|
+`**args`
+ |
+
+dict, the extra keyword args that are passed to DEFINE.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_integer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_integer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..0d0ea32c0e8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_integer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
+description: Registers a flag whose value must be an integer.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.DEFINE_integer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Registers a flag whose value must be an integer.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.DEFINE_integer`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.DEFINE_integer(
+ name, default, help, lower_bound=None, upper_bound=None,
+ flag_values=_flagvalues.FLAGS, **args
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+If lower_bound, or upper_bound are set, then this flag must be
+within the given range.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+str, the flag name.
+ |
+
+|
+`default`
+ |
+
+int|str|None, the default value of the flag.
+ |
+
+|
+`help`
+ |
+
+str, the help message.
+ |
+
+|
+`lower_bound`
+ |
+
+int, min value of the flag.
+ |
+
+|
+`upper_bound`
+ |
+
+int, max value of the flag.
+ |
+
+|
+`flag_values`
+ |
+
+FlagValues, the FlagValues instance with which the flag will
+be registered. This should almost never need to be overridden.
+ |
+
+|
+`**args`
+ |
+
+dict, the extra keyword args that are passed to DEFINE.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_list.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_list.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..f0179cdf67b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_list.md
@@ -0,0 +1,87 @@
+description: Registers a flag whose value is a comma-separated list of strings.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.DEFINE_list
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Registers a flag whose value is a comma-separated list of strings.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.DEFINE_list`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.DEFINE_list(
+ name, default, help, flag_values=_flagvalues.FLAGS, **args
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The flag value is parsed with a CSV parser.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+str, the flag name.
+ |
+
+|
+`default`
+ |
+
+list|str|None, the default value of the flag.
+ |
+
+|
+`help`
+ |
+
+str, the help message.
+ |
+
+|
+`flag_values`
+ |
+
+FlagValues, the FlagValues instance with which the flag will
+be registered. This should almost never need to be overridden.
+ |
+
+|
+`**args`
+ |
+
+Dictionary with extra keyword args that are passed to the
+Flag __init__.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_multi.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_multi.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..428e29aea12
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_multi.md
@@ -0,0 +1,118 @@
+description: Registers a generic MultiFlag that parses its args with a given parser.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.DEFINE_multi
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Registers a generic MultiFlag that parses its args with a given parser.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.DEFINE_multi`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.DEFINE_multi(
+ parser, serializer, name, default, help, flag_values=_flagvalues.FLAGS,
+ module_name=None, **args
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Auxiliary function. Normal users should NOT use it directly.
+
+Developers who need to create their own 'Parser' classes for options
+which can appear multiple times can call this module function to
+register their flags.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`parser`
+ |
+
+ArgumentParser, used to parse the flag arguments.
+ |
+
+|
+`serializer`
+ |
+
+ArgumentSerializer, the flag serializer instance.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+str, the flag name.
+ |
+
+|
+`default`
+ |
+
+Union[Iterable[T], Text, None], the default value of the flag.
+If the value is text, it will be parsed as if it was provided from
+the command line. If the value is a non-string iterable, it will be
+iterated over to create a shallow copy of the values. If it is None,
+it is left as-is.
+ |
+
+|
+`help`
+ |
+
+str, the help message.
+ |
+
+|
+`flag_values`
+ |
+
+FlagValues, the FlagValues instance with which the flag will
+be registered. This should almost never need to be overridden.
+ |
+
+|
+`module_name`
+ |
+
+A string, the name of the Python module declaring this flag.
+If not provided, it will be computed using the stack trace of this call.
+ |
+
+|
+`**args`
+ |
+
+Dictionary with extra keyword args that are passed to the
+Flag __init__.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_multi_enum.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_multi_enum.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a57e85b28fe
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_multi_enum.md
@@ -0,0 +1,107 @@
+description: Registers a flag whose value can be a list strings from enum_values.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.DEFINE_multi_enum
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Registers a flag whose value can be a list strings from enum_values.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.DEFINE_multi_enum`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.DEFINE_multi_enum(
+ name, default, enum_values, help, flag_values=_flagvalues.FLAGS,
+ case_sensitive=(True), **args
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Use the flag on the command line multiple times to place multiple
+enum values into the list. The 'default' may be a single string
+(which will be converted into a single-element list) or a list of
+strings.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+str, the flag name.
+ |
+
+|
+`default`
+ |
+
+Union[Iterable[Text], Text, None], the default value of the flag;
+see `DEFINE_multi`.
+ |
+
+|
+`enum_values`
+ |
+
+[str], a non-empty list of strings with the possible values for
+the flag.
+ |
+
+|
+`help`
+ |
+
+str, the help message.
+ |
+
+|
+`flag_values`
+ |
+
+FlagValues, the FlagValues instance with which the flag will
+be registered. This should almost never need to be overridden.
+ |
+
+|
+`case_sensitive`
+ |
+
+Whether or not the enum is to be case-sensitive.
+ |
+
+|
+`**args`
+ |
+
+Dictionary with extra keyword args that are passed to the
+Flag __init__.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_multi_enum_class.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_multi_enum_class.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a0dea08db4a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_multi_enum_class.md
@@ -0,0 +1,103 @@
+description: Registers a flag whose value can be a list of enum members.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.DEFINE_multi_enum_class
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Registers a flag whose value can be a list of enum members.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.DEFINE_multi_enum_class`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.DEFINE_multi_enum_class(
+ name, default, enum_class, help, flag_values=_flagvalues.FLAGS,
+ module_name=None, **args
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Use the flag on the command line multiple times to place multiple
+enum values into the list.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+str, the flag name.
+ |
+
+|
+`default`
+ |
+
+Union[Iterable[Enum], Iterable[Text], Enum, Text, None], the
+default value of the flag; see
+`DEFINE_multi`; only differences are documented here. If the value is
+a single Enum, it is treated as a single-item list of that Enum value.
+If it is an iterable, text values within the iterable will be converted
+to the equivalent Enum objects.
+ |
+
+|
+`enum_class`
+ |
+
+class, the Enum class with all the possible values for the flag.
+help: str, the help message.
+ |
+
+|
+`flag_values`
+ |
+
+FlagValues, the FlagValues instance with which the flag will be
+registered. This should almost never need to be overridden.
+ |
+
+|
+`module_name`
+ |
+
+A string, the name of the Python module declaring this flag. If
+not provided, it will be computed using the stack trace of this call.
+ |
+
+|
+`**args`
+ |
+
+Dictionary with extra keyword args that are passed to the Flag
+__init__.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_multi_float.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_multi_float.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..4b34729cc82
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_multi_float.md
@@ -0,0 +1,106 @@
+description: Registers a flag whose value can be a list of arbitrary floats.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.DEFINE_multi_float
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Registers a flag whose value can be a list of arbitrary floats.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.DEFINE_multi_float`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.DEFINE_multi_float(
+ name, default, help, lower_bound=None, upper_bound=None,
+ flag_values=_flagvalues.FLAGS, **args
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Use the flag on the command line multiple times to place multiple
+float values into the list. The 'default' may be a single float
+(which will be converted into a single-element list) or a list of
+floats.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+str, the flag name.
+ |
+
+|
+`default`
+ |
+
+Union[Iterable[float], Text, None], the default value of the flag;
+see `DEFINE_multi`.
+ |
+
+|
+`help`
+ |
+
+str, the help message.
+ |
+
+|
+`lower_bound`
+ |
+
+float, min values of the flag.
+ |
+
+|
+`upper_bound`
+ |
+
+float, max values of the flag.
+ |
+
+|
+`flag_values`
+ |
+
+FlagValues, the FlagValues instance with which the flag will
+be registered. This should almost never need to be overridden.
+ |
+
+|
+`**args`
+ |
+
+Dictionary with extra keyword args that are passed to the
+Flag __init__.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_multi_integer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_multi_integer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a61998272b4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_multi_integer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,106 @@
+description: Registers a flag whose value can be a list of arbitrary integers.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.DEFINE_multi_integer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Registers a flag whose value can be a list of arbitrary integers.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.DEFINE_multi_integer`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.DEFINE_multi_integer(
+ name, default, help, lower_bound=None, upper_bound=None,
+ flag_values=_flagvalues.FLAGS, **args
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Use the flag on the command line multiple times to place multiple
+integer values into the list. The 'default' may be a single integer
+(which will be converted into a single-element list) or a list of
+integers.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+str, the flag name.
+ |
+
+|
+`default`
+ |
+
+Union[Iterable[int], Text, None], the default value of the flag;
+see `DEFINE_multi`.
+ |
+
+|
+`help`
+ |
+
+str, the help message.
+ |
+
+|
+`lower_bound`
+ |
+
+int, min values of the flag.
+ |
+
+|
+`upper_bound`
+ |
+
+int, max values of the flag.
+ |
+
+|
+`flag_values`
+ |
+
+FlagValues, the FlagValues instance with which the flag will
+be registered. This should almost never need to be overridden.
+ |
+
+|
+`**args`
+ |
+
+Dictionary with extra keyword args that are passed to the
+Flag __init__.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_multi_string.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_multi_string.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..c3058da3a1c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_multi_string.md
@@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
+description: Registers a flag whose value can be a list of any strings.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.DEFINE_multi_string
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Registers a flag whose value can be a list of any strings.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.DEFINE_multi_string`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.DEFINE_multi_string(
+ name, default, help, flag_values=_flagvalues.FLAGS, **args
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Use the flag on the command line multiple times to place multiple
+string values into the list. The 'default' may be a single string
+(which will be converted into a single-element list) or a list of
+strings.
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+str, the flag name.
+ |
+
+|
+`default`
+ |
+
+Union[Iterable[Text], Text, None], the default value of the flag;
+see `DEFINE_multi`.
+ |
+
+|
+`help`
+ |
+
+str, the help message.
+ |
+
+|
+`flag_values`
+ |
+
+FlagValues, the FlagValues instance with which the flag will
+be registered. This should almost never need to be overridden.
+ |
+
+|
+`**args`
+ |
+
+Dictionary with extra keyword args that are passed to the
+Flag __init__.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_spaceseplist.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_spaceseplist.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..8244b0028a3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_spaceseplist.md
@@ -0,0 +1,96 @@
+description: Registers a flag whose value is a whitespace-separated list of strings.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.DEFINE_spaceseplist
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Registers a flag whose value is a whitespace-separated list of strings.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.DEFINE_spaceseplist`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.DEFINE_spaceseplist(
+ name, default, help, comma_compat=(False), flag_values=_flagvalues.FLAGS, **args
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Any whitespace can be used as a separator.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+str, the flag name.
+ |
+
+|
+`default`
+ |
+
+list|str|None, the default value of the flag.
+ |
+
+|
+`help`
+ |
+
+str, the help message.
+ |
+
+|
+`comma_compat`
+ |
+
+bool - Whether to support comma as an additional separator.
+If false then only whitespace is supported. This is intended only for
+backwards compatibility with flags that used to be comma-separated.
+ |
+
+|
+`flag_values`
+ |
+
+FlagValues, the FlagValues instance with which the flag will
+be registered. This should almost never need to be overridden.
+ |
+
+|
+`**args`
+ |
+
+Dictionary with extra keyword args that are passed to the
+Flag __init__.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_string.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_string.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..2ebac771dee
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DEFINE_string.md
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
+description: Registers a flag whose value can be any string.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.DEFINE_string
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Registers a flag whose value can be any string.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.DEFINE_string`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.DEFINE_string(
+ name, default, help, flag_values=_flagvalues.FLAGS, **args
+)
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DuplicateFlagError.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DuplicateFlagError.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..1119dfcab41
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/DuplicateFlagError.md
@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
+description: Raised if there is a flag naming conflict.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.DuplicateFlagError
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raised if there is a flag naming conflict.
+
+Inherits From: [`Error`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/Error.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.DuplicateFlagError`
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+from_flag
+
+
+@classmethod
+from_flag(
+ flagname, flag_values, other_flag_values=None
+)
+
+
+Creates a DuplicateFlagError by providing flag name and values.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`flagname`
+ |
+
+str, the name of the flag being redefined.
+ |
+
+|
+`flag_values`
+ |
+
+FlagValues, the FlagValues instance containing the first
+definition of flagname.
+ |
+
+|
+`other_flag_values`
+ |
+
+FlagValues, if it is not None, it should be the
+FlagValues object where the second definition of flagname occurs.
+If it is None, we assume that we're being called when attempting
+to create the flag a second time, and we use the module calling
+this one as the source of the second definition.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An instance of DuplicateFlagError.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/EnumClassFlag.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/EnumClassFlag.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..2d45084c0a3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/EnumClassFlag.md
@@ -0,0 +1,189 @@
+description: Basic enum flag; its value is an enum class's member.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.EnumClassFlag
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Basic enum flag; its value is an enum class's member.
+
+Inherits From: [`Flag`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/Flag.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.EnumClassFlag`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.EnumClassFlag(
+ name, default, help, enum_class, short_name=None, **args
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+flag_type
+
+
+flag_type()
+
+
+Returns a str that describes the type of the flag.
+
+NOTE: we use strings, and not the types.*Type constants because
+our flags can have more exotic types, e.g., 'comma separated list
+of strings', 'whitespace separated list of strings', etc.
+
+parse
+
+
+parse(
+ argument
+)
+
+
+Parses string and sets flag value.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`argument`
+ |
+
+str or the correct flag value type, argument to be parsed.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+serialize
+
+
+serialize()
+
+
+Serializes the flag.
+
+
+unparse
+
+
+unparse()
+
+
+
+
+
+__eq__
+
+
+__eq__(
+ other
+)
+
+
+Return self==value.
+
+
+__ge__
+
+
+__ge__(
+ other, NotImplemented=NotImplemented
+)
+
+
+Return a >= b. Computed by @total_ordering from (not a < b).
+
+
+__gt__
+
+
+__gt__(
+ other, NotImplemented=NotImplemented
+)
+
+
+Return a > b. Computed by @total_ordering from (not a < b) and (a != b).
+
+
+__le__
+
+
+__le__(
+ other, NotImplemented=NotImplemented
+)
+
+
+Return a <= b. Computed by @total_ordering from (a < b) or (a == b).
+
+
+__lt__
+
+
+__lt__(
+ other
+)
+
+
+Return self
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.EnumClassParser
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Parser of an Enum class member.
+
+Inherits From: [`ArgumentParser`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/ArgumentParser.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.EnumClassParser`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.EnumClassParser(
+ enum_class
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`enum_class`
+ |
+
+class, the Enum class with all possible flag values.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+When enum_class is not a subclass of Enum.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+When enum_class is empty.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+flag_type
+
+
+flag_type()
+
+
+See base class.
+
+
+parse
+
+
+parse(
+ argument
+)
+
+
+Determines validity of argument and returns the correct element of enum.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`argument`
+ |
+
+str or Enum class member, the supplied flag value.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The first matching Enum class member in Enum class.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+Raised when argument didn't match anything in enum.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `syntactic_help = ''`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/EnumFlag.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/EnumFlag.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..27fbaf05705
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/EnumFlag.md
@@ -0,0 +1,189 @@
+description: Basic enum flag; its value can be any string from list of enum_values.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.EnumFlag
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Basic enum flag; its value can be any string from list of enum_values.
+
+Inherits From: [`Flag`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/Flag.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.EnumFlag`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.EnumFlag(
+ name, default, help, enum_values, short_name=None, case_sensitive=(True), **args
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+flag_type
+
+
+flag_type()
+
+
+Returns a str that describes the type of the flag.
+
+NOTE: we use strings, and not the types.*Type constants because
+our flags can have more exotic types, e.g., 'comma separated list
+of strings', 'whitespace separated list of strings', etc.
+
+parse
+
+
+parse(
+ argument
+)
+
+
+Parses string and sets flag value.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`argument`
+ |
+
+str or the correct flag value type, argument to be parsed.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+serialize
+
+
+serialize()
+
+
+Serializes the flag.
+
+
+unparse
+
+
+unparse()
+
+
+
+
+
+__eq__
+
+
+__eq__(
+ other
+)
+
+
+Return self==value.
+
+
+__ge__
+
+
+__ge__(
+ other, NotImplemented=NotImplemented
+)
+
+
+Return a >= b. Computed by @total_ordering from (not a < b).
+
+
+__gt__
+
+
+__gt__(
+ other, NotImplemented=NotImplemented
+)
+
+
+Return a > b. Computed by @total_ordering from (not a < b) and (a != b).
+
+
+__le__
+
+
+__le__(
+ other, NotImplemented=NotImplemented
+)
+
+
+Return a <= b. Computed by @total_ordering from (a < b) or (a == b).
+
+
+__lt__
+
+
+__lt__(
+ other
+)
+
+
+Return self
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.EnumParser
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Parser of a string enum value (a string value from a given set).
+
+Inherits From: [`ArgumentParser`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/ArgumentParser.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.EnumParser`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.EnumParser(
+ enum_values, case_sensitive=(True)
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`enum_values`
+ |
+
+[str], a non-empty list of string values in the enum.
+ |
+
+|
+`case_sensitive`
+ |
+
+bool, whether or not the enum is to be case-sensitive.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+When enum_values is empty.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+flag_type
+
+
+flag_type()
+
+
+See base class.
+
+
+parse
+
+
+parse(
+ argument
+)
+
+
+Determines validity of argument and returns the correct element of enum.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`argument`
+ |
+
+str, the supplied flag value.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The first matching element from enum_values.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+Raised when argument didn't match anything in enum.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `syntactic_help = ''`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/Error.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/Error.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..62c3cc936c6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/Error.md
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+description: The base class for all flags errors.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.Error
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The base class for all flags errors.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.Error`
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/FLAGS.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/FLAGS.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..bd780869013
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/FLAGS.md
@@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
+description: Registry of 'Flag' objects.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.FLAGS
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Registry of 'Flag' objects.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.FLAGS`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.FLAGS(
+ *args, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A 'FlagValues' can then scan command line arguments, passing flag
+arguments through to the 'Flag' objects that it owns. It also
+provides easy access to the flag values. Typically only one
+'FlagValues' object is needed by an application: flags.FLAGS
+
+This class is heavily overloaded:
+
+'Flag' objects are registered via __setitem__:
+ FLAGS['longname'] = x # register a new flag
+
+The .value attribute of the registered 'Flag' objects can be accessed
+as attributes of this 'FlagValues' object, through __getattr__. Both
+the long and short name of the original 'Flag' objects can be used to
+access its value:
+ FLAGS.longname # parsed flag value
+ FLAGS.x # parsed flag value (short name)
+
+Command line arguments are scanned and passed to the registered 'Flag'
+objects through the __call__ method. Unparsed arguments, including
+argv[0] (e.g. the program name) are returned.
+ argv = FLAGS(sys.argv) # scan command line arguments
+
+The original registered Flag objects can be retrieved through the use
+of the dictionary-like operator, __getitem__:
+ x = FLAGS['longname'] # access the registered Flag object
+
+The str() operator of a 'FlagValues' object provides help for all of
+the registered 'Flag' objects.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/Flag.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/Flag.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..8d6df3d0d0e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/Flag.md
@@ -0,0 +1,229 @@
+description: Information about a command-line flag.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.Flag
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Information about a command-line flag.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.Flag`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.Flag(
+ parser, serializer, name, default, help_string, short_name=None,
+ boolean=(False), allow_override=(False), allow_override_cpp=(False),
+ allow_hide_cpp=(False), allow_overwrite=(True), allow_using_method_names=(False)
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+'Flag' objects define the following fields:
+ .name - the name for this flag;
+ .default - the default value for this flag;
+ .default_unparsed - the unparsed default value for this flag.
+ .default_as_str - default value as repr'd string, e.g., "'true'" (or None);
+ .value - the most recent parsed value of this flag; set by parse();
+ .help - a help string or None if no help is available;
+ .short_name - the single letter alias for this flag (or None);
+ .boolean - if 'true', this flag does not accept arguments;
+ .present - true if this flag was parsed from command line flags;
+ .parser - an ArgumentParser object;
+ .serializer - an ArgumentSerializer object;
+ .allow_override - the flag may be redefined without raising an error, and
+ newly defined flag overrides the old one.
+ .allow_override_cpp - use the flag from C++ if available; the flag
+ definition is replaced by the C++ flag after init;
+ .allow_hide_cpp - use the Python flag despite having a C++ flag with
+ the same name (ignore the C++ flag);
+ .using_default_value - the flag value has not been set by user;
+ .allow_overwrite - the flag may be parsed more than once without raising
+ an error, the last set value will be used;
+ .allow_using_method_names - whether this flag can be defined even if it has
+ a name that conflicts with a FlagValues method.
+
+The only public method of a 'Flag' object is parse(), but it is
+typically only called by a 'FlagValues' object. The parse() method is
+a thin wrapper around the 'ArgumentParser' parse() method. The parsed
+value is saved in .value, and the .present attribute is updated. If
+this flag was already present, an Error is raised.
+
+parse() is also called during __init__ to parse the default value and
+initialize the .value attribute. This enables other python modules to
+safely use flags even if the __main__ module neglects to parse the
+command line arguments. The .present attribute is cleared after
+__init__ parsing. If the default value is set to None, then the
+__init__ parsing step is skipped and the .value attribute is
+initialized to None.
+
+Note: The default value is also presented to the user in the help
+string, so it is important that it be a legal value for this flag.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+flag_type
+
+
+flag_type()
+
+
+Returns a str that describes the type of the flag.
+
+NOTE: we use strings, and not the types.*Type constants because
+our flags can have more exotic types, e.g., 'comma separated list
+of strings', 'whitespace separated list of strings', etc.
+
+parse
+
+
+parse(
+ argument
+)
+
+
+Parses string and sets flag value.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`argument`
+ |
+
+str or the correct flag value type, argument to be parsed.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+serialize
+
+
+serialize()
+
+
+Serializes the flag.
+
+
+unparse
+
+
+unparse()
+
+
+
+
+
+__eq__
+
+
+__eq__(
+ other
+)
+
+
+Return self==value.
+
+
+__ge__
+
+
+__ge__(
+ other, NotImplemented=NotImplemented
+)
+
+
+Return a >= b. Computed by @total_ordering from (not a < b).
+
+
+__gt__
+
+
+__gt__(
+ other, NotImplemented=NotImplemented
+)
+
+
+Return a > b. Computed by @total_ordering from (not a < b) and (a != b).
+
+
+__le__
+
+
+__le__(
+ other, NotImplemented=NotImplemented
+)
+
+
+Return a <= b. Computed by @total_ordering from (a < b) or (a == b).
+
+
+__lt__
+
+
+__lt__(
+ other
+)
+
+
+Return self
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.FlagNameConflictsWithMethodError
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raised when a flag name conflicts with FlagValues methods.
+
+Inherits From: [`Error`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/Error.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.FlagNameConflictsWithMethodError`
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/FlagValues.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/FlagValues.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..50975736452
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/FlagValues.md
@@ -0,0 +1,1104 @@
+description: Registry of 'Flag' objects.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.FlagValues
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Registry of 'Flag' objects.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.FlagValues`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.FlagValues()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A 'FlagValues' can then scan command line arguments, passing flag
+arguments through to the 'Flag' objects that it owns. It also
+provides easy access to the flag values. Typically only one
+'FlagValues' object is needed by an application: flags.FLAGS
+
+This class is heavily overloaded:
+
+'Flag' objects are registered via __setitem__:
+ FLAGS['longname'] = x # register a new flag
+
+The .value attribute of the registered 'Flag' objects can be accessed
+as attributes of this 'FlagValues' object, through __getattr__. Both
+the long and short name of the original 'Flag' objects can be used to
+access its value:
+ FLAGS.longname # parsed flag value
+ FLAGS.x # parsed flag value (short name)
+
+Command line arguments are scanned and passed to the registered 'Flag'
+objects through the __call__ method. Unparsed arguments, including
+argv[0] (e.g. the program name) are returned.
+ argv = FLAGS(sys.argv) # scan command line arguments
+
+The original registered Flag objects can be retrieved through the use
+of the dictionary-like operator, __getitem__:
+ x = FLAGS['longname'] # access the registered Flag object
+
+The str() operator of a 'FlagValues' object provides help for all of
+the registered 'Flag' objects.
+
+## Methods
+
+append_flag_values
+
+
+append_flag_values(
+ flag_values
+)
+
+
+Appends flags registered in another FlagValues instance.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`flag_values`
+ |
+
+FlagValues, the FlagValues instance from which to copy flags.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+append_flags_into_file
+
+
+append_flags_into_file(
+ filename
+)
+
+
+Appends all flags assignments from this FlagInfo object to a file.
+
+Output will be in the format of a flagfile.
+
+NOTE: MUST mirror the behavior of the C++ AppendFlagsIntoFile
+from https://github.com/gflags/gflags.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`filename`
+ |
+
+str, name of the file.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+find_module_defining_flag
+
+
+find_module_defining_flag(
+ flagname, default=None
+)
+
+
+Return the name of the module defining this flag, or default.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`flagname`
+ |
+
+str, name of the flag to lookup.
+ |
+
+|
+`default`
+ |
+
+Value to return if flagname is not defined. Defaults
+to None.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The name of the module which registered the flag with this name.
+If no such module exists (i.e. no flag with this name exists),
+we return default.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+find_module_id_defining_flag
+
+
+find_module_id_defining_flag(
+ flagname, default=None
+)
+
+
+Return the ID of the module defining this flag, or default.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`flagname`
+ |
+
+str, name of the flag to lookup.
+ |
+
+|
+`default`
+ |
+
+Value to return if flagname is not defined. Defaults
+to None.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The ID of the module which registered the flag with this name.
+If no such module exists (i.e. no flag with this name exists),
+we return default.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+flag_values_dict
+
+
+flag_values_dict()
+
+
+Returns a dictionary that maps flag names to flag values.
+
+
+flags_by_module_dict
+
+
+flags_by_module_dict()
+
+
+Returns the dictionary of module_name -> list of defined flags.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A dictionary. Its keys are module names (strings). Its values
+are lists of Flag objects.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+flags_by_module_id_dict
+
+
+flags_by_module_id_dict()
+
+
+Returns the dictionary of module_id -> list of defined flags.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A dictionary. Its keys are module IDs (ints). Its values
+are lists of Flag objects.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+flags_into_string
+
+
+flags_into_string()
+
+
+Returns a string with the flags assignments from this FlagValues object.
+
+This function ignores flags whose value is None. Each flag
+assignment is separated by a newline.
+
+NOTE: MUST mirror the behavior of the C++ CommandlineFlagsIntoString
+from https://github.com/gflags/gflags.
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+str, the string with the flags assignments from this FlagValues object.
+The flags are ordered by (module_name, flag_name).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_flag_value
+
+
+get_flag_value(
+ name, default
+)
+
+
+Returns the value of a flag (if not None) or a default value.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+str, the name of a flag.
+ |
+
+|
+`default`
+ |
+
+Default value to use if the flag value is None.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Requested flag value or default.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_help
+
+
+get_help(
+ prefix='', include_special_flags=(True)
+)
+
+
+Returns a help string for all known flags.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`prefix`
+ |
+
+str, per-line output prefix.
+ |
+
+|
+`include_special_flags`
+ |
+
+bool, whether to include description of
+SPECIAL_FLAGS, i.e. --flagfile and --undefok.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+str, formatted help message.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_key_flags_for_module
+
+
+get_key_flags_for_module(
+ module
+)
+
+
+Returns the list of key flags for a module.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`module`
+ |
+
+module|str, the module to get key flags from.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+[Flag], a new list of Flag instances. Caller may update this list as
+ |
+
+
+|
+`desired`
+ |
+
+none of those changes will affect the internals of this
+FlagValue instance.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+is_gnu_getopt
+
+
+is_gnu_getopt()
+
+
+
+
+
+is_parsed
+
+
+is_parsed()
+
+
+Returns whether flags were parsed.
+
+
+key_flags_by_module_dict
+
+
+key_flags_by_module_dict()
+
+
+Returns the dictionary of module_name -> list of key flags.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A dictionary. Its keys are module names (strings). Its values
+are lists of Flag objects.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+main_module_help
+
+
+main_module_help()
+
+
+Describes the key flags of the main module.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+str, describing the key flags of the main module.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+mark_as_parsed
+
+
+mark_as_parsed()
+
+
+Explicitly marks flags as parsed.
+
+Use this when the caller knows that this FlagValues has been parsed as if
+a __call__() invocation has happened. This is only a public method for
+use by things like appcommands which do additional command like parsing.
+
+module_help
+
+
+module_help(
+ module
+)
+
+
+Describes the key flags of a module.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`module`
+ |
+
+module|str, the module to describe the key flags for.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+str, describing the key flags of a module.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+read_flags_from_files
+
+
+read_flags_from_files(
+ argv, force_gnu=(True)
+)
+
+
+Processes command line args, but also allow args to be read from file.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`argv`
+ |
+
+[str], a list of strings, usually sys.argv[1:], which may contain
+one or more flagfile directives of the form --flagfile="./filename".
+Note that the name of the program (sys.argv[0]) should be omitted.
+ |
+
+|
+`force_gnu`
+ |
+
+bool, if False, --flagfile parsing obeys the
+FLAGS.is_gnu_getopt() value. If True, ignore the value and always
+follow gnu_getopt semantics.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A new list which has the original list combined with what we read
+from any flagfile(s).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`IllegalFlagValueError`
+ |
+
+Raised when --flagfile is provided with no
+argument.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+This function is called by FLAGS(argv).
+It scans the input list for a flag that looks like:
+--flagfile=. Then it opens , reads all valid key
+and value pairs and inserts them into the input list in exactly the
+place where the --flagfile arg is found.
+
+Note that your application's flags are still defined the usual way
+using absl.flags DEFINE_flag() type functions.
+
+Notes (assuming we're getting a commandline of some sort as our input):
+--> For duplicate flags, the last one we hit should "win".
+--> Since flags that appear later win, a flagfile's settings can be "weak"
+ if the --flagfile comes at the beginning of the argument sequence,
+ and it can be "strong" if the --flagfile comes at the end.
+--> A further "--flagfile=" CAN be nested in a flagfile.
+ It will be expanded in exactly the spot where it is found.
+--> In a flagfile, a line beginning with # or // is a comment.
+--> Entirely blank lines _should_ be ignored.
+
+register_flag_by_module
+
+
+register_flag_by_module(
+ module_name, flag
+)
+
+
+Records the module that defines a specific flag.
+
+We keep track of which flag is defined by which module so that we
+can later sort the flags by module.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`module_name`
+ |
+
+str, the name of a Python module.
+ |
+
+|
+`flag`
+ |
+
+Flag, the Flag instance that is key to the module.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+register_flag_by_module_id
+
+
+register_flag_by_module_id(
+ module_id, flag
+)
+
+
+Records the module that defines a specific flag.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`module_id`
+ |
+
+int, the ID of the Python module.
+ |
+
+|
+`flag`
+ |
+
+Flag, the Flag instance that is key to the module.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+register_key_flag_for_module
+
+
+register_key_flag_for_module(
+ module_name, flag
+)
+
+
+Specifies that a flag is a key flag for a module.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`module_name`
+ |
+
+str, the name of a Python module.
+ |
+
+|
+`flag`
+ |
+
+Flag, the Flag instance that is key to the module.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+remove_flag_values
+
+
+remove_flag_values(
+ flag_values
+)
+
+
+Remove flags that were previously appended from another FlagValues.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`flag_values`
+ |
+
+FlagValues, the FlagValues instance containing flags to
+remove.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+set_default
+
+
+set_default(
+ name, value
+)
+
+
+Changes the default value of the named flag object.
+
+The flag's current value is also updated if the flag is currently using
+the default value, i.e. not specified in the command line, and not set
+by FLAGS.name = value.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+str, the name of the flag to modify.
+ |
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+The new default value.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`UnrecognizedFlagError`
+ |
+
+Raised when there is no registered flag named name.
+ |
+
+|
+`IllegalFlagValueError`
+ |
+
+Raised when value is not valid.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+set_gnu_getopt
+
+
+set_gnu_getopt(
+ gnu_getopt=(True)
+)
+
+
+Sets whether or not to use GNU style scanning.
+
+GNU style allows mixing of flag and non-flag arguments. See
+http://docs.python.org/library/getopt.html#getopt.gnu_getopt
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`gnu_getopt`
+ |
+
+bool, whether or not to use GNU style scanning.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+unparse_flags
+
+
+unparse_flags()
+
+
+Unparses all flags to the point before any FLAGS(argv) was called.
+
+
+
+
+
+write_help_in_xml_format(
+ outfile=None
+)
+
+
+Outputs flag documentation in XML format.
+
+NOTE: We use element names that are consistent with those used by
+the C++ command-line flag library, from
+https://github.com/gflags/gflags.
+We also use a few new elements (e.g., ), but we do not
+interfere / overlap with existing XML elements used by the C++
+library. Please maintain this consistency.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`outfile`
+ |
+
+File object we write to. Default None means sys.stdout.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+__call__
+
+
+__call__(
+ argv, known_only=(False)
+)
+
+
+Parses flags from argv; stores parsed flags into this FlagValues object.
+
+All unparsed arguments are returned.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`argv`
+ |
+
+a tuple/list of strings.
+ |
+
+|
+`known_only`
+ |
+
+bool, if True, parse and remove known flags; return the rest
+untouched. Unknown flags specified by --undefok are not returned.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The list of arguments not parsed as options, including argv[0].
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`Error`
+ |
+
+Raised on any parsing error.
+ |
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+Raised on passing wrong type of arguments.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+Raised on flag value parsing error.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+__contains__
+
+
+__contains__(
+ name
+)
+
+
+Returns True if name is a value (flag) in the dict.
+
+
+__getitem__
+
+
+__getitem__(
+ name
+)
+
+
+Returns the Flag object for the flag --name.
+
+
+__iter__
+
+
+__iter__()
+
+
+
+
+
+__len__
+
+
+__len__()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/FloatParser.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/FloatParser.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..b8a8a276865
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/FloatParser.md
@@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
+description: Parser of floating point values.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.FloatParser
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Parser of floating point values.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.FloatParser`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.FloatParser(
+ lower_bound=None, upper_bound=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Parsed value may be bounded to a given upper and lower bound.
+
+## Methods
+
+convert
+
+
+convert(
+ argument
+)
+
+
+Returns the float value of argument.
+
+
+flag_type
+
+
+flag_type()
+
+
+See base class.
+
+
+is_outside_bounds
+
+
+is_outside_bounds(
+ val
+)
+
+
+Returns whether the value is outside the bounds or not.
+
+
+parse
+
+
+parse(
+ argument
+)
+
+
+See base class.
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `number_article = 'a'`
+* `number_name = 'number'`
+* `syntactic_help = 'a number'`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/IllegalFlagValueError.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/IllegalFlagValueError.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e5dbc965298
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/IllegalFlagValueError.md
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
+description: Raised when the flag command line argument is illegal.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.IllegalFlagValueError
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raised when the flag command line argument is illegal.
+
+Inherits From: [`Error`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/Error.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.IllegalFlagValueError`
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/IntegerParser.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/IntegerParser.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..dcd249260c8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/IntegerParser.md
@@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
+description: Parser of an integer value.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.IntegerParser
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Parser of an integer value.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.IntegerParser`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.IntegerParser(
+ lower_bound=None, upper_bound=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Parsed value may be bounded to a given upper and lower bound.
+
+## Methods
+
+convert
+
+
+convert(
+ argument
+)
+
+
+Returns the int value of argument.
+
+
+flag_type
+
+
+flag_type()
+
+
+See base class.
+
+
+is_outside_bounds
+
+
+is_outside_bounds(
+ val
+)
+
+
+Returns whether the value is outside the bounds or not.
+
+
+parse
+
+
+parse(
+ argument
+)
+
+
+See base class.
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `number_article = 'an'`
+* `number_name = 'integer'`
+* `syntactic_help = 'an integer'`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/ListParser.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/ListParser.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e707e07ba85
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/ListParser.md
@@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
+description: Parser for a comma-separated list of strings.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.ListParser
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Parser for a comma-separated list of strings.
+
+Inherits From: [`BaseListParser`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/BaseListParser.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.ListParser`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.ListParser()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+flag_type
+
+
+flag_type()
+
+
+See base class.
+
+
+parse
+
+
+parse(
+ argument
+)
+
+
+Parses argument as comma-separated list of strings.
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `syntactic_help = ''`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/ListSerializer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/ListSerializer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..0930fb36a6d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/ListSerializer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+description: Base class for generating string representations of a flag value.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.ListSerializer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Base class for generating string representations of a flag value.
+
+Inherits From: [`ArgumentSerializer`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/ArgumentSerializer.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.ListSerializer`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.ListSerializer(
+ list_sep
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+serialize
+
+
+serialize(
+ value
+)
+
+
+See base class.
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/MultiEnumClassFlag.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/MultiEnumClassFlag.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..d35a9ea30dd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/MultiEnumClassFlag.md
@@ -0,0 +1,191 @@
+description: A multi_enum_class flag.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.MultiEnumClassFlag
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A multi_enum_class flag.
+
+Inherits From: [`MultiFlag`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/MultiFlag.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.MultiEnumClassFlag`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.MultiEnumClassFlag(
+ name, default, help_string, enum_class, **args
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+See the __doc__ for MultiFlag for most behaviors of this class. In addition,
+this class knows how to handle enum.Enum instances as values for this flag
+type.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+flag_type
+
+
+flag_type()
+
+
+See base class.
+
+
+parse
+
+
+parse(
+ arguments
+)
+
+
+Parses one or more arguments with the installed parser.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`arguments`
+ |
+
+a single argument or a list of arguments (typically a
+list of default values); a single argument is converted
+internally into a list containing one item.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+serialize
+
+
+serialize()
+
+
+Serializes the flag.
+
+
+unparse
+
+
+unparse()
+
+
+
+
+
+__eq__
+
+
+__eq__(
+ other
+)
+
+
+Return self==value.
+
+
+__ge__
+
+
+__ge__(
+ other, NotImplemented=NotImplemented
+)
+
+
+Return a >= b. Computed by @total_ordering from (not a < b).
+
+
+__gt__
+
+
+__gt__(
+ other, NotImplemented=NotImplemented
+)
+
+
+Return a > b. Computed by @total_ordering from (not a < b) and (a != b).
+
+
+__le__
+
+
+__le__(
+ other, NotImplemented=NotImplemented
+)
+
+
+Return a <= b. Computed by @total_ordering from (a < b) or (a == b).
+
+
+__lt__
+
+
+__lt__(
+ other
+)
+
+
+Return self
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.MultiFlag
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A flag that can appear multiple time on the command-line.
+
+Inherits From: [`Flag`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/Flag.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.MultiFlag`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.MultiFlag(
+ *args, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The value of such a flag is a list that contains the individual values
+from all the appearances of that flag on the command-line.
+
+See the __doc__ for Flag for most behavior of this class. Only
+differences in behavior are described here:
+
+ * The default value may be either a single value or an iterable of values.
+ A single value is transformed into a single-item list of that value.
+
+ * The value of the flag is always a list, even if the option was
+ only supplied once, and even if the default value is a single
+ value
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+flag_type
+
+
+flag_type()
+
+
+See base class.
+
+
+parse
+
+
+parse(
+ arguments
+)
+
+
+Parses one or more arguments with the installed parser.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`arguments`
+ |
+
+a single argument or a list of arguments (typically a
+list of default values); a single argument is converted
+internally into a list containing one item.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+serialize
+
+
+serialize()
+
+
+Serializes the flag.
+
+
+unparse
+
+
+unparse()
+
+
+
+
+
+__eq__
+
+
+__eq__(
+ other
+)
+
+
+Return self==value.
+
+
+__ge__
+
+
+__ge__(
+ other, NotImplemented=NotImplemented
+)
+
+
+Return a >= b. Computed by @total_ordering from (not a < b).
+
+
+__gt__
+
+
+__gt__(
+ other, NotImplemented=NotImplemented
+)
+
+
+Return a > b. Computed by @total_ordering from (not a < b) and (a != b).
+
+
+__le__
+
+
+__le__(
+ other, NotImplemented=NotImplemented
+)
+
+
+Return a <= b. Computed by @total_ordering from (a < b) or (a == b).
+
+
+__lt__
+
+
+__lt__(
+ other
+)
+
+
+Return self
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.UnparsedFlagAccessError
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raised when accessing the flag value from unparsed FlagValues.
+
+Inherits From: [`Error`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/Error.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.UnparsedFlagAccessError`
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/UnrecognizedFlagError.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/UnrecognizedFlagError.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..bc7fe6c1809
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/UnrecognizedFlagError.md
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
+description: Raised when a flag is unrecognized.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.UnrecognizedFlagError
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raised when a flag is unrecognized.
+
+Inherits From: [`Error`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/Error.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.UnrecognizedFlagError`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.UnrecognizedFlagError(
+ flagname, flagvalue='', suggestions=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`flagname`
+ |
+
+str, the name of the unrecognized flag.
+ |
+
+|
+`flagvalue`
+ |
+
+The value of the flag, empty if the flag is not defined.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/ValidationError.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/ValidationError.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..c5d452c4cfa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/ValidationError.md
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
+description: Raised when flag validator constraint is not satisfied.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.ValidationError
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raised when flag validator constraint is not satisfied.
+
+Inherits From: [`Error`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/Error.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.ValidationError`
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/WhitespaceSeparatedListParser.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/WhitespaceSeparatedListParser.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..0bb4db23c02
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/WhitespaceSeparatedListParser.md
@@ -0,0 +1,125 @@
+description: Parser for a whitespace-separated list of strings.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.WhitespaceSeparatedListParser
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Parser for a whitespace-separated list of strings.
+
+Inherits From: [`BaseListParser`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/BaseListParser.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.WhitespaceSeparatedListParser`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.WhitespaceSeparatedListParser(
+ comma_compat=(False)
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`comma_compat`
+ |
+
+bool, whether to support comma as an additional separator.
+If False then only whitespace is supported. This is intended only for
+backwards compatibility with flags that used to be comma-separated.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+flag_type
+
+
+flag_type()
+
+
+See base class.
+
+
+parse
+
+
+parse(
+ argument
+)
+
+
+Parses argument as whitespace-separated list of strings.
+
+It also parses argument as comma-separated list of strings if requested.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`argument`
+ |
+
+string argument passed in the commandline.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+[str], the parsed flag value.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `syntactic_help = ''`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/adopt_module_key_flags.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/adopt_module_key_flags.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..b8a81a12a8f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/adopt_module_key_flags.md
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
+description: Declares that all flags key to a module are key to the current module.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.adopt_module_key_flags
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Declares that all flags key to a module are key to the current module.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.adopt_module_key_flags`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.adopt_module_key_flags(
+ module, flag_values=_flagvalues.FLAGS
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`module`
+ |
+
+module, the module object from which all key flags will be declared
+as key flags to the current module.
+ |
+
+|
+`flag_values`
+ |
+
+FlagValues, the FlagValues instance in which the flags will
+be declared as key flags. This should almost never need to be
+overridden.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`Error`
+ |
+
+Raised when given an argument that is a module name (a string),
+instead of a module object.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/declare_key_flag.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/declare_key_flag.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..100c8d2d883
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/declare_key_flag.md
@@ -0,0 +1,96 @@
+description: Declares one flag as key to the current module.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.declare_key_flag
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Declares one flag as key to the current module.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.declare_key_flag`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.declare_key_flag(
+ flag_name, flag_values=_flagvalues.FLAGS
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Key flags are flags that are deemed really important for a module.
+They are important when listing help messages; e.g., if the
+--helpshort command-line flag is used, then only the key flags of the
+main module are listed (instead of all flags, as in the case of
+--helpfull).
+
+#### Sample usage:
+
+
+flags.declare_key_flag('flag_1')
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`flag_name`
+ |
+
+str, the name of an already declared flag.
+(Redeclaring flags as key, including flags implicitly key
+because they were declared in this module, is a no-op.)
+ |
+
+|
+`flag_values`
+ |
+
+FlagValues, the FlagValues instance in which the flag will
+be declared as a key flag. This should almost never need to be
+overridden.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+Raised if flag_name not defined as a Python flag.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/disclaim_key_flags.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/disclaim_key_flags.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..686c67799af
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/disclaim_key_flags.md
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
+description: Declares that the current module will not define any more key flags.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.disclaim_key_flags
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Declares that the current module will not define any more key flags.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.disclaim_key_flags`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.disclaim_key_flags()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Normally, the module that calls the DEFINE_xxx functions claims the
+flag to be its key flag. This is undesirable for modules that
+define additional DEFINE_yyy functions with its own flag parsers and
+serializers, since that module will accidentally claim flags defined
+by DEFINE_yyy as its key flags. After calling this function, the
+module disclaims flag definitions thereafter, so the key flags will
+be correctly attributed to the caller of DEFINE_yyy.
+
+After calling this function, the module will not be able to define
+any more flags. This function will affect all FlagValues objects.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/doc_to_help.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/doc_to_help.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..73a705ec187
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/doc_to_help.md
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
+description: Takes a __doc__ string and reformats it as help.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.doc_to_help
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Takes a __doc__ string and reformats it as help.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.doc_to_help`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.doc_to_help(
+ doc
+)
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/flag_dict_to_args.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/flag_dict_to_args.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e0695e9d6a5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/flag_dict_to_args.md
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
+description: Convert a dict of values into process call parameters.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.flag_dict_to_args
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Convert a dict of values into process call parameters.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.flag_dict_to_args`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.flag_dict_to_args(
+ flag_map
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This method is used to convert a dictionary into a sequence of parameters
+for a binary that parses arguments using this module.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`flag_map`
+ |
+
+dict, a mapping where the keys are flag names (strings).
+values are treated according to their type:
+* If value is None, then only the name is emitted.
+* If value is True, then only the name is emitted.
+* If value is False, then only the name prepended with 'no' is emitted.
+* If value is a string then --name=value is emitted.
+* If value is a collection, this will emit --name=value1,value2,value3.
+* Everything else is converted to string an passed as such.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Yields:
+
+sequence of string suitable for a subprocess execution.
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/get_help_width.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/get_help_width.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..6ced1791f9c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/get_help_width.md
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
+description: Returns the integer width of help lines that is used in TextWrap.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.get_help_width
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns the integer width of help lines that is used in TextWrap.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.get_help_width`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.get_help_width()
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/mark_bool_flags_as_mutual_exclusive.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/mark_bool_flags_as_mutual_exclusive.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..c891074ecf6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/mark_bool_flags_as_mutual_exclusive.md
@@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
+description: Ensures that only one flag among flag_names is True.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.mark_bool_flags_as_mutual_exclusive
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Ensures that only one flag among flag_names is True.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.mark_bool_flags_as_mutual_exclusive`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.mark_bool_flags_as_mutual_exclusive(
+ flag_names, required=(False), flag_values=_flagvalues.FLAGS
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`flag_names`
+ |
+
+[str], names of the flags.
+ |
+
+|
+`required`
+ |
+
+bool. If true, exactly one flag must be True. Otherwise, at most
+one flag can be True, and it is valid for all flags to be False.
+ |
+
+|
+`flag_values`
+ |
+
+flags.FlagValues, optional FlagValues instance where the flags
+are defined.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/mark_flag_as_required.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/mark_flag_as_required.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..11f159d088e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/mark_flag_as_required.md
@@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
+description: Ensures that flag is not None during program execution.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.mark_flag_as_required
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Ensures that flag is not None during program execution.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.mark_flag_as_required`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.mark_flag_as_required(
+ flag_name, flag_values=_flagvalues.FLAGS
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Registers a flag validator, which will follow usual validator rules.
+Important note: validator will pass for any non-None value, such as False,
+0 (zero), '' (empty string) and so on.
+
+It is recommended to call this method like this:
+
+ if __name__ == '__main__':
+ flags.mark_flag_as_required('your_flag_name')
+ app.run()
+
+Because validation happens at app.run() we want to ensure required-ness
+is enforced at that time. You generally do not want to force users who import
+your code to have additional required flags for their own binaries or tests.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`flag_name`
+ |
+
+str, name of the flag
+ |
+
+|
+`flag_values`
+ |
+
+flags.FlagValues, optional FlagValues instance where the flag
+is defined.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`AttributeError`
+ |
+
+Raised when flag_name is not registered as a valid flag
+name.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/mark_flags_as_mutual_exclusive.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/mark_flags_as_mutual_exclusive.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..ebad5b32411
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/mark_flags_as_mutual_exclusive.md
@@ -0,0 +1,78 @@
+description: Ensures that only one flag among flag_names is not None.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.mark_flags_as_mutual_exclusive
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Ensures that only one flag among flag_names is not None.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.mark_flags_as_mutual_exclusive`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.mark_flags_as_mutual_exclusive(
+ flag_names, required=(False), flag_values=_flagvalues.FLAGS
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Important note: This validator checks if flag values are None, and it does not
+distinguish between default and explicit values. Therefore, this validator
+does not make sense when applied to flags with default values other than None,
+including other false values (e.g. False, 0, '', []). That includes multi
+flags with a default value of [] instead of None.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`flag_names`
+ |
+
+[str], names of the flags.
+ |
+
+|
+`required`
+ |
+
+bool. If true, exactly one of the flags must have a value other
+than None. Otherwise, at most one of the flags can have a value other
+than None, and it is valid for all of the flags to be None.
+ |
+
+|
+`flag_values`
+ |
+
+flags.FlagValues, optional FlagValues instance where the flags
+are defined.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/mark_flags_as_required.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/mark_flags_as_required.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..9ea4f5d4302
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/mark_flags_as_required.md
@@ -0,0 +1,90 @@
+description: Ensures that flags are not None during program execution.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.mark_flags_as_required
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Ensures that flags are not None during program execution.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.mark_flags_as_required`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.mark_flags_as_required(
+ flag_names, flag_values=_flagvalues.FLAGS
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Recommended usage:
+
+
+if __name__ == '__main__':
+ flags.mark_flags_as_required(['flag1', 'flag2', 'flag3'])
+ app.run()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`flag_names`
+ |
+
+Sequence[str], names of the flags.
+ |
+
+|
+`flag_values`
+ |
+
+flags.FlagValues, optional FlagValues instance where the flags
+are defined.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`AttributeError`
+ |
+
+If any of flag name has not already been defined as a flag.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/multi_flags_validator.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/multi_flags_validator.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..58bf31c4f7e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/multi_flags_validator.md
@@ -0,0 +1,112 @@
+description: A function decorator for defining a multi-flag validator.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.multi_flags_validator
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A function decorator for defining a multi-flag validator.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.multi_flags_validator`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.multi_flags_validator(
+ flag_names, message='Flag validation failed', flag_values=_flagvalues.FLAGS
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Registers the decorated function as a validator for flag_names, e.g.
+
+@flags.multi_flags_validator(['foo', 'bar'])
+def _CheckFooBar(flags_dict):
+ ...
+
+See register_multi_flags_validator() for the specification of checker
+function.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`flag_names`
+ |
+
+[str], a list of the flag names to be checked.
+ |
+
+|
+`message`
+ |
+
+str, error text to be shown to the user if checker returns False.
+If checker raises flags.ValidationError, message from the raised
+error will be shown.
+ |
+
+|
+`flag_values`
+ |
+
+flags.FlagValues, optional FlagValues instance to validate
+against.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A function decorator that registers its function argument as a validator.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`AttributeError`
+ |
+
+Raised when a flag is not registered as a valid flag name.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/register_multi_flags_validator.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/register_multi_flags_validator.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3a783bc9cc3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/register_multi_flags_validator.md
@@ -0,0 +1,105 @@
+description: Adds a constraint to multiple flags.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.register_multi_flags_validator
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Adds a constraint to multiple flags.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.register_multi_flags_validator`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.register_multi_flags_validator(
+ flag_names, multi_flags_checker, message='Flags validation failed',
+ flag_values=_flagvalues.FLAGS
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The constraint is validated when flags are initially parsed, and after each
+change of the corresponding flag's value.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`flag_names`
+ |
+
+[str], a list of the flag names to be checked.
+ |
+
+|
+`multi_flags_checker`
+ |
+
+callable, a function to validate the flag.
+input - dict, with keys() being flag_names, and value for each key
+being the value of the corresponding flag (string, boolean, etc).
+output - bool, True if validator constraint is satisfied.
+If constraint is not satisfied, it should either return False or
+raise flags.ValidationError.
+ |
+
+|
+`message`
+ |
+
+str, error text to be shown to the user if checker returns False.
+If checker raises flags.ValidationError, message from the raised
+error will be shown.
+ |
+
+|
+`flag_values`
+ |
+
+flags.FlagValues, optional FlagValues instance to validate
+against.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`AttributeError`
+ |
+
+Raised when a flag is not registered as a valid flag name.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/register_validator.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/register_validator.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..d71ffa5fee0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/register_validator.md
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+description: Adds a constraint, which will be enforced during program execution.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.register_validator
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Adds a constraint, which will be enforced during program execution.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.register_validator`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.register_validator(
+ flag_name, checker, message='Flag validation failed',
+ flag_values=_flagvalues.FLAGS
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The constraint is validated when flags are initially parsed, and after each
+change of the corresponding flag's value.
+Args:
+ flag_name: str, name of the flag to be checked.
+ checker: callable, a function to validate the flag.
+ input - A single positional argument: The value of the corresponding
+ flag (string, boolean, etc. This value will be passed to checker
+ by the library).
+ output - bool, True if validator constraint is satisfied.
+ If constraint is not satisfied, it should either return False or
+ raise flags.ValidationError(desired_error_message).
+ message: str, error text to be shown to the user if checker returns False.
+ If checker raises flags.ValidationError, message from the raised
+ error will be shown.
+ flag_values: flags.FlagValues, optional FlagValues instance to validate
+ against.
+Raises:
+ AttributeError: Raised when flag_name is not registered as a valid flag
+ name.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/text_wrap.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/text_wrap.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..839de4bddeb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/text_wrap.md
@@ -0,0 +1,111 @@
+description: Wraps a given text to a maximum line length and returns it.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.text_wrap
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Wraps a given text to a maximum line length and returns it.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.text_wrap`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.text_wrap(
+ text, length=None, indent='', firstline_indent=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+It turns lines that only contain whitespace into empty lines, keeps new lines,
+and expands tabs using 4 spaces.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`text`
+ |
+
+str, text to wrap.
+ |
+
+|
+`length`
+ |
+
+int, maximum length of a line, includes indentation.
+If this is None then use get_help_width()
+ |
+
+|
+`indent`
+ |
+
+str, indent for all but first line.
+ |
+
+|
+`firstline_indent`
+ |
+
+str, indent for first line; if None, fall back to indent.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+str, the wrapped text.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+Raised if indent or firstline_indent not shorter than length.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..b513867ed62
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator.md
@@ -0,0 +1,97 @@
+description: Base TFDecorator class and utility functions for working with decorators.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.flags.tf_decorator
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Base TFDecorator class and utility functions for working with decorators.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.tf_decorator`
+
+
+
+
+There are two ways to create decorators that TensorFlow can introspect into.
+This is important for documentation generation purposes, so that function
+signatures aren't obscured by the (*args, **kwds) signature that decorators
+often provide.
+
+1. Call `tf_decorator.make_decorator` on your wrapper function. If your
+decorator is stateless, or can capture all of the variables it needs to work
+with through lexical closure, this is the simplest option. Create your wrapper
+function as usual, but instead of returning it, return
+`tf_decorator.make_decorator(target, your_wrapper)`. This will attach some
+decorator introspection metadata onto your wrapper and return it.
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+def print_hello_before_calling(target):
+ def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
+ print('hello')
+ return target(*args, **kwargs)
+ return tf_decorator.make_decorator(target, wrapper)
+
+
+2. Derive from TFDecorator. If your decorator needs to be stateful, you can
+implement it in terms of a TFDecorator. Store whatever state you need in your
+derived class, and implement the `__call__` method to do your work before
+calling into your target. You can retrieve the target via
+`super(MyDecoratorClass, self).decorated_target`, and call it with whatever
+parameters it needs.
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+class CallCounter(tf_decorator.TFDecorator):
+ def __init__(self, target):
+ super(CallCounter, self).__init__('count_calls', target)
+ self.call_count = 0
+
+ def __call__(self, *args, **kwargs):
+ self.call_count += 1
+ return super(CallCounter, self).decorated_target(*args, **kwargs)
+
+def count_calls(target):
+ return CallCounter(target)
+
+
+## Modules
+
+[`tf_stack`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/tf_stack.md) module: Functions used to extract and analyze stacks. Faster than Python libs.
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class TFDecorator`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/TFDecorator.md): Base class for all TensorFlow decorators.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`make_decorator(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/make_decorator.md): Make a decorator from a wrapper and a target.
+
+[`rewrap(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/rewrap.md): Injects a new target into a function built by make_decorator.
+
+[`unwrap(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/unwrap.md): Unwraps an object into a list of TFDecorators and a final target.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/TFDecorator.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/TFDecorator.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..9706946731c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/TFDecorator.md
@@ -0,0 +1,107 @@
+description: Base class for all TensorFlow decorators.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.tf_decorator.TFDecorator
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Base class for all TensorFlow decorators.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.tf_decorator.TFDecorator`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.tf_decorator.TFDecorator(
+ decorator_name, target, decorator_doc='', decorator_argspec=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+TFDecorator captures and exposes the wrapped target, and provides details
+about the current decorator.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`decorated_target`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`decorator_argspec`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`decorator_doc`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`decorator_name`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+__call__
+
+View source
+
+
+__call__(
+ *args, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+Call self as a function.
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/make_decorator.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/make_decorator.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..46a883095c4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/make_decorator.md
@@ -0,0 +1,106 @@
+description: Make a decorator from a wrapper and a target.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.tf_decorator.make_decorator
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Make a decorator from a wrapper and a target.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.tf_decorator.make_decorator`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.tf_decorator.make_decorator(
+ target, decorator_func, decorator_name=None, decorator_doc='',
+ decorator_argspec=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`target`
+ |
+
+The final callable to be wrapped.
+ |
+
+|
+`decorator_func`
+ |
+
+The wrapper function.
+ |
+
+|
+`decorator_name`
+ |
+
+The name of the decorator. If `None`, the name of the
+function calling make_decorator.
+ |
+
+|
+`decorator_doc`
+ |
+
+Documentation specific to this application of
+`decorator_func` to `target`.
+ |
+
+|
+`decorator_argspec`
+ |
+
+The new callable signature of this decorator.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The `decorator_func` argument with new metadata attached.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/rewrap.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/rewrap.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..2209bc00e18
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/rewrap.md
@@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
+description: Injects a new target into a function built by make_decorator.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.tf_decorator.rewrap
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Injects a new target into a function built by make_decorator.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.tf_decorator.rewrap`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.tf_decorator.rewrap(
+ decorator_func, previous_target, new_target
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This function allows replacing a function wrapped by `decorator_func`,
+assuming the decorator that wraps the function is written as described below.
+
+The decorator function must use `.__wrapped__` instead of the
+wrapped function that is normally used:
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+# Instead of this:
+def simple_parametrized_wrapper(*args, **kwds):
+ return wrapped_fn(*args, **kwds)
+
+tf_decorator.make_decorator(simple_parametrized_wrapper, wrapped_fn)
+
+# Write this:
+def simple_parametrized_wrapper(*args, **kwds):
+ return simple_parametrized_wrapper.__wrapped__(*args, **kwds)
+
+tf_decorator.make_decorator(simple_parametrized_wrapper, wrapped_fn)
+
+
+Note that this process modifies decorator_func.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`decorator_func`
+ |
+
+Callable returned by `wrap`.
+ |
+
+|
+`previous_target`
+ |
+
+Callable that needs to be replaced.
+ |
+
+|
+`new_target`
+ |
+
+Callable to replace previous_target with.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The updated decorator. If decorator_func is not a tf_decorator, new_target
+is returned.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/tf_stack.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/tf_stack.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..cd036fe6c31
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/tf_stack.md
@@ -0,0 +1,55 @@
+description: Functions used to extract and analyze stacks. Faster than Python libs.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.flags.tf_decorator.tf_stack
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Functions used to extract and analyze stacks. Faster than Python libs.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.tf_decorator.tf_stack`
+
+
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class CurrentModuleFilter`](../../../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/tf_stack/CurrentModuleFilter.md): Filters stack frames from the module where this is used (best effort).
+
+[`class FrameSummary`](../../../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/tf_stack/FrameSummary.md)
+
+[`class StackSummary`](../../../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/tf_stack/StackSummary.md)
+
+[`class StackTraceFilter`](../../../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/tf_stack/StackTraceFilter.md): Allows filtering traceback information by removing superfluous frames.
+
+[`class StackTraceMapper`](../../../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/tf_stack/StackTraceMapper.md): Allows remapping traceback information to different source code.
+
+[`class StackTraceTransform`](../../../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/tf_stack/StackTraceTransform.md): Base class for stack trace transformation functions.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`extract_stack(...)`](../../../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/tf_stack/extract_stack.md): A lightweight, extensible re-implementation of traceback.extract_stack.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/tf_stack/CurrentModuleFilter.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/tf_stack/CurrentModuleFilter.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..bdebf1974a5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/tf_stack/CurrentModuleFilter.md
@@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
+description: Filters stack frames from the module where this is used (best effort).
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.tf_decorator.tf_stack.CurrentModuleFilter
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Filters stack frames from the module where this is used (best effort).
+
+Inherits From: [`StackTraceFilter`](../../../../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/tf_stack/StackTraceFilter.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.tf_decorator.tf_stack.CurrentModuleFilter`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.tf_decorator.tf_stack.CurrentModuleFilter()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+get_filtered_filenames
+
+View source
+
+
+get_filtered_filenames()
+
+
+
+
+
+reset
+
+View source
+
+
+reset()
+
+
+
+
+
+__enter__
+
+View source
+
+
+__enter__()
+
+
+
+
+
+__exit__
+
+View source
+
+
+__exit__(
+ unused_type, unused_value, unused_traceback
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/tf_stack/FrameSummary.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/tf_stack/FrameSummary.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..f7d9c192e31
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/tf_stack/FrameSummary.md
@@ -0,0 +1,140 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.tf_decorator.tf_stack.FrameSummary
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.tf_decorator.tf_stack.FrameSummary`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.tf_decorator.tf_stack.FrameSummary(
+ *args, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`filename`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`line`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`lineno`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+__eq__
+
+
+__eq__()
+
+
+__eq__(self: tensorflow.python._tf_stack.FrameSummary, arg0: tensorflow.python._tf_stack.FrameSummary) -> bool
+
+
+__getitem__
+
+
+__getitem__()
+
+
+__getitem__(self: tensorflow.python._tf_stack.FrameSummary, arg0: object) -> object
+
+
+__iter__
+
+
+__iter__()
+
+
+__iter__(self: tensorflow.python._tf_stack.FrameSummary) -> iterator
+
+
+__len__
+
+
+__len__()
+
+
+__len__(self: tensorflow.python._tf_stack.FrameSummary) -> int
+
+
+__ne__
+
+
+__ne__()
+
+
+__ne__(self: tensorflow.python._tf_stack.FrameSummary, arg0: tensorflow.python._tf_stack.FrameSummary) -> bool
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/tf_stack/StackSummary.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/tf_stack/StackSummary.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..89af27ec374
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/tf_stack/StackSummary.md
@@ -0,0 +1,208 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.tf_decorator.tf_stack.StackSummary
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.tf_decorator.tf_stack.StackSummary`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.tf_decorator.tf_stack.StackSummary()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+append
+
+
+append()
+
+
+append(self: tensorflow.python._tf_stack.StackSummary, x: tensorflow.python._tf_stack.FrameSummary) -> None
+
+Add an item to the end of the list
+
+count
+
+
+count()
+
+
+count(self: tensorflow.python._tf_stack.StackSummary, x: tensorflow.python._tf_stack.FrameSummary) -> int
+
+Return the number of times ``x`` appears in the list
+
+extend
+
+
+extend()
+
+
+extend(*args, **kwargs)
+Overloaded function.
+
+1. extend(self: tensorflow.python._tf_stack.StackSummary, L: tensorflow.python._tf_stack.StackSummary) -> None
+
+Extend the list by appending all the items in the given list
+
+2. extend(self: tensorflow.python._tf_stack.StackSummary, L: iterable) -> None
+
+Extend the list by appending all the items in the given list
+
+insert
+
+
+insert()
+
+
+insert(self: tensorflow.python._tf_stack.StackSummary, i: int, x: tensorflow.python._tf_stack.FrameSummary) -> None
+
+Insert an item at a given position.
+
+pop
+
+
+pop()
+
+
+pop(*args, **kwargs)
+Overloaded function.
+
+1. pop(self: tensorflow.python._tf_stack.StackSummary) -> tensorflow.python._tf_stack.FrameSummary
+
+Remove and return the last item
+
+2. pop(self: tensorflow.python._tf_stack.StackSummary, i: int) -> tensorflow.python._tf_stack.FrameSummary
+
+Remove and return the item at index ``i``
+
+remove
+
+
+remove()
+
+
+remove(self: tensorflow.python._tf_stack.StackSummary, x: tensorflow.python._tf_stack.FrameSummary) -> None
+
+Remove the first item from the list whose value is x. It is an error if there is no such item.
+
+__bool__
+
+
+__bool__()
+
+
+__bool__(self: tensorflow.python._tf_stack.StackSummary) -> bool
+
+Check whether the list is nonempty
+
+__contains__
+
+
+__contains__()
+
+
+__contains__(self: tensorflow.python._tf_stack.StackSummary, x: tensorflow.python._tf_stack.FrameSummary) -> bool
+
+Return true the container contains ``x``
+
+__eq__
+
+
+__eq__()
+
+
+__eq__(self: tensorflow.python._tf_stack.StackSummary, arg0: tensorflow.python._tf_stack.StackSummary) -> bool
+
+
+__getitem__
+
+
+__getitem__()
+
+
+__getitem__(*args, **kwargs)
+Overloaded function.
+
+1. __getitem__(self: tensorflow.python._tf_stack.StackSummary, s: slice) -> tensorflow.python._tf_stack.StackSummary
+
+Retrieve list elements using a slice object
+
+2. __getitem__(self: tensorflow.python._tf_stack.StackSummary, arg0: int) -> tensorflow.python._tf_stack.FrameSummary
+
+3. __getitem__(self: tensorflow.python._tf_stack.StackSummary, arg0: int) -> tensorflow.python._tf_stack.FrameSummary
+
+__iter__
+
+
+__iter__()
+
+
+__iter__(self: tensorflow.python._tf_stack.StackSummary) -> iterator
+
+
+__len__
+
+
+__len__()
+
+
+__len__(self: tensorflow.python._tf_stack.StackSummary) -> int
+
+
+__ne__
+
+
+__ne__()
+
+
+__ne__(self: tensorflow.python._tf_stack.StackSummary, arg0: tensorflow.python._tf_stack.StackSummary) -> bool
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/tf_stack/StackTraceFilter.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/tf_stack/StackTraceFilter.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..8216e98a5b9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/tf_stack/StackTraceFilter.md
@@ -0,0 +1,94 @@
+description: Allows filtering traceback information by removing superfluous frames.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.tf_decorator.tf_stack.StackTraceFilter
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Allows filtering traceback information by removing superfluous frames.
+
+Inherits From: [`StackTraceTransform`](../../../../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/tf_stack/StackTraceTransform.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.tf_decorator.tf_stack.StackTraceFilter`
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+get_filtered_filenames
+
+View source
+
+
+get_filtered_filenames()
+
+
+
+
+
+reset
+
+View source
+
+
+reset()
+
+
+
+
+
+__enter__
+
+View source
+
+
+__enter__()
+
+
+
+
+
+__exit__
+
+View source
+
+
+__exit__(
+ unused_type, unused_value, unused_traceback
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/tf_stack/StackTraceMapper.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/tf_stack/StackTraceMapper.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..55c039adf3d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/tf_stack/StackTraceMapper.md
@@ -0,0 +1,94 @@
+description: Allows remapping traceback information to different source code.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.tf_decorator.tf_stack.StackTraceMapper
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Allows remapping traceback information to different source code.
+
+Inherits From: [`StackTraceTransform`](../../../../../../tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/tf_stack/StackTraceTransform.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.tf_decorator.tf_stack.StackTraceMapper`
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+get_effective_source_map
+
+View source
+
+
+get_effective_source_map()
+
+
+Returns a map (filename, lineno) -> (filename, lineno, function_name).
+
+
+reset
+
+View source
+
+
+reset()
+
+
+
+
+
+__enter__
+
+View source
+
+
+__enter__()
+
+
+
+
+
+__exit__
+
+View source
+
+
+__exit__(
+ unused_type, unused_value, unused_traceback
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/tf_stack/StackTraceTransform.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/tf_stack/StackTraceTransform.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..02b1eaa39fa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/tf_stack/StackTraceTransform.md
@@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
+description: Base class for stack trace transformation functions.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.tf_decorator.tf_stack.StackTraceTransform
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Base class for stack trace transformation functions.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.tf_decorator.tf_stack.StackTraceTransform`
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+reset
+
+View source
+
+
+reset()
+
+
+
+
+
+__enter__
+
+View source
+
+
+__enter__()
+
+
+
+
+
+__exit__
+
+View source
+
+
+__exit__(
+ unused_type, unused_value, unused_traceback
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/tf_stack/extract_stack.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/tf_stack/extract_stack.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..7dcb18fbd7b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/tf_stack/extract_stack.md
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+description: A lightweight, extensible re-implementation of traceback.extract_stack.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.tf_decorator.tf_stack.extract_stack
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A lightweight, extensible re-implementation of traceback.extract_stack.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.tf_decorator.tf_stack.extract_stack`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.tf_decorator.tf_stack.extract_stack(
+ limit=-1
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+NOTE(mrry): traceback.extract_stack eagerly retrieves the line of code for
+ each stack frame using linecache, which results in an abundance of stat()
+ calls. This implementation does not retrieve the code, and any consumer
+ should apply _convert_stack to the result to obtain a traceback that can
+ be formatted etc. using traceback methods.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`limit`
+ |
+
+A limit on the number of frames to return.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A sequence of FrameSummary objects (filename, lineno, name, line)
+corresponding to the call stack of the current thread.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/unwrap.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/unwrap.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..f27f57ef632
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/tf_decorator/unwrap.md
@@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
+description: Unwraps an object into a list of TFDecorators and a final target.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.tf_decorator.unwrap
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Unwraps an object into a list of TFDecorators and a final target.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.tf_decorator.unwrap`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.tf_decorator.unwrap(
+ maybe_tf_decorator
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`maybe_tf_decorator`
+ |
+
+Any callable object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A tuple whose first element is an list of TFDecorator-derived objects that
+were applied to the final callable target, and whose second element is the
+final undecorated callable target. If the `maybe_tf_decorator` parameter is
+not decorated by any TFDecorators, the first tuple element will be an empty
+list. The `TFDecorator` list is ordered from outermost to innermost
+decorators.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/validator.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/validator.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..4992cad6784
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/flags/validator.md
@@ -0,0 +1,112 @@
+description: A function decorator for defining a flag validator.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.flags.validator
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A function decorator for defining a flag validator.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.app.flags.validator`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.flags.validator(
+ flag_name, message='Flag validation failed', flag_values=_flagvalues.FLAGS
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Registers the decorated function as a validator for flag_name, e.g.
+
+@flags.validator('foo')
+def _CheckFoo(foo):
+ ...
+
+See register_validator() for the specification of checker function.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`flag_name`
+ |
+
+str, name of the flag to be checked.
+ |
+
+|
+`message`
+ |
+
+str, error text to be shown to the user if checker returns False.
+If checker raises flags.ValidationError, message from the raised
+error will be shown.
+ |
+
+|
+`flag_values`
+ |
+
+flags.FlagValues, optional FlagValues instance to validate
+against.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A function decorator that registers its function argument as a validator.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`AttributeError`
+ |
+
+Raised when flag_name is not registered as a valid flag
+name.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/floor_div.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/floor_div.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3e6617753a3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/floor_div.md
@@ -0,0 +1,75 @@
+description: Returns x // y element-wise.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.floor_div
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns x // y element-wise.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.floor_div(
+ x, y, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+*NOTE*: `floor_div` supports broadcasting. More about broadcasting
+[here](http://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/user/basics.broadcasting.html)
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`x`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `bfloat16`, `half`, `float32`, `float64`, `uint8`, `int8`, `uint16`, `int16`, `int32`, `int64`, `complex64`, `complex128`.
+ |
+
+|
+`y`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must have the same type as `x`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `x`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/foldl.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/foldl.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..6cdb2fe764c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/foldl.md
@@ -0,0 +1,156 @@
+description: foldl on the list of tensors unpacked from elems on dimension 0.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.foldl
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+foldl on the list of tensors unpacked from `elems` on dimension 0.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.foldl(
+ fn, elems, initializer=None, parallel_iterations=10, back_prop=(True),
+ swap_memory=(False), name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This foldl operator repeatedly applies the callable `fn` to a sequence
+of elements from first to last. The elements are made of the tensors
+unpacked from `elems` on dimension 0. The callable fn takes two tensors as
+arguments. The first argument is the accumulated value computed from the
+preceding invocation of fn, and the second is the value at the current
+position of `elems`. If `initializer` is None, `elems` must contain at least
+one element, and its first element is used as the initializer.
+
+Suppose that `elems` is unpacked into `values`, a list of tensors. The shape
+of the result tensor is fn(initializer, values[0]).shape`.
+
+This method also allows multi-arity `elems` and output of `fn`. If `elems`
+is a (possibly nested) list or tuple of tensors, then each of these tensors
+must have a matching first (unpack) dimension. The signature of `fn` may
+match the structure of `elems`. That is, if `elems` is
+`(t1, [t2, t3, [t4, t5]])`, then an appropriate signature for `fn` is:
+`fn = lambda (t1, [t2, t3, [t4, t5]]):`.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`fn`
+ |
+
+The callable to be performed.
+ |
+
+|
+`elems`
+ |
+
+A tensor or (possibly nested) sequence of tensors, each of which will
+be unpacked along their first dimension. The nested sequence of the
+resulting slices will be the first argument to `fn`.
+ |
+
+|
+`initializer`
+ |
+
+(optional) A tensor or (possibly nested) sequence of tensors,
+as the initial value for the accumulator.
+ |
+
+|
+`parallel_iterations`
+ |
+
+(optional) The number of iterations allowed to run in
+parallel.
+ |
+
+|
+`back_prop`
+ |
+
+(optional) True enables support for back propagation.
+ |
+
+|
+`swap_memory`
+ |
+
+(optional) True enables GPU-CPU memory swapping.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+(optional) Name prefix for the returned tensors.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A tensor or (possibly nested) sequence of tensors, resulting from applying
+`fn` consecutively to the list of tensors unpacked from `elems`, from first
+to last.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+if `fn` is not callable.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Example:
+
+```python
+elems = tf.constant([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
+sum = foldl(lambda a, x: a + x, elems)
+# sum == 21
+```
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/foldr.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/foldr.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..30ca1c7bcc8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/foldr.md
@@ -0,0 +1,156 @@
+description: foldr on the list of tensors unpacked from elems on dimension 0.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.foldr
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+foldr on the list of tensors unpacked from `elems` on dimension 0.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.foldr(
+ fn, elems, initializer=None, parallel_iterations=10, back_prop=(True),
+ swap_memory=(False), name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This foldr operator repeatedly applies the callable `fn` to a sequence
+of elements from last to first. The elements are made of the tensors
+unpacked from `elems`. The callable fn takes two tensors as arguments.
+The first argument is the accumulated value computed from the preceding
+invocation of fn, and the second is the value at the current position of
+`elems`. If `initializer` is None, `elems` must contain at least one element,
+and its first element is used as the initializer.
+
+Suppose that `elems` is unpacked into `values`, a list of tensors. The shape
+of the result tensor is `fn(initializer, values[0]).shape`.
+
+This method also allows multi-arity `elems` and output of `fn`. If `elems`
+is a (possibly nested) list or tuple of tensors, then each of these tensors
+must have a matching first (unpack) dimension. The signature of `fn` may
+match the structure of `elems`. That is, if `elems` is
+`(t1, [t2, t3, [t4, t5]])`, then an appropriate signature for `fn` is:
+`fn = lambda (t1, [t2, t3, [t4, t5]]):`.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`fn`
+ |
+
+The callable to be performed.
+ |
+
+|
+`elems`
+ |
+
+A tensor or (possibly nested) sequence of tensors, each of which will
+be unpacked along their first dimension. The nested sequence of the
+resulting slices will be the first argument to `fn`.
+ |
+
+|
+`initializer`
+ |
+
+(optional) A tensor or (possibly nested) sequence of tensors,
+as the initial value for the accumulator.
+ |
+
+|
+`parallel_iterations`
+ |
+
+(optional) The number of iterations allowed to run in
+parallel.
+ |
+
+|
+`back_prop`
+ |
+
+(optional) True enables support for back propagation.
+ |
+
+|
+`swap_memory`
+ |
+
+(optional) True enables GPU-CPU memory swapping.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+(optional) Name prefix for the returned tensors.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A tensor or (possibly nested) sequence of tensors, resulting from applying
+`fn` consecutively to the list of tensors unpacked from `elems`, from last
+to first.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+if `fn` is not callable.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Example:
+
+```python
+elems = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
+sum = foldr(lambda a, x: a + x, elems)
+# sum == 21
+```
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gather.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gather.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..c7ad1dd3878
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gather.md
@@ -0,0 +1,154 @@
+description: Gather slices from params axis axis according to indices.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.gather
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Gather slices from params axis `axis` according to indices.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.gather(
+ params, indices, validate_indices=None, name=None, axis=None, batch_dims=0
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Gather slices from params axis `axis` according to `indices`. `indices` must
+be an integer tensor of any dimension (usually 0-D or 1-D).
+
+For 0-D (scalar) `indices`:
+
+$$\begin{align*}
+output[p_0, ..., p_{axis-1}, && &&& p_{axis + 1}, ..., p_{N-1}] = \\
+params[p_0, ..., p_{axis-1}, && indices, &&& p_{axis + 1}, ..., p_{N-1}]
+\end{align*}$$
+
+Where *N* = `ndims(params)`.
+
+For 1-D (vector) `indices` with `batch_dims=0`:
+
+$$\begin{align*}
+output[p_0, ..., p_{axis-1}, && &i, &&p_{axis + 1}, ..., p_{N-1}] =\\
+params[p_0, ..., p_{axis-1}, && indices[&i], &&p_{axis + 1}, ..., p_{N-1}]
+\end{align*}$$
+
+In the general case, produces an output tensor where:
+
+$$\begin{align*}
+output[p_0, &..., p_{axis-1}, &
+ &i_{B}, ..., i_{M-1}, &
+ p_{axis + 1}, &..., p_{N-1}] = \\
+params[p_0, &..., p_{axis-1}, &
+ indices[p_0, ..., p_{B-1}, &i_{B}, ..., i_{M-1}], &
+ p_{axis + 1}, &..., p_{N-1}]
+\end{align*}$$
+
+Where *N* = `ndims(params)`, *M* = `ndims(indices)`, and *B* = `batch_dims`.
+Note that `params.shape[:batch_dims]` must be identical to
+`indices.shape[:batch_dims]`.
+
+The shape of the output tensor is:
+
+> `output.shape = params.shape[:axis] + indices.shape[batch_dims:] +
+> params.shape[axis + 1:]`.
+
+Note that on CPU, if an out of bound index is found, an error is returned.
+On GPU, if an out of bound index is found, a 0 is stored in the corresponding
+output value.
+
+See also tf.gather_nd.
+
+
+
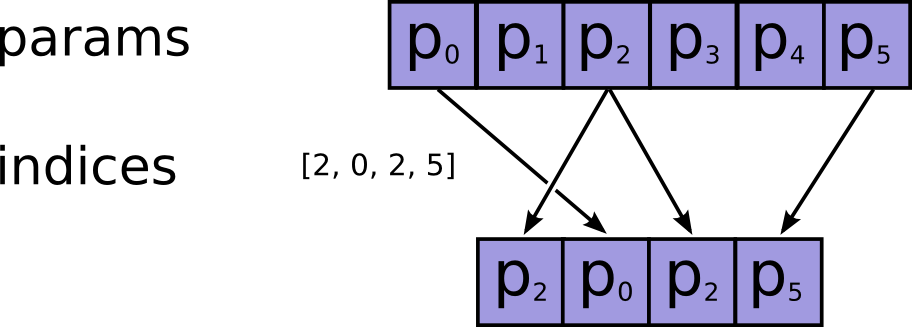
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`params`
+ |
+
+The `Tensor` from which to gather values. Must be at least rank
+`axis + 1`.
+ |
+
+|
+`indices`
+ |
+
+The index `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `int32`,
+`int64`. Must be in range `[0, params.shape[axis])`.
+ |
+
+|
+`validate_indices`
+ |
+
+Deprecated, does nothing.
+ |
+
+|
+`axis`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `int32`, `int64`. The
+`axis` in `params` to gather `indices` from. Must be greater than or equal
+to `batch_dims`. Defaults to the first non-batch dimension. Supports
+negative indexes.
+ |
+
+|
+`batch_dims`
+ |
+
+An `integer`. The number of batch dimensions. Must be less
+than or equal to `rank(indices)`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `params`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gather_nd.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gather_nd.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..1bf3ee2674c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gather_nd.md
@@ -0,0 +1,230 @@
+description: Gather slices from params into a Tensor with shape specified by indices.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.gather_nd
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Gather slices from `params` into a Tensor with shape specified by `indices`.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.manip.gather_nd`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.gather_nd(
+ params, indices, name=None, batch_dims=0
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+`indices` is an K-dimensional integer tensor, best thought of as a
+(K-1)-dimensional tensor of indices into `params`, where each element defines
+a slice of `params`:
+
+ output[\\(i_0, ..., i_{K-2}\\)] = params[indices[\\(i_0, ..., i_{K-2}\\)]]
+
+Whereas in tf.gather `indices` defines slices into the first
+dimension of `params`, in tf.gather_nd, `indices` defines slices into the
+first `N` dimensions of `params`, where `N = indices.shape[-1]`.
+
+The last dimension of `indices` can be at most the rank of
+`params`:
+
+ indices.shape[-1] <= params.rank
+
+The last dimension of `indices` corresponds to elements
+(if `indices.shape[-1] == params.rank`) or slices
+(if `indices.shape[-1] < params.rank`) along dimension `indices.shape[-1]`
+of `params`. The output tensor has shape
+
+ indices.shape[:-1] + params.shape[indices.shape[-1]:]
+
+Additionally both 'params' and 'indices' can have M leading batch
+dimensions that exactly match. In this case 'batch_dims' must be M.
+
+Note that on CPU, if an out of bound index is found, an error is returned.
+On GPU, if an out of bound index is found, a 0 is stored in the
+corresponding output value.
+
+Some examples below.
+
+Simple indexing into a matrix:
+
+```python
+ indices = [[0, 0], [1, 1]]
+ params = [['a', 'b'], ['c', 'd']]
+ output = ['a', 'd']
+```
+
+Slice indexing into a matrix:
+
+```python
+ indices = [[1], [0]]
+ params = [['a', 'b'], ['c', 'd']]
+ output = [['c', 'd'], ['a', 'b']]
+```
+
+Indexing into a 3-tensor:
+
+```python
+ indices = [[1]]
+ params = [[['a0', 'b0'], ['c0', 'd0']],
+ [['a1', 'b1'], ['c1', 'd1']]]
+ output = [[['a1', 'b1'], ['c1', 'd1']]]
+
+
+ indices = [[0, 1], [1, 0]]
+ params = [[['a0', 'b0'], ['c0', 'd0']],
+ [['a1', 'b1'], ['c1', 'd1']]]
+ output = [['c0', 'd0'], ['a1', 'b1']]
+
+
+ indices = [[0, 0, 1], [1, 0, 1]]
+ params = [[['a0', 'b0'], ['c0', 'd0']],
+ [['a1', 'b1'], ['c1', 'd1']]]
+ output = ['b0', 'b1']
+```
+
+The examples below are for the case when only indices have leading extra
+dimensions. If both 'params' and 'indices' have leading batch dimensions, use
+the 'batch_dims' parameter to run gather_nd in batch mode.
+
+Batched indexing into a matrix:
+
+```python
+ indices = [[[0, 0]], [[0, 1]]]
+ params = [['a', 'b'], ['c', 'd']]
+ output = [['a'], ['b']]
+```
+
+Batched slice indexing into a matrix:
+
+```python
+ indices = [[[1]], [[0]]]
+ params = [['a', 'b'], ['c', 'd']]
+ output = [[['c', 'd']], [['a', 'b']]]
+```
+
+Batched indexing into a 3-tensor:
+
+```python
+ indices = [[[1]], [[0]]]
+ params = [[['a0', 'b0'], ['c0', 'd0']],
+ [['a1', 'b1'], ['c1', 'd1']]]
+ output = [[[['a1', 'b1'], ['c1', 'd1']]],
+ [[['a0', 'b0'], ['c0', 'd0']]]]
+
+ indices = [[[0, 1], [1, 0]], [[0, 0], [1, 1]]]
+ params = [[['a0', 'b0'], ['c0', 'd0']],
+ [['a1', 'b1'], ['c1', 'd1']]]
+ output = [[['c0', 'd0'], ['a1', 'b1']],
+ [['a0', 'b0'], ['c1', 'd1']]]
+
+
+ indices = [[[0, 0, 1], [1, 0, 1]], [[0, 1, 1], [1, 1, 0]]]
+ params = [[['a0', 'b0'], ['c0', 'd0']],
+ [['a1', 'b1'], ['c1', 'd1']]]
+ output = [['b0', 'b1'], ['d0', 'c1']]
+```
+
+Examples with batched 'params' and 'indices':
+
+```python
+ batch_dims = 1
+ indices = [[1], [0]]
+ params = [[['a0', 'b0'], ['c0', 'd0']],
+ [['a1', 'b1'], ['c1', 'd1']]]
+ output = [['c0', 'd0'], ['a1', 'b1']]
+
+ batch_dims = 1
+ indices = [[[1]], [[0]]]
+ params = [[['a0', 'b0'], ['c0', 'd0']],
+ [['a1', 'b1'], ['c1', 'd1']]]
+ output = [[['c0', 'd0']], [['a1', 'b1']]]
+
+ batch_dims = 1
+ indices = [[[1, 0]], [[0, 1]]]
+ params = [[['a0', 'b0'], ['c0', 'd0']],
+ [['a1', 'b1'], ['c1', 'd1']]]
+ output = [['c0'], ['b1']]
+```
+
+See also tf.gather.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`params`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. The tensor from which to gather values.
+ |
+
+|
+`indices`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `int32`, `int64`.
+Index tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`batch_dims`
+ |
+
+An integer or a scalar 'Tensor'. The number of batch dimensions.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `params`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/get_collection.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/get_collection.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e3d8219321f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/get_collection.md
@@ -0,0 +1,87 @@
+description: Wrapper for Graph.get_collection() using the default graph.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.get_collection
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Wrapper for `Graph.get_collection()` using the default graph.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.get_collection(
+ key, scope=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+See tf.Graph.get_collection
+for more details.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`key`
+ |
+
+The key for the collection. For example, the `GraphKeys` class contains
+many standard names for collections.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope`
+ |
+
+(Optional.) If supplied, the resulting list is filtered to include
+only items whose `name` attribute matches using `re.match`. Items without
+a `name` attribute are never returned if a scope is supplied and the
+choice or `re.match` means that a `scope` without special tokens filters
+by prefix.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The list of values in the collection with the given `name`, or
+an empty list if no value has been added to that collection. The
+list contains the values in the order under which they were
+collected.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+Collections are not supported when eager execution is enabled.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/get_collection_ref.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/get_collection_ref.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..d9be8d6fc77
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/get_collection_ref.md
@@ -0,0 +1,76 @@
+description: Wrapper for Graph.get_collection_ref() using the default graph.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.get_collection_ref
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Wrapper for `Graph.get_collection_ref()` using the default graph.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.get_collection_ref(
+ key
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+See tf.Graph.get_collection_ref
+for more details.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`key`
+ |
+
+The key for the collection. For example, the `GraphKeys` class contains
+many standard names for collections.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The list of values in the collection with the given `name`, or an empty
+list if no value has been added to that collection. Note that this returns
+the collection list itself, which can be modified in place to change the
+collection.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+Collections are not supported when eager execution is enabled.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/get_default_graph.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/get_default_graph.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..6f9f43125f1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/get_default_graph.md
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+description: Returns the default graph for the current thread.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.get_default_graph
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns the default graph for the current thread.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.get_default_graph()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The returned graph will be the innermost graph on which a
+`Graph.as_default()` context has been entered, or a global default
+graph if none has been explicitly created.
+
+NOTE: The default graph is a property of the current thread. If you
+create a new thread, and wish to use the default graph in that
+thread, you must explicitly add a `with g.as_default():` in that
+thread's function.
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The default `Graph` being used in the current thread.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/get_default_session.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/get_default_session.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..fedd113eb9b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/get_default_session.md
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
+description: Returns the default session for the current thread.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.get_default_session
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns the default session for the current thread.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.get_default_session()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The returned `Session` will be the innermost session on which a
+`Session` or `Session.as_default()` context has been entered.
+
+NOTE: The default session is a property of the current thread. If you
+create a new thread, and wish to use the default session in that
+thread, you must explicitly add a `with sess.as_default():` in that
+thread's function.
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The default `Session` being used in the current thread.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/get_local_variable.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/get_local_variable.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..85e8fccd718
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/get_local_variable.md
@@ -0,0 +1,253 @@
+description: Gets an existing *local* variable or creates a new one.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.get_local_variable
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Gets an existing *local* variable or creates a new one.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.get_local_variable(
+ name, shape=None, dtype=None, initializer=None, regularizer=None,
+ trainable=(False), collections=None, caching_device=None, partitioner=None,
+ validate_shape=(True), use_resource=None, custom_getter=None, constraint=None,
+ synchronization=tf.VariableSynchronization.AUTO,
+ aggregation=tf.compat.v1.VariableAggregation.NONE
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Behavior is the same as in `get_variable`, except that variables are
+added to the `LOCAL_VARIABLES` collection and `trainable` is set to
+`False`.
+This function prefixes the name with the current variable scope
+and performs reuse checks. See the
+[Variable Scope How To](https://tensorflow.org/guide/variables)
+for an extensive description of how reusing works. Here is a basic example:
+
+```python
+def foo():
+ with tf.variable_scope("foo", reuse=tf.AUTO_REUSE):
+ v = tf.get_variable("v", [1])
+ return v
+
+v1 = foo() # Creates v.
+v2 = foo() # Gets the same, existing v.
+assert v1 == v2
+```
+
+If initializer is `None` (the default), the default initializer passed in
+the variable scope will be used. If that one is `None` too, a
+`glorot_uniform_initializer` will be used. The initializer can also be
+a Tensor, in which case the variable is initialized to this value and shape.
+
+Similarly, if the regularizer is `None` (the default), the default regularizer
+passed in the variable scope will be used (if that is `None` too,
+then by default no regularization is performed).
+
+If a partitioner is provided, a `PartitionedVariable` is returned.
+Accessing this object as a `Tensor` returns the shards concatenated along
+the partition axis.
+
+Some useful partitioners are available. See, e.g.,
+`variable_axis_size_partitioner` and `min_max_variable_partitioner`.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+The name of the new or existing variable.
+ |
+
+|
+`shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of the new or existing variable.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+Type of the new or existing variable (defaults to `DT_FLOAT`).
+ |
+
+|
+`initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer for the variable if one is created. Can either be
+an initializer object or a Tensor. If it's a Tensor, its shape must be known
+unless validate_shape is False.
+ |
+
+|
+`regularizer`
+ |
+
+A (Tensor -> Tensor or None) function; the result of
+applying it on a newly created variable will be added to the collection
+`tf.GraphKeys.REGULARIZATION_LOSSES` and can be used for regularization.
+ |
+
+|
+`collections`
+ |
+
+List of graph collections keys to add the Variable to.
+Defaults to `[GraphKeys.LOCAL_VARIABLES]` (see tf.Variable).
+ |
+
+|
+`caching_device`
+ |
+
+Optional device string or function describing where the
+Variable should be cached for reading. Defaults to the Variable's
+device. If not `None`, caches on another device. Typical use is to
+cache on the device where the Ops using the Variable reside, to
+deduplicate copying through `Switch` and other conditional statements.
+ |
+
+|
+`partitioner`
+ |
+
+Optional callable that accepts a fully defined `TensorShape`
+and `dtype` of the Variable to be created, and returns a list of
+partitions for each axis (currently only one axis can be partitioned).
+ |
+
+|
+`validate_shape`
+ |
+
+If False, allows the variable to be initialized with a
+value of unknown shape. If True, the default, the shape of initial_value
+must be known. For this to be used the initializer must be a Tensor and
+not an initializer object.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_resource`
+ |
+
+If False, creates a regular Variable. If true, creates an
+experimental ResourceVariable instead with well-defined semantics.
+Defaults to False (will later change to True). When eager execution is
+enabled this argument is always forced to be True.
+ |
+
+|
+`custom_getter`
+ |
+
+Callable that takes as a first argument the true getter, and
+allows overwriting the internal get_variable method.
+The signature of `custom_getter` should match that of this method,
+but the most future-proof version will allow for changes:
+`def custom_getter(getter, *args, **kwargs)`. Direct access to
+all `get_variable` parameters is also allowed:
+`def custom_getter(getter, name, *args, **kwargs)`. A simple identity
+custom getter that simply creates variables with modified names is:
+```python
+def custom_getter(getter, name, *args, **kwargs):
+return getter(name + '_suffix', *args, **kwargs)
+```
+ |
+
+|
+`constraint`
+ |
+
+An optional projection function to be applied to the variable
+after being updated by an `Optimizer` (e.g. used to implement norm
+constraints or value constraints for layer weights). The function must
+take as input the unprojected Tensor representing the value of the
+variable and return the Tensor for the projected value
+(which must have the same shape). Constraints are not safe to
+use when doing asynchronous distributed training.
+ |
+
+|
+`synchronization`
+ |
+
+Indicates when a distributed a variable will be
+aggregated. Accepted values are constants defined in the class
+tf.VariableSynchronization. By default the synchronization is set to
+`AUTO` and the current `DistributionStrategy` chooses
+when to synchronize.
+ |
+
+|
+`aggregation`
+ |
+
+Indicates how a distributed variable will be aggregated.
+Accepted values are constants defined in the class
+tf.VariableAggregation.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The created or existing `Variable` (or `PartitionedVariable`, if a
+partitioner was used).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+when creating a new variable and shape is not declared,
+when violating reuse during variable creation, or when `initializer` dtype
+and `dtype` don't match. Reuse is set inside `variable_scope`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/get_seed.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/get_seed.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e10eb6d244b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/get_seed.md
@@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
+description: Returns the local seeds an operation should use given an op-specific seed.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.get_seed
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns the local seeds an operation should use given an op-specific seed.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.random.get_seed`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.get_seed(
+ op_seed
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Given operation-specific seed, `op_seed`, this helper function returns two
+seeds derived from graph-level and op-level seeds. Many random operations
+internally use the two seeds to allow user to change the seed globally for a
+graph, or for only specific operations.
+
+For details on how the graph-level seed interacts with op seeds, see
+tf.compat.v1.random.set_random_seed.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`op_seed`
+ |
+
+integer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A tuple of two integers that should be used for the local seed of this
+operation.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/get_session_handle.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/get_session_handle.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..26bef727a3b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/get_session_handle.md
@@ -0,0 +1,110 @@
+description: Return the handle of data.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.get_session_handle
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Return the handle of `data`.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.get_session_handle(
+ data, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This is EXPERIMENTAL and subject to change.
+
+Keep `data` "in-place" in the runtime and create a handle that can be
+used to retrieve `data` in a subsequent run().
+
+Combined with `get_session_tensor`, we can keep a tensor produced in
+one run call in place, and use it as the input in a future run call.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`data`
+ |
+
+A tensor to be stored in the session.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name prefix for the return tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A scalar string tensor representing a unique handle for `data`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+if `data` is not a Tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+c = tf.multiply(a, b)
+h = tf.compat.v1.get_session_handle(c)
+h = sess.run(h)
+
+p, a = tf.compat.v1.get_session_tensor(h.handle, tf.float32)
+b = tf.multiply(a, 10)
+c = sess.run(b, feed_dict={p: h.handle})
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/get_session_tensor.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/get_session_tensor.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..c445bc08266
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/get_session_tensor.md
@@ -0,0 +1,100 @@
+description: Get the tensor of type dtype by feeding a tensor handle.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.get_session_tensor
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Get the tensor of type `dtype` by feeding a tensor handle.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.get_session_tensor(
+ handle, dtype, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This is EXPERIMENTAL and subject to change.
+
+Get the value of the tensor from a tensor handle. The tensor
+is produced in a previous run() and stored in the state of the
+session.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`handle`
+ |
+
+The string representation of a persistent tensor handle.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+The type of the output tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name prefix for the return tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A pair of tensors. The first is a placeholder for feeding a
+tensor handle and the second is the tensor in the session state
+keyed by the tensor handle.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+c = tf.multiply(a, b)
+h = tf.compat.v1.get_session_handle(c)
+h = sess.run(h)
+
+p, a = tf.compat.v1.get_session_tensor(h.handle, tf.float32)
+b = tf.multiply(a, 10)
+c = sess.run(b, feed_dict={p: h.handle})
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/get_variable.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/get_variable.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e27c5dcda4a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/get_variable.md
@@ -0,0 +1,258 @@
+description: Gets an existing variable with these parameters or create a new one.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.get_variable
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Gets an existing variable with these parameters or create a new one.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.get_variable(
+ name, shape=None, dtype=None, initializer=None, regularizer=None,
+ trainable=None, collections=None, caching_device=None, partitioner=None,
+ validate_shape=(True), use_resource=None, custom_getter=None, constraint=None,
+ synchronization=tf.VariableSynchronization.AUTO,
+ aggregation=tf.compat.v1.VariableAggregation.NONE
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This function prefixes the name with the current variable scope
+and performs reuse checks. See the
+[Variable Scope How To](https://tensorflow.org/guide/variables)
+for an extensive description of how reusing works. Here is a basic example:
+
+```python
+def foo():
+ with tf.variable_scope("foo", reuse=tf.AUTO_REUSE):
+ v = tf.get_variable("v", [1])
+ return v
+
+v1 = foo() # Creates v.
+v2 = foo() # Gets the same, existing v.
+assert v1 == v2
+```
+
+If initializer is `None` (the default), the default initializer passed in
+the variable scope will be used. If that one is `None` too, a
+`glorot_uniform_initializer` will be used. The initializer can also be
+a Tensor, in which case the variable is initialized to this value and shape.
+
+Similarly, if the regularizer is `None` (the default), the default regularizer
+passed in the variable scope will be used (if that is `None` too,
+then by default no regularization is performed).
+
+If a partitioner is provided, a `PartitionedVariable` is returned.
+Accessing this object as a `Tensor` returns the shards concatenated along
+the partition axis.
+
+Some useful partitioners are available. See, e.g.,
+`variable_axis_size_partitioner` and `min_max_variable_partitioner`.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+The name of the new or existing variable.
+ |
+
+|
+`shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of the new or existing variable.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+Type of the new or existing variable (defaults to `DT_FLOAT`).
+ |
+
+|
+`initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer for the variable if one is created. Can either be
+an initializer object or a Tensor. If it's a Tensor, its shape must be known
+unless validate_shape is False.
+ |
+
+|
+`regularizer`
+ |
+
+A (Tensor -> Tensor or None) function; the result of
+applying it on a newly created variable will be added to the collection
+`tf.GraphKeys.REGULARIZATION_LOSSES` and can be used for regularization.
+ |
+
+|
+`trainable`
+ |
+
+If `True` also add the variable to the graph collection
+`GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES` (see tf.Variable).
+ |
+
+|
+`collections`
+ |
+
+List of graph collections keys to add the Variable to.
+Defaults to `[GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES]` (see tf.Variable).
+ |
+
+|
+`caching_device`
+ |
+
+Optional device string or function describing where the
+Variable should be cached for reading. Defaults to the Variable's
+device. If not `None`, caches on another device. Typical use is to
+cache on the device where the Ops using the Variable reside, to
+deduplicate copying through `Switch` and other conditional statements.
+ |
+
+|
+`partitioner`
+ |
+
+Optional callable that accepts a fully defined `TensorShape`
+and `dtype` of the Variable to be created, and returns a list of
+partitions for each axis (currently only one axis can be partitioned).
+ |
+
+|
+`validate_shape`
+ |
+
+If False, allows the variable to be initialized with a
+value of unknown shape. If True, the default, the shape of initial_value
+must be known. For this to be used the initializer must be a Tensor and
+not an initializer object.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_resource`
+ |
+
+If False, creates a regular Variable. If true, creates an
+experimental ResourceVariable instead with well-defined semantics.
+Defaults to False (will later change to True). When eager execution is
+enabled this argument is always forced to be True.
+ |
+
+|
+`custom_getter`
+ |
+
+Callable that takes as a first argument the true getter, and
+allows overwriting the internal get_variable method.
+The signature of `custom_getter` should match that of this method,
+but the most future-proof version will allow for changes:
+`def custom_getter(getter, *args, **kwargs)`. Direct access to
+all `get_variable` parameters is also allowed:
+`def custom_getter(getter, name, *args, **kwargs)`. A simple identity
+custom getter that simply creates variables with modified names is:
+```python
+def custom_getter(getter, name, *args, **kwargs):
+return getter(name + '_suffix', *args, **kwargs)
+```
+ |
+
+|
+`constraint`
+ |
+
+An optional projection function to be applied to the variable
+after being updated by an `Optimizer` (e.g. used to implement norm
+constraints or value constraints for layer weights). The function must
+take as input the unprojected Tensor representing the value of the
+variable and return the Tensor for the projected value
+(which must have the same shape). Constraints are not safe to
+use when doing asynchronous distributed training.
+ |
+
+|
+`synchronization`
+ |
+
+Indicates when a distributed a variable will be
+aggregated. Accepted values are constants defined in the class
+tf.VariableSynchronization. By default the synchronization is set to
+`AUTO` and the current `DistributionStrategy` chooses
+when to synchronize.
+ |
+
+|
+`aggregation`
+ |
+
+Indicates how a distributed variable will be aggregated.
+Accepted values are constants defined in the class
+tf.VariableAggregation.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The created or existing `Variable` (or `PartitionedVariable`, if a
+partitioner was used).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+when creating a new variable and shape is not declared,
+when violating reuse during variable creation, or when `initializer` dtype
+and `dtype` don't match. Reuse is set inside `variable_scope`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/get_variable_scope.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/get_variable_scope.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..bc515b35fce
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/get_variable_scope.md
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+description: Returns the current variable scope.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.get_variable_scope
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns the current variable scope.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.get_variable_scope()
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e3e827a0367
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile.md
@@ -0,0 +1,55 @@
+description: Import router for file_io.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.gfile
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Import router for file_io.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class FastGFile`](../../../tf/compat/v1/gfile/FastGFile.md): File I/O wrappers without thread locking.
+
+[`class GFile`](../../../tf/io/gfile/GFile.md): File I/O wrappers without thread locking.
+
+[`class Open`](../../../tf/io/gfile/GFile.md): File I/O wrappers without thread locking.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`Copy(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/gfile/Copy.md): Copies data from `oldpath` to `newpath`.
+
+[`DeleteRecursively(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/gfile/DeleteRecursively.md): Deletes everything under dirname recursively.
+
+[`Exists(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/gfile/Exists.md): Determines whether a path exists or not.
+
+[`Glob(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/gfile/Glob.md): Returns a list of files that match the given pattern(s).
+
+[`IsDirectory(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/gfile/IsDirectory.md): Returns whether the path is a directory or not.
+
+[`ListDirectory(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/gfile/ListDirectory.md): Returns a list of entries contained within a directory.
+
+[`MakeDirs(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/gfile/MakeDirs.md): Creates a directory and all parent/intermediate directories.
+
+[`MkDir(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/gfile/MkDir.md): Creates a directory with the name `dirname`.
+
+[`Remove(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/gfile/Remove.md): Deletes the file located at 'filename'.
+
+[`Rename(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/gfile/Rename.md): Rename or move a file / directory.
+
+[`Stat(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/gfile/Stat.md): Returns file statistics for a given path.
+
+[`Walk(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/gfile/Walk.md): Recursive directory tree generator for directories.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/Copy.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/Copy.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..ae7b1bb7db5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/Copy.md
@@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
+description: Copies data from oldpath to newpath.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.gfile.Copy
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Copies data from `oldpath` to `newpath`.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.gfile.Copy(
+ oldpath, newpath, overwrite=(False)
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`oldpath`
+ |
+
+string, name of the file who's contents need to be copied
+ |
+
+|
+`newpath`
+ |
+
+string, name of the file to which to copy to
+ |
+
+|
+`overwrite`
+ |
+
+boolean, if false it's an error for `newpath` to be occupied by
+an existing file.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`errors.OpError`
+ |
+
+If the operation fails.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/DeleteRecursively.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/DeleteRecursively.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..64d959b7896
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/DeleteRecursively.md
@@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
+description: Deletes everything under dirname recursively.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.gfile.DeleteRecursively
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Deletes everything under dirname recursively.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.gfile.DeleteRecursively(
+ dirname
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`dirname`
+ |
+
+string, a path to a directory
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`errors.OpError`
+ |
+
+If the operation fails.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/Exists.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/Exists.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..611ad187a1c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/Exists.md
@@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
+description: Determines whether a path exists or not.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.gfile.Exists
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Determines whether a path exists or not.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.gfile.Exists(
+ filename
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`filename`
+ |
+
+string, a path
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+True if the path exists, whether it's a file or a directory.
+False if the path does not exist and there are no filesystem errors.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`errors.OpError`
+ |
+
+Propagates any errors reported by the FileSystem API.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/FastGFile.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/FastGFile.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..362dacbf126
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/FastGFile.md
@@ -0,0 +1,313 @@
+description: File I/O wrappers without thread locking.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.gfile.FastGFile
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+File I/O wrappers without thread locking.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.gfile.FastGFile(
+ name, mode='r'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Note, that this is somewhat like builtin Python file I/O, but
+there are semantic differences to make it more efficient for
+some backing filesystems. For example, a write mode file will
+not be opened until the first write call (to minimize RPC
+invocations in network filesystems).
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`mode`
+ |
+
+Returns the mode in which the file was opened.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Returns the file name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+close
+
+View source
+
+
+close()
+
+
+Closes FileIO. Should be called for the WritableFile to be flushed.
+
+
+flush
+
+View source
+
+
+flush()
+
+
+Flushes the Writable file.
+
+This only ensures that the data has made its way out of the process without
+any guarantees on whether it's written to disk. This means that the
+data would survive an application crash but not necessarily an OS crash.
+
+next
+
+View source
+
+
+next()
+
+
+
+
+
+read
+
+View source
+
+
+read(
+ n=-1
+)
+
+
+Returns the contents of a file as a string.
+
+Starts reading from current position in file.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`n`
+ |
+
+Read `n` bytes if `n != -1`. If `n = -1`, reads to end of file.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`n` bytes of the file (or whole file) in bytes mode or `n` bytes of the
+string if in string (regular) mode.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+readline
+
+View source
+
+
+readline()
+
+
+Reads the next line from the file. Leaves the '\n' at the end.
+
+
+readlines
+
+View source
+
+
+readlines()
+
+
+Returns all lines from the file in a list.
+
+
+seek
+
+View source
+
+
+seek(
+ offset=None, whence=0, position=None
+)
+
+
+Seeks to the offset in the file. (deprecated arguments)
+
+Warning: SOME ARGUMENTS ARE DEPRECATED: `(position)`. They will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+position is deprecated in favor of the offset argument.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`offset`
+ |
+
+The byte count relative to the whence argument.
+ |
+
+|
+`whence`
+ |
+
+Valid values for whence are:
+0: start of the file (default)
+1: relative to the current position of the file
+2: relative to the end of file. `offset` is usually negative.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+seekable
+
+View source
+
+
+seekable()
+
+
+Returns True as FileIO supports random access ops of seek()/tell()
+
+
+size
+
+View source
+
+
+size()
+
+
+Returns the size of the file.
+
+
+tell
+
+View source
+
+
+tell()
+
+
+Returns the current position in the file.
+
+
+write
+
+View source
+
+
+write(
+ file_content
+)
+
+
+Writes file_content to the file. Appends to the end of the file.
+
+
+__enter__
+
+View source
+
+
+__enter__()
+
+
+Make usable with "with" statement.
+
+
+__exit__
+
+View source
+
+
+__exit__(
+ unused_type, unused_value, unused_traceback
+)
+
+
+Make usable with "with" statement.
+
+
+__iter__
+
+View source
+
+
+__iter__()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/Glob.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/Glob.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..c0c814c0e74
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/Glob.md
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+description: Returns a list of files that match the given pattern(s).
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.gfile.Glob
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns a list of files that match the given pattern(s).
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.gfile.Glob(
+ filename
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`filename`
+ |
+
+string or iterable of strings. The glob pattern(s).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of strings containing filenames that match the given pattern(s).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`errors.OpError`
+ |
+
+If there are filesystem / directory listing errors.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/IsDirectory.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/IsDirectory.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e02228b3fc1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/IsDirectory.md
@@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
+description: Returns whether the path is a directory or not.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.gfile.IsDirectory
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns whether the path is a directory or not.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.gfile.IsDirectory(
+ dirname
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`dirname`
+ |
+
+string, path to a potential directory
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+True, if the path is a directory; False otherwise
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/ListDirectory.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/ListDirectory.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..6b1e20c76f5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/ListDirectory.md
@@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
+description: Returns a list of entries contained within a directory.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.gfile.ListDirectory
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns a list of entries contained within a directory.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.gfile.ListDirectory(
+ dirname
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The list is in arbitrary order. It does not contain the special entries "."
+and "..".
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`dirname`
+ |
+
+string, path to a directory
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+[filename1, filename2, ... filenameN] as strings
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+|
+errors.NotFoundError if directory doesn't exist
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/MakeDirs.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/MakeDirs.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..60979f0ff01
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/MakeDirs.md
@@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
+description: Creates a directory and all parent/intermediate directories.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.gfile.MakeDirs
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Creates a directory and all parent/intermediate directories.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.gfile.MakeDirs(
+ dirname
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+It succeeds if dirname already exists and is writable.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`dirname`
+ |
+
+string, name of the directory to be created
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`errors.OpError`
+ |
+
+If the operation fails.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/MkDir.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/MkDir.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..2c5b5f4c1d4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/MkDir.md
@@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
+description: Creates a directory with the name dirname.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.gfile.MkDir
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Creates a directory with the name `dirname`.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.gfile.MkDir(
+ dirname
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`dirname`
+ |
+
+string, name of the directory to be created
+ |
+
+
+
+
+Notes: The parent directories need to exist. Use tf.io.gfile.makedirs
+ instead if there is the possibility that the parent dirs don't exist.
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`errors.OpError`
+ |
+
+If the operation fails.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/Remove.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/Remove.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..fc262753436
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/Remove.md
@@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
+description: Deletes the file located at 'filename'.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.gfile.Remove
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Deletes the file located at 'filename'.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.gfile.Remove(
+ filename
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`filename`
+ |
+
+string, a filename
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`errors.OpError`
+ |
+
+Propagates any errors reported by the FileSystem API. E.g.,
+`NotFoundError` if the file does not exist.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/Rename.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/Rename.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3dc29198614
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/Rename.md
@@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
+description: Rename or move a file / directory.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.gfile.Rename
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Rename or move a file / directory.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.gfile.Rename(
+ oldname, newname, overwrite=(False)
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`oldname`
+ |
+
+string, pathname for a file
+ |
+
+|
+`newname`
+ |
+
+string, pathname to which the file needs to be moved
+ |
+
+|
+`overwrite`
+ |
+
+boolean, if false it's an error for `newname` to be occupied by
+an existing file.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`errors.OpError`
+ |
+
+If the operation fails.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/Stat.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/Stat.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..057910dd341
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/Stat.md
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+description: Returns file statistics for a given path.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.gfile.Stat
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns file statistics for a given path.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.gfile.Stat(
+ filename
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`filename`
+ |
+
+string, path to a file
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+FileStatistics struct that contains information about the path
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`errors.OpError`
+ |
+
+If the operation fails.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/Walk.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/Walk.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e4a3ae294de
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gfile/Walk.md
@@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
+description: Recursive directory tree generator for directories.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.gfile.Walk
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Recursive directory tree generator for directories.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.gfile.Walk(
+ top, in_order=(True)
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`top`
+ |
+
+string, a Directory name
+ |
+
+|
+`in_order`
+ |
+
+bool, Traverse in order if True, post order if False. Errors that
+happen while listing directories are ignored.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Yields:
+
+Each yield is a 3-tuple: the pathname of a directory, followed by lists of
+all its subdirectories and leaf files. That is, each yield looks like:
+`(dirname, [subdirname, subdirname, ...], [filename, filename, ...])`.
+Each item is a string.
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/global_variables.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/global_variables.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..9dc5502d172
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/global_variables.md
@@ -0,0 +1,76 @@
+description: Returns global variables.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.global_variables
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns global variables.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.global_variables(
+ scope=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Global variables are variables that are shared across machines in a
+distributed environment. The `Variable()` constructor or `get_variable()`
+automatically adds new variables to the graph collection
+`GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES`.
+This convenience function returns the contents of that collection.
+
+An alternative to global variables are local variables. See
+tf.compat.v1.local_variables
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`scope`
+ |
+
+(Optional.) A string. If supplied, the resulting list is filtered to
+include only items whose `name` attribute matches `scope` using
+`re.match`. Items without a `name` attribute are never returned if a scope
+is supplied. The choice of `re.match` means that a `scope` without special
+tokens filters by prefix.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of `Variable` objects.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/global_variables_initializer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/global_variables_initializer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..ddda71c540d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/global_variables_initializer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
+description: Returns an Op that initializes global variables.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.global_variables_initializer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns an Op that initializes global variables.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.initializers.global_variables`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.global_variables_initializer()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This is just a shortcut for `variables_initializer(global_variables())`
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Op that initializes global variables in the graph.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gradients.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gradients.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..2cf2e0f030a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/gradients.md
@@ -0,0 +1,241 @@
+description: Constructs symbolic derivatives of sum of ys w.r.t. x in xs.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.gradients
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Constructs symbolic derivatives of sum of `ys` w.r.t. x in `xs`.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.gradients(
+ ys, xs, grad_ys=None, name='gradients', colocate_gradients_with_ops=(False),
+ gate_gradients=(False), aggregation_method=None, stop_gradients=None,
+ unconnected_gradients=tf.UnconnectedGradients.NONE
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+`ys` and `xs` are each a `Tensor` or a list of tensors. `grad_ys`
+is a list of `Tensor`, holding the gradients received by the
+`ys`. The list must be the same length as `ys`.
+
+`gradients()` adds ops to the graph to output the derivatives of `ys` with
+respect to `xs`. It returns a list of `Tensor` of length `len(xs)` where
+each tensor is the `sum(dy/dx)` for y in `ys` and for x in `xs`.
+
+`grad_ys` is a list of tensors of the same length as `ys` that holds
+the initial gradients for each y in `ys`. When `grad_ys` is None,
+we fill in a tensor of '1's of the shape of y for each y in `ys`. A
+user can provide their own initial `grad_ys` to compute the
+derivatives using a different initial gradient for each y (e.g., if
+one wanted to weight the gradient differently for each value in
+each y).
+
+`stop_gradients` is a `Tensor` or a list of tensors to be considered constant
+with respect to all `xs`. These tensors will not be backpropagated through,
+as though they had been explicitly disconnected using `stop_gradient`. Among
+other things, this allows computation of partial derivatives as opposed to
+total derivatives. For example:
+
+```python
+a = tf.constant(0.)
+b = 2 * a
+g = tf.gradients(a + b, [a, b], stop_gradients=[a, b])
+```
+
+Here the partial derivatives `g` evaluate to `[1.0, 1.0]`, compared to the
+total derivatives `tf.gradients(a + b, [a, b])`, which take into account the
+influence of `a` on `b` and evaluate to `[3.0, 1.0]`. Note that the above is
+equivalent to:
+
+```python
+a = tf.stop_gradient(tf.constant(0.))
+b = tf.stop_gradient(2 * a)
+g = tf.gradients(a + b, [a, b])
+```
+
+`stop_gradients` provides a way of stopping gradient after the graph has
+already been constructed, as compared to tf.stop_gradient which is used
+during graph construction. When the two approaches are combined,
+backpropagation stops at both tf.stop_gradient nodes and nodes in
+`stop_gradients`, whichever is encountered first.
+
+All integer tensors are considered constant with respect to all `xs`, as if
+they were included in `stop_gradients`.
+
+`unconnected_gradients` determines the value returned for each x in xs if it
+is unconnected in the graph to ys. By default this is None to safeguard
+against errors. Mathematically these gradients are zero which can be requested
+using the `'zero'` option. `tf.UnconnectedGradients` provides the
+following options and behaviors:
+
+```python
+a = tf.ones([1, 2])
+b = tf.ones([3, 1])
+g1 = tf.gradients([b], [a], unconnected_gradients='none')
+sess.run(g1) # [None]
+
+g2 = tf.gradients([b], [a], unconnected_gradients='zero')
+sess.run(g2) # [array([[0., 0.]], dtype=float32)]
+```
+
+Let us take one practical example which comes during the back propogation
+phase. This function is used to evaluate the derivatives of the cost function
+with respect to Weights `Ws` and Biases `bs`. Below sample implementation
+provides the exaplantion of what it is actually used for :
+
+```python
+Ws = tf.constant(0.)
+bs = 2 * Ws
+cost = Ws + bs # This is just an example. So, please ignore the formulas.
+g = tf.gradients(cost, [Ws, bs])
+dCost_dW, dCost_db = g
+```
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ys`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` or list of tensors to be differentiated.
+ |
+
+|
+`xs`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` or list of tensors to be used for differentiation.
+ |
+
+|
+`grad_ys`
+ |
+
+Optional. A `Tensor` or list of tensors the same size as
+`ys` and holding the gradients computed for each y in `ys`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name to use for grouping all the gradient ops together.
+defaults to 'gradients'.
+ |
+
+|
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops`
+ |
+
+If True, try colocating gradients with
+the corresponding op.
+ |
+
+|
+`gate_gradients`
+ |
+
+If True, add a tuple around the gradients returned
+for an operations. This avoids some race conditions.
+ |
+
+|
+`aggregation_method`
+ |
+
+Specifies the method used to combine gradient terms.
+Accepted values are constants defined in the class `AggregationMethod`.
+ |
+
+|
+`stop_gradients`
+ |
+
+Optional. A `Tensor` or list of tensors not to differentiate
+through.
+ |
+
+|
+`unconnected_gradients`
+ |
+
+Optional. Specifies the gradient value returned when
+the given input tensors are unconnected. Accepted values are constants
+defined in the class tf.UnconnectedGradients and the default value is
+`none`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of `Tensor` of length `len(xs)` where each tensor is the `sum(dy/dx)`
+for y in `ys` and for x in `xs`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`LookupError`
+ |
+
+if one of the operations between `x` and `y` does not
+have a registered gradient function.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if the arguments are invalid.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+if called in Eager mode.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/graph_util.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/graph_util.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..fcea01add2c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/graph_util.md
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
+description: Helpers to manipulate a tensor graph in python.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.graph_util
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Helpers to manipulate a tensor graph in python.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`convert_variables_to_constants(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/graph_util/convert_variables_to_constants.md): Replaces all the variables in a graph with constants of the same values. (deprecated)
+
+[`extract_sub_graph(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/graph_util/extract_sub_graph.md): Extract the subgraph that can reach any of the nodes in 'dest_nodes'. (deprecated)
+
+[`import_graph_def(...)`](../../../tf/graph_util/import_graph_def.md): Imports the graph from `graph_def` into the current default `Graph`. (deprecated arguments)
+
+[`must_run_on_cpu(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/graph_util/must_run_on_cpu.md): Returns True if the given node_def must run on CPU, otherwise False. (deprecated)
+
+[`remove_training_nodes(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/graph_util/remove_training_nodes.md): Prunes out nodes that aren't needed for inference. (deprecated)
+
+[`tensor_shape_from_node_def_name(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/graph_util/tensor_shape_from_node_def_name.md): Convenience function to get a shape from a NodeDef's input string. (deprecated)
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/graph_util/convert_variables_to_constants.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/graph_util/convert_variables_to_constants.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..541a0a2eef3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/graph_util/convert_variables_to_constants.md
@@ -0,0 +1,121 @@
+description: Replaces all the variables in a graph with constants of the same values. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.graph_util.convert_variables_to_constants
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Replaces all the variables in a graph with constants of the same values. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.graph_util.convert_variables_to_constants(
+ sess, input_graph_def, output_node_names, variable_names_whitelist=None,
+ variable_names_blacklist=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use tf.compat.v1.graph_util.convert_variables_to_constants
+
+If you have a trained graph containing Variable ops, it can be convenient to
+convert them all to Const ops holding the same values. This makes it possible
+to describe the network fully with a single GraphDef file, and allows the
+removal of a lot of ops related to loading and saving the variables.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sess`
+ |
+
+Active TensorFlow session containing the variables.
+ |
+
+|
+`input_graph_def`
+ |
+
+GraphDef object holding the network.
+ |
+
+|
+`output_node_names`
+ |
+
+List of name strings for the result nodes of the graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`variable_names_whitelist`
+ |
+
+The set of variable names to convert (by default,
+all variables are converted).
+ |
+
+|
+`variable_names_blacklist`
+ |
+
+The set of variable names to omit converting
+to constants.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+GraphDef containing a simplified version of the original.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+if a DT_RESOURCE op is found whose ancestor Variables are both
+blacklisted AND whitelisted for freezing.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/graph_util/extract_sub_graph.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/graph_util/extract_sub_graph.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..0de6694eb92
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/graph_util/extract_sub_graph.md
@@ -0,0 +1,91 @@
+description: Extract the subgraph that can reach any of the nodes in 'dest_nodes'. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.graph_util.extract_sub_graph
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Extract the subgraph that can reach any of the nodes in 'dest_nodes'. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.graph_util.extract_sub_graph(
+ graph_def, dest_nodes
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use tf.compat.v1.graph_util.extract_sub_graph
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph_def`
+ |
+
+A graph_pb2.GraphDef proto.
+ |
+
+|
+`dest_nodes`
+ |
+
+A list of strings specifying the destination node names.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The GraphDef of the sub-graph.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If 'graph_def' is not a graph_pb2.GraphDef proto.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/graph_util/must_run_on_cpu.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/graph_util/must_run_on_cpu.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..74aa6072c74
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/graph_util/must_run_on_cpu.md
@@ -0,0 +1,76 @@
+description: Returns True if the given node_def must run on CPU, otherwise False. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.graph_util.must_run_on_cpu
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns True if the given node_def must run on CPU, otherwise False. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.graph_util.must_run_on_cpu(
+ node, pin_variables_on_cpu=(False)
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use tf.compat.v1.graph_util.must_run_on_cpu
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`node`
+ |
+
+The node to be assigned to a device. Could be either an ops.Operation
+or NodeDef.
+ |
+
+|
+`pin_variables_on_cpu`
+ |
+
+If True, this function will return False if node_def
+represents a variable-related op.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+True if the given node must run on CPU, otherwise False.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/graph_util/remove_training_nodes.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/graph_util/remove_training_nodes.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..197bb60b8ed
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/graph_util/remove_training_nodes.md
@@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
+description: Prunes out nodes that aren't needed for inference. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.graph_util.remove_training_nodes
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Prunes out nodes that aren't needed for inference. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.graph_util.remove_training_nodes(
+ input_graph, protected_nodes=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use tf.compat.v1.graph_util.remove_training_nodes
+
+There are nodes like Identity and CheckNumerics that are only useful
+during training, and can be removed in graphs that will be used for
+nothing but inference. Here we identify and remove them, returning an
+equivalent graph. To be specific, CheckNumerics nodes are always removed, and
+Identity nodes that aren't involved in control edges are spliced out so that
+their input and outputs are directly connected.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_graph`
+ |
+
+Model to analyze and prune.
+ |
+
+|
+`protected_nodes`
+ |
+
+An optional list of names of nodes to be kept
+unconditionally. This is for example useful to preserve Identity output
+nodes.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of nodes with the unnecessary ones removed.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/graph_util/tensor_shape_from_node_def_name.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/graph_util/tensor_shape_from_node_def_name.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..6d71c0ec976
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/graph_util/tensor_shape_from_node_def_name.md
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
+description: Convenience function to get a shape from a NodeDef's input string. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.graph_util.tensor_shape_from_node_def_name
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Convenience function to get a shape from a NodeDef's input string. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.graph_util.tensor_shape_from_node_def_name(
+ graph, input_name
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use tf.compat.v1.graph_util.tensor_shape_from_node_def_name
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/hessians.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/hessians.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..5ab14acaea1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/hessians.md
@@ -0,0 +1,125 @@
+description: Constructs the Hessian of sum of ys with respect to x in xs.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.hessians
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Constructs the Hessian of sum of `ys` with respect to `x` in `xs`.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.hessians(
+ ys, xs, name='hessians', colocate_gradients_with_ops=(False),
+ gate_gradients=(False), aggregation_method=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+`hessians()` adds ops to the graph to output the Hessian matrix of `ys`
+with respect to `xs`. It returns a list of `Tensor` of length `len(xs)`
+where each tensor is the Hessian of `sum(ys)`.
+
+The Hessian is a matrix of second-order partial derivatives of a scalar
+tensor (see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hessian_matrix for more details).
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ys`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` or list of tensors to be differentiated.
+ |
+
+|
+`xs`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` or list of tensors to be used for differentiation.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name to use for grouping all the gradient ops together.
+defaults to 'hessians'.
+ |
+
+|
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops`
+ |
+
+See `gradients()` documentation for details.
+ |
+
+|
+`gate_gradients`
+ |
+
+See `gradients()` documentation for details.
+ |
+
+|
+`aggregation_method`
+ |
+
+See `gradients()` documentation for details.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of Hessian matrices of `sum(ys)` for each `x` in `xs`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`LookupError`
+ |
+
+if one of the operations between `xs` and `ys` does not
+have a registered gradient function.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..2c07b854535
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image.md
@@ -0,0 +1,294 @@
+description: Image ops.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.image
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Image ops.
+
+
+The tf.image module contains various functions for image
+processing and decoding-encoding Ops.
+
+Many of the encoding/decoding functions are also available in the
+core tf.io module.
+
+## Image processing
+
+### Resizing
+
+The resizing Ops accept input images as tensors of several types. They always
+output resized images as float32 tensors.
+
+The convenience function tf.image.resize supports both 4-D
+and 3-D tensors as input and output. 4-D tensors are for batches of images,
+3-D tensors for individual images.
+
+Resized images will be distorted if their original aspect ratio is not the
+same as size. To avoid distortions see tf.image.resize_with_pad.
+
+* tf.image.resize
+* tf.image.resize_with_pad
+* tf.image.resize_with_crop_or_pad
+
+The Class tf.image.ResizeMethod provides various resize methods like
+`bilinear`, `nearest_neighbor`.
+
+### Converting Between Colorspaces
+
+Image ops work either on individual images or on batches of images, depending on
+the shape of their input Tensor.
+
+If 3-D, the shape is `[height, width, channels]`, and the Tensor represents one
+image. If 4-D, the shape is `[batch_size, height, width, channels]`, and the
+Tensor represents `batch_size` images.
+
+Currently, `channels` can usefully be 1, 2, 3, or 4. Single-channel images are
+grayscale, images with 3 channels are encoded as either RGB or HSV. Images
+with 2 or 4 channels include an alpha channel, which has to be stripped from the
+image before passing the image to most image processing functions (and can be
+re-attached later).
+
+Internally, images are either stored in as one `float32` per channel per pixel
+(implicitly, values are assumed to lie in `[0,1)`) or one `uint8` per channel
+per pixel (values are assumed to lie in `[0,255]`).
+
+TensorFlow can convert between images in RGB or HSV or YIQ.
+
+* tf.image.rgb_to_grayscale, tf.image.grayscale_to_rgb
+* tf.image.rgb_to_hsv, tf.image.hsv_to_rgb
+* tf.image.rgb_to_yiq, tf.image.yiq_to_rgb
+* tf.image.rgb_to_yuv, tf.image.yuv_to_rgb
+* tf.image.image_gradients
+* tf.image.convert_image_dtype
+
+### Image Adjustments
+
+TensorFlow provides functions to adjust images in various ways: brightness,
+contrast, hue, and saturation. Each adjustment can be done with predefined
+parameters or with random parameters picked from predefined intervals. Random
+adjustments are often useful to expand a training set and reduce overfitting.
+
+If several adjustments are chained it is advisable to minimize the number of
+redundant conversions by first converting the images to the most natural data
+type and representation.
+
+* tf.image.adjust_brightness
+* tf.image.adjust_contrast
+* tf.image.adjust_gamma
+* tf.image.adjust_hue
+* tf.image.adjust_jpeg_quality
+* tf.image.adjust_saturation
+* tf.image.random_brightness
+* tf.image.random_contrast
+* tf.image.random_hue
+* tf.image.random_saturation
+* tf.image.per_image_standardization
+
+### Working with Bounding Boxes
+
+* tf.image.draw_bounding_boxes
+* tf.image.combined_non_max_suppression
+* tf.image.generate_bounding_box_proposals
+* tf.image.non_max_suppression
+* tf.image.non_max_suppression_overlaps
+* tf.image.non_max_suppression_padded
+* tf.image.non_max_suppression_with_scores
+* tf.image.pad_to_bounding_box
+* tf.image.sample_distorted_bounding_box
+
+### Cropping
+
+* tf.image.central_crop
+* tf.image.crop_and_resize
+* tf.image.crop_to_bounding_box
+* tf.io.decode_and_crop_jpeg
+* tf.image.extract_glimpse
+* tf.image.random_crop
+* tf.image.resize_with_crop_or_pad
+
+### Flipping, Rotating and Transposing
+
+* tf.image.flip_left_right
+* tf.image.flip_up_down
+* tf.image.random_flip_left_right
+* tf.image.random_flip_up_down
+* tf.image.rot90
+* tf.image.transpose
+
+## Image decoding and encoding
+
+TensorFlow provides Ops to decode and encode JPEG and PNG formats. Encoded
+images are represented by scalar string Tensors, decoded images by 3-D uint8
+tensors of shape `[height, width, channels]`. (PNG also supports uint16.)
+
+Note: `decode_gif` returns a 4-D array `[num_frames, height, width, 3]`
+
+The encode and decode Ops apply to one image at a time. Their input and output
+are all of variable size. If you need fixed size images, pass the output of
+the decode Ops to one of the cropping and resizing Ops.
+
+* tf.io.decode_bmp
+* tf.io.decode_gif
+* tf.io.decode_image
+* tf.io.decode_jpeg
+* tf.io.decode_and_crop_jpeg
+* tf.io.decode_png
+* tf.io.encode_jpeg
+* tf.image.encode_png
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class ResizeMethod`](../../../tf/compat/v1/image/ResizeMethod.md): See v1.image.resize for details.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`adjust_brightness(...)`](../../../tf/image/adjust_brightness.md): Adjust the brightness of RGB or Grayscale images.
+
+[`adjust_contrast(...)`](../../../tf/image/adjust_contrast.md): Adjust contrast of RGB or grayscale images.
+
+[`adjust_gamma(...)`](../../../tf/image/adjust_gamma.md): Performs [Gamma Correction](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma_correction).
+
+[`adjust_hue(...)`](../../../tf/image/adjust_hue.md): Adjust hue of RGB images.
+
+[`adjust_jpeg_quality(...)`](../../../tf/image/adjust_jpeg_quality.md): Adjust jpeg encoding quality of an image.
+
+[`adjust_saturation(...)`](../../../tf/image/adjust_saturation.md): Adjust saturation of RGB images.
+
+[`central_crop(...)`](../../../tf/image/central_crop.md): Crop the central region of the image(s).
+
+[`combined_non_max_suppression(...)`](../../../tf/image/combined_non_max_suppression.md): Greedily selects a subset of bounding boxes in descending order of score.
+
+[`convert_image_dtype(...)`](../../../tf/image/convert_image_dtype.md): Convert `image` to `dtype`, scaling its values if needed.
+
+[`crop_and_resize(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/image/crop_and_resize.md): Extracts crops from the input image tensor and resizes them.
+
+[`crop_to_bounding_box(...)`](../../../tf/image/crop_to_bounding_box.md): Crops an image to a specified bounding box.
+
+[`decode_and_crop_jpeg(...)`](../../../tf/io/decode_and_crop_jpeg.md): Decode and Crop a JPEG-encoded image to a uint8 tensor.
+
+[`decode_bmp(...)`](../../../tf/io/decode_bmp.md): Decode the first frame of a BMP-encoded image to a uint8 tensor.
+
+[`decode_gif(...)`](../../../tf/io/decode_gif.md): Decode the frame(s) of a GIF-encoded image to a uint8 tensor.
+
+[`decode_image(...)`](../../../tf/io/decode_image.md): Function for `decode_bmp`, `decode_gif`, `decode_jpeg`, and `decode_png`.
+
+[`decode_jpeg(...)`](../../../tf/io/decode_jpeg.md): Decode a JPEG-encoded image to a uint8 tensor.
+
+[`decode_png(...)`](../../../tf/io/decode_png.md): Decode a PNG-encoded image to a uint8 or uint16 tensor.
+
+[`draw_bounding_boxes(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/image/draw_bounding_boxes.md): Draw bounding boxes on a batch of images.
+
+[`encode_jpeg(...)`](../../../tf/io/encode_jpeg.md): JPEG-encode an image.
+
+[`encode_png(...)`](../../../tf/image/encode_png.md): PNG-encode an image.
+
+[`extract_glimpse(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/image/extract_glimpse.md): Extracts a glimpse from the input tensor.
+
+[`extract_image_patches(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/extract_image_patches.md): Extract `patches` from `images` and put them in the "depth" output dimension.
+
+[`extract_jpeg_shape(...)`](../../../tf/io/extract_jpeg_shape.md): Extract the shape information of a JPEG-encoded image.
+
+[`extract_patches(...)`](../../../tf/image/extract_patches.md): Extract `patches` from `images`.
+
+[`flip_left_right(...)`](../../../tf/image/flip_left_right.md): Flip an image horizontally (left to right).
+
+[`flip_up_down(...)`](../../../tf/image/flip_up_down.md): Flip an image vertically (upside down).
+
+[`generate_bounding_box_proposals(...)`](../../../tf/image/generate_bounding_box_proposals.md): Generate bounding box proposals from encoded bounding boxes.
+
+[`grayscale_to_rgb(...)`](../../../tf/image/grayscale_to_rgb.md): Converts one or more images from Grayscale to RGB.
+
+[`hsv_to_rgb(...)`](../../../tf/image/hsv_to_rgb.md): Convert one or more images from HSV to RGB.
+
+[`image_gradients(...)`](../../../tf/image/image_gradients.md): Returns image gradients (dy, dx) for each color channel.
+
+[`is_jpeg(...)`](../../../tf/io/is_jpeg.md): Convenience function to check if the 'contents' encodes a JPEG image.
+
+[`non_max_suppression(...)`](../../../tf/image/non_max_suppression.md): Greedily selects a subset of bounding boxes in descending order of score.
+
+[`non_max_suppression_overlaps(...)`](../../../tf/image/non_max_suppression_overlaps.md): Greedily selects a subset of bounding boxes in descending order of score.
+
+[`non_max_suppression_padded(...)`](../../../tf/image/non_max_suppression_padded.md): Greedily selects a subset of bounding boxes in descending order of score.
+
+[`non_max_suppression_with_scores(...)`](../../../tf/image/non_max_suppression_with_scores.md): Greedily selects a subset of bounding boxes in descending order of score.
+
+[`pad_to_bounding_box(...)`](../../../tf/image/pad_to_bounding_box.md): Pad `image` with zeros to the specified `height` and `width`.
+
+[`per_image_standardization(...)`](../../../tf/image/per_image_standardization.md): Linearly scales each image in `image` to have mean 0 and variance 1.
+
+[`psnr(...)`](../../../tf/image/psnr.md): Returns the Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio between a and b.
+
+[`random_brightness(...)`](../../../tf/image/random_brightness.md): Adjust the brightness of images by a random factor.
+
+[`random_contrast(...)`](../../../tf/image/random_contrast.md): Adjust the contrast of an image or images by a random factor.
+
+[`random_crop(...)`](../../../tf/image/random_crop.md): Randomly crops a tensor to a given size.
+
+[`random_flip_left_right(...)`](../../../tf/image/random_flip_left_right.md): Randomly flip an image horizontally (left to right).
+
+[`random_flip_up_down(...)`](../../../tf/image/random_flip_up_down.md): Randomly flips an image vertically (upside down).
+
+[`random_hue(...)`](../../../tf/image/random_hue.md): Adjust the hue of RGB images by a random factor.
+
+[`random_jpeg_quality(...)`](../../../tf/image/random_jpeg_quality.md): Randomly changes jpeg encoding quality for inducing jpeg noise.
+
+[`random_saturation(...)`](../../../tf/image/random_saturation.md): Adjust the saturation of RGB images by a random factor.
+
+[`resize(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/image/resize.md): Resize `images` to `size` using the specified `method`.
+
+[`resize_area(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/image/resize_area.md): Resize `images` to `size` using area interpolation.
+
+[`resize_bicubic(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/image/resize_bicubic.md)
+
+[`resize_bilinear(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/image/resize_bilinear.md)
+
+[`resize_image_with_crop_or_pad(...)`](../../../tf/image/resize_with_crop_or_pad.md): Crops and/or pads an image to a target width and height.
+
+[`resize_image_with_pad(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/image/resize_image_with_pad.md): Resizes and pads an image to a target width and height.
+
+[`resize_images(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/image/resize.md): Resize `images` to `size` using the specified `method`.
+
+[`resize_nearest_neighbor(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/image/resize_nearest_neighbor.md)
+
+[`resize_with_crop_or_pad(...)`](../../../tf/image/resize_with_crop_or_pad.md): Crops and/or pads an image to a target width and height.
+
+[`rgb_to_grayscale(...)`](../../../tf/image/rgb_to_grayscale.md): Converts one or more images from RGB to Grayscale.
+
+[`rgb_to_hsv(...)`](../../../tf/image/rgb_to_hsv.md): Converts one or more images from RGB to HSV.
+
+[`rgb_to_yiq(...)`](../../../tf/image/rgb_to_yiq.md): Converts one or more images from RGB to YIQ.
+
+[`rgb_to_yuv(...)`](../../../tf/image/rgb_to_yuv.md): Converts one or more images from RGB to YUV.
+
+[`rot90(...)`](../../../tf/image/rot90.md): Rotate image(s) counter-clockwise by 90 degrees.
+
+[`sample_distorted_bounding_box(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/image/sample_distorted_bounding_box.md): Generate a single randomly distorted bounding box for an image. (deprecated)
+
+[`sobel_edges(...)`](../../../tf/image/sobel_edges.md): Returns a tensor holding Sobel edge maps.
+
+[`ssim(...)`](../../../tf/image/ssim.md): Computes SSIM index between img1 and img2.
+
+[`ssim_multiscale(...)`](../../../tf/image/ssim_multiscale.md): Computes the MS-SSIM between img1 and img2.
+
+[`total_variation(...)`](../../../tf/image/total_variation.md): Calculate and return the total variation for one or more images.
+
+[`transpose(...)`](../../../tf/image/transpose.md): Transpose image(s) by swapping the height and width dimension.
+
+[`transpose_image(...)`](../../../tf/image/transpose.md): Transpose image(s) by swapping the height and width dimension.
+
+[`yiq_to_rgb(...)`](../../../tf/image/yiq_to_rgb.md): Converts one or more images from YIQ to RGB.
+
+[`yuv_to_rgb(...)`](../../../tf/image/yuv_to_rgb.md): Converts one or more images from YUV to RGB.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image/ResizeMethod.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image/ResizeMethod.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..bd6100c8f3d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image/ResizeMethod.md
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
+description: See v1.image.resize for details.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.image.ResizeMethod
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+See v1.image.resize for details.
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `AREA = 3`
+* `BICUBIC = 2`
+* `BILINEAR = 0`
+* `NEAREST_NEIGHBOR = 1`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image/crop_and_resize.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image/crop_and_resize.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..853c642b3e9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image/crop_and_resize.md
@@ -0,0 +1,144 @@
+description: Extracts crops from the input image tensor and resizes them.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.image.crop_and_resize
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Extracts crops from the input image tensor and resizes them.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.image.crop_and_resize(
+ image, boxes, box_ind=None, crop_size=None, method='bilinear',
+ extrapolation_value=0, name=None, box_indices=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Extracts crops from the input image tensor and resizes them using bilinear
+sampling or nearest neighbor sampling (possibly with aspect ratio change) to a
+common output size specified by `crop_size`. This is more general than the
+`crop_to_bounding_box` op which extracts a fixed size slice from the input image
+and does not allow resizing or aspect ratio change.
+
+Returns a tensor with `crops` from the input `image` at positions defined at the
+bounding box locations in `boxes`. The cropped boxes are all resized (with
+bilinear or nearest neighbor interpolation) to a fixed
+`size = [crop_height, crop_width]`. The result is a 4-D tensor
+`[num_boxes, crop_height, crop_width, depth]`. The resizing is corner aligned.
+In particular, if `boxes = [[0, 0, 1, 1]]`, the method will give identical
+results to using `tf.image.resize_bilinear()` or
+`tf.image.resize_nearest_neighbor()`(depends on the `method` argument) with
+`align_corners=True`.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`image`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `uint8`, `uint16`, `int8`, `int16`, `int32`, `int64`, `half`, `float32`, `float64`.
+A 4-D tensor of shape `[batch, image_height, image_width, depth]`.
+Both `image_height` and `image_width` need to be positive.
+ |
+
+|
+`boxes`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `float32`.
+A 2-D tensor of shape `[num_boxes, 4]`. The `i`-th row of the tensor
+specifies the coordinates of a box in the `box_ind[i]` image and is specified
+in normalized coordinates `[y1, x1, y2, x2]`. A normalized coordinate value of
+`y` is mapped to the image coordinate at `y * (image_height - 1)`, so as the
+`[0, 1]` interval of normalized image height is mapped to
+`[0, image_height - 1]` in image height coordinates. We do allow `y1` > `y2`, in
+which case the sampled crop is an up-down flipped version of the original
+image. The width dimension is treated similarly. Normalized coordinates
+outside the `[0, 1]` range are allowed, in which case we use
+`extrapolation_value` to extrapolate the input image values.
+ |
+
+|
+`box_ind`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `int32`.
+A 1-D tensor of shape `[num_boxes]` with int32 values in `[0, batch)`.
+The value of `box_ind[i]` specifies the image that the `i`-th box refers to.
+ |
+
+|
+`crop_size`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `int32`.
+A 1-D tensor of 2 elements, `size = [crop_height, crop_width]`. All
+cropped image patches are resized to this size. The aspect ratio of the image
+content is not preserved. Both `crop_height` and `crop_width` need to be
+positive.
+ |
+
+|
+`method`
+ |
+
+An optional `string` from: `"bilinear", "nearest"`. Defaults to `"bilinear"`.
+A string specifying the sampling method for resizing. It can be either
+`"bilinear"` or `"nearest"` and default to `"bilinear"`. Currently two sampling
+methods are supported: Bilinear and Nearest Neighbor.
+ |
+
+|
+`extrapolation_value`
+ |
+
+An optional `float`. Defaults to `0`.
+Value used for extrapolation, when applicable.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` of type `float32`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image/draw_bounding_boxes.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image/draw_bounding_boxes.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..5f16d88f0ed
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image/draw_bounding_boxes.md
@@ -0,0 +1,125 @@
+description: Draw bounding boxes on a batch of images.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.image.draw_bounding_boxes
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Draw bounding boxes on a batch of images.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.image.draw_bounding_boxes(
+ images, boxes, name=None, colors=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Outputs a copy of `images` but draws on top of the pixels zero or more
+bounding boxes specified by the locations in `boxes`. The coordinates of the
+each bounding box in `boxes` are encoded as `[y_min, x_min, y_max, x_max]`.
+The bounding box coordinates are floats in `[0.0, 1.0]` relative to the width
+and the height of the underlying image.
+
+For example, if an image is 100 x 200 pixels (height x width) and the bounding
+box is `[0.1, 0.2, 0.5, 0.9]`, the upper-left and bottom-right coordinates of
+the bounding box will be `(40, 10)` to `(180, 50)` (in (x,y) coordinates).
+
+Parts of the bounding box may fall outside the image.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`images`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `float32`, `half`.
+4-D with shape `[batch, height, width, depth]`. A batch of images.
+ |
+
+|
+`boxes`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `float32`. 3-D with shape `[batch,
+num_bounding_boxes, 4]` containing bounding boxes.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`colors`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `float32`. 2-D. A list of RGBA colors to cycle
+through for the boxes.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `images`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Usage Example:
+
+
+
+```
+>>> # create an empty image
+>>> img = tf.zeros([1, 3, 3, 3])
+>>> # draw a box around the image
+>>> box = np.array([0, 0, 1, 1])
+>>> boxes = box.reshape([1, 1, 4])
+>>> # alternate between red and blue
+>>> colors = np.array([[1.0, 0.0, 0.0], [0.0, 0.0, 1.0]])
+>>> tf.image.draw_bounding_boxes(img, boxes, colors)
+
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image/extract_glimpse.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image/extract_glimpse.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e353958f37a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image/extract_glimpse.md
@@ -0,0 +1,162 @@
+description: Extracts a glimpse from the input tensor.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.image.extract_glimpse
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Extracts a glimpse from the input tensor.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.image.extract_glimpse(
+ input, size, offsets, centered=(True), normalized=(True), uniform_noise=(True),
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns a set of windows called glimpses extracted at location
+`offsets` from the input tensor. If the windows only partially
+overlaps the inputs, the non-overlapping areas will be filled with
+random noise.
+
+The result is a 4-D tensor of shape `[batch_size, glimpse_height,
+glimpse_width, channels]`. The channels and batch dimensions are the
+same as that of the input tensor. The height and width of the output
+windows are specified in the `size` parameter.
+
+The argument `normalized` and `centered` controls how the windows are built:
+
+* If the coordinates are normalized but not centered, 0.0 and 1.0
+ correspond to the minimum and maximum of each height and width
+ dimension.
+* If the coordinates are both normalized and centered, they range from
+ -1.0 to 1.0. The coordinates (-1.0, -1.0) correspond to the upper
+ left corner, the lower right corner is located at (1.0, 1.0) and the
+ center is at (0, 0).
+* If the coordinates are not normalized they are interpreted as
+ numbers of pixels.
+
+#### Usage Example:
+
+
+
+```
+>>> x = [[[[0.0],
+... [1.0],
+... [2.0]],
+... [[3.0],
+... [4.0],
+... [5.0]],
+... [[6.0],
+... [7.0],
+... [8.0]]]]
+>>> tf.image.extract_glimpse(x, size=(2, 2), offsets=[[1, 1]],
+... centered=False, normalized=False)
+
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `float32`. A 4-D float tensor of shape
+`[batch_size, height, width, channels]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`size`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `int32`. A 1-D tensor of 2 elements containing the
+size of the glimpses to extract. The glimpse height must be specified
+first, following by the glimpse width.
+ |
+
+|
+`offsets`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `float32`. A 2-D integer tensor of shape
+`[batch_size, 2]` containing the y, x locations of the center of each
+window.
+ |
+
+|
+`centered`
+ |
+
+An optional `bool`. Defaults to `True`. indicates if the offset
+coordinates are centered relative to the image, in which case the (0, 0)
+offset is relative to the center of the input images. If false, the (0,0)
+offset corresponds to the upper left corner of the input images.
+ |
+
+|
+`normalized`
+ |
+
+An optional `bool`. Defaults to `True`. indicates if the offset
+coordinates are normalized.
+ |
+
+|
+`uniform_noise`
+ |
+
+An optional `bool`. Defaults to `True`. indicates if the
+noise should be generated using a uniform distribution or a Gaussian
+distribution.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` of type `float32`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image/resize.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image/resize.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..d0b2ea96516
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image/resize.md
@@ -0,0 +1,172 @@
+description: Resize images to size using the specified method.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.image.resize
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Resize `images` to `size` using the specified `method`.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.image.resize_images`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.image.resize(
+ images, size, method=ResizeMethodV1.BILINEAR, align_corners=(False),
+ preserve_aspect_ratio=(False), name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Resized images will be distorted if their original aspect ratio is not
+the same as `size`. To avoid distortions see
+tf.image.resize_with_pad or tf.image.resize_with_crop_or_pad.
+
+The `method` can be one of:
+
+* `ResizeMethod.BILINEAR`: [Bilinear interpolation.](
+ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bilinear_interpolation)
+* `ResizeMethod.NEAREST_NEIGHBOR`: [Nearest neighbor interpolation.](
+ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nearest-neighbor_interpolation)
+* `ResizeMethod.BICUBIC`: [Bicubic interpolation.](
+ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bicubic_interpolation)
+* `ResizeMethod.AREA`: Area interpolation.
+
+The return value has the same type as `images` if `method` is
+`ResizeMethod.NEAREST_NEIGHBOR`. It will also have the same type as `images`
+if the size of `images` can be statically determined to be the same as `size`,
+because `images` is returned in this case. Otherwise, the return value has
+type `float32`.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`images`
+ |
+
+4-D Tensor of shape `[batch, height, width, channels]` or 3-D Tensor
+of shape `[height, width, channels]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`size`
+ |
+
+A 1-D int32 Tensor of 2 elements: `new_height, new_width`. The new
+size for the images.
+ |
+
+|
+`method`
+ |
+
+ResizeMethod. Defaults to `ResizeMethod.BILINEAR`.
+ |
+
+|
+`align_corners`
+ |
+
+bool. If True, the centers of the 4 corner pixels of the
+input and output tensors are aligned, preserving the values at the corner
+pixels. Defaults to `False`.
+ |
+
+|
+`preserve_aspect_ratio`
+ |
+
+Whether to preserve the aspect ratio. If this is set,
+then `images` will be resized to a size that fits in `size` while
+preserving the aspect ratio of the original image. Scales up the image if
+`size` is bigger than the current size of the `image`. Defaults to False.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for this operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if the shape of `images` is incompatible with the
+shape arguments to this function
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `size` has invalid shape or type.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if an unsupported resize method is specified.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+If `images` was 4-D, a 4-D float Tensor of shape
+`[batch, new_height, new_width, channels]`.
+If `images` was 3-D, a 3-D float Tensor of shape
+`[new_height, new_width, channels]`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image/resize_area.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image/resize_area.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..bd0505ef551
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image/resize_area.md
@@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
+description: Resize images to size using area interpolation.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.image.resize_area
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Resize `images` to `size` using area interpolation.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.image.resize_area(
+ images, size, align_corners=(False), name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Input images can be of different types but output images are always float.
+
+The range of pixel values for the output image might be slightly different
+from the range for the input image because of limited numerical precision.
+To guarantee an output range, for example `[0.0, 1.0]`, apply
+tf.clip_by_value to the output.
+
+Each output pixel is computed by first transforming the pixel's footprint into
+the input tensor and then averaging the pixels that intersect the footprint. An
+input pixel's contribution to the average is weighted by the fraction of its
+area that intersects the footprint. This is the same as OpenCV's INTER_AREA.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`images`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `int8`, `uint8`, `int16`, `uint16`, `int32`, `int64`, `half`, `float32`, `float64`.
+4-D with shape `[batch, height, width, channels]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`size`
+ |
+
+A 1-D int32 Tensor of 2 elements: `new_height, new_width`. The
+new size for the images.
+ |
+
+|
+`align_corners`
+ |
+
+An optional `bool`. Defaults to `False`.
+If true, the centers of the 4 corner pixels of the input and output tensors are
+aligned, preserving the values at the corner pixels. Defaults to false.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` of type `float32`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image/resize_bicubic.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image/resize_bicubic.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..2873b28bdfb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image/resize_bicubic.md
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.image.resize_bicubic
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.image.resize_bicubic(
+ images, size, align_corners=(False), name=None, half_pixel_centers=(False)
+)
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image/resize_bilinear.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image/resize_bilinear.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..dc6c2712705
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image/resize_bilinear.md
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.image.resize_bilinear
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.image.resize_bilinear(
+ images, size, align_corners=(False), name=None, half_pixel_centers=(False)
+)
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image/resize_image_with_pad.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image/resize_image_with_pad.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..8fd2e7a9ef5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image/resize_image_with_pad.md
@@ -0,0 +1,122 @@
+description: Resizes and pads an image to a target width and height.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.image.resize_image_with_pad
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Resizes and pads an image to a target width and height.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.image.resize_image_with_pad(
+ image, target_height, target_width, method=ResizeMethodV1.BILINEAR,
+ align_corners=(False)
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Resizes an image to a target width and height by keeping
+the aspect ratio the same without distortion. If the target
+dimensions don't match the image dimensions, the image
+is resized and then padded with zeroes to match requested
+dimensions.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`image`
+ |
+
+4-D Tensor of shape `[batch, height, width, channels]` or 3-D Tensor
+of shape `[height, width, channels]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`target_height`
+ |
+
+Target height.
+ |
+
+|
+`target_width`
+ |
+
+Target width.
+ |
+
+|
+`method`
+ |
+
+Method to use for resizing image. See `resize_images()`
+ |
+
+|
+`align_corners`
+ |
+
+bool. If True, the centers of the 4 corner pixels of the
+input and output tensors are aligned, preserving the values at the corner
+pixels. Defaults to `False`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `target_height` or `target_width` are zero or negative.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Resized and padded image.
+If `images` was 4-D, a 4-D float Tensor of shape
+`[batch, new_height, new_width, channels]`.
+If `images` was 3-D, a 3-D float Tensor of shape
+`[new_height, new_width, channels]`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image/resize_nearest_neighbor.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image/resize_nearest_neighbor.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..d1465a02478
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image/resize_nearest_neighbor.md
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.image.resize_nearest_neighbor
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.image.resize_nearest_neighbor(
+ images, size, align_corners=(False), name=None, half_pixel_centers=(False)
+)
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image/sample_distorted_bounding_box.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image/sample_distorted_bounding_box.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a86497ef200
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/image/sample_distorted_bounding_box.md
@@ -0,0 +1,217 @@
+description: Generate a single randomly distorted bounding box for an image. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.image.sample_distorted_bounding_box
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Generate a single randomly distorted bounding box for an image. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.image.sample_distorted_bounding_box(
+ image_size, bounding_boxes, seed=None, seed2=None, min_object_covered=0.1,
+ aspect_ratio_range=None, area_range=None, max_attempts=None,
+ use_image_if_no_bounding_boxes=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+`seed2` arg is deprecated.Use sample_distorted_bounding_box_v2 instead.
+
+Bounding box annotations are often supplied in addition to ground-truth labels
+in image recognition or object localization tasks. A common technique for
+training such a system is to randomly distort an image while preserving
+its content, i.e. *data augmentation*. This Op outputs a randomly distorted
+localization of an object, i.e. bounding box, given an `image_size`,
+`bounding_boxes` and a series of constraints.
+
+The output of this Op is a single bounding box that may be used to crop the
+original image. The output is returned as 3 tensors: `begin`, `size` and
+`bboxes`. The first 2 tensors can be fed directly into tf.slice to crop the
+image. The latter may be supplied to tf.image.draw_bounding_boxes to
+visualize what the bounding box looks like.
+
+Bounding boxes are supplied and returned as `[y_min, x_min, y_max, x_max]`.
+The
+bounding box coordinates are floats in `[0.0, 1.0]` relative to the width and
+height of the underlying image.
+
+For example,
+
+```python
+ # Generate a single distorted bounding box.
+ begin, size, bbox_for_draw = tf.image.sample_distorted_bounding_box(
+ tf.shape(image),
+ bounding_boxes=bounding_boxes,
+ min_object_covered=0.1)
+
+ # Draw the bounding box in an image summary.
+ image_with_box = tf.image.draw_bounding_boxes(tf.expand_dims(image, 0),
+ bbox_for_draw)
+ tf.compat.v1.summary.image('images_with_box', image_with_box)
+
+ # Employ the bounding box to distort the image.
+ distorted_image = tf.slice(image, begin, size)
+```
+
+Note that if no bounding box information is available, setting
+`use_image_if_no_bounding_boxes = True` will assume there is a single implicit
+bounding box covering the whole image. If `use_image_if_no_bounding_boxes` is
+false and no bounding boxes are supplied, an error is raised.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`image_size`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `uint8`, `int8`,
+`int16`, `int32`, `int64`. 1-D, containing `[height, width, channels]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`bounding_boxes`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `float32`. 3-D with shape `[batch, N, 4]`
+describing the N bounding boxes associated with the image.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+An optional `int`. Defaults to `0`. If either `seed` or `seed2` are
+set to non-zero, the random number generator is seeded by the given
+`seed`. Otherwise, it is seeded by a random seed.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed2`
+ |
+
+An optional `int`. Defaults to `0`. A second seed to avoid seed
+collision.
+ |
+
+|
+`min_object_covered`
+ |
+
+A Tensor of type `float32`. Defaults to `0.1`. The
+cropped area of the image must contain at least this fraction of any
+bounding box supplied. The value of this parameter should be non-negative.
+In the case of 0, the cropped area does not need to overlap any of the
+bounding boxes supplied.
+ |
+
+|
+`aspect_ratio_range`
+ |
+
+An optional list of `floats`. Defaults to `[0.75,
+1.33]`. The cropped area of the image must have an aspect ratio = width /
+height within this range.
+ |
+
+|
+`area_range`
+ |
+
+An optional list of `floats`. Defaults to `[0.05, 1]`. The
+cropped area of the image must contain a fraction of the supplied image
+within this range.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_attempts`
+ |
+
+An optional `int`. Defaults to `100`. Number of attempts at
+generating a cropped region of the image of the specified constraints.
+After `max_attempts` failures, return the entire image.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_image_if_no_bounding_boxes`
+ |
+
+An optional `bool`. Defaults to `False`.
+Controls behavior if no bounding boxes supplied. If true, assume an
+implicit bounding box covering the whole input. If false, raise an error.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A tuple of `Tensor` objects (begin, size, bboxes).
+ |
+
+
+|
+`begin`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `image_size`. 1-D, containing
+`[offset_height, offset_width, 0]`. Provide as input to
+tf.slice.
+ |
+
+|
+`size`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `image_size`. 1-D, containing
+`[target_height, target_width, -1]`. Provide as input to
+tf.slice.
+ |
+
+|
+`bboxes`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `float32`. 3-D with shape `[1, 1, 4]` containing
+the distorted bounding box.
+Provide as input to tf.image.draw_bounding_boxes.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/initialize_all_tables.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/initialize_all_tables.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..6a80253f1dd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/initialize_all_tables.md
@@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
+description: Returns an Op that initializes all tables of the default graph. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.initialize_all_tables
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns an Op that initializes all tables of the default graph. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.initialize_all_tables(
+ name='init_all_tables'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use `tf.tables_initializer` instead.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the initialization op.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Op that initializes all tables. Note that if there are
+not tables the returned Op is a NoOp.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/initialize_all_variables.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/initialize_all_variables.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..78788ab0b94
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/initialize_all_variables.md
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
+description: See tf.compat.v1.global_variables_initializer. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.initialize_all_variables
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+See tf.compat.v1.global_variables_initializer. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.initialize_all_variables()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed after 2017-03-02.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use `tf.global_variables_initializer` instead.
+
+ **NOTE** The output of this function should be used. If it is not, a warning will be logged or an error may be raised. To mark the output as used, call its .mark_used() method.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/initialize_local_variables.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/initialize_local_variables.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..1cb3e2c30b5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/initialize_local_variables.md
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
+description: See tf.compat.v1.local_variables_initializer. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.initialize_local_variables
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+See tf.compat.v1.local_variables_initializer. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.initialize_local_variables()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed after 2017-03-02.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use `tf.local_variables_initializer` instead.
+
+ **NOTE** The output of this function should be used. If it is not, a warning will be logged or an error may be raised. To mark the output as used, call its .mark_used() method.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/initialize_variables.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/initialize_variables.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..bbf6ec5a383
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/initialize_variables.md
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
+description: See tf.compat.v1.variables_initializer. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.initialize_variables
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+See tf.compat.v1.variables_initializer. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.initialize_variables(
+ var_list, name='init'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed after 2017-03-02.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use `tf.variables_initializer` instead.
+
+ **NOTE** The output of this function should be used. If it is not, a warning will be logged or an error may be raised. To mark the output as used, call its .mark_used() method.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/initializers.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/initializers.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a1e8c9cb49e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/initializers.md
@@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
+description: Public API for tf.initializers namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.initializers
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.initializers namespace.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class constant`](../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Constant.md): Initializer that generates tensors with constant values.
+
+[`class glorot_normal`](../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/glorot_normal.md): The Glorot normal initializer, also called Xavier normal initializer.
+
+[`class glorot_uniform`](../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/glorot_uniform.md): The Glorot uniform initializer, also called Xavier uniform initializer.
+
+[`class identity`](../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Identity.md): Initializer that generates the identity matrix.
+
+[`class ones`](../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Ones.md): Initializer that generates tensors initialized to 1.
+
+[`class orthogonal`](../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Orthogonal.md): Initializer that generates an orthogonal matrix.
+
+[`class random_normal`](../../../tf/compat/v1/random_normal_initializer.md): Initializer that generates tensors with a normal distribution.
+
+[`class random_uniform`](../../../tf/compat/v1/random_uniform_initializer.md): Initializer that generates tensors with a uniform distribution.
+
+[`class truncated_normal`](../../../tf/compat/v1/truncated_normal_initializer.md): Initializer that generates a truncated normal distribution.
+
+[`class uniform_unit_scaling`](../../../tf/compat/v1/uniform_unit_scaling_initializer.md): Initializer that generates tensors without scaling variance.
+
+[`class variance_scaling`](../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/VarianceScaling.md): Initializer capable of adapting its scale to the shape of weights tensors.
+
+[`class zeros`](../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Zeros.md): Initializer that generates tensors initialized to 0.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`global_variables(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/global_variables_initializer.md): Returns an Op that initializes global variables.
+
+[`he_normal(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/he_normal.md): He normal initializer.
+
+[`he_uniform(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/he_uniform.md): He uniform variance scaling initializer.
+
+[`lecun_normal(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/lecun_normal.md): LeCun normal initializer.
+
+[`lecun_uniform(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/lecun_uniform.md): LeCun uniform initializer.
+
+[`local_variables(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/local_variables_initializer.md): Returns an Op that initializes all local variables.
+
+[`tables_initializer(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/tables_initializer.md): Returns an Op that initializes all tables of the default graph.
+
+[`variables(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/variables_initializer.md): Returns an Op that initializes a list of variables.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/io.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/io.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..b8710e04bb2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/io.md
@@ -0,0 +1,117 @@
+description: Public API for tf.io namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.io
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.io namespace.
+
+
+
+## Modules
+
+[`gfile`](../../../tf/compat/v1/io/gfile.md) module: Public API for tf.io.gfile namespace.
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class FixedLenFeature`](../../../tf/io/FixedLenFeature.md): Configuration for parsing a fixed-length input feature.
+
+[`class FixedLenSequenceFeature`](../../../tf/io/FixedLenSequenceFeature.md): Configuration for parsing a variable-length input feature into a `Tensor`.
+
+[`class PaddingFIFOQueue`](../../../tf/queue/PaddingFIFOQueue.md): A FIFOQueue that supports batching variable-sized tensors by padding.
+
+[`class PriorityQueue`](../../../tf/queue/PriorityQueue.md): A queue implementation that dequeues elements in prioritized order.
+
+[`class QueueBase`](../../../tf/queue/QueueBase.md): Base class for queue implementations.
+
+[`class RaggedFeature`](../../../tf/io/RaggedFeature.md): Configuration for passing a RaggedTensor input feature.
+
+[`class RandomShuffleQueue`](../../../tf/queue/RandomShuffleQueue.md): A queue implementation that dequeues elements in a random order.
+
+[`class SparseFeature`](../../../tf/io/SparseFeature.md): Configuration for parsing a sparse input feature from an `Example`.
+
+[`class TFRecordCompressionType`](../../../tf/compat/v1/io/TFRecordCompressionType.md): The type of compression for the record.
+
+[`class TFRecordOptions`](../../../tf/io/TFRecordOptions.md): Options used for manipulating TFRecord files.
+
+[`class TFRecordWriter`](../../../tf/io/TFRecordWriter.md): A class to write records to a TFRecords file.
+
+[`class VarLenFeature`](../../../tf/io/VarLenFeature.md): Configuration for parsing a variable-length input feature.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`decode_and_crop_jpeg(...)`](../../../tf/io/decode_and_crop_jpeg.md): Decode and Crop a JPEG-encoded image to a uint8 tensor.
+
+[`decode_base64(...)`](../../../tf/io/decode_base64.md): Decode web-safe base64-encoded strings.
+
+[`decode_bmp(...)`](../../../tf/io/decode_bmp.md): Decode the first frame of a BMP-encoded image to a uint8 tensor.
+
+[`decode_compressed(...)`](../../../tf/io/decode_compressed.md): Decompress strings.
+
+[`decode_csv(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/decode_csv.md): Convert CSV records to tensors. Each column maps to one tensor.
+
+[`decode_gif(...)`](../../../tf/io/decode_gif.md): Decode the frame(s) of a GIF-encoded image to a uint8 tensor.
+
+[`decode_image(...)`](../../../tf/io/decode_image.md): Function for `decode_bmp`, `decode_gif`, `decode_jpeg`, and `decode_png`.
+
+[`decode_jpeg(...)`](../../../tf/io/decode_jpeg.md): Decode a JPEG-encoded image to a uint8 tensor.
+
+[`decode_json_example(...)`](../../../tf/io/decode_json_example.md): Convert JSON-encoded Example records to binary protocol buffer strings.
+
+[`decode_png(...)`](../../../tf/io/decode_png.md): Decode a PNG-encoded image to a uint8 or uint16 tensor.
+
+[`decode_proto(...)`](../../../tf/io/decode_proto.md): The op extracts fields from a serialized protocol buffers message into tensors.
+
+[`decode_raw(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/decode_raw.md): Convert raw byte strings into tensors. (deprecated arguments)
+
+[`deserialize_many_sparse(...)`](../../../tf/io/deserialize_many_sparse.md): Deserialize and concatenate `SparseTensors` from a serialized minibatch.
+
+[`encode_base64(...)`](../../../tf/io/encode_base64.md): Encode strings into web-safe base64 format.
+
+[`encode_jpeg(...)`](../../../tf/io/encode_jpeg.md): JPEG-encode an image.
+
+[`encode_proto(...)`](../../../tf/io/encode_proto.md): The op serializes protobuf messages provided in the input tensors.
+
+[`extract_jpeg_shape(...)`](../../../tf/io/extract_jpeg_shape.md): Extract the shape information of a JPEG-encoded image.
+
+[`is_jpeg(...)`](../../../tf/io/is_jpeg.md): Convenience function to check if the 'contents' encodes a JPEG image.
+
+[`match_filenames_once(...)`](../../../tf/io/match_filenames_once.md): Save the list of files matching pattern, so it is only computed once.
+
+[`matching_files(...)`](../../../tf/io/matching_files.md): Returns the set of files matching one or more glob patterns.
+
+[`parse_example(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/parse_example.md): Parses `Example` protos into a `dict` of tensors.
+
+[`parse_sequence_example(...)`](../../../tf/io/parse_sequence_example.md): Parses a batch of `SequenceExample` protos.
+
+[`parse_single_example(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/parse_single_example.md): Parses a single `Example` proto.
+
+[`parse_single_sequence_example(...)`](../../../tf/io/parse_single_sequence_example.md): Parses a single `SequenceExample` proto.
+
+[`parse_tensor(...)`](../../../tf/io/parse_tensor.md): Transforms a serialized tensorflow.TensorProto proto into a Tensor.
+
+[`read_file(...)`](../../../tf/io/read_file.md): Reads and outputs the entire contents of the input filename.
+
+[`serialize_many_sparse(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/serialize_many_sparse.md): Serialize `N`-minibatch `SparseTensor` into an `[N, 3]` `Tensor`.
+
+[`serialize_sparse(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/serialize_sparse.md): Serialize a `SparseTensor` into a 3-vector (1-D `Tensor`) object.
+
+[`serialize_tensor(...)`](../../../tf/io/serialize_tensor.md): Transforms a Tensor into a serialized TensorProto proto.
+
+[`tf_record_iterator(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/io/tf_record_iterator.md): An iterator that read the records from a TFRecords file. (deprecated)
+
+[`write_file(...)`](../../../tf/io/write_file.md): Writes contents to the file at input filename. Creates file and recursively
+
+[`write_graph(...)`](../../../tf/io/write_graph.md): Writes a graph proto to a file.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/io/TFRecordCompressionType.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/io/TFRecordCompressionType.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a01c6ad6c2a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/io/TFRecordCompressionType.md
@@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
+description: The type of compression for the record.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.io.TFRecordCompressionType
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The type of compression for the record.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.python_io.TFRecordCompressionType`
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `GZIP = 2`
+* `NONE = 0`
+* `ZLIB = 1`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/io/gfile.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/io/gfile.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3258f8be295
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/io/gfile.md
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
+description: Public API for tf.io.gfile namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.io.gfile
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.io.gfile namespace.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class GFile`](../../../../tf/io/gfile/GFile.md): File I/O wrappers without thread locking.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`copy(...)`](../../../../tf/io/gfile/copy.md): Copies data from `src` to `dst`.
+
+[`exists(...)`](../../../../tf/io/gfile/exists.md): Determines whether a path exists or not.
+
+[`glob(...)`](../../../../tf/io/gfile/glob.md): Returns a list of files that match the given pattern(s).
+
+[`isdir(...)`](../../../../tf/io/gfile/isdir.md): Returns whether the path is a directory or not.
+
+[`listdir(...)`](../../../../tf/io/gfile/listdir.md): Returns a list of entries contained within a directory.
+
+[`makedirs(...)`](../../../../tf/io/gfile/makedirs.md): Creates a directory and all parent/intermediate directories.
+
+[`mkdir(...)`](../../../../tf/io/gfile/mkdir.md): Creates a directory with the name given by `path`.
+
+[`remove(...)`](../../../../tf/io/gfile/remove.md): Deletes the path located at 'path'.
+
+[`rename(...)`](../../../../tf/io/gfile/rename.md): Rename or move a file / directory.
+
+[`rmtree(...)`](../../../../tf/io/gfile/rmtree.md): Deletes everything under path recursively.
+
+[`stat(...)`](../../../../tf/io/gfile/stat.md): Returns file statistics for a given path.
+
+[`walk(...)`](../../../../tf/io/gfile/walk.md): Recursive directory tree generator for directories.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/io/tf_record_iterator.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/io/tf_record_iterator.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..6e9cb157c80
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/io/tf_record_iterator.md
@@ -0,0 +1,103 @@
+description: An iterator that read the records from a TFRecords file. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.io.tf_record_iterator
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+An iterator that read the records from a TFRecords file. (deprecated)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.python_io.tf_record_iterator`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.io.tf_record_iterator(
+ path, options=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use eager execution and:
+tf.data.TFRecordDataset(path)
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`path`
+ |
+
+The path to the TFRecords file.
+ |
+
+|
+`options`
+ |
+
+(optional) A TFRecordOptions object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An iterator of serialized TFRecords.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`IOError`
+ |
+
+If `path` cannot be opened for reading.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/is_variable_initialized.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/is_variable_initialized.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..c17fd315f25
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/is_variable_initialized.md
@@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
+description: Tests if a variable has been initialized.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.is_variable_initialized
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Tests if a variable has been initialized.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.is_variable_initialized(
+ variable
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`variable`
+ |
+
+A `Variable`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Returns a scalar boolean Tensor, `True` if the variable has been
+initialized, `False` otherwise.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+**NOTE** The output of this function should be used. If it is not, a warning will be logged or an error may be raised. To mark the output as used, call its .mark_used() method.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..9341eb74718
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras.md
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
+description: Implementation of the Keras API meant to be a high-level API for TensorFlow.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Implementation of the Keras API meant to be a high-level API for TensorFlow.
+
+
+Detailed documentation and user guides are available at
+[tensorflow.org](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/keras).
+
+## Modules
+
+[`activations`](../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/activations.md) module: Built-in activation functions.
+
+[`applications`](../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/applications.md) module: Keras Applications are canned architectures with pre-trained weights.
+
+[`backend`](../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/backend.md) module: Keras backend API.
+
+[`callbacks`](../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/callbacks.md) module: Callbacks: utilities called at certain points during model training.
+
+[`constraints`](../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/constraints.md) module: Constraints: functions that impose constraints on weight values.
+
+[`datasets`](../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/datasets.md) module: Public API for tf.keras.datasets namespace.
+
+[`estimator`](../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/estimator.md) module: Keras estimator API.
+
+[`experimental`](../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/experimental.md) module: Public API for tf.keras.experimental namespace.
+
+[`initializers`](../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers.md) module: Keras initializer serialization / deserialization.
+
+[`layers`](../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/layers.md) module: Keras layers API.
+
+[`losses`](../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/losses.md) module: Built-in loss functions.
+
+[`metrics`](../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/metrics.md) module: Built-in metrics.
+
+[`mixed_precision`](../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/mixed_precision.md) module: Public API for tf.keras.mixed_precision namespace.
+
+[`models`](../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/models.md) module: Code for model cloning, plus model-related API entries.
+
+[`optimizers`](../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/optimizers.md) module: Built-in optimizer classes.
+
+[`preprocessing`](../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/preprocessing.md) module: Keras data preprocessing utils.
+
+[`regularizers`](../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/regularizers.md) module: Built-in regularizers.
+
+[`utils`](../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/utils.md) module: Public API for tf.keras.utils namespace.
+
+[`wrappers`](../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/wrappers.md) module: Public API for tf.keras.wrappers namespace.
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class Model`](../../../tf/keras/Model.md): `Model` groups layers into an object with training and inference features.
+
+[`class Sequential`](../../../tf/keras/Sequential.md): `Sequential` groups a linear stack of layers into a tf.keras.Model.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`Input(...)`](../../../tf/keras/Input.md): `Input()` is used to instantiate a Keras tensor.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/activations.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/activations.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..615eb38fd4e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/activations.md
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+description: Built-in activation functions.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.activations
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Built-in activation functions.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`deserialize(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/activations/deserialize.md): Returns activation function denoted by input string.
+
+[`elu(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/activations/elu.md): Exponential linear unit.
+
+[`exponential(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/activations/exponential.md): Exponential activation function.
+
+[`get(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/activations/get.md): Returns function.
+
+[`hard_sigmoid(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/activations/hard_sigmoid.md): Hard sigmoid activation function.
+
+[`linear(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/activations/linear.md): Linear activation function.
+
+[`relu(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/activations/relu.md): Applies the rectified linear unit activation function.
+
+[`selu(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/activations/selu.md): Scaled Exponential Linear Unit (SELU).
+
+[`serialize(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/activations/serialize.md): Returns name attribute (`__name__`) of function.
+
+[`sigmoid(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/activations/sigmoid.md): Sigmoid activation function.
+
+[`softmax(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/activations/softmax.md): Softmax converts a real vector to a vector of categorical probabilities.
+
+[`softplus(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/activations/softplus.md): Softplus activation function.
+
+[`softsign(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/activations/softsign.md): Softsign activation function.
+
+[`swish(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/activations/swish.md): Swish activation function.
+
+[`tanh(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/activations/tanh.md): Hyperbolic tangent activation function.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..891c5977239
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications.md
@@ -0,0 +1,87 @@
+description: Keras Applications are canned architectures with pre-trained weights.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.applications
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Keras Applications are canned architectures with pre-trained weights.
+
+
+
+## Modules
+
+[`densenet`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/densenet.md) module: DenseNet models for Keras.
+
+[`imagenet_utils`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/imagenet_utils.md) module: Utilities for ImageNet data preprocessing & prediction decoding.
+
+[`inception_resnet_v2`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/inception_resnet_v2.md) module: Inception-ResNet V2 model for Keras.
+
+[`inception_v3`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/inception_v3.md) module: Inception V3 model for Keras.
+
+[`mobilenet`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/mobilenet.md) module: MobileNet v1 models for Keras.
+
+[`mobilenet_v2`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/mobilenet_v2.md) module: MobileNet v2 models for Keras.
+
+[`nasnet`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/nasnet.md) module: NASNet-A models for Keras.
+
+[`resnet`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/resnet.md) module: ResNet models for Keras.
+
+[`resnet50`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/resnet50.md) module: Public API for tf.keras.applications.resnet50 namespace.
+
+[`resnet_v2`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/resnet_v2.md) module: ResNet v2 models for Keras.
+
+[`vgg16`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/vgg16.md) module: VGG16 model for Keras.
+
+[`vgg19`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/vgg19.md) module: VGG19 model for Keras.
+
+[`xception`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/xception.md) module: Xception V1 model for Keras.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`DenseNet121(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/applications/DenseNet121.md): Instantiates the Densenet121 architecture.
+
+[`DenseNet169(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/applications/DenseNet169.md): Instantiates the Densenet169 architecture.
+
+[`DenseNet201(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/applications/DenseNet201.md): Instantiates the Densenet201 architecture.
+
+[`InceptionResNetV2(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/applications/InceptionResNetV2.md): Instantiates the Inception-ResNet v2 architecture.
+
+[`InceptionV3(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/applications/InceptionV3.md): Instantiates the Inception v3 architecture.
+
+[`MobileNet(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/applications/MobileNet.md): Instantiates the MobileNet architecture.
+
+[`MobileNetV2(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/applications/MobileNetV2.md): Instantiates the MobileNetV2 architecture.
+
+[`NASNetLarge(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/applications/NASNetLarge.md): Instantiates a NASNet model in ImageNet mode.
+
+[`NASNetMobile(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/applications/NASNetMobile.md): Instantiates a Mobile NASNet model in ImageNet mode.
+
+[`ResNet101(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/applications/ResNet101.md): Instantiates the ResNet101 architecture.
+
+[`ResNet101V2(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/applications/ResNet101V2.md): Instantiates the ResNet101V2 architecture.
+
+[`ResNet152(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/applications/ResNet152.md): Instantiates the ResNet152 architecture.
+
+[`ResNet152V2(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/applications/ResNet152V2.md): Instantiates the ResNet152V2 architecture.
+
+[`ResNet50(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/applications/ResNet50.md): Instantiates the ResNet50 architecture.
+
+[`ResNet50V2(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/applications/ResNet50V2.md): Instantiates the ResNet50V2 architecture.
+
+[`VGG16(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/applications/VGG16.md): Instantiates the VGG16 model.
+
+[`VGG19(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/applications/VGG19.md): Instantiates the VGG19 architecture.
+
+[`Xception(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/applications/Xception.md): Instantiates the Xception architecture.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/densenet.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/densenet.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..b4125b6539f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/densenet.md
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
+description: DenseNet models for Keras.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.applications.densenet
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+DenseNet models for Keras.
+
+
+
+#### Reference paper:
+
+- [Densely Connected Convolutional Networks]
+ (https://arxiv.org/abs/1608.06993) (CVPR 2017 Best Paper Award)
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`DenseNet121(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/DenseNet121.md): Instantiates the Densenet121 architecture.
+
+[`DenseNet169(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/DenseNet169.md): Instantiates the Densenet169 architecture.
+
+[`DenseNet201(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/DenseNet201.md): Instantiates the Densenet201 architecture.
+
+[`decode_predictions(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/densenet/decode_predictions.md): Decodes the prediction of an ImageNet model.
+
+[`preprocess_input(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/densenet/preprocess_input.md): Preprocesses a tensor or Numpy array encoding a batch of images.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/imagenet_utils.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/imagenet_utils.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..2c355159131
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/imagenet_utils.md
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
+description: Utilities for ImageNet data preprocessing & prediction decoding.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.applications.imagenet_utils
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Utilities for ImageNet data preprocessing & prediction decoding.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`decode_predictions(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/imagenet_utils/decode_predictions.md): Decodes the prediction of an ImageNet model.
+
+[`preprocess_input(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/imagenet_utils/preprocess_input.md): Preprocesses a tensor or Numpy array encoding a batch of images.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/inception_resnet_v2.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/inception_resnet_v2.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..26216d21638
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/inception_resnet_v2.md
@@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
+description: Inception-ResNet V2 model for Keras.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.applications.inception_resnet_v2
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Inception-ResNet V2 model for Keras.
+
+
+
+#### Reference paper:
+
+- [Inception-v4, Inception-ResNet and the Impact of
+ Residual Connections on Learning](https://arxiv.org/abs/1602.07261)
+ (AAAI 2017)
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`InceptionResNetV2(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/InceptionResNetV2.md): Instantiates the Inception-ResNet v2 architecture.
+
+[`decode_predictions(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/inception_resnet_v2/decode_predictions.md): Decodes the prediction of an ImageNet model.
+
+[`preprocess_input(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/inception_resnet_v2/preprocess_input.md): Preprocesses a tensor or Numpy array encoding a batch of images.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/inception_v3.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/inception_v3.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..4e630045daf
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/inception_v3.md
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
+description: Inception V3 model for Keras.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.applications.inception_v3
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Inception V3 model for Keras.
+
+
+
+#### Reference paper:
+
+- [Rethinking the Inception Architecture for Computer Vision](
+ http://arxiv.org/abs/1512.00567) (CVPR 2016)
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`InceptionV3(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/InceptionV3.md): Instantiates the Inception v3 architecture.
+
+[`decode_predictions(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/inception_v3/decode_predictions.md): Decodes the prediction of an ImageNet model.
+
+[`preprocess_input(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/inception_v3/preprocess_input.md): Preprocesses a tensor or Numpy array encoding a batch of images.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/mobilenet.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/mobilenet.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..2859d6ae391
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/mobilenet.md
@@ -0,0 +1,75 @@
+description: MobileNet v1 models for Keras.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.applications.mobilenet
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+MobileNet v1 models for Keras.
+
+
+MobileNet is a general architecture and can be used for multiple use cases.
+Depending on the use case, it can use different input layer size and
+different width factors. This allows different width models to reduce
+the number of multiply-adds and thereby
+reduce inference cost on mobile devices.
+
+MobileNets support any input size greater than 32 x 32, with larger image sizes
+offering better performance.
+The number of parameters and number of multiply-adds
+can be modified by using the `alpha` parameter,
+which increases/decreases the number of filters in each layer.
+By altering the image size and `alpha` parameter,
+all 16 models from the paper can be built, with ImageNet weights provided.
+
+The paper demonstrates the performance of MobileNets using `alpha` values of
+1.0 (also called 100 % MobileNet), 0.75, 0.5 and 0.25.
+For each of these `alpha` values, weights for 4 different input image sizes
+are provided (224, 192, 160, 128).
+
+The following table describes the size and accuracy of the 100% MobileNet
+on size 224 x 224:
+----------------------------------------------------------------------------
+Width Multiplier (alpha) | ImageNet Acc | Multiply-Adds (M) | Params (M)
+----------------------------------------------------------------------------
+| 1.0 MobileNet-224 | 70.6 % | 529 | 4.2 |
+| 0.75 MobileNet-224 | 68.4 % | 325 | 2.6 |
+| 0.50 MobileNet-224 | 63.7 % | 149 | 1.3 |
+| 0.25 MobileNet-224 | 50.6 % | 41 | 0.5 |
+----------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+The following table describes the performance of
+the 100 % MobileNet on various input sizes:
+------------------------------------------------------------------------
+ Resolution | ImageNet Acc | Multiply-Adds (M) | Params (M)
+------------------------------------------------------------------------
+| 1.0 MobileNet-224 | 70.6 % | 529 | 4.2 |
+| 1.0 MobileNet-192 | 69.1 % | 529 | 4.2 |
+| 1.0 MobileNet-160 | 67.2 % | 529 | 4.2 |
+| 1.0 MobileNet-128 | 64.4 % | 529 | 4.2 |
+------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+#### Reference paper:
+
+- [MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for
+ Mobile Vision Applications](https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.04861)
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`MobileNet(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/MobileNet.md): Instantiates the MobileNet architecture.
+
+[`decode_predictions(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/mobilenet/decode_predictions.md): Decodes the prediction of an ImageNet model.
+
+[`preprocess_input(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/mobilenet/preprocess_input.md): Preprocesses a tensor or Numpy array encoding a batch of images.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/mobilenet_v2.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/mobilenet_v2.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..df2ceccf923
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/mobilenet_v2.md
@@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
+description: MobileNet v2 models for Keras.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.applications.mobilenet_v2
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+MobileNet v2 models for Keras.
+
+
+MobileNetV2 is a general architecture and can be used for multiple use cases.
+Depending on the use case, it can use different input layer size and
+different width factors. This allows different width models to reduce
+the number of multiply-adds and thereby
+reduce inference cost on mobile devices.
+
+MobileNetV2 is very similar to the original MobileNet,
+except that it uses inverted residual blocks with
+bottlenecking features. It has a drastically lower
+parameter count than the original MobileNet.
+MobileNets support any input size greater
+than 32 x 32, with larger image sizes
+offering better performance.
+
+The number of parameters and number of multiply-adds
+can be modified by using the `alpha` parameter,
+which increases/decreases the number of filters in each layer.
+By altering the image size and `alpha` parameter,
+all 22 models from the paper can be built, with ImageNet weights provided.
+
+The paper demonstrates the performance of MobileNets using `alpha` values of
+1.0 (also called 100 % MobileNet), 0.35, 0.5, 0.75, 1.0, 1.3, and 1.4
+For each of these `alpha` values, weights for 5 different input image sizes
+are provided (224, 192, 160, 128, and 96).
+
+The following table describes the performance of
+MobileNet on various input sizes:
+------------------------------------------------------------------------
+MACs stands for Multiply Adds
+ Classification Checkpoint|MACs (M)|Parameters (M)|Top 1 Accuracy|Top 5 Accuracy
+--------------------------|------------|---------------|---------|----|---------
+| [mobilenet_v2_1.4_224] | 582 | 6.06 | 75.0 | 92.5 |
+| [mobilenet_v2_1.3_224] | 509 | 5.34 | 74.4 | 92.1 |
+| [mobilenet_v2_1.0_224] | 300 | 3.47 | 71.8 | 91.0 |
+| [mobilenet_v2_1.0_192] | 221 | 3.47 | 70.7 | 90.1 |
+| [mobilenet_v2_1.0_160] | 154 | 3.47 | 68.8 | 89.0 |
+| [mobilenet_v2_1.0_128] | 99 | 3.47 | 65.3 | 86.9 |
+| [mobilenet_v2_1.0_96] | 56 | 3.47 | 60.3 | 83.2 |
+| [mobilenet_v2_0.75_224] | 209 | 2.61 | 69.8 | 89.6 |
+| [mobilenet_v2_0.75_192] | 153 | 2.61 | 68.7 | 88.9 |
+| [mobilenet_v2_0.75_160] | 107 | 2.61 | 66.4 | 87.3 |
+| [mobilenet_v2_0.75_128] | 69 | 2.61 | 63.2 | 85.3 |
+| [mobilenet_v2_0.75_96] | 39 | 2.61 | 58.8 | 81.6 |
+| [mobilenet_v2_0.5_224] | 97 | 1.95 | 65.4 | 86.4 |
+| [mobilenet_v2_0.5_192] | 71 | 1.95 | 63.9 | 85.4 |
+| [mobilenet_v2_0.5_160] | 50 | 1.95 | 61.0 | 83.2 |
+| [mobilenet_v2_0.5_128] | 32 | 1.95 | 57.7 | 80.8 |
+| [mobilenet_v2_0.5_96] | 18 | 1.95 | 51.2 | 75.8 |
+| [mobilenet_v2_0.35_224] | 59 | 1.66 | 60.3 | 82.9 |
+| [mobilenet_v2_0.35_192] | 43 | 1.66 | 58.2 | 81.2 |
+| [mobilenet_v2_0.35_160] | 30 | 1.66 | 55.7 | 79.1 |
+| [mobilenet_v2_0.35_128] | 20 | 1.66 | 50.8 | 75.0 |
+| [mobilenet_v2_0.35_96] | 11 | 1.66 | 45.5 | 70.4 |
+
+## Functions
+
+[`MobileNetV2(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/MobileNetV2.md): Instantiates the MobileNetV2 architecture.
+
+[`decode_predictions(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/mobilenet_v2/decode_predictions.md): Decodes the prediction of an ImageNet model.
+
+[`preprocess_input(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/mobilenet_v2/preprocess_input.md): Preprocesses a tensor or Numpy array encoding a batch of images.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/nasnet.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/nasnet.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..0834737a7ea
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/nasnet.md
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
+description: NASNet-A models for Keras.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.applications.nasnet
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+NASNet-A models for Keras.
+
+
+NASNet refers to Neural Architecture Search Network, a family of models
+that were designed automatically by learning the model architectures
+directly on the dataset of interest.
+
+Here we consider NASNet-A, the highest performance model that was found
+for the CIFAR-10 dataset, and then extended to ImageNet 2012 dataset,
+obtaining state of the art performance on CIFAR-10 and ImageNet 2012.
+Only the NASNet-A models, and their respective weights, which are suited
+for ImageNet 2012 are provided.
+
+The below table describes the performance on ImageNet 2012:
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+ Architecture | Top-1 Acc | Top-5 Acc | Multiply-Adds | Params (M)
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+| NASNet-A (4 @ 1056) | 74.0 % | 91.6 % | 564 M | 5.3 |
+| NASNet-A (6 @ 4032) | 82.7 % | 96.2 % | 23.8 B | 88.9 |
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+#### References:
+
+- [Learning Transferable Architectures for Scalable Image Recognition]
+ (https://arxiv.org/abs/1707.07012) (CVPR 2018)
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`NASNetLarge(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/NASNetLarge.md): Instantiates a NASNet model in ImageNet mode.
+
+[`NASNetMobile(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/NASNetMobile.md): Instantiates a Mobile NASNet model in ImageNet mode.
+
+[`decode_predictions(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/nasnet/decode_predictions.md): Decodes the prediction of an ImageNet model.
+
+[`preprocess_input(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/nasnet/preprocess_input.md): Preprocesses a tensor or Numpy array encoding a batch of images.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/resnet.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/resnet.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a70342a3f3e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/resnet.md
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+description: ResNet models for Keras.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.applications.resnet
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ResNet models for Keras.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`ResNet101(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/ResNet101.md): Instantiates the ResNet101 architecture.
+
+[`ResNet152(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/ResNet152.md): Instantiates the ResNet152 architecture.
+
+[`ResNet50(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/ResNet50.md): Instantiates the ResNet50 architecture.
+
+[`decode_predictions(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/resnet/decode_predictions.md): Decodes the prediction of an ImageNet model.
+
+[`preprocess_input(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/resnet/preprocess_input.md): Preprocesses a tensor or Numpy array encoding a batch of images.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/resnet50.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/resnet50.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..80c33a0f170
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/resnet50.md
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+description: Public API for tf.keras.applications.resnet50 namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.applications.resnet50
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.keras.applications.resnet50 namespace.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`ResNet50(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/ResNet50.md): Instantiates the ResNet50 architecture.
+
+[`decode_predictions(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/resnet/decode_predictions.md): Decodes the prediction of an ImageNet model.
+
+[`preprocess_input(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/resnet/preprocess_input.md): Preprocesses a tensor or Numpy array encoding a batch of images.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/resnet_v2.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/resnet_v2.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..76f42b012d7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/resnet_v2.md
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+description: ResNet v2 models for Keras.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.applications.resnet_v2
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ResNet v2 models for Keras.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`ResNet101V2(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/ResNet101V2.md): Instantiates the ResNet101V2 architecture.
+
+[`ResNet152V2(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/ResNet152V2.md): Instantiates the ResNet152V2 architecture.
+
+[`ResNet50V2(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/ResNet50V2.md): Instantiates the ResNet50V2 architecture.
+
+[`decode_predictions(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/resnet_v2/decode_predictions.md): Decodes the prediction of an ImageNet model.
+
+[`preprocess_input(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/resnet_v2/preprocess_input.md): Preprocesses a tensor or Numpy array encoding a batch of images.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/vgg16.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/vgg16.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..747c2abbcfc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/vgg16.md
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+description: VGG16 model for Keras.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.applications.vgg16
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+VGG16 model for Keras.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`VGG16(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/VGG16.md): Instantiates the VGG16 model.
+
+[`decode_predictions(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/vgg16/decode_predictions.md): Decodes the prediction of an ImageNet model.
+
+[`preprocess_input(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/vgg16/preprocess_input.md): Preprocesses a tensor or Numpy array encoding a batch of images.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/vgg19.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/vgg19.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..206f5a81731
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/vgg19.md
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
+description: VGG19 model for Keras.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.applications.vgg19
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+VGG19 model for Keras.
+
+
+
+#### Reference:
+
+- [Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition](
+ https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556) (ICLR 2015)
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`VGG19(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/VGG19.md): Instantiates the VGG19 architecture.
+
+[`decode_predictions(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/vgg19/decode_predictions.md): Decodes the prediction of an ImageNet model.
+
+[`preprocess_input(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/vgg19/preprocess_input.md): Preprocesses a tensor or Numpy array encoding a batch of images.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/xception.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/xception.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..5c50e752ade
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/applications/xception.md
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
+description: Xception V1 model for Keras.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.applications.xception
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Xception V1 model for Keras.
+
+
+On ImageNet, this model gets to a top-1 validation accuracy of 0.790
+and a top-5 validation accuracy of 0.945.
+
+#### Reference paper:
+
+- [Xception: Deep Learning with Depthwise Separable Convolutions](
+ https://arxiv.org/abs/1610.02357) (CVPR 2017)
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`Xception(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/Xception.md): Instantiates the Xception architecture.
+
+[`decode_predictions(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/xception/decode_predictions.md): Decodes the prediction of an ImageNet model.
+
+[`preprocess_input(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/applications/xception/preprocess_input.md): Preprocesses a tensor or Numpy array encoding a batch of images.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/backend.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/backend.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..8f0454ee6b0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/backend.md
@@ -0,0 +1,317 @@
+description: Keras backend API.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.backend
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Keras backend API.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class name_scope`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/backend/name_scope.md): A context manager for use when defining a Python op.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`abs(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/abs.md): Element-wise absolute value.
+
+[`all(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/all.md): Bitwise reduction (logical AND).
+
+[`any(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/any.md): Bitwise reduction (logical OR).
+
+[`arange(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/arange.md): Creates a 1D tensor containing a sequence of integers.
+
+[`argmax(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/argmax.md): Returns the index of the maximum value along an axis.
+
+[`argmin(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/argmin.md): Returns the index of the minimum value along an axis.
+
+[`backend(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/backend.md): Publicly accessible method for determining the current backend.
+
+[`batch_dot(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/batch_dot.md): Batchwise dot product.
+
+[`batch_flatten(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/batch_flatten.md): Turn a nD tensor into a 2D tensor with same 0th dimension.
+
+[`batch_get_value(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/batch_get_value.md): Returns the value of more than one tensor variable.
+
+[`batch_normalization(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/batch_normalization.md): Applies batch normalization on x given mean, var, beta and gamma.
+
+[`batch_set_value(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/batch_set_value.md): Sets the values of many tensor variables at once.
+
+[`bias_add(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/bias_add.md): Adds a bias vector to a tensor.
+
+[`binary_crossentropy(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/binary_crossentropy.md): Binary crossentropy between an output tensor and a target tensor.
+
+[`cast(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/cast.md): Casts a tensor to a different dtype and returns it.
+
+[`cast_to_floatx(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/cast_to_floatx.md): Cast a Numpy array to the default Keras float type.
+
+[`categorical_crossentropy(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/categorical_crossentropy.md): Categorical crossentropy between an output tensor and a target tensor.
+
+[`clear_session(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/clear_session.md): Destroys the current TF graph and session, and creates a new one.
+
+[`clip(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/clip.md): Element-wise value clipping.
+
+[`concatenate(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/concatenate.md): Concatenates a list of tensors alongside the specified axis.
+
+[`constant(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/constant.md): Creates a constant tensor.
+
+[`conv1d(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/conv1d.md): 1D convolution.
+
+[`conv2d(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/conv2d.md): 2D convolution.
+
+[`conv2d_transpose(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/conv2d_transpose.md): 2D deconvolution (i.e.
+
+[`conv3d(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/conv3d.md): 3D convolution.
+
+[`cos(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/cos.md): Computes cos of x element-wise.
+
+[`count_params(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/count_params.md): Returns the static number of elements in a variable or tensor.
+
+[`ctc_batch_cost(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/ctc_batch_cost.md): Runs CTC loss algorithm on each batch element.
+
+[`ctc_decode(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/ctc_decode.md): Decodes the output of a softmax.
+
+[`ctc_label_dense_to_sparse(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/ctc_label_dense_to_sparse.md): Converts CTC labels from dense to sparse.
+
+[`cumprod(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/cumprod.md): Cumulative product of the values in a tensor, alongside the specified axis.
+
+[`cumsum(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/cumsum.md): Cumulative sum of the values in a tensor, alongside the specified axis.
+
+[`depthwise_conv2d(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/depthwise_conv2d.md): 2D convolution with separable filters.
+
+[`dot(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/dot.md): Multiplies 2 tensors (and/or variables) and returns a tensor.
+
+[`dropout(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/dropout.md): Sets entries in `x` to zero at random, while scaling the entire tensor.
+
+[`dtype(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/dtype.md): Returns the dtype of a Keras tensor or variable, as a string.
+
+[`elu(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/elu.md): Exponential linear unit.
+
+[`epsilon(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/epsilon.md): Returns the value of the fuzz factor used in numeric expressions.
+
+[`equal(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/equal.md): Element-wise equality between two tensors.
+
+[`eval(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/eval.md): Evaluates the value of a variable.
+
+[`exp(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/exp.md): Element-wise exponential.
+
+[`expand_dims(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/expand_dims.md): Adds a 1-sized dimension at index "axis".
+
+[`eye(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/eye.md): Instantiate an identity matrix and returns it.
+
+[`flatten(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/flatten.md): Flatten a tensor.
+
+[`floatx(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/floatx.md): Returns the default float type, as a string.
+
+[`foldl(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/foldl.md): Reduce elems using fn to combine them from left to right.
+
+[`foldr(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/foldr.md): Reduce elems using fn to combine them from right to left.
+
+[`function(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/function.md): Instantiates a Keras function.
+
+[`gather(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/gather.md): Retrieves the elements of indices `indices` in the tensor `reference`.
+
+[`get_session(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/backend/get_session.md): Returns the TF session to be used by the backend.
+
+[`get_uid(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/get_uid.md): Associates a string prefix with an integer counter in a TensorFlow graph.
+
+[`get_value(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/get_value.md): Returns the value of a variable.
+
+[`gradients(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/gradients.md): Returns the gradients of `loss` w.r.t. `variables`.
+
+[`greater(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/greater.md): Element-wise truth value of (x > y).
+
+[`greater_equal(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/greater_equal.md): Element-wise truth value of (x >= y).
+
+[`hard_sigmoid(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/hard_sigmoid.md): Segment-wise linear approximation of sigmoid.
+
+[`image_data_format(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/image_data_format.md): Returns the default image data format convention.
+
+[`in_test_phase(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/in_test_phase.md): Selects `x` in test phase, and `alt` otherwise.
+
+[`in_top_k(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/in_top_k.md): Returns whether the `targets` are in the top `k` `predictions`.
+
+[`in_train_phase(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/in_train_phase.md): Selects `x` in train phase, and `alt` otherwise.
+
+[`int_shape(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/int_shape.md): Returns the shape of tensor or variable as a tuple of int or None entries.
+
+[`is_keras_tensor(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/is_keras_tensor.md): Returns whether `x` is a Keras tensor.
+
+[`is_sparse(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/is_sparse.md): Returns whether a tensor is a sparse tensor.
+
+[`l2_normalize(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/l2_normalize.md): Normalizes a tensor wrt the L2 norm alongside the specified axis.
+
+[`learning_phase(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/learning_phase.md): Returns the learning phase flag.
+
+[`learning_phase_scope(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/learning_phase_scope.md): Provides a scope within which the learning phase is equal to `value`.
+
+[`less(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/less.md): Element-wise truth value of (x < y).
+
+[`less_equal(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/less_equal.md): Element-wise truth value of (x <= y).
+
+[`local_conv1d(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/local_conv1d.md): Apply 1D conv with un-shared weights.
+
+[`local_conv2d(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/local_conv2d.md): Apply 2D conv with un-shared weights.
+
+[`log(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/log.md): Element-wise log.
+
+[`manual_variable_initialization(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/manual_variable_initialization.md): Sets the manual variable initialization flag.
+
+[`map_fn(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/map_fn.md): Map the function fn over the elements elems and return the outputs.
+
+[`max(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/max.md): Maximum value in a tensor.
+
+[`maximum(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/maximum.md): Element-wise maximum of two tensors.
+
+[`mean(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/mean.md): Mean of a tensor, alongside the specified axis.
+
+[`min(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/min.md): Minimum value in a tensor.
+
+[`minimum(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/minimum.md): Element-wise minimum of two tensors.
+
+[`moving_average_update(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/moving_average_update.md): Compute the moving average of a variable.
+
+[`ndim(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/ndim.md): Returns the number of axes in a tensor, as an integer.
+
+[`normalize_batch_in_training(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/normalize_batch_in_training.md): Computes mean and std for batch then apply batch_normalization on batch.
+
+[`not_equal(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/not_equal.md): Element-wise inequality between two tensors.
+
+[`one_hot(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/one_hot.md): Computes the one-hot representation of an integer tensor.
+
+[`ones(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/ones.md): Instantiates an all-ones variable and returns it.
+
+[`ones_like(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/ones_like.md): Instantiates an all-ones variable of the same shape as another tensor.
+
+[`permute_dimensions(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/permute_dimensions.md): Permutes axes in a tensor.
+
+[`placeholder(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/placeholder.md): Instantiates a placeholder tensor and returns it.
+
+[`pool2d(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/pool2d.md): 2D Pooling.
+
+[`pool3d(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/pool3d.md): 3D Pooling.
+
+[`pow(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/pow.md): Element-wise exponentiation.
+
+[`print_tensor(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/print_tensor.md): Prints `message` and the tensor value when evaluated.
+
+[`prod(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/prod.md): Multiplies the values in a tensor, alongside the specified axis.
+
+[`random_binomial(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/random_binomial.md): Returns a tensor with random binomial distribution of values.
+
+[`random_normal(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/random_normal.md): Returns a tensor with normal distribution of values.
+
+[`random_normal_variable(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/random_normal_variable.md): Instantiates a variable with values drawn from a normal distribution.
+
+[`random_uniform(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/random_uniform.md): Returns a tensor with uniform distribution of values.
+
+[`random_uniform_variable(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/random_uniform_variable.md): Instantiates a variable with values drawn from a uniform distribution.
+
+[`relu(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/relu.md): Rectified linear unit.
+
+[`repeat(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/repeat.md): Repeats a 2D tensor.
+
+[`repeat_elements(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/repeat_elements.md): Repeats the elements of a tensor along an axis, like `np.repeat`.
+
+[`reset_uids(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/reset_uids.md): Resets graph identifiers.
+
+[`reshape(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/reshape.md): Reshapes a tensor to the specified shape.
+
+[`resize_images(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/resize_images.md): Resizes the images contained in a 4D tensor.
+
+[`resize_volumes(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/resize_volumes.md): Resizes the volume contained in a 5D tensor.
+
+[`reverse(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/reverse.md): Reverse a tensor along the specified axes.
+
+[`rnn(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/rnn.md): Iterates over the time dimension of a tensor.
+
+[`round(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/round.md): Element-wise rounding to the closest integer.
+
+[`separable_conv2d(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/separable_conv2d.md): 2D convolution with separable filters.
+
+[`set_epsilon(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/set_epsilon.md): Sets the value of the fuzz factor used in numeric expressions.
+
+[`set_floatx(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/set_floatx.md): Sets the default float type.
+
+[`set_image_data_format(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/set_image_data_format.md): Sets the value of the image data format convention.
+
+[`set_learning_phase(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/set_learning_phase.md): Sets the learning phase to a fixed value.
+
+[`set_session(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/backend/set_session.md): Sets the global TensorFlow session.
+
+[`set_value(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/set_value.md): Sets the value of a variable, from a Numpy array.
+
+[`shape(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/shape.md): Returns the symbolic shape of a tensor or variable.
+
+[`sigmoid(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/sigmoid.md): Element-wise sigmoid.
+
+[`sign(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/sign.md): Element-wise sign.
+
+[`sin(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/sin.md): Computes sin of x element-wise.
+
+[`softmax(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/softmax.md): Softmax of a tensor.
+
+[`softplus(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/softplus.md): Softplus of a tensor.
+
+[`softsign(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/softsign.md): Softsign of a tensor.
+
+[`sparse_categorical_crossentropy(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/sparse_categorical_crossentropy.md): Categorical crossentropy with integer targets.
+
+[`spatial_2d_padding(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/spatial_2d_padding.md): Pads the 2nd and 3rd dimensions of a 4D tensor.
+
+[`spatial_3d_padding(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/spatial_3d_padding.md): Pads 5D tensor with zeros along the depth, height, width dimensions.
+
+[`sqrt(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/sqrt.md): Element-wise square root.
+
+[`square(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/square.md): Element-wise square.
+
+[`squeeze(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/squeeze.md): Removes a 1-dimension from the tensor at index "axis".
+
+[`stack(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/stack.md): Stacks a list of rank `R` tensors into a rank `R+1` tensor.
+
+[`std(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/std.md): Standard deviation of a tensor, alongside the specified axis.
+
+[`stop_gradient(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/stop_gradient.md): Returns `variables` but with zero gradient w.r.t. every other variable.
+
+[`sum(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/sum.md): Sum of the values in a tensor, alongside the specified axis.
+
+[`switch(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/switch.md): Switches between two operations depending on a scalar value.
+
+[`tanh(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/tanh.md): Element-wise tanh.
+
+[`temporal_padding(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/temporal_padding.md): Pads the middle dimension of a 3D tensor.
+
+[`tile(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/tile.md): Creates a tensor by tiling `x` by `n`.
+
+[`to_dense(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/to_dense.md): Converts a sparse tensor into a dense tensor and returns it.
+
+[`transpose(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/transpose.md): Transposes a tensor and returns it.
+
+[`truncated_normal(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/truncated_normal.md): Returns a tensor with truncated random normal distribution of values.
+
+[`update(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/update.md)
+
+[`update_add(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/update_add.md): Update the value of `x` by adding `increment`.
+
+[`update_sub(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/update_sub.md): Update the value of `x` by subtracting `decrement`.
+
+[`var(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/var.md): Variance of a tensor, alongside the specified axis.
+
+[`variable(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/variable.md): Instantiates a variable and returns it.
+
+[`zeros(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/zeros.md): Instantiates an all-zeros variable and returns it.
+
+[`zeros_like(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/backend/zeros_like.md): Instantiates an all-zeros variable of the same shape as another tensor.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/backend/get_session.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/backend/get_session.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..25441109060
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/backend/get_session.md
@@ -0,0 +1,76 @@
+description: Returns the TF session to be used by the backend.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.keras.backend.get_session
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns the TF session to be used by the backend.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.keras.backend.get_session(
+ op_input_list=()
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+If a default TensorFlow session is available, we will return it.
+
+Else, we will return the global Keras session assuming it matches
+the current graph.
+
+If no global Keras session exists at this point:
+we will create a new global session.
+
+Note that you can manually set the global session
+via `K.set_session(sess)`.
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`op_input_list`
+ |
+
+An option sequence of tensors or ops, which will be used
+to determine the current graph. Otherwise the default graph will be
+used.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A TensorFlow session.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/backend/name_scope.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/backend/name_scope.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..ebf2d053a5e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/backend/name_scope.md
@@ -0,0 +1,161 @@
+description: A context manager for use when defining a Python op.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.keras.backend.name_scope
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A context manager for use when defining a Python op.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.name_scope`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.keras.backend.name_scope(
+ name, default_name=None, values=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This context manager validates that the given `values` are from the
+same graph, makes that graph the default graph, and pushes a
+name scope in that graph (see
+tf.Graph.name_scope
+for more details on that).
+
+For example, to define a new Python op called `my_op`:
+
+```python
+def my_op(a, b, c, name=None):
+ with tf.name_scope(name, "MyOp", [a, b, c]) as scope:
+ a = tf.convert_to_tensor(a, name="a")
+ b = tf.convert_to_tensor(b, name="b")
+ c = tf.convert_to_tensor(c, name="c")
+ # Define some computation that uses `a`, `b`, and `c`.
+ return foo_op(..., name=scope)
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+The name argument that is passed to the op function.
+ |
+
+|
+`default_name`
+ |
+
+The default name to use if the `name` argument is `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`values`
+ |
+
+The list of `Tensor` arguments that are passed to the op function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+if `default_name` is passed in but not a string.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+__enter__
+
+View source
+
+
+__enter__()
+
+
+
+
+
+__exit__
+
+View source
+
+
+__exit__(
+ *exc_info
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/backend/set_session.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/backend/set_session.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..d6cd68c8f98
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/backend/set_session.md
@@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
+description: Sets the global TensorFlow session.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.keras.backend.set_session
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Sets the global TensorFlow session.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.keras.backend.set_session(
+ session
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`session`
+ |
+
+A TF Session.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/callbacks.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/callbacks.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..80fe8783b92
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/callbacks.md
@@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
+description: Callbacks: utilities called at certain points during model training.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.callbacks
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Callbacks: utilities called at certain points during model training.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class BaseLogger`](../../../../tf/keras/callbacks/BaseLogger.md): Callback that accumulates epoch averages of metrics.
+
+[`class CSVLogger`](../../../../tf/keras/callbacks/CSVLogger.md): Callback that streams epoch results to a csv file.
+
+[`class Callback`](../../../../tf/keras/callbacks/Callback.md): Abstract base class used to build new callbacks.
+
+[`class EarlyStopping`](../../../../tf/keras/callbacks/EarlyStopping.md): Stop training when a monitored metric has stopped improving.
+
+[`class History`](../../../../tf/keras/callbacks/History.md): Callback that records events into a `History` object.
+
+[`class LambdaCallback`](../../../../tf/keras/callbacks/LambdaCallback.md): Callback for creating simple, custom callbacks on-the-fly.
+
+[`class LearningRateScheduler`](../../../../tf/keras/callbacks/LearningRateScheduler.md): Learning rate scheduler.
+
+[`class ModelCheckpoint`](../../../../tf/keras/callbacks/ModelCheckpoint.md): Callback to save the Keras model or model weights at some frequency.
+
+[`class ProgbarLogger`](../../../../tf/keras/callbacks/ProgbarLogger.md): Callback that prints metrics to stdout.
+
+[`class ReduceLROnPlateau`](../../../../tf/keras/callbacks/ReduceLROnPlateau.md): Reduce learning rate when a metric has stopped improving.
+
+[`class RemoteMonitor`](../../../../tf/keras/callbacks/RemoteMonitor.md): Callback used to stream events to a server.
+
+[`class TensorBoard`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/callbacks/TensorBoard.md): Enable visualizations for TensorBoard.
+
+[`class TerminateOnNaN`](../../../../tf/keras/callbacks/TerminateOnNaN.md): Callback that terminates training when a NaN loss is encountered.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/callbacks/TensorBoard.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/callbacks/TensorBoard.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..00275584315
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/callbacks/TensorBoard.md
@@ -0,0 +1,236 @@
+description: Enable visualizations for TensorBoard.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.keras.callbacks.TensorBoard
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Enable visualizations for TensorBoard.
+
+Inherits From: [`Callback`](../../../../../tf/keras/callbacks/Callback.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.keras.callbacks.TensorBoard(
+ log_dir='./logs', histogram_freq=0, batch_size=32, write_graph=(True),
+ write_grads=(False), write_images=(False), embeddings_freq=0,
+ embeddings_layer_names=None, embeddings_metadata=None, embeddings_data=None,
+ update_freq='epoch', profile_batch=2
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+TensorBoard is a visualization tool provided with TensorFlow.
+
+This callback logs events for TensorBoard, including:
+* Metrics summary plots
+* Training graph visualization
+* Activation histograms
+* Sampled profiling
+
+If you have installed TensorFlow with pip, you should be able
+to launch TensorBoard from the command line:
+
+```sh
+tensorboard --logdir=path_to_your_logs
+```
+
+You can find more information about TensorBoard
+[here](https://www.tensorflow.org/get_started/summaries_and_tensorboard).
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`log_dir`
+ |
+
+the path of the directory where to save the log files to be
+parsed by TensorBoard.
+ |
+
+|
+`histogram_freq`
+ |
+
+frequency (in epochs) at which to compute activation and
+weight histograms for the layers of the model. If set to 0, histograms
+won't be computed. Validation data (or split) must be specified for
+histogram visualizations.
+ |
+
+|
+`write_graph`
+ |
+
+whether to visualize the graph in TensorBoard. The log file
+can become quite large when write_graph is set to True.
+ |
+
+|
+`write_grads`
+ |
+
+whether to visualize gradient histograms in TensorBoard.
+`histogram_freq` must be greater than 0.
+ |
+
+|
+`batch_size`
+ |
+
+size of batch of inputs to feed to the network for histograms
+computation.
+ |
+
+|
+`write_images`
+ |
+
+whether to write model weights to visualize as image in
+TensorBoard.
+ |
+
+|
+`embeddings_freq`
+ |
+
+frequency (in epochs) at which selected embedding layers
+will be saved. If set to 0, embeddings won't be computed. Data to be
+visualized in TensorBoard's Embedding tab must be passed as
+`embeddings_data`.
+ |
+
+|
+`embeddings_layer_names`
+ |
+
+a list of names of layers to keep eye on. If None
+or empty list all the embedding layer will be watched.
+ |
+
+|
+`embeddings_metadata`
+ |
+
+a dictionary which maps layer name to a file name in
+which metadata for this embedding layer is saved. See the
+[details](https://www.tensorflow.org/how_tos/embedding_viz/#metadata_optional)
+about metadata files format. In case if the same metadata file is
+used for all embedding layers, string can be passed.
+ |
+
+|
+`embeddings_data`
+ |
+
+data to be embedded at layers specified in
+`embeddings_layer_names`. Numpy array (if the model has a single input)
+or list of Numpy arrays (if the model has multiple inputs). Learn [more
+about
+embeddings](https://www.tensorflow.org/programmers_guide/embedding)
+ |
+
+|
+`update_freq`
+ |
+
+`'batch'` or `'epoch'` or integer. When using `'batch'`,
+writes the losses and metrics to TensorBoard after each batch. The same
+applies for `'epoch'`. If using an integer, let's say `1000`, the
+callback will write the metrics and losses to TensorBoard every 1000
+samples. Note that writing too frequently to TensorBoard can slow down
+your training.
+ |
+
+|
+`profile_batch`
+ |
+
+Profile the batch to sample compute characteristics. By
+default, it will profile the second batch. Set profile_batch=0 to
+disable profiling.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If histogram_freq is set and no validation data is provided.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+Using the `TensorBoard` callback will work when eager execution is enabled,
+with the restriction that outputting histogram summaries of weights and
+gradients is not supported. Consequently, `histogram_freq` will be ignored.
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+set_model
+
+View source
+
+
+set_model(
+ model
+)
+
+
+Sets Keras model and creates summary ops.
+
+
+set_params
+
+View source
+
+
+set_params(
+ params
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/constraints.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/constraints.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..dbdbd4ea0fd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/constraints.md
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+description: Constraints: functions that impose constraints on weight values.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.constraints
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Constraints: functions that impose constraints on weight values.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class Constraint`](../../../../tf/keras/constraints/Constraint.md)
+
+[`class MaxNorm`](../../../../tf/keras/constraints/MaxNorm.md): MaxNorm weight constraint.
+
+[`class MinMaxNorm`](../../../../tf/keras/constraints/MinMaxNorm.md): MinMaxNorm weight constraint.
+
+[`class NonNeg`](../../../../tf/keras/constraints/NonNeg.md): Constrains the weights to be non-negative.
+
+[`class RadialConstraint`](../../../../tf/keras/constraints/RadialConstraint.md): Constrains `Conv2D` kernel weights to be the same for each radius.
+
+[`class UnitNorm`](../../../../tf/keras/constraints/UnitNorm.md): Constrains the weights incident to each hidden unit to have unit norm.
+
+[`class max_norm`](../../../../tf/keras/constraints/MaxNorm.md): MaxNorm weight constraint.
+
+[`class min_max_norm`](../../../../tf/keras/constraints/MinMaxNorm.md): MinMaxNorm weight constraint.
+
+[`class non_neg`](../../../../tf/keras/constraints/NonNeg.md): Constrains the weights to be non-negative.
+
+[`class radial_constraint`](../../../../tf/keras/constraints/RadialConstraint.md): Constrains `Conv2D` kernel weights to be the same for each radius.
+
+[`class unit_norm`](../../../../tf/keras/constraints/UnitNorm.md): Constrains the weights incident to each hidden unit to have unit norm.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`deserialize(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/constraints/deserialize.md)
+
+[`get(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/constraints/get.md)
+
+[`serialize(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/constraints/serialize.md)
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/datasets.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/datasets.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e9768ef785b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/datasets.md
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
+description: Public API for tf.keras.datasets namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.datasets
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.keras.datasets namespace.
+
+
+
+## Modules
+
+[`boston_housing`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/datasets/boston_housing.md) module: Boston housing price regression dataset.
+
+[`cifar10`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/datasets/cifar10.md) module: CIFAR10 small images classification dataset.
+
+[`cifar100`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/datasets/cifar100.md) module: CIFAR100 small images classification dataset.
+
+[`fashion_mnist`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/datasets/fashion_mnist.md) module: Fashion-MNIST dataset.
+
+[`imdb`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/datasets/imdb.md) module: IMDB sentiment classification dataset.
+
+[`mnist`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/datasets/mnist.md) module: MNIST handwritten digits dataset.
+
+[`reuters`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/datasets/reuters.md) module: Reuters topic classification dataset.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/datasets/boston_housing.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/datasets/boston_housing.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..06f5ce15912
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/datasets/boston_housing.md
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+description: Boston housing price regression dataset.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.datasets.boston_housing
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Boston housing price regression dataset.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`load_data(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/datasets/boston_housing/load_data.md): Loads the Boston Housing dataset.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/datasets/cifar10.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/datasets/cifar10.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..971003fd00a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/datasets/cifar10.md
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+description: CIFAR10 small images classification dataset.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.datasets.cifar10
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+CIFAR10 small images classification dataset.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`load_data(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/datasets/cifar10/load_data.md): Loads [CIFAR10 dataset](https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar.html).
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/datasets/cifar100.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/datasets/cifar100.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..b0a9762ebe6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/datasets/cifar100.md
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+description: CIFAR100 small images classification dataset.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.datasets.cifar100
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+CIFAR100 small images classification dataset.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`load_data(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/datasets/cifar100/load_data.md): Loads [CIFAR100 dataset](https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar.html).
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/datasets/fashion_mnist.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/datasets/fashion_mnist.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..ad83c4252a2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/datasets/fashion_mnist.md
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+description: Fashion-MNIST dataset.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.datasets.fashion_mnist
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Fashion-MNIST dataset.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`load_data(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/datasets/fashion_mnist/load_data.md): Loads the Fashion-MNIST dataset.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/datasets/imdb.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/datasets/imdb.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a716828dd3f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/datasets/imdb.md
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
+description: IMDB sentiment classification dataset.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.datasets.imdb
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+IMDB sentiment classification dataset.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`get_word_index(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/datasets/imdb/get_word_index.md): Retrieves a dict mapping words to their index in the IMDB dataset.
+
+[`load_data(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/datasets/imdb/load_data.md): Loads the [IMDB dataset](https://ai.stanford.edu/~amaas/data/sentiment/).
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/datasets/mnist.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/datasets/mnist.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..f7b4ad9fdc0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/datasets/mnist.md
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+description: MNIST handwritten digits dataset.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.datasets.mnist
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+MNIST handwritten digits dataset.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`load_data(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/datasets/mnist/load_data.md): Loads the [MNIST dataset](http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/).
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/datasets/reuters.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/datasets/reuters.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..5e2f324dfd0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/datasets/reuters.md
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
+description: Reuters topic classification dataset.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.datasets.reuters
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Reuters topic classification dataset.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`get_word_index(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/datasets/reuters/get_word_index.md): Retrieves a dict mapping words to their index in the Reuters dataset.
+
+[`load_data(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/datasets/reuters/load_data.md): Loads the Reuters newswire classification dataset.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/estimator.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/estimator.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..b10ba8840be
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/estimator.md
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+description: Keras estimator API.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.estimator
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Keras estimator API.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`model_to_estimator(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/estimator/model_to_estimator.md): Constructs an `Estimator` instance from given keras model.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/estimator/model_to_estimator.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/estimator/model_to_estimator.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..4528683c67b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/estimator/model_to_estimator.md
@@ -0,0 +1,198 @@
+description: Constructs an Estimator instance from given keras model.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.keras.estimator.model_to_estimator
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Constructs an `Estimator` instance from given keras model.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.keras.estimator.model_to_estimator(
+ keras_model=None, keras_model_path=None, custom_objects=None, model_dir=None,
+ config=None, checkpoint_format='saver'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+If you use infrastructure or other tooling that relies on Estimators, you can
+still build a Keras model and use model_to_estimator to convert the Keras
+model to an Estimator for use with downstream systems.
+
+For usage example, please see:
+[Creating estimators from Keras
+Models](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/estimators#creating_estimators_from_keras_models).
+
+#### Sample Weights:
+
+
+Estimators returned by `model_to_estimator` are configured so that they can
+handle sample weights (similar to `keras_model.fit(x, y, sample_weights)`).
+
+To pass sample weights when training or evaluating the Estimator, the first
+item returned by the input function should be a dictionary with keys
+`features` and `sample_weights`. Example below:
+
+```python
+keras_model = tf.keras.Model(...)
+keras_model.compile(...)
+
+estimator = tf.keras.estimator.model_to_estimator(keras_model)
+
+def input_fn():
+ return dataset_ops.Dataset.from_tensors(
+ ({'features': features, 'sample_weights': sample_weights},
+ targets))
+
+estimator.train(input_fn, steps=1)
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`keras_model`
+ |
+
+A compiled Keras model object. This argument is mutually
+exclusive with `keras_model_path`. Estimator's `model_fn` uses the
+structure of the model to clone the model. Defaults to `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`keras_model_path`
+ |
+
+Path to a compiled Keras model saved on disk, in HDF5
+format, which can be generated with the `save()` method of a Keras model.
+This argument is mutually exclusive with `keras_model`.
+Defaults to `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`custom_objects`
+ |
+
+Dictionary for cloning customized objects. This is
+used with classes that is not part of this pip package. For example, if
+user maintains a `relu6` class that inherits from tf.keras.layers.Layer,
+then pass `custom_objects={'relu6': relu6}`. Defaults to `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`model_dir`
+ |
+
+Directory to save `Estimator` model parameters, graph, summary
+files for TensorBoard, etc. If unset a directory will be created with
+`tempfile.mkdtemp`
+ |
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+`RunConfig` to config `Estimator`. Allows setting up things in
+`model_fn` based on configuration such as `num_ps_replicas`, or
+`model_dir`. Defaults to `None`. If both `config.model_dir` and the
+`model_dir` argument (above) are specified the `model_dir` **argument**
+takes precedence.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_format`
+ |
+
+Sets the format of the checkpoint saved by the estimator
+when training. May be `saver` or `checkpoint`, depending on whether to
+save checkpoints from `tf.train.Saver` or tf.train.Checkpoint. This
+argument currently defaults to `saver`. When 2.0 is released, the default
+will be `checkpoint`. Estimators use name-based `tf.train.Saver`
+checkpoints, while Keras models use object-based checkpoints from
+tf.train.Checkpoint. Currently, saving object-based checkpoints from
+`model_to_estimator` is only supported by Functional and Sequential
+models. Defaults to 'saver'.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Estimator from given keras model.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If neither keras_model nor keras_model_path was given.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If both keras_model and keras_model_path was given.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the keras_model_path is a GCS URI.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If keras_model has not been compiled.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If an invalid checkpoint_format was given.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/experimental.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/experimental.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..8e061d4b22f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/experimental.md
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
+description: Public API for tf.keras.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.experimental
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.keras.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class CosineDecay`](../../../../tf/keras/experimental/CosineDecay.md): A LearningRateSchedule that uses a cosine decay schedule.
+
+[`class CosineDecayRestarts`](../../../../tf/keras/experimental/CosineDecayRestarts.md): A LearningRateSchedule that uses a cosine decay schedule with restarts.
+
+[`class LinearCosineDecay`](../../../../tf/keras/experimental/LinearCosineDecay.md): A LearningRateSchedule that uses a linear cosine decay schedule.
+
+[`class LinearModel`](../../../../tf/keras/experimental/LinearModel.md): Linear Model for regression and classification problems.
+
+[`class NoisyLinearCosineDecay`](../../../../tf/keras/experimental/NoisyLinearCosineDecay.md): A LearningRateSchedule that uses a noisy linear cosine decay schedule.
+
+[`class PeepholeLSTMCell`](../../../../tf/keras/experimental/PeepholeLSTMCell.md): Equivalent to LSTMCell class but adds peephole connections.
+
+[`class SequenceFeatures`](../../../../tf/keras/experimental/SequenceFeatures.md): A layer for sequence input.
+
+[`class WideDeepModel`](../../../../tf/keras/experimental/WideDeepModel.md): Wide & Deep Model for regression and classification problems.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`export_saved_model(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/experimental/export_saved_model.md): Exports a tf.keras.Model as a Tensorflow SavedModel. (deprecated)
+
+[`load_from_saved_model(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/experimental/load_from_saved_model.md): Loads a keras Model from a SavedModel created by `export_saved_model()`. (deprecated)
+
+[`terminate_keras_multiprocessing_pools(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/experimental/terminate_keras_multiprocessing_pools.md): Destroy Keras' multiprocessing pools to prevent deadlocks.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/experimental/export_saved_model.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/experimental/export_saved_model.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..51fc7409212
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/experimental/export_saved_model.md
@@ -0,0 +1,165 @@
+description: Exports a tf.keras.Model as a Tensorflow SavedModel. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.keras.experimental.export_saved_model
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Exports a tf.keras.Model as a Tensorflow SavedModel. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.keras.experimental.export_saved_model(
+ model, saved_model_path, custom_objects=None, as_text=(False),
+ input_signature=None, serving_only=(False)
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Please use `model.save(..., save_format="tf")` or `tf.keras.models.save_model(..., save_format="tf")`.
+
+Note that at this time, subclassed models can only be saved using
+`serving_only=True`.
+
+The exported `SavedModel` is a standalone serialization of Tensorflow objects,
+and is supported by TF language APIs and the Tensorflow Serving system.
+To load the model, use the function
+`tf.keras.experimental.load_from_saved_model`.
+
+The `SavedModel` contains:
+
+1. a checkpoint containing the model weights.
+2. a `SavedModel` proto containing the Tensorflow backend graph. Separate
+ graphs are saved for prediction (serving), train, and evaluation. If
+ the model has not been compiled, then only the graph computing predictions
+ will be exported.
+3. the model's json config. If the model is subclassed, this will only be
+ included if the model's `get_config()` method is overwritten.
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+import tensorflow as tf
+
+# Create a tf.keras model.
+model = tf.keras.Sequential()
+model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(1, input_shape=[10]))
+model.summary()
+
+# Save the tf.keras model in the SavedModel format.
+path = '/tmp/simple_keras_model'
+tf.keras.experimental.export_saved_model(model, path)
+
+# Load the saved keras model back.
+new_model = tf.keras.experimental.load_from_saved_model(path)
+new_model.summary()
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`model`
+ |
+
+A tf.keras.Model to be saved. If the model is subclassed, the flag
+`serving_only` must be set to True.
+ |
+
+|
+`saved_model_path`
+ |
+
+a string specifying the path to the SavedModel directory.
+ |
+
+|
+`custom_objects`
+ |
+
+Optional dictionary mapping string names to custom classes
+or functions (e.g. custom loss functions).
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+bool, `False` by default. Whether to write the `SavedModel` proto
+in text format. Currently unavailable in serving-only mode.
+ |
+
+|
+`input_signature`
+ |
+
+A possibly nested sequence of tf.TensorSpec objects, used
+to specify the expected model inputs. See tf.function for more details.
+ |
+
+|
+`serving_only`
+ |
+
+bool, `False` by default. When this is true, only the
+prediction graph is saved.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`NotImplementedError`
+ |
+
+If the model is a subclassed model, and serving_only is
+False.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the input signature cannot be inferred from the model.
+ |
+
+|
+`AssertionError`
+ |
+
+If the SavedModel directory already exists and isn't empty.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/experimental/load_from_saved_model.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/experimental/load_from_saved_model.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3ab746e7dff
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/experimental/load_from_saved_model.md
@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
+description: Loads a keras Model from a SavedModel created by export_saved_model(). (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.keras.experimental.load_from_saved_model
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Loads a keras Model from a SavedModel created by `export_saved_model()`. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.keras.experimental.load_from_saved_model(
+ saved_model_path, custom_objects=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+The experimental save and load functions have been deprecated. Please switch to tf.keras.models.load_model.
+
+This function reinstantiates model state by:
+1) loading model topology from json (this will eventually come
+ from metagraph).
+2) loading model weights from checkpoint.
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+import tensorflow as tf
+
+# Create a tf.keras model.
+model = tf.keras.Sequential()
+model.add(tf.keras.layers.Dense(1, input_shape=[10]))
+model.summary()
+
+# Save the tf.keras model in the SavedModel format.
+path = '/tmp/simple_keras_model'
+tf.keras.experimental.export_saved_model(model, path)
+
+# Load the saved keras model back.
+new_model = tf.keras.experimental.load_from_saved_model(path)
+new_model.summary()
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`saved_model_path`
+ |
+
+a string specifying the path to an existing SavedModel.
+ |
+
+|
+`custom_objects`
+ |
+
+Optional dictionary mapping names
+(strings) to custom classes or functions to be
+considered during deserialization.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+a keras.Model instance.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..58d4b638220
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers.md
@@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
+description: Keras initializer serialization / deserialization.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Keras initializer serialization / deserialization.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class Constant`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Constant.md): Initializer that generates tensors with constant values.
+
+[`class Identity`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Identity.md): Initializer that generates the identity matrix.
+
+[`class Initializer`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Initializer.md): Initializer base class: all initializers inherit from this class.
+
+[`class Ones`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Ones.md): Initializer that generates tensors initialized to 1.
+
+[`class Orthogonal`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Orthogonal.md): Initializer that generates an orthogonal matrix.
+
+[`class RandomNormal`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/RandomNormal.md): Initializer that generates tensors with a normal distribution.
+
+[`class RandomUniform`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/RandomUniform.md): Initializer that generates tensors with a uniform distribution.
+
+[`class TruncatedNormal`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/TruncatedNormal.md): Initializer that generates a truncated normal distribution.
+
+[`class VarianceScaling`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/VarianceScaling.md): Initializer capable of adapting its scale to the shape of weights tensors.
+
+[`class Zeros`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Zeros.md): Initializer that generates tensors initialized to 0.
+
+[`class constant`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Constant.md): Initializer that generates tensors with constant values.
+
+[`class glorot_normal`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/glorot_normal.md): The Glorot normal initializer, also called Xavier normal initializer.
+
+[`class glorot_uniform`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/glorot_uniform.md): The Glorot uniform initializer, also called Xavier uniform initializer.
+
+[`class identity`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Identity.md): Initializer that generates the identity matrix.
+
+[`class normal`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/RandomNormal.md): Initializer that generates tensors with a normal distribution.
+
+[`class ones`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Ones.md): Initializer that generates tensors initialized to 1.
+
+[`class orthogonal`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Orthogonal.md): Initializer that generates an orthogonal matrix.
+
+[`class random_normal`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/RandomNormal.md): Initializer that generates tensors with a normal distribution.
+
+[`class random_uniform`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/RandomUniform.md): Initializer that generates tensors with a uniform distribution.
+
+[`class truncated_normal`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/TruncatedNormal.md): Initializer that generates a truncated normal distribution.
+
+[`class uniform`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/RandomUniform.md): Initializer that generates tensors with a uniform distribution.
+
+[`class zeros`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Zeros.md): Initializer that generates tensors initialized to 0.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`deserialize(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/initializers/deserialize.md): Return an `Initializer` object from its config.
+
+[`get(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/initializers/get.md)
+
+[`he_normal(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/he_normal.md): He normal initializer.
+
+[`he_uniform(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/he_uniform.md): He uniform variance scaling initializer.
+
+[`lecun_normal(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/lecun_normal.md): LeCun normal initializer.
+
+[`lecun_uniform(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/lecun_uniform.md): LeCun uniform initializer.
+
+[`serialize(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/initializers/serialize.md)
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Constant.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Constant.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..21ebedbb45c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Constant.md
@@ -0,0 +1,289 @@
+description: Initializer that generates tensors with constant values.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.Constant
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Initializer that generates tensors with constant values.
+
+Inherits From: [`Initializer`](../../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Initializer.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.constant_initializer`, `tf.compat.v1.initializers.constant`, `tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.constant`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.Constant(
+ value=0, dtype=tf.dtypes.float32, verify_shape=(False)
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The resulting tensor is populated with values of type `dtype`, as
+specified by arguments `value` following the desired `shape` of the
+new tensor (see examples below).
+
+The argument `value` can be a constant value, or a list of values of type
+`dtype`. If `value` is a list, then the length of the list must be less
+than or equal to the number of elements implied by the desired shape of the
+tensor. In the case where the total number of elements in `value` is less
+than the number of elements required by the tensor shape, the last element
+in `value` will be used to fill the remaining entries. If the total number of
+elements in `value` is greater than the number of elements required by the
+tensor shape, the initializer will raise a `ValueError`.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+A Python scalar, list or tuple of values, or a N-dimensional numpy
+array. All elements of the initialized variable will be set to the
+corresponding value in the `value` argument.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+Default data type, used if no `dtype` argument is provided when
+calling the initializer.
+ |
+
+|
+`verify_shape`
+ |
+
+Boolean that enables verification of the shape of `value`. If
+`True`, the initializer will throw an error if the shape of `value` is not
+compatible with the shape of the initialized tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If the input `value` is not one of the expected types.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Examples:
+
+The following example can be rewritten using a numpy.ndarray instead
+of the `value` list, even reshaped, as shown in the two commented lines
+below the `value` list initialization.
+
+
+```
+>>> value = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
+>>> init = tf.compat.v1.constant_initializer(value)
+>>> # fitting shape
+>>> with tf.compat.v1.Session():
+... x = tf.compat.v1.get_variable('x', shape=[2, 4], initializer=init)
+... x.initializer.run()
+... print(x.eval())
+[[0. 1. 2. 3.]
+ [4. 5. 6. 7.]]
+>>> # Larger shape
+>>> with tf.compat.v1.Session():
+... y = tf.compat.v1.get_variable('y', shape=[3, 4], initializer=init)
+... y.initializer.run()
+... print(y.eval())
+[[0. 1. 2. 3.]
+ [4. 5. 6. 7.]
+ [7. 7. 7. 7.]]
+>>> # Smaller shape
+>>> with tf.compat.v1.Session():
+... z = tf.compat.v1.get_variable('z', shape=[2, 3], initializer=init)
+Traceback (most recent call last):
+...
+ValueError: Too many elements provided. Needed at most 6, but received 8
+>>> # Shape verification
+>>> init_verify = tf.compat.v1.constant_initializer(value, verify_shape=True)
+>>> with tf.compat.v1.Session():
+... u = tf.compat.v1.get_variable('u', shape=[3, 4],
+... initializer=init_verify)
+Traceback (most recent call last):
+...
+TypeError: Expected Tensor's shape: (3, 4), got (8,).
+```
+
+## Methods
+
+from_config
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+from_config(
+ config
+)
+
+
+Instantiates an initializer from a configuration dictionary.
+
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+initializer = RandomUniform(-1, 1)
+config = initializer.get_config()
+initializer = RandomUniform.from_config(config)
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+A Python dictionary. It will typically be the output of
+`get_config`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Initializer instance.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_config
+
+View source
+
+
+get_config()
+
+
+Returns the configuration of the initializer as a JSON-serializable dict.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A JSON-serializable Python dict.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+__call__
+
+View source
+
+
+__call__(
+ shape, dtype=None, partition_info=None, verify_shape=None
+)
+
+
+Returns a tensor object initialized as specified by the initializer.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of the tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+Optional dtype of the tensor. If not provided use the initializer
+dtype.
+ |
+
+|
+`partition_info`
+ |
+
+Optional information about the possible partitioning of a
+tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Identity.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Identity.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e18f100f482
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Identity.md
@@ -0,0 +1,209 @@
+description: Initializer that generates the identity matrix.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.Identity
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Initializer that generates the identity matrix.
+
+Inherits From: [`Initializer`](../../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Initializer.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.initializers.identity`, `tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.identity`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.Identity(
+ gain=1.0, dtype=tf.dtypes.float32
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Only use for 2D matrices.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`gain`
+ |
+
+Multiplicative factor to apply to the identity matrix.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+Default data type, used if no `dtype` argument is provided when
+calling the initializer. Only floating point types are supported.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+from_config
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+from_config(
+ config
+)
+
+
+Instantiates an initializer from a configuration dictionary.
+
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+initializer = RandomUniform(-1, 1)
+config = initializer.get_config()
+initializer = RandomUniform.from_config(config)
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+A Python dictionary. It will typically be the output of
+`get_config`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Initializer instance.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_config
+
+View source
+
+
+get_config()
+
+
+Returns the configuration of the initializer as a JSON-serializable dict.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A JSON-serializable Python dict.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+__call__
+
+View source
+
+
+__call__(
+ shape, dtype=None, partition_info=None
+)
+
+
+Returns a tensor object initialized as specified by the initializer.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of the tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+Optional dtype of the tensor. If not provided use the initializer
+dtype.
+ |
+
+|
+`partition_info`
+ |
+
+Optional information about the possible partitioning of a
+tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Initializer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Initializer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..994937e3c9e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Initializer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,161 @@
+description: Initializer base class: all initializers inherit from this class.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.Initializer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Initializer base class: all initializers inherit from this class.
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+from_config
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+from_config(
+ config
+)
+
+
+Instantiates an initializer from a configuration dictionary.
+
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+initializer = RandomUniform(-1, 1)
+config = initializer.get_config()
+initializer = RandomUniform.from_config(config)
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+A Python dictionary. It will typically be the output of
+`get_config`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Initializer instance.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_config
+
+View source
+
+
+get_config()
+
+
+Returns the configuration of the initializer as a JSON-serializable dict.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A JSON-serializable Python dict.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+__call__
+
+View source
+
+
+__call__(
+ shape, dtype=None, partition_info=None
+)
+
+
+Returns a tensor object initialized as specified by the initializer.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of the tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+Optional dtype of the tensor. If not provided use the initializer
+dtype.
+ |
+
+|
+`partition_info`
+ |
+
+Optional information about the possible partitioning of a
+tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Ones.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Ones.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..b7a0ab88c6e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Ones.md
@@ -0,0 +1,183 @@
+description: Initializer that generates tensors initialized to 1.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.Ones
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Initializer that generates tensors initialized to 1.
+
+Inherits From: [`Initializer`](../../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Initializer.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.initializers.ones`, `tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.ones`, `tf.compat.v1.ones_initializer`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.Ones(
+ dtype=tf.dtypes.float32
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+from_config
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+from_config(
+ config
+)
+
+
+Instantiates an initializer from a configuration dictionary.
+
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+initializer = RandomUniform(-1, 1)
+config = initializer.get_config()
+initializer = RandomUniform.from_config(config)
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+A Python dictionary. It will typically be the output of
+`get_config`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Initializer instance.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_config
+
+View source
+
+
+get_config()
+
+
+Returns the configuration of the initializer as a JSON-serializable dict.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A JSON-serializable Python dict.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+__call__
+
+View source
+
+
+__call__(
+ shape, dtype=None, partition_info=None
+)
+
+
+Returns a tensor object initialized as specified by the initializer.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of the tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+Optional dtype of the tensor. If not provided use the initializer
+dtype.
+ |
+
+|
+`partition_info`
+ |
+
+Optional information about the possible partitioning of a
+tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Orthogonal.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Orthogonal.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..2906fa10acf
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Orthogonal.md
@@ -0,0 +1,232 @@
+description: Initializer that generates an orthogonal matrix.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.Orthogonal
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Initializer that generates an orthogonal matrix.
+
+Inherits From: [`Initializer`](../../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Initializer.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.initializers.orthogonal`, `tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.orthogonal`, `tf.compat.v1.orthogonal_initializer`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.Orthogonal(
+ gain=1.0, seed=None, dtype=tf.dtypes.float32
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+If the shape of the tensor to initialize is two-dimensional, it is initialized
+with an orthogonal matrix obtained from the QR decomposition of a matrix of
+random numbers drawn from a normal distribution.
+If the matrix has fewer rows than columns then the output will have orthogonal
+rows. Otherwise, the output will have orthogonal columns.
+
+If the shape of the tensor to initialize is more than two-dimensional,
+a matrix of shape `(shape[0] * ... * shape[n - 2], shape[n - 1])`
+is initialized, where `n` is the length of the shape vector.
+The matrix is subsequently reshaped to give a tensor of the desired shape.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`gain`
+ |
+
+multiplicative factor to apply to the orthogonal matrix
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+A Python integer. Used to create random seeds. See
+tf.compat.v1.set_random_seed for behavior.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+Default data type, used if no `dtype` argument is provided when
+calling the initializer. Only floating point types are supported.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### References:
+
+[Saxe et al., 2014](https://openreview.net/forum?id=_wzZwKpTDF_9C)
+([pdf](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1312.6120.pdf))
+
+
+## Methods
+
+from_config
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+from_config(
+ config
+)
+
+
+Instantiates an initializer from a configuration dictionary.
+
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+initializer = RandomUniform(-1, 1)
+config = initializer.get_config()
+initializer = RandomUniform.from_config(config)
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+A Python dictionary. It will typically be the output of
+`get_config`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Initializer instance.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_config
+
+View source
+
+
+get_config()
+
+
+Returns the configuration of the initializer as a JSON-serializable dict.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A JSON-serializable Python dict.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+__call__
+
+View source
+
+
+__call__(
+ shape, dtype=None, partition_info=None
+)
+
+
+Returns a tensor object initialized as specified by the initializer.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of the tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+Optional dtype of the tensor. If not provided use the initializer
+dtype.
+ |
+
+|
+`partition_info`
+ |
+
+Optional information about the possible partitioning of a
+tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/RandomNormal.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/RandomNormal.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..5da5db242b9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/RandomNormal.md
@@ -0,0 +1,238 @@
+description: Initializer that generates tensors with a normal distribution.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.RandomNormal
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Initializer that generates tensors with a normal distribution.
+
+Inherits From: [`random_normal_initializer`](../../../../../tf/compat/v1/random_normal_initializer.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.normal`, `tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.random_normal`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.RandomNormal(
+ mean=0.0, stddev=0.05, seed=None, dtype=tf.dtypes.float32
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`mean`
+ |
+
+a python scalar or a scalar tensor. Mean of the random values to
+generate. Defaults to 0.
+ |
+
+|
+`stddev`
+ |
+
+a python scalar or a scalar tensor. Standard deviation of the random
+values to generate. Defaults to 0.05.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+A Python integer. Used to create random seeds. See
+tf.compat.v1.set_random_seed for behavior.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+The data type. Only floating point types are supported.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+RandomNormal instance.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+from_config
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+from_config(
+ config
+)
+
+
+Instantiates an initializer from a configuration dictionary.
+
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+initializer = RandomUniform(-1, 1)
+config = initializer.get_config()
+initializer = RandomUniform.from_config(config)
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+A Python dictionary. It will typically be the output of
+`get_config`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Initializer instance.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_config
+
+View source
+
+
+get_config()
+
+
+Returns the configuration of the initializer as a JSON-serializable dict.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A JSON-serializable Python dict.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+__call__
+
+View source
+
+
+__call__(
+ shape, dtype=None, partition_info=None
+)
+
+
+Returns a tensor object initialized as specified by the initializer.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of the tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+Optional dtype of the tensor. If not provided use the initializer
+dtype.
+ |
+
+|
+`partition_info`
+ |
+
+Optional information about the possible partitioning of a
+tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/RandomUniform.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/RandomUniform.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..189e442034e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/RandomUniform.md
@@ -0,0 +1,238 @@
+description: Initializer that generates tensors with a uniform distribution.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.RandomUniform
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Initializer that generates tensors with a uniform distribution.
+
+Inherits From: [`random_uniform_initializer`](../../../../../tf/compat/v1/random_uniform_initializer.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.random_uniform`, `tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.uniform`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.RandomUniform(
+ minval=-0.05, maxval=0.05, seed=None, dtype=tf.dtypes.float32
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`minval`
+ |
+
+A python scalar or a scalar tensor. Lower bound of the range of
+random values to generate. Defaults to -0.05.
+ |
+
+|
+`maxval`
+ |
+
+A python scalar or a scalar tensor. Upper bound of the range of
+random values to generate. Defaults to 0.05.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+A Python integer. Used to create random seeds. See
+tf.compat.v1.set_random_seed for behavior.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+The data type.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A RandomUniform instance.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+from_config
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+from_config(
+ config
+)
+
+
+Instantiates an initializer from a configuration dictionary.
+
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+initializer = RandomUniform(-1, 1)
+config = initializer.get_config()
+initializer = RandomUniform.from_config(config)
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+A Python dictionary. It will typically be the output of
+`get_config`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Initializer instance.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_config
+
+View source
+
+
+get_config()
+
+
+Returns the configuration of the initializer as a JSON-serializable dict.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A JSON-serializable Python dict.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+__call__
+
+View source
+
+
+__call__(
+ shape, dtype=None, partition_info=None
+)
+
+
+Returns a tensor object initialized as specified by the initializer.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of the tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+Optional dtype of the tensor. If not provided use the initializer
+dtype.
+ |
+
+|
+`partition_info`
+ |
+
+Optional information about the possible partitioning of a
+tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/TruncatedNormal.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/TruncatedNormal.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..1599f602eb6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/TruncatedNormal.md
@@ -0,0 +1,242 @@
+description: Initializer that generates a truncated normal distribution.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.TruncatedNormal
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Initializer that generates a truncated normal distribution.
+
+Inherits From: [`truncated_normal_initializer`](../../../../../tf/compat/v1/truncated_normal_initializer.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.truncated_normal`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.TruncatedNormal(
+ mean=0.0, stddev=0.05, seed=None, dtype=tf.dtypes.float32
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+These values are similar to values from a `random_normal_initializer`
+except that values more than two standard deviations from the mean
+are discarded and re-drawn. This is the recommended initializer for
+neural network weights and filters.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`mean`
+ |
+
+a python scalar or a scalar tensor. Mean of the random values to
+generate. Defaults to 0.
+ |
+
+|
+`stddev`
+ |
+
+a python scalar or a scalar tensor. Standard deviation of the random
+values to generate. Defaults to 0.05.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+A Python integer. Used to create random seeds. See
+tf.compat.v1.set_random_seed for behavior.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+The data type. Only floating point types are supported.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A TruncatedNormal instance.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+from_config
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+from_config(
+ config
+)
+
+
+Instantiates an initializer from a configuration dictionary.
+
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+initializer = RandomUniform(-1, 1)
+config = initializer.get_config()
+initializer = RandomUniform.from_config(config)
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+A Python dictionary. It will typically be the output of
+`get_config`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Initializer instance.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_config
+
+View source
+
+
+get_config()
+
+
+Returns the configuration of the initializer as a JSON-serializable dict.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A JSON-serializable Python dict.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+__call__
+
+View source
+
+
+__call__(
+ shape, dtype=None, partition_info=None
+)
+
+
+Returns a tensor object initialized as specified by the initializer.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of the tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+Optional dtype of the tensor. If not provided use the initializer
+dtype.
+ |
+
+|
+`partition_info`
+ |
+
+Optional information about the possible partitioning of a
+tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/VarianceScaling.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/VarianceScaling.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..78227810fde
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/VarianceScaling.md
@@ -0,0 +1,260 @@
+description: Initializer capable of adapting its scale to the shape of weights tensors.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.VarianceScaling
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Initializer capable of adapting its scale to the shape of weights tensors.
+
+Inherits From: [`Initializer`](../../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Initializer.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.initializers.variance_scaling`, `tf.compat.v1.variance_scaling_initializer`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.VarianceScaling(
+ scale=1.0, mode='fan_in', distribution='truncated_normal', seed=None,
+ dtype=tf.dtypes.float32
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+With `distribution="truncated_normal" or "untruncated_normal"`,
+samples are drawn from a truncated/untruncated normal
+distribution with a mean of zero and a standard deviation (after truncation,
+if used) `stddev = sqrt(scale / n)`
+where n is:
+ - number of input units in the weight tensor, if mode = "fan_in"
+ - number of output units, if mode = "fan_out"
+ - average of the numbers of input and output units, if mode = "fan_avg"
+
+With `distribution="uniform"`, samples are drawn from a uniform distribution
+within [-limit, limit], with `limit = sqrt(3 * scale / n)`.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`scale`
+ |
+
+Scaling factor (positive float).
+ |
+
+|
+`mode`
+ |
+
+One of "fan_in", "fan_out", "fan_avg".
+ |
+
+|
+`distribution`
+ |
+
+Random distribution to use. One of "normal", "uniform".
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+A Python integer. Used to create random seeds. See
+tf.compat.v1.set_random_seed for behavior.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+Default data type, used if no `dtype` argument is provided when
+calling the initializer. Only floating point types are supported.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+In case of an invalid value for the "scale", mode" or
+"distribution" arguments.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+from_config
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+from_config(
+ config
+)
+
+
+Instantiates an initializer from a configuration dictionary.
+
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+initializer = RandomUniform(-1, 1)
+config = initializer.get_config()
+initializer = RandomUniform.from_config(config)
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+A Python dictionary. It will typically be the output of
+`get_config`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Initializer instance.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_config
+
+View source
+
+
+get_config()
+
+
+Returns the configuration of the initializer as a JSON-serializable dict.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A JSON-serializable Python dict.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+__call__
+
+View source
+
+
+__call__(
+ shape, dtype=None, partition_info=None
+)
+
+
+Returns a tensor object initialized as specified by the initializer.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of the tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+Optional dtype of the tensor. If not provided use the initializer
+dtype.
+ |
+
+|
+`partition_info`
+ |
+
+Optional information about the possible partitioning of a
+tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Zeros.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Zeros.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..6d0c6c824ca
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Zeros.md
@@ -0,0 +1,183 @@
+description: Initializer that generates tensors initialized to 0.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.Zeros
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Initializer that generates tensors initialized to 0.
+
+Inherits From: [`Initializer`](../../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Initializer.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.initializers.zeros`, `tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.zeros`, `tf.compat.v1.zeros_initializer`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.Zeros(
+ dtype=tf.dtypes.float32
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+from_config
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+from_config(
+ config
+)
+
+
+Instantiates an initializer from a configuration dictionary.
+
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+initializer = RandomUniform(-1, 1)
+config = initializer.get_config()
+initializer = RandomUniform.from_config(config)
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+A Python dictionary. It will typically be the output of
+`get_config`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Initializer instance.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_config
+
+View source
+
+
+get_config()
+
+
+Returns the configuration of the initializer as a JSON-serializable dict.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A JSON-serializable Python dict.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+__call__
+
+View source
+
+
+__call__(
+ shape, dtype=None, partition_info=None
+)
+
+
+Returns a tensor object initialized as specified by the initializer.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of the tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+Optional dtype of the tensor. If not provided use the initializer
+dtype.
+ |
+
+|
+`partition_info`
+ |
+
+Optional information about the possible partitioning of a
+tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/glorot_normal.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/glorot_normal.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..be1e4e69aa7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/glorot_normal.md
@@ -0,0 +1,220 @@
+description: The Glorot normal initializer, also called Xavier normal initializer.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.glorot_normal
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The Glorot normal initializer, also called Xavier normal initializer.
+
+Inherits From: [`VarianceScaling`](../../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/VarianceScaling.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.glorot_normal_initializer`, `tf.compat.v1.initializers.glorot_normal`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.glorot_normal(
+ seed=None, dtype=tf.dtypes.float32
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+It draws samples from a truncated normal distribution centered on 0
+with standard deviation (after truncation) given by
+`stddev = sqrt(2 / (fan_in + fan_out))` where `fan_in` is the number
+of input units in the weight tensor and `fan_out` is the number of
+output units in the weight tensor.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+A Python integer. Used to create random seeds. See
+tf.compat.v1.set_random_seed for behavior.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+Default data type, used if no `dtype` argument is provided when
+calling the initializer. Only floating point types are supported.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### References:
+
+[Glorot et al., 2010](http://proceedings.mlr.press/v9/glorot10a.html)
+([pdf](http://jmlr.org/proceedings/papers/v9/glorot10a/glorot10a.pdf))
+
+
+## Methods
+
+from_config
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+from_config(
+ config
+)
+
+
+Instantiates an initializer from a configuration dictionary.
+
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+initializer = RandomUniform(-1, 1)
+config = initializer.get_config()
+initializer = RandomUniform.from_config(config)
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+A Python dictionary. It will typically be the output of
+`get_config`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Initializer instance.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_config
+
+View source
+
+
+get_config()
+
+
+Returns the configuration of the initializer as a JSON-serializable dict.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A JSON-serializable Python dict.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+__call__
+
+View source
+
+
+__call__(
+ shape, dtype=None, partition_info=None
+)
+
+
+Returns a tensor object initialized as specified by the initializer.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of the tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+Optional dtype of the tensor. If not provided use the initializer
+dtype.
+ |
+
+|
+`partition_info`
+ |
+
+Optional information about the possible partitioning of a
+tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/glorot_uniform.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/glorot_uniform.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3576f96619d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/glorot_uniform.md
@@ -0,0 +1,219 @@
+description: The Glorot uniform initializer, also called Xavier uniform initializer.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.glorot_uniform
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The Glorot uniform initializer, also called Xavier uniform initializer.
+
+Inherits From: [`VarianceScaling`](../../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/VarianceScaling.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.glorot_uniform_initializer`, `tf.compat.v1.initializers.glorot_uniform`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.glorot_uniform(
+ seed=None, dtype=tf.dtypes.float32
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+It draws samples from a uniform distribution within [-limit, limit]
+where `limit` is `sqrt(6 / (fan_in + fan_out))`
+where `fan_in` is the number of input units in the weight tensor
+and `fan_out` is the number of output units in the weight tensor.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+A Python integer. Used to create random seeds. See
+tf.compat.v1.set_random_seed for behavior.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+Default data type, used if no `dtype` argument is provided when
+calling the initializer. Only floating point types are supported.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### References:
+
+[Glorot et al., 2010](http://proceedings.mlr.press/v9/glorot10a.html)
+([pdf](http://jmlr.org/proceedings/papers/v9/glorot10a/glorot10a.pdf))
+
+
+## Methods
+
+from_config
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+from_config(
+ config
+)
+
+
+Instantiates an initializer from a configuration dictionary.
+
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+initializer = RandomUniform(-1, 1)
+config = initializer.get_config()
+initializer = RandomUniform.from_config(config)
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+A Python dictionary. It will typically be the output of
+`get_config`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Initializer instance.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_config
+
+View source
+
+
+get_config()
+
+
+Returns the configuration of the initializer as a JSON-serializable dict.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A JSON-serializable Python dict.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+__call__
+
+View source
+
+
+__call__(
+ shape, dtype=None, partition_info=None
+)
+
+
+Returns a tensor object initialized as specified by the initializer.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of the tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+Optional dtype of the tensor. If not provided use the initializer
+dtype.
+ |
+
+|
+`partition_info`
+ |
+
+Optional information about the possible partitioning of a
+tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/he_normal.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/he_normal.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..1661573dd13
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/he_normal.md
@@ -0,0 +1,87 @@
+description: He normal initializer.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.he_normal
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+He normal initializer.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.initializers.he_normal`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.he_normal(
+ seed=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+It draws samples from a truncated normal distribution centered on 0
+with standard deviation (after truncation) given by
+`stddev = sqrt(2 / fan_in)` where `fan_in` is the number of
+input units in the weight tensor.
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+A Python integer. Used to seed the random generator.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An initializer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### References:
+
+[He et al., 2015]
+(https://www.cv-foundation.org/openaccess/content_iccv_2015/html/He_Delving_Deep_into_ICCV_2015_paper.html)
+
+([pdf](https://www.cv-foundation.org/openaccess/content_iccv_2015/papers/He_Delving_Deep_into_ICCV_2015_paper.pdf))
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/he_uniform.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/he_uniform.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a8b0d9ba44e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/he_uniform.md
@@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
+description: He uniform variance scaling initializer.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.he_uniform
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+He uniform variance scaling initializer.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.initializers.he_uniform`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.he_uniform(
+ seed=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+It draws samples from a uniform distribution within [-limit, limit]
+where `limit` is `sqrt(6 / fan_in)`
+where `fan_in` is the number of input units in the weight tensor.
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+A Python integer. Used to seed the random generator.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An initializer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### References:
+
+[He et al., 2015]
+(https://www.cv-foundation.org/openaccess/content_iccv_2015/html/He_Delving_Deep_into_ICCV_2015_paper.html)
+
+([pdf](https://www.cv-foundation.org/openaccess/content_iccv_2015/papers/He_Delving_Deep_into_ICCV_2015_paper.pdf))
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/lecun_normal.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/lecun_normal.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..d4cf805bd9b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/lecun_normal.md
@@ -0,0 +1,90 @@
+description: LeCun normal initializer.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.lecun_normal
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+LeCun normal initializer.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.initializers.lecun_normal`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.lecun_normal(
+ seed=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+It draws samples from a truncated normal distribution centered on 0
+with standard deviation (after truncation) given by
+`stddev = sqrt(1 / fan_in)` where `fan_in` is the number of
+input units in the weight tensor.
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+A Python integer. Used to seed the random generator.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An initializer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### References:
+
+- Self-Normalizing Neural Networks,
+[Klambauer et al.,
+2017](https://papers.nips.cc/paper/6698-self-normalizing-neural-networks)
+
+([pdf](https://papers.nips.cc/paper/6698-self-normalizing-neural-networks.pdf))
+- Efficient Backprop,
+[Lecun et al., 1998](http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/publis/pdf/lecun-98b.pdf)
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/lecun_uniform.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/lecun_uniform.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..21f415334ed
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/lecun_uniform.md
@@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
+description: LeCun uniform initializer.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.lecun_uniform
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+LeCun uniform initializer.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.initializers.lecun_uniform`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.keras.initializers.lecun_uniform(
+ seed=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+It draws samples from a uniform distribution within [-limit, limit]
+where `limit` is `sqrt(3 / fan_in)`
+where `fan_in` is the number of input units in the weight tensor.
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+A Python integer. Used to seed the random generator.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An initializer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### References:
+
+- Self-Normalizing Neural Networks,
+[Klambauer et al.,
+2017](https://papers.nips.cc/paper/6698-self-normalizing-neural-networks)
+
+([pdf](https://papers.nips.cc/paper/6698-self-normalizing-neural-networks.pdf))
+- Efficient Backprop,
+[Lecun et al., 1998](http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/publis/pdf/lecun-98b.pdf)
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e8727853886
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers.md
@@ -0,0 +1,259 @@
+description: Keras layers API.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.layers
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Keras layers API.
+
+
+
+## Modules
+
+[`experimental`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/experimental.md) module: Public API for tf.keras.layers.experimental namespace.
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class AbstractRNNCell`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/AbstractRNNCell.md): Abstract object representing an RNN cell.
+
+[`class Activation`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Activation.md): Applies an activation function to an output.
+
+[`class ActivityRegularization`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/ActivityRegularization.md): Layer that applies an update to the cost function based input activity.
+
+[`class Add`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Add.md): Layer that adds a list of inputs.
+
+[`class AdditiveAttention`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/AdditiveAttention.md): Additive attention layer, a.k.a. Bahdanau-style attention.
+
+[`class AlphaDropout`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/AlphaDropout.md): Applies Alpha Dropout to the input.
+
+[`class Attention`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Attention.md): Dot-product attention layer, a.k.a. Luong-style attention.
+
+[`class Average`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Average.md): Layer that averages a list of inputs element-wise.
+
+[`class AveragePooling1D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/AveragePooling1D.md): Average pooling for temporal data.
+
+[`class AveragePooling2D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/AveragePooling2D.md): Average pooling operation for spatial data.
+
+[`class AveragePooling3D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/AveragePooling3D.md): Average pooling operation for 3D data (spatial or spatio-temporal).
+
+[`class AvgPool1D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/AveragePooling1D.md): Average pooling for temporal data.
+
+[`class AvgPool2D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/AveragePooling2D.md): Average pooling operation for spatial data.
+
+[`class AvgPool3D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/AveragePooling3D.md): Average pooling operation for 3D data (spatial or spatio-temporal).
+
+[`class BatchNormalization`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/BatchNormalization.md): Normalize and scale inputs or activations. (Ioffe and Szegedy, 2014).
+
+[`class Bidirectional`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Bidirectional.md): Bidirectional wrapper for RNNs.
+
+[`class Concatenate`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Concatenate.md): Layer that concatenates a list of inputs.
+
+[`class Conv1D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Conv1D.md): 1D convolution layer (e.g. temporal convolution).
+
+[`class Conv2D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Conv2D.md): 2D convolution layer (e.g. spatial convolution over images).
+
+[`class Conv2DTranspose`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Conv2DTranspose.md): Transposed convolution layer (sometimes called Deconvolution).
+
+[`class Conv3D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Conv3D.md): 3D convolution layer (e.g. spatial convolution over volumes).
+
+[`class Conv3DTranspose`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Conv3DTranspose.md): Transposed convolution layer (sometimes called Deconvolution).
+
+[`class ConvLSTM2D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/ConvLSTM2D.md): Convolutional LSTM.
+
+[`class Convolution1D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Conv1D.md): 1D convolution layer (e.g. temporal convolution).
+
+[`class Convolution2D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Conv2D.md): 2D convolution layer (e.g. spatial convolution over images).
+
+[`class Convolution2DTranspose`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Conv2DTranspose.md): Transposed convolution layer (sometimes called Deconvolution).
+
+[`class Convolution3D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Conv3D.md): 3D convolution layer (e.g. spatial convolution over volumes).
+
+[`class Convolution3DTranspose`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Conv3DTranspose.md): Transposed convolution layer (sometimes called Deconvolution).
+
+[`class Cropping1D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Cropping1D.md): Cropping layer for 1D input (e.g. temporal sequence).
+
+[`class Cropping2D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Cropping2D.md): Cropping layer for 2D input (e.g. picture).
+
+[`class Cropping3D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Cropping3D.md): Cropping layer for 3D data (e.g. spatial or spatio-temporal).
+
+[`class CuDNNGRU`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/CuDNNGRU.md): Fast GRU implementation backed by cuDNN.
+
+[`class CuDNNLSTM`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/CuDNNLSTM.md): Fast LSTM implementation backed by cuDNN.
+
+[`class Dense`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Dense.md): Just your regular densely-connected NN layer.
+
+[`class DenseFeatures`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/DenseFeatures.md): A layer that produces a dense `Tensor` based on given `feature_columns`.
+
+[`class DepthwiseConv2D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/DepthwiseConv2D.md): Depthwise separable 2D convolution.
+
+[`class Dot`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Dot.md): Layer that computes a dot product between samples in two tensors.
+
+[`class Dropout`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Dropout.md): Applies Dropout to the input.
+
+[`class ELU`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/ELU.md): Exponential Linear Unit.
+
+[`class Embedding`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Embedding.md): Turns positive integers (indexes) into dense vectors of fixed size.
+
+[`class Flatten`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Flatten.md): Flattens the input. Does not affect the batch size.
+
+[`class GRU`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/GRU.md): Gated Recurrent Unit - Cho et al. 2014.
+
+[`class GRUCell`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/GRUCell.md): Cell class for the GRU layer.
+
+[`class GaussianDropout`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/GaussianDropout.md): Apply multiplicative 1-centered Gaussian noise.
+
+[`class GaussianNoise`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/GaussianNoise.md): Apply additive zero-centered Gaussian noise.
+
+[`class GlobalAveragePooling1D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/GlobalAveragePooling1D.md): Global average pooling operation for temporal data.
+
+[`class GlobalAveragePooling2D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/GlobalAveragePooling2D.md): Global average pooling operation for spatial data.
+
+[`class GlobalAveragePooling3D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/GlobalAveragePooling3D.md): Global Average pooling operation for 3D data.
+
+[`class GlobalAvgPool1D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/GlobalAveragePooling1D.md): Global average pooling operation for temporal data.
+
+[`class GlobalAvgPool2D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/GlobalAveragePooling2D.md): Global average pooling operation for spatial data.
+
+[`class GlobalAvgPool3D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/GlobalAveragePooling3D.md): Global Average pooling operation for 3D data.
+
+[`class GlobalMaxPool1D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/GlobalMaxPool1D.md): Global max pooling operation for 1D temporal data.
+
+[`class GlobalMaxPool2D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/GlobalMaxPool2D.md): Global max pooling operation for spatial data.
+
+[`class GlobalMaxPool3D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/GlobalMaxPool3D.md): Global Max pooling operation for 3D data.
+
+[`class GlobalMaxPooling1D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/GlobalMaxPool1D.md): Global max pooling operation for 1D temporal data.
+
+[`class GlobalMaxPooling2D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/GlobalMaxPool2D.md): Global max pooling operation for spatial data.
+
+[`class GlobalMaxPooling3D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/GlobalMaxPool3D.md): Global Max pooling operation for 3D data.
+
+[`class InputLayer`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/InputLayer.md): Layer to be used as an entry point into a Network (a graph of layers).
+
+[`class InputSpec`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/InputSpec.md): Specifies the rank, dtype and shape of every input to a layer.
+
+[`class LSTM`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/LSTM.md): Long Short-Term Memory layer - Hochreiter 1997.
+
+[`class LSTMCell`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/LSTMCell.md): Cell class for the LSTM layer.
+
+[`class Lambda`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Lambda.md): Wraps arbitrary expressions as a `Layer` object.
+
+[`class Layer`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Layer.md): This is the class from which all layers inherit.
+
+[`class LayerNormalization`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/LayerNormalization.md): Layer normalization layer (Ba et al., 2016).
+
+[`class LeakyReLU`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/LeakyReLU.md): Leaky version of a Rectified Linear Unit.
+
+[`class LocallyConnected1D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/LocallyConnected1D.md): Locally-connected layer for 1D inputs.
+
+[`class LocallyConnected2D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/LocallyConnected2D.md): Locally-connected layer for 2D inputs.
+
+[`class Masking`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Masking.md): Masks a sequence by using a mask value to skip timesteps.
+
+[`class MaxPool1D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/MaxPool1D.md): Max pooling operation for 1D temporal data.
+
+[`class MaxPool2D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/MaxPool2D.md): Max pooling operation for 2D spatial data.
+
+[`class MaxPool3D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/MaxPool3D.md): Max pooling operation for 3D data (spatial or spatio-temporal).
+
+[`class MaxPooling1D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/MaxPool1D.md): Max pooling operation for 1D temporal data.
+
+[`class MaxPooling2D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/MaxPool2D.md): Max pooling operation for 2D spatial data.
+
+[`class MaxPooling3D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/MaxPool3D.md): Max pooling operation for 3D data (spatial or spatio-temporal).
+
+[`class Maximum`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Maximum.md): Layer that computes the maximum (element-wise) a list of inputs.
+
+[`class Minimum`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Minimum.md): Layer that computes the minimum (element-wise) a list of inputs.
+
+[`class Multiply`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Multiply.md): Layer that multiplies (element-wise) a list of inputs.
+
+[`class PReLU`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/PReLU.md): Parametric Rectified Linear Unit.
+
+[`class Permute`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Permute.md): Permutes the dimensions of the input according to a given pattern.
+
+[`class RNN`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/RNN.md): Base class for recurrent layers.
+
+[`class ReLU`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/ReLU.md): Rectified Linear Unit activation function.
+
+[`class RepeatVector`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/RepeatVector.md): Repeats the input n times.
+
+[`class Reshape`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Reshape.md): Layer that reshapes inputs into the given shape.
+
+[`class SeparableConv1D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/SeparableConv1D.md): Depthwise separable 1D convolution.
+
+[`class SeparableConv2D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/SeparableConv2D.md): Depthwise separable 2D convolution.
+
+[`class SeparableConvolution1D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/SeparableConv1D.md): Depthwise separable 1D convolution.
+
+[`class SeparableConvolution2D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/SeparableConv2D.md): Depthwise separable 2D convolution.
+
+[`class SimpleRNN`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/SimpleRNN.md): Fully-connected RNN where the output is to be fed back to input.
+
+[`class SimpleRNNCell`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/SimpleRNNCell.md): Cell class for SimpleRNN.
+
+[`class Softmax`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Softmax.md): Softmax activation function.
+
+[`class SpatialDropout1D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/SpatialDropout1D.md): Spatial 1D version of Dropout.
+
+[`class SpatialDropout2D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/SpatialDropout2D.md): Spatial 2D version of Dropout.
+
+[`class SpatialDropout3D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/SpatialDropout3D.md): Spatial 3D version of Dropout.
+
+[`class StackedRNNCells`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/StackedRNNCells.md): Wrapper allowing a stack of RNN cells to behave as a single cell.
+
+[`class Subtract`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Subtract.md): Layer that subtracts two inputs.
+
+[`class ThresholdedReLU`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/ThresholdedReLU.md): Thresholded Rectified Linear Unit.
+
+[`class TimeDistributed`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/TimeDistributed.md): This wrapper allows to apply a layer to every temporal slice of an input.
+
+[`class UpSampling1D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/UpSampling1D.md): Upsampling layer for 1D inputs.
+
+[`class UpSampling2D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/UpSampling2D.md): Upsampling layer for 2D inputs.
+
+[`class UpSampling3D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/UpSampling3D.md): Upsampling layer for 3D inputs.
+
+[`class Wrapper`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Wrapper.md): Abstract wrapper base class.
+
+[`class ZeroPadding1D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/ZeroPadding1D.md): Zero-padding layer for 1D input (e.g. temporal sequence).
+
+[`class ZeroPadding2D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/ZeroPadding2D.md): Zero-padding layer for 2D input (e.g. picture).
+
+[`class ZeroPadding3D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/ZeroPadding3D.md): Zero-padding layer for 3D data (spatial or spatio-temporal).
+
+## Functions
+
+[`Input(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/Input.md): `Input()` is used to instantiate a Keras tensor.
+
+[`add(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/add.md): Functional interface to the tf.keras.layers.Add layer.
+
+[`average(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/average.md): Functional interface to the tf.keras.layers.Average layer.
+
+[`concatenate(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/concatenate.md): Functional interface to the `Concatenate` layer.
+
+[`deserialize(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/deserialize.md): Instantiates a layer from a config dictionary.
+
+[`dot(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/dot.md): Functional interface to the `Dot` layer.
+
+[`maximum(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/maximum.md): Functional interface to compute maximum (element-wise) list of `inputs`.
+
+[`minimum(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/minimum.md): Functional interface to the `Minimum` layer.
+
+[`multiply(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/multiply.md): Functional interface to the `Multiply` layer.
+
+[`serialize(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/serialize.md)
+
+[`subtract(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/subtract.md): Functional interface to the `Subtract` layer.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/BatchNormalization.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/BatchNormalization.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..af45c102876
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/BatchNormalization.md
@@ -0,0 +1,300 @@
+description: Normalize and scale inputs or activations. (Ioffe and Szegedy, 2014).
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.keras.layers.BatchNormalization
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Normalize and scale inputs or activations. (Ioffe and Szegedy, 2014).
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.keras.layers.BatchNormalization(
+ axis=-1, momentum=0.99, epsilon=0.001, center=(True), scale=(True),
+ beta_initializer='zeros', gamma_initializer='ones',
+ moving_mean_initializer='zeros', moving_variance_initializer='ones',
+ beta_regularizer=None, gamma_regularizer=None, beta_constraint=None,
+ gamma_constraint=None, renorm=(False), renorm_clipping=None,
+ renorm_momentum=0.99, fused=None, trainable=(True), virtual_batch_size=None,
+ adjustment=None, name=None, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Normalize the activations of the previous layer at each batch,
+i.e. applies a transformation that maintains the mean activation
+close to 0 and the activation standard deviation close to 1.
+
+Batch normalization differs from other layers in several key aspects:
+
+1) Adding BatchNormalization with `training=True` to a model causes the
+result of one example to depend on the contents of all other examples in a
+minibatch. Be careful when padding batches or masking examples, as these can
+change the minibatch statistics and affect other examples.
+
+2) Updates to the weights (moving statistics) are based on the forward pass
+of a model rather than the result of gradient computations.
+
+3) When performing inference using a model containing batch normalization, it
+is generally (though not always) desirable to use accumulated statistics
+rather than mini-batch statistics. This is accomplished by passing
+`training=False` when calling the model, or using `model.predict`.
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`axis`
+ |
+
+Integer, the axis that should be normalized
+(typically the features axis).
+For instance, after a `Conv2D` layer with
+`data_format="channels_first"`,
+set `axis=1` in `BatchNormalization`.
+ |
+
+|
+`momentum`
+ |
+
+Momentum for the moving average.
+ |
+
+|
+`epsilon`
+ |
+
+Small float added to variance to avoid dividing by zero.
+ |
+
+|
+`center`
+ |
+
+If True, add offset of `beta` to normalized tensor.
+If False, `beta` is ignored.
+ |
+
+|
+`scale`
+ |
+
+If True, multiply by `gamma`.
+If False, `gamma` is not used.
+When the next layer is linear (also e.g. `nn.relu`),
+this can be disabled since the scaling
+will be done by the next layer.
+ |
+
+|
+`beta_initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer for the beta weight.
+ |
+
+|
+`gamma_initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer for the gamma weight.
+ |
+
+|
+`moving_mean_initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer for the moving mean.
+ |
+
+|
+`moving_variance_initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer for the moving variance.
+ |
+
+|
+`beta_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the beta weight.
+ |
+
+|
+`gamma_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the gamma weight.
+ |
+
+|
+`beta_constraint`
+ |
+
+Optional constraint for the beta weight.
+ |
+
+|
+`gamma_constraint`
+ |
+
+Optional constraint for the gamma weight.
+ |
+
+|
+`renorm`
+ |
+
+Whether to use Batch Renormalization
+(https://arxiv.org/abs/1702.03275). This adds extra variables during
+training. The inference is the same for either value of this parameter.
+ |
+
+|
+`renorm_clipping`
+ |
+
+A dictionary that may map keys 'rmax', 'rmin', 'dmax' to
+scalar `Tensors` used to clip the renorm correction. The correction
+`(r, d)` is used as `corrected_value = normalized_value * r + d`, with
+`r` clipped to [rmin, rmax], and `d` to [-dmax, dmax]. Missing rmax, rmin,
+dmax are set to inf, 0, inf, respectively.
+ |
+
+|
+`renorm_momentum`
+ |
+
+Momentum used to update the moving means and standard
+deviations with renorm. Unlike `momentum`, this affects training
+and should be neither too small (which would add noise) nor too large
+(which would give stale estimates). Note that `momentum` is still applied
+to get the means and variances for inference.
+ |
+
+|
+`fused`
+ |
+
+if `None` or `True`, use a faster, fused implementation if possible.
+If `False`, use the system recommended implementation.
+ |
+
+|
+`trainable`
+ |
+
+Boolean, if `True` the variables will be marked as trainable.
+ |
+
+|
+`virtual_batch_size`
+ |
+
+An `int`. By default, `virtual_batch_size` is `None`,
+which means batch normalization is performed across the whole batch. When
+`virtual_batch_size` is not `None`, instead perform "Ghost Batch
+Normalization", which creates virtual sub-batches which are each
+normalized separately (with shared gamma, beta, and moving statistics).
+Must divide the actual batch size during execution.
+ |
+
+|
+`adjustment`
+ |
+
+A function taking the `Tensor` containing the (dynamic) shape of
+the input tensor and returning a pair (scale, bias) to apply to the
+normalized values (before gamma and beta), only during training. For
+example, if axis==-1,
+`adjustment = lambda shape: (
+tf.random.uniform(shape[-1:], 0.93, 1.07),
+tf.random.uniform(shape[-1:], -0.1, 0.1))`
+will scale the normalized value by up to 7% up or down, then shift the
+result by up to 0.1 (with independent scaling and bias for each feature
+but shared across all examples), and finally apply gamma and/or beta. If
+`None`, no adjustment is applied. Cannot be specified if
+virtual_batch_size is specified.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Call arguments:
+
+
+* `inputs`: Input tensor (of any rank).
+* `training`: Python boolean indicating whether the layer should behave in
+ training mode or in inference mode.
+ - `training=True`: The layer will normalize its inputs using the
+ mean and variance of the current batch of inputs.
+ - `training=False`: The layer will normalize its inputs using the
+ mean and variance of its moving statistics, learned during training.
+
+
+#### Input shape:
+
+Arbitrary. Use the keyword argument `input_shape`
+(tuple of integers, does not include the samples axis)
+when using this layer as the first layer in a model.
+
+
+
+#### Output shape:
+
+Same shape as input.
+
+
+
+
+Normalization equations:
+ Consider the intermediate activations \(x\) of a mini-batch of size
+ \\(m\\):
+
+ We can compute the mean and variance of the batch
+
+ \\({\mu_B} = \frac{1}{m} \sum_{i=1}^{m} {x_i}\\)
+
+ \\({\sigma_B^2} = \frac{1}{m} \sum_{i=1}^{m} ({x_i} - {\mu_B})^2\\)
+
+ and then compute a normalized \\(x\\), including a small factor
+ \\({\epsilon}\\) for numerical stability.
+
+ \\(\hat{x_i} = \frac{x_i - \mu_B}{\sqrt{\sigma_B^2 + \epsilon}}\\)
+
+ And finally \\(\hat{x}\) is linearly transformed by \({\gamma}\\)
+ and \\({\beta}\\), which are learned parameters:
+
+ \\({y_i} = {\gamma * \hat{x_i} + \beta}\\)
+
+#### References:
+
+
+- [Batch Normalization: Accelerating Deep Network Training by Reducing
+ Internal Covariate Shift](https://arxiv.org/abs/1502.03167)
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/CuDNNGRU.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/CuDNNGRU.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..6b9007e0b36
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/CuDNNGRU.md
@@ -0,0 +1,252 @@
+description: Fast GRU implementation backed by cuDNN.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.keras.layers.CuDNNGRU
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Fast GRU implementation backed by cuDNN.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.keras.layers.CuDNNGRU(
+ units, kernel_initializer='glorot_uniform', recurrent_initializer='orthogonal',
+ bias_initializer='zeros', kernel_regularizer=None, recurrent_regularizer=None,
+ bias_regularizer=None, activity_regularizer=None, kernel_constraint=None,
+ recurrent_constraint=None, bias_constraint=None, return_sequences=(False),
+ return_state=(False), go_backwards=(False), stateful=(False), **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+More information about cuDNN can be found on the [NVIDIA
+developer website](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn).
+Can only be run on GPU.
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`units`
+ |
+
+Positive integer, dimensionality of the output space.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer for the `kernel` weights matrix, used for
+the linear transformation of the inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer for the `recurrent_kernel` weights
+matrix, used for the linear transformation of the recurrent state.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer for the bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Regularizer function applied to the `kernel` weights
+matrix.
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Regularizer function applied to the
+`recurrent_kernel` weights matrix.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Regularizer function applied to the bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`activity_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Regularizer function applied to the output of the
+layer (its "activation").
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_constraint`
+ |
+
+Constraint function applied to the `kernel` weights
+matrix.
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_constraint`
+ |
+
+Constraint function applied to the
+`recurrent_kernel` weights matrix.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_constraint`
+ |
+
+Constraint function applied to the bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`return_sequences`
+ |
+
+Boolean. Whether to return the last output in the output
+sequence, or the full sequence.
+ |
+
+|
+`return_state`
+ |
+
+Boolean. Whether to return the last state in addition to the
+output.
+ |
+
+|
+`go_backwards`
+ |
+
+Boolean (default False). If True, process the input sequence
+backwards and return the reversed sequence.
+ |
+
+|
+`stateful`
+ |
+
+Boolean (default False). If True, the last state for each sample
+at index i in a batch will be used as initial state for the sample of
+index i in the following batch.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cell`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`states`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+reset_states
+
+View source
+
+
+reset_states(
+ states=None
+)
+
+
+Reset the recorded states for the stateful RNN layer.
+
+Can only be used when RNN layer is constructed with `stateful` = `True`.
+Args:
+ states: Numpy arrays that contains the value for the initial state, which
+ will be feed to cell at the first time step. When the value is None,
+ zero filled numpy array will be created based on the cell state size.
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`AttributeError`
+ |
+
+When the RNN layer is not stateful.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+When the batch size of the RNN layer is unknown.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+When the input numpy array is not compatible with the RNN
+layer state, either size wise or dtype wise.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/CuDNNLSTM.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/CuDNNLSTM.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3141255f7ed
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/CuDNNLSTM.md
@@ -0,0 +1,263 @@
+description: Fast LSTM implementation backed by cuDNN.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.keras.layers.CuDNNLSTM
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Fast LSTM implementation backed by cuDNN.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.keras.layers.CuDNNLSTM(
+ units, kernel_initializer='glorot_uniform', recurrent_initializer='orthogonal',
+ bias_initializer='zeros', unit_forget_bias=(True), kernel_regularizer=None,
+ recurrent_regularizer=None, bias_regularizer=None, activity_regularizer=None,
+ kernel_constraint=None, recurrent_constraint=None, bias_constraint=None,
+ return_sequences=(False), return_state=(False), go_backwards=(False),
+ stateful=(False), **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+More information about cuDNN can be found on the [NVIDIA
+developer website](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn).
+Can only be run on GPU.
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`units`
+ |
+
+Positive integer, dimensionality of the output space.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer for the `kernel` weights matrix, used for
+the linear transformation of the inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`unit_forget_bias`
+ |
+
+Boolean. If True, add 1 to the bias of the forget gate
+at initialization. Setting it to true will also force
+`bias_initializer="zeros"`. This is recommended in [Jozefowicz et
+al.](http://www.jmlr.org/proceedings/papers/v37/jozefowicz15.pdf)
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer for the `recurrent_kernel` weights
+matrix, used for the linear transformation of the recurrent state.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer for the bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Regularizer function applied to the `kernel` weights
+matrix.
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Regularizer function applied to the
+`recurrent_kernel` weights matrix.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Regularizer function applied to the bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`activity_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Regularizer function applied to the output of the
+layer (its "activation").
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_constraint`
+ |
+
+Constraint function applied to the `kernel` weights
+matrix.
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_constraint`
+ |
+
+Constraint function applied to the
+`recurrent_kernel` weights matrix.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_constraint`
+ |
+
+Constraint function applied to the bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`return_sequences`
+ |
+
+Boolean. Whether to return the last output. in the
+output sequence, or the full sequence.
+ |
+
+|
+`return_state`
+ |
+
+Boolean. Whether to return the last state in addition to the
+output.
+ |
+
+|
+`go_backwards`
+ |
+
+Boolean (default False). If True, process the input sequence
+backwards and return the reversed sequence.
+ |
+
+|
+`stateful`
+ |
+
+Boolean (default False). If True, the last state for each sample
+at index i in a batch will be used as initial state for the sample of
+index i in the following batch.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cell`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`states`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+reset_states
+
+View source
+
+
+reset_states(
+ states=None
+)
+
+
+Reset the recorded states for the stateful RNN layer.
+
+Can only be used when RNN layer is constructed with `stateful` = `True`.
+Args:
+ states: Numpy arrays that contains the value for the initial state, which
+ will be feed to cell at the first time step. When the value is None,
+ zero filled numpy array will be created based on the cell state size.
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`AttributeError`
+ |
+
+When the RNN layer is not stateful.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+When the batch size of the RNN layer is unknown.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+When the input numpy array is not compatible with the RNN
+layer state, either size wise or dtype wise.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/DenseFeatures.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/DenseFeatures.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..fff212540b3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/DenseFeatures.md
@@ -0,0 +1,140 @@
+description: A layer that produces a dense Tensor based on given feature_columns.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.keras.layers.DenseFeatures
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A layer that produces a dense `Tensor` based on given `feature_columns`.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.keras.layers.DenseFeatures(
+ feature_columns, trainable=(True), name=None, partitioner=None, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Generally a single example in training data is described with FeatureColumns.
+At the first layer of the model, this column-oriented data should be converted
+to a single `Tensor`.
+
+This layer can be called multiple times with different features.
+
+This is the V1 version of this layer that uses variable_scope's or partitioner
+to create variables which works well with PartitionedVariables. Variable
+scopes are deprecated in V2, so the V2 version uses name_scopes instead. But
+currently that lacks support for partitioned variables. Use this if you need
+partitioned variables. Use the partitioner argument if you have a Keras model
+and uses tf.compat.v1.keras.estimator.model_to_estimator for training.
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+price = tf.feature_column.numeric_column('price')
+keywords_embedded = tf.feature_column.embedding_column(
+ tf.feature_column.categorical_column_with_hash_bucket("keywords", 10K),
+ dimensions=16)
+columns = [price, keywords_embedded, ...]
+partitioner = tf.compat.v1.fixed_size_partitioner(num_shards=4)
+feature_layer = tf.compat.v1.keras.layers.DenseFeatures(
+ feature_columns=columns, partitioner=partitioner)
+
+features = tf.io.parse_example(
+ ..., features=tf.feature_column.make_parse_example_spec(columns))
+dense_tensor = feature_layer(features)
+for units in [128, 64, 32]:
+ dense_tensor = tf.compat.v1.keras.layers.Dense(
+ units, activation='relu')(dense_tensor)
+prediction = tf.compat.v1.keras.layers.Dense(1)(dense_tensor)
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`feature_columns`
+ |
+
+An iterable containing the FeatureColumns to use as
+inputs to your model. All items should be instances of classes derived
+from `DenseColumn` such as `numeric_column`, `embedding_column`,
+`bucketized_column`, `indicator_column`. If you have categorical
+features, you can wrap them with an `embedding_column` or
+`indicator_column`.
+ |
+
+|
+`trainable`
+ |
+
+Boolean, whether the layer's variables will be updated via
+gradient descent during training.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name to give to the DenseFeatures.
+ |
+
+|
+`partitioner`
+ |
+
+Partitioner for input layer. Defaults to None.
+ |
+
+|
+`**kwargs`
+ |
+
+Keyword arguments to construct a layer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if an item in `feature_columns` is not a `DenseColumn`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/GRU.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/GRU.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a90c58083aa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/GRU.md
@@ -0,0 +1,482 @@
+description: Gated Recurrent Unit - Cho et al. 2014.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.keras.layers.GRU
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Gated Recurrent Unit - Cho et al. 2014.
+
+Inherits From: [`RNN`](../../../../../tf/keras/layers/RNN.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.keras.layers.GRU(
+ units, activation='tanh', recurrent_activation='hard_sigmoid', use_bias=(True),
+ kernel_initializer='glorot_uniform', recurrent_initializer='orthogonal',
+ bias_initializer='zeros', kernel_regularizer=None, recurrent_regularizer=None,
+ bias_regularizer=None, activity_regularizer=None, kernel_constraint=None,
+ recurrent_constraint=None, bias_constraint=None, dropout=0.0,
+ recurrent_dropout=0.0, implementation=1, return_sequences=(False),
+ return_state=(False), go_backwards=(False), stateful=(False), unroll=(False),
+ reset_after=(False), **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+There are two variants. The default one is based on 1406.1078v3 and
+has reset gate applied to hidden state before matrix multiplication. The
+other one is based on original 1406.1078v1 and has the order reversed.
+
+The second variant is compatible with CuDNNGRU (GPU-only) and allows
+inference on CPU. Thus it has separate biases for `kernel` and
+`recurrent_kernel`. Use `'reset_after'=True` and
+`recurrent_activation='sigmoid'`.
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`units`
+ |
+
+Positive integer, dimensionality of the output space.
+ |
+
+|
+`activation`
+ |
+
+Activation function to use.
+Default: hyperbolic tangent (`tanh`).
+If you pass `None`, no activation is applied
+(ie. "linear" activation: `a(x) = x`).
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_activation`
+ |
+
+Activation function to use
+for the recurrent step.
+Default: hard sigmoid (`hard_sigmoid`).
+If you pass `None`, no activation is applied
+(ie. "linear" activation: `a(x) = x`).
+ |
+
+|
+`use_bias`
+ |
+
+Boolean, whether the layer uses a bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer for the `kernel` weights matrix,
+used for the linear transformation of the inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer for the `recurrent_kernel`
+weights matrix, used for the linear transformation of the recurrent state.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer for the bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Regularizer function applied to
+the `kernel` weights matrix.
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Regularizer function applied to
+the `recurrent_kernel` weights matrix.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Regularizer function applied to the bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`activity_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Regularizer function applied to
+the output of the layer (its "activation")..
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_constraint`
+ |
+
+Constraint function applied to
+the `kernel` weights matrix.
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_constraint`
+ |
+
+Constraint function applied to
+the `recurrent_kernel` weights matrix.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_constraint`
+ |
+
+Constraint function applied to the bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`dropout`
+ |
+
+Float between 0 and 1.
+Fraction of the units to drop for
+the linear transformation of the inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_dropout`
+ |
+
+Float between 0 and 1.
+Fraction of the units to drop for
+the linear transformation of the recurrent state.
+ |
+
+|
+`implementation`
+ |
+
+Implementation mode, either 1 or 2.
+Mode 1 will structure its operations as a larger number of
+smaller dot products and additions, whereas mode 2 will
+batch them into fewer, larger operations. These modes will
+have different performance profiles on different hardware and
+for different applications.
+ |
+
+|
+`return_sequences`
+ |
+
+Boolean. Whether to return the last output
+in the output sequence, or the full sequence.
+ |
+
+|
+`return_state`
+ |
+
+Boolean. Whether to return the last state
+in addition to the output.
+ |
+
+|
+`go_backwards`
+ |
+
+Boolean (default False).
+If True, process the input sequence backwards and return the
+reversed sequence.
+ |
+
+|
+`stateful`
+ |
+
+Boolean (default False). If True, the last state
+for each sample at index i in a batch will be used as initial
+state for the sample of index i in the following batch.
+ |
+
+|
+`unroll`
+ |
+
+Boolean (default False).
+If True, the network will be unrolled,
+else a symbolic loop will be used.
+Unrolling can speed-up a RNN,
+although it tends to be more memory-intensive.
+Unrolling is only suitable for short sequences.
+ |
+
+|
+`time_major`
+ |
+
+The shape format of the `inputs` and `outputs` tensors.
+If True, the inputs and outputs will be in shape
+`(timesteps, batch, ...)`, whereas in the False case, it will be
+`(batch, timesteps, ...)`. Using `time_major = True` is a bit more
+efficient because it avoids transposes at the beginning and end of the
+RNN calculation. However, most TensorFlow data is batch-major, so by
+default this function accepts input and emits output in batch-major
+form.
+ |
+
+|
+`reset_after`
+ |
+
+GRU convention (whether to apply reset gate after or
+before matrix multiplication). False = "before" (default),
+True = "after" (CuDNN compatible).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Call arguments:
+
+
+* `inputs`: A 3D tensor.
+* `mask`: Binary tensor of shape `(samples, timesteps)` indicating whether
+ a given timestep should be masked.
+* `training`: Python boolean indicating whether the layer should behave in
+ training mode or in inference mode. This argument is passed to the cell
+ when calling it. This is only relevant if `dropout` or
+ `recurrent_dropout` is used.
+* `initial_state`: List of initial state tensors to be passed to the first
+ call of the cell.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`activation`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_constraint`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_initializer`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_regularizer`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`dropout`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`implementation`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_constraint`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_initializer`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_regularizer`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_activation`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_constraint`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_dropout`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_initializer`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_regularizer`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`reset_after`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`states`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`units`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`use_bias`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+reset_states
+
+View source
+
+
+reset_states(
+ states=None
+)
+
+
+Reset the recorded states for the stateful RNN layer.
+
+Can only be used when RNN layer is constructed with `stateful` = `True`.
+Args:
+ states: Numpy arrays that contains the value for the initial state, which
+ will be feed to cell at the first time step. When the value is None,
+ zero filled numpy array will be created based on the cell state size.
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`AttributeError`
+ |
+
+When the RNN layer is not stateful.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+When the batch size of the RNN layer is unknown.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+When the input numpy array is not compatible with the RNN
+layer state, either size wise or dtype wise.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/GRUCell.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/GRUCell.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..ae6ac65b9fd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/GRUCell.md
@@ -0,0 +1,387 @@
+description: Cell class for the GRU layer.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.keras.layers.GRUCell
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Cell class for the GRU layer.
+
+Inherits From: [`Layer`](../../../../../tf/keras/layers/Layer.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.keras.layers.GRUCell(
+ units, activation='tanh', recurrent_activation='hard_sigmoid', use_bias=(True),
+ kernel_initializer='glorot_uniform', recurrent_initializer='orthogonal',
+ bias_initializer='zeros', kernel_regularizer=None, recurrent_regularizer=None,
+ bias_regularizer=None, kernel_constraint=None, recurrent_constraint=None,
+ bias_constraint=None, dropout=0.0, recurrent_dropout=0.0, implementation=1,
+ reset_after=(False), **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`units`
+ |
+
+Positive integer, dimensionality of the output space.
+ |
+
+|
+`activation`
+ |
+
+Activation function to use.
+Default: hyperbolic tangent (`tanh`).
+If you pass None, no activation is applied
+(ie. "linear" activation: `a(x) = x`).
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_activation`
+ |
+
+Activation function to use
+for the recurrent step.
+Default: hard sigmoid (`hard_sigmoid`).
+If you pass `None`, no activation is applied
+(ie. "linear" activation: `a(x) = x`).
+ |
+
+|
+`use_bias`
+ |
+
+Boolean, whether the layer uses a bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer for the `kernel` weights matrix,
+used for the linear transformation of the inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer for the `recurrent_kernel`
+weights matrix,
+used for the linear transformation of the recurrent state.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer for the bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Regularizer function applied to
+the `kernel` weights matrix.
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Regularizer function applied to
+the `recurrent_kernel` weights matrix.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Regularizer function applied to the bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_constraint`
+ |
+
+Constraint function applied to
+the `kernel` weights matrix.
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_constraint`
+ |
+
+Constraint function applied to
+the `recurrent_kernel` weights matrix.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_constraint`
+ |
+
+Constraint function applied to the bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`dropout`
+ |
+
+Float between 0 and 1.
+Fraction of the units to drop for the linear transformation of the inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_dropout`
+ |
+
+Float between 0 and 1.
+Fraction of the units to drop for
+the linear transformation of the recurrent state.
+ |
+
+|
+`implementation`
+ |
+
+Implementation mode, either 1 or 2.
+Mode 1 will structure its operations as a larger number of
+smaller dot products and additions, whereas mode 2 will
+batch them into fewer, larger operations. These modes will
+have different performance profiles on different hardware and
+for different applications.
+ |
+
+|
+`reset_after`
+ |
+
+GRU convention (whether to apply reset gate after or
+before matrix multiplication). False = "before" (default),
+True = "after" (CuDNN compatible).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Call arguments:
+
+
+* `inputs`: A 2D tensor.
+* `states`: List of state tensors corresponding to the previous timestep.
+* `training`: Python boolean indicating whether the layer should behave in
+ training mode or in inference mode. Only relevant when `dropout` or
+ `recurrent_dropout` is used.
+
+
+## Methods
+
+get_dropout_mask_for_cell
+
+View source
+
+
+get_dropout_mask_for_cell(
+ inputs, training, count=1
+)
+
+
+Get the dropout mask for RNN cell's input.
+
+It will create mask based on context if there isn't any existing cached
+mask. If a new mask is generated, it will update the cache in the cell.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+The input tensor whose shape will be used to generate dropout
+mask.
+ |
+
+|
+`training`
+ |
+
+Boolean tensor, whether its in training mode, dropout will be
+ignored in non-training mode.
+ |
+
+|
+`count`
+ |
+
+Int, how many dropout mask will be generated. It is useful for cell
+that has internal weights fused together.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+List of mask tensor, generated or cached mask based on context.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_initial_state
+
+View source
+
+
+get_initial_state(
+ inputs=None, batch_size=None, dtype=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+get_recurrent_dropout_mask_for_cell
+
+View source
+
+
+get_recurrent_dropout_mask_for_cell(
+ inputs, training, count=1
+)
+
+
+Get the recurrent dropout mask for RNN cell.
+
+It will create mask based on context if there isn't any existing cached
+mask. If a new mask is generated, it will update the cache in the cell.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+The input tensor whose shape will be used to generate dropout
+mask.
+ |
+
+|
+`training`
+ |
+
+Boolean tensor, whether its in training mode, dropout will be
+ignored in non-training mode.
+ |
+
+|
+`count`
+ |
+
+Int, how many dropout mask will be generated. It is useful for cell
+that has internal weights fused together.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+List of mask tensor, generated or cached mask based on context.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+reset_dropout_mask
+
+View source
+
+
+reset_dropout_mask()
+
+
+Reset the cached dropout masks if any.
+
+This is important for the RNN layer to invoke this in it call() method so
+that the cached mask is cleared before calling the cell.call(). The mask
+should be cached across the timestep within the same batch, but shouldn't
+be cached between batches. Otherwise it will introduce unreasonable bias
+against certain index of data within the batch.
+
+reset_recurrent_dropout_mask
+
+View source
+
+
+reset_recurrent_dropout_mask()
+
+
+Reset the cached recurrent dropout masks if any.
+
+This is important for the RNN layer to invoke this in it call() method so
+that the cached mask is cleared before calling the cell.call(). The mask
+should be cached across the timestep within the same batch, but shouldn't
+be cached between batches. Otherwise it will introduce unreasonable bias
+against certain index of data within the batch.
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/LSTM.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/LSTM.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..711735e34a8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/LSTM.md
@@ -0,0 +1,479 @@
+description: Long Short-Term Memory layer - Hochreiter 1997.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.keras.layers.LSTM
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Long Short-Term Memory layer - Hochreiter 1997.
+
+Inherits From: [`RNN`](../../../../../tf/keras/layers/RNN.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.keras.layers.LSTM(
+ units, activation='tanh', recurrent_activation='hard_sigmoid', use_bias=(True),
+ kernel_initializer='glorot_uniform', recurrent_initializer='orthogonal',
+ bias_initializer='zeros', unit_forget_bias=(True), kernel_regularizer=None,
+ recurrent_regularizer=None, bias_regularizer=None, activity_regularizer=None,
+ kernel_constraint=None, recurrent_constraint=None, bias_constraint=None,
+ dropout=0.0, recurrent_dropout=0.0, implementation=1, return_sequences=(False),
+ return_state=(False), go_backwards=(False), stateful=(False), unroll=(False),
+ **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ Note that this cell is not optimized for performance on GPU. Please use
+tf.compat.v1.keras.layers.CuDNNLSTM for better performance on GPU.
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`units`
+ |
+
+Positive integer, dimensionality of the output space.
+ |
+
+|
+`activation`
+ |
+
+Activation function to use.
+Default: hyperbolic tangent (`tanh`).
+If you pass `None`, no activation is applied
+(ie. "linear" activation: `a(x) = x`).
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_activation`
+ |
+
+Activation function to use
+for the recurrent step.
+Default: hard sigmoid (`hard_sigmoid`).
+If you pass `None`, no activation is applied
+(ie. "linear" activation: `a(x) = x`).
+ |
+
+|
+`use_bias`
+ |
+
+Boolean, whether the layer uses a bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer for the `kernel` weights matrix,
+used for the linear transformation of the inputs..
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer for the `recurrent_kernel`
+weights matrix,
+used for the linear transformation of the recurrent state.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer for the bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`unit_forget_bias`
+ |
+
+Boolean.
+If True, add 1 to the bias of the forget gate at initialization.
+Setting it to true will also force `bias_initializer="zeros"`.
+This is recommended in [Jozefowicz et
+al.](http://www.jmlr.org/proceedings/papers/v37/jozefowicz15.pdf).
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Regularizer function applied to
+the `kernel` weights matrix.
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Regularizer function applied to
+the `recurrent_kernel` weights matrix.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Regularizer function applied to the bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`activity_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Regularizer function applied to
+the output of the layer (its "activation")..
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_constraint`
+ |
+
+Constraint function applied to
+the `kernel` weights matrix.
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_constraint`
+ |
+
+Constraint function applied to
+the `recurrent_kernel` weights matrix.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_constraint`
+ |
+
+Constraint function applied to the bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`dropout`
+ |
+
+Float between 0 and 1.
+Fraction of the units to drop for
+the linear transformation of the inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_dropout`
+ |
+
+Float between 0 and 1.
+Fraction of the units to drop for
+the linear transformation of the recurrent state.
+ |
+
+|
+`implementation`
+ |
+
+Implementation mode, either 1 or 2.
+Mode 1 will structure its operations as a larger number of
+smaller dot products and additions, whereas mode 2 will
+batch them into fewer, larger operations. These modes will
+have different performance profiles on different hardware and
+for different applications.
+ |
+
+|
+`return_sequences`
+ |
+
+Boolean. Whether to return the last output.
+in the output sequence, or the full sequence.
+ |
+
+|
+`return_state`
+ |
+
+Boolean. Whether to return the last state
+in addition to the output.
+ |
+
+|
+`go_backwards`
+ |
+
+Boolean (default False).
+If True, process the input sequence backwards and return the
+reversed sequence.
+ |
+
+|
+`stateful`
+ |
+
+Boolean (default False). If True, the last state
+for each sample at index i in a batch will be used as initial
+state for the sample of index i in the following batch.
+ |
+
+|
+`unroll`
+ |
+
+Boolean (default False).
+If True, the network will be unrolled,
+else a symbolic loop will be used.
+Unrolling can speed-up a RNN,
+although it tends to be more memory-intensive.
+Unrolling is only suitable for short sequences.
+ |
+
+|
+`time_major`
+ |
+
+The shape format of the `inputs` and `outputs` tensors.
+If True, the inputs and outputs will be in shape
+`(timesteps, batch, ...)`, whereas in the False case, it will be
+`(batch, timesteps, ...)`. Using `time_major = True` is a bit more
+efficient because it avoids transposes at the beginning and end of the
+RNN calculation. However, most TensorFlow data is batch-major, so by
+default this function accepts input and emits output in batch-major
+form.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Call arguments:
+
+
+* `inputs`: A 3D tensor.
+* `mask`: Binary tensor of shape `(samples, timesteps)` indicating whether
+ a given timestep should be masked.
+* `training`: Python boolean indicating whether the layer should behave in
+ training mode or in inference mode. This argument is passed to the cell
+ when calling it. This is only relevant if `dropout` or
+ `recurrent_dropout` is used.
+* `initial_state`: List of initial state tensors to be passed to the first
+ call of the cell.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`activation`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_constraint`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_initializer`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_regularizer`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`dropout`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`implementation`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_constraint`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_initializer`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_regularizer`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_activation`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_constraint`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_dropout`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_initializer`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_regularizer`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`states`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`unit_forget_bias`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`units`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`use_bias`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+reset_states
+
+View source
+
+
+reset_states(
+ states=None
+)
+
+
+Reset the recorded states for the stateful RNN layer.
+
+Can only be used when RNN layer is constructed with `stateful` = `True`.
+Args:
+ states: Numpy arrays that contains the value for the initial state, which
+ will be feed to cell at the first time step. When the value is None,
+ zero filled numpy array will be created based on the cell state size.
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`AttributeError`
+ |
+
+When the RNN layer is not stateful.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+When the batch size of the RNN layer is unknown.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+When the input numpy array is not compatible with the RNN
+layer state, either size wise or dtype wise.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/LSTMCell.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/LSTMCell.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..2b8be96362c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/LSTMCell.md
@@ -0,0 +1,390 @@
+description: Cell class for the LSTM layer.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.keras.layers.LSTMCell
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Cell class for the LSTM layer.
+
+Inherits From: [`Layer`](../../../../../tf/keras/layers/Layer.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.keras.layers.LSTMCell(
+ units, activation='tanh', recurrent_activation='hard_sigmoid', use_bias=(True),
+ kernel_initializer='glorot_uniform', recurrent_initializer='orthogonal',
+ bias_initializer='zeros', unit_forget_bias=(True), kernel_regularizer=None,
+ recurrent_regularizer=None, bias_regularizer=None, kernel_constraint=None,
+ recurrent_constraint=None, bias_constraint=None, dropout=0.0,
+ recurrent_dropout=0.0, implementation=1, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`units`
+ |
+
+Positive integer, dimensionality of the output space.
+ |
+
+|
+`activation`
+ |
+
+Activation function to use.
+Default: hyperbolic tangent (`tanh`).
+If you pass `None`, no activation is applied
+(ie. "linear" activation: `a(x) = x`).
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_activation`
+ |
+
+Activation function to use
+for the recurrent step.
+Default: hard sigmoid (`hard_sigmoid`).
+If you pass `None`, no activation is applied
+(ie. "linear" activation: `a(x) = x`).
+ |
+
+|
+`use_bias`
+ |
+
+Boolean, whether the layer uses a bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer for the `kernel` weights matrix,
+used for the linear transformation of the inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer for the `recurrent_kernel`
+weights matrix,
+used for the linear transformation of the recurrent state.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer for the bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`unit_forget_bias`
+ |
+
+Boolean.
+If True, add 1 to the bias of the forget gate at initialization.
+Setting it to true will also force `bias_initializer="zeros"`.
+This is recommended in [Jozefowicz et
+al.](http://www.jmlr.org/proceedings/papers/v37/jozefowicz15.pdf)
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Regularizer function applied to
+the `kernel` weights matrix.
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Regularizer function applied to
+the `recurrent_kernel` weights matrix.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Regularizer function applied to the bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_constraint`
+ |
+
+Constraint function applied to
+the `kernel` weights matrix.
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_constraint`
+ |
+
+Constraint function applied to
+the `recurrent_kernel` weights matrix.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_constraint`
+ |
+
+Constraint function applied to the bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`dropout`
+ |
+
+Float between 0 and 1.
+Fraction of the units to drop for
+the linear transformation of the inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`recurrent_dropout`
+ |
+
+Float between 0 and 1.
+Fraction of the units to drop for
+the linear transformation of the recurrent state.
+ |
+
+|
+`implementation`
+ |
+
+Implementation mode, either 1 or 2.
+Mode 1 will structure its operations as a larger number of
+smaller dot products and additions, whereas mode 2 will
+batch them into fewer, larger operations. These modes will
+have different performance profiles on different hardware and
+for different applications.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Call arguments:
+
+
+* `inputs`: A 2D tensor.
+* `states`: List of state tensors corresponding to the previous timestep.
+* `training`: Python boolean indicating whether the layer should behave in
+ training mode or in inference mode. Only relevant when `dropout` or
+ `recurrent_dropout` is used.
+
+
+## Methods
+
+get_dropout_mask_for_cell
+
+View source
+
+
+get_dropout_mask_for_cell(
+ inputs, training, count=1
+)
+
+
+Get the dropout mask for RNN cell's input.
+
+It will create mask based on context if there isn't any existing cached
+mask. If a new mask is generated, it will update the cache in the cell.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+The input tensor whose shape will be used to generate dropout
+mask.
+ |
+
+|
+`training`
+ |
+
+Boolean tensor, whether its in training mode, dropout will be
+ignored in non-training mode.
+ |
+
+|
+`count`
+ |
+
+Int, how many dropout mask will be generated. It is useful for cell
+that has internal weights fused together.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+List of mask tensor, generated or cached mask based on context.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_initial_state
+
+View source
+
+
+get_initial_state(
+ inputs=None, batch_size=None, dtype=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+get_recurrent_dropout_mask_for_cell
+
+View source
+
+
+get_recurrent_dropout_mask_for_cell(
+ inputs, training, count=1
+)
+
+
+Get the recurrent dropout mask for RNN cell.
+
+It will create mask based on context if there isn't any existing cached
+mask. If a new mask is generated, it will update the cache in the cell.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+The input tensor whose shape will be used to generate dropout
+mask.
+ |
+
+|
+`training`
+ |
+
+Boolean tensor, whether its in training mode, dropout will be
+ignored in non-training mode.
+ |
+
+|
+`count`
+ |
+
+Int, how many dropout mask will be generated. It is useful for cell
+that has internal weights fused together.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+List of mask tensor, generated or cached mask based on context.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+reset_dropout_mask
+
+View source
+
+
+reset_dropout_mask()
+
+
+Reset the cached dropout masks if any.
+
+This is important for the RNN layer to invoke this in it call() method so
+that the cached mask is cleared before calling the cell.call(). The mask
+should be cached across the timestep within the same batch, but shouldn't
+be cached between batches. Otherwise it will introduce unreasonable bias
+against certain index of data within the batch.
+
+reset_recurrent_dropout_mask
+
+View source
+
+
+reset_recurrent_dropout_mask()
+
+
+Reset the cached recurrent dropout masks if any.
+
+This is important for the RNN layer to invoke this in it call() method so
+that the cached mask is cleared before calling the cell.call(). The mask
+should be cached across the timestep within the same batch, but shouldn't
+be cached between batches. Otherwise it will introduce unreasonable bias
+against certain index of data within the batch.
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/experimental.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/experimental.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..eac283cd929
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/experimental.md
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+description: Public API for tf.keras.layers.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.layers.experimental
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.keras.layers.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+## Modules
+
+[`preprocessing`](../../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/experimental/preprocessing.md) module: Public API for tf.keras.layers.experimental.preprocessing namespace.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/experimental/preprocessing.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/experimental/preprocessing.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..9f1fa0509c8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/experimental/preprocessing.md
@@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
+description: Public API for tf.keras.layers.experimental.preprocessing namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.layers.experimental.preprocessing
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.keras.layers.experimental.preprocessing namespace.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class CenterCrop`](../../../../../../tf/keras/layers/experimental/preprocessing/CenterCrop.md): Crop the central portion of the images to target height and width.
+
+[`class Normalization`](../../../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/experimental/preprocessing/Normalization.md): Feature-wise normalization of the data.
+
+[`class PreprocessingLayer`](../../../../../../tf/keras/layers/experimental/preprocessing/PreprocessingLayer.md): Base class for PreprocessingLayers.
+
+[`class RandomContrast`](../../../../../../tf/keras/layers/experimental/preprocessing/RandomContrast.md): Adjust the contrast of an image or images by a random factor.
+
+[`class RandomCrop`](../../../../../../tf/keras/layers/experimental/preprocessing/RandomCrop.md): Randomly crop the images to target height and width.
+
+[`class RandomFlip`](../../../../../../tf/keras/layers/experimental/preprocessing/RandomFlip.md): Randomly flip each image horizontally and vertically.
+
+[`class RandomHeight`](../../../../../../tf/keras/layers/experimental/preprocessing/RandomHeight.md): Randomly vary the height of a batch of images during training.
+
+[`class RandomRotation`](../../../../../../tf/keras/layers/experimental/preprocessing/RandomRotation.md): Randomly rotate each image.
+
+[`class RandomTranslation`](../../../../../../tf/keras/layers/experimental/preprocessing/RandomTranslation.md): Randomly translate each image during training.
+
+[`class RandomWidth`](../../../../../../tf/keras/layers/experimental/preprocessing/RandomWidth.md): Randomly vary the width of a batch of images during training.
+
+[`class Rescaling`](../../../../../../tf/keras/layers/experimental/preprocessing/Rescaling.md): Multiply inputs by `scale`.
+
+[`class Resizing`](../../../../../../tf/keras/layers/experimental/preprocessing/Resizing.md): Image resizing layer.
+
+[`class TextVectorization`](../../../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/experimental/preprocessing/TextVectorization.md): Text vectorization layer.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/experimental/preprocessing/Normalization.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/experimental/preprocessing/Normalization.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..da7b16d3bb1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/experimental/preprocessing/Normalization.md
@@ -0,0 +1,114 @@
+description: Feature-wise normalization of the data.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.keras.layers.experimental.preprocessing.Normalization
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Feature-wise normalization of the data.
+
+Inherits From: [`Normalization`](../../../../../../../tf/keras/layers/experimental/preprocessing/Normalization.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.keras.layers.experimental.preprocessing.Normalization(
+ axis=-1, dtype=None, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This layer will coerce its inputs into a normal distribution centered around
+0 with standard deviation 1. It accomplishes this by precomputing the mean and
+variance of the data, and calling (input-mean)/sqrt(var) at runtime.
+
+What happens in `adapt`: Compute mean and variance of the data and store them
+ as the layer's weights. `adapt` should be called before `fit`, `evaluate`,
+ or `predict`.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`axis`
+ |
+
+Integer or tuple of integers, the axis or axes that should be
+normalized (typically the features axis). We will normalize each element
+in the specified axis. The default is '-1' (the innermost axis); 0 (the
+batch axis) is not allowed.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+adapt
+
+View source
+
+
+adapt(
+ data, reset_state=(True)
+)
+
+
+Fits the state of the preprocessing layer to the data being passed.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`data`
+ |
+
+The data to train on. It can be passed either as a tf.data Dataset,
+or as a numpy array.
+ |
+
+|
+`reset_state`
+ |
+
+Optional argument specifying whether to clear the state of
+the layer at the start of the call to `adapt`, or whether to start from
+the existing state. Subclasses may choose to throw if reset_state is set
+to 'False'.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/experimental/preprocessing/TextVectorization.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/experimental/preprocessing/TextVectorization.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..ce7639df258
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/experimental/preprocessing/TextVectorization.md
@@ -0,0 +1,286 @@
+description: Text vectorization layer.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.keras.layers.experimental.preprocessing.TextVectorization
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Text vectorization layer.
+
+Inherits From: [`TextVectorization`](../../../../../../../tf/keras/layers/experimental/preprocessing/TextVectorization.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.keras.layers.experimental.preprocessing.TextVectorization(
+ max_tokens=None, standardize=LOWER_AND_STRIP_PUNCTUATION,
+ split=SPLIT_ON_WHITESPACE, ngrams=None, output_mode=INT,
+ output_sequence_length=None, pad_to_max_tokens=(True), **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This layer has basic options for managing text in a Keras model. It
+transforms a batch of strings (one sample = one string) into either a list of
+token indices (one sample = 1D tensor of integer token indices) or a dense
+representation (one sample = 1D tensor of float values representing data about
+the sample's tokens).
+
+The processing of each sample contains the following steps:
+ 1) standardize each sample (usually lowercasing + punctuation stripping)
+ 2) split each sample into substrings (usually words)
+ 3) recombine substrings into tokens (usually ngrams)
+ 4) index tokens (associate a unique int value with each token)
+ 5) transform each sample using this index, either into a vector of ints or
+ a dense float vector.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`max_tokens`
+ |
+
+The maximum size of the vocabulary for this layer. If None,
+there is no cap on the size of the vocabulary.
+ |
+
+|
+`standardize`
+ |
+
+Optional specification for standardization to apply to the
+input text. Values can be None (no standardization),
+LOWER_AND_STRIP_PUNCTUATION (lowercase and remove punctuation) or a
+Callable.
+ |
+
+|
+`split`
+ |
+
+Optional specification for splitting the input text. Values can be
+None (no splitting), SPLIT_ON_WHITESPACE (split on ASCII whitespace), or a
+Callable.
+ |
+
+|
+`ngrams`
+ |
+
+Optional specification for ngrams to create from the possibly-split
+input text. Values can be None, an integer or tuple of integers; passing
+an integer will create ngrams up to that integer, and passing a tuple of
+integers will create ngrams for the specified values in the tuple. Passing
+None means that no ngrams will be created.
+ |
+
+|
+`output_mode`
+ |
+
+Optional specification for the output of the layer. Values can
+be INT, BINARY, COUNT or TFIDF, which control the outputs as follows:
+INT: Outputs integer indices, one integer index per split string token.
+BINARY: Outputs a single int array per batch, of either vocab_size or
+max_tokens size, containing 1s in all elements where the token mapped
+to that index exists at least once in the batch item.
+COUNT: As BINARY, but the int array contains a count of the number of
+times the token at that index appeared in the batch item.
+TFIDF: As BINARY, but the TF-IDF algorithm is applied to find the value
+in each token slot.
+ |
+
+|
+`output_sequence_length`
+ |
+
+Optional length for the output tensor. If set, the
+output will be padded or truncated to this value in INT mode.
+ |
+
+|
+`pad_to_max_tokens`
+ |
+
+If True, BINARY, COUNT, and TFIDF modes will have their
+outputs padded to max_tokens, even if the number of unique tokens in the
+vocabulary is less than max_tokens.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+adapt
+
+View source
+
+
+adapt(
+ data, reset_state=(True)
+)
+
+
+Fits the state of the preprocessing layer to the dataset.
+
+Overrides the default adapt method to apply relevant preprocessing to the
+inputs before passing to the combiner.
+
+
+
+
+| Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`data`
+ |
+
+The data to train on. It can be passed either as a tf.data Dataset,
+or as a numpy array.
+ |
+
+|
+`reset_state`
+ |
+
+Optional argument specifying whether to clear the state of
+the layer at the start of the call to `adapt`. This must be True for
+this layer, which does not support repeated calls to `adapt`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+get_vocabulary
+
+View source
+
+
+get_vocabulary()
+
+
+
+
+
+set_vocabulary
+
+View source
+
+
+set_vocabulary(
+ vocab, df_data=None, oov_df_value=None, append=(False)
+)
+
+
+Sets vocabulary (and optionally document frequency) data for this layer.
+
+This method sets the vocabulary and DF data for this layer directly, instead
+of analyzing a dataset through 'adapt'. It should be used whenever the vocab
+(and optionally document frequency) information is already known. If
+vocabulary data is already present in the layer, this method will either
+replace it, if 'append' is set to False, or append to it (if 'append' is set
+to True).
+
+
+
+
+| Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`vocab`
+ |
+
+An array of string tokens.
+ |
+
+|
+`df_data`
+ |
+
+An array of document frequency data. Only necessary if the layer
+output_mode is TFIDF.
+ |
+
+|
+`oov_df_value`
+ |
+
+The document frequency of the OOV token. Only necessary if
+output_mode is TFIDF. OOV data is optional when appending additional
+data in TFIDF mode; if an OOV value is supplied it will overwrite the
+existing OOV value.
+ |
+
+|
+`append`
+ |
+
+Whether to overwrite or append any existing vocabulary data.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If there are too many inputs, the inputs do not match, or
+input data is missing.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If the vocabulary cannot be set when this function is
+called. This happens when "binary", "count", and "tfidf" modes,
+if "pad_to_max_tokens" is False and the layer itself has already been
+called.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/losses.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/losses.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e7d88dff74d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/losses.md
@@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
+description: Built-in loss functions.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.losses
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Built-in loss functions.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class BinaryCrossentropy`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/BinaryCrossentropy.md): Computes the cross-entropy loss between true labels and predicted labels.
+
+[`class CategoricalCrossentropy`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/CategoricalCrossentropy.md): Computes the crossentropy loss between the labels and predictions.
+
+[`class CategoricalHinge`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/CategoricalHinge.md): Computes the categorical hinge loss between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`class CosineSimilarity`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/CosineSimilarity.md): Computes the cosine similarity between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`class Hinge`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/Hinge.md): Computes the hinge loss between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`class Huber`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/Huber.md): Computes the Huber loss between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`class KLDivergence`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/KLDivergence.md): Computes Kullback-Leibler divergence loss between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`class LogCosh`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/LogCosh.md): Computes the logarithm of the hyperbolic cosine of the prediction error.
+
+[`class Loss`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/Loss.md): Loss base class.
+
+[`class MeanAbsoluteError`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/MeanAbsoluteError.md): Computes the mean of absolute difference between labels and predictions.
+
+[`class MeanAbsolutePercentageError`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/MeanAbsolutePercentageError.md): Computes the mean absolute percentage error between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`class MeanSquaredError`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/MeanSquaredError.md): Computes the mean of squares of errors between labels and predictions.
+
+[`class MeanSquaredLogarithmicError`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/MeanSquaredLogarithmicError.md): Computes the mean squared logarithmic error between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`class Poisson`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/Poisson.md): Computes the Poisson loss between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`class SparseCategoricalCrossentropy`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/SparseCategoricalCrossentropy.md): Computes the crossentropy loss between the labels and predictions.
+
+[`class SquaredHinge`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/SquaredHinge.md): Computes the squared hinge loss between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`KLD(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/KLD.md): Computes Kullback-Leibler divergence loss between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`MAE(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/MAE.md): Computes the mean absolute error between labels and predictions.
+
+[`MAPE(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/MAPE.md): Computes the mean absolute percentage error between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`MSE(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/MSE.md): Computes the mean squared error between labels and predictions.
+
+[`MSLE(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/MSLE.md): Computes the mean squared logarithmic error between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`binary_crossentropy(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/binary_crossentropy.md): Computes the binary crossentropy loss.
+
+[`categorical_crossentropy(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/categorical_crossentropy.md): Computes the categorical crossentropy loss.
+
+[`categorical_hinge(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/categorical_hinge.md): Computes the categorical hinge loss between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`cosine(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/cosine_similarity.md): Computes the cosine similarity between labels and predictions.
+
+[`cosine_proximity(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/cosine_similarity.md): Computes the cosine similarity between labels and predictions.
+
+[`cosine_similarity(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/cosine_similarity.md): Computes the cosine similarity between labels and predictions.
+
+[`deserialize(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/deserialize.md): Deserializes a serialized loss class/function instance.
+
+[`get(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/get.md): Retrieves a Keras loss function.
+
+[`hinge(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/hinge.md): Computes the hinge loss between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`kld(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/KLD.md): Computes Kullback-Leibler divergence loss between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`kullback_leibler_divergence(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/KLD.md): Computes Kullback-Leibler divergence loss between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`logcosh(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/logcosh.md): Logarithm of the hyperbolic cosine of the prediction error.
+
+[`mae(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/MAE.md): Computes the mean absolute error between labels and predictions.
+
+[`mape(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/MAPE.md): Computes the mean absolute percentage error between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`mean_absolute_error(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/MAE.md): Computes the mean absolute error between labels and predictions.
+
+[`mean_absolute_percentage_error(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/MAPE.md): Computes the mean absolute percentage error between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`mean_squared_error(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/MSE.md): Computes the mean squared error between labels and predictions.
+
+[`mean_squared_logarithmic_error(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/MSLE.md): Computes the mean squared logarithmic error between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`mse(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/MSE.md): Computes the mean squared error between labels and predictions.
+
+[`msle(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/MSLE.md): Computes the mean squared logarithmic error between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`poisson(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/poisson.md): Computes the Poisson loss between y_true and y_pred.
+
+[`serialize(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/serialize.md): Serializes loss function or `Loss` instance.
+
+[`sparse_categorical_crossentropy(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/sparse_categorical_crossentropy.md): Computes the sparse categorical crossentropy loss.
+
+[`squared_hinge(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/squared_hinge.md): Computes the squared hinge loss between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/metrics.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/metrics.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..74963c8de86
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/metrics.md
@@ -0,0 +1,163 @@
+description: Built-in metrics.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.metrics
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Built-in metrics.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class AUC`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/AUC.md): Computes the approximate AUC (Area under the curve) via a Riemann sum.
+
+[`class Accuracy`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/Accuracy.md): Calculates how often predictions equals labels.
+
+[`class BinaryAccuracy`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/BinaryAccuracy.md): Calculates how often predictions matches binary labels.
+
+[`class BinaryCrossentropy`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/BinaryCrossentropy.md): Computes the crossentropy metric between the labels and predictions.
+
+[`class CategoricalAccuracy`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/CategoricalAccuracy.md): Calculates how often predictions matches one-hot labels.
+
+[`class CategoricalCrossentropy`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/CategoricalCrossentropy.md): Computes the crossentropy metric between the labels and predictions.
+
+[`class CategoricalHinge`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/CategoricalHinge.md): Computes the categorical hinge metric between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`class CosineSimilarity`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/CosineSimilarity.md): Computes the cosine similarity between the labels and predictions.
+
+[`class FalseNegatives`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/FalseNegatives.md): Calculates the number of false negatives.
+
+[`class FalsePositives`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/FalsePositives.md): Calculates the number of false positives.
+
+[`class Hinge`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/Hinge.md): Computes the hinge metric between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`class KLDivergence`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/KLDivergence.md): Computes Kullback-Leibler divergence metric between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`class LogCoshError`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/LogCoshError.md): Computes the logarithm of the hyperbolic cosine of the prediction error.
+
+[`class Mean`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/Mean.md): Computes the (weighted) mean of the given values.
+
+[`class MeanAbsoluteError`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/MeanAbsoluteError.md): Computes the mean absolute error between the labels and predictions.
+
+[`class MeanAbsolutePercentageError`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/MeanAbsolutePercentageError.md): Computes the mean absolute percentage error between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`class MeanIoU`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/MeanIoU.md): Computes the mean Intersection-Over-Union metric.
+
+[`class MeanRelativeError`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/MeanRelativeError.md): Computes the mean relative error by normalizing with the given values.
+
+[`class MeanSquaredError`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/MeanSquaredError.md): Computes the mean squared error between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`class MeanSquaredLogarithmicError`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/MeanSquaredLogarithmicError.md): Computes the mean squared logarithmic error between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`class MeanTensor`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/MeanTensor.md): Computes the element-wise (weighted) mean of the given tensors.
+
+[`class Metric`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/Metric.md): Encapsulates metric logic and state.
+
+[`class Poisson`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/Poisson.md): Computes the Poisson metric between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`class Precision`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/Precision.md): Computes the precision of the predictions with respect to the labels.
+
+[`class PrecisionAtRecall`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/PrecisionAtRecall.md): Computes the precision at a given recall.
+
+[`class Recall`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/Recall.md): Computes the recall of the predictions with respect to the labels.
+
+[`class RecallAtPrecision`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/RecallAtPrecision.md): Computes the maximally achievable recall at a required precision.
+
+[`class RootMeanSquaredError`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/RootMeanSquaredError.md): Computes root mean squared error metric between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`class SensitivityAtSpecificity`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/SensitivityAtSpecificity.md): Computes the sensitivity at a given specificity.
+
+[`class SparseCategoricalAccuracy`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/SparseCategoricalAccuracy.md): Calculates how often predictions matches integer labels.
+
+[`class SparseCategoricalCrossentropy`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/SparseCategoricalCrossentropy.md): Computes the crossentropy metric between the labels and predictions.
+
+[`class SparseTopKCategoricalAccuracy`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/SparseTopKCategoricalAccuracy.md): Computes how often integer targets are in the top `K` predictions.
+
+[`class SpecificityAtSensitivity`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/SpecificityAtSensitivity.md): Computes the specificity at a given sensitivity.
+
+[`class SquaredHinge`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/SquaredHinge.md): Computes the squared hinge metric between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`class Sum`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/Sum.md): Computes the (weighted) sum of the given values.
+
+[`class TopKCategoricalAccuracy`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/TopKCategoricalAccuracy.md): Computes how often targets are in the top `K` predictions.
+
+[`class TrueNegatives`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/TrueNegatives.md): Calculates the number of true negatives.
+
+[`class TruePositives`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/TruePositives.md): Calculates the number of true positives.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`KLD(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/KLD.md): Computes Kullback-Leibler divergence loss between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`MAE(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/MAE.md): Computes the mean absolute error between labels and predictions.
+
+[`MAPE(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/MAPE.md): Computes the mean absolute percentage error between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`MSE(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/MSE.md): Computes the mean squared error between labels and predictions.
+
+[`MSLE(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/MSLE.md): Computes the mean squared logarithmic error between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`binary_accuracy(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/binary_accuracy.md): Calculates how often predictions matches binary labels.
+
+[`binary_crossentropy(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/binary_crossentropy.md): Computes the binary crossentropy loss.
+
+[`categorical_accuracy(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/categorical_accuracy.md): Calculates how often predictions matches one-hot labels.
+
+[`categorical_crossentropy(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/categorical_crossentropy.md): Computes the categorical crossentropy loss.
+
+[`cosine(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/cosine_similarity.md): Computes the cosine similarity between labels and predictions.
+
+[`cosine_proximity(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/cosine_similarity.md): Computes the cosine similarity between labels and predictions.
+
+[`deserialize(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/deserialize.md)
+
+[`get(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/get.md): Return a metric given its identifer.
+
+[`hinge(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/hinge.md): Computes the hinge loss between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`kld(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/KLD.md): Computes Kullback-Leibler divergence loss between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`kullback_leibler_divergence(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/KLD.md): Computes Kullback-Leibler divergence loss between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`mae(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/MAE.md): Computes the mean absolute error between labels and predictions.
+
+[`mape(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/MAPE.md): Computes the mean absolute percentage error between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`mean_absolute_error(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/MAE.md): Computes the mean absolute error between labels and predictions.
+
+[`mean_absolute_percentage_error(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/MAPE.md): Computes the mean absolute percentage error between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`mean_squared_error(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/MSE.md): Computes the mean squared error between labels and predictions.
+
+[`mean_squared_logarithmic_error(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/MSLE.md): Computes the mean squared logarithmic error between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`mse(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/MSE.md): Computes the mean squared error between labels and predictions.
+
+[`msle(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/MSLE.md): Computes the mean squared logarithmic error between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`poisson(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/poisson.md): Computes the Poisson loss between y_true and y_pred.
+
+[`serialize(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/serialize.md)
+
+[`sparse_categorical_accuracy(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/sparse_categorical_accuracy.md): Calculates how often predictions matches integer labels.
+
+[`sparse_categorical_crossentropy(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/sparse_categorical_crossentropy.md): Computes the sparse categorical crossentropy loss.
+
+[`sparse_top_k_categorical_accuracy(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/sparse_top_k_categorical_accuracy.md): Computes how often integer targets are in the top `K` predictions.
+
+[`squared_hinge(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/losses/squared_hinge.md): Computes the squared hinge loss between `y_true` and `y_pred`.
+
+[`top_k_categorical_accuracy(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/metrics/top_k_categorical_accuracy.md): Computes how often targets are in the top `K` predictions.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/mixed_precision.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/mixed_precision.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..1b3d673f4ed
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/mixed_precision.md
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+description: Public API for tf.keras.mixed_precision namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.mixed_precision
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.keras.mixed_precision namespace.
+
+
+
+## Modules
+
+[`experimental`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/mixed_precision/experimental.md) module: Public API for tf.keras.mixed_precision.experimental namespace.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/mixed_precision/experimental.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/mixed_precision/experimental.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..6e54e53f5bf
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/mixed_precision/experimental.md
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
+description: Public API for tf.keras.mixed_precision.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.mixed_precision.experimental
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.keras.mixed_precision.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class LossScaleOptimizer`](../../../../../tf/keras/mixed_precision/experimental/LossScaleOptimizer.md): An optimizer that applies loss scaling.
+
+[`class Policy`](../../../../../tf/keras/mixed_precision/experimental/Policy.md): A dtype policy for a Keras layer.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`get_layer_policy(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/mixed_precision/experimental/get_layer_policy.md): Returns the dtype policy of a layer.
+
+[`global_policy(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/mixed_precision/experimental/global_policy.md): Returns the global Policy.
+
+[`set_policy(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/mixed_precision/experimental/set_policy.md): Sets the global Policy.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/models.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/models.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e1de61b0b51
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/models.md
@@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
+description: Code for model cloning, plus model-related API entries.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.models
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Code for model cloning, plus model-related API entries.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class Model`](../../../../tf/keras/Model.md): `Model` groups layers into an object with training and inference features.
+
+[`class Sequential`](../../../../tf/keras/Sequential.md): `Sequential` groups a linear stack of layers into a tf.keras.Model.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`clone_model(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/models/clone_model.md): Clone any `Model` instance.
+
+[`load_model(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/models/load_model.md): Loads a model saved via `save_model`.
+
+[`model_from_config(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/models/model_from_config.md): Instantiates a Keras model from its config.
+
+[`model_from_json(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/models/model_from_json.md): Parses a JSON model configuration string and returns a model instance.
+
+[`model_from_yaml(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/models/model_from_yaml.md): Parses a yaml model configuration file and returns a model instance.
+
+[`save_model(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/models/save_model.md): Saves a model as a TensorFlow SavedModel or HDF5 file.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/optimizers.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/optimizers.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..0e48b87af06
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/optimizers.md
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+description: Built-in optimizer classes.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.optimizers
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Built-in optimizer classes.
+
+
+
+## Modules
+
+[`schedules`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/optimizers/schedules.md) module: Public API for tf.keras.optimizers.schedules namespace.
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class Adadelta`](../../../../tf/keras/optimizers/Adadelta.md): Optimizer that implements the Adadelta algorithm.
+
+[`class Adagrad`](../../../../tf/keras/optimizers/Adagrad.md): Optimizer that implements the Adagrad algorithm.
+
+[`class Adam`](../../../../tf/keras/optimizers/Adam.md): Optimizer that implements the Adam algorithm.
+
+[`class Adamax`](../../../../tf/keras/optimizers/Adamax.md): Optimizer that implements the Adamax algorithm.
+
+[`class Ftrl`](../../../../tf/keras/optimizers/Ftrl.md): Optimizer that implements the FTRL algorithm.
+
+[`class Nadam`](../../../../tf/keras/optimizers/Nadam.md): Optimizer that implements the NAdam algorithm.
+
+[`class Optimizer`](../../../../tf/keras/optimizers/Optimizer.md): Updated base class for optimizers.
+
+[`class RMSprop`](../../../../tf/keras/optimizers/RMSprop.md): Optimizer that implements the RMSprop algorithm.
+
+[`class SGD`](../../../../tf/keras/optimizers/SGD.md): Stochastic gradient descent and momentum optimizer.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`deserialize(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/optimizers/deserialize.md): Inverse of the `serialize` function.
+
+[`get(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/optimizers/get.md): Retrieves a Keras Optimizer instance.
+
+[`serialize(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/optimizers/serialize.md)
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/optimizers/schedules.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/optimizers/schedules.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..4bea804ec25
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/optimizers/schedules.md
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
+description: Public API for tf.keras.optimizers.schedules namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.optimizers.schedules
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.keras.optimizers.schedules namespace.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class ExponentialDecay`](../../../../../tf/keras/optimizers/schedules/ExponentialDecay.md): A LearningRateSchedule that uses an exponential decay schedule.
+
+[`class InverseTimeDecay`](../../../../../tf/keras/optimizers/schedules/InverseTimeDecay.md): A LearningRateSchedule that uses an inverse time decay schedule.
+
+[`class LearningRateSchedule`](../../../../../tf/keras/optimizers/schedules/LearningRateSchedule.md): A serializable learning rate decay schedule.
+
+[`class PiecewiseConstantDecay`](../../../../../tf/keras/optimizers/schedules/PiecewiseConstantDecay.md): A LearningRateSchedule that uses a piecewise constant decay schedule.
+
+[`class PolynomialDecay`](../../../../../tf/keras/optimizers/schedules/PolynomialDecay.md): A LearningRateSchedule that uses a polynomial decay schedule.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`deserialize(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/optimizers/schedules/deserialize.md)
+
+[`serialize(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/optimizers/schedules/serialize.md)
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/preprocessing.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/preprocessing.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..af4bdee99fe
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/preprocessing.md
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+description: Keras data preprocessing utils.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.preprocessing
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Keras data preprocessing utils.
+
+
+
+## Modules
+
+[`image`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/preprocessing/image.md) module: Set of tools for real-time data augmentation on image data.
+
+[`sequence`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/preprocessing/sequence.md) module: Utilities for preprocessing sequence data.
+
+[`text`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/preprocessing/text.md) module: Utilities for text input preprocessing.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/preprocessing/image.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/preprocessing/image.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..954b2765ef9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/preprocessing/image.md
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
+description: Set of tools for real-time data augmentation on image data.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.preprocessing.image
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Set of tools for real-time data augmentation on image data.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class DirectoryIterator`](../../../../../tf/keras/preprocessing/image/DirectoryIterator.md): Iterator capable of reading images from a directory on disk.
+
+[`class ImageDataGenerator`](../../../../../tf/keras/preprocessing/image/ImageDataGenerator.md): Generate batches of tensor image data with real-time data augmentation.
+
+[`class Iterator`](../../../../../tf/keras/preprocessing/image/Iterator.md): Base class for image data iterators.
+
+[`class NumpyArrayIterator`](../../../../../tf/keras/preprocessing/image/NumpyArrayIterator.md): Iterator yielding data from a Numpy array.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`apply_affine_transform(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/preprocessing/image/apply_affine_transform.md): Applies an affine transformation specified by the parameters given.
+
+[`apply_brightness_shift(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/preprocessing/image/apply_brightness_shift.md): Performs a brightness shift.
+
+[`apply_channel_shift(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/preprocessing/image/apply_channel_shift.md): Performs a channel shift.
+
+[`array_to_img(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/preprocessing/image/array_to_img.md): Converts a 3D Numpy array to a PIL Image instance.
+
+[`img_to_array(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/preprocessing/image/img_to_array.md): Converts a PIL Image instance to a Numpy array.
+
+[`load_img(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/preprocessing/image/load_img.md): Loads an image into PIL format.
+
+[`random_brightness(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/preprocessing/image/random_brightness.md): Performs a random brightness shift.
+
+[`random_channel_shift(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/preprocessing/image/random_channel_shift.md): Performs a random channel shift.
+
+[`random_rotation(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/preprocessing/image/random_rotation.md): Performs a random rotation of a Numpy image tensor.
+
+[`random_shear(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/preprocessing/image/random_shear.md): Performs a random spatial shear of a Numpy image tensor.
+
+[`random_shift(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/preprocessing/image/random_shift.md): Performs a random spatial shift of a Numpy image tensor.
+
+[`random_zoom(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/preprocessing/image/random_zoom.md): Performs a random spatial zoom of a Numpy image tensor.
+
+[`save_img(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/preprocessing/image/save_img.md): Saves an image stored as a Numpy array to a path or file object.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/preprocessing/sequence.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/preprocessing/sequence.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..723bc2f1aec
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/preprocessing/sequence.md
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+description: Utilities for preprocessing sequence data.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.preprocessing.sequence
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Utilities for preprocessing sequence data.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class TimeseriesGenerator`](../../../../../tf/keras/preprocessing/sequence/TimeseriesGenerator.md): Utility class for generating batches of temporal data.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`make_sampling_table(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/preprocessing/sequence/make_sampling_table.md): Generates a word rank-based probabilistic sampling table.
+
+[`pad_sequences(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/preprocessing/sequence/pad_sequences.md): Pads sequences to the same length.
+
+[`skipgrams(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/preprocessing/sequence/skipgrams.md): Generates skipgram word pairs.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/preprocessing/text.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/preprocessing/text.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a9d0885d00d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/preprocessing/text.md
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
+description: Utilities for text input preprocessing.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.preprocessing.text
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Utilities for text input preprocessing.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class Tokenizer`](../../../../../tf/keras/preprocessing/text/Tokenizer.md): Text tokenization utility class.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`hashing_trick(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/preprocessing/text/hashing_trick.md): Converts a text to a sequence of indexes in a fixed-size hashing space.
+
+[`one_hot(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/preprocessing/text/one_hot.md): One-hot encodes a text into a list of word indexes of size n.
+
+[`text_to_word_sequence(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/preprocessing/text/text_to_word_sequence.md): Converts a text to a sequence of words (or tokens).
+
+[`tokenizer_from_json(...)`](../../../../../tf/keras/preprocessing/text/tokenizer_from_json.md): Parses a JSON tokenizer configuration file and returns a
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/regularizers.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/regularizers.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..d5235ebb396
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/regularizers.md
@@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
+description: Built-in regularizers.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.regularizers
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Built-in regularizers.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class L1L2`](../../../../tf/keras/regularizers/L1L2.md): A regularizer that applies both L1 and L2 regularization penalties.
+
+[`class Regularizer`](../../../../tf/keras/regularizers/Regularizer.md): Regularizer base class.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`deserialize(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/regularizers/deserialize.md)
+
+[`get(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/regularizers/get.md)
+
+[`l1(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/regularizers/l1.md): Create a regularizer that applies an L1 regularization penalty.
+
+[`l1_l2(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/regularizers/l1_l2.md): Create a regularizer that applies both L1 and L2 penalties.
+
+[`l2(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/regularizers/l2.md): Create a regularizer that applies an L2 regularization penalty.
+
+[`serialize(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/regularizers/serialize.md)
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/utils.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/utils.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..1a506d32692
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/utils.md
@@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
+description: Public API for tf.keras.utils namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.utils
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.keras.utils namespace.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class CustomObjectScope`](../../../../tf/keras/utils/CustomObjectScope.md): Provides a scope that changes to `_GLOBAL_CUSTOM_OBJECTS` cannot escape.
+
+[`class GeneratorEnqueuer`](../../../../tf/keras/utils/GeneratorEnqueuer.md): Builds a queue out of a data generator.
+
+[`class HDF5Matrix`](../../../../tf/keras/utils/HDF5Matrix.md): Representation of HDF5 dataset to be used instead of a Numpy array.
+
+[`class OrderedEnqueuer`](../../../../tf/keras/utils/OrderedEnqueuer.md): Builds a Enqueuer from a Sequence.
+
+[`class Progbar`](../../../../tf/keras/utils/Progbar.md): Displays a progress bar.
+
+[`class Sequence`](../../../../tf/keras/utils/Sequence.md): Base object for fitting to a sequence of data, such as a dataset.
+
+[`class SequenceEnqueuer`](../../../../tf/keras/utils/SequenceEnqueuer.md): Base class to enqueue inputs.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`convert_all_kernels_in_model(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/utils/convert_all_kernels_in_model.md): Converts all convolution kernels in a model from Theano to TensorFlow. (deprecated)
+
+[`custom_object_scope(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/utils/custom_object_scope.md): Provides a scope that changes to `_GLOBAL_CUSTOM_OBJECTS` cannot escape.
+
+[`deserialize_keras_object(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/utils/deserialize_keras_object.md)
+
+[`get_custom_objects(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/utils/get_custom_objects.md): Retrieves a live reference to the global dictionary of custom objects.
+
+[`get_file(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/utils/get_file.md): Downloads a file from a URL if it not already in the cache.
+
+[`get_registered_name(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/utils/get_registered_name.md): Returns the name registered to an object within the Keras framework.
+
+[`get_registered_object(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/utils/get_registered_object.md): Returns the class associated with `name` if it is registered with Keras.
+
+[`get_source_inputs(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/utils/get_source_inputs.md): Returns the list of input tensors necessary to compute `tensor`.
+
+[`model_to_dot(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/utils/model_to_dot.md): Convert a Keras model to dot format.
+
+[`multi_gpu_model(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/utils/multi_gpu_model.md): Replicates a model on different GPUs. (deprecated)
+
+[`normalize(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/utils/normalize.md): Normalizes a Numpy array.
+
+[`plot_model(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/utils/plot_model.md): Converts a Keras model to dot format and save to a file.
+
+[`register_keras_serializable(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/utils/register_keras_serializable.md): Registers an object with the Keras serialization framework.
+
+[`serialize_keras_object(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/utils/serialize_keras_object.md): Serialize Keras object into JSON.
+
+[`to_categorical(...)`](../../../../tf/keras/utils/to_categorical.md): Converts a class vector (integers) to binary class matrix.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/wrappers.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/wrappers.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..dcf864363cb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/wrappers.md
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+description: Public API for tf.keras.wrappers namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.wrappers
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.keras.wrappers namespace.
+
+
+
+## Modules
+
+[`scikit_learn`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/wrappers/scikit_learn.md) module: Wrapper for using the Scikit-Learn API with Keras models.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/wrappers/scikit_learn.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/wrappers/scikit_learn.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..5f3351ac4ab
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/keras/wrappers/scikit_learn.md
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
+description: Wrapper for using the Scikit-Learn API with Keras models.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.keras.wrappers.scikit_learn
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Wrapper for using the Scikit-Learn API with Keras models.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class KerasClassifier`](../../../../../tf/keras/wrappers/scikit_learn/KerasClassifier.md): Implementation of the scikit-learn classifier API for Keras.
+
+[`class KerasRegressor`](../../../../../tf/keras/wrappers/scikit_learn/KerasRegressor.md): Implementation of the scikit-learn regressor API for Keras.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e8ef4fded92
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers.md
@@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
+description: Public API for tf.layers namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.layers
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.layers namespace.
+
+
+
+## Modules
+
+[`experimental`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/experimental.md) module: Public API for tf.layers.experimental namespace.
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class AveragePooling1D`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/AveragePooling1D.md): Average Pooling layer for 1D inputs.
+
+[`class AveragePooling2D`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/AveragePooling2D.md): Average pooling layer for 2D inputs (e.g. images).
+
+[`class AveragePooling3D`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/AveragePooling3D.md): Average pooling layer for 3D inputs (e.g. volumes).
+
+[`class BatchNormalization`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/BatchNormalization.md): Batch Normalization layer from (Ioffe et al., 2015).
+
+[`class Conv1D`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/Conv1D.md): 1D convolution layer (e.g. temporal convolution).
+
+[`class Conv2D`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/Conv2D.md): 2D convolution layer (e.g. spatial convolution over images).
+
+[`class Conv2DTranspose`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/Conv2DTranspose.md): Transposed 2D convolution layer (sometimes called 2D Deconvolution).
+
+[`class Conv3D`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/Conv3D.md): 3D convolution layer (e.g. spatial convolution over volumes).
+
+[`class Conv3DTranspose`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/Conv3DTranspose.md): Transposed 3D convolution layer (sometimes called 3D Deconvolution).
+
+[`class Dense`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/Dense.md): Densely-connected layer class.
+
+[`class Dropout`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/Dropout.md): Applies Dropout to the input.
+
+[`class Flatten`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/Flatten.md): Flattens an input tensor while preserving the batch axis (axis 0).
+
+[`class InputSpec`](../../../tf/keras/layers/InputSpec.md): Specifies the rank, dtype and shape of every input to a layer.
+
+[`class Layer`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/Layer.md): Base layer class.
+
+[`class MaxPooling1D`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/MaxPooling1D.md): Max Pooling layer for 1D inputs.
+
+[`class MaxPooling2D`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/MaxPooling2D.md): Max pooling layer for 2D inputs (e.g. images).
+
+[`class MaxPooling3D`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/MaxPooling3D.md): Max pooling layer for 3D inputs (e.g. volumes).
+
+[`class SeparableConv1D`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/SeparableConv1D.md): Depthwise separable 1D convolution.
+
+[`class SeparableConv2D`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/SeparableConv2D.md): Depthwise separable 2D convolution.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`average_pooling1d(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/average_pooling1d.md): Average Pooling layer for 1D inputs. (deprecated)
+
+[`average_pooling2d(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/average_pooling2d.md): Average pooling layer for 2D inputs (e.g. images). (deprecated)
+
+[`average_pooling3d(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/average_pooling3d.md): Average pooling layer for 3D inputs (e.g. volumes). (deprecated)
+
+[`batch_normalization(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/batch_normalization.md): Functional interface for the batch normalization layer from_config(Ioffe et al., 2015). (deprecated)
+
+[`conv1d(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/conv1d.md): Functional interface for 1D convolution layer (e.g. temporal convolution). (deprecated)
+
+[`conv2d(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/conv2d.md): Functional interface for the 2D convolution layer. (deprecated)
+
+[`conv2d_transpose(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/conv2d_transpose.md): Functional interface for transposed 2D convolution layer. (deprecated)
+
+[`conv3d(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/conv3d.md): Functional interface for the 3D convolution layer. (deprecated)
+
+[`conv3d_transpose(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/conv3d_transpose.md): Functional interface for transposed 3D convolution layer. (deprecated)
+
+[`dense(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/dense.md): Functional interface for the densely-connected layer. (deprecated)
+
+[`dropout(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/dropout.md): Applies Dropout to the input. (deprecated)
+
+[`flatten(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/flatten.md): Flattens an input tensor while preserving the batch axis (axis 0). (deprecated)
+
+[`max_pooling1d(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/max_pooling1d.md): Max Pooling layer for 1D inputs. (deprecated)
+
+[`max_pooling2d(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/max_pooling2d.md): Max pooling layer for 2D inputs (e.g. images). (deprecated)
+
+[`max_pooling3d(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/max_pooling3d.md): Max pooling layer for 3D inputs (e.g. (deprecated)
+
+[`separable_conv1d(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/separable_conv1d.md): Functional interface for the depthwise separable 1D convolution layer. (deprecated)
+
+[`separable_conv2d(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/separable_conv2d.md): Functional interface for the depthwise separable 2D convolution layer. (deprecated)
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/AveragePooling1D.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/AveragePooling1D.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..64bed08fb45
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/AveragePooling1D.md
@@ -0,0 +1,122 @@
+description: Average Pooling layer for 1D inputs.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.AveragePooling1D
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Average Pooling layer for 1D inputs.
+
+Inherits From: [`AveragePooling1D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/AveragePooling1D.md), [`Layer`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/Layer.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.AveragePooling1D(
+ pool_size, strides, padding='valid', data_format='channels_last', name=None,
+ **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`pool_size`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of a single integer,
+representing the size of the pooling window.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of a single integer, specifying the
+strides of the pooling operation.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+A string. The padding method, either 'valid' or 'same'.
+Case-insensitive.
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+A string, one of `channels_last` (default) or `channels_first`.
+The ordering of the dimensions in the inputs.
+`channels_last` corresponds to inputs with shape
+`(batch, length, channels)` while `channels_first` corresponds to
+inputs with shape `(batch, channels, length)`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string, the name of the layer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+DEPRECATED FUNCTION
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Stop using this property because tf.layers layers no longer track their graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope_name`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/AveragePooling2D.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/AveragePooling2D.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..b5da3d67263
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/AveragePooling2D.md
@@ -0,0 +1,126 @@
+description: Average pooling layer for 2D inputs (e.g. images).
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.AveragePooling2D
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Average pooling layer for 2D inputs (e.g. images).
+
+Inherits From: [`AveragePooling2D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/AveragePooling2D.md), [`Layer`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/Layer.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.AveragePooling2D(
+ pool_size, strides, padding='valid', data_format='channels_last', name=None,
+ **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`pool_size`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of 2 integers: (pool_height, pool_width)
+specifying the size of the pooling window.
+Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
+all spatial dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of 2 integers,
+specifying the strides of the pooling operation.
+Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
+all spatial dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+A string. The padding method, either 'valid' or 'same'.
+Case-insensitive.
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+A string. The ordering of the dimensions in the inputs.
+`channels_last` (default) and `channels_first` are supported.
+`channels_last` corresponds to inputs with shape
+`(batch, height, width, channels)` while `channels_first` corresponds to
+inputs with shape `(batch, channels, height, width)`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string, the name of the layer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+DEPRECATED FUNCTION
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Stop using this property because tf.layers layers no longer track their graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope_name`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/AveragePooling3D.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/AveragePooling3D.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..47ede51cdb2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/AveragePooling3D.md
@@ -0,0 +1,128 @@
+description: Average pooling layer for 3D inputs (e.g. volumes).
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.AveragePooling3D
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Average pooling layer for 3D inputs (e.g. volumes).
+
+Inherits From: [`AveragePooling3D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/AveragePooling3D.md), [`Layer`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/Layer.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.AveragePooling3D(
+ pool_size, strides, padding='valid', data_format='channels_last', name=None,
+ **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`pool_size`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of 3 integers:
+(pool_depth, pool_height, pool_width)
+specifying the size of the pooling window.
+Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
+all spatial dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of 3 integers,
+specifying the strides of the pooling operation.
+Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
+all spatial dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+A string. The padding method, either 'valid' or 'same'.
+Case-insensitive.
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+A string. The ordering of the dimensions in the inputs.
+`channels_last` (default) and `channels_first` are supported.
+`channels_last` corresponds to inputs with shape
+`(batch, depth, height, width, channels)` while `channels_first`
+corresponds to inputs with shape
+`(batch, channels, depth, height, width)`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string, the name of the layer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+DEPRECATED FUNCTION
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Stop using this property because tf.layers layers no longer track their graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope_name`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/BatchNormalization.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/BatchNormalization.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..512be112d54
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/BatchNormalization.md
@@ -0,0 +1,301 @@
+description: Batch Normalization layer from (Ioffe et al., 2015).
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.BatchNormalization
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Batch Normalization layer from (Ioffe et al., 2015).
+
+Inherits From: [`BatchNormalization`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/layers/BatchNormalization.md), [`Layer`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/Layer.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.BatchNormalization(
+ axis=-1, momentum=0.99, epsilon=0.001, center=(True), scale=(True),
+ beta_initializer=tf.zeros_initializer(),
+ gamma_initializer=tf.ones_initializer(),
+ moving_mean_initializer=tf.zeros_initializer(),
+ moving_variance_initializer=tf.ones_initializer(), beta_regularizer=None,
+ gamma_regularizer=None, beta_constraint=None, gamma_constraint=None,
+ renorm=(False), renorm_clipping=None, renorm_momentum=0.99, fused=None,
+ trainable=(True), virtual_batch_size=None, adjustment=None, name=None, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Keras APIs handle BatchNormalization updates to the moving_mean and
+moving_variance as part of their `fit()` and `evaluate()` loops. However, if a
+custom training loop is used with an instance of `Model`, these updates need
+to be explicitly included. Here's a simple example of how it can be done:
+
+```python
+ # model is an instance of Model that contains BatchNormalization layer.
+ update_ops = model.get_updates_for(None) + model.get_updates_for(features)
+ train_op = optimizer.minimize(loss)
+ train_op = tf.group([train_op, update_ops])
+```
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`axis`
+ |
+
+An `int` or list of `int`, the axis or axes that should be normalized,
+typically the features axis/axes. For instance, after a `Conv2D` layer
+with `data_format="channels_first"`, set `axis=1`. If a list of axes is
+provided, each axis in `axis` will be normalized
+simultaneously. Default is `-1` which uses the last axis. Note: when
+using multi-axis batch norm, the `beta`, `gamma`, `moving_mean`, and
+`moving_variance` variables are the same rank as the input Tensor,
+with dimension size 1 in all reduced (non-axis) dimensions).
+ |
+
+|
+`momentum`
+ |
+
+Momentum for the moving average.
+ |
+
+|
+`epsilon`
+ |
+
+Small float added to variance to avoid dividing by zero.
+ |
+
+|
+`center`
+ |
+
+If True, add offset of `beta` to normalized tensor. If False, `beta`
+is ignored.
+ |
+
+|
+`scale`
+ |
+
+If True, multiply by `gamma`. If False, `gamma` is not used. When the
+next layer is linear (also e.g. `nn.relu`), this can be disabled since the
+scaling can be done by the next layer.
+ |
+
+|
+`beta_initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer for the beta weight.
+ |
+
+|
+`gamma_initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer for the gamma weight.
+ |
+
+|
+`moving_mean_initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer for the moving mean.
+ |
+
+|
+`moving_variance_initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer for the moving variance.
+ |
+
+|
+`beta_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the beta weight.
+ |
+
+|
+`gamma_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the gamma weight.
+ |
+
+|
+`beta_constraint`
+ |
+
+An optional projection function to be applied to the `beta`
+weight after being updated by an `Optimizer` (e.g. used to implement norm
+constraints or value constraints for layer weights). The function must
+take as input the unprojected variable and must return the projected
+variable (which must have the same shape). Constraints are not safe to use
+when doing asynchronous distributed training.
+ |
+
+|
+`gamma_constraint`
+ |
+
+An optional projection function to be applied to the
+`gamma` weight after being updated by an `Optimizer`.
+ |
+
+|
+`renorm`
+ |
+
+Whether to use Batch Renormalization (Ioffe, 2017). This adds extra
+variables during training. The inference is the same for either value of
+this parameter.
+ |
+
+|
+`renorm_clipping`
+ |
+
+A dictionary that may map keys 'rmax', 'rmin', 'dmax' to
+scalar `Tensors` used to clip the renorm correction. The correction `(r,
+d)` is used as `corrected_value = normalized_value * r + d`, with `r`
+clipped to [rmin, rmax], and `d` to [-dmax, dmax]. Missing rmax, rmin,
+dmax are set to inf, 0, inf, respectively.
+ |
+
+|
+`renorm_momentum`
+ |
+
+Momentum used to update the moving means and standard
+deviations with renorm. Unlike `momentum`, this affects training and
+should be neither too small (which would add noise) nor too large (which
+would give stale estimates). Note that `momentum` is still applied to get
+the means and variances for inference.
+ |
+
+|
+`fused`
+ |
+
+if `None` or `True`, use a faster, fused implementation if possible.
+If `False`, use the system recommended implementation.
+ |
+
+|
+`trainable`
+ |
+
+Boolean, if `True` also add variables to the graph collection
+`GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES` (see tf.Variable).
+ |
+
+|
+`virtual_batch_size`
+ |
+
+An `int`. By default, `virtual_batch_size` is `None`,
+which means batch normalization is performed across the whole batch. When
+`virtual_batch_size` is not `None`, instead perform "Ghost Batch
+Normalization", which creates virtual sub-batches which are each
+normalized separately (with shared gamma, beta, and moving statistics).
+Must divide the actual batch size during execution.
+ |
+
+|
+`adjustment`
+ |
+
+A function taking the `Tensor` containing the (dynamic) shape of
+the input tensor and returning a pair (scale, bias) to apply to the
+normalized values (before gamma and beta), only during training. For
+example, if axis==-1,
+`adjustment = lambda shape: (
+tf.random.uniform(shape[-1:], 0.93, 1.07),
+tf.random.uniform(shape[-1:], -0.1, 0.1))` will scale the normalized
+value by up to 7% up or down, then shift the result by up to 0.1
+(with independent scaling and bias for each feature but shared
+across all examples), and finally apply gamma and/or beta. If
+`None`, no adjustment is applied. Cannot be specified if
+virtual_batch_size is specified.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string, the name of the layer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### References:
+
+Batch Normalization - Accelerating Deep Network Training by Reducing
+ Internal Covariate Shift:
+ [Ioffe et al., 2015](http://proceedings.mlr.press/v37/ioffe15.html)
+ ([pdf](http://proceedings.mlr.press/v37/ioffe15.pdf))
+Batch Renormalization - Towards Reducing Minibatch Dependence in
+ Batch-Normalized Models:
+ [Ioffe,
+ 2017](http://papers.nips.cc/paper/6790-batch-renormalization-towards-reducing-minibatch-dependence-in-batch-normalized-models)
+ ([pdf](http://papers.nips.cc/paper/6790-batch-renormalization-towards-reducing-minibatch-dependence-in-batch-normalized-models.pdf))
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+DEPRECATED FUNCTION
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Stop using this property because tf.layers layers no longer track their graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope_name`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/Conv1D.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/Conv1D.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..20b8001ce4e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/Conv1D.md
@@ -0,0 +1,228 @@
+description: 1D convolution layer (e.g. temporal convolution).
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.Conv1D
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+1D convolution layer (e.g. temporal convolution).
+
+Inherits From: [`Conv1D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Conv1D.md), [`Layer`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/Layer.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.Conv1D(
+ filters, kernel_size, strides=1, padding='valid', data_format='channels_last',
+ dilation_rate=1, activation=None, use_bias=(True), kernel_initializer=None,
+ bias_initializer=tf.zeros_initializer(), kernel_regularizer=None,
+ bias_regularizer=None, activity_regularizer=None, kernel_constraint=None,
+ bias_constraint=None, trainable=(True), name=None, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This layer creates a convolution kernel that is convolved
+(actually cross-correlated) with the layer input to produce a tensor of
+outputs. If `use_bias` is True (and a `bias_initializer` is provided),
+a bias vector is created and added to the outputs. Finally, if
+`activation` is not `None`, it is applied to the outputs as well.
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`filters`
+ |
+
+Integer, the dimensionality of the output space (i.e. the number
+of filters in the convolution).
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_size`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of a single integer, specifying the
+length of the 1D convolution window.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of a single integer,
+specifying the stride length of the convolution.
+Specifying any stride value != 1 is incompatible with specifying
+any `dilation_rate` value != 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+One of `"valid"` or `"same"` (case-insensitive).
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+A string, one of `channels_last` (default) or `channels_first`.
+The ordering of the dimensions in the inputs.
+`channels_last` corresponds to inputs with shape
+`(batch, length, channels)` while `channels_first` corresponds to
+inputs with shape `(batch, channels, length)`.
+ |
+
+|
+`dilation_rate`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of a single integer, specifying
+the dilation rate to use for dilated convolution.
+Currently, specifying any `dilation_rate` value != 1 is
+incompatible with specifying any `strides` value != 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`activation`
+ |
+
+Activation function. Set it to None to maintain a
+linear activation.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_bias`
+ |
+
+Boolean, whether the layer uses a bias.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_initializer`
+ |
+
+An initializer for the convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_initializer`
+ |
+
+An initializer for the bias vector. If None, the default
+initializer will be used.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`activity_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer function for the output.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_constraint`
+ |
+
+Optional projection function to be applied to the
+kernel after being updated by an `Optimizer` (e.g. used to implement
+norm constraints or value constraints for layer weights). The function
+must take as input the unprojected variable and must return the
+projected variable (which must have the same shape). Constraints are
+not safe to use when doing asynchronous distributed training.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_constraint`
+ |
+
+Optional projection function to be applied to the
+bias after being updated by an `Optimizer`.
+ |
+
+|
+`trainable`
+ |
+
+Boolean, if `True` also add variables to the graph collection
+`GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES` (see tf.Variable).
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string, the name of the layer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+DEPRECATED FUNCTION
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Stop using this property because tf.layers layers no longer track their graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope_name`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/Conv2D.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/Conv2D.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..b790dcc86ec
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/Conv2D.md
@@ -0,0 +1,235 @@
+description: 2D convolution layer (e.g. spatial convolution over images).
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.Conv2D
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+2D convolution layer (e.g. spatial convolution over images).
+
+Inherits From: [`Conv2D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Conv2D.md), [`Layer`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/Layer.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.Conv2D(
+ filters, kernel_size, strides=(1, 1), padding='valid',
+ data_format='channels_last', dilation_rate=(1, 1), activation=None,
+ use_bias=(True), kernel_initializer=None,
+ bias_initializer=tf.zeros_initializer(), kernel_regularizer=None,
+ bias_regularizer=None, activity_regularizer=None, kernel_constraint=None,
+ bias_constraint=None, trainable=(True), name=None, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This layer creates a convolution kernel that is convolved
+(actually cross-correlated) with the layer input to produce a tensor of
+outputs. If `use_bias` is True (and a `bias_initializer` is provided),
+a bias vector is created and added to the outputs. Finally, if
+`activation` is not `None`, it is applied to the outputs as well.
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`filters`
+ |
+
+Integer, the dimensionality of the output space (i.e. the number
+of filters in the convolution).
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_size`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of 2 integers, specifying the
+height and width of the 2D convolution window.
+Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
+all spatial dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of 2 integers,
+specifying the strides of the convolution along the height and width.
+Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
+all spatial dimensions.
+Specifying any stride value != 1 is incompatible with specifying
+any `dilation_rate` value != 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+One of `"valid"` or `"same"` (case-insensitive).
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+A string, one of `channels_last` (default) or `channels_first`.
+The ordering of the dimensions in the inputs.
+`channels_last` corresponds to inputs with shape
+`(batch, height, width, channels)` while `channels_first` corresponds to
+inputs with shape `(batch, channels, height, width)`.
+ |
+
+|
+`dilation_rate`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of 2 integers, specifying
+the dilation rate to use for dilated convolution.
+Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
+all spatial dimensions.
+Currently, specifying any `dilation_rate` value != 1 is
+incompatible with specifying any stride value != 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`activation`
+ |
+
+Activation function. Set it to None to maintain a
+linear activation.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_bias`
+ |
+
+Boolean, whether the layer uses a bias.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_initializer`
+ |
+
+An initializer for the convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_initializer`
+ |
+
+An initializer for the bias vector. If None, the default
+initializer will be used.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`activity_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer function for the output.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_constraint`
+ |
+
+Optional projection function to be applied to the
+kernel after being updated by an `Optimizer` (e.g. used to implement
+norm constraints or value constraints for layer weights). The function
+must take as input the unprojected variable and must return the
+projected variable (which must have the same shape). Constraints are
+not safe to use when doing asynchronous distributed training.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_constraint`
+ |
+
+Optional projection function to be applied to the
+bias after being updated by an `Optimizer`.
+ |
+
+|
+`trainable`
+ |
+
+Boolean, if `True` also add variables to the graph collection
+`GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES` (see tf.Variable).
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string, the name of the layer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+DEPRECATED FUNCTION
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Stop using this property because tf.layers layers no longer track their graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope_name`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/Conv2DTranspose.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/Conv2DTranspose.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..c03856c9fe7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/Conv2DTranspose.md
@@ -0,0 +1,220 @@
+description: Transposed 2D convolution layer (sometimes called 2D Deconvolution).
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.Conv2DTranspose
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Transposed 2D convolution layer (sometimes called 2D Deconvolution).
+
+Inherits From: [`Conv2DTranspose`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Conv2DTranspose.md), [`Layer`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/Layer.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.Conv2DTranspose(
+ filters, kernel_size, strides=(1, 1), padding='valid',
+ data_format='channels_last', activation=None, use_bias=(True),
+ kernel_initializer=None, bias_initializer=tf.zeros_initializer(),
+ kernel_regularizer=None, bias_regularizer=None, activity_regularizer=None,
+ kernel_constraint=None, bias_constraint=None, trainable=(True), name=None,
+ **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The need for transposed convolutions generally arises
+from the desire to use a transformation going in the opposite direction
+of a normal convolution, i.e., from something that has the shape of the
+output of some convolution to something that has the shape of its input
+while maintaining a connectivity pattern that is compatible with
+said convolution.
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`filters`
+ |
+
+Integer, the dimensionality of the output space (i.e. the number
+of filters in the convolution).
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_size`
+ |
+
+A tuple or list of 2 positive integers specifying the spatial
+dimensions of the filters. Can be a single integer to specify the same
+value for all spatial dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+A tuple or list of 2 positive integers specifying the strides
+of the convolution. Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
+all spatial dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+one of `"valid"` or `"same"` (case-insensitive).
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+A string, one of `channels_last` (default) or `channels_first`.
+The ordering of the dimensions in the inputs.
+`channels_last` corresponds to inputs with shape
+`(batch, height, width, channels)` while `channels_first` corresponds to
+inputs with shape `(batch, channels, height, width)`.
+ |
+
+|
+`activation`
+ |
+
+Activation function. Set it to None to maintain a
+linear activation.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_bias`
+ |
+
+Boolean, whether the layer uses a bias.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_initializer`
+ |
+
+An initializer for the convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_initializer`
+ |
+
+An initializer for the bias vector. If None, the default
+initializer will be used.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`activity_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer function for the output.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_constraint`
+ |
+
+Optional projection function to be applied to the
+kernel after being updated by an `Optimizer` (e.g. used to implement
+norm constraints or value constraints for layer weights). The function
+must take as input the unprojected variable and must return the
+projected variable (which must have the same shape). Constraints are
+not safe to use when doing asynchronous distributed training.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_constraint`
+ |
+
+Optional projection function to be applied to the
+bias after being updated by an `Optimizer`.
+ |
+
+|
+`trainable`
+ |
+
+Boolean, if `True` also add variables to the graph collection
+`GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES` (see tf.Variable).
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string, the name of the layer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+DEPRECATED FUNCTION
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Stop using this property because tf.layers layers no longer track their graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope_name`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/Conv3D.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/Conv3D.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..4c87a2c8458
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/Conv3D.md
@@ -0,0 +1,237 @@
+description: 3D convolution layer (e.g. spatial convolution over volumes).
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.Conv3D
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+3D convolution layer (e.g. spatial convolution over volumes).
+
+Inherits From: [`Conv3D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Conv3D.md), [`Layer`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/Layer.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.Conv3D(
+ filters, kernel_size, strides=(1, 1, 1), padding='valid',
+ data_format='channels_last', dilation_rate=(1, 1, 1), activation=None,
+ use_bias=(True), kernel_initializer=None,
+ bias_initializer=tf.zeros_initializer(), kernel_regularizer=None,
+ bias_regularizer=None, activity_regularizer=None, kernel_constraint=None,
+ bias_constraint=None, trainable=(True), name=None, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This layer creates a convolution kernel that is convolved
+(actually cross-correlated) with the layer input to produce a tensor of
+outputs. If `use_bias` is True (and a `bias_initializer` is provided),
+a bias vector is created and added to the outputs. Finally, if
+`activation` is not `None`, it is applied to the outputs as well.
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`filters`
+ |
+
+Integer, the dimensionality of the output space (i.e. the number
+of filters in the convolution).
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_size`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of 3 integers, specifying the
+depth, height and width of the 3D convolution window.
+Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
+all spatial dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of 3 integers,
+specifying the strides of the convolution along the depth,
+height and width.
+Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
+all spatial dimensions.
+Specifying any stride value != 1 is incompatible with specifying
+any `dilation_rate` value != 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+One of `"valid"` or `"same"` (case-insensitive).
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+A string, one of `channels_last` (default) or `channels_first`.
+The ordering of the dimensions in the inputs.
+`channels_last` corresponds to inputs with shape
+`(batch, depth, height, width, channels)` while `channels_first`
+corresponds to inputs with shape
+`(batch, channels, depth, height, width)`.
+ |
+
+|
+`dilation_rate`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of 3 integers, specifying
+the dilation rate to use for dilated convolution.
+Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
+all spatial dimensions.
+Currently, specifying any `dilation_rate` value != 1 is
+incompatible with specifying any stride value != 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`activation`
+ |
+
+Activation function. Set it to None to maintain a
+linear activation.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_bias`
+ |
+
+Boolean, whether the layer uses a bias.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_initializer`
+ |
+
+An initializer for the convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_initializer`
+ |
+
+An initializer for the bias vector. If None, the default
+initializer will be used.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`activity_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer function for the output.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_constraint`
+ |
+
+Optional projection function to be applied to the
+kernel after being updated by an `Optimizer` (e.g. used to implement
+norm constraints or value constraints for layer weights). The function
+must take as input the unprojected variable and must return the
+projected variable (which must have the same shape). Constraints are
+not safe to use when doing asynchronous distributed training.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_constraint`
+ |
+
+Optional projection function to be applied to the
+bias after being updated by an `Optimizer`.
+ |
+
+|
+`trainable`
+ |
+
+Boolean, if `True` also add variables to the graph collection
+`GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES` (see tf.Variable).
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string, the name of the layer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+DEPRECATED FUNCTION
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Stop using this property because tf.layers layers no longer track their graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope_name`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/Conv3DTranspose.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/Conv3DTranspose.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..f20b1e406e8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/Conv3DTranspose.md
@@ -0,0 +1,217 @@
+description: Transposed 3D convolution layer (sometimes called 3D Deconvolution).
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.Conv3DTranspose
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Transposed 3D convolution layer (sometimes called 3D Deconvolution).
+
+Inherits From: [`Conv3DTranspose`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Conv3DTranspose.md), [`Layer`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/Layer.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.Conv3DTranspose(
+ filters, kernel_size, strides=(1, 1, 1), padding='valid',
+ data_format='channels_last', activation=None, use_bias=(True),
+ kernel_initializer=None, bias_initializer=tf.zeros_initializer(),
+ kernel_regularizer=None, bias_regularizer=None, activity_regularizer=None,
+ kernel_constraint=None, bias_constraint=None, trainable=(True), name=None,
+ **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`filters`
+ |
+
+Integer, the dimensionality of the output space (i.e. the number
+of filters in the convolution).
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_size`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of 3 integers, specifying the
+depth, height and width of the 3D convolution window.
+Can be a single integer to specify the same value for all spatial
+dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of 3 integers, specifying the strides
+of the convolution along the depth, height and width.
+Can be a single integer to specify the same value for all spatial
+dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+One of `"valid"` or `"same"` (case-insensitive).
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+A string, one of `channels_last` (default) or `channels_first`.
+The ordering of the dimensions in the inputs.
+`channels_last` corresponds to inputs with shape
+`(batch, depth, height, width, channels)` while `channels_first`
+corresponds to inputs with shape
+`(batch, channels, depth, height, width)`.
+ |
+
+|
+`activation`
+ |
+
+Activation function. Set it to `None` to maintain a
+linear activation.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_bias`
+ |
+
+Boolean, whether the layer uses a bias.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_initializer`
+ |
+
+An initializer for the convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_initializer`
+ |
+
+An initializer for the bias vector. If `None`, the default
+initializer will be used.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`activity_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer function for the output.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_constraint`
+ |
+
+Optional projection function to be applied to the
+kernel after being updated by an `Optimizer` (e.g. used to implement
+norm constraints or value constraints for layer weights). The function
+must take as input the unprojected variable and must return the
+projected variable (which must have the same shape). Constraints are
+not safe to use when doing asynchronous distributed training.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_constraint`
+ |
+
+Optional projection function to be applied to the
+bias after being updated by an `Optimizer`.
+ |
+
+|
+`trainable`
+ |
+
+Boolean, if `True` also add variables to the graph collection
+`GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES` (see tf.Variable).
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string, the name of the layer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+DEPRECATED FUNCTION
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Stop using this property because tf.layers layers no longer track their graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope_name`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/Dense.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/Dense.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..504ab7ff26a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/Dense.md
@@ -0,0 +1,208 @@
+description: Densely-connected layer class.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.Dense
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Densely-connected layer class.
+
+Inherits From: [`Dense`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Dense.md), [`Layer`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/Layer.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.Dense(
+ units, activation=None, use_bias=(True), kernel_initializer=None,
+ bias_initializer=tf.zeros_initializer(), kernel_regularizer=None,
+ bias_regularizer=None, activity_regularizer=None, kernel_constraint=None,
+ bias_constraint=None, trainable=(True), name=None, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This layer implements the operation:
+`outputs = activation(inputs * kernel + bias)`
+Where `activation` is the activation function passed as the `activation`
+argument (if not `None`), `kernel` is a weights matrix created by the layer,
+and `bias` is a bias vector created by the layer
+(only if `use_bias` is `True`).
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`units`
+ |
+
+Integer or Long, dimensionality of the output space.
+ |
+
+|
+`activation`
+ |
+
+Activation function (callable). Set it to None to maintain a
+linear activation.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_bias`
+ |
+
+Boolean, whether the layer uses a bias.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer function for the weight matrix.
+If `None` (default), weights are initialized using the default
+initializer used by tf.compat.v1.get_variable.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer function for the bias.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Regularizer function for the weight matrix.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Regularizer function for the bias.
+ |
+
+|
+`activity_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Regularizer function for the output.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_constraint`
+ |
+
+An optional projection function to be applied to the
+kernel after being updated by an `Optimizer` (e.g. used to implement
+norm constraints or value constraints for layer weights). The function
+must take as input the unprojected variable and must return the
+projected variable (which must have the same shape). Constraints are
+not safe to use when doing asynchronous distributed training.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_constraint`
+ |
+
+An optional projection function to be applied to the
+bias after being updated by an `Optimizer`.
+ |
+
+|
+`trainable`
+ |
+
+Boolean, if `True` also add variables to the graph collection
+`GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES` (see tf.Variable).
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+String, the name of the layer. Layers with the same name will
+share weights, but to avoid mistakes we require reuse=True in such cases.
+ |
+
+|
+`_reuse`
+ |
+
+Boolean, whether to reuse the weights of a previous layer
+by the same name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Properties:
+
+
+* `units`: Python integer, dimensionality of the output space.
+* `activation`: Activation function (callable).
+* `use_bias`: Boolean, whether the layer uses a bias.
+* `kernel_initializer`: Initializer instance (or name) for the kernel matrix.
+* `bias_initializer`: Initializer instance (or name) for the bias.
+* `kernel_regularizer`: Regularizer instance for the kernel matrix (callable)
+* `bias_regularizer`: Regularizer instance for the bias (callable).
+* `activity_regularizer`: Regularizer instance for the output (callable)
+* `kernel_constraint`: Constraint function for the kernel matrix.
+* `bias_constraint`: Constraint function for the bias.
+* `kernel`: Weight matrix (TensorFlow variable or tensor).
+* `bias`: Bias vector, if applicable (TensorFlow variable or tensor).
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+DEPRECATED FUNCTION
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Stop using this property because tf.layers layers no longer track their graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope_name`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/Dropout.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/Dropout.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..ce1d53a5395
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/Dropout.md
@@ -0,0 +1,119 @@
+description: Applies Dropout to the input.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.Dropout
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Applies Dropout to the input.
+
+Inherits From: [`Dropout`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Dropout.md), [`Layer`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/Layer.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.Dropout(
+ rate=0.5, noise_shape=None, seed=None, name=None, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Dropout consists in randomly setting a fraction `rate` of input units to 0
+at each update during training time, which helps prevent overfitting.
+The units that are kept are scaled by `1 / (1 - rate)`, so that their
+sum is unchanged at training time and inference time.
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`rate`
+ |
+
+The dropout rate, between 0 and 1. E.g. `rate=0.1` would drop out
+10% of input units.
+ |
+
+|
+`noise_shape`
+ |
+
+1D tensor of type `int32` representing the shape of the
+binary dropout mask that will be multiplied with the input.
+For instance, if your inputs have shape
+`(batch_size, timesteps, features)`, and you want the dropout mask
+to be the same for all timesteps, you can use
+`noise_shape=[batch_size, 1, features]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+A Python integer. Used to create random seeds. See
+tf.compat.v1.set_random_seed.
+for behavior.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+The name of the layer (string).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+DEPRECATED FUNCTION
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Stop using this property because tf.layers layers no longer track their graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope_name`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/Flatten.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/Flatten.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..43f983fbc2f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/Flatten.md
@@ -0,0 +1,104 @@
+description: Flattens an input tensor while preserving the batch axis (axis 0).
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.Flatten
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Flattens an input tensor while preserving the batch axis (axis 0).
+
+Inherits From: [`Flatten`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Flatten.md), [`Layer`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/Layer.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.Flatten(
+ data_format=None, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+A string, one of `channels_last` (default) or `channels_first`.
+The ordering of the dimensions in the inputs.
+`channels_last` corresponds to inputs with shape
+`(batch, ..., channels)` while `channels_first` corresponds to
+inputs with shape `(batch, channels, ...)`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Examples:
+
+
+
+```
+ x = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(shape=(None, 4, 4), dtype='float32')
+ y = Flatten()(x)
+ # now `y` has shape `(None, 16)`
+
+ x = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(shape=(None, 3, None), dtype='float32')
+ y = Flatten()(x)
+ # now `y` has shape `(None, None)`
+```
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+DEPRECATED FUNCTION
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Stop using this property because tf.layers layers no longer track their graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope_name`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/Layer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/Layer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..fb7aeacade7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/Layer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,126 @@
+description: Base layer class.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.Layer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Base layer class.
+
+Inherits From: [`Layer`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/Layer.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.Layer(
+ trainable=(True), name=None, dtype=None, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+It is considered legacy, and we recommend the use of tf.keras.layers.Layer
+instead.
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`trainable`
+ |
+
+Boolean, whether the layer's variables should be trainable.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+String name of the layer.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+Default dtype of the layer's weights (default of `None` means use the
+type of the first input).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+Read-only properties:
+ name: The name of the layer (string).
+ dtype: Default dtype of the layer's weights (default of `None` means use the
+ type of the first input).
+ trainable_variables: List of trainable variables.
+ non_trainable_variables: List of non-trainable variables.
+ variables: List of all variables of this layer, trainable and
+ non-trainable.
+ updates: List of update ops of this layer.
+ losses: List of losses added by this layer.
+ trainable_weights: List of variables to be included in backprop.
+ non_trainable_weights: List of variables that should not be
+ included in backprop.
+ weights: The concatenation of the lists trainable_weights and
+ non_trainable_weights (in this order).
+
+#### Mutable properties:
+
+
+* `trainable`: Whether the layer should be trained (boolean).
+* `input_spec`: Optional (list of) `InputSpec` object(s) specifying the
+ constraints on inputs that can be accepted by the layer.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+DEPRECATED FUNCTION
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Stop using this property because tf.layers layers no longer track their graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope_name`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/MaxPooling1D.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/MaxPooling1D.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..1798a01c9c1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/MaxPooling1D.md
@@ -0,0 +1,122 @@
+description: Max Pooling layer for 1D inputs.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.MaxPooling1D
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Max Pooling layer for 1D inputs.
+
+Inherits From: [`MaxPool1D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/MaxPool1D.md), [`Layer`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/Layer.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.MaxPooling1D(
+ pool_size, strides, padding='valid', data_format='channels_last', name=None,
+ **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`pool_size`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of a single integer,
+representing the size of the pooling window.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of a single integer, specifying the
+strides of the pooling operation.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+A string. The padding method, either 'valid' or 'same'.
+Case-insensitive.
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+A string, one of `channels_last` (default) or `channels_first`.
+The ordering of the dimensions in the inputs.
+`channels_last` corresponds to inputs with shape
+`(batch, length, channels)` while `channels_first` corresponds to
+inputs with shape `(batch, channels, length)`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string, the name of the layer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+DEPRECATED FUNCTION
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Stop using this property because tf.layers layers no longer track their graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope_name`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/MaxPooling2D.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/MaxPooling2D.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..7651710071a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/MaxPooling2D.md
@@ -0,0 +1,126 @@
+description: Max pooling layer for 2D inputs (e.g. images).
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.MaxPooling2D
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Max pooling layer for 2D inputs (e.g. images).
+
+Inherits From: [`MaxPool2D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/MaxPool2D.md), [`Layer`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/Layer.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.MaxPooling2D(
+ pool_size, strides, padding='valid', data_format='channels_last', name=None,
+ **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`pool_size`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of 2 integers: (pool_height, pool_width)
+specifying the size of the pooling window.
+Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
+all spatial dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of 2 integers,
+specifying the strides of the pooling operation.
+Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
+all spatial dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+A string. The padding method, either 'valid' or 'same'.
+Case-insensitive.
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+A string. The ordering of the dimensions in the inputs.
+`channels_last` (default) and `channels_first` are supported.
+`channels_last` corresponds to inputs with shape
+`(batch, height, width, channels)` while `channels_first` corresponds to
+inputs with shape `(batch, channels, height, width)`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string, the name of the layer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+DEPRECATED FUNCTION
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Stop using this property because tf.layers layers no longer track their graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope_name`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/MaxPooling3D.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/MaxPooling3D.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..358ca872c8b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/MaxPooling3D.md
@@ -0,0 +1,128 @@
+description: Max pooling layer for 3D inputs (e.g. volumes).
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.MaxPooling3D
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Max pooling layer for 3D inputs (e.g. volumes).
+
+Inherits From: [`MaxPool3D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/MaxPool3D.md), [`Layer`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/Layer.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.MaxPooling3D(
+ pool_size, strides, padding='valid', data_format='channels_last', name=None,
+ **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`pool_size`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of 3 integers:
+(pool_depth, pool_height, pool_width)
+specifying the size of the pooling window.
+Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
+all spatial dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of 3 integers,
+specifying the strides of the pooling operation.
+Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
+all spatial dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+A string. The padding method, either 'valid' or 'same'.
+Case-insensitive.
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+A string. The ordering of the dimensions in the inputs.
+`channels_last` (default) and `channels_first` are supported.
+`channels_last` corresponds to inputs with shape
+`(batch, depth, height, width, channels)` while `channels_first`
+corresponds to inputs with shape
+`(batch, channels, depth, height, width)`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string, the name of the layer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+DEPRECATED FUNCTION
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Stop using this property because tf.layers layers no longer track their graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope_name`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/SeparableConv1D.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/SeparableConv1D.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..53abfd62d8a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/SeparableConv1D.md
@@ -0,0 +1,263 @@
+description: Depthwise separable 1D convolution.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.SeparableConv1D
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Depthwise separable 1D convolution.
+
+Inherits From: [`SeparableConv1D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/SeparableConv1D.md), [`Layer`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/Layer.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.SeparableConv1D(
+ filters, kernel_size, strides=1, padding='valid', data_format='channels_last',
+ dilation_rate=1, depth_multiplier=1, activation=None, use_bias=(True),
+ depthwise_initializer=None, pointwise_initializer=None,
+ bias_initializer=tf.zeros_initializer(), depthwise_regularizer=None,
+ pointwise_regularizer=None, bias_regularizer=None, activity_regularizer=None,
+ depthwise_constraint=None, pointwise_constraint=None, bias_constraint=None,
+ trainable=(True), name=None, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This layer performs a depthwise convolution that acts separately on
+channels, followed by a pointwise convolution that mixes channels.
+If `use_bias` is True and a bias initializer is provided,
+it adds a bias vector to the output.
+It then optionally applies an activation function to produce the final output.
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`filters`
+ |
+
+Integer, the dimensionality of the output space (i.e. the number
+of filters in the convolution).
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_size`
+ |
+
+A single integer specifying the spatial
+dimensions of the filters.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+A single integer specifying the strides
+of the convolution.
+Specifying any `stride` value != 1 is incompatible with specifying
+any `dilation_rate` value != 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+One of `"valid"` or `"same"` (case-insensitive).
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+A string, one of `channels_last` (default) or `channels_first`.
+The ordering of the dimensions in the inputs.
+`channels_last` corresponds to inputs with shape
+`(batch, length, channels)` while `channels_first` corresponds to
+inputs with shape `(batch, channels, length)`.
+ |
+
+|
+`dilation_rate`
+ |
+
+A single integer, specifying
+the dilation rate to use for dilated convolution.
+Currently, specifying any `dilation_rate` value != 1 is
+incompatible with specifying any stride value != 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`depth_multiplier`
+ |
+
+The number of depthwise convolution output channels for
+each input channel. The total number of depthwise convolution output
+channels will be equal to `num_filters_in * depth_multiplier`.
+ |
+
+|
+`activation`
+ |
+
+Activation function. Set it to None to maintain a
+linear activation.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_bias`
+ |
+
+Boolean, whether the layer uses a bias.
+ |
+
+|
+`depthwise_initializer`
+ |
+
+An initializer for the depthwise convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`pointwise_initializer`
+ |
+
+An initializer for the pointwise convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_initializer`
+ |
+
+An initializer for the bias vector. If None, the default
+initializer will be used.
+ |
+
+|
+`depthwise_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the depthwise
+convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`pointwise_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the pointwise
+convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`activity_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer function for the output.
+ |
+
+|
+`depthwise_constraint`
+ |
+
+Optional projection function to be applied to the
+depthwise kernel after being updated by an `Optimizer` (e.g. used for
+norm constraints or value constraints for layer weights). The function
+must take as input the unprojected variable and must return the
+projected variable (which must have the same shape). Constraints are
+not safe to use when doing asynchronous distributed training.
+ |
+
+|
+`pointwise_constraint`
+ |
+
+Optional projection function to be applied to the
+pointwise kernel after being updated by an `Optimizer`.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_constraint`
+ |
+
+Optional projection function to be applied to the
+bias after being updated by an `Optimizer`.
+ |
+
+|
+`trainable`
+ |
+
+Boolean, if `True` also add variables to the graph collection
+`GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES` (see tf.Variable).
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string, the name of the layer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+DEPRECATED FUNCTION
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Stop using this property because tf.layers layers no longer track their graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope_name`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/SeparableConv2D.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/SeparableConv2D.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e693838db4b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/SeparableConv2D.md
@@ -0,0 +1,267 @@
+description: Depthwise separable 2D convolution.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.SeparableConv2D
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Depthwise separable 2D convolution.
+
+Inherits From: [`SeparableConv2D`](../../../../tf/keras/layers/SeparableConv2D.md), [`Layer`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/Layer.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.SeparableConv2D(
+ filters, kernel_size, strides=(1, 1), padding='valid',
+ data_format='channels_last', dilation_rate=(1, 1), depth_multiplier=1,
+ activation=None, use_bias=(True), depthwise_initializer=None,
+ pointwise_initializer=None, bias_initializer=tf.zeros_initializer(),
+ depthwise_regularizer=None, pointwise_regularizer=None, bias_regularizer=None,
+ activity_regularizer=None, depthwise_constraint=None, pointwise_constraint=None,
+ bias_constraint=None, trainable=(True), name=None, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This layer performs a depthwise convolution that acts separately on
+channels, followed by a pointwise convolution that mixes channels.
+If `use_bias` is True and a bias initializer is provided,
+it adds a bias vector to the output.
+It then optionally applies an activation function to produce the final output.
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`filters`
+ |
+
+Integer, the dimensionality of the output space (i.e. the number
+of filters in the convolution).
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_size`
+ |
+
+A tuple or list of 2 integers specifying the spatial
+dimensions of the filters. Can be a single integer to specify the same
+value for all spatial dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+A tuple or list of 2 positive integers specifying the strides
+of the convolution. Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
+all spatial dimensions.
+Specifying any `stride` value != 1 is incompatible with specifying
+any `dilation_rate` value != 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+One of `"valid"` or `"same"` (case-insensitive).
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+A string, one of `channels_last` (default) or `channels_first`.
+The ordering of the dimensions in the inputs.
+`channels_last` corresponds to inputs with shape
+`(batch, height, width, channels)` while `channels_first` corresponds to
+inputs with shape `(batch, channels, height, width)`.
+ |
+
+|
+`dilation_rate`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of 2 integers, specifying
+the dilation rate to use for dilated convolution.
+Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
+all spatial dimensions.
+Currently, specifying any `dilation_rate` value != 1 is
+incompatible with specifying any stride value != 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`depth_multiplier`
+ |
+
+The number of depthwise convolution output channels for
+each input channel. The total number of depthwise convolution output
+channels will be equal to `num_filters_in * depth_multiplier`.
+ |
+
+|
+`activation`
+ |
+
+Activation function. Set it to None to maintain a
+linear activation.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_bias`
+ |
+
+Boolean, whether the layer uses a bias.
+ |
+
+|
+`depthwise_initializer`
+ |
+
+An initializer for the depthwise convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`pointwise_initializer`
+ |
+
+An initializer for the pointwise convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_initializer`
+ |
+
+An initializer for the bias vector. If None, the default
+initializer will be used.
+ |
+
+|
+`depthwise_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the depthwise
+convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`pointwise_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the pointwise
+convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`activity_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer function for the output.
+ |
+
+|
+`depthwise_constraint`
+ |
+
+Optional projection function to be applied to the
+depthwise kernel after being updated by an `Optimizer` (e.g. used for
+norm constraints or value constraints for layer weights). The function
+must take as input the unprojected variable and must return the
+projected variable (which must have the same shape). Constraints are
+not safe to use when doing asynchronous distributed training.
+ |
+
+|
+`pointwise_constraint`
+ |
+
+Optional projection function to be applied to the
+pointwise kernel after being updated by an `Optimizer`.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_constraint`
+ |
+
+Optional projection function to be applied to the
+bias after being updated by an `Optimizer`.
+ |
+
+|
+`trainable`
+ |
+
+Boolean, if `True` also add variables to the graph collection
+`GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES` (see tf.Variable).
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string, the name of the layer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+DEPRECATED FUNCTION
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Stop using this property because tf.layers layers no longer track their graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope_name`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/average_pooling1d.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/average_pooling1d.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..06182a6cbed
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/average_pooling1d.md
@@ -0,0 +1,127 @@
+description: Average Pooling layer for 1D inputs. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.average_pooling1d
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Average Pooling layer for 1D inputs. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.average_pooling1d(
+ inputs, pool_size, strides, padding='valid', data_format='channels_last',
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use keras.layers.AveragePooling1D instead.
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+The tensor over which to pool. Must have rank 3.
+ |
+
+|
+`pool_size`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of a single integer,
+representing the size of the pooling window.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of a single integer, specifying the
+strides of the pooling operation.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+A string. The padding method, either 'valid' or 'same'.
+Case-insensitive.
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+A string, one of `channels_last` (default) or `channels_first`.
+The ordering of the dimensions in the inputs.
+`channels_last` corresponds to inputs with shape
+`(batch, length, channels)` while `channels_first` corresponds to
+inputs with shape `(batch, channels, length)`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string, the name of the layer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The output tensor, of rank 3.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/average_pooling2d.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/average_pooling2d.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..999069c3571
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/average_pooling2d.md
@@ -0,0 +1,131 @@
+description: Average pooling layer for 2D inputs (e.g. images). (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.average_pooling2d
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Average pooling layer for 2D inputs (e.g. images). (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.average_pooling2d(
+ inputs, pool_size, strides, padding='valid', data_format='channels_last',
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use keras.layers.AveragePooling2D instead.
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+The tensor over which to pool. Must have rank 4.
+ |
+
+|
+`pool_size`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of 2 integers: (pool_height, pool_width)
+specifying the size of the pooling window.
+Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
+all spatial dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of 2 integers,
+specifying the strides of the pooling operation.
+Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
+all spatial dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+A string. The padding method, either 'valid' or 'same'.
+Case-insensitive.
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+A string. The ordering of the dimensions in the inputs.
+`channels_last` (default) and `channels_first` are supported.
+`channels_last` corresponds to inputs with shape
+`(batch, height, width, channels)` while `channels_first` corresponds to
+inputs with shape `(batch, channels, height, width)`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string, the name of the layer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Output tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/average_pooling3d.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/average_pooling3d.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..921472d15d5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/average_pooling3d.md
@@ -0,0 +1,133 @@
+description: Average pooling layer for 3D inputs (e.g. volumes). (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.average_pooling3d
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Average pooling layer for 3D inputs (e.g. volumes). (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.average_pooling3d(
+ inputs, pool_size, strides, padding='valid', data_format='channels_last',
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use keras.layers.AveragePooling3D instead.
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+The tensor over which to pool. Must have rank 5.
+ |
+
+|
+`pool_size`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of 3 integers:
+(pool_depth, pool_height, pool_width)
+specifying the size of the pooling window.
+Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
+all spatial dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of 3 integers,
+specifying the strides of the pooling operation.
+Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
+all spatial dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+A string. The padding method, either 'valid' or 'same'.
+Case-insensitive.
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+A string. The ordering of the dimensions in the inputs.
+`channels_last` (default) and `channels_first` are supported.
+`channels_last` corresponds to inputs with shape
+`(batch, depth, height, width, channels)` while `channels_first`
+corresponds to inputs with shape
+`(batch, channels, depth, height, width)`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string, the name of the layer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Output tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/batch_normalization.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/batch_normalization.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e82ca877f09
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/batch_normalization.md
@@ -0,0 +1,328 @@
+description: Functional interface for the batch normalization layer from_config(Ioffe et al., 2015). (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.batch_normalization
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Functional interface for the batch normalization layer from_config(Ioffe et al., 2015). (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.batch_normalization(
+ inputs, axis=-1, momentum=0.99, epsilon=0.001, center=(True), scale=(True),
+ beta_initializer=tf.zeros_initializer(),
+ gamma_initializer=tf.ones_initializer(),
+ moving_mean_initializer=tf.zeros_initializer(),
+ moving_variance_initializer=tf.ones_initializer(), beta_regularizer=None,
+ gamma_regularizer=None, beta_constraint=None, gamma_constraint=None,
+ training=(False), trainable=(True), name=None, reuse=None, renorm=(False),
+ renorm_clipping=None, renorm_momentum=0.99, fused=None, virtual_batch_size=None,
+ adjustment=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use keras.layers.BatchNormalization instead. In particular, tf.control_dependencies(tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS) should not be used (consult the tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization documentation).
+
+Note: when training, the moving_mean and moving_variance need to be updated.
+By default the update ops are placed in `tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS`, so they
+need to be executed alongside the `train_op`. Also, be sure to add any
+batch_normalization ops before getting the update_ops collection. Otherwise,
+update_ops will be empty, and training/inference will not work properly. For
+example:
+
+```python
+ x_norm = tf.compat.v1.layers.batch_normalization(x, training=training)
+
+ # ...
+
+ update_ops = tf.compat.v1.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS)
+ train_op = optimizer.minimize(loss)
+ train_op = tf.group([train_op, update_ops])
+```
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+Tensor input.
+ |
+
+|
+`axis`
+ |
+
+An `int`, the axis that should be normalized (typically the features
+axis). For instance, after a `Convolution2D` layer with
+`data_format="channels_first"`, set `axis=1` in `BatchNormalization`.
+ |
+
+|
+`momentum`
+ |
+
+Momentum for the moving average.
+ |
+
+|
+`epsilon`
+ |
+
+Small float added to variance to avoid dividing by zero.
+ |
+
+|
+`center`
+ |
+
+If True, add offset of `beta` to normalized tensor. If False, `beta`
+is ignored.
+ |
+
+|
+`scale`
+ |
+
+If True, multiply by `gamma`. If False, `gamma` is not used. When the
+next layer is linear (also e.g. `nn.relu`), this can be disabled since the
+scaling can be done by the next layer.
+ |
+
+|
+`beta_initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer for the beta weight.
+ |
+
+|
+`gamma_initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer for the gamma weight.
+ |
+
+|
+`moving_mean_initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer for the moving mean.
+ |
+
+|
+`moving_variance_initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer for the moving variance.
+ |
+
+|
+`beta_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the beta weight.
+ |
+
+|
+`gamma_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the gamma weight.
+ |
+
+|
+`beta_constraint`
+ |
+
+An optional projection function to be applied to the `beta`
+weight after being updated by an `Optimizer` (e.g. used to implement norm
+constraints or value constraints for layer weights). The function must
+take as input the unprojected variable and must return the projected
+variable (which must have the same shape). Constraints are not safe to use
+when doing asynchronous distributed training.
+ |
+
+|
+`gamma_constraint`
+ |
+
+An optional projection function to be applied to the
+`gamma` weight after being updated by an `Optimizer`.
+ |
+
+|
+`training`
+ |
+
+Either a Python boolean, or a TensorFlow boolean scalar tensor
+(e.g. a placeholder). Whether to return the output in training mode
+(normalized with statistics of the current batch) or in inference mode
+(normalized with moving statistics). **NOTE**: make sure to set this
+parameter correctly, or else your training/inference will not work
+properly.
+ |
+
+|
+`trainable`
+ |
+
+Boolean, if `True` also add variables to the graph collection
+`GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES` (see tf.Variable).
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+String, the name of the layer.
+ |
+
+|
+`reuse`
+ |
+
+Boolean, whether to reuse the weights of a previous layer by the same
+name.
+ |
+
+|
+`renorm`
+ |
+
+Whether to use Batch Renormalization (Ioffe, 2017). This adds extra
+variables during training. The inference is the same for either value of
+this parameter.
+ |
+
+|
+`renorm_clipping`
+ |
+
+A dictionary that may map keys 'rmax', 'rmin', 'dmax' to
+scalar `Tensors` used to clip the renorm correction. The correction `(r,
+d)` is used as `corrected_value = normalized_value * r + d`, with `r`
+clipped to [rmin, rmax], and `d` to [-dmax, dmax]. Missing rmax, rmin,
+dmax are set to inf, 0, inf, respectively.
+ |
+
+|
+`renorm_momentum`
+ |
+
+Momentum used to update the moving means and standard
+deviations with renorm. Unlike `momentum`, this affects training and
+should be neither too small (which would add noise) nor too large (which
+would give stale estimates). Note that `momentum` is still applied to get
+the means and variances for inference.
+ |
+
+|
+`fused`
+ |
+
+if `None` or `True`, use a faster, fused implementation if possible.
+If `False`, use the system recommended implementation.
+ |
+
+|
+`virtual_batch_size`
+ |
+
+An `int`. By default, `virtual_batch_size` is `None`,
+which means batch normalization is performed across the whole batch. When
+`virtual_batch_size` is not `None`, instead perform "Ghost Batch
+Normalization", which creates virtual sub-batches which are each
+normalized separately (with shared gamma, beta, and moving statistics).
+Must divide the actual batch size during execution.
+ |
+
+|
+`adjustment`
+ |
+
+A function taking the `Tensor` containing the (dynamic) shape of
+the input tensor and returning a pair (scale, bias) to apply to the
+normalized values (before gamma and beta), only during training. For
+example, if axis==-1,
+`adjustment = lambda shape: (
+tf.random.uniform(shape[-1:], 0.93, 1.07),
+tf.random.uniform(shape[-1:], -0.1, 0.1))` will scale the normalized
+value by up to 7% up or down, then shift the result by up to 0.1
+(with independent scaling and bias for each feature but shared
+across all examples), and finally apply gamma and/or beta. If
+`None`, no adjustment is applied. Cannot be specified if
+virtual_batch_size is specified.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Output tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### References:
+
+Batch Normalization - Accelerating Deep Network Training by Reducing
+Internal Covariate Shift:
+ [Ioffe et al., 2015](http://proceedings.mlr.press/v37/ioffe15.html)
+ ([pdf](http://proceedings.mlr.press/v37/ioffe15.pdf))
+Batch Renormalization - Towards Reducing Minibatch Dependence in
+Batch-Normalized Models:
+ [Ioffe,
+ 2017](http://papers.nips.cc/paper/6790-batch-renormalization-towards-reducing-minibatch-dependence-in-batch-normalized-models)
+ ([pdf](http://papers.nips.cc/paper/6790-batch-renormalization-towards-reducing-minibatch-dependence-in-batch-normalized-models.pdf))
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/conv1d.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/conv1d.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..51d19c9b24e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/conv1d.md
@@ -0,0 +1,243 @@
+description: Functional interface for 1D convolution layer (e.g. temporal convolution). (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.conv1d
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Functional interface for 1D convolution layer (e.g. temporal convolution). (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.conv1d(
+ inputs, filters, kernel_size, strides=1, padding='valid',
+ data_format='channels_last', dilation_rate=1, activation=None, use_bias=(True),
+ kernel_initializer=None, bias_initializer=tf.zeros_initializer(),
+ kernel_regularizer=None, bias_regularizer=None, activity_regularizer=None,
+ kernel_constraint=None, bias_constraint=None, trainable=(True), name=None,
+ reuse=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use tf.keras.layers.Conv1D instead.
+
+This layer creates a convolution kernel that is convolved
+(actually cross-correlated) with the layer input to produce a tensor of
+outputs. If `use_bias` is True (and a `bias_initializer` is provided),
+a bias vector is created and added to the outputs. Finally, if
+`activation` is not `None`, it is applied to the outputs as well.
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+Tensor input.
+ |
+
+|
+`filters`
+ |
+
+Integer, the dimensionality of the output space (i.e. the number
+of filters in the convolution).
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_size`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of a single integer, specifying the
+length of the 1D convolution window.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of a single integer,
+specifying the stride length of the convolution.
+Specifying any stride value != 1 is incompatible with specifying
+any `dilation_rate` value != 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+One of `"valid"` or `"same"` (case-insensitive).
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+A string, one of `channels_last` (default) or `channels_first`.
+The ordering of the dimensions in the inputs.
+`channels_last` corresponds to inputs with shape
+`(batch, length, channels)` while `channels_first` corresponds to
+inputs with shape `(batch, channels, length)`.
+ |
+
+|
+`dilation_rate`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of a single integer, specifying
+the dilation rate to use for dilated convolution.
+Currently, specifying any `dilation_rate` value != 1 is
+incompatible with specifying any `strides` value != 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`activation`
+ |
+
+Activation function. Set it to None to maintain a
+linear activation.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_bias`
+ |
+
+Boolean, whether the layer uses a bias.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_initializer`
+ |
+
+An initializer for the convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_initializer`
+ |
+
+An initializer for the bias vector. If None, the default
+initializer will be used.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`activity_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer function for the output.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_constraint`
+ |
+
+Optional projection function to be applied to the
+kernel after being updated by an `Optimizer` (e.g. used to implement
+norm constraints or value constraints for layer weights). The function
+must take as input the unprojected variable and must return the
+projected variable (which must have the same shape). Constraints are
+not safe to use when doing asynchronous distributed training.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_constraint`
+ |
+
+Optional projection function to be applied to the
+bias after being updated by an `Optimizer`.
+ |
+
+|
+`trainable`
+ |
+
+Boolean, if `True` also add variables to the graph collection
+`GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES` (see tf.Variable).
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string, the name of the layer.
+ |
+
+|
+`reuse`
+ |
+
+Boolean, whether to reuse the weights of a previous layer
+by the same name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Output tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/conv2d.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/conv2d.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..510b9d90eda
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/conv2d.md
@@ -0,0 +1,249 @@
+description: Functional interface for the 2D convolution layer. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.conv2d
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Functional interface for the 2D convolution layer. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.conv2d(
+ inputs, filters, kernel_size, strides=(1, 1), padding='valid',
+ data_format='channels_last', dilation_rate=(1, 1), activation=None,
+ use_bias=(True), kernel_initializer=None,
+ bias_initializer=tf.zeros_initializer(), kernel_regularizer=None,
+ bias_regularizer=None, activity_regularizer=None, kernel_constraint=None,
+ bias_constraint=None, trainable=(True), name=None, reuse=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use tf.keras.layers.Conv2D instead.
+
+This layer creates a convolution kernel that is convolved
+(actually cross-correlated) with the layer input to produce a tensor of
+outputs. If `use_bias` is True (and a `bias_initializer` is provided),
+a bias vector is created and added to the outputs. Finally, if
+`activation` is not `None`, it is applied to the outputs as well.
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+Tensor input.
+ |
+
+|
+`filters`
+ |
+
+Integer, the dimensionality of the output space (i.e. the number
+of filters in the convolution).
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_size`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of 2 integers, specifying the
+height and width of the 2D convolution window.
+Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
+all spatial dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of 2 integers,
+specifying the strides of the convolution along the height and width.
+Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
+all spatial dimensions.
+Specifying any stride value != 1 is incompatible with specifying
+any `dilation_rate` value != 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+One of `"valid"` or `"same"` (case-insensitive).
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+A string, one of `channels_last` (default) or `channels_first`.
+The ordering of the dimensions in the inputs.
+`channels_last` corresponds to inputs with shape
+`(batch, height, width, channels)` while `channels_first` corresponds to
+inputs with shape `(batch, channels, height, width)`.
+ |
+
+|
+`dilation_rate`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of 2 integers, specifying
+the dilation rate to use for dilated convolution.
+Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
+all spatial dimensions.
+Currently, specifying any `dilation_rate` value != 1 is
+incompatible with specifying any stride value != 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`activation`
+ |
+
+Activation function. Set it to None to maintain a
+linear activation.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_bias`
+ |
+
+Boolean, whether the layer uses a bias.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_initializer`
+ |
+
+An initializer for the convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_initializer`
+ |
+
+An initializer for the bias vector. If None, the default
+initializer will be used.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`activity_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer function for the output.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_constraint`
+ |
+
+Optional projection function to be applied to the
+kernel after being updated by an `Optimizer` (e.g. used to implement
+norm constraints or value constraints for layer weights). The function
+must take as input the unprojected variable and must return the
+projected variable (which must have the same shape). Constraints are
+not safe to use when doing asynchronous distributed training.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_constraint`
+ |
+
+Optional projection function to be applied to the
+bias after being updated by an `Optimizer`.
+ |
+
+|
+`trainable`
+ |
+
+Boolean, if `True` also add variables to the graph collection
+`GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES` (see tf.Variable).
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string, the name of the layer.
+ |
+
+|
+`reuse`
+ |
+
+Boolean, whether to reuse the weights of a previous layer
+by the same name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Output tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/conv2d_transpose.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/conv2d_transpose.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..25f356b274c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/conv2d_transpose.md
@@ -0,0 +1,234 @@
+description: Functional interface for transposed 2D convolution layer. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.conv2d_transpose
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Functional interface for transposed 2D convolution layer. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.conv2d_transpose(
+ inputs, filters, kernel_size, strides=(1, 1), padding='valid',
+ data_format='channels_last', activation=None, use_bias=(True),
+ kernel_initializer=None, bias_initializer=tf.zeros_initializer(),
+ kernel_regularizer=None, bias_regularizer=None, activity_regularizer=None,
+ kernel_constraint=None, bias_constraint=None, trainable=(True), name=None,
+ reuse=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use tf.keras.layers.Conv2DTranspose instead.
+
+The need for transposed convolutions generally arises
+from the desire to use a transformation going in the opposite direction
+of a normal convolution, i.e., from something that has the shape of the
+output of some convolution to something that has the shape of its input
+while maintaining a connectivity pattern that is compatible with
+said convolution.
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+Input tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`filters`
+ |
+
+Integer, the dimensionality of the output space (i.e. the number
+of filters in the convolution).
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_size`
+ |
+
+A tuple or list of 2 positive integers specifying the spatial
+dimensions of the filters. Can be a single integer to specify the same
+value for all spatial dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+A tuple or list of 2 positive integers specifying the strides
+of the convolution. Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
+all spatial dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+one of `"valid"` or `"same"` (case-insensitive).
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+A string, one of `channels_last` (default) or `channels_first`.
+The ordering of the dimensions in the inputs.
+`channels_last` corresponds to inputs with shape
+`(batch, height, width, channels)` while `channels_first` corresponds to
+inputs with shape `(batch, channels, height, width)`.
+ |
+
+|
+`activation`
+ |
+
+Activation function. Set it to `None` to maintain a
+linear activation.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_bias`
+ |
+
+Boolean, whether the layer uses a bias.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_initializer`
+ |
+
+An initializer for the convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_initializer`
+ |
+
+An initializer for the bias vector. If `None`, the default
+initializer will be used.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`activity_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer function for the output.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_constraint`
+ |
+
+Optional projection function to be applied to the
+kernel after being updated by an `Optimizer` (e.g. used to implement
+norm constraints or value constraints for layer weights). The function
+must take as input the unprojected variable and must return the
+projected variable (which must have the same shape). Constraints are
+not safe to use when doing asynchronous distributed training.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_constraint`
+ |
+
+Optional projection function to be applied to the
+bias after being updated by an `Optimizer`.
+ |
+
+|
+`trainable`
+ |
+
+Boolean, if `True` also add variables to the graph collection
+`GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES` (see tf.Variable).
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string, the name of the layer.
+ |
+
+|
+`reuse`
+ |
+
+Boolean, whether to reuse the weights of a previous layer
+by the same name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Output tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/conv3d.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/conv3d.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..7a8a68b77da
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/conv3d.md
@@ -0,0 +1,251 @@
+description: Functional interface for the 3D convolution layer. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.conv3d
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Functional interface for the 3D convolution layer. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.conv3d(
+ inputs, filters, kernel_size, strides=(1, 1, 1), padding='valid',
+ data_format='channels_last', dilation_rate=(1, 1, 1), activation=None,
+ use_bias=(True), kernel_initializer=None,
+ bias_initializer=tf.zeros_initializer(), kernel_regularizer=None,
+ bias_regularizer=None, activity_regularizer=None, kernel_constraint=None,
+ bias_constraint=None, trainable=(True), name=None, reuse=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use tf.keras.layers.Conv3D instead.
+
+This layer creates a convolution kernel that is convolved
+(actually cross-correlated) with the layer input to produce a tensor of
+outputs. If `use_bias` is True (and a `bias_initializer` is provided),
+a bias vector is created and added to the outputs. Finally, if
+`activation` is not `None`, it is applied to the outputs as well.
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+Tensor input.
+ |
+
+|
+`filters`
+ |
+
+Integer, the dimensionality of the output space (i.e. the number
+of filters in the convolution).
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_size`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of 3 integers, specifying the
+depth, height and width of the 3D convolution window.
+Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
+all spatial dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of 3 integers,
+specifying the strides of the convolution along the depth,
+height and width.
+Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
+all spatial dimensions.
+Specifying any stride value != 1 is incompatible with specifying
+any `dilation_rate` value != 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+One of `"valid"` or `"same"` (case-insensitive).
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+A string, one of `channels_last` (default) or `channels_first`.
+The ordering of the dimensions in the inputs.
+`channels_last` corresponds to inputs with shape
+`(batch, depth, height, width, channels)` while `channels_first`
+corresponds to inputs with shape
+`(batch, channels, depth, height, width)`.
+ |
+
+|
+`dilation_rate`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of 3 integers, specifying
+the dilation rate to use for dilated convolution.
+Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
+all spatial dimensions.
+Currently, specifying any `dilation_rate` value != 1 is
+incompatible with specifying any stride value != 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`activation`
+ |
+
+Activation function. Set it to None to maintain a
+linear activation.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_bias`
+ |
+
+Boolean, whether the layer uses a bias.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_initializer`
+ |
+
+An initializer for the convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_initializer`
+ |
+
+An initializer for the bias vector. If None, the default
+initializer will be used.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`activity_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer function for the output.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_constraint`
+ |
+
+Optional projection function to be applied to the
+kernel after being updated by an `Optimizer` (e.g. used to implement
+norm constraints or value constraints for layer weights). The function
+must take as input the unprojected variable and must return the
+projected variable (which must have the same shape). Constraints are
+not safe to use when doing asynchronous distributed training.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_constraint`
+ |
+
+Optional projection function to be applied to the
+bias after being updated by an `Optimizer`.
+ |
+
+|
+`trainable`
+ |
+
+Boolean, if `True` also add variables to the graph collection
+`GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES` (see tf.Variable).
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string, the name of the layer.
+ |
+
+|
+`reuse`
+ |
+
+Boolean, whether to reuse the weights of a previous layer
+by the same name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Output tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/conv3d_transpose.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/conv3d_transpose.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..b2a219d4e90
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/conv3d_transpose.md
@@ -0,0 +1,228 @@
+description: Functional interface for transposed 3D convolution layer. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.conv3d_transpose
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Functional interface for transposed 3D convolution layer. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.conv3d_transpose(
+ inputs, filters, kernel_size, strides=(1, 1, 1), padding='valid',
+ data_format='channels_last', activation=None, use_bias=(True),
+ kernel_initializer=None, bias_initializer=tf.zeros_initializer(),
+ kernel_regularizer=None, bias_regularizer=None, activity_regularizer=None,
+ kernel_constraint=None, bias_constraint=None, trainable=(True), name=None,
+ reuse=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use tf.keras.layers.Conv3DTranspose instead.
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+Input tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`filters`
+ |
+
+Integer, the dimensionality of the output space (i.e. the number
+of filters in the convolution).
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_size`
+ |
+
+A tuple or list of 3 positive integers specifying the spatial
+dimensions of the filters. Can be a single integer to specify the same
+value for all spatial dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+A tuple or list of 3 positive integers specifying the strides
+of the convolution. Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
+all spatial dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+one of `"valid"` or `"same"` (case-insensitive).
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+A string, one of `channels_last` (default) or `channels_first`.
+The ordering of the dimensions in the inputs.
+`channels_last` corresponds to inputs with shape
+`(batch, depth, height, width, channels)` while `channels_first`
+corresponds to inputs with shape
+`(batch, channels, depth, height, width)`.
+ |
+
+|
+`activation`
+ |
+
+Activation function. Set it to None to maintain a
+linear activation.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_bias`
+ |
+
+Boolean, whether the layer uses a bias.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_initializer`
+ |
+
+An initializer for the convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_initializer`
+ |
+
+An initializer for the bias vector. If None, the default
+initializer will be used.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`activity_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer function for the output.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_constraint`
+ |
+
+Optional projection function to be applied to the
+kernel after being updated by an `Optimizer` (e.g. used to implement
+norm constraints or value constraints for layer weights). The function
+must take as input the unprojected variable and must return the
+projected variable (which must have the same shape). Constraints are
+not safe to use when doing asynchronous distributed training.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_constraint`
+ |
+
+Optional projection function to be applied to the
+bias after being updated by an `Optimizer`.
+ |
+
+|
+`trainable`
+ |
+
+Boolean, if `True` also add variables to the graph collection
+`GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES` (see tf.Variable).
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string, the name of the layer.
+ |
+
+|
+`reuse`
+ |
+
+Boolean, whether to reuse the weights of a previous layer
+by the same name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Output tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/dense.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/dense.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..ff4471e3163
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/dense.md
@@ -0,0 +1,197 @@
+description: Functional interface for the densely-connected layer. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.dense
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Functional interface for the densely-connected layer. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.dense(
+ inputs, units, activation=None, use_bias=(True), kernel_initializer=None,
+ bias_initializer=tf.zeros_initializer(), kernel_regularizer=None,
+ bias_regularizer=None, activity_regularizer=None, kernel_constraint=None,
+ bias_constraint=None, trainable=(True), name=None, reuse=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use keras.layers.Dense instead.
+
+This layer implements the operation:
+`outputs = activation(inputs * kernel + bias)`
+where `activation` is the activation function passed as the `activation`
+argument (if not `None`), `kernel` is a weights matrix created by the layer,
+and `bias` is a bias vector created by the layer
+(only if `use_bias` is `True`).
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+Tensor input.
+ |
+
+|
+`units`
+ |
+
+Integer or Long, dimensionality of the output space.
+ |
+
+|
+`activation`
+ |
+
+Activation function (callable). Set it to None to maintain a
+linear activation.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_bias`
+ |
+
+Boolean, whether the layer uses a bias.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer function for the weight matrix.
+If `None` (default), weights are initialized using the default
+initializer used by tf.compat.v1.get_variable.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_initializer`
+ |
+
+Initializer function for the bias.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Regularizer function for the weight matrix.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Regularizer function for the bias.
+ |
+
+|
+`activity_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Regularizer function for the output.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_constraint`
+ |
+
+An optional projection function to be applied to the
+kernel after being updated by an `Optimizer` (e.g. used to implement
+norm constraints or value constraints for layer weights). The function
+must take as input the unprojected variable and must return the
+projected variable (which must have the same shape). Constraints are
+not safe to use when doing asynchronous distributed training.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_constraint`
+ |
+
+An optional projection function to be applied to the
+bias after being updated by an `Optimizer`.
+ |
+
+|
+`trainable`
+ |
+
+Boolean, if `True` also add variables to the graph collection
+`GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES` (see tf.Variable).
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+String, the name of the layer.
+ |
+
+|
+`reuse`
+ |
+
+Boolean, whether to reuse the weights of a previous layer
+by the same name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Output tensor the same shape as `inputs` except the last dimension is of
+size `units`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/dropout.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/dropout.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a15a5acb446
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/dropout.md
@@ -0,0 +1,134 @@
+description: Applies Dropout to the input. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.dropout
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Applies Dropout to the input. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.dropout(
+ inputs, rate=0.5, noise_shape=None, seed=None, training=(False), name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use keras.layers.dropout instead.
+
+Dropout consists in randomly setting a fraction `rate` of input units to 0
+at each update during training time, which helps prevent overfitting.
+The units that are kept are scaled by `1 / (1 - rate)`, so that their
+sum is unchanged at training time and inference time.
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+Tensor input.
+ |
+
+|
+`rate`
+ |
+
+The dropout rate, between 0 and 1. E.g. "rate=0.1" would drop out
+10% of input units.
+ |
+
+|
+`noise_shape`
+ |
+
+1D tensor of type `int32` representing the shape of the
+binary dropout mask that will be multiplied with the input.
+For instance, if your inputs have shape
+`(batch_size, timesteps, features)`, and you want the dropout mask
+to be the same for all timesteps, you can use
+`noise_shape=[batch_size, 1, features]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+A Python integer. Used to create random seeds. See
+tf.compat.v1.set_random_seed
+for behavior.
+ |
+
+|
+`training`
+ |
+
+Either a Python boolean, or a TensorFlow boolean scalar tensor
+(e.g. a placeholder). Whether to return the output in training mode
+(apply dropout) or in inference mode (return the input untouched).
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+The name of the layer (string).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Output tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/experimental.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/experimental.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a23cd8041e3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/experimental.md
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
+description: Public API for tf.layers.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.layers.experimental
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.layers.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`keras_style_scope(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/experimental/keras_style_scope.md): Use Keras-style variable management.
+
+[`set_keras_style(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/experimental/set_keras_style.md): Use Keras-style variable management.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/experimental/keras_style_scope.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/experimental/keras_style_scope.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..247e383a4f5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/experimental/keras_style_scope.md
@@ -0,0 +1,90 @@
+description: Use Keras-style variable management.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.experimental.keras_style_scope
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Use Keras-style variable management.
+
+
+@tf_contextlib.contextmanager
+tf.compat.v1.layers.experimental.keras_style_scope()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+All tf.layers and tf RNN cells created in this scope use Keras-style
+variable management. Creating such layers with a scope= argument is
+disallowed, and reuse=True is disallowed.
+
+The purpose of this scope is to allow users of existing layers to
+slowly transition to a Keras layers API without breaking existing
+functionality.
+
+One example of this is when using TensorFlow's RNN classes with Keras
+Models or Networks. Because Keras models do not properly set variable
+scopes, users of RNNs may either accidentally share scopes between two
+different models, or get errors about variables that already exist.
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+class RNNModel(tf.keras.Model):
+
+ def __init__(self, name):
+ super(RNNModel, self).__init__(name=name)
+ self.rnn = tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.MultiRNNCell(
+ [tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.LSTMCell(64) for _ in range(2)])
+
+ def call(self, input, state):
+ return self.rnn(input, state)
+
+model_1 = RNNModel("model_1")
+model_2 = RNNModel("model_2")
+
+# OK
+output_1, next_state_1 = model_1(input, state)
+# Raises an error about trying to create an already existing variable.
+output_2, next_state_2 = model_2(input, state)
+```
+
+The solution is to wrap the model construction and execution in a keras-style
+scope:
+
+```python
+with keras_style_scope():
+ model_1 = RNNModel("model_1")
+ model_2 = RNNModel("model_2")
+
+ # model_1 and model_2 are guaranteed to create their own variables.
+ output_1, next_state_1 = model_1(input, state)
+ output_2, next_state_2 = model_2(input, state)
+
+ assert len(model_1.weights) > 0
+ assert len(model_2.weights) > 0
+ assert(model_1.weights != model_2.weights)
+```
+
+#### Yields:
+
+A keras layer style scope.
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/experimental/set_keras_style.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/experimental/set_keras_style.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3bd77661ee2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/experimental/set_keras_style.md
@@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
+description: Use Keras-style variable management.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.experimental.set_keras_style
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Use Keras-style variable management.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.experimental.set_keras_style()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+All tf.layers and tf RNN cells created after keras style ha been enabled
+use Keras-style variable management. Creating such layers with a
+scope= argument is disallowed, and reuse=True is disallowed.
+
+The purpose of this function is to allow users of existing layers to
+slowly transition to Keras layers API without breaking existing
+functionality.
+
+For more details, see the documentation for `keras_style_scope`.
+
+Note, once keras style has been set, it is set globally for the entire
+program and cannot be unset.
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+set_keras_style()
+
+model_1 = RNNModel(name="model_1")
+model_2 = RNNModel(name="model_2")
+
+# model_1 and model_2 are guaranteed to create their own variables.
+output_1, next_state_1 = model_1(input, state)
+output_2, next_state_2 = model_2(input, state)
+
+assert len(model_1.weights) > 0
+assert len(model_2.weights) > 0
+assert(model_1.weights != model_2.weights)
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/flatten.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/flatten.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..59eb351b39e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/flatten.md
@@ -0,0 +1,100 @@
+description: Flattens an input tensor while preserving the batch axis (axis 0). (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.flatten
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Flattens an input tensor while preserving the batch axis (axis 0). (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.flatten(
+ inputs, name=None, data_format='channels_last'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use keras.layers.Flatten instead.
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+Tensor input.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+The name of the layer (string).
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+A string, one of `channels_last` (default) or `channels_first`.
+The ordering of the dimensions in the inputs.
+`channels_last` corresponds to inputs with shape
+`(batch, height, width, channels)` while `channels_first` corresponds to
+inputs with shape `(batch, channels, height, width)`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Reshaped tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Examples:
+
+
+
+```
+ x = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(shape=(None, 4, 4), dtype='float32')
+ y = flatten(x)
+ # now `y` has shape `(None, 16)`
+
+ x = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(shape=(None, 3, None), dtype='float32')
+ y = flatten(x)
+ # now `y` has shape `(None, None)`
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/max_pooling1d.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/max_pooling1d.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..dbbaca34ad0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/max_pooling1d.md
@@ -0,0 +1,127 @@
+description: Max Pooling layer for 1D inputs. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.max_pooling1d
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Max Pooling layer for 1D inputs. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.max_pooling1d(
+ inputs, pool_size, strides, padding='valid', data_format='channels_last',
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use keras.layers.MaxPooling1D instead.
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+The tensor over which to pool. Must have rank 3.
+ |
+
+|
+`pool_size`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of a single integer,
+representing the size of the pooling window.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of a single integer, specifying the
+strides of the pooling operation.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+A string. The padding method, either 'valid' or 'same'.
+Case-insensitive.
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+A string, one of `channels_last` (default) or `channels_first`.
+The ordering of the dimensions in the inputs.
+`channels_last` corresponds to inputs with shape
+`(batch, length, channels)` while `channels_first` corresponds to
+inputs with shape `(batch, channels, length)`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string, the name of the layer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The output tensor, of rank 3.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/max_pooling2d.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/max_pooling2d.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..abb947e0802
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/max_pooling2d.md
@@ -0,0 +1,131 @@
+description: Max pooling layer for 2D inputs (e.g. images). (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.max_pooling2d
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Max pooling layer for 2D inputs (e.g. images). (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.max_pooling2d(
+ inputs, pool_size, strides, padding='valid', data_format='channels_last',
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use keras.layers.MaxPooling2D instead.
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+The tensor over which to pool. Must have rank 4.
+ |
+
+|
+`pool_size`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of 2 integers: (pool_height, pool_width)
+specifying the size of the pooling window.
+Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
+all spatial dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of 2 integers,
+specifying the strides of the pooling operation.
+Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
+all spatial dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+A string. The padding method, either 'valid' or 'same'.
+Case-insensitive.
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+A string. The ordering of the dimensions in the inputs.
+`channels_last` (default) and `channels_first` are supported.
+`channels_last` corresponds to inputs with shape
+`(batch, height, width, channels)` while `channels_first` corresponds to
+inputs with shape `(batch, channels, height, width)`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string, the name of the layer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Output tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/max_pooling3d.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/max_pooling3d.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..04784f01380
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/max_pooling3d.md
@@ -0,0 +1,131 @@
+description: Max pooling layer for 3D inputs (e.g. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.max_pooling3d
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Max pooling layer for 3D inputs (e.g. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.max_pooling3d(
+ inputs, pool_size, strides, padding='valid', data_format='channels_last',
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use keras.layers.MaxPooling3D instead.
+
+volumes).
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+The tensor over which to pool. Must have rank 5.
+ |
+
+|
+`pool_size`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of 3 integers: (pool_depth, pool_height,
+pool_width) specifying the size of the pooling window. Can be a single
+integer to specify the same value for all spatial dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of 3 integers, specifying the strides of
+the pooling operation. Can be a single integer to specify the same value
+for all spatial dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+A string. The padding method, either 'valid' or 'same'.
+Case-insensitive.
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+A string. The ordering of the dimensions in the inputs.
+`channels_last` (default) and `channels_first` are supported.
+`channels_last` corresponds to inputs with shape `(batch, depth, height,
+width, channels)` while `channels_first` corresponds to inputs with shape
+`(batch, channels, depth, height, width)`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string, the name of the layer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Output tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/separable_conv1d.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/separable_conv1d.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e8e9deb69bd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/separable_conv1d.md
@@ -0,0 +1,277 @@
+description: Functional interface for the depthwise separable 1D convolution layer. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.separable_conv1d
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Functional interface for the depthwise separable 1D convolution layer. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.separable_conv1d(
+ inputs, filters, kernel_size, strides=1, padding='valid',
+ data_format='channels_last', dilation_rate=1, depth_multiplier=1,
+ activation=None, use_bias=(True), depthwise_initializer=None,
+ pointwise_initializer=None, bias_initializer=tf.zeros_initializer(),
+ depthwise_regularizer=None, pointwise_regularizer=None, bias_regularizer=None,
+ activity_regularizer=None, depthwise_constraint=None, pointwise_constraint=None,
+ bias_constraint=None, trainable=(True), name=None, reuse=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use tf.keras.layers.SeparableConv1D instead.
+
+This layer performs a depthwise convolution that acts separately on
+channels, followed by a pointwise convolution that mixes channels.
+If `use_bias` is True and a bias initializer is provided,
+it adds a bias vector to the output.
+It then optionally applies an activation function to produce the final output.
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+Input tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`filters`
+ |
+
+Integer, the dimensionality of the output space (i.e. the number
+of filters in the convolution).
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_size`
+ |
+
+A single integer specifying the spatial
+dimensions of the filters.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+A single integer specifying the strides
+of the convolution.
+Specifying any `stride` value != 1 is incompatible with specifying
+any `dilation_rate` value != 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+One of `"valid"` or `"same"` (case-insensitive).
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+A string, one of `channels_last` (default) or `channels_first`.
+The ordering of the dimensions in the inputs.
+`channels_last` corresponds to inputs with shape
+`(batch, length, channels)` while `channels_first` corresponds to
+inputs with shape `(batch, channels, length)`.
+ |
+
+|
+`dilation_rate`
+ |
+
+A single integer, specifying
+the dilation rate to use for dilated convolution.
+Currently, specifying any `dilation_rate` value != 1 is
+incompatible with specifying any stride value != 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`depth_multiplier`
+ |
+
+The number of depthwise convolution output channels for
+each input channel. The total number of depthwise convolution output
+channels will be equal to `num_filters_in * depth_multiplier`.
+ |
+
+|
+`activation`
+ |
+
+Activation function. Set it to None to maintain a
+linear activation.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_bias`
+ |
+
+Boolean, whether the layer uses a bias.
+ |
+
+|
+`depthwise_initializer`
+ |
+
+An initializer for the depthwise convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`pointwise_initializer`
+ |
+
+An initializer for the pointwise convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_initializer`
+ |
+
+An initializer for the bias vector. If None, the default
+initializer will be used.
+ |
+
+|
+`depthwise_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the depthwise
+convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`pointwise_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the pointwise
+convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`activity_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer function for the output.
+ |
+
+|
+`depthwise_constraint`
+ |
+
+Optional projection function to be applied to the
+depthwise kernel after being updated by an `Optimizer` (e.g. used for
+norm constraints or value constraints for layer weights). The function
+must take as input the unprojected variable and must return the
+projected variable (which must have the same shape). Constraints are
+not safe to use when doing asynchronous distributed training.
+ |
+
+|
+`pointwise_constraint`
+ |
+
+Optional projection function to be applied to the
+pointwise kernel after being updated by an `Optimizer`.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_constraint`
+ |
+
+Optional projection function to be applied to the
+bias after being updated by an `Optimizer`.
+ |
+
+|
+`trainable`
+ |
+
+Boolean, if `True` also add variables to the graph collection
+`GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES` (see tf.Variable).
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string, the name of the layer.
+ |
+
+|
+`reuse`
+ |
+
+Boolean, whether to reuse the weights of a previous layer
+by the same name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Output tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/separable_conv2d.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/separable_conv2d.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..0eea9872dc1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/layers/separable_conv2d.md
@@ -0,0 +1,281 @@
+description: Functional interface for the depthwise separable 2D convolution layer. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.layers.separable_conv2d
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Functional interface for the depthwise separable 2D convolution layer. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.layers.separable_conv2d(
+ inputs, filters, kernel_size, strides=(1, 1), padding='valid',
+ data_format='channels_last', dilation_rate=(1, 1), depth_multiplier=1,
+ activation=None, use_bias=(True), depthwise_initializer=None,
+ pointwise_initializer=None, bias_initializer=tf.zeros_initializer(),
+ depthwise_regularizer=None, pointwise_regularizer=None, bias_regularizer=None,
+ activity_regularizer=None, depthwise_constraint=None, pointwise_constraint=None,
+ bias_constraint=None, trainable=(True), name=None, reuse=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use tf.keras.layers.SeparableConv2D instead.
+
+This layer performs a depthwise convolution that acts separately on
+channels, followed by a pointwise convolution that mixes channels.
+If `use_bias` is True and a bias initializer is provided,
+it adds a bias vector to the output.
+It then optionally applies an activation function to produce the final output.
+
+
+
+
+Arguments |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+Input tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`filters`
+ |
+
+Integer, the dimensionality of the output space (i.e. the number
+of filters in the convolution).
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_size`
+ |
+
+A tuple or list of 2 integers specifying the spatial
+dimensions of the filters. Can be a single integer to specify the same
+value for all spatial dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+A tuple or list of 2 positive integers specifying the strides
+of the convolution. Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
+all spatial dimensions.
+Specifying any `stride` value != 1 is incompatible with specifying
+any `dilation_rate` value != 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+One of `"valid"` or `"same"` (case-insensitive).
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+A string, one of `channels_last` (default) or `channels_first`.
+The ordering of the dimensions in the inputs.
+`channels_last` corresponds to inputs with shape
+`(batch, height, width, channels)` while `channels_first` corresponds to
+inputs with shape `(batch, channels, height, width)`.
+ |
+
+|
+`dilation_rate`
+ |
+
+An integer or tuple/list of 2 integers, specifying
+the dilation rate to use for dilated convolution.
+Can be a single integer to specify the same value for
+all spatial dimensions.
+Currently, specifying any `dilation_rate` value != 1 is
+incompatible with specifying any stride value != 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`depth_multiplier`
+ |
+
+The number of depthwise convolution output channels for
+each input channel. The total number of depthwise convolution output
+channels will be equal to `num_filters_in * depth_multiplier`.
+ |
+
+|
+`activation`
+ |
+
+Activation function. Set it to None to maintain a
+linear activation.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_bias`
+ |
+
+Boolean, whether the layer uses a bias.
+ |
+
+|
+`depthwise_initializer`
+ |
+
+An initializer for the depthwise convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`pointwise_initializer`
+ |
+
+An initializer for the pointwise convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_initializer`
+ |
+
+An initializer for the bias vector. If None, the default
+initializer will be used.
+ |
+
+|
+`depthwise_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the depthwise
+convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`pointwise_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the pointwise
+convolution kernel.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer for the bias vector.
+ |
+
+|
+`activity_regularizer`
+ |
+
+Optional regularizer function for the output.
+ |
+
+|
+`depthwise_constraint`
+ |
+
+Optional projection function to be applied to the
+depthwise kernel after being updated by an `Optimizer` (e.g. used for
+norm constraints or value constraints for layer weights). The function
+must take as input the unprojected variable and must return the
+projected variable (which must have the same shape). Constraints are
+not safe to use when doing asynchronous distributed training.
+ |
+
+|
+`pointwise_constraint`
+ |
+
+Optional projection function to be applied to the
+pointwise kernel after being updated by an `Optimizer`.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_constraint`
+ |
+
+Optional projection function to be applied to the
+bias after being updated by an `Optimizer`.
+ |
+
+|
+`trainable`
+ |
+
+Boolean, if `True` also add variables to the graph collection
+`GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES` (see tf.Variable).
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string, the name of the layer.
+ |
+
+|
+`reuse`
+ |
+
+Boolean, whether to reuse the weights of a previous layer
+by the same name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Output tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/linalg.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/linalg.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..8f375ca5d3e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/linalg.md
@@ -0,0 +1,159 @@
+description: Operations for linear algebra.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.linalg
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Operations for linear algebra.
+
+
+
+## Modules
+
+[`experimental`](../../../tf/compat/v1/linalg/experimental.md) module: Public API for tf.linalg.experimental namespace.
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class LinearOperator`](../../../tf/linalg/LinearOperator.md): Base class defining a [batch of] linear operator[s].
+
+[`class LinearOperatorAdjoint`](../../../tf/linalg/LinearOperatorAdjoint.md): `LinearOperator` representing the adjoint of another operator.
+
+[`class LinearOperatorBlockDiag`](../../../tf/linalg/LinearOperatorBlockDiag.md): Combines one or more `LinearOperators` in to a Block Diagonal matrix.
+
+[`class LinearOperatorBlockLowerTriangular`](../../../tf/linalg/LinearOperatorBlockLowerTriangular.md): Combines `LinearOperators` into a blockwise lower-triangular matrix.
+
+[`class LinearOperatorCirculant`](../../../tf/linalg/LinearOperatorCirculant.md): `LinearOperator` acting like a circulant matrix.
+
+[`class LinearOperatorCirculant2D`](../../../tf/linalg/LinearOperatorCirculant2D.md): `LinearOperator` acting like a block circulant matrix.
+
+[`class LinearOperatorCirculant3D`](../../../tf/linalg/LinearOperatorCirculant3D.md): `LinearOperator` acting like a nested block circulant matrix.
+
+[`class LinearOperatorComposition`](../../../tf/linalg/LinearOperatorComposition.md): Composes one or more `LinearOperators`.
+
+[`class LinearOperatorDiag`](../../../tf/linalg/LinearOperatorDiag.md): `LinearOperator` acting like a [batch] square diagonal matrix.
+
+[`class LinearOperatorFullMatrix`](../../../tf/linalg/LinearOperatorFullMatrix.md): `LinearOperator` that wraps a [batch] matrix.
+
+[`class LinearOperatorHouseholder`](../../../tf/linalg/LinearOperatorHouseholder.md): `LinearOperator` acting like a [batch] of Householder transformations.
+
+[`class LinearOperatorIdentity`](../../../tf/linalg/LinearOperatorIdentity.md): `LinearOperator` acting like a [batch] square identity matrix.
+
+[`class LinearOperatorInversion`](../../../tf/linalg/LinearOperatorInversion.md): `LinearOperator` representing the inverse of another operator.
+
+[`class LinearOperatorKronecker`](../../../tf/linalg/LinearOperatorKronecker.md): Kronecker product between two `LinearOperators`.
+
+[`class LinearOperatorLowRankUpdate`](../../../tf/linalg/LinearOperatorLowRankUpdate.md): Perturb a `LinearOperator` with a rank `K` update.
+
+[`class LinearOperatorLowerTriangular`](../../../tf/linalg/LinearOperatorLowerTriangular.md): `LinearOperator` acting like a [batch] square lower triangular matrix.
+
+[`class LinearOperatorPermutation`](../../../tf/linalg/LinearOperatorPermutation.md): `LinearOperator` acting like a [batch] of permutation matrices.
+
+[`class LinearOperatorScaledIdentity`](../../../tf/linalg/LinearOperatorScaledIdentity.md): `LinearOperator` acting like a scaled [batch] identity matrix `A = c I`.
+
+[`class LinearOperatorToeplitz`](../../../tf/linalg/LinearOperatorToeplitz.md): `LinearOperator` acting like a [batch] of toeplitz matrices.
+
+[`class LinearOperatorTridiag`](../../../tf/linalg/LinearOperatorTridiag.md): `LinearOperator` acting like a [batch] square tridiagonal matrix.
+
+[`class LinearOperatorZeros`](../../../tf/linalg/LinearOperatorZeros.md): `LinearOperator` acting like a [batch] zero matrix.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`adjoint(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/adjoint.md): Transposes the last two dimensions of and conjugates tensor `matrix`.
+
+[`band_part(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/band_part.md): Copy a tensor setting everything outside a central band in each innermost matrix
+
+[`cholesky(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/cholesky.md): Computes the Cholesky decomposition of one or more square matrices.
+
+[`cholesky_solve(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/cholesky_solve.md): Solves systems of linear eqns `A X = RHS`, given Cholesky factorizations.
+
+[`cross(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/cross.md): Compute the pairwise cross product.
+
+[`det(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/det.md): Computes the determinant of one or more square matrices.
+
+[`diag(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/diag.md): Returns a batched diagonal tensor with given batched diagonal values.
+
+[`diag_part(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/diag_part.md): Returns the batched diagonal part of a batched tensor.
+
+[`eigh(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/eigh.md): Computes the eigen decomposition of a batch of self-adjoint matrices.
+
+[`eigvalsh(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/eigvalsh.md): Computes the eigenvalues of one or more self-adjoint matrices.
+
+[`einsum(...)`](../../../tf/einsum.md): Tensor contraction over specified indices and outer product.
+
+[`expm(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/expm.md): Computes the matrix exponential of one or more square matrices.
+
+[`eye(...)`](../../../tf/eye.md): Construct an identity matrix, or a batch of matrices.
+
+[`global_norm(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/global_norm.md): Computes the global norm of multiple tensors.
+
+[`inv(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/inv.md): Computes the inverse of one or more square invertible matrices or their
+
+[`l2_normalize(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/linalg/l2_normalize.md): Normalizes along dimension `axis` using an L2 norm. (deprecated arguments)
+
+[`logdet(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/logdet.md): Computes log of the determinant of a hermitian positive definite matrix.
+
+[`logm(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/logm.md): Computes the matrix logarithm of one or more square matrices:
+
+[`lstsq(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/lstsq.md): Solves one or more linear least-squares problems.
+
+[`lu(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/lu.md): Computes the LU decomposition of one or more square matrices.
+
+[`lu_matrix_inverse(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/lu_matrix_inverse.md): Computes the inverse given the LU decomposition(s) of one or more matrices.
+
+[`lu_reconstruct(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/lu_reconstruct.md): The reconstruct one or more matrices from their LU decomposition(s).
+
+[`lu_solve(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/lu_solve.md): Solves systems of linear eqns `A X = RHS`, given LU factorizations.
+
+[`matmul(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/matmul.md): Multiplies matrix `a` by matrix `b`, producing `a` * `b`.
+
+[`matrix_rank(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/matrix_rank.md): Compute the matrix rank of one or more matrices.
+
+[`matrix_transpose(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/matrix_transpose.md): Transposes last two dimensions of tensor `a`.
+
+[`matvec(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/matvec.md): Multiplies matrix `a` by vector `b`, producing `a` * `b`.
+
+[`norm(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/norm.md): Computes the norm of vectors, matrices, and tensors. (deprecated arguments)
+
+[`normalize(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/normalize.md): Normalizes `tensor` along dimension `axis` using specified norm.
+
+[`pinv(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/pinv.md): Compute the Moore-Penrose pseudo-inverse of one or more matrices.
+
+[`qr(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/qr.md): Computes the QR decompositions of one or more matrices.
+
+[`set_diag(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/set_diag.md): Returns a batched matrix tensor with new batched diagonal values.
+
+[`slogdet(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/slogdet.md): Computes the sign and the log of the absolute value of the determinant of
+
+[`solve(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/solve.md): Solves systems of linear equations.
+
+[`sqrtm(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/sqrtm.md): Computes the matrix square root of one or more square matrices:
+
+[`svd(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/svd.md): Computes the singular value decompositions of one or more matrices.
+
+[`tensor_diag(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/tensor_diag.md): Returns a diagonal tensor with a given diagonal values.
+
+[`tensor_diag_part(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/tensor_diag_part.md): Returns the diagonal part of the tensor.
+
+[`tensordot(...)`](../../../tf/tensordot.md): Tensor contraction of a and b along specified axes and outer product.
+
+[`trace(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/trace.md): Compute the trace of a tensor `x`.
+
+[`transpose(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/matrix_transpose.md): Transposes last two dimensions of tensor `a`.
+
+[`triangular_solve(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/triangular_solve.md): Solve systems of linear equations with upper or lower triangular matrices.
+
+[`tridiagonal_matmul(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/tridiagonal_matmul.md): Multiplies tridiagonal matrix by matrix.
+
+[`tridiagonal_solve(...)`](../../../tf/linalg/tridiagonal_solve.md): Solves tridiagonal systems of equations.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/linalg/experimental.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/linalg/experimental.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..089ee032914
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/linalg/experimental.md
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+description: Public API for tf.linalg.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.linalg.experimental
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.linalg.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`conjugate_gradient(...)`](../../../../tf/linalg/experimental/conjugate_gradient.md): Conjugate gradient solver.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/linalg/l2_normalize.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/linalg/l2_normalize.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e07bfe7979a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/linalg/l2_normalize.md
@@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
+description: Normalizes along dimension axis using an L2 norm. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.linalg.l2_normalize
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Normalizes along dimension `axis` using an L2 norm. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.math.l2_normalize`, `tf.compat.v1.nn.l2_normalize`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.linalg.l2_normalize(
+ x, axis=None, epsilon=1e-12, name=None, dim=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: SOME ARGUMENTS ARE DEPRECATED: `(dim)`. They will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+dim is deprecated, use axis instead
+
+For a 1-D tensor with `axis = 0`, computes
+
+ output = x / sqrt(max(sum(x**2), epsilon))
+
+For `x` with more dimensions, independently normalizes each 1-D slice along
+dimension `axis`.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`x`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`axis`
+ |
+
+Dimension along which to normalize. A scalar or a vector of
+integers.
+ |
+
+|
+`epsilon`
+ |
+
+A lower bound value for the norm. Will use `sqrt(epsilon)` as the
+divisor if `norm < sqrt(epsilon)`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for this operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`dim`
+ |
+
+Deprecated alias for axis.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` with the same shape as `x`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..56f5b6944f7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite.md
@@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
+description: Public API for tf.lite namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.lite
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.lite namespace.
+
+
+
+## Modules
+
+[`constants`](../../../tf/compat/v1/lite/constants.md) module: Public API for tf.lite.constants namespace.
+
+[`experimental`](../../../tf/compat/v1/lite/experimental.md) module: Public API for tf.lite.experimental namespace.
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class Interpreter`](../../../tf/lite/Interpreter.md): Interpreter interface for TensorFlow Lite Models.
+
+[`class OpHint`](../../../tf/compat/v1/lite/OpHint.md): A class that helps build tflite function invocations.
+
+[`class OpsSet`](../../../tf/lite/OpsSet.md): Enum class defining the sets of ops available to generate TFLite models.
+
+[`class Optimize`](../../../tf/lite/Optimize.md): Enum defining the optimizations to apply when generating tflite graphs.
+
+[`class RepresentativeDataset`](../../../tf/lite/RepresentativeDataset.md): Representative dataset to evaluate optimizations.
+
+[`class TFLiteConverter`](../../../tf/compat/v1/lite/TFLiteConverter.md): Convert a TensorFlow model into `output_format`.
+
+[`class TargetSpec`](../../../tf/lite/TargetSpec.md): Specification of target device.
+
+[`class TocoConverter`](../../../tf/compat/v1/lite/TocoConverter.md): Convert a TensorFlow model into `output_format` using TOCO.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`toco_convert(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/lite/toco_convert.md): Convert a model using TOCO. (deprecated)
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/OpHint.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/OpHint.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..888b8dab108
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/OpHint.md
@@ -0,0 +1,355 @@
+description: A class that helps build tflite function invocations.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.lite.OpHint
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A class that helps build tflite function invocations.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.lite.OpHint(
+ function_name, level=1, children_inputs_mappings=None, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+It allows you to take a bunch of TensorFlow ops and annotate the construction
+such that toco knows how to convert it to tflite. This embeds a pseudo
+function in a TensorFlow graph. This allows embedding high-level API usage
+information in a lower level TensorFlow implementation so that an alternative
+implementation can be substituted later.
+
+Essentially, any "input" into this pseudo op is fed into an identity, and
+attributes are added to that input before being used by the constituent ops
+that make up the pseudo op. A similar process is done to any output that
+is to be exported from the current op.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`function_name`
+ |
+
+Name of the function (the custom op name in tflite)
+ |
+
+|
+`level`
+ |
+
+OpHint level.
+ |
+
+|
+`children_inputs_mappings`
+ |
+
+Children OpHint inputs/outputs mapping.
+children_inputs_mappings should like below:
+"parent_first_child_input":
+[{"parent_input_index": num, "child_input_index": num}, ...]
+"parent_last_child_output":
+[{"parent_output_index": num, "child_output_index": num}, ...]
+"internal_children_input_output":
+[{"child_input_index": num, "child_output_index": num}, ...]
+ |
+
+|
+`**kwargs`
+ |
+
+Keyword arguments of any constant attributes for the function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Child Classes
+[`class OpHintArgumentTracker`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/lite/OpHint/OpHintArgumentTracker.md)
+
+## Methods
+
+
+
+View source
+
+
+add_input(
+ *args, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+Add a wrapped input argument to the hint.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`*args`
+ |
+
+The input tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`**kwargs`
+ |
+
+"name" label
+"tag" a tag to group multiple arguments that will be aggregated. I.e.
+a string like 'cool_input'. Basically multiple inputs can be added
+to the same hint for parallel operations that will eventually be
+combined. An example would be static_rnn which creates multiple copies
+of state or inputs.
+"aggregate" aggregation strategy that is valid only for tag non None.
+Acceptable values are OpHint.AGGREGATE_FIRST, OpHint.AGGREGATE_LAST,
+and OpHint.AGGREGATE_STACK.
+"index_override" The global index to use. This corresponds to the
+argument order in the final stub that will be generated.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The wrapped input tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+View source
+
+
+add_inputs(
+ *args, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+Add a sequence of inputs to the function invocation.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`*args`
+ |
+
+List of inputs to be converted (should be Tf.Tensor).
+ |
+
+|
+`**kwargs`
+ |
+
+This allows 'names' which should be a list of names.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Wrapped inputs (identity standins that have additional metadata). These
+are also are also tf.Tensor's.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+add_output
+
+View source
+
+
+add_output(
+ *args, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+Add a wrapped output argument to the hint.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`*args`
+ |
+
+The output tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`**kwargs`
+ |
+
+"name" label
+"tag" a tag to group multiple arguments that will be aggregated. I.e.
+a string like 'cool_input'. Basically multiple inputs can be added
+to the same hint for parallel operations that will eventually be
+combined. An example would be static_rnn which creates multiple copies
+of state or inputs.
+"aggregate" aggregation strategy that is valid only for tag non None.
+Acceptable values are OpHint.AGGREGATE_FIRST, OpHint.AGGREGATE_LAST,
+and OpHint.AGGREGATE_STACK.
+"index_override" The global index to use. This corresponds to the
+argument order in the final stub that will be generated.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The wrapped output tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+add_outputs
+
+View source
+
+
+add_outputs(
+ *args, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+Add a sequence of outputs to the function invocation.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`*args`
+ |
+
+List of outputs to be converted (should be tf.Tensor).
+ |
+
+|
+`**kwargs`
+ |
+
+See
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Wrapped outputs (identity standins that have additional metadata). These
+are also tf.Tensor's.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `AGGREGATE_FIRST = 'first'`
+* `AGGREGATE_LAST = 'last'`
+* `AGGREGATE_STACK = 'stack'`
+* `CHILDREN_INPUTS_MAPPINGS = '_tflite_children_ophint_inputs_mapping'`
+* `FUNCTION_AGGREGATE_ATTR = '_tflite_function_aggregate'`
+* `FUNCTION_INPUT_INDEX_ATTR = '_tflite_function_input_index'`
+* `FUNCTION_LEVEL_ATTR = '_tflite_ophint_level'`
+* `FUNCTION_NAME_ATTR = '_tflite_function_name'`
+* `FUNCTION_OUTPUT_INDEX_ATTR = '_tflite_function_output_index'`
+* `FUNCTION_SORT_INDEX_ATTR = '_tflite_function_sort_index'`
+* `FUNCTION_UUID_ATTR = '_tflite_function_uuid'`
+* `TFLITE_INPUT_INDICES = '_tflite_input_indices'`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/OpHint/OpHintArgumentTracker.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/OpHint/OpHintArgumentTracker.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..cb796780093
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/OpHint/OpHintArgumentTracker.md
@@ -0,0 +1,192 @@
+description: Conceptually tracks indices of arguments of "OpHint functions".
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.lite.OpHint.OpHintArgumentTracker
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Conceptually tracks indices of arguments of "OpHint functions".
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.lite.OpHint.OpHintArgumentTracker(
+ function_name, unique_function_id, node_name_prefix, attr_name, level=1,
+ children_inputs_mappings=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The inputs and arguments of these functions both use an instance
+of the class so they can have independent numbering.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`function_name`
+ |
+
+Name of the function that this tracks arguments for.
+ |
+
+|
+`unique_function_id`
+ |
+
+UUID of function that this tracks arguments for.
+ |
+
+|
+`node_name_prefix`
+ |
+
+How identities that are created are named.
+ |
+
+|
+`attr_name`
+ |
+
+Name of attribute to use to store the index for this hint.
+i.e. FUNCTION_INPUT_INDEX or FUNCTION_OUTPUT_INDEX
+ |
+
+|
+`level`
+ |
+
+Hierarchical level of the Ophint node, a number.
+ |
+
+|
+`children_inputs_mappings`
+ |
+
+Inputs/Outputs mapping for children hints.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+add
+
+View source
+
+
+add(
+ arg, tag=None, name=None, aggregate=None, index_override=None
+)
+
+
+Return a wrapped tensor of an input tensor as an argument.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`arg`
+ |
+
+A TensorFlow tensor that should be considered an argument.
+ |
+
+|
+`tag`
+ |
+
+String tag to identify arguments that should be packed.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of argument. This is included in the Identity hint op names.
+ |
+
+|
+`aggregate`
+ |
+
+Strategy to aggregate.
+Acceptable values are OpHint.AGGREGATE_FIRST, OpHint.AGGREGATE_LAST,
+and OpHint.AGGREGATE_STACK.
+Note, aggregate is only valid if tag is specified.
+ |
+
+|
+`index_override`
+ |
+
+Specify what input/output index should this be in the
+final stub. i.e. add(arg0, index=1); add(arg1, index=0) will make the
+final stub be as stub_func(inputs[arg1, arg0], outputs=[]) rather than
+the default call order based ordering.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A tensor representing the wrapped argument.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+When indices are not consistent.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/TFLiteConverter.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/TFLiteConverter.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..f858cb2dae3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/TFLiteConverter.md
@@ -0,0 +1,744 @@
+description: Convert a TensorFlow model into output_format.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.lite.TFLiteConverter
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Convert a TensorFlow model into `output_format`.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.lite.TFLiteConverter(
+ graph_def, input_tensors, output_tensors, input_arrays_with_shape=None,
+ output_arrays=None, experimental_debug_info_func=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This is used to convert from a TensorFlow GraphDef, SavedModel or tf.keras
+model into either a TFLite FlatBuffer or graph visualization.
+
+#### Example usage:
+
+
+```python
+# Converting a GraphDef from session.
+converter = lite.TFLiteConverter.from_session(sess, in_tensors, out_tensors)
+tflite_model = converter.convert()
+open("converted_model.tflite", "wb").write(tflite_model)
+
+# Converting a GraphDef from file.
+converter = lite.TFLiteConverter.from_frozen_graph(
+ graph_def_file, input_arrays, output_arrays)
+tflite_model = converter.convert()
+open("converted_model.tflite", "wb").write(tflite_model)
+
+# Converting a SavedModel.
+converter = lite.TFLiteConverter.from_saved_model(saved_model_dir)
+tflite_model = converter.convert()
+open("converted_model.tflite", "wb").write(tflite_model)
+
+# Converting a tf.keras model.
+converter = lite.TFLiteConverter.from_keras_model_file(keras_model)
+tflite_model = converter.convert()
+open("converted_model.tflite", "wb").write(tflite_model)
+```
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph_def`
+ |
+
+Frozen TensorFlow GraphDef.
+ |
+
+|
+`input_tensors`
+ |
+
+List of input tensors. Type and shape are computed using
+`foo.shape` and `foo.dtype`.
+ |
+
+|
+`output_tensors`
+ |
+
+List of output tensors (only .name is used from this).
+ |
+
+|
+`input_arrays_with_shape`
+ |
+
+Tuple of strings representing input tensor names
+and list of integers representing input shapes
+(e.g., [("foo" : [1, 16, 16, 3])]). Use only when graph cannot be loaded
+into TensorFlow and when `input_tensors` and `output_tensors` are
+None. (default None)
+ |
+
+|
+`output_arrays`
+ |
+
+List of output tensors to freeze graph with. Use only when
+graph cannot be loaded into TensorFlow and when `input_tensors` and
+`output_tensors` are None. (default None)
+ |
+
+|
+`experimental_debug_info_func`
+ |
+
+An experimental function to retrieve the
+graph debug info for a set of nodes from the `graph_def`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+Invalid arguments.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`inference_type`
+ |
+
+Target data type of real-number arrays in the output file.
+Must be `{tf.float32, tf.uint8}`. If `optimzations` are provided, this
+parameter is ignored. (default tf.float32)
+ |
+
+|
+`inference_input_type`
+ |
+
+Target data type of real-number input arrays. Allows
+for a different type for input arrays.
+If an integer type is provided and `optimizations` are not used,
+`quantized_inputs_stats` must be provided.
+If `inference_type` is tf.uint8, signaling conversion to a fully quantized
+model from a quantization-aware trained input model, then
+`inference_input_type` defaults to tf.uint8.
+In all other cases, `inference_input_type` defaults to tf.float32.
+Must be `{tf.float32, tf.uint8, tf.int8}`
+ |
+
+|
+`inference_output_type`
+ |
+
+Target data type of real-number output arrays. Allows
+for a different type for output arrays.
+If `inference_type` is tf.uint8, signaling conversion to a fully quantized
+model from a quantization-aware trained output model, then
+`inference_output_type` defaults to tf.uint8.
+In all other cases, `inference_output_type` must be tf.float32, an error
+will be thrown otherwise.
+Must be `{tf.float32, tf.uint8, tf.int8}`
+ |
+
+|
+`output_format`
+ |
+
+Output file format. Currently must be `{TFLITE,
+GRAPHVIZ_DOT}`. (default TFLITE)
+ |
+
+|
+`quantized_input_stats`
+ |
+
+Dict of strings representing input tensor names
+mapped to tuple of floats representing the mean and standard deviation
+of the training data (e.g., {"foo" : (0., 1.)}). Only need if
+`inference_input_type` is `QUANTIZED_UINT8`.
+real_input_value = (quantized_input_value - mean_value) / std_dev_value.
+(default {})
+ |
+
+|
+`default_ranges_stats`
+ |
+
+Tuple of integers representing (min, max) range values
+for all arrays without a specified range. Intended for experimenting with
+quantization via "dummy quantization". (default None)
+ |
+
+|
+`drop_control_dependency`
+ |
+
+Boolean indicating whether to drop control
+dependencies silently. This is due to TFLite not supporting control
+dependencies. (default True)
+ |
+
+|
+`reorder_across_fake_quant`
+ |
+
+Boolean indicating whether to reorder FakeQuant
+nodes in unexpected locations. Used when the location of the FakeQuant
+nodes is preventing graph transformations necessary to convert the graph.
+Results in a graph that differs from the quantized training graph,
+potentially causing differing arithmetic behavior. (default False)
+ |
+
+|
+`change_concat_input_ranges`
+ |
+
+Boolean to change behavior of min/max ranges for
+inputs and outputs of the concat operator for quantized models. Changes
+the ranges of concat operator overlap when true. (default False)
+ |
+
+|
+`allow_custom_ops`
+ |
+
+Boolean indicating whether to allow custom operations.
+When false any unknown operation is an error. When true, custom ops are
+created for any op that is unknown. The developer will need to provide
+these to the TensorFlow Lite runtime with a custom resolver.
+(default False)
+ |
+
+|
+`post_training_quantize`
+ |
+
+Deprecated. Please specify `[Optimize.DEFAULT]` for
+`optimizations` instead. Boolean indicating whether to quantize the
+weights of the converted float model. Model size will be reduced and
+there will be latency improvements (at the cost of accuracy).
+(default False)
+ |
+
+|
+`dump_graphviz_dir`
+ |
+
+Full filepath of folder to dump the graphs at various
+stages of processing GraphViz .dot files. Preferred over
+--output_format=GRAPHVIZ_DOT in order to keep the requirements of the
+output file. (default None)
+ |
+
+|
+`dump_graphviz_video`
+ |
+
+Boolean indicating whether to dump the graph after
+every graph transformation. (default False)
+ |
+
+|
+`conversion_summary_dir`
+ |
+
+A string indicating the path to the generated
+conversion logs.
+ |
+
+|
+`target_ops`
+ |
+
+Deprecated. Please specify `target_spec.supported_ops` instead.
+Set of OpsSet options indicating which converter to use.
+(default set([OpsSet.TFLITE_BUILTINS]))
+ |
+
+|
+`target_spec`
+ |
+
+Experimental flag, subject to change. Specification of target
+device.
+ |
+
+|
+`optimizations`
+ |
+
+Experimental flag, subject to change. A list of optimizations
+to apply when converting the model. E.g. `[Optimize.DEFAULT]`
+ |
+
+|
+`representative_dataset`
+ |
+
+A representative dataset that can be used to
+generate input and output samples for the model. The converter can use
+the dataset to evaluate different optimizations.
+ |
+
+|
+`experimental_new_converter`
+ |
+
+Experimental flag, subject to change.
+Enables MLIR-based conversion instead of TOCO conversion.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+convert
+
+View source
+
+
+convert()
+
+
+Converts a TensorFlow GraphDef based on instance variables.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The converted data in serialized format. Either a TFLite Flatbuffer or a
+Graphviz graph depending on value in `output_format`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+Input shape is not specified.
+None value for dimension in input_tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+from_frozen_graph
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+from_frozen_graph(
+ graph_def_file, input_arrays, output_arrays, input_shapes=None
+)
+
+
+Creates a TFLiteConverter class from a file containing a frozen GraphDef.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph_def_file`
+ |
+
+Full filepath of file containing frozen GraphDef.
+ |
+
+|
+`input_arrays`
+ |
+
+List of input tensors to freeze graph with.
+ |
+
+|
+`output_arrays`
+ |
+
+List of output tensors to freeze graph with.
+ |
+
+|
+`input_shapes`
+ |
+
+Dict of strings representing input tensor names to list of
+integers representing input shapes (e.g., {"foo" : [1, 16, 16, 3]}).
+Automatically determined when input shapes is None (e.g., {"foo" :
+None}). (default None)
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+TFLiteConverter class.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`IOError`
+ |
+
+File not found.
+Unable to parse input file.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+The graph is not frozen.
+input_arrays or output_arrays contains an invalid tensor name.
+input_shapes is not correctly defined when required
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+from_keras_model_file
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+from_keras_model_file(
+ model_file, input_arrays=None, input_shapes=None, output_arrays=None,
+ custom_objects=None
+)
+
+
+Creates a TFLiteConverter class from a tf.keras model file.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`model_file`
+ |
+
+Full filepath of HDF5 file containing the tf.keras model.
+ |
+
+|
+`input_arrays`
+ |
+
+List of input tensors to freeze graph with. Uses input
+arrays from SignatureDef when none are provided. (default None)
+ |
+
+|
+`input_shapes`
+ |
+
+Dict of strings representing input tensor names to list of
+integers representing input shapes (e.g., {"foo" : [1, 16, 16, 3]}).
+Automatically determined when input shapes is None (e.g., {"foo" :
+None}). (default None)
+ |
+
+|
+`output_arrays`
+ |
+
+List of output tensors to freeze graph with. Uses output
+arrays from SignatureDef when none are provided. (default None)
+ |
+
+|
+`custom_objects`
+ |
+
+Dict mapping names (strings) to custom classes or
+functions to be considered during model deserialization. (default None)
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+TFLiteConverter class.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+from_saved_model
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+from_saved_model(
+ saved_model_dir, input_arrays=None, input_shapes=None, output_arrays=None,
+ tag_set=None, signature_key=None
+)
+
+
+Creates a TFLiteConverter class from a SavedModel.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`saved_model_dir`
+ |
+
+SavedModel directory to convert.
+ |
+
+|
+`input_arrays`
+ |
+
+List of input tensors to freeze graph with. Uses input
+arrays from SignatureDef when none are provided. (default None)
+ |
+
+|
+`input_shapes`
+ |
+
+Dict of strings representing input tensor names to list of
+integers representing input shapes (e.g., {"foo" : [1, 16, 16, 3]}).
+Automatically determined when input shapes is None (e.g., {"foo" :
+None}). (default None)
+ |
+
+|
+`output_arrays`
+ |
+
+List of output tensors to freeze graph with. Uses output
+arrays from SignatureDef when none are provided. (default None)
+ |
+
+|
+`tag_set`
+ |
+
+Set of tags identifying the MetaGraphDef within the SavedModel to
+analyze. All tags in the tag set must be present. (default set("serve"))
+ |
+
+|
+`signature_key`
+ |
+
+Key identifying SignatureDef containing inputs and outputs.
+(default DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY)
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+TFLiteConverter class.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+from_session
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+from_session(
+ sess, input_tensors, output_tensors
+)
+
+
+Creates a TFLiteConverter class from a TensorFlow Session.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sess`
+ |
+
+TensorFlow Session.
+ |
+
+|
+`input_tensors`
+ |
+
+List of input tensors. Type and shape are computed using
+`foo.shape` and `foo.dtype`.
+ |
+
+|
+`output_tensors`
+ |
+
+List of output tensors (only .name is used from this).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+TFLiteConverter class.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+View source
+
+
+get_input_arrays()
+
+
+Returns a list of the names of the input tensors.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+List of strings.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/TocoConverter.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/TocoConverter.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..06cc35a3a62
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/TocoConverter.md
@@ -0,0 +1,105 @@
+description: Convert a TensorFlow model into output_format using TOCO.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.lite.TocoConverter
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Convert a TensorFlow model into `output_format` using TOCO.
+
+
+
+This class has been deprecated. Please use `lite.TFLiteConverter` instead.
+
+## Methods
+
+from_frozen_graph
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+from_frozen_graph(
+ graph_def_file, input_arrays, output_arrays, input_shapes=None
+)
+
+
+Creates a TocoConverter class from a file containing a frozen graph. (deprecated)
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use `lite.TFLiteConverter.from_frozen_graph` instead.
+
+from_keras_model_file
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+from_keras_model_file(
+ model_file, input_arrays=None, input_shapes=None, output_arrays=None
+)
+
+
+Creates a TocoConverter class from a tf.keras model file. (deprecated)
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use `lite.TFLiteConverter.from_keras_model_file` instead.
+
+from_saved_model
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+from_saved_model(
+ saved_model_dir, input_arrays=None, input_shapes=None, output_arrays=None,
+ tag_set=None, signature_key=None
+)
+
+
+Creates a TocoConverter class from a SavedModel. (deprecated)
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use `lite.TFLiteConverter.from_saved_model` instead.
+
+from_session
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+from_session(
+ sess, input_tensors, output_tensors
+)
+
+
+Creates a TocoConverter class from a TensorFlow Session. (deprecated)
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use `lite.TFLiteConverter.from_session` instead.
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/constants.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/constants.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..19c2a89219e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/constants.md
@@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
+description: Public API for tf.lite.constants namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.lite.constants
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.lite.constants namespace.
+
+
+
+## Other Members
+
+* `FLOAT`
+* `FLOAT16`
+* `GRAPHVIZ_DOT = 3`
+* `INT32`
+* `INT64`
+* `INT8`
+* `QUANTIZED_UINT8`
+* `STRING`
+* `TFLITE = 2`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/experimental.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/experimental.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..c8526ebce60
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/experimental.md
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+description: Public API for tf.lite.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.lite.experimental
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.lite.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+## Modules
+
+[`nn`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/lite/experimental/nn.md) module: Public API for tf.lite.experimental.nn namespace.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`convert_op_hints_to_stubs(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/lite/experimental/convert_op_hints_to_stubs.md): Converts a graphdef with LiteOp hints into stub operations.
+
+[`get_potentially_supported_ops(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/lite/experimental/get_potentially_supported_ops.md): Returns operations potentially supported by TensorFlow Lite.
+
+[`load_delegate(...)`](../../../../tf/lite/experimental/load_delegate.md): Returns loaded Delegate object.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/experimental/convert_op_hints_to_stubs.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/experimental/convert_op_hints_to_stubs.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..feb54e518fd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/experimental/convert_op_hints_to_stubs.md
@@ -0,0 +1,99 @@
+description: Converts a graphdef with LiteOp hints into stub operations.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.lite.experimental.convert_op_hints_to_stubs
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Converts a graphdef with LiteOp hints into stub operations.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.lite.experimental.convert_op_hints_to_stubs(
+ session=None, graph_def=None, write_callback=(lambda graph_def, comments: None)
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This is used to prepare for toco conversion of complex intrinsic usages.
+Note: only one of session or graph_def should be used, not both.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`session`
+ |
+
+A TensorFlow session that contains the graph to convert.
+ |
+
+|
+`graph_def`
+ |
+
+A graph def that we should convert.
+ |
+
+|
+`write_callback`
+ |
+
+A function pointer that can be used to write intermediate
+steps of graph transformation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A new graphdef with all ops contained in OpHints being replaced by
+a single op call with the right parameters.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If both session and graph_def are provided.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/experimental/get_potentially_supported_ops.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/experimental/get_potentially_supported_ops.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..b03304b8d3f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/experimental/get_potentially_supported_ops.md
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
+description: Returns operations potentially supported by TensorFlow Lite.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.lite.experimental.get_potentially_supported_ops
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns operations potentially supported by TensorFlow Lite.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.lite.experimental.get_potentially_supported_ops()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The potentially support list contains a list of ops that are partially or
+fully supported, which is derived by simply scanning op names to check whether
+they can be handled without real conversion and specific parameters.
+
+Given that some ops may be partially supported, the optimal way to determine
+if a model's operations are supported is by converting using the TensorFlow
+Lite converter.
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of SupportedOp.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/experimental/nn.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/experimental/nn.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..d184676f03c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/experimental/nn.md
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+description: Public API for tf.lite.experimental.nn namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.lite.experimental.nn
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.lite.experimental.nn namespace.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class TFLiteLSTMCell`](../../../../../tf/compat/v1/lite/experimental/nn/TFLiteLSTMCell.md): Long short-term memory unit (LSTM) recurrent network cell.
+
+[`class TfLiteRNNCell`](../../../../../tf/compat/v1/lite/experimental/nn/TfLiteRNNCell.md): The most basic RNN cell.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`dynamic_rnn(...)`](../../../../../tf/compat/v1/lite/experimental/nn/dynamic_rnn.md): Creates a recurrent neural network specified by RNNCell `cell`.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/experimental/nn/TFLiteLSTMCell.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/experimental/nn/TFLiteLSTMCell.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..9098f786826
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/experimental/nn/TFLiteLSTMCell.md
@@ -0,0 +1,313 @@
+description: Long short-term memory unit (LSTM) recurrent network cell.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.lite.experimental.nn.TFLiteLSTMCell
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Long short-term memory unit (LSTM) recurrent network cell.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.lite.experimental.nn.TFLiteLSTMCell(
+ num_units, use_peepholes=(False), cell_clip=None, initializer=None,
+ num_proj=None, proj_clip=None, num_unit_shards=None, num_proj_shards=None,
+ forget_bias=1.0, state_is_tuple=(True), activation=None, reuse=None, name=None,
+ dtype=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This is used only for TfLite, it provides hints and it also makes the
+variables in the desired for the tflite ops (transposed and seaparated).
+
+The default non-peephole implementation is based on:
+
+ https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/1154/0131eae85b2e11d53df7f1360eeb6476e7f4.pdf
+
+Felix Gers, Jurgen Schmidhuber, and Fred Cummins.
+"Learning to forget: Continual prediction with LSTM." IET, 850-855, 1999.
+
+The peephole implementation is based on:
+
+ https://research.google.com/pubs/archive/43905.pdf
+
+Hasim Sak, Andrew Senior, and Francoise Beaufays.
+"Long short-term memory recurrent neural network architectures for
+ large scale acoustic modeling." INTERSPEECH, 2014.
+
+The class uses optional peep-hole connections, optional cell clipping, and
+an optional projection layer.
+
+Note that this cell is not optimized for performance. Please use
+`tf.contrib.cudnn_rnn.CudnnLSTM` for better performance on GPU, or
+`tf.contrib.rnn.LSTMBlockCell` and `tf.contrib.rnn.LSTMBlockFusedCell` for
+better performance on CPU.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`num_units`
+ |
+
+int, The number of units in the LSTM cell.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_peepholes`
+ |
+
+bool, set True to enable diagonal/peephole connections.
+ |
+
+|
+`cell_clip`
+ |
+
+(optional) A float value, if provided the cell state is clipped
+by this value prior to the cell output activation.
+ |
+
+|
+`initializer`
+ |
+
+(optional) The initializer to use for the weight and
+projection matrices.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_proj`
+ |
+
+(optional) int, The output dimensionality for the projection
+matrices. If None, no projection is performed.
+ |
+
+|
+`proj_clip`
+ |
+
+(optional) A float value. If `num_proj > 0` and `proj_clip` is
+provided, then the projected values are clipped elementwise to within
+`[-proj_clip, proj_clip]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_unit_shards`
+ |
+
+Deprecated, will be removed by Jan. 2017. Use a
+variable_scope partitioner instead.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_proj_shards`
+ |
+
+Deprecated, will be removed by Jan. 2017. Use a
+variable_scope partitioner instead.
+ |
+
+|
+`forget_bias`
+ |
+
+Biases of the forget gate are initialized by default to 1 in
+order to reduce the scale of forgetting at the beginning of the
+training. Must set it manually to `0.0` when restoring from CudnnLSTM
+trained checkpoints.
+ |
+
+|
+`state_is_tuple`
+ |
+
+If True, accepted and returned states are 2-tuples of the
+`c_state` and `m_state`. If False, they are concatenated along the
+column axis. This latter behavior will soon be deprecated.
+ |
+
+|
+`activation`
+ |
+
+Activation function of the inner states. Default: `tanh`.
+ |
+
+|
+`reuse`
+ |
+
+(optional) Python boolean describing whether to reuse variables in
+an existing scope. If not `True`, and the existing scope already has
+the given variables, an error is raised.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+String, the name of the layer. Layers with the same name will share
+weights, but to avoid mistakes we require reuse=True in such cases.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+Default dtype of the layer (default of `None` means use the type of
+the first input). Required when `build` is called before `call`. When
+restoring from CudnnLSTM-trained checkpoints, use
+`CudnnCompatibleLSTMCell` instead.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+DEPRECATED FUNCTION
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Stop using this property because tf.layers layers no longer track their graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`output_size`
+ |
+
+Integer or TensorShape: size of outputs produced by this cell.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope_name`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`state_size`
+ |
+
+size(s) of state(s) used by this cell.
+
+It can be represented by an Integer, a TensorShape or a tuple of Integers
+or TensorShapes.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+get_initial_state
+
+View source
+
+
+get_initial_state(
+ inputs=None, batch_size=None, dtype=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+zero_state
+
+View source
+
+
+zero_state(
+ batch_size, dtype
+)
+
+
+Return zero-filled state tensor(s).
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`batch_size`
+ |
+
+int, float, or unit Tensor representing the batch size.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+the data type to use for the state.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+If `state_size` is an int or TensorShape, then the return value is a
+`N-D` tensor of shape `[batch_size, state_size]` filled with zeros.
+
+If `state_size` is a nested list or tuple, then the return value is
+a nested list or tuple (of the same structure) of `2-D` tensors with
+the shapes `[batch_size, s]` for each s in `state_size`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/experimental/nn/TfLiteRNNCell.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/experimental/nn/TfLiteRNNCell.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..6014002632e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/experimental/nn/TfLiteRNNCell.md
@@ -0,0 +1,236 @@
+description: The most basic RNN cell.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.lite.experimental.nn.TfLiteRNNCell
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The most basic RNN cell.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.lite.experimental.nn.TfLiteRNNCell(
+ num_units, activation=None, reuse=None, name=None, dtype=None, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This is used only for TfLite, it provides hints and it also makes the
+variables in the desired for the tflite ops.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`num_units`
+ |
+
+int, The number of units in the RNN cell.
+ |
+
+|
+`activation`
+ |
+
+Nonlinearity to use. Default: `tanh`. It could also be string
+that is within Keras activation function names.
+ |
+
+|
+`reuse`
+ |
+
+(optional) Python boolean describing whether to reuse variables in
+an existing scope. Raises an error if not `True` and the existing scope
+already has the given variables.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+String, the name of the layer. Layers with the same name will share
+weights, but to avoid mistakes we require reuse=True in such cases.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+Default dtype of the layer (default of `None` means use the type of
+the first input). Required when `build` is called before `call`.
+ |
+
+|
+`**kwargs`
+ |
+
+Dict, keyword named properties for common layer attributes, like
+`trainable` etc when constructing the cell from configs of get_config().
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the existing scope already has the given variables.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+DEPRECATED FUNCTION
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Stop using this property because tf.layers layers no longer track their graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`output_size`
+ |
+
+Integer or TensorShape: size of outputs produced by this cell.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope_name`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`state_size`
+ |
+
+size(s) of state(s) used by this cell.
+
+It can be represented by an Integer, a TensorShape or a tuple of Integers
+or TensorShapes.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+get_initial_state
+
+View source
+
+
+get_initial_state(
+ inputs=None, batch_size=None, dtype=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+zero_state
+
+View source
+
+
+zero_state(
+ batch_size, dtype
+)
+
+
+Return zero-filled state tensor(s).
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`batch_size`
+ |
+
+int, float, or unit Tensor representing the batch size.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+the data type to use for the state.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+If `state_size` is an int or TensorShape, then the return value is a
+`N-D` tensor of shape `[batch_size, state_size]` filled with zeros.
+
+If `state_size` is a nested list or tuple, then the return value is
+a nested list or tuple (of the same structure) of `2-D` tensors with
+the shapes `[batch_size, s]` for each s in `state_size`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/experimental/nn/dynamic_rnn.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/experimental/nn/dynamic_rnn.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a330190e4a0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/experimental/nn/dynamic_rnn.md
@@ -0,0 +1,250 @@
+description: Creates a recurrent neural network specified by RNNCell cell.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.lite.experimental.nn.dynamic_rnn
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Creates a recurrent neural network specified by RNNCell `cell`.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.lite.experimental.nn.dynamic_rnn(
+ cell, inputs, sequence_length=None, initial_state=None, dtype=None,
+ parallel_iterations=None, swap_memory=(False), time_major=(True), scope=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Performs fully dynamic unrolling of `inputs`.
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+# create a BasicRNNCell
+rnn_cell = tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.BasicRNNCell(hidden_size)
+
+# 'outputs' is a tensor of shape [batch_size, max_time, cell_state_size]
+
+# defining initial state
+initial_state = rnn_cell.zero_state(batch_size, dtype=tf.float32)
+
+# 'state' is a tensor of shape [batch_size, cell_state_size]
+outputs, state = tf.compat.v1.nn.dynamic_rnn(rnn_cell, input_data,
+ initial_state=initial_state,
+ dtype=tf.float32)
+```
+
+```python
+# create 2 LSTMCells
+rnn_layers = [tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.LSTMCell(size) for size in [128, 256]]
+
+# create a RNN cell composed sequentially of a number of RNNCells
+multi_rnn_cell = tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.MultiRNNCell(rnn_layers)
+
+# 'outputs' is a tensor of shape [batch_size, max_time, 256]
+# 'state' is a N-tuple where N is the number of LSTMCells containing a
+# tf.nn.rnn_cell.LSTMStateTuple for each cell
+outputs, state = tf.compat.v1.nn.dynamic_rnn(cell=multi_rnn_cell,
+ inputs=data,
+ dtype=tf.float32)
+```
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cell`
+ |
+
+An instance of RNNCell.
+ |
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+The RNN inputs.
+If `time_major == False` (default), this must be a `Tensor` of shape:
+`[batch_size, max_time, ...]`, or a nested tuple of such elements.
+If `time_major == True`, this must be a `Tensor` of shape: `[max_time,
+batch_size, ...]`, or a nested tuple of such elements. This may also be
+a (possibly nested) tuple of Tensors satisfying this property. The
+first two dimensions must match across all the inputs, but otherwise the
+ranks and other shape components may differ. In this case, input to
+`cell` at each time-step will replicate the structure of these tuples,
+except for the time dimension (from which the time is taken). The input
+to `cell` at each time step will be a `Tensor` or (possibly nested)
+tuple of Tensors each with dimensions `[batch_size, ...]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`sequence_length`
+ |
+
+(optional) An int32/int64 vector sized `[batch_size]`. Used
+to copy-through state and zero-out outputs when past a batch element's
+sequence length. So it's more for performance than correctness.
+ |
+
+|
+`initial_state`
+ |
+
+(optional) An initial state for the RNN. If `cell.state_size`
+is an integer, this must be a `Tensor` of appropriate type and shape
+`[batch_size, cell.state_size]`. If `cell.state_size` is a tuple, this
+should be a tuple of tensors having shapes `[batch_size, s] for s in
+cell.state_size`.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+(optional) The data type for the initial state and expected output.
+Required if initial_state is not provided or RNN state has a heterogeneous
+dtype.
+ |
+
+|
+`parallel_iterations`
+ |
+
+(Default: 32). The number of iterations to run in
+parallel. Those operations which do not have any temporal dependency and
+can be run in parallel, will be. This parameter trades off time for
+space. Values >> 1 use more memory but take less time, while smaller
+values use less memory but computations take longer.
+ |
+
+|
+`swap_memory`
+ |
+
+Transparently swap the tensors produced in forward inference
+but needed for back prop from GPU to CPU. This allows training RNNs which
+would typically not fit on a single GPU, with very minimal (or no)
+performance penalty.
+ |
+
+|
+`time_major`
+ |
+
+The shape format of the `inputs` and `outputs` Tensors. If true,
+these `Tensors` must be shaped `[max_time, batch_size, depth]`. If false,
+these `Tensors` must be shaped `[batch_size, max_time, depth]`. Using
+`time_major = True` is a bit more efficient because it avoids transposes
+at the beginning and end of the RNN calculation. However, most TensorFlow
+data is batch-major, so by default this function accepts input and emits
+output in batch-major form.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope`
+ |
+
+VariableScope for the created subgraph; defaults to "rnn".
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A pair (outputs, state) where:
+ |
+
+
+|
+`outputs`
+ |
+
+The RNN output `Tensor`.
+
+If time_major == False (default), this will be a `Tensor` shaped:
+`[batch_size, max_time, cell.output_size]`.
+
+If time_major == True, this will be a `Tensor` shaped:
+`[max_time, batch_size, cell.output_size]`.
+
+Note, if `cell.output_size` is a (possibly nested) tuple of integers
+or `TensorShape` objects, then `outputs` will be a tuple having the
+same structure as `cell.output_size`, containing Tensors having shapes
+corresponding to the shape data in `cell.output_size`.
+ |
+
+|
+`state`
+ |
+
+The final state. If `cell.state_size` is an int, this
+will be shaped `[batch_size, cell.state_size]`. If it is a
+`TensorShape`, this will be shaped `[batch_size] + cell.state_size`.
+If it is a (possibly nested) tuple of ints or `TensorShape`, this will
+be a tuple having the corresponding shapes. If cells are `LSTMCells`
+`state` will be a tuple containing a `LSTMStateTuple` for each cell.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `cell` is not an instance of RNNCell.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If inputs is None or an empty list.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If not using control flow v2.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/toco_convert.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/toco_convert.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..4e7c0635b51
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lite/toco_convert.md
@@ -0,0 +1,116 @@
+description: Convert a model using TOCO. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.lite.toco_convert
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Convert a model using TOCO. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.lite.toco_convert(
+ input_data, input_tensors, output_tensors, *args, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use `lite.TFLiteConverter` instead.
+
+Typically this function is used to convert from TensorFlow GraphDef to TFLite.
+Conversion can be customized by providing arguments that are forwarded to
+`build_toco_convert_protos` (see documentation for details). This function has
+been deprecated. Please use `lite.TFLiteConverter` instead.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_data`
+ |
+
+Input data (i.e. often `sess.graph_def`),
+ |
+
+|
+`input_tensors`
+ |
+
+List of input tensors. Type and shape are computed using
+`foo.shape` and `foo.dtype`.
+ |
+
+|
+`output_tensors`
+ |
+
+List of output tensors (only .name is used from this).
+ |
+
+|
+`*args`
+ |
+
+See `build_toco_convert_protos`,
+ |
+
+|
+`**kwargs`
+ |
+
+See `build_toco_convert_protos`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The converted data. For example if TFLite was the destination, then
+this will be a tflite flatbuffer in a bytes array.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+|
+Defined in `build_toco_convert_protos`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/load_file_system_library.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/load_file_system_library.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e8bfbf8529b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/load_file_system_library.md
@@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
+description: Loads a TensorFlow plugin, containing file system implementation. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.load_file_system_library
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Loads a TensorFlow plugin, containing file system implementation. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.load_file_system_library(
+ library_filename
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use tf.load_library instead.
+
+Pass `library_filename` to a platform-specific mechanism for dynamically
+loading a library. The rules for determining the exact location of the
+library are platform-specific and are not documented here.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`library_filename`
+ |
+
+Path to the plugin.
+Relative or absolute filesystem path to a dynamic library file.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+None.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+when unable to load the library.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/local_variables.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/local_variables.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..7f6a66887cb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/local_variables.md
@@ -0,0 +1,78 @@
+description: Returns local variables.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.local_variables
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns local variables.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.local_variables(
+ scope=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Local variables - per process variables, usually not saved/restored to
+checkpoint and used for temporary or intermediate values.
+For example, they can be used as counters for metrics computation or
+number of epochs this machine has read data.
+The `tf.contrib.framework.local_variable()` function automatically adds the
+new variable to `GraphKeys.LOCAL_VARIABLES`.
+This convenience function returns the contents of that collection.
+
+An alternative to local variables are global variables. See
+tf.compat.v1.global_variables
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`scope`
+ |
+
+(Optional.) A string. If supplied, the resulting list is filtered to
+include only items whose `name` attribute matches `scope` using
+`re.match`. Items without a `name` attribute are never returned if a scope
+is supplied. The choice of `re.match` means that a `scope` without special
+tokens filters by prefix.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of local `Variable` objects.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/local_variables_initializer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/local_variables_initializer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..11a3c34be61
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/local_variables_initializer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
+description: Returns an Op that initializes all local variables.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.local_variables_initializer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns an Op that initializes all local variables.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.initializers.local_variables`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.local_variables_initializer()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This is just a shortcut for `variables_initializer(local_variables())`
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Op that initializes all local variables in the graph.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..83ad40da954
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging.md
@@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
+description: Logging and Summary Operations.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.logging
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Logging and Summary Operations.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`TaskLevelStatusMessage(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/logging/TaskLevelStatusMessage.md)
+
+[`debug(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/logging/debug.md)
+
+[`error(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/logging/error.md)
+
+[`fatal(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/logging/fatal.md)
+
+[`flush(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/logging/flush.md)
+
+[`get_verbosity(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/logging/get_verbosity.md): Return how much logging output will be produced.
+
+[`info(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/logging/info.md)
+
+[`log(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/logging/log.md)
+
+[`log_every_n(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/logging/log_every_n.md): Log 'msg % args' at level 'level' once per 'n' times.
+
+[`log_first_n(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/logging/log_first_n.md): Log 'msg % args' at level 'level' only first 'n' times.
+
+[`log_if(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/logging/log_if.md): Log 'msg % args' at level 'level' only if condition is fulfilled.
+
+[`set_verbosity(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/logging/set_verbosity.md): Sets the threshold for what messages will be logged.
+
+[`vlog(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/logging/vlog.md)
+
+[`warn(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/logging/warn.md)
+
+[`warning(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/logging/warning.md)
+
+## Other Members
+
+* `DEBUG = 10`
+* `ERROR = 40`
+* `FATAL = 50`
+* `INFO = 20`
+* `WARN = 30`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/TaskLevelStatusMessage.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/TaskLevelStatusMessage.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..f5f4af4d8e2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/TaskLevelStatusMessage.md
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.logging.TaskLevelStatusMessage
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.logging.TaskLevelStatusMessage(
+ msg
+)
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/debug.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/debug.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..96be7bd470e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/debug.md
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.logging.debug
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.logging.debug(
+ msg, *args, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/error.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/error.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..ef27371c5aa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/error.md
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.logging.error
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.logging.error(
+ msg, *args, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/fatal.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/fatal.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..0aec19d73a6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/fatal.md
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.logging.fatal
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.logging.fatal(
+ msg, *args, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/flush.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/flush.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..285d08fa970
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/flush.md
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.logging.flush
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.logging.flush()
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/get_verbosity.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/get_verbosity.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..f8c6adaafc2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/get_verbosity.md
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+description: Return how much logging output will be produced.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.logging.get_verbosity
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Return how much logging output will be produced.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.logging.get_verbosity()
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/info.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/info.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..31daefc8a11
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/info.md
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.logging.info
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.logging.info(
+ msg, *args, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/log.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/log.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..c1efeb986aa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/log.md
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.logging.log
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.logging.log(
+ level, msg, *args, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/log_every_n.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/log_every_n.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..8df93d12d6b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/log_every_n.md
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
+description: Log 'msg % args' at level 'level' once per 'n' times.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.logging.log_every_n
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Log 'msg % args' at level 'level' once per 'n' times.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.logging.log_every_n(
+ level, msg, n, *args
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Logs the 1st call, (N+1)st call, (2N+1)st call, etc.
+Not threadsafe.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`level`
+ |
+
+The level at which to log.
+ |
+
+|
+`msg`
+ |
+
+The message to be logged.
+ |
+
+|
+`n`
+ |
+
+The number of times this should be called before it is logged.
+ |
+
+|
+`*args`
+ |
+
+The args to be substituted into the msg.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/log_first_n.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/log_first_n.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3bc3316ab43
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/log_first_n.md
@@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
+description: Log 'msg % args' at level 'level' only first 'n' times.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.logging.log_first_n
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Log 'msg % args' at level 'level' only first 'n' times.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.logging.log_first_n(
+ level, msg, n, *args
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Not threadsafe.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`level`
+ |
+
+The level at which to log.
+ |
+
+|
+`msg`
+ |
+
+The message to be logged.
+ |
+
+|
+`n`
+ |
+
+The number of times this should be called before it is logged.
+ |
+
+|
+`*args`
+ |
+
+The args to be substituted into the msg.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/log_if.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/log_if.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..ff76ab8711d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/log_if.md
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+description: Log 'msg % args' at level 'level' only if condition is fulfilled.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.logging.log_if
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Log 'msg % args' at level 'level' only if condition is fulfilled.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.logging.log_if(
+ level, msg, condition, *args
+)
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/set_verbosity.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/set_verbosity.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..5d59c69f462
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/set_verbosity.md
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+description: Sets the threshold for what messages will be logged.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.logging.set_verbosity
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Sets the threshold for what messages will be logged.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.logging.set_verbosity(
+ v
+)
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/vlog.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/vlog.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..7e1d936b3e2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/vlog.md
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.logging.vlog
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.logging.vlog(
+ level, msg, *args, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/warn.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/warn.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..655f097fc17
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/warn.md
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.logging.warn
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.logging.warn(
+ msg, *args, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/warning.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/warning.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..b0a3ce39356
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/logging/warning.md
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.logging.warning
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.logging.warning(
+ msg, *args, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lookup.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lookup.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..8983ab72545
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lookup.md
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
+description: Public API for tf.lookup namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.lookup
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.lookup namespace.
+
+
+
+## Modules
+
+[`experimental`](../../../tf/compat/v1/lookup/experimental.md) module: Public API for tf.lookup.experimental namespace.
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class KeyValueTensorInitializer`](../../../tf/lookup/KeyValueTensorInitializer.md): Table initializers given `keys` and `values` tensors.
+
+[`class StaticHashTable`](../../../tf/compat/v1/lookup/StaticHashTable.md): A generic hash table that is immutable once initialized.
+
+[`class StaticVocabularyTable`](../../../tf/compat/v1/lookup/StaticVocabularyTable.md): String to Id table wrapper that assigns out-of-vocabulary keys to buckets.
+
+[`class TextFileIndex`](../../../tf/lookup/TextFileIndex.md): The key and value content to get from each line.
+
+[`class TextFileInitializer`](../../../tf/lookup/TextFileInitializer.md): Table initializers from a text file.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lookup/StaticHashTable.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lookup/StaticHashTable.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..7fb6b6a5e5a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lookup/StaticHashTable.md
@@ -0,0 +1,318 @@
+description: A generic hash table that is immutable once initialized.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.lookup.StaticHashTable
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A generic hash table that is immutable once initialized.
+
+Inherits From: [`StaticHashTable`](../../../../tf/lookup/StaticHashTable.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.lookup.StaticHashTable(
+ initializer, default_value, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+When running in graph mode, you must evaluate the tensor returned by
+`tf.tables_initializer()` before evaluating the tensor returned by
+this class's `lookup()` method. Example usage in graph mode:
+
+```python
+keys_tensor = tf.constant([1, 2])
+vals_tensor = tf.constant([3, 4])
+input_tensor = tf.constant([1, 5])
+table = tf.lookup.StaticHashTable(
+ tf.lookup.KeyValueTensorInitializer(keys_tensor, vals_tensor), -1)
+out = table.lookup(input_tensor)
+with tf.Session() as sess:
+ sess.run(tf.tables_initializer())
+ print(sess.run(out))
+```
+
+In eager mode, no special code is needed to initialize the table.
+Example usage in eager mode:
+
+```python
+tf.enable_eager_execution()
+keys_tensor = tf.constant([1, 2])
+vals_tensor = tf.constant([3, 4])
+input_tensor = tf.constant([1, 5])
+table = tf.lookup.StaticHashTable(
+ tf.lookup.KeyValueTensorInitializer(keys_tensor, vals_tensor), -1)
+print(table.lookup(input_tensor))
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`initializer`
+ |
+
+The table initializer to use. See `HashTable` kernel for
+supported key and value types.
+ |
+
+|
+`default_value`
+ |
+
+The value to use if a key is missing in the table.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`default_value`
+ |
+
+The default value of the table.
+ |
+
+|
+`initializer`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`key_dtype`
+ |
+
+The table key dtype.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+The name of the table.
+ |
+
+|
+`resource_handle`
+ |
+
+Returns the resource handle associated with this Resource.
+ |
+
+|
+`value_dtype`
+ |
+
+The table value dtype.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+export
+
+View source
+
+
+export(
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+Returns tensors of all keys and values in the table.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A pair of tensors with the first tensor containing all keys and the
+second tensors containing all values in the table.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+lookup
+
+View source
+
+
+lookup(
+ keys, name=None
+)
+
+
+Looks up `keys` in a table, outputs the corresponding values.
+
+The `default_value` is used for keys not present in the table.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`keys`
+ |
+
+Keys to look up. May be either a `SparseTensor` or dense `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `SparseTensor` if keys are sparse, otherwise a dense `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+when `keys` or `default_value` doesn't match the table data
+types.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+size
+
+View source
+
+
+size(
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+Compute the number of elements in this table.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A scalar tensor containing the number of elements in this table.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lookup/StaticVocabularyTable.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lookup/StaticVocabularyTable.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..c16aa1f6a61
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lookup/StaticVocabularyTable.md
@@ -0,0 +1,283 @@
+description: String to Id table wrapper that assigns out-of-vocabulary keys to buckets.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.lookup.StaticVocabularyTable
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+String to Id table wrapper that assigns out-of-vocabulary keys to buckets.
+
+Inherits From: [`StaticVocabularyTable`](../../../../tf/lookup/StaticVocabularyTable.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.lookup.StaticVocabularyTable(
+ initializer, num_oov_buckets, lookup_key_dtype=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+For example, if an instance of `StaticVocabularyTable` is initialized with a
+string-to-id initializer that maps:
+
+* `emerson -> 0`
+* `lake -> 1`
+* `palmer -> 2`
+
+The `Vocabulary` object will performs the following mapping:
+
+* `emerson -> 0`
+* `lake -> 1`
+* `palmer -> 2`
+* ` -> bucket_id`, where bucket_id will be between `3` and
+`3 + num_oov_buckets - 1`, calculated by:
+`hash() % num_oov_buckets + vocab_size`
+
+If input_tensor is `["emerson", "lake", "palmer", "king", "crimson"]`,
+the lookup result is `[0, 1, 2, 4, 7]`.
+
+If `initializer` is None, only out-of-vocabulary buckets are used.
+
+#### Example usage:
+
+
+
+```python
+num_oov_buckets = 3
+input_tensor = tf.constant(["emerson", "lake", "palmer", "king", "crimnson"])
+table = tf.lookup.StaticVocabularyTable(
+ tf.lookup.TextFileInitializer(
+ filename,
+ key_dtype=tf.string, key_index=tf.lookup.TextFileIndex.WHOLE_LINE,
+ value_dtype=tf.int64, value_index=tf.lookup.TextFileIndex.LINE_NUMBER,
+ delimiter="\t"),
+ num_oov_buckets)
+out = table.lookup(input_tensor).
+table.init.run()
+print(out.eval())
+```
+
+The hash function used for generating out-of-vocabulary buckets ID is
+Fingerprint64.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`initializer`
+ |
+
+A TableInitializerBase object that contains the data used to
+initialize the table. If None, then we only use out-of-vocab buckets.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_oov_buckets`
+ |
+
+Number of buckets to use for out-of-vocabulary keys. Must
+be greater than zero.
+ |
+
+|
+`lookup_key_dtype`
+ |
+
+Data type of keys passed to `lookup`. Defaults to
+`initializer.key_dtype` if `initializer` is specified, otherwise
+tf.string. Must be string or integer, and must be castable to
+`initializer.key_dtype`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+when `num_oov_buckets` is not positive.
+ |
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+when lookup_key_dtype or initializer.key_dtype are not
+integer or string. Also when initializer.value_dtype != int64.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`initializer`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`key_dtype`
+ |
+
+The table key dtype.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+The name of the table.
+ |
+
+|
+`resource_handle`
+ |
+
+Returns the resource handle associated with this Resource.
+ |
+
+|
+`value_dtype`
+ |
+
+The table value dtype.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+lookup
+
+View source
+
+
+lookup(
+ keys, name=None
+)
+
+
+Looks up `keys` in the table, outputs the corresponding values.
+
+It assigns out-of-vocabulary keys to buckets based in their hashes.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`keys`
+ |
+
+Keys to look up. May be either a `SparseTensor` or dense `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the op.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `SparseTensor` if keys are sparse, otherwise a dense `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+when `keys` doesn't match the table key data type.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+size
+
+View source
+
+
+size(
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+Compute the number of elements in this table.
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lookup/experimental.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lookup/experimental.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..99edb6c2be1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/lookup/experimental.md
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+description: Public API for tf.lookup.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.lookup.experimental
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.lookup.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class DenseHashTable`](../../../../tf/lookup/experimental/DenseHashTable.md): A generic mutable hash table implementation using tensors as backing store.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..43fedded7a3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses.md
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+description: Loss operations for use in neural networks.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.losses
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Loss operations for use in neural networks.
+
+
+Note: All the losses are added to the `GraphKeys.LOSSES` collection by default.
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class Reduction`](../../../tf/compat/v1/losses/Reduction.md): Types of loss reduction.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`absolute_difference(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/losses/absolute_difference.md): Adds an Absolute Difference loss to the training procedure.
+
+[`add_loss(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/losses/add_loss.md): Adds a externally defined loss to the collection of losses.
+
+[`compute_weighted_loss(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/losses/compute_weighted_loss.md): Computes the weighted loss.
+
+[`cosine_distance(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/losses/cosine_distance.md): Adds a cosine-distance loss to the training procedure. (deprecated arguments)
+
+[`get_losses(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/losses/get_losses.md): Gets the list of losses from the loss_collection.
+
+[`get_regularization_loss(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/losses/get_regularization_loss.md): Gets the total regularization loss.
+
+[`get_regularization_losses(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/losses/get_regularization_losses.md): Gets the list of regularization losses.
+
+[`get_total_loss(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/losses/get_total_loss.md): Returns a tensor whose value represents the total loss.
+
+[`hinge_loss(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/losses/hinge_loss.md): Adds a hinge loss to the training procedure.
+
+[`huber_loss(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/losses/huber_loss.md): Adds a [Huber Loss](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Huber_loss) term to the training procedure.
+
+[`log_loss(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/losses/log_loss.md): Adds a Log Loss term to the training procedure.
+
+[`mean_pairwise_squared_error(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/losses/mean_pairwise_squared_error.md): Adds a pairwise-errors-squared loss to the training procedure.
+
+[`mean_squared_error(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/losses/mean_squared_error.md): Adds a Sum-of-Squares loss to the training procedure.
+
+[`sigmoid_cross_entropy(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/losses/sigmoid_cross_entropy.md): Creates a cross-entropy loss using tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits.
+
+[`softmax_cross_entropy(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/losses/softmax_cross_entropy.md): Creates a cross-entropy loss using tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2.
+
+[`sparse_softmax_cross_entropy(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/losses/sparse_softmax_cross_entropy.md): Cross-entropy loss using tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/Reduction.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/Reduction.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..5336d44e0d8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/Reduction.md
@@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
+description: Types of loss reduction.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.losses.Reduction
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Types of loss reduction.
+
+
+
+Contains the following values:
+
+* `NONE`: Un-reduced weighted losses with the same shape as input.
+* `SUM`: Scalar sum of weighted losses.
+* `MEAN`: Scalar `SUM` divided by sum of weights. DEPRECATED.
+* `SUM_OVER_BATCH_SIZE`: Scalar `SUM` divided by number of elements in losses.
+* `SUM_OVER_NONZERO_WEIGHTS`: Scalar `SUM` divided by number of non-zero
+ weights. DEPRECATED.
+* `SUM_BY_NONZERO_WEIGHTS`: Same as `SUM_OVER_NONZERO_WEIGHTS`. DEPRECATED.
+
+## Methods
+
+all
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+all()
+
+
+
+
+
+validate
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+validate(
+ key
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `MEAN = 'weighted_mean'`
+* `NONE = 'none'`
+* `SUM = 'weighted_sum'`
+* `SUM_BY_NONZERO_WEIGHTS = 'weighted_sum_by_nonzero_weights'`
+* `SUM_OVER_BATCH_SIZE = 'weighted_sum_over_batch_size'`
+* `SUM_OVER_NONZERO_WEIGHTS = 'weighted_sum_by_nonzero_weights'`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/absolute_difference.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/absolute_difference.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..260ad47a0be
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/absolute_difference.md
@@ -0,0 +1,136 @@
+description: Adds an Absolute Difference loss to the training procedure.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.losses.absolute_difference
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Adds an Absolute Difference loss to the training procedure.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.losses.absolute_difference(
+ labels, predictions, weights=1.0, scope=None,
+ loss_collection=tf.GraphKeys.LOSSES, reduction=Reduction.SUM_BY_NONZERO_WEIGHTS
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+`weights` acts as a coefficient for the loss. If a scalar is provided, then
+the loss is simply scaled by the given value. If `weights` is a `Tensor` of
+shape `[batch_size]`, then the total loss for each sample of the batch is
+rescaled by the corresponding element in the `weights` vector. If the shape of
+`weights` matches the shape of `predictions`, then the loss of each
+measurable element of `predictions` is scaled by the corresponding value of
+`weights`.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+The ground truth output tensor, same dimensions as 'predictions'.
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions`
+ |
+
+The predicted outputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Optional `Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or the same rank as
+`labels`, and must be broadcastable to `labels` (i.e., all dimensions must
+be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `losses` dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`scope`
+ |
+
+The scope for the operations performed in computing the loss.
+ |
+
+|
+`loss_collection`
+ |
+
+collection to which this loss will be added.
+ |
+
+|
+`reduction`
+ |
+
+Type of reduction to apply to loss.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Weighted loss float `Tensor`. If `reduction` is `NONE`, this has the same
+shape as `labels`; otherwise, it is scalar.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the shape of `predictions` doesn't match that of
+`labels` or if the shape of `weights` is invalid or if `labels`
+or `predictions` is None.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+The `loss_collection` argument is ignored when executing eagerly. Consider
+holding on to the return value or collecting losses via a tf.keras.Model.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/add_loss.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/add_loss.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e332e18254a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/add_loss.md
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
+description: Adds a externally defined loss to the collection of losses.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.losses.add_loss
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Adds a externally defined loss to the collection of losses.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.losses.add_loss(
+ loss, loss_collection=tf.GraphKeys.LOSSES
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`loss`
+ |
+
+A loss `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`loss_collection`
+ |
+
+Optional collection to add the loss to.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/compute_weighted_loss.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/compute_weighted_loss.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..49abf950161
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/compute_weighted_loss.md
@@ -0,0 +1,132 @@
+description: Computes the weighted loss.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.losses.compute_weighted_loss
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the weighted loss.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.losses.compute_weighted_loss(
+ losses, weights=1.0, scope=None, loss_collection=tf.GraphKeys.LOSSES,
+ reduction=Reduction.SUM_BY_NONZERO_WEIGHTS
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`losses`
+ |
+
+`Tensor` of shape `[batch_size, d1, ... dN]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Optional `Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or the same rank as
+`losses`, and must be broadcastable to `losses` (i.e., all dimensions must
+be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `losses` dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`scope`
+ |
+
+the scope for the operations performed in computing the loss.
+ |
+
+|
+`loss_collection`
+ |
+
+the loss will be added to these collections.
+ |
+
+|
+`reduction`
+ |
+
+Type of reduction to apply to loss.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Weighted loss `Tensor` of the same type as `losses`. If `reduction` is
+`NONE`, this has the same shape as `losses`; otherwise, it is scalar.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `weights` is `None` or the shape is not compatible with
+`losses`, or if the number of dimensions (rank) of either `losses` or
+`weights` is missing.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Note:
+
+When calculating the gradient of a weighted loss contributions from
+both `losses` and `weights` are considered. If your `weights` depend
+on some model parameters but you do not want this to affect the loss
+gradient, you need to apply tf.stop_gradient to `weights` before
+passing them to `compute_weighted_loss`.
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+The `loss_collection` argument is ignored when executing eagerly. Consider
+holding on to the return value or collecting losses via a tf.keras.Model.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/cosine_distance.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/cosine_distance.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..445b19a5f18
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/cosine_distance.md
@@ -0,0 +1,149 @@
+description: Adds a cosine-distance loss to the training procedure. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.losses.cosine_distance
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Adds a cosine-distance loss to the training procedure. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.losses.cosine_distance(
+ labels, predictions, axis=None, weights=1.0, scope=None,
+ loss_collection=tf.GraphKeys.LOSSES, reduction=Reduction.SUM_BY_NONZERO_WEIGHTS,
+ dim=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: SOME ARGUMENTS ARE DEPRECATED: `(dim)`. They will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+dim is deprecated, use axis instead
+
+Note that the function assumes that `predictions` and `labels` are already
+unit-normalized.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+`Tensor` whose shape matches 'predictions'
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions`
+ |
+
+An arbitrary matrix.
+ |
+
+|
+`axis`
+ |
+
+The dimension along which the cosine distance is computed.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Optional `Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or the same rank as
+`labels`, and must be broadcastable to `labels` (i.e., all dimensions must
+be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `losses` dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`scope`
+ |
+
+The scope for the operations performed in computing the loss.
+ |
+
+|
+`loss_collection`
+ |
+
+collection to which this loss will be added.
+ |
+
+|
+`reduction`
+ |
+
+Type of reduction to apply to loss.
+ |
+
+|
+`dim`
+ |
+
+The old (deprecated) name for `axis`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Weighted loss float `Tensor`. If `reduction` is `NONE`, this has the same
+shape as `labels`; otherwise, it is scalar.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `predictions` shape doesn't match `labels` shape, or
+`axis`, `labels`, `predictions` or `weights` is `None`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+The `loss_collection` argument is ignored when executing eagerly. Consider
+holding on to the return value or collecting losses via a tf.keras.Model.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/get_losses.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/get_losses.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..30a8d1ca386
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/get_losses.md
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
+description: Gets the list of losses from the loss_collection.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.losses.get_losses
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Gets the list of losses from the loss_collection.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.losses.get_losses(
+ scope=None, loss_collection=tf.GraphKeys.LOSSES
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`scope`
+ |
+
+An optional scope name for filtering the losses to return.
+ |
+
+|
+`loss_collection`
+ |
+
+Optional losses collection.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+a list of loss tensors.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/get_regularization_loss.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/get_regularization_loss.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..72214b4ceb1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/get_regularization_loss.md
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
+description: Gets the total regularization loss.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.losses.get_regularization_loss
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Gets the total regularization loss.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.losses.get_regularization_loss(
+ scope=None, name='total_regularization_loss'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`scope`
+ |
+
+An optional scope name for filtering the losses to return.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+The name of the returned tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A scalar regularization loss.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/get_regularization_losses.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/get_regularization_losses.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..d28900d7ffd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/get_regularization_losses.md
@@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
+description: Gets the list of regularization losses.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.losses.get_regularization_losses
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Gets the list of regularization losses.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.losses.get_regularization_losses(
+ scope=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`scope`
+ |
+
+An optional scope name for filtering the losses to return.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of regularization losses as Tensors.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/get_total_loss.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/get_total_loss.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..1f29ea1950c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/get_total_loss.md
@@ -0,0 +1,103 @@
+description: Returns a tensor whose value represents the total loss.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.losses.get_total_loss
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns a tensor whose value represents the total loss.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.losses.get_total_loss(
+ add_regularization_losses=(True), name='total_loss', scope=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+In particular, this adds any losses you have added with `tf.add_loss()` to
+any regularization losses that have been added by regularization parameters
+on layers constructors e.g. `tf.layers`. Be very sure to use this if you
+are constructing a loss_op manually. Otherwise regularization arguments
+on `tf.layers` methods will not function.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`add_regularization_losses`
+ |
+
+A boolean indicating whether or not to use the
+regularization losses in the sum.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+The name of the returned tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope`
+ |
+
+An optional scope name for filtering the losses to return. Note that
+this filters the losses added with `tf.add_loss()` as well as the
+regularization losses to that scope.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` whose value represents the total loss.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `losses` is not iterable.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/hinge_loss.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/hinge_loss.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..15e262b4d2b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/hinge_loss.md
@@ -0,0 +1,132 @@
+description: Adds a hinge loss to the training procedure.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.losses.hinge_loss
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Adds a hinge loss to the training procedure.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.losses.hinge_loss(
+ labels, logits, weights=1.0, scope=None, loss_collection=tf.GraphKeys.LOSSES,
+ reduction=Reduction.SUM_BY_NONZERO_WEIGHTS
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+The ground truth output tensor. Its shape should match the shape of
+logits. The values of the tensor are expected to be 0.0 or 1.0. Internally
+the {0,1} labels are converted to {-1,1} when calculating the hinge loss.
+ |
+
+|
+`logits`
+ |
+
+The logits, a float tensor. Note that logits are assumed to be
+unbounded and 0-centered. A value > 0 (resp. < 0) is considered a positive
+(resp. negative) binary prediction.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Optional `Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or the same rank as
+`labels`, and must be broadcastable to `labels` (i.e., all dimensions must
+be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `losses` dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`scope`
+ |
+
+The scope for the operations performed in computing the loss.
+ |
+
+|
+`loss_collection`
+ |
+
+collection to which the loss will be added.
+ |
+
+|
+`reduction`
+ |
+
+Type of reduction to apply to loss.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Weighted loss float `Tensor`. If `reduction` is `NONE`, this has the same
+shape as `labels`; otherwise, it is scalar.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the shapes of `logits` and `labels` don't match or
+if `labels` or `logits` is None.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+The `loss_collection` argument is ignored when executing eagerly. Consider
+holding on to the return value or collecting losses via a tf.keras.Model.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/huber_loss.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/huber_loss.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..0d55df00f70
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/huber_loss.md
@@ -0,0 +1,153 @@
+description: Adds a [Huber Loss](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Huber_loss) term to the training procedure.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.losses.huber_loss
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Adds a [Huber Loss](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Huber_loss) term to the training procedure.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.losses.huber_loss(
+ labels, predictions, weights=1.0, delta=1.0, scope=None,
+ loss_collection=tf.GraphKeys.LOSSES, reduction=Reduction.SUM_BY_NONZERO_WEIGHTS
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+For each value x in `error=labels-predictions`, the following is calculated:
+
+```
+ 0.5 * x^2 if |x| <= d
+ 0.5 * d^2 + d * (|x| - d) if |x| > d
+```
+
+where d is `delta`.
+
+`weights` acts as a coefficient for the loss. If a scalar is provided, then
+the loss is simply scaled by the given value. If `weights` is a tensor of size
+`[batch_size]`, then the total loss for each sample of the batch is rescaled
+by the corresponding element in the `weights` vector. If the shape of
+`weights` matches the shape of `predictions`, then the loss of each
+measurable element of `predictions` is scaled by the corresponding value of
+`weights`.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+The ground truth output tensor, same dimensions as 'predictions'.
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions`
+ |
+
+The predicted outputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Optional `Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or the same rank as
+`labels`, and must be broadcastable to `labels` (i.e., all dimensions must
+be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `losses` dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`delta`
+ |
+
+`float`, the point where the huber loss function changes from a
+quadratic to linear.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope`
+ |
+
+The scope for the operations performed in computing the loss.
+ |
+
+|
+`loss_collection`
+ |
+
+collection to which the loss will be added.
+ |
+
+|
+`reduction`
+ |
+
+Type of reduction to apply to loss.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Weighted loss float `Tensor`. If `reduction` is `NONE`, this has the same
+shape as `labels`; otherwise, it is scalar.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the shape of `predictions` doesn't match that of `labels` or
+if the shape of `weights` is invalid. Also if `labels` or
+`predictions` is None.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+The `loss_collection` argument is ignored when executing eagerly. Consider
+holding on to the return value or collecting losses via a tf.keras.Model.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/log_loss.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/log_loss.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..9e89d772a9d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/log_loss.md
@@ -0,0 +1,143 @@
+description: Adds a Log Loss term to the training procedure.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.losses.log_loss
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Adds a Log Loss term to the training procedure.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.losses.log_loss(
+ labels, predictions, weights=1.0, epsilon=1e-07, scope=None,
+ loss_collection=tf.GraphKeys.LOSSES, reduction=Reduction.SUM_BY_NONZERO_WEIGHTS
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+`weights` acts as a coefficient for the loss. If a scalar is provided, then
+the loss is simply scaled by the given value. If `weights` is a tensor of size
+`[batch_size]`, then the total loss for each sample of the batch is rescaled
+by the corresponding element in the `weights` vector. If the shape of
+`weights` matches the shape of `predictions`, then the loss of each
+measurable element of `predictions` is scaled by the corresponding value of
+`weights`.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+The ground truth output tensor, same dimensions as 'predictions'.
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions`
+ |
+
+The predicted outputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Optional `Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or the same rank as
+`labels`, and must be broadcastable to `labels` (i.e., all dimensions must
+be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `losses` dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`epsilon`
+ |
+
+A small increment to add to avoid taking a log of zero.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope`
+ |
+
+The scope for the operations performed in computing the loss.
+ |
+
+|
+`loss_collection`
+ |
+
+collection to which the loss will be added.
+ |
+
+|
+`reduction`
+ |
+
+Type of reduction to apply to loss.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Weighted loss float `Tensor`. If `reduction` is `NONE`, this has the same
+shape as `labels`; otherwise, it is scalar.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the shape of `predictions` doesn't match that of `labels` or
+if the shape of `weights` is invalid. Also if `labels` or `predictions`
+is None.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+The `loss_collection` argument is ignored when executing eagerly. Consider
+holding on to the return value or collecting losses via a tf.keras.Model.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/mean_pairwise_squared_error.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/mean_pairwise_squared_error.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..0b4c9196f1c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/mean_pairwise_squared_error.md
@@ -0,0 +1,142 @@
+description: Adds a pairwise-errors-squared loss to the training procedure.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.losses.mean_pairwise_squared_error
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Adds a pairwise-errors-squared loss to the training procedure.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.losses.mean_pairwise_squared_error(
+ labels, predictions, weights=1.0, scope=None,
+ loss_collection=tf.GraphKeys.LOSSES
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Unlike `mean_squared_error`, which is a measure of the differences between
+corresponding elements of `predictions` and `labels`,
+`mean_pairwise_squared_error` is a measure of the differences between pairs of
+corresponding elements of `predictions` and `labels`.
+
+For example, if `labels`=[a, b, c] and `predictions`=[x, y, z], there are
+three pairs of differences are summed to compute the loss:
+ loss = [ ((a-b) - (x-y)).^2 + ((a-c) - (x-z)).^2 + ((b-c) - (y-z)).^2 ] / 3
+
+Note that since the inputs are of shape `[batch_size, d0, ... dN]`, the
+corresponding pairs are computed within each batch sample but not across
+samples within a batch. For example, if `predictions` represents a batch of
+16 grayscale images of dimension [batch_size, 100, 200], then the set of pairs
+is drawn from each image, but not across images.
+
+`weights` acts as a coefficient for the loss. If a scalar is provided, then
+the loss is simply scaled by the given value. If `weights` is a tensor of size
+`[batch_size]`, then the total loss for each sample of the batch is rescaled
+by the corresponding element in the `weights` vector.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+The ground truth output tensor, whose shape must match the shape of
+`predictions`.
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions`
+ |
+
+The predicted outputs, a tensor of size
+`[batch_size, d0, .. dN]` where N+1 is the total number of dimensions in
+`predictions`.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Coefficients for the loss a scalar, a tensor of shape
+`[batch_size]` or a tensor whose shape matches `predictions`.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope`
+ |
+
+The scope for the operations performed in computing the loss.
+ |
+
+|
+`loss_collection`
+ |
+
+collection to which the loss will be added.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A scalar `Tensor` that returns the weighted loss.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the shape of `predictions` doesn't match that of `labels` or
+if the shape of `weights` is invalid. Also if `labels` or `predictions`
+is None.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+The `loss_collection` argument is ignored when executing eagerly. Consider
+holding on to the return value or collecting losses via a tf.keras.Model.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/mean_squared_error.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/mean_squared_error.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..ad95c0d1de0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/mean_squared_error.md
@@ -0,0 +1,136 @@
+description: Adds a Sum-of-Squares loss to the training procedure.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.losses.mean_squared_error
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Adds a Sum-of-Squares loss to the training procedure.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.losses.mean_squared_error(
+ labels, predictions, weights=1.0, scope=None,
+ loss_collection=tf.GraphKeys.LOSSES, reduction=Reduction.SUM_BY_NONZERO_WEIGHTS
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+`weights` acts as a coefficient for the loss. If a scalar is provided, then
+the loss is simply scaled by the given value. If `weights` is a tensor of size
+`[batch_size]`, then the total loss for each sample of the batch is rescaled
+by the corresponding element in the `weights` vector. If the shape of
+`weights` matches the shape of `predictions`, then the loss of each
+measurable element of `predictions` is scaled by the corresponding value of
+`weights`.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+The ground truth output tensor, same dimensions as 'predictions'.
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions`
+ |
+
+The predicted outputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Optional `Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or the same rank as
+`labels`, and must be broadcastable to `labels` (i.e., all dimensions must
+be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `losses` dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`scope`
+ |
+
+The scope for the operations performed in computing the loss.
+ |
+
+|
+`loss_collection`
+ |
+
+collection to which the loss will be added.
+ |
+
+|
+`reduction`
+ |
+
+Type of reduction to apply to loss.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Weighted loss float `Tensor`. If `reduction` is `NONE`, this has the same
+shape as `labels`; otherwise, it is scalar.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the shape of `predictions` doesn't match that of `labels` or
+if the shape of `weights` is invalid. Also if `labels` or `predictions`
+is None.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+The `loss_collection` argument is ignored when executing eagerly. Consider
+holding on to the return value or collecting losses via a tf.keras.Model.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/sigmoid_cross_entropy.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/sigmoid_cross_entropy.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..75f92ca69f3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/sigmoid_cross_entropy.md
@@ -0,0 +1,146 @@
+description: Creates a cross-entropy loss using tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.losses.sigmoid_cross_entropy
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Creates a cross-entropy loss using tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.losses.sigmoid_cross_entropy(
+ multi_class_labels, logits, weights=1.0, label_smoothing=0, scope=None,
+ loss_collection=tf.GraphKeys.LOSSES, reduction=Reduction.SUM_BY_NONZERO_WEIGHTS
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+`weights` acts as a coefficient for the loss. If a scalar is provided,
+then the loss is simply scaled by the given value. If `weights` is a
+tensor of shape `[batch_size]`, then the loss weights apply to each
+corresponding sample.
+
+If `label_smoothing` is nonzero, smooth the labels towards 1/2:
+
+ new_multiclass_labels = multiclass_labels * (1 - label_smoothing)
+ + 0.5 * label_smoothing
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`multi_class_labels`
+ |
+
+`[batch_size, num_classes]` target integer labels in
+`{0, 1}`.
+ |
+
+|
+`logits`
+ |
+
+Float `[batch_size, num_classes]` logits outputs of the network.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Optional `Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or the same rank as
+`labels`, and must be broadcastable to `labels` (i.e., all dimensions must
+be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `losses` dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`label_smoothing`
+ |
+
+If greater than `0` then smooth the labels.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope`
+ |
+
+The scope for the operations performed in computing the loss.
+ |
+
+|
+`loss_collection`
+ |
+
+collection to which the loss will be added.
+ |
+
+|
+`reduction`
+ |
+
+Type of reduction to apply to loss.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Weighted loss `Tensor` of the same type as `logits`. If `reduction` is
+`NONE`, this has the same shape as `logits`; otherwise, it is scalar.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the shape of `logits` doesn't match that of
+`multi_class_labels` or if the shape of `weights` is invalid, or if
+`weights` is None. Also if `multi_class_labels` or `logits` is None.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+The `loss_collection` argument is ignored when executing eagerly. Consider
+holding on to the return value or collecting losses via a tf.keras.Model.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/softmax_cross_entropy.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/softmax_cross_entropy.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..f880f195ee1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/softmax_cross_entropy.md
@@ -0,0 +1,148 @@
+description: Creates a cross-entropy loss using tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.losses.softmax_cross_entropy
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Creates a cross-entropy loss using tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.losses.softmax_cross_entropy(
+ onehot_labels, logits, weights=1.0, label_smoothing=0, scope=None,
+ loss_collection=tf.GraphKeys.LOSSES, reduction=Reduction.SUM_BY_NONZERO_WEIGHTS
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+`weights` acts as a coefficient for the loss. If a scalar is provided,
+then the loss is simply scaled by the given value. If `weights` is a
+tensor of shape `[batch_size]`, then the loss weights apply to each
+corresponding sample.
+
+If `label_smoothing` is nonzero, smooth the labels towards 1/num_classes:
+ new_onehot_labels = onehot_labels * (1 - label_smoothing)
+ + label_smoothing / num_classes
+
+Note that `onehot_labels` and `logits` must have the same shape,
+e.g. `[batch_size, num_classes]`. The shape of `weights` must be
+broadcastable to loss, whose shape is decided by the shape of `logits`.
+In case the shape of `logits` is `[batch_size, num_classes]`, loss is
+a `Tensor` of shape `[batch_size]`.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`onehot_labels`
+ |
+
+One-hot-encoded labels.
+ |
+
+|
+`logits`
+ |
+
+Logits outputs of the network.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Optional `Tensor` that is broadcastable to loss.
+ |
+
+|
+`label_smoothing`
+ |
+
+If greater than 0 then smooth the labels.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope`
+ |
+
+the scope for the operations performed in computing the loss.
+ |
+
+|
+`loss_collection`
+ |
+
+collection to which the loss will be added.
+ |
+
+|
+`reduction`
+ |
+
+Type of reduction to apply to loss.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Weighted loss `Tensor` of the same type as `logits`. If `reduction` is
+`NONE`, this has shape `[batch_size]`; otherwise, it is scalar.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the shape of `logits` doesn't match that of `onehot_labels`
+or if the shape of `weights` is invalid or if `weights` is None. Also if
+`onehot_labels` or `logits` is None.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+The `loss_collection` argument is ignored when executing eagerly. Consider
+holding on to the return value or collecting losses via a tf.keras.Model.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/sparse_softmax_cross_entropy.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/sparse_softmax_cross_entropy.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a25b24f8095
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/losses/sparse_softmax_cross_entropy.md
@@ -0,0 +1,137 @@
+description: Cross-entropy loss using tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.losses.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Cross-entropy loss using tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.losses.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy(
+ labels, logits, weights=1.0, scope=None, loss_collection=tf.GraphKeys.LOSSES,
+ reduction=Reduction.SUM_BY_NONZERO_WEIGHTS
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+`weights` acts as a coefficient for the loss. If a scalar is provided,
+then the loss is simply scaled by the given value. If `weights` is a
+tensor of shape `[batch_size]`, then the loss weights apply to each
+corresponding sample.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+`Tensor` of shape `[d_0, d_1, ..., d_{r-1}]` (where `r` is rank of
+`labels` and result) and dtype `int32` or `int64`. Each entry in `labels`
+must be an index in `[0, num_classes)`. Other values will raise an
+exception when this op is run on CPU, and return `NaN` for corresponding
+loss and gradient rows on GPU.
+ |
+
+|
+`logits`
+ |
+
+Unscaled log probabilities of shape
+`[d_0, d_1, ..., d_{r-1}, num_classes]` and dtype `float16`, `float32` or
+`float64`.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Coefficients for the loss. This must be scalar or broadcastable to
+`labels` (i.e. same rank and each dimension is either 1 or the same).
+ |
+
+|
+`scope`
+ |
+
+the scope for the operations performed in computing the loss.
+ |
+
+|
+`loss_collection`
+ |
+
+collection to which the loss will be added.
+ |
+
+|
+`reduction`
+ |
+
+Type of reduction to apply to loss.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Weighted loss `Tensor` of the same type as `logits`. If `reduction` is
+`NONE`, this has the same shape as `labels`; otherwise, it is scalar.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the shapes of `logits`, `labels`, and `weights` are
+incompatible, or if any of them are None.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+The `loss_collection` argument is ignored when executing eagerly. Consider
+holding on to the return value or collecting losses via a tf.keras.Model.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/make_template.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/make_template.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..b3a7f9a976d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/make_template.md
@@ -0,0 +1,208 @@
+description: Given an arbitrary function, wrap it so that it does variable sharing.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.make_template
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Given an arbitrary function, wrap it so that it does variable sharing.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.make_template(
+ name_, func_, create_scope_now_=(False), unique_name_=None, custom_getter_=None,
+ **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This wraps `func_` in a Template and partially evaluates it. Templates are
+functions that create variables the first time they are called and reuse them
+thereafter. In order for `func_` to be compatible with a `Template` it must
+have the following properties:
+
+* The function should create all trainable variables and any variables that
+ should be reused by calling tf.compat.v1.get_variable. If a trainable
+ variable is
+ created using tf.Variable, then a ValueError will be thrown. Variables
+ that are intended to be locals can be created by specifying
+ tf.Variable(..., trainable=false).
+* The function may use variable scopes and other templates internally to
+ create and reuse variables, but it shouldn't use
+ tf.compat.v1.global_variables to
+ capture variables that are defined outside of the scope of the function.
+* Internal scopes and variable names should not depend on any arguments that
+ are not supplied to `make_template`. In general you will get a ValueError
+ telling you that you are trying to reuse a variable that doesn't exist
+ if you make a mistake.
+
+In the following example, both `z` and `w` will be scaled by the same `y`. It
+is important to note that if we didn't assign `scalar_name` and used a
+different name for z and w that a `ValueError` would be thrown because it
+couldn't reuse the variable.
+
+```python
+def my_op(x, scalar_name):
+ var1 = tf.compat.v1.get_variable(scalar_name,
+ shape=[],
+ initializer=tf.compat.v1.constant_initializer(1))
+ return x * var1
+
+scale_by_y = tf.compat.v1.make_template('scale_by_y', my_op, scalar_name='y')
+
+z = scale_by_y(input1)
+w = scale_by_y(input2)
+```
+
+As a safe-guard, the returned function will raise a `ValueError` after the
+first call if trainable variables are created by calling tf.Variable.
+
+If all of these are true, then 2 properties are enforced by the template:
+
+1. Calling the same template multiple times will share all non-local
+ variables.
+2. Two different templates are guaranteed to be unique, unless you reenter the
+ same variable scope as the initial definition of a template and redefine
+ it. An examples of this exception:
+
+```python
+def my_op(x, scalar_name):
+ var1 = tf.compat.v1.get_variable(scalar_name,
+ shape=[],
+ initializer=tf.compat.v1.constant_initializer(1))
+ return x * var1
+
+with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope('scope') as vs:
+ scale_by_y = tf.compat.v1.make_template('scale_by_y', my_op,
+ scalar_name='y')
+ z = scale_by_y(input1)
+ w = scale_by_y(input2)
+
+# Creates a template that reuses the variables above.
+with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope(vs, reuse=True):
+ scale_by_y2 = tf.compat.v1.make_template('scale_by_y', my_op,
+ scalar_name='y')
+ z2 = scale_by_y2(input1)
+ w2 = scale_by_y2(input2)
+```
+
+Depending on the value of `create_scope_now_`, the full variable scope may be
+captured either at the time of first call or at the time of construction. If
+this option is set to True, then all Tensors created by repeated calls to the
+template will have an extra trailing _N+1 to their name, as the first time the
+scope is entered in the Template constructor no Tensors are created.
+
+Note: `name_`, `func_` and `create_scope_now_` have a trailing underscore to
+reduce the likelihood of collisions with kwargs.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name_`
+ |
+
+A name for the scope created by this template. If necessary, the name
+will be made unique by appending `_N` to the name.
+ |
+
+|
+`func_`
+ |
+
+The function to wrap.
+ |
+
+|
+`create_scope_now_`
+ |
+
+Boolean controlling whether the scope should be created
+when the template is constructed or when the template is called. Default
+is False, meaning the scope is created when the template is called.
+ |
+
+|
+`unique_name_`
+ |
+
+When used, it overrides name_ and is not made unique. If a
+template of the same scope/unique_name already exists and reuse is false,
+an error is raised. Defaults to None.
+ |
+
+|
+`custom_getter_`
+ |
+
+Optional custom getter for variables used in `func_`. See
+the tf.compat.v1.get_variable `custom_getter` documentation for more
+information.
+ |
+
+|
+`**kwargs`
+ |
+
+Keyword arguments to apply to `func_`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A function to encapsulate a set of variables which should be created once
+and reused. An enclosing scope will be created either when `make_template`
+is called or when the result is called, depending on the value of
+`create_scope_now_`. Regardless of the value, the first time the template
+is called it will enter the scope with no reuse, and call `func_` to create
+variables, which are guaranteed to be unique. All subsequent calls will
+re-enter the scope and reuse those variables.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `name_` is None.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/manip.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/manip.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..87bde1100dc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/manip.md
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
+description: Operators for manipulating tensors.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.manip
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Operators for manipulating tensors.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`batch_to_space_nd(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/batch_to_space_nd.md): BatchToSpace for N-D tensors of type T.
+
+[`gather_nd(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/gather_nd.md): Gather slices from `params` into a Tensor with shape specified by `indices`.
+
+[`reshape(...)`](../../../tf/reshape.md): Reshapes a tensor.
+
+[`reverse(...)`](../../../tf/reverse.md): Reverses specific dimensions of a tensor.
+
+[`roll(...)`](../../../tf/roll.md): Rolls the elements of a tensor along an axis.
+
+[`scatter_nd(...)`](../../../tf/scatter_nd.md): Scatter `updates` into a new tensor according to `indices`.
+
+[`space_to_batch_nd(...)`](../../../tf/space_to_batch_nd.md): SpaceToBatch for N-D tensors of type T.
+
+[`tile(...)`](../../../tf/tile.md): Constructs a tensor by tiling a given tensor.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/map_fn.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/map_fn.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e622f58e159
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/map_fn.md
@@ -0,0 +1,228 @@
+description: map on the list of tensors unpacked from elems on dimension 0.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.map_fn
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+map on the list of tensors unpacked from `elems` on dimension 0.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.map_fn(
+ fn, elems, dtype=None, parallel_iterations=None, back_prop=(True),
+ swap_memory=(False), infer_shape=(True), name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The simplest version of `map_fn` repeatedly applies the callable `fn` to a
+sequence of elements from first to last. The elements are made of the
+tensors unpacked from `elems`. `dtype` is the data type of the return
+value of `fn`. Users must provide `dtype` if it is different from
+the data type of `elems`.
+
+Suppose that `elems` is unpacked into `values`, a list of tensors. The shape
+of the result tensor is `[values.shape[0]] + fn(values[0]).shape`.
+
+This method also allows multi-arity `elems` and output of `fn`. If `elems`
+is a (possibly nested) list or tuple of tensors, then each of these tensors
+must have a matching first (unpack) dimension. The signature of `fn` may
+match the structure of `elems`. That is, if `elems` is
+`(t1, [t2, t3, [t4, t5]])`, then an appropriate signature for `fn` is:
+`fn = lambda (t1, [t2, t3, [t4, t5]]):`.
+
+Furthermore, `fn` may emit a different structure than its input. For example,
+`fn` may look like: `fn = lambda t1: return (t1 + 1, t1 - 1)`. In this case,
+the `dtype` parameter is not optional: `dtype` must be a type or (possibly
+nested) tuple of types matching the output of `fn`.
+
+To apply a functional operation to the nonzero elements of a SparseTensor
+one of the following methods is recommended. First, if the function is
+expressible as TensorFlow ops, use
+
+```python
+ result = SparseTensor(input.indices, fn(input.values), input.dense_shape)
+```
+
+If, however, the function is not expressible as a TensorFlow op, then use
+
+```python
+result = SparseTensor(
+ input.indices, map_fn(fn, input.values), input.dense_shape)
+```
+
+instead.
+
+When executing eagerly, map_fn does not execute in parallel even if
+`parallel_iterations` is set to a value > 1. You can still get the
+performance benefits of running a function in parallel by using the
+tf.function decorator,
+
+```python
+# Assume the function being used in map_fn is fn.
+# To ensure map_fn calls fn in parallel, use the tf.function decorator.
+@tf.function
+def func(tensor):
+ return tf.map_fn(fn, tensor)
+```
+
+Note that if you use the tf.function decorator, any non-TensorFlow Python
+code that you may have written in your function won't get executed. See
+[`tf.function`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/function) for
+more details. The recommendation would be to debug without tf.function but
+switch to it to get performance benefits of running `map_fn` in parallel.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`fn`
+ |
+
+The callable to be performed. It accepts one argument, which will
+have the same (possibly nested) structure as `elems`. Its output
+must have the same structure as `dtype` if one is provided, otherwise
+it must have the same structure as `elems`.
+ |
+
+|
+`elems`
+ |
+
+A tensor or (possibly nested) sequence of tensors, each of which
+will be unpacked along their first dimension. The nested sequence
+of the resulting slices will be applied to `fn`.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+(optional) The output type(s) of `fn`. If `fn` returns a structure
+of Tensors differing from the structure of `elems`, then `dtype` is not
+optional and must have the same structure as the output of `fn`.
+ |
+
+|
+`parallel_iterations`
+ |
+
+(optional) The number of iterations allowed to run
+in parallel. When graph building, the default value is 10. While executing
+eagerly, the default value is set to 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`back_prop`
+ |
+
+(optional) True enables support for back propagation.
+ |
+
+|
+`swap_memory`
+ |
+
+(optional) True enables GPU-CPU memory swapping.
+ |
+
+|
+`infer_shape`
+ |
+
+(optional) False disables tests for consistent output shapes.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+(optional) Name prefix for the returned tensors.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A tensor or (possibly nested) sequence of tensors. Each tensor packs the
+results of applying `fn` to tensors unpacked from `elems` along the first
+dimension, from first to last.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+if `fn` is not callable or the structure of the output of
+`fn` and `dtype` do not match, or if elems is a SparseTensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if the lengths of the output of `fn` and `dtype` do not match.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Examples:
+
+```python
+elems = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
+squares = map_fn(lambda x: x * x, elems)
+# squares == [1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36]
+```
+
+```python
+elems = (np.array([1, 2, 3]), np.array([-1, 1, -1]))
+alternate = map_fn(lambda x: x[0] * x[1], elems, dtype=tf.int64)
+# alternate == [-1, 2, -3]
+```
+
+```python
+elems = np.array([1, 2, 3])
+alternates = map_fn(lambda x: (x, -x), elems, dtype=(tf.int64, tf.int64))
+# alternates[0] == [1, 2, 3]
+# alternates[1] == [-1, -2, -3]
+```
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/math.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/math.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..9930504e0e8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/math.md
@@ -0,0 +1,335 @@
+description: Math Operations.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.math
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Math Operations.
+
+
+Note: Functions taking `Tensor` arguments can also take anything accepted by
+tf.convert_to_tensor.
+
+Note: Elementwise binary operations in TensorFlow follow [numpy-style
+broadcasting](http://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/user/basics.broadcasting.html).
+
+TensorFlow provides a variety of math functions including:
+
+* Basic arithmetic operators and trigonometric functions.
+* Special math functions (like: tf.math.igamma and tf.math.zeta)
+* Complex number functions (like: tf.math.imag and tf.math.angle)
+* Reductions and scans (like: tf.math.reduce_mean and tf.math.cumsum)
+* Segment functions (like: tf.math.segment_sum)
+
+See: tf.linalg for matrix and tensor functions.
+
+
+
+## About Segmentation
+
+TensorFlow provides several operations that you can use to perform common
+math computations on tensor segments.
+Here a segmentation is a partitioning of a tensor along
+the first dimension, i.e. it defines a mapping from the first dimension onto
+`segment_ids`. The `segment_ids` tensor should be the size of
+the first dimension, `d0`, with consecutive IDs in the range `0` to `k`,
+where `k [[0 0 0 0]
+# [5 6 7 8]]
+```
+
+The standard `segment_*` functions assert that the segment indices are sorted.
+If you have unsorted indices use the equivalent `unsorted_segment_` function.
+These functions take an additional argument `num_segments` so that the output
+tensor can be efficiently allocated.
+
+``` python
+c = tf.constant([[1,2,3,4], [-1,-2,-3,-4], [5,6,7,8]])
+tf.math.unsorted_segment_sum(c, tf.constant([0, 1, 0]), num_segments=2)
+# ==> [[ 6, 8, 10, 12],
+# [-1, -2, -3, -4]]
+```
+
+## Modules
+
+[`special`](../../../tf/compat/v1/math/special.md) module: Public API for tf.math.special namespace.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`abs(...)`](../../../tf/math/abs.md): Computes the absolute value of a tensor.
+
+[`accumulate_n(...)`](../../../tf/math/accumulate_n.md): Returns the element-wise sum of a list of tensors.
+
+[`acos(...)`](../../../tf/math/acos.md): Computes acos of x element-wise.
+
+[`acosh(...)`](../../../tf/math/acosh.md): Computes inverse hyperbolic cosine of x element-wise.
+
+[`add(...)`](../../../tf/math/add.md): Returns x + y element-wise.
+
+[`add_n(...)`](../../../tf/math/add_n.md): Adds all input tensors element-wise.
+
+[`angle(...)`](../../../tf/math/angle.md): Returns the element-wise argument of a complex (or real) tensor.
+
+[`argmax(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/argmax.md): Returns the index with the largest value across axes of a tensor. (deprecated arguments)
+
+[`argmin(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/argmin.md): Returns the index with the smallest value across axes of a tensor. (deprecated arguments)
+
+[`asin(...)`](../../../tf/math/asin.md): Computes the trignometric inverse sine of x element-wise.
+
+[`asinh(...)`](../../../tf/math/asinh.md): Computes inverse hyperbolic sine of x element-wise.
+
+[`atan(...)`](../../../tf/math/atan.md): Computes the trignometric inverse tangent of x element-wise.
+
+[`atan2(...)`](../../../tf/math/atan2.md): Computes arctangent of `y/x` element-wise, respecting signs of the arguments.
+
+[`atanh(...)`](../../../tf/math/atanh.md): Computes inverse hyperbolic tangent of x element-wise.
+
+[`bessel_i0(...)`](../../../tf/math/bessel_i0.md): Computes the Bessel i0 function of `x` element-wise.
+
+[`bessel_i0e(...)`](../../../tf/math/bessel_i0e.md): Computes the Bessel i0e function of `x` element-wise.
+
+[`bessel_i1(...)`](../../../tf/math/bessel_i1.md): Computes the Bessel i1 function of `x` element-wise.
+
+[`bessel_i1e(...)`](../../../tf/math/bessel_i1e.md): Computes the Bessel i1e function of `x` element-wise.
+
+[`betainc(...)`](../../../tf/math/betainc.md): Compute the regularized incomplete beta integral \\(I_x(a, b)\\).
+
+[`bincount(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/bincount.md): Counts the number of occurrences of each value in an integer array.
+
+[`ceil(...)`](../../../tf/math/ceil.md): Return the ceiling of the input, element-wise.
+
+[`confusion_matrix(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/confusion_matrix.md): Computes the confusion matrix from predictions and labels.
+
+[`conj(...)`](../../../tf/math/conj.md): Returns the complex conjugate of a complex number.
+
+[`cos(...)`](../../../tf/math/cos.md): Computes cos of x element-wise.
+
+[`cosh(...)`](../../../tf/math/cosh.md): Computes hyperbolic cosine of x element-wise.
+
+[`count_nonzero(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/count_nonzero.md): Computes number of nonzero elements across dimensions of a tensor. (deprecated arguments) (deprecated arguments)
+
+[`cumprod(...)`](../../../tf/math/cumprod.md): Compute the cumulative product of the tensor `x` along `axis`.
+
+[`cumsum(...)`](../../../tf/math/cumsum.md): Compute the cumulative sum of the tensor `x` along `axis`.
+
+[`cumulative_logsumexp(...)`](../../../tf/math/cumulative_logsumexp.md): Compute the cumulative log-sum-exp of the tensor `x` along `axis`.
+
+[`digamma(...)`](../../../tf/math/digamma.md): Computes Psi, the derivative of Lgamma (the log of the absolute value of
+
+[`divide(...)`](../../../tf/math/divide.md): Computes Python style division of `x` by `y`.
+
+[`divide_no_nan(...)`](../../../tf/math/divide_no_nan.md): Computes a safe divide which returns 0 if the y is zero.
+
+[`equal(...)`](../../../tf/math/equal.md): Returns the truth value of (x == y) element-wise.
+
+[`erf(...)`](../../../tf/math/erf.md): Computes the Gauss error function of `x` element-wise.
+
+[`erfc(...)`](../../../tf/math/erfc.md): Computes the complementary error function of `x` element-wise.
+
+[`erfinv(...)`](../../../tf/math/erfinv.md): Compute inverse error function.
+
+[`exp(...)`](../../../tf/math/exp.md): Computes exponential of x element-wise. \\(y = e^x\\).
+
+[`expm1(...)`](../../../tf/math/expm1.md): Computes `exp(x) - 1` element-wise.
+
+[`floor(...)`](../../../tf/math/floor.md): Returns element-wise largest integer not greater than x.
+
+[`floordiv(...)`](../../../tf/math/floordiv.md): Divides `x / y` elementwise, rounding toward the most negative integer.
+
+[`floormod(...)`](../../../tf/math/floormod.md): Returns element-wise remainder of division. When `x < 0` xor `y < 0` is
+
+[`greater(...)`](../../../tf/math/greater.md): Returns the truth value of (x > y) element-wise.
+
+[`greater_equal(...)`](../../../tf/math/greater_equal.md): Returns the truth value of (x >= y) element-wise.
+
+[`igamma(...)`](../../../tf/math/igamma.md): Compute the lower regularized incomplete Gamma function `P(a, x)`.
+
+[`igammac(...)`](../../../tf/math/igammac.md): Compute the upper regularized incomplete Gamma function `Q(a, x)`.
+
+[`imag(...)`](../../../tf/math/imag.md): Returns the imaginary part of a complex (or real) tensor.
+
+[`in_top_k(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/math/in_top_k.md): Says whether the targets are in the top `K` predictions.
+
+[`invert_permutation(...)`](../../../tf/math/invert_permutation.md): Computes the inverse permutation of a tensor.
+
+[`is_finite(...)`](../../../tf/math/is_finite.md): Returns which elements of x are finite.
+
+[`is_inf(...)`](../../../tf/math/is_inf.md): Returns which elements of x are Inf.
+
+[`is_nan(...)`](../../../tf/math/is_nan.md): Returns which elements of x are NaN.
+
+[`is_non_decreasing(...)`](../../../tf/math/is_non_decreasing.md): Returns `True` if `x` is non-decreasing.
+
+[`is_strictly_increasing(...)`](../../../tf/math/is_strictly_increasing.md): Returns `True` if `x` is strictly increasing.
+
+[`l2_normalize(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/linalg/l2_normalize.md): Normalizes along dimension `axis` using an L2 norm. (deprecated arguments)
+
+[`lbeta(...)`](../../../tf/math/lbeta.md): Computes \\(ln(|Beta(x)|)\\), reducing along the last dimension.
+
+[`less(...)`](../../../tf/math/less.md): Returns the truth value of (x < y) element-wise.
+
+[`less_equal(...)`](../../../tf/math/less_equal.md): Returns the truth value of (x <= y) element-wise.
+
+[`lgamma(...)`](../../../tf/math/lgamma.md): Computes the log of the absolute value of `Gamma(x)` element-wise.
+
+[`log(...)`](../../../tf/math/log.md): Computes natural logarithm of x element-wise.
+
+[`log1p(...)`](../../../tf/math/log1p.md): Computes natural logarithm of (1 + x) element-wise.
+
+[`log_sigmoid(...)`](../../../tf/math/log_sigmoid.md): Computes log sigmoid of `x` element-wise.
+
+[`log_softmax(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/math/log_softmax.md): Computes log softmax activations. (deprecated arguments)
+
+[`logical_and(...)`](../../../tf/math/logical_and.md): Logical AND function.
+
+[`logical_not(...)`](../../../tf/math/logical_not.md): Returns the truth value of `NOT x` element-wise.
+
+[`logical_or(...)`](../../../tf/math/logical_or.md): Returns the truth value of x OR y element-wise.
+
+[`logical_xor(...)`](../../../tf/math/logical_xor.md): Logical XOR function.
+
+[`maximum(...)`](../../../tf/math/maximum.md): Returns the max of x and y (i.e. x > y ? x : y) element-wise.
+
+[`minimum(...)`](../../../tf/math/minimum.md): Returns the min of x and y (i.e. x < y ? x : y) element-wise.
+
+[`mod(...)`](../../../tf/math/floormod.md): Returns element-wise remainder of division. When `x < 0` xor `y < 0` is
+
+[`multiply(...)`](../../../tf/math/multiply.md): Returns an element-wise x * y.
+
+[`multiply_no_nan(...)`](../../../tf/math/multiply_no_nan.md): Computes the product of x and y and returns 0 if the y is zero, even if x is NaN or infinite.
+
+[`ndtri(...)`](../../../tf/math/ndtri.md): Compute quantile of Standard Normal.
+
+[`negative(...)`](../../../tf/math/negative.md): Computes numerical negative value element-wise.
+
+[`nextafter(...)`](../../../tf/math/nextafter.md): Returns the next representable value of `x1` in the direction of `x2`, element-wise.
+
+[`not_equal(...)`](../../../tf/math/not_equal.md): Returns the truth value of (x != y) element-wise.
+
+[`polygamma(...)`](../../../tf/math/polygamma.md): Compute the polygamma function \\(\psi^{(n)}(x)\\).
+
+[`polyval(...)`](../../../tf/math/polyval.md): Computes the elementwise value of a polynomial.
+
+[`pow(...)`](../../../tf/math/pow.md): Computes the power of one value to another.
+
+[`real(...)`](../../../tf/math/real.md): Returns the real part of a complex (or real) tensor.
+
+[`reciprocal(...)`](../../../tf/math/reciprocal.md): Computes the reciprocal of x element-wise.
+
+[`reciprocal_no_nan(...)`](../../../tf/math/reciprocal_no_nan.md): Performs a safe reciprocal operation, element wise.
+
+[`reduce_all(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/reduce_all.md): Computes the "logical and" of elements across dimensions of a tensor. (deprecated arguments)
+
+[`reduce_any(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/reduce_any.md): Computes the "logical or" of elements across dimensions of a tensor. (deprecated arguments)
+
+[`reduce_euclidean_norm(...)`](../../../tf/math/reduce_euclidean_norm.md): Computes the Euclidean norm of elements across dimensions of a tensor.
+
+[`reduce_logsumexp(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/reduce_logsumexp.md): Computes log(sum(exp(elements across dimensions of a tensor))). (deprecated arguments)
+
+[`reduce_max(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/reduce_max.md): Computes the maximum of elements across dimensions of a tensor. (deprecated arguments)
+
+[`reduce_mean(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/reduce_mean.md): Computes the mean of elements across dimensions of a tensor.
+
+[`reduce_min(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/reduce_min.md): Computes the minimum of elements across dimensions of a tensor. (deprecated arguments)
+
+[`reduce_prod(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/reduce_prod.md): Computes the product of elements across dimensions of a tensor. (deprecated arguments)
+
+[`reduce_std(...)`](../../../tf/math/reduce_std.md): Computes the standard deviation of elements across dimensions of a tensor.
+
+[`reduce_sum(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/reduce_sum.md): Computes the sum of elements across dimensions of a tensor. (deprecated arguments)
+
+[`reduce_variance(...)`](../../../tf/math/reduce_variance.md): Computes the variance of elements across dimensions of a tensor.
+
+[`rint(...)`](../../../tf/math/rint.md): Returns element-wise integer closest to x.
+
+[`round(...)`](../../../tf/math/round.md): Rounds the values of a tensor to the nearest integer, element-wise.
+
+[`rsqrt(...)`](../../../tf/math/rsqrt.md): Computes reciprocal of square root of x element-wise.
+
+[`scalar_mul(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/scalar_mul.md): Multiplies a scalar times a `Tensor` or `IndexedSlices` object.
+
+[`segment_max(...)`](../../../tf/math/segment_max.md): Computes the maximum along segments of a tensor.
+
+[`segment_mean(...)`](../../../tf/math/segment_mean.md): Computes the mean along segments of a tensor.
+
+[`segment_min(...)`](../../../tf/math/segment_min.md): Computes the minimum along segments of a tensor.
+
+[`segment_prod(...)`](../../../tf/math/segment_prod.md): Computes the product along segments of a tensor.
+
+[`segment_sum(...)`](../../../tf/math/segment_sum.md): Computes the sum along segments of a tensor.
+
+[`sigmoid(...)`](../../../tf/math/sigmoid.md): Computes sigmoid of `x` element-wise.
+
+[`sign(...)`](../../../tf/math/sign.md): Returns an element-wise indication of the sign of a number.
+
+[`sin(...)`](../../../tf/math/sin.md): Computes sine of x element-wise.
+
+[`sinh(...)`](../../../tf/math/sinh.md): Computes hyperbolic sine of x element-wise.
+
+[`sobol_sample(...)`](../../../tf/math/sobol_sample.md): Generates points from the Sobol sequence.
+
+[`softmax(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/math/softmax.md): Computes softmax activations. (deprecated arguments)
+
+[`softplus(...)`](../../../tf/math/softplus.md): Computes softplus: `log(exp(features) + 1)`.
+
+[`softsign(...)`](../../../tf/nn/softsign.md): Computes softsign: `features / (abs(features) + 1)`.
+
+[`sqrt(...)`](../../../tf/math/sqrt.md): Computes element-wise square root of the input tensor.
+
+[`square(...)`](../../../tf/math/square.md): Computes square of x element-wise.
+
+[`squared_difference(...)`](../../../tf/math/squared_difference.md): Returns (x - y)(x - y) element-wise.
+
+[`subtract(...)`](../../../tf/math/subtract.md): Returns x - y element-wise.
+
+[`tan(...)`](../../../tf/math/tan.md): Computes tan of x element-wise.
+
+[`tanh(...)`](../../../tf/math/tanh.md): Computes hyperbolic tangent of `x` element-wise.
+
+[`top_k(...)`](../../../tf/math/top_k.md): Finds values and indices of the `k` largest entries for the last dimension.
+
+[`truediv(...)`](../../../tf/math/truediv.md): Divides x / y elementwise (using Python 3 division operator semantics).
+
+[`unsorted_segment_max(...)`](../../../tf/math/unsorted_segment_max.md): Computes the maximum along segments of a tensor.
+
+[`unsorted_segment_mean(...)`](../../../tf/math/unsorted_segment_mean.md): Computes the mean along segments of a tensor.
+
+[`unsorted_segment_min(...)`](../../../tf/math/unsorted_segment_min.md): Computes the minimum along segments of a tensor.
+
+[`unsorted_segment_prod(...)`](../../../tf/math/unsorted_segment_prod.md): Computes the product along segments of a tensor.
+
+[`unsorted_segment_sqrt_n(...)`](../../../tf/math/unsorted_segment_sqrt_n.md): Computes the sum along segments of a tensor divided by the sqrt(N).
+
+[`unsorted_segment_sum(...)`](../../../tf/math/unsorted_segment_sum.md): Computes the sum along segments of a tensor.
+
+[`xdivy(...)`](../../../tf/math/xdivy.md): Returns 0 if x == 0, and x / y otherwise, elementwise.
+
+[`xlog1py(...)`](../../../tf/math/xlog1py.md): Compute x * log1p(y).
+
+[`xlogy(...)`](../../../tf/math/xlogy.md): Returns 0 if x == 0, and x * log(y) otherwise, elementwise.
+
+[`zero_fraction(...)`](../../../tf/math/zero_fraction.md): Returns the fraction of zeros in `value`.
+
+[`zeta(...)`](../../../tf/math/zeta.md): Compute the Hurwitz zeta function \\(\zeta(x, q)\\).
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/math/in_top_k.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/math/in_top_k.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..165182f743f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/math/in_top_k.md
@@ -0,0 +1,112 @@
+description: Says whether the targets are in the top K predictions.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.math.in_top_k
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Says whether the targets are in the top `K` predictions.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.nn.in_top_k`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.math.in_top_k(
+ predictions, targets, k, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This outputs a `batch_size` bool array, an entry `out[i]` is `true` if the
+prediction for the target class is finite (not inf, -inf, or nan) and among
+the top `k` predictions among all predictions for example `i`. Note that the
+behavior of `InTopK` differs from the `TopK` op in its handling of ties; if
+multiple classes have the same prediction value and straddle the top-`k`
+boundary, all of those classes are considered to be in the top `k`.
+
+More formally, let
+
+ \\(predictions_i\\) be the predictions for all classes for example `i`,
+ \\(targets_i\\) be the target class for example `i`,
+ \\(out_i\\) be the output for example `i`,
+
+$$out_i = predictions_{i, targets_i} \in TopKIncludingTies(predictions_i)$$
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`predictions`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `float32`.
+A `batch_size` x `classes` tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`targets`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `int32`, `int64`.
+A `batch_size` vector of class ids.
+ |
+
+|
+`k`
+ |
+
+An `int`. Number of top elements to look at for computing precision.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` of type `bool`. Computed Precision at `k` as a `bool Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/math/log_softmax.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/math/log_softmax.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..d7a23b5b270
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/math/log_softmax.md
@@ -0,0 +1,123 @@
+description: Computes log softmax activations. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.math.log_softmax
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes log softmax activations. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.nn.log_softmax`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.math.log_softmax(
+ logits, axis=None, name=None, dim=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: SOME ARGUMENTS ARE DEPRECATED: `(dim)`. They will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+dim is deprecated, use axis instead
+
+For each batch `i` and class `j` we have
+
+ logsoftmax = logits - log(reduce_sum(exp(logits), axis))
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`logits`
+ |
+
+A non-empty `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `half`,
+`float32`, `float64`.
+ |
+
+|
+`axis`
+ |
+
+The dimension softmax would be performed on. The default is -1 which
+indicates the last dimension.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`dim`
+ |
+
+Deprecated alias for `axis`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `logits`. Same shape as `logits`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`InvalidArgumentError`
+ |
+
+if `logits` is empty or `axis` is beyond the last
+dimension of `logits`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/math/softmax.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/math/softmax.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..741b61860cd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/math/softmax.md
@@ -0,0 +1,149 @@
+description: Computes softmax activations. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.math.softmax
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes softmax activations. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.nn.softmax`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.math.softmax(
+ logits, axis=None, name=None, dim=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: SOME ARGUMENTS ARE DEPRECATED: `(dim)`. They will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+dim is deprecated, use axis instead
+
+This function performs the equivalent of
+
+ softmax = tf.exp(logits) / tf.reduce_sum(tf.exp(logits), axis)
+
+See: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Softmax_function
+
+#### Example usage:
+
+
+>>> tf.nn.softmax([-1, 0., 1.])
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`logits`
+ |
+
+A non-empty `Tensor`, or an object whose type has a registered
+`Tensor` conversion function. Must be one of the following types:
+`half`,`float32`, `float64`. See also `convert_to_tensor`
+ |
+
+|
+`axis`
+ |
+
+The dimension softmax would be performed on. The default is -1 which
+indicates the last dimension.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`dim`
+ |
+
+Deprecated alias for `axis`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor`. Has the same type and shape as `logits`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`InvalidArgumentError`
+ |
+
+if `logits` is empty or `axis` is beyond the last
+dimension of `logits`.
+ |
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If no conversion function is registered for `logits` to
+Tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If a registered conversion function returns an invalid
+value.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/math/special.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/math/special.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..0efa544db90
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/math/special.md
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+description: Public API for tf.math.special namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.math.special
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.math.special namespace.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`dawsn(...)`](../../../../tf/math/special/dawsn.md): Computes Dawson's integral of `x` element-wise.
+
+[`expint(...)`](../../../../tf/math/special/expint.md): Computes the Exponential integral of `x` element-wise.
+
+[`fresnel_cos(...)`](../../../../tf/math/special/fresnel_cos.md): Computes Fresnel's cosine integral of `x` element-wise.
+
+[`fresnel_sin(...)`](../../../../tf/math/special/fresnel_sin.md): Computes Fresnel's sine integral of `x` element-wise.
+
+[`spence(...)`](../../../../tf/math/special/spence.md): Computes Spence's integral of `x` element-wise.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..81a342ccade
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics.md
@@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
+description: Evaluation-related metrics.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.metrics
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Evaluation-related metrics.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`accuracy(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/metrics/accuracy.md): Calculates how often `predictions` matches `labels`.
+
+[`auc(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/metrics/auc.md): Computes the approximate AUC via a Riemann sum. (deprecated)
+
+[`average_precision_at_k(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/metrics/average_precision_at_k.md): Computes average precision@k of predictions with respect to sparse labels.
+
+[`false_negatives(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/metrics/false_negatives.md): Computes the total number of false negatives.
+
+[`false_negatives_at_thresholds(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/metrics/false_negatives_at_thresholds.md): Computes false negatives at provided threshold values.
+
+[`false_positives(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/metrics/false_positives.md): Sum the weights of false positives.
+
+[`false_positives_at_thresholds(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/metrics/false_positives_at_thresholds.md): Computes false positives at provided threshold values.
+
+[`mean(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/metrics/mean.md): Computes the (weighted) mean of the given values.
+
+[`mean_absolute_error(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/metrics/mean_absolute_error.md): Computes the mean absolute error between the labels and predictions.
+
+[`mean_cosine_distance(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/metrics/mean_cosine_distance.md): Computes the cosine distance between the labels and predictions.
+
+[`mean_iou(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/metrics/mean_iou.md): Calculate per-step mean Intersection-Over-Union (mIOU).
+
+[`mean_per_class_accuracy(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/metrics/mean_per_class_accuracy.md): Calculates the mean of the per-class accuracies.
+
+[`mean_relative_error(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/metrics/mean_relative_error.md): Computes the mean relative error by normalizing with the given values.
+
+[`mean_squared_error(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/metrics/mean_squared_error.md): Computes the mean squared error between the labels and predictions.
+
+[`mean_tensor(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/metrics/mean_tensor.md): Computes the element-wise (weighted) mean of the given tensors.
+
+[`percentage_below(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/metrics/percentage_below.md): Computes the percentage of values less than the given threshold.
+
+[`precision(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/metrics/precision.md): Computes the precision of the predictions with respect to the labels.
+
+[`precision_at_k(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/metrics/precision_at_k.md): Computes precision@k of the predictions with respect to sparse labels.
+
+[`precision_at_thresholds(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/metrics/precision_at_thresholds.md): Computes precision values for different `thresholds` on `predictions`.
+
+[`precision_at_top_k(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/metrics/precision_at_top_k.md): Computes precision@k of the predictions with respect to sparse labels.
+
+[`recall(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/metrics/recall.md): Computes the recall of the predictions with respect to the labels.
+
+[`recall_at_k(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/metrics/recall_at_k.md): Computes recall@k of the predictions with respect to sparse labels.
+
+[`recall_at_thresholds(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/metrics/recall_at_thresholds.md): Computes various recall values for different `thresholds` on `predictions`.
+
+[`recall_at_top_k(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/metrics/recall_at_top_k.md): Computes recall@k of top-k predictions with respect to sparse labels.
+
+[`root_mean_squared_error(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/metrics/root_mean_squared_error.md): Computes the root mean squared error between the labels and predictions.
+
+[`sensitivity_at_specificity(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/metrics/sensitivity_at_specificity.md): Computes the specificity at a given sensitivity.
+
+[`sparse_average_precision_at_k(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/metrics/sparse_average_precision_at_k.md): Renamed to `average_precision_at_k`, please use that method instead. (deprecated)
+
+[`sparse_precision_at_k(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/metrics/sparse_precision_at_k.md): Renamed to `precision_at_k`, please use that method instead. (deprecated)
+
+[`specificity_at_sensitivity(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/metrics/specificity_at_sensitivity.md): Computes the specificity at a given sensitivity.
+
+[`true_negatives(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/metrics/true_negatives.md): Sum the weights of true_negatives.
+
+[`true_negatives_at_thresholds(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/metrics/true_negatives_at_thresholds.md): Computes true negatives at provided threshold values.
+
+[`true_positives(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/metrics/true_positives.md): Sum the weights of true_positives.
+
+[`true_positives_at_thresholds(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/metrics/true_positives_at_thresholds.md): Computes true positives at provided threshold values.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/accuracy.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/accuracy.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..998a202971a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/accuracy.md
@@ -0,0 +1,158 @@
+description: Calculates how often predictions matches labels.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.metrics.accuracy
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Calculates how often `predictions` matches `labels`.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.metrics.accuracy(
+ labels, predictions, weights=None, metrics_collections=None,
+ updates_collections=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The `accuracy` function creates two local variables, `total` and
+`count` that are used to compute the frequency with which `predictions`
+matches `labels`. This frequency is ultimately returned as `accuracy`: an
+idempotent operation that simply divides `total` by `count`.
+
+For estimation of the metric over a stream of data, the function creates an
+`update_op` operation that updates these variables and returns the `accuracy`.
+Internally, an `is_correct` operation computes a `Tensor` with elements 1.0
+where the corresponding elements of `predictions` and `labels` match and 0.0
+otherwise. Then `update_op` increments `total` with the reduced sum of the
+product of `weights` and `is_correct`, and it increments `count` with the
+reduced sum of `weights`.
+
+If `weights` is `None`, weights default to 1. Use weights of 0 to mask values.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+The ground truth values, a `Tensor` whose shape matches
+`predictions`.
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions`
+ |
+
+The predicted values, a `Tensor` of any shape.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Optional `Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or the same rank as
+`labels`, and must be broadcastable to `labels` (i.e., all dimensions must
+be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `labels` dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`metrics_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that `accuracy` should
+be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that `update_op` should
+be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+An optional variable_scope name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`accuracy`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` representing the accuracy, the value of `total` divided
+by `count`.
+ |
+
+|
+`update_op`
+ |
+
+An operation that increments the `total` and `count` variables
+appropriately and whose value matches `accuracy`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `predictions` and `labels` have mismatched shapes, or if
+`weights` is not `None` and its shape doesn't match `predictions`, or if
+either `metrics_collections` or `updates_collections` are not a list or
+tuple.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/auc.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/auc.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..b5b3377c11a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/auc.md
@@ -0,0 +1,221 @@
+description: Computes the approximate AUC via a Riemann sum. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.metrics.auc
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the approximate AUC via a Riemann sum. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.metrics.auc(
+ labels, predictions, weights=None, num_thresholds=200, metrics_collections=None,
+ updates_collections=None, curve='ROC', name=None,
+ summation_method='trapezoidal', thresholds=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+The value of AUC returned by this may race with the update so this is deprecated. Please use tf.keras.metrics.AUC instead.
+
+The `auc` function creates four local variables, `true_positives`,
+`true_negatives`, `false_positives` and `false_negatives` that are used to
+compute the AUC. To discretize the AUC curve, a linearly spaced set of
+thresholds is used to compute pairs of recall and precision values. The area
+under the ROC-curve is therefore computed using the height of the recall
+values by the false positive rate, while the area under the PR-curve is the
+computed using the height of the precision values by the recall.
+
+This value is ultimately returned as `auc`, an idempotent operation that
+computes the area under a discretized curve of precision versus recall values
+(computed using the aforementioned variables). The `num_thresholds` variable
+controls the degree of discretization with larger numbers of thresholds more
+closely approximating the true AUC. The quality of the approximation may vary
+dramatically depending on `num_thresholds`.
+
+For best results, `predictions` should be distributed approximately uniformly
+in the range [0, 1] and not peaked around 0 or 1. The quality of the AUC
+approximation may be poor if this is not the case. Setting `summation_method`
+to 'minoring' or 'majoring' can help quantify the error in the approximation
+by providing lower or upper bound estimate of the AUC. The `thresholds`
+parameter can be used to manually specify thresholds which split the
+predictions more evenly.
+
+For estimation of the metric over a stream of data, the function creates an
+`update_op` operation that updates these variables and returns the `auc`.
+
+If `weights` is `None`, weights default to 1. Use weights of 0 to mask values.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` whose shape matches `predictions`. Will be cast to
+`bool`.
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions`
+ |
+
+A floating point `Tensor` of arbitrary shape and whose values
+are in the range `[0, 1]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Optional `Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or the same rank as
+`labels`, and must be broadcastable to `labels` (i.e., all dimensions must
+be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `labels` dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`num_thresholds`
+ |
+
+The number of thresholds to use when discretizing the roc
+curve.
+ |
+
+|
+`metrics_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that `auc` should be
+added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that `update_op` should
+be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`curve`
+ |
+
+Specifies the name of the curve to be computed, 'ROC' [default] or
+'PR' for the Precision-Recall-curve.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+An optional variable_scope name.
+ |
+
+|
+`summation_method`
+ |
+
+Specifies the Riemann summation method used
+(https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Riemann_sum): 'trapezoidal' [default] that
+applies the trapezoidal rule; 'careful_interpolation', a variant of it
+differing only by a more correct interpolation scheme for PR-AUC -
+interpolating (true/false) positives but not the ratio that is precision;
+'minoring' that applies left summation for increasing intervals and right
+summation for decreasing intervals; 'majoring' that does the opposite.
+Note that 'careful_interpolation' is strictly preferred to 'trapezoidal'
+(to be deprecated soon) as it applies the same method for ROC, and a
+better one (see Davis & Goadrich 2006 for details) for the PR curve.
+ |
+
+|
+`thresholds`
+ |
+
+An optional list of floating point values to use as the
+thresholds for discretizing the curve. If set, the `num_thresholds`
+parameter is ignored. Values should be in [0, 1]. Endpoint thresholds
+equal to {-epsilon, 1+epsilon} for a small positive epsilon value will be
+automatically included with these to correctly handle predictions equal to
+exactly 0 or 1.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`auc`
+ |
+
+A scalar `Tensor` representing the current area-under-curve.
+ |
+
+|
+`update_op`
+ |
+
+An operation that increments the `true_positives`,
+`true_negatives`, `false_positives` and `false_negatives` variables
+appropriately and whose value matches `auc`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `predictions` and `labels` have mismatched shapes, or if
+`weights` is not `None` and its shape doesn't match `predictions`, or if
+either `metrics_collections` or `updates_collections` are not a list or
+tuple.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/average_precision_at_k.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/average_precision_at_k.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..0c3b8298868
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/average_precision_at_k.md
@@ -0,0 +1,173 @@
+description: Computes average precision@k of predictions with respect to sparse labels.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.metrics.average_precision_at_k
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes average precision@k of predictions with respect to sparse labels.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.metrics.average_precision_at_k(
+ labels, predictions, k, weights=None, metrics_collections=None,
+ updates_collections=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+`average_precision_at_k` creates two local variables,
+`average_precision_at_/total` and `average_precision_at_/max`, that
+are used to compute the frequency. This frequency is ultimately returned as
+`average_precision_at_`: an idempotent operation that simply divides
+`average_precision_at_/total` by `average_precision_at_/max`.
+
+For estimation of the metric over a stream of data, the function creates an
+`update_op` operation that updates these variables and returns the
+`precision_at_`. Internally, a `top_k` operation computes a `Tensor`
+indicating the top `k` `predictions`. Set operations applied to `top_k` and
+`labels` calculate the true positives and false positives weighted by
+`weights`. Then `update_op` increments `true_positive_at_` and
+`false_positive_at_` using these values.
+
+If `weights` is `None`, weights default to 1. Use weights of 0 to mask values.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+`int64` `Tensor` or `SparseTensor` with shape
+[D1, ... DN, num_labels] or [D1, ... DN], where the latter implies
+num_labels=1. N >= 1 and num_labels is the number of target classes for
+the associated prediction. Commonly, N=1 and `labels` has shape
+[batch_size, num_labels]. [D1, ... DN] must match `predictions`. Values
+should be in range [0, num_classes), where num_classes is the last
+dimension of `predictions`. Values outside this range are ignored.
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions`
+ |
+
+Float `Tensor` with shape [D1, ... DN, num_classes] where
+N >= 1. Commonly, N=1 and `predictions` has shape
+[batch size, num_classes]. The final dimension contains the logit values
+for each class. [D1, ... DN] must match `labels`.
+ |
+
+|
+`k`
+ |
+
+Integer, k for @k metric. This will calculate an average precision for
+range `[1,k]`, as documented above.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+`Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or n-1, where n is the rank of
+`labels`. If the latter, it must be broadcastable to `labels` (i.e., all
+dimensions must be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `labels`
+dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`metrics_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that values should
+be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that updates should
+be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of new update operation, and namespace for other dependent ops.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`mean_average_precision`
+ |
+
+Scalar `float64` `Tensor` with the mean average
+precision values.
+ |
+
+|
+`update`
+ |
+
+`Operation` that increments variables appropriately, and whose
+value matches `metric`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if k is invalid.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/false_negatives.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/false_negatives.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..be75b02511a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/false_negatives.md
@@ -0,0 +1,143 @@
+description: Computes the total number of false negatives.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.metrics.false_negatives
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the total number of false negatives.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.metrics.false_negatives(
+ labels, predictions, weights=None, metrics_collections=None,
+ updates_collections=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+If `weights` is `None`, weights default to 1. Use weights of 0 to mask values.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+The ground truth values, a `Tensor` whose dimensions must match
+`predictions`. Will be cast to `bool`.
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions`
+ |
+
+The predicted values, a `Tensor` of arbitrary dimensions. Will
+be cast to `bool`.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Optional `Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or the same rank as
+`labels`, and must be broadcastable to `labels` (i.e., all dimensions must
+be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `labels` dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`metrics_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that the metric
+value variable should be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that the metric update
+ops should be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+An optional variable_scope name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value_tensor`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` representing the current value of the metric.
+ |
+
+|
+`update_op`
+ |
+
+An operation that accumulates the error from a batch of data.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `weights` is not `None` and its shape doesn't match `values`,
+or if either `metrics_collections` or `updates_collections` are not a list
+or tuple.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/false_negatives_at_thresholds.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/false_negatives_at_thresholds.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a011084810f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/false_negatives_at_thresholds.md
@@ -0,0 +1,152 @@
+description: Computes false negatives at provided threshold values.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.metrics.false_negatives_at_thresholds
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes false negatives at provided threshold values.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.metrics.false_negatives_at_thresholds(
+ labels, predictions, thresholds, weights=None, metrics_collections=None,
+ updates_collections=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+If `weights` is `None`, weights default to 1. Use weights of 0 to mask values.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` whose shape matches `predictions`. Will be cast to
+`bool`.
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions`
+ |
+
+A floating point `Tensor` of arbitrary shape and whose values
+are in the range `[0, 1]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`thresholds`
+ |
+
+A python list or tuple of float thresholds in `[0, 1]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Optional `Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or the same rank as
+`labels`, and must be broadcastable to `labels` (i.e., all dimensions must
+be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `labels` dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`metrics_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that `false_negatives`
+should be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that `update_op` should
+be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+An optional variable_scope name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`false_negatives`
+ |
+
+A float `Tensor` of shape `[len(thresholds)]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`update_op`
+ |
+
+An operation that updates the `false_negatives` variable and
+returns its current value.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `predictions` and `labels` have mismatched shapes, or if
+`weights` is not `None` and its shape doesn't match `predictions`, or if
+either `metrics_collections` or `updates_collections` are not a list or
+tuple.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/false_positives.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/false_positives.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..dcca3f82e17
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/false_positives.md
@@ -0,0 +1,144 @@
+description: Sum the weights of false positives.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.metrics.false_positives
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Sum the weights of false positives.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.metrics.false_positives(
+ labels, predictions, weights=None, metrics_collections=None,
+ updates_collections=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+If `weights` is `None`, weights default to 1. Use weights of 0 to mask values.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+The ground truth values, a `Tensor` whose dimensions must match
+`predictions`. Will be cast to `bool`.
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions`
+ |
+
+The predicted values, a `Tensor` of arbitrary dimensions. Will
+be cast to `bool`.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Optional `Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or the same rank as
+`labels`, and must be broadcastable to `labels` (i.e., all dimensions must
+be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `labels` dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`metrics_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that the metric
+value variable should be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that the metric update
+ops should be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+An optional variable_scope name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value_tensor`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` representing the current value of the metric.
+ |
+
+|
+`update_op`
+ |
+
+An operation that accumulates the error from a batch of data.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `predictions` and `labels` have mismatched shapes, or if
+`weights` is not `None` and its shape doesn't match `predictions`, or if
+either `metrics_collections` or `updates_collections` are not a list or
+tuple.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/false_positives_at_thresholds.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/false_positives_at_thresholds.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a834dbd1017
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/false_positives_at_thresholds.md
@@ -0,0 +1,152 @@
+description: Computes false positives at provided threshold values.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.metrics.false_positives_at_thresholds
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes false positives at provided threshold values.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.metrics.false_positives_at_thresholds(
+ labels, predictions, thresholds, weights=None, metrics_collections=None,
+ updates_collections=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+If `weights` is `None`, weights default to 1. Use weights of 0 to mask values.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` whose shape matches `predictions`. Will be cast to
+`bool`.
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions`
+ |
+
+A floating point `Tensor` of arbitrary shape and whose values
+are in the range `[0, 1]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`thresholds`
+ |
+
+A python list or tuple of float thresholds in `[0, 1]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Optional `Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or the same rank as
+`labels`, and must be broadcastable to `labels` (i.e., all dimensions must
+be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `labels` dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`metrics_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that `false_positives`
+should be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that `update_op` should
+be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+An optional variable_scope name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`false_positives`
+ |
+
+A float `Tensor` of shape `[len(thresholds)]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`update_op`
+ |
+
+An operation that updates the `false_positives` variable and
+returns its current value.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `predictions` and `labels` have mismatched shapes, or if
+`weights` is not `None` and its shape doesn't match `predictions`, or if
+either `metrics_collections` or `updates_collections` are not a list or
+tuple.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/mean.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/mean.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a46c279a20a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/mean.md
@@ -0,0 +1,146 @@
+description: Computes the (weighted) mean of the given values.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.metrics.mean
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the (weighted) mean of the given values.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.metrics.mean(
+ values, weights=None, metrics_collections=None, updates_collections=None,
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The `mean` function creates two local variables, `total` and `count`
+that are used to compute the average of `values`. This average is ultimately
+returned as `mean` which is an idempotent operation that simply divides
+`total` by `count`.
+
+For estimation of the metric over a stream of data, the function creates an
+`update_op` operation that updates these variables and returns the `mean`.
+`update_op` increments `total` with the reduced sum of the product of `values`
+and `weights`, and it increments `count` with the reduced sum of `weights`.
+
+If `weights` is `None`, weights default to 1. Use weights of 0 to mask values.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`values`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of arbitrary dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Optional `Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or the same rank as
+`values`, and must be broadcastable to `values` (i.e., all dimensions must
+be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `values` dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`metrics_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that `mean`
+should be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that `update_op`
+should be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+An optional variable_scope name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`mean`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` representing the current mean, the value of `total` divided
+by `count`.
+ |
+
+|
+`update_op`
+ |
+
+An operation that increments the `total` and `count` variables
+appropriately and whose value matches `mean_value`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `weights` is not `None` and its shape doesn't match `values`,
+or if either `metrics_collections` or `updates_collections` are not a list
+or tuple.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/mean_absolute_error.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/mean_absolute_error.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3da96072365
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/mean_absolute_error.md
@@ -0,0 +1,158 @@
+description: Computes the mean absolute error between the labels and predictions.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.metrics.mean_absolute_error
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the mean absolute error between the labels and predictions.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.metrics.mean_absolute_error(
+ labels, predictions, weights=None, metrics_collections=None,
+ updates_collections=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The `mean_absolute_error` function creates two local variables,
+`total` and `count` that are used to compute the mean absolute error. This
+average is weighted by `weights`, and it is ultimately returned as
+`mean_absolute_error`: an idempotent operation that simply divides `total` by
+`count`.
+
+For estimation of the metric over a stream of data, the function creates an
+`update_op` operation that updates these variables and returns the
+`mean_absolute_error`. Internally, an `absolute_errors` operation computes the
+absolute value of the differences between `predictions` and `labels`. Then
+`update_op` increments `total` with the reduced sum of the product of
+`weights` and `absolute_errors`, and it increments `count` with the reduced
+sum of `weights`
+
+If `weights` is `None`, weights default to 1. Use weights of 0 to mask values.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of the same shape as `predictions`.
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of arbitrary shape.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Optional `Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or the same rank as
+`labels`, and must be broadcastable to `labels` (i.e., all dimensions must
+be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `labels` dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`metrics_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that
+`mean_absolute_error` should be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that `update_op` should
+be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+An optional variable_scope name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`mean_absolute_error`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` representing the current mean, the value of
+`total` divided by `count`.
+ |
+
+|
+`update_op`
+ |
+
+An operation that increments the `total` and `count` variables
+appropriately and whose value matches `mean_absolute_error`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `predictions` and `labels` have mismatched shapes, or if
+`weights` is not `None` and its shape doesn't match `predictions`, or if
+either `metrics_collections` or `updates_collections` are not a list or
+tuple.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/mean_cosine_distance.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/mean_cosine_distance.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..cba46832b08
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/mean_cosine_distance.md
@@ -0,0 +1,162 @@
+description: Computes the cosine distance between the labels and predictions.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.metrics.mean_cosine_distance
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the cosine distance between the labels and predictions.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.metrics.mean_cosine_distance(
+ labels, predictions, dim, weights=None, metrics_collections=None,
+ updates_collections=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The `mean_cosine_distance` function creates two local variables,
+`total` and `count` that are used to compute the average cosine distance
+between `predictions` and `labels`. This average is weighted by `weights`,
+and it is ultimately returned as `mean_distance`, which is an idempotent
+operation that simply divides `total` by `count`.
+
+For estimation of the metric over a stream of data, the function creates an
+`update_op` operation that updates these variables and returns the
+`mean_distance`.
+
+If `weights` is `None`, weights default to 1. Use weights of 0 to mask values.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of arbitrary shape.
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of the same shape as `labels`.
+ |
+
+|
+`dim`
+ |
+
+The dimension along which the cosine distance is computed.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Optional `Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or the same rank as
+`labels`, and must be broadcastable to `labels` (i.e., all dimensions must
+be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `labels` dimension). Also,
+dimension `dim` must be `1`.
+ |
+
+|
+`metrics_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that the metric
+value variable should be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that the metric update
+ops should be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+An optional variable_scope name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`mean_distance`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` representing the current mean, the value of
+`total` divided by `count`.
+ |
+
+|
+`update_op`
+ |
+
+An operation that increments the `total` and `count` variables
+appropriately.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `predictions` and `labels` have mismatched shapes, or if
+`weights` is not `None` and its shape doesn't match `predictions`, or if
+either `metrics_collections` or `updates_collections` are not a list or
+tuple.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/mean_iou.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/mean_iou.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..bd63d5a1d52
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/mean_iou.md
@@ -0,0 +1,165 @@
+description: Calculate per-step mean Intersection-Over-Union (mIOU).
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.metrics.mean_iou
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Calculate per-step mean Intersection-Over-Union (mIOU).
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.metrics.mean_iou(
+ labels, predictions, num_classes, weights=None, metrics_collections=None,
+ updates_collections=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Mean Intersection-Over-Union is a common evaluation metric for
+semantic image segmentation, which first computes the IOU for each
+semantic class and then computes the average over classes.
+IOU is defined as follows:
+ IOU = true_positive / (true_positive + false_positive + false_negative).
+The predictions are accumulated in a confusion matrix, weighted by `weights`,
+and mIOU is then calculated from it.
+
+For estimation of the metric over a stream of data, the function creates an
+`update_op` operation that updates these variables and returns the `mean_iou`.
+
+If `weights` is `None`, weights default to 1. Use weights of 0 to mask values.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of ground truth labels with shape [batch size] and of
+type `int32` or `int64`. The tensor will be flattened if its rank > 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of prediction results for semantic labels, whose
+shape is [batch size] and type `int32` or `int64`. The tensor will be
+flattened if its rank > 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_classes`
+ |
+
+The possible number of labels the prediction task can
+have. This value must be provided, since a confusion matrix of
+dimension = [num_classes, num_classes] will be allocated.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Optional `Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or the same rank as
+`labels`, and must be broadcastable to `labels` (i.e., all dimensions must
+be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `labels` dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`metrics_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that `mean_iou`
+should be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections `update_op` should be
+added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+An optional variable_scope name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`mean_iou`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` representing the mean intersection-over-union.
+ |
+
+|
+`update_op`
+ |
+
+An operation that increments the confusion matrix.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `predictions` and `labels` have mismatched shapes, or if
+`weights` is not `None` and its shape doesn't match `predictions`, or if
+either `metrics_collections` or `updates_collections` are not a list or
+tuple.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/mean_per_class_accuracy.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/mean_per_class_accuracy.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..08458b88e0e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/mean_per_class_accuracy.md
@@ -0,0 +1,161 @@
+description: Calculates the mean of the per-class accuracies.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.metrics.mean_per_class_accuracy
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Calculates the mean of the per-class accuracies.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.metrics.mean_per_class_accuracy(
+ labels, predictions, num_classes, weights=None, metrics_collections=None,
+ updates_collections=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Calculates the accuracy for each class, then takes the mean of that.
+
+For estimation of the metric over a stream of data, the function creates an
+`update_op` operation that updates the accuracy of each class and returns
+them.
+
+If `weights` is `None`, weights default to 1. Use weights of 0 to mask values.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of ground truth labels with shape [batch size] and of
+type `int32` or `int64`. The tensor will be flattened if its rank > 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of prediction results for semantic labels, whose
+shape is [batch size] and type `int32` or `int64`. The tensor will be
+flattened if its rank > 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_classes`
+ |
+
+The possible number of labels the prediction task can
+have. This value must be provided, since two variables with shape =
+[num_classes] will be allocated.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Optional `Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or the same rank as
+`labels`, and must be broadcastable to `labels` (i.e., all dimensions must
+be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `labels` dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`metrics_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that
+`mean_per_class_accuracy'
+should be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections `update_op` should be
+added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+An optional variable_scope name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`mean_accuracy`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` representing the mean per class accuracy.
+ |
+
+|
+`update_op`
+ |
+
+An operation that updates the accuracy tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `predictions` and `labels` have mismatched shapes, or if
+`weights` is not `None` and its shape doesn't match `predictions`, or if
+either `metrics_collections` or `updates_collections` are not a list or
+tuple.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/mean_relative_error.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/mean_relative_error.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..4339e6c89cc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/mean_relative_error.md
@@ -0,0 +1,165 @@
+description: Computes the mean relative error by normalizing with the given values.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.metrics.mean_relative_error
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the mean relative error by normalizing with the given values.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.metrics.mean_relative_error(
+ labels, predictions, normalizer, weights=None, metrics_collections=None,
+ updates_collections=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The `mean_relative_error` function creates two local variables,
+`total` and `count` that are used to compute the mean relative absolute error.
+This average is weighted by `weights`, and it is ultimately returned as
+`mean_relative_error`: an idempotent operation that simply divides `total` by
+`count`.
+
+For estimation of the metric over a stream of data, the function creates an
+`update_op` operation that updates these variables and returns the
+`mean_reative_error`. Internally, a `relative_errors` operation divides the
+absolute value of the differences between `predictions` and `labels` by the
+`normalizer`. Then `update_op` increments `total` with the reduced sum of the
+product of `weights` and `relative_errors`, and it increments `count` with the
+reduced sum of `weights`.
+
+If `weights` is `None`, weights default to 1. Use weights of 0 to mask values.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of the same shape as `predictions`.
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of arbitrary shape.
+ |
+
+|
+`normalizer`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of the same shape as `predictions`.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Optional `Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or the same rank as
+`labels`, and must be broadcastable to `labels` (i.e., all dimensions must
+be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `labels` dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`metrics_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that
+`mean_relative_error` should be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that `update_op` should
+be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+An optional variable_scope name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`mean_relative_error`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` representing the current mean, the value of
+`total` divided by `count`.
+ |
+
+|
+`update_op`
+ |
+
+An operation that increments the `total` and `count` variables
+appropriately and whose value matches `mean_relative_error`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `predictions` and `labels` have mismatched shapes, or if
+`weights` is not `None` and its shape doesn't match `predictions`, or if
+either `metrics_collections` or `updates_collections` are not a list or
+tuple.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/mean_squared_error.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/mean_squared_error.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..65fccb226ff
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/mean_squared_error.md
@@ -0,0 +1,158 @@
+description: Computes the mean squared error between the labels and predictions.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.metrics.mean_squared_error
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the mean squared error between the labels and predictions.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.metrics.mean_squared_error(
+ labels, predictions, weights=None, metrics_collections=None,
+ updates_collections=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The `mean_squared_error` function creates two local variables,
+`total` and `count` that are used to compute the mean squared error.
+This average is weighted by `weights`, and it is ultimately returned as
+`mean_squared_error`: an idempotent operation that simply divides `total` by
+`count`.
+
+For estimation of the metric over a stream of data, the function creates an
+`update_op` operation that updates these variables and returns the
+`mean_squared_error`. Internally, a `squared_error` operation computes the
+element-wise square of the difference between `predictions` and `labels`. Then
+`update_op` increments `total` with the reduced sum of the product of
+`weights` and `squared_error`, and it increments `count` with the reduced sum
+of `weights`.
+
+If `weights` is `None`, weights default to 1. Use weights of 0 to mask values.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of the same shape as `predictions`.
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of arbitrary shape.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Optional `Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or the same rank as
+`labels`, and must be broadcastable to `labels` (i.e., all dimensions must
+be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `labels` dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`metrics_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that
+`mean_squared_error` should be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that `update_op` should
+be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+An optional variable_scope name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`mean_squared_error`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` representing the current mean, the value of
+`total` divided by `count`.
+ |
+
+|
+`update_op`
+ |
+
+An operation that increments the `total` and `count` variables
+appropriately and whose value matches `mean_squared_error`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `predictions` and `labels` have mismatched shapes, or if
+`weights` is not `None` and its shape doesn't match `predictions`, or if
+either `metrics_collections` or `updates_collections` are not a list or
+tuple.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/mean_tensor.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/mean_tensor.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..2da9fe4430c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/mean_tensor.md
@@ -0,0 +1,150 @@
+description: Computes the element-wise (weighted) mean of the given tensors.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.metrics.mean_tensor
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the element-wise (weighted) mean of the given tensors.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.metrics.mean_tensor(
+ values, weights=None, metrics_collections=None, updates_collections=None,
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+In contrast to the `mean` function which returns a scalar with the
+mean, this function returns an average tensor with the same shape as the
+input tensors.
+
+The `mean_tensor` function creates two local variables,
+`total_tensor` and `count_tensor` that are used to compute the average of
+`values`. This average is ultimately returned as `mean` which is an idempotent
+operation that simply divides `total` by `count`.
+
+For estimation of the metric over a stream of data, the function creates an
+`update_op` operation that updates these variables and returns the `mean`.
+`update_op` increments `total` with the reduced sum of the product of `values`
+and `weights`, and it increments `count` with the reduced sum of `weights`.
+
+If `weights` is `None`, weights default to 1. Use weights of 0 to mask values.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`values`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of arbitrary dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Optional `Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or the same rank as
+`values`, and must be broadcastable to `values` (i.e., all dimensions must
+be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `values` dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`metrics_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that `mean`
+should be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that `update_op`
+should be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+An optional variable_scope name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`mean`
+ |
+
+A float `Tensor` representing the current mean, the value of `total`
+divided by `count`.
+ |
+
+|
+`update_op`
+ |
+
+An operation that increments the `total` and `count` variables
+appropriately and whose value matches `mean_value`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `weights` is not `None` and its shape doesn't match `values`,
+or if either `metrics_collections` or `updates_collections` are not a list
+or tuple.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/percentage_below.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/percentage_below.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..f89b37a0372
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/percentage_below.md
@@ -0,0 +1,153 @@
+description: Computes the percentage of values less than the given threshold.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.metrics.percentage_below
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the percentage of values less than the given threshold.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.metrics.percentage_below(
+ values, threshold, weights=None, metrics_collections=None,
+ updates_collections=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The `percentage_below` function creates two local variables,
+`total` and `count` that are used to compute the percentage of `values` that
+fall below `threshold`. This rate is weighted by `weights`, and it is
+ultimately returned as `percentage` which is an idempotent operation that
+simply divides `total` by `count`.
+
+For estimation of the metric over a stream of data, the function creates an
+`update_op` operation that updates these variables and returns the
+`percentage`.
+
+If `weights` is `None`, weights default to 1. Use weights of 0 to mask values.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`values`
+ |
+
+A numeric `Tensor` of arbitrary size.
+ |
+
+|
+`threshold`
+ |
+
+A scalar threshold.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Optional `Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or the same rank as
+`values`, and must be broadcastable to `values` (i.e., all dimensions must
+be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `values` dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`metrics_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that the metric
+value variable should be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that the metric update
+ops should be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+An optional variable_scope name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`percentage`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` representing the current mean, the value of `total`
+divided by `count`.
+ |
+
+|
+`update_op`
+ |
+
+An operation that increments the `total` and `count` variables
+appropriately.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `weights` is not `None` and its shape doesn't match `values`,
+or if either `metrics_collections` or `updates_collections` are not a list
+or tuple.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/precision.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/precision.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a7967620a8d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/precision.md
@@ -0,0 +1,158 @@
+description: Computes the precision of the predictions with respect to the labels.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.metrics.precision
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the precision of the predictions with respect to the labels.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.metrics.precision(
+ labels, predictions, weights=None, metrics_collections=None,
+ updates_collections=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The `precision` function creates two local variables,
+`true_positives` and `false_positives`, that are used to compute the
+precision. This value is ultimately returned as `precision`, an idempotent
+operation that simply divides `true_positives` by the sum of `true_positives`
+and `false_positives`.
+
+For estimation of the metric over a stream of data, the function creates an
+`update_op` operation that updates these variables and returns the
+`precision`. `update_op` weights each prediction by the corresponding value in
+`weights`.
+
+If `weights` is `None`, weights default to 1. Use weights of 0 to mask values.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+The ground truth values, a `Tensor` whose dimensions must match
+`predictions`. Will be cast to `bool`.
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions`
+ |
+
+The predicted values, a `Tensor` of arbitrary dimensions. Will
+be cast to `bool`.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Optional `Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or the same rank as
+`labels`, and must be broadcastable to `labels` (i.e., all dimensions must
+be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `labels` dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`metrics_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that `precision` should
+be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that `update_op` should
+be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+An optional variable_scope name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`precision`
+ |
+
+Scalar float `Tensor` with the value of `true_positives`
+divided by the sum of `true_positives` and `false_positives`.
+ |
+
+|
+`update_op`
+ |
+
+`Operation` that increments `true_positives` and
+`false_positives` variables appropriately and whose value matches
+`precision`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `predictions` and `labels` have mismatched shapes, or if
+`weights` is not `None` and its shape doesn't match `predictions`, or if
+either `metrics_collections` or `updates_collections` are not a list or
+tuple.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/precision_at_k.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/precision_at_k.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..fd3dcca72d9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/precision_at_k.md
@@ -0,0 +1,194 @@
+description: Computes precision@k of the predictions with respect to sparse labels.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.metrics.precision_at_k
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes precision@k of the predictions with respect to sparse labels.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.metrics.precision_at_k(
+ labels, predictions, k, class_id=None, weights=None, metrics_collections=None,
+ updates_collections=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+If `class_id` is specified, we calculate precision by considering only the
+ entries in the batch for which `class_id` is in the top-k highest
+ `predictions`, and computing the fraction of them for which `class_id` is
+ indeed a correct label.
+If `class_id` is not specified, we'll calculate precision as how often on
+ average a class among the top-k classes with the highest predicted values
+ of a batch entry is correct and can be found in the label for that entry.
+
+`precision_at_k` creates two local variables,
+`true_positive_at_` and `false_positive_at_`, that are used to compute
+the precision@k frequency. This frequency is ultimately returned as
+`precision_at_`: an idempotent operation that simply divides
+`true_positive_at_` by total (`true_positive_at_` +
+`false_positive_at_`).
+
+For estimation of the metric over a stream of data, the function creates an
+`update_op` operation that updates these variables and returns the
+`precision_at_`. Internally, a `top_k` operation computes a `Tensor`
+indicating the top `k` `predictions`. Set operations applied to `top_k` and
+`labels` calculate the true positives and false positives weighted by
+`weights`. Then `update_op` increments `true_positive_at_` and
+`false_positive_at_` using these values.
+
+If `weights` is `None`, weights default to 1. Use weights of 0 to mask values.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+`int64` `Tensor` or `SparseTensor` with shape
+[D1, ... DN, num_labels] or [D1, ... DN], where the latter implies
+num_labels=1. N >= 1 and num_labels is the number of target classes for
+the associated prediction. Commonly, N=1 and `labels` has shape
+[batch_size, num_labels]. [D1, ... DN] must match `predictions`. Values
+should be in range [0, num_classes), where num_classes is the last
+dimension of `predictions`. Values outside this range are ignored.
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions`
+ |
+
+Float `Tensor` with shape [D1, ... DN, num_classes] where
+N >= 1. Commonly, N=1 and predictions has shape [batch size, num_classes].
+The final dimension contains the logit values for each class. [D1, ... DN]
+must match `labels`.
+ |
+
+|
+`k`
+ |
+
+Integer, k for @k metric.
+ |
+
+|
+`class_id`
+ |
+
+Integer class ID for which we want binary metrics. This should be
+in range [0, num_classes], where num_classes is the last dimension of
+`predictions`. If `class_id` is outside this range, the method returns
+NAN.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+`Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or n-1, where n is the rank of
+`labels`. If the latter, it must be broadcastable to `labels` (i.e., all
+dimensions must be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `labels`
+dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`metrics_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that values should
+be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that updates should
+be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of new update operation, and namespace for other dependent ops.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`precision`
+ |
+
+Scalar `float64` `Tensor` with the value of `true_positives`
+divided by the sum of `true_positives` and `false_positives`.
+ |
+
+|
+`update_op`
+ |
+
+`Operation` that increments `true_positives` and
+`false_positives` variables appropriately, and whose value matches
+`precision`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `weights` is not `None` and its shape doesn't match
+`predictions`, or if either `metrics_collections` or `updates_collections`
+are not a list or tuple.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/precision_at_thresholds.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/precision_at_thresholds.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..8c29f880bde
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/precision_at_thresholds.md
@@ -0,0 +1,165 @@
+description: Computes precision values for different thresholds on predictions.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.metrics.precision_at_thresholds
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes precision values for different `thresholds` on `predictions`.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.metrics.precision_at_thresholds(
+ labels, predictions, thresholds, weights=None, metrics_collections=None,
+ updates_collections=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The `precision_at_thresholds` function creates four local variables,
+`true_positives`, `true_negatives`, `false_positives` and `false_negatives`
+for various values of thresholds. `precision[i]` is defined as the total
+weight of values in `predictions` above `thresholds[i]` whose corresponding
+entry in `labels` is `True`, divided by the total weight of values in
+`predictions` above `thresholds[i]` (`true_positives[i] / (true_positives[i] +
+false_positives[i])`).
+
+For estimation of the metric over a stream of data, the function creates an
+`update_op` operation that updates these variables and returns the
+`precision`.
+
+If `weights` is `None`, weights default to 1. Use weights of 0 to mask values.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+The ground truth values, a `Tensor` whose dimensions must match
+`predictions`. Will be cast to `bool`.
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions`
+ |
+
+A floating point `Tensor` of arbitrary shape and whose values
+are in the range `[0, 1]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`thresholds`
+ |
+
+A python list or tuple of float thresholds in `[0, 1]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Optional `Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or the same rank as
+`labels`, and must be broadcastable to `labels` (i.e., all dimensions must
+be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `labels` dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`metrics_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that `auc` should be
+added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that `update_op` should
+be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+An optional variable_scope name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`precision`
+ |
+
+A float `Tensor` of shape `[len(thresholds)]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`update_op`
+ |
+
+An operation that increments the `true_positives`,
+`true_negatives`, `false_positives` and `false_negatives` variables that
+are used in the computation of `precision`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `predictions` and `labels` have mismatched shapes, or if
+`weights` is not `None` and its shape doesn't match `predictions`, or if
+either `metrics_collections` or `updates_collections` are not a list or
+tuple.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/precision_at_top_k.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/precision_at_top_k.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..16f91f33aac
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/precision_at_top_k.md
@@ -0,0 +1,173 @@
+description: Computes precision@k of the predictions with respect to sparse labels.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.metrics.precision_at_top_k
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes precision@k of the predictions with respect to sparse labels.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.metrics.precision_at_top_k(
+ labels, predictions_idx, k=None, class_id=None, weights=None,
+ metrics_collections=None, updates_collections=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Differs from `sparse_precision_at_k` in that predictions must be in the form
+of top `k` class indices, whereas `sparse_precision_at_k` expects logits.
+Refer to `sparse_precision_at_k` for more details.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+`int64` `Tensor` or `SparseTensor` with shape
+[D1, ... DN, num_labels] or [D1, ... DN], where the latter implies
+num_labels=1. N >= 1 and num_labels is the number of target classes for
+the associated prediction. Commonly, N=1 and `labels` has shape
+[batch_size, num_labels]. [D1, ... DN] must match `predictions`. Values
+should be in range [0, num_classes), where num_classes is the last
+dimension of `predictions`. Values outside this range are ignored.
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions_idx`
+ |
+
+Integer `Tensor` with shape [D1, ... DN, k] where
+N >= 1. Commonly, N=1 and predictions has shape [batch size, k].
+The final dimension contains the top `k` predicted class indices.
+[D1, ... DN] must match `labels`.
+ |
+
+|
+`k`
+ |
+
+Integer, k for @k metric. Only used for the default op name.
+ |
+
+|
+`class_id`
+ |
+
+Integer class ID for which we want binary metrics. This should be
+in range [0, num_classes], where num_classes is the last dimension of
+`predictions`. If `class_id` is outside this range, the method returns
+NAN.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+`Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or n-1, where n is the rank of
+`labels`. If the latter, it must be broadcastable to `labels` (i.e., all
+dimensions must be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `labels`
+dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`metrics_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that values should
+be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that updates should
+be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of new update operation, and namespace for other dependent ops.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`precision`
+ |
+
+Scalar `float64` `Tensor` with the value of `true_positives`
+divided by the sum of `true_positives` and `false_positives`.
+ |
+
+|
+`update_op`
+ |
+
+`Operation` that increments `true_positives` and
+`false_positives` variables appropriately, and whose value matches
+`precision`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `weights` is not `None` and its shape doesn't match
+`predictions`, or if either `metrics_collections` or `updates_collections`
+are not a list or tuple.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/recall.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/recall.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..4c44617670c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/recall.md
@@ -0,0 +1,156 @@
+description: Computes the recall of the predictions with respect to the labels.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.metrics.recall
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the recall of the predictions with respect to the labels.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.metrics.recall(
+ labels, predictions, weights=None, metrics_collections=None,
+ updates_collections=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The `recall` function creates two local variables, `true_positives`
+and `false_negatives`, that are used to compute the recall. This value is
+ultimately returned as `recall`, an idempotent operation that simply divides
+`true_positives` by the sum of `true_positives` and `false_negatives`.
+
+For estimation of the metric over a stream of data, the function creates an
+`update_op` that updates these variables and returns the `recall`. `update_op`
+weights each prediction by the corresponding value in `weights`.
+
+If `weights` is `None`, weights default to 1. Use weights of 0 to mask values.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+The ground truth values, a `Tensor` whose dimensions must match
+`predictions`. Will be cast to `bool`.
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions`
+ |
+
+The predicted values, a `Tensor` of arbitrary dimensions. Will
+be cast to `bool`.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Optional `Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or the same rank as
+`labels`, and must be broadcastable to `labels` (i.e., all dimensions must
+be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `labels` dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`metrics_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that `recall` should
+be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that `update_op` should
+be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+An optional variable_scope name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`recall`
+ |
+
+Scalar float `Tensor` with the value of `true_positives` divided
+by the sum of `true_positives` and `false_negatives`.
+ |
+
+|
+`update_op`
+ |
+
+`Operation` that increments `true_positives` and
+`false_negatives` variables appropriately and whose value matches
+`recall`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `predictions` and `labels` have mismatched shapes, or if
+`weights` is not `None` and its shape doesn't match `predictions`, or if
+either `metrics_collections` or `updates_collections` are not a list or
+tuple.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/recall_at_k.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/recall_at_k.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..c1ddf9794ef
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/recall_at_k.md
@@ -0,0 +1,193 @@
+description: Computes recall@k of the predictions with respect to sparse labels.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.metrics.recall_at_k
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes recall@k of the predictions with respect to sparse labels.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.metrics.recall_at_k(
+ labels, predictions, k, class_id=None, weights=None, metrics_collections=None,
+ updates_collections=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+If `class_id` is specified, we calculate recall by considering only the
+ entries in the batch for which `class_id` is in the label, and computing
+ the fraction of them for which `class_id` is in the top-k `predictions`.
+If `class_id` is not specified, we'll calculate recall as how often on
+ average a class among the labels of a batch entry is in the top-k
+ `predictions`.
+
+`sparse_recall_at_k` creates two local variables,
+`true_positive_at_` and `false_negative_at_`, that are used to compute
+the recall_at_k frequency. This frequency is ultimately returned as
+`recall_at_`: an idempotent operation that simply divides
+`true_positive_at_` by total (`true_positive_at_` +
+`false_negative_at_`).
+
+For estimation of the metric over a stream of data, the function creates an
+`update_op` operation that updates these variables and returns the
+`recall_at_`. Internally, a `top_k` operation computes a `Tensor`
+indicating the top `k` `predictions`. Set operations applied to `top_k` and
+`labels` calculate the true positives and false negatives weighted by
+`weights`. Then `update_op` increments `true_positive_at_` and
+`false_negative_at_` using these values.
+
+If `weights` is `None`, weights default to 1. Use weights of 0 to mask values.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+`int64` `Tensor` or `SparseTensor` with shape
+[D1, ... DN, num_labels] or [D1, ... DN], where the latter implies
+num_labels=1. N >= 1 and num_labels is the number of target classes for
+the associated prediction. Commonly, N=1 and `labels` has shape
+[batch_size, num_labels]. [D1, ... DN] must match `predictions`. Values
+should be in range [0, num_classes), where num_classes is the last
+dimension of `predictions`. Values outside this range always count
+towards `false_negative_at_`.
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions`
+ |
+
+Float `Tensor` with shape [D1, ... DN, num_classes] where
+N >= 1. Commonly, N=1 and predictions has shape [batch size, num_classes].
+The final dimension contains the logit values for each class. [D1, ... DN]
+must match `labels`.
+ |
+
+|
+`k`
+ |
+
+Integer, k for @k metric.
+ |
+
+|
+`class_id`
+ |
+
+Integer class ID for which we want binary metrics. This should be
+in range [0, num_classes), where num_classes is the last dimension of
+`predictions`. If class_id is outside this range, the method returns NAN.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+`Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or n-1, where n is the rank of
+`labels`. If the latter, it must be broadcastable to `labels` (i.e., all
+dimensions must be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `labels`
+dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`metrics_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that values should
+be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that updates should
+be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of new update operation, and namespace for other dependent ops.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`recall`
+ |
+
+Scalar `float64` `Tensor` with the value of `true_positives` divided
+by the sum of `true_positives` and `false_negatives`.
+ |
+
+|
+`update_op`
+ |
+
+`Operation` that increments `true_positives` and
+`false_negatives` variables appropriately, and whose value matches
+`recall`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `weights` is not `None` and its shape doesn't match
+`predictions`, or if either `metrics_collections` or `updates_collections`
+are not a list or tuple.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/recall_at_thresholds.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/recall_at_thresholds.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..76cbad44f7f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/recall_at_thresholds.md
@@ -0,0 +1,163 @@
+description: Computes various recall values for different thresholds on predictions.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.metrics.recall_at_thresholds
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes various recall values for different `thresholds` on `predictions`.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.metrics.recall_at_thresholds(
+ labels, predictions, thresholds, weights=None, metrics_collections=None,
+ updates_collections=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The `recall_at_thresholds` function creates four local variables,
+`true_positives`, `true_negatives`, `false_positives` and `false_negatives`
+for various values of thresholds. `recall[i]` is defined as the total weight
+of values in `predictions` above `thresholds[i]` whose corresponding entry in
+`labels` is `True`, divided by the total weight of `True` values in `labels`
+(`true_positives[i] / (true_positives[i] + false_negatives[i])`).
+
+For estimation of the metric over a stream of data, the function creates an
+`update_op` operation that updates these variables and returns the `recall`.
+
+If `weights` is `None`, weights default to 1. Use weights of 0 to mask values.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+The ground truth values, a `Tensor` whose dimensions must match
+`predictions`. Will be cast to `bool`.
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions`
+ |
+
+A floating point `Tensor` of arbitrary shape and whose values
+are in the range `[0, 1]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`thresholds`
+ |
+
+A python list or tuple of float thresholds in `[0, 1]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Optional `Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or the same rank as
+`labels`, and must be broadcastable to `labels` (i.e., all dimensions must
+be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `labels` dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`metrics_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that `recall` should be
+added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that `update_op` should
+be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+An optional variable_scope name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`recall`
+ |
+
+A float `Tensor` of shape `[len(thresholds)]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`update_op`
+ |
+
+An operation that increments the `true_positives`,
+`true_negatives`, `false_positives` and `false_negatives` variables that
+are used in the computation of `recall`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `predictions` and `labels` have mismatched shapes, or if
+`weights` is not `None` and its shape doesn't match `predictions`, or if
+either `metrics_collections` or `updates_collections` are not a list or
+tuple.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/recall_at_top_k.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/recall_at_top_k.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..5049c6b1857
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/recall_at_top_k.md
@@ -0,0 +1,166 @@
+description: Computes recall@k of top-k predictions with respect to sparse labels.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.metrics.recall_at_top_k
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes recall@k of top-k predictions with respect to sparse labels.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.metrics.recall_at_top_k(
+ labels, predictions_idx, k=None, class_id=None, weights=None,
+ metrics_collections=None, updates_collections=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Differs from `recall_at_k` in that predictions must be in the form of top `k`
+class indices, whereas `recall_at_k` expects logits. Refer to `recall_at_k`
+for more details.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+`int64` `Tensor` or `SparseTensor` with shape
+[D1, ... DN, num_labels] or [D1, ... DN], where the latter implies
+num_labels=1. N >= 1 and num_labels is the number of target classes for
+the associated prediction. Commonly, N=1 and `labels` has shape
+[batch_size, num_labels]. [D1, ... DN] must match `predictions`. Values
+should be in range [0, num_classes), where num_classes is the last
+dimension of `predictions`. Values outside this range always count
+towards `false_negative_at_`.
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions_idx`
+ |
+
+Integer `Tensor` with shape [D1, ... DN, k] where N >= 1.
+Commonly, N=1 and predictions has shape [batch size, k]. The final
+dimension contains the top `k` predicted class indices. [D1, ... DN] must
+match `labels`.
+ |
+
+|
+`k`
+ |
+
+Integer, k for @k metric. Only used for the default op name.
+ |
+
+|
+`class_id`
+ |
+
+Integer class ID for which we want binary metrics. This should be
+in range [0, num_classes), where num_classes is the last dimension of
+`predictions`. If class_id is outside this range, the method returns NAN.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+`Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or n-1, where n is the rank of
+`labels`. If the latter, it must be broadcastable to `labels` (i.e., all
+dimensions must be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `labels`
+dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`metrics_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that values should
+be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that updates should
+be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name of new update operation, and namespace for other dependent ops.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`recall`
+ |
+
+Scalar `float64` `Tensor` with the value of `true_positives` divided
+by the sum of `true_positives` and `false_negatives`.
+ |
+
+|
+`update_op`
+ |
+
+`Operation` that increments `true_positives` and
+`false_negatives` variables appropriately, and whose value matches
+`recall`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `weights` is not `None` and its shape doesn't match
+`predictions`, or if either `metrics_collections` or `updates_collections`
+are not a list or tuple.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/root_mean_squared_error.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/root_mean_squared_error.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..9cb0fd03008
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/root_mean_squared_error.md
@@ -0,0 +1,158 @@
+description: Computes the root mean squared error between the labels and predictions.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.metrics.root_mean_squared_error
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the root mean squared error between the labels and predictions.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.metrics.root_mean_squared_error(
+ labels, predictions, weights=None, metrics_collections=None,
+ updates_collections=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The `root_mean_squared_error` function creates two local variables,
+`total` and `count` that are used to compute the root mean squared error.
+This average is weighted by `weights`, and it is ultimately returned as
+`root_mean_squared_error`: an idempotent operation that takes the square root
+of the division of `total` by `count`.
+
+For estimation of the metric over a stream of data, the function creates an
+`update_op` operation that updates these variables and returns the
+`root_mean_squared_error`. Internally, a `squared_error` operation computes
+the element-wise square of the difference between `predictions` and `labels`.
+Then `update_op` increments `total` with the reduced sum of the product of
+`weights` and `squared_error`, and it increments `count` with the reduced sum
+of `weights`.
+
+If `weights` is `None`, weights default to 1. Use weights of 0 to mask values.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of the same shape as `predictions`.
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of arbitrary shape.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Optional `Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or the same rank as
+`labels`, and must be broadcastable to `labels` (i.e., all dimensions must
+be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `labels` dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`metrics_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that
+`root_mean_squared_error` should be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that `update_op` should
+be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+An optional variable_scope name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`root_mean_squared_error`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` representing the current mean, the value
+of `total` divided by `count`.
+ |
+
+|
+`update_op`
+ |
+
+An operation that increments the `total` and `count` variables
+appropriately and whose value matches `root_mean_squared_error`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `predictions` and `labels` have mismatched shapes, or if
+`weights` is not `None` and its shape doesn't match `predictions`, or if
+either `metrics_collections` or `updates_collections` are not a list or
+tuple.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/sensitivity_at_specificity.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/sensitivity_at_specificity.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..562fa7a8e0d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/sensitivity_at_specificity.md
@@ -0,0 +1,177 @@
+description: Computes the specificity at a given sensitivity.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.metrics.sensitivity_at_specificity
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the specificity at a given sensitivity.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.metrics.sensitivity_at_specificity(
+ labels, predictions, specificity, weights=None, num_thresholds=200,
+ metrics_collections=None, updates_collections=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The `sensitivity_at_specificity` function creates four local
+variables, `true_positives`, `true_negatives`, `false_positives` and
+`false_negatives` that are used to compute the sensitivity at the given
+specificity value. The threshold for the given specificity value is computed
+and used to evaluate the corresponding sensitivity.
+
+For estimation of the metric over a stream of data, the function creates an
+`update_op` operation that updates these variables and returns the
+`sensitivity`. `update_op` increments the `true_positives`, `true_negatives`,
+`false_positives` and `false_negatives` counts with the weight of each case
+found in the `predictions` and `labels`.
+
+If `weights` is `None`, weights default to 1. Use weights of 0 to mask values.
+
+For additional information about specificity and sensitivity, see the
+following: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sensitivity_and_specificity
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+The ground truth values, a `Tensor` whose dimensions must match
+`predictions`. Will be cast to `bool`.
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions`
+ |
+
+A floating point `Tensor` of arbitrary shape and whose values
+are in the range `[0, 1]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`specificity`
+ |
+
+A scalar value in range `[0, 1]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Optional `Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or the same rank as
+`labels`, and must be broadcastable to `labels` (i.e., all dimensions must
+be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `labels` dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`num_thresholds`
+ |
+
+The number of thresholds to use for matching the given
+specificity.
+ |
+
+|
+`metrics_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that `sensitivity`
+should be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that `update_op` should
+be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+An optional variable_scope name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sensitivity`
+ |
+
+A scalar `Tensor` representing the sensitivity at the given
+`specificity` value.
+ |
+
+|
+`update_op`
+ |
+
+An operation that increments the `true_positives`,
+`true_negatives`, `false_positives` and `false_negatives` variables
+appropriately and whose value matches `sensitivity`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `predictions` and `labels` have mismatched shapes, if
+`weights` is not `None` and its shape doesn't match `predictions`, or if
+`specificity` is not between 0 and 1, or if either `metrics_collections`
+or `updates_collections` are not a list or tuple.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/sparse_average_precision_at_k.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/sparse_average_precision_at_k.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..94ba541e580
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/sparse_average_precision_at_k.md
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
+description: Renamed to average_precision_at_k, please use that method instead. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.metrics.sparse_average_precision_at_k
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Renamed to `average_precision_at_k`, please use that method instead. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.metrics.sparse_average_precision_at_k(
+ labels, predictions, k, weights=None, metrics_collections=None,
+ updates_collections=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use average_precision_at_k instead
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/sparse_precision_at_k.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/sparse_precision_at_k.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..03d3c6ecd84
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/sparse_precision_at_k.md
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
+description: Renamed to precision_at_k, please use that method instead. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.metrics.sparse_precision_at_k
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Renamed to `precision_at_k`, please use that method instead. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.metrics.sparse_precision_at_k(
+ labels, predictions, k, class_id=None, weights=None, metrics_collections=None,
+ updates_collections=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use precision_at_k instead
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/specificity_at_sensitivity.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/specificity_at_sensitivity.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..638c7119458
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/specificity_at_sensitivity.md
@@ -0,0 +1,177 @@
+description: Computes the specificity at a given sensitivity.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.metrics.specificity_at_sensitivity
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the specificity at a given sensitivity.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.metrics.specificity_at_sensitivity(
+ labels, predictions, sensitivity, weights=None, num_thresholds=200,
+ metrics_collections=None, updates_collections=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The `specificity_at_sensitivity` function creates four local
+variables, `true_positives`, `true_negatives`, `false_positives` and
+`false_negatives` that are used to compute the specificity at the given
+sensitivity value. The threshold for the given sensitivity value is computed
+and used to evaluate the corresponding specificity.
+
+For estimation of the metric over a stream of data, the function creates an
+`update_op` operation that updates these variables and returns the
+`specificity`. `update_op` increments the `true_positives`, `true_negatives`,
+`false_positives` and `false_negatives` counts with the weight of each case
+found in the `predictions` and `labels`.
+
+If `weights` is `None`, weights default to 1. Use weights of 0 to mask values.
+
+For additional information about specificity and sensitivity, see the
+following: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sensitivity_and_specificity
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+The ground truth values, a `Tensor` whose dimensions must match
+`predictions`. Will be cast to `bool`.
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions`
+ |
+
+A floating point `Tensor` of arbitrary shape and whose values
+are in the range `[0, 1]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`sensitivity`
+ |
+
+A scalar value in range `[0, 1]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Optional `Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or the same rank as
+`labels`, and must be broadcastable to `labels` (i.e., all dimensions must
+be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `labels` dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`num_thresholds`
+ |
+
+The number of thresholds to use for matching the given
+sensitivity.
+ |
+
+|
+`metrics_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that `specificity`
+should be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that `update_op` should
+be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+An optional variable_scope name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`specificity`
+ |
+
+A scalar `Tensor` representing the specificity at the given
+`sensitivity` value.
+ |
+
+|
+`update_op`
+ |
+
+An operation that increments the `true_positives`,
+`true_negatives`, `false_positives` and `false_negatives` variables
+appropriately and whose value matches `specificity`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `predictions` and `labels` have mismatched shapes, if
+`weights` is not `None` and its shape doesn't match `predictions`, or if
+`sensitivity` is not between 0 and 1, or if either `metrics_collections`
+or `updates_collections` are not a list or tuple.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/true_negatives.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/true_negatives.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..7b2ca269a0e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/true_negatives.md
@@ -0,0 +1,144 @@
+description: Sum the weights of true_negatives.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.metrics.true_negatives
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Sum the weights of true_negatives.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.metrics.true_negatives(
+ labels, predictions, weights=None, metrics_collections=None,
+ updates_collections=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+If `weights` is `None`, weights default to 1. Use weights of 0 to mask values.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+The ground truth values, a `Tensor` whose dimensions must match
+`predictions`. Will be cast to `bool`.
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions`
+ |
+
+The predicted values, a `Tensor` of arbitrary dimensions. Will
+be cast to `bool`.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Optional `Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or the same rank as
+`labels`, and must be broadcastable to `labels` (i.e., all dimensions must
+be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `labels` dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`metrics_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that the metric
+value variable should be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that the metric update
+ops should be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+An optional variable_scope name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value_tensor`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` representing the current value of the metric.
+ |
+
+|
+`update_op`
+ |
+
+An operation that accumulates the error from a batch of data.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `predictions` and `labels` have mismatched shapes, or if
+`weights` is not `None` and its shape doesn't match `predictions`, or if
+either `metrics_collections` or `updates_collections` are not a list or
+tuple.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/true_negatives_at_thresholds.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/true_negatives_at_thresholds.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3fd2eb15206
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/true_negatives_at_thresholds.md
@@ -0,0 +1,152 @@
+description: Computes true negatives at provided threshold values.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.metrics.true_negatives_at_thresholds
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes true negatives at provided threshold values.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.metrics.true_negatives_at_thresholds(
+ labels, predictions, thresholds, weights=None, metrics_collections=None,
+ updates_collections=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+If `weights` is `None`, weights default to 1. Use weights of 0 to mask values.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` whose shape matches `predictions`. Will be cast to
+`bool`.
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions`
+ |
+
+A floating point `Tensor` of arbitrary shape and whose values
+are in the range `[0, 1]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`thresholds`
+ |
+
+A python list or tuple of float thresholds in `[0, 1]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Optional `Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or the same rank as
+`labels`, and must be broadcastable to `labels` (i.e., all dimensions must
+be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `labels` dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`metrics_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that `true_negatives`
+should be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that `update_op` should
+be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+An optional variable_scope name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`true_negatives`
+ |
+
+A float `Tensor` of shape `[len(thresholds)]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`update_op`
+ |
+
+An operation that updates the `true_negatives` variable and
+returns its current value.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `predictions` and `labels` have mismatched shapes, or if
+`weights` is not `None` and its shape doesn't match `predictions`, or if
+either `metrics_collections` or `updates_collections` are not a list or
+tuple.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/true_positives.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/true_positives.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..0c4e383d8c9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/true_positives.md
@@ -0,0 +1,144 @@
+description: Sum the weights of true_positives.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.metrics.true_positives
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Sum the weights of true_positives.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.metrics.true_positives(
+ labels, predictions, weights=None, metrics_collections=None,
+ updates_collections=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+If `weights` is `None`, weights default to 1. Use weights of 0 to mask values.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+The ground truth values, a `Tensor` whose dimensions must match
+`predictions`. Will be cast to `bool`.
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions`
+ |
+
+The predicted values, a `Tensor` of arbitrary dimensions. Will
+be cast to `bool`.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Optional `Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or the same rank as
+`labels`, and must be broadcastable to `labels` (i.e., all dimensions must
+be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `labels` dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`metrics_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that the metric
+value variable should be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that the metric update
+ops should be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+An optional variable_scope name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value_tensor`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` representing the current value of the metric.
+ |
+
+|
+`update_op`
+ |
+
+An operation that accumulates the error from a batch of data.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `predictions` and `labels` have mismatched shapes, or if
+`weights` is not `None` and its shape doesn't match `predictions`, or if
+either `metrics_collections` or `updates_collections` are not a list or
+tuple.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/true_positives_at_thresholds.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/true_positives_at_thresholds.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..fbfcdadf766
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/metrics/true_positives_at_thresholds.md
@@ -0,0 +1,152 @@
+description: Computes true positives at provided threshold values.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.metrics.true_positives_at_thresholds
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes true positives at provided threshold values.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.metrics.true_positives_at_thresholds(
+ labels, predictions, thresholds, weights=None, metrics_collections=None,
+ updates_collections=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+If `weights` is `None`, weights default to 1. Use weights of 0 to mask values.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` whose shape matches `predictions`. Will be cast to
+`bool`.
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions`
+ |
+
+A floating point `Tensor` of arbitrary shape and whose values
+are in the range `[0, 1]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`thresholds`
+ |
+
+A python list or tuple of float thresholds in `[0, 1]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+Optional `Tensor` whose rank is either 0, or the same rank as
+`labels`, and must be broadcastable to `labels` (i.e., all dimensions must
+be either `1`, or the same as the corresponding `labels` dimension).
+ |
+
+|
+`metrics_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that `true_positives`
+should be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates_collections`
+ |
+
+An optional list of collections that `update_op` should
+be added to.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+An optional variable_scope name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`true_positives`
+ |
+
+A float `Tensor` of shape `[len(thresholds)]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`update_op`
+ |
+
+An operation that updates the `true_positives` variable and
+returns its current value.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `predictions` and `labels` have mismatched shapes, or if
+`weights` is not `None` and its shape doesn't match `predictions`, or if
+either `metrics_collections` or `updates_collections` are not a list or
+tuple.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/min_max_variable_partitioner.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/min_max_variable_partitioner.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..cb209c23a66
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/min_max_variable_partitioner.md
@@ -0,0 +1,93 @@
+description: Partitioner to allocate minimum size per slice.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.min_max_variable_partitioner
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Partitioner to allocate minimum size per slice.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.min_max_variable_partitioner(
+ max_partitions=1, axis=0, min_slice_size=(256 << 10),
+ bytes_per_string_element=16
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns a partitioner that partitions the variable of given shape and dtype
+such that each partition has a minimum of `min_slice_size` slice of the
+variable. The maximum number of such partitions (upper bound) is given by
+`max_partitions`.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`max_partitions`
+ |
+
+Upper bound on the number of partitions. Defaults to 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`axis`
+ |
+
+Axis along which to partition the variable. Defaults to 0.
+ |
+
+|
+`min_slice_size`
+ |
+
+Minimum size of the variable slice per partition. Defaults
+to 256K.
+ |
+
+|
+`bytes_per_string_element`
+ |
+
+If the `Variable` is of type string, this provides
+an estimate of how large each scalar in the `Variable` is.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A partition function usable as the `partitioner` argument to
+`variable_scope` and `get_variable`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/mixed_precision.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/mixed_precision.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..00fe0c10237
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/mixed_precision.md
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+description: Public API for tf.mixed_precision namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.mixed_precision
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.mixed_precision namespace.
+
+
+
+## Modules
+
+[`experimental`](../../../tf/compat/v1/mixed_precision/experimental.md) module: Public API for tf.mixed_precision.experimental namespace.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/mixed_precision/experimental.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/mixed_precision/experimental.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..9f939f916b6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/mixed_precision/experimental.md
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+description: Public API for tf.mixed_precision.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.mixed_precision.experimental
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.mixed_precision.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class DynamicLossScale`](../../../../tf/mixed_precision/experimental/DynamicLossScale.md): Loss scale that dynamically adjusts itself.
+
+[`class FixedLossScale`](../../../../tf/mixed_precision/experimental/FixedLossScale.md): Loss scale with a fixed value.
+
+[`class LossScale`](../../../../tf/mixed_precision/experimental/LossScale.md): Base class for all loss scales.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/mlir.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/mlir.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..da9d5f2fb27
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/mlir.md
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+description: Public API for tf.mlir namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.mlir
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.mlir namespace.
+
+
+
+## Modules
+
+[`experimental`](../../../tf/compat/v1/mlir/experimental.md) module: Public API for tf.mlir.experimental namespace.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/mlir/experimental.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/mlir/experimental.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..9483dc67d22
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/mlir/experimental.md
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+description: Public API for tf.mlir.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.mlir.experimental
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.mlir.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`convert_graph_def(...)`](../../../../tf/mlir/experimental/convert_graph_def.md): Import a GraphDef and convert it to a textual MLIR module.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/model_variables.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/model_variables.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..c77eb4efe84
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/model_variables.md
@@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
+description: Returns all variables in the MODEL_VARIABLES collection.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.model_variables
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns all variables in the MODEL_VARIABLES collection.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.model_variables(
+ scope=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`scope`
+ |
+
+(Optional.) A string. If supplied, the resulting list is filtered to
+include only items whose `name` attribute matches `scope` using
+`re.match`. Items without a `name` attribute are never returned if a scope
+is supplied. The choice of `re.match` means that a `scope` without special
+tokens filters by prefix.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of local Variable objects.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/moving_average_variables.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/moving_average_variables.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e06bce65275
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/moving_average_variables.md
@@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
+description: Returns all variables that maintain their moving averages.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.moving_average_variables
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns all variables that maintain their moving averages.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.moving_average_variables(
+ scope=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+If an `ExponentialMovingAverage` object is created and the `apply()`
+method is called on a list of variables, these variables will
+be added to the `GraphKeys.MOVING_AVERAGE_VARIABLES` collection.
+This convenience function returns the contents of that collection.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`scope`
+ |
+
+(Optional.) A string. If supplied, the resulting list is filtered to
+include only items whose `name` attribute matches `scope` using
+`re.match`. Items without a `name` attribute are never returned if a scope
+is supplied. The choice of `re.match` means that a `scope` without special
+tokens filters by prefix.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of Variable objects.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/multinomial.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/multinomial.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..360d8eeda95
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/multinomial.md
@@ -0,0 +1,118 @@
+description: Draws samples from a multinomial distribution. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.multinomial
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Draws samples from a multinomial distribution. (deprecated)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.random.multinomial`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.multinomial(
+ logits, num_samples, seed=None, name=None, output_dtype=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use tf.random.categorical instead.
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+# samples has shape [1, 5], where each value is either 0 or 1 with equal
+# probability.
+samples = tf.random.categorical(tf.math.log([[0.5, 0.5]]), 5)
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`logits`
+ |
+
+2-D Tensor with shape `[batch_size, num_classes]`. Each slice
+`[i, :]` represents the unnormalized log-probabilities for all classes.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_samples`
+ |
+
+0-D. Number of independent samples to draw for each row slice.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+A Python integer. Used to create a random seed for the distribution.
+See tf.random.set_seed for behavior.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the operation.
+ |
+
+|
+`output_dtype`
+ |
+
+integer type to use for the output. Defaults to int64.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The drawn samples of shape `[batch_size, num_samples]`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nest.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nest.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..5e1aa27f380
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nest.md
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+description: Public API for tf.nest namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.nest
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.nest namespace.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`assert_same_structure(...)`](../../../tf/nest/assert_same_structure.md): Asserts that two structures are nested in the same way.
+
+[`flatten(...)`](../../../tf/nest/flatten.md): Returns a flat list from a given nested structure.
+
+[`is_nested(...)`](../../../tf/nest/is_nested.md): Returns true if its input is a collections.abc.Sequence (except strings).
+
+[`map_structure(...)`](../../../tf/nest/map_structure.md): Applies `func` to each entry in `structure` and returns a new structure.
+
+[`pack_sequence_as(...)`](../../../tf/nest/pack_sequence_as.md): Returns a given flattened sequence packed into a given structure.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a31c6d3182e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn.md
@@ -0,0 +1,243 @@
+description: Wrappers for primitive Neural Net (NN) Operations.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.nn
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Wrappers for primitive Neural Net (NN) Operations.
+
+
+
+## Modules
+
+[`rnn_cell`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell.md) module: Module for constructing RNN Cells.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`all_candidate_sampler(...)`](../../../tf/random/all_candidate_sampler.md): Generate the set of all classes.
+
+[`atrous_conv2d(...)`](../../../tf/nn/atrous_conv2d.md): Atrous convolution (a.k.a. convolution with holes or dilated convolution).
+
+[`atrous_conv2d_transpose(...)`](../../../tf/nn/atrous_conv2d_transpose.md): The transpose of `atrous_conv2d`.
+
+[`avg_pool(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/avg_pool.md): Performs the average pooling on the input.
+
+[`avg_pool1d(...)`](../../../tf/nn/avg_pool1d.md): Performs the average pooling on the input.
+
+[`avg_pool2d(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/avg_pool.md): Performs the average pooling on the input.
+
+[`avg_pool3d(...)`](../../../tf/nn/avg_pool3d.md): Performs the average pooling on the input.
+
+[`avg_pool_v2(...)`](../../../tf/nn/avg_pool.md): Performs the avg pooling on the input.
+
+[`batch_norm_with_global_normalization(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/batch_norm_with_global_normalization.md): Batch normalization.
+
+[`batch_normalization(...)`](../../../tf/nn/batch_normalization.md): Batch normalization.
+
+[`bias_add(...)`](../../../tf/nn/bias_add.md): Adds `bias` to `value`.
+
+[`bidirectional_dynamic_rnn(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/bidirectional_dynamic_rnn.md): Creates a dynamic version of bidirectional recurrent neural network. (deprecated)
+
+[`collapse_repeated(...)`](../../../tf/nn/collapse_repeated.md): Merge repeated labels into single labels.
+
+[`compute_accidental_hits(...)`](../../../tf/nn/compute_accidental_hits.md): Compute the position ids in `sampled_candidates` matching `true_classes`.
+
+[`compute_average_loss(...)`](../../../tf/nn/compute_average_loss.md): Scales per-example losses with sample_weights and computes their average.
+
+[`conv1d(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/conv1d.md): Computes a 1-D convolution given 3-D input and filter tensors. (deprecated argument values) (deprecated argument values)
+
+[`conv1d_transpose(...)`](../../../tf/nn/conv1d_transpose.md): The transpose of `conv1d`.
+
+[`conv2d(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/conv2d.md): Computes a 2-D convolution given 4-D `input` and `filter` tensors.
+
+[`conv2d_backprop_filter(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/conv2d_backprop_filter.md): Computes the gradients of convolution with respect to the filter.
+
+[`conv2d_backprop_input(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/conv2d_backprop_input.md): Computes the gradients of convolution with respect to the input.
+
+[`conv2d_transpose(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/conv2d_transpose.md): The transpose of `conv2d`.
+
+[`conv3d(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/conv3d.md): Computes a 3-D convolution given 5-D `input` and `filter` tensors.
+
+[`conv3d_backprop_filter(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/conv3d_backprop_filter.md): Computes the gradients of 3-D convolution with respect to the filter.
+
+[`conv3d_backprop_filter_v2(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/conv3d_backprop_filter.md): Computes the gradients of 3-D convolution with respect to the filter.
+
+[`conv3d_transpose(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/conv3d_transpose.md): The transpose of `conv3d`.
+
+[`conv_transpose(...)`](../../../tf/nn/conv_transpose.md): The transpose of `convolution`.
+
+[`convolution(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/convolution.md): Computes sums of N-D convolutions (actually cross-correlation).
+
+[`crelu(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/crelu.md): Computes Concatenated ReLU.
+
+[`ctc_beam_search_decoder(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/ctc_beam_search_decoder.md): Performs beam search decoding on the logits given in input.
+
+[`ctc_beam_search_decoder_v2(...)`](../../../tf/nn/ctc_beam_search_decoder.md): Performs beam search decoding on the logits given in input.
+
+[`ctc_greedy_decoder(...)`](../../../tf/nn/ctc_greedy_decoder.md): Performs greedy decoding on the logits given in input (best path).
+
+[`ctc_loss(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/ctc_loss.md): Computes the CTC (Connectionist Temporal Classification) Loss.
+
+[`ctc_loss_v2(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/ctc_loss_v2.md): Computes CTC (Connectionist Temporal Classification) loss.
+
+[`ctc_unique_labels(...)`](../../../tf/nn/ctc_unique_labels.md): Get unique labels and indices for batched labels for tf.nn.ctc_loss.
+
+[`depth_to_space(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/depth_to_space.md): DepthToSpace for tensors of type T.
+
+[`depthwise_conv2d(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/depthwise_conv2d.md): Depthwise 2-D convolution.
+
+[`depthwise_conv2d_backprop_filter(...)`](../../../tf/nn/depthwise_conv2d_backprop_filter.md): Computes the gradients of depthwise convolution with respect to the filter.
+
+[`depthwise_conv2d_backprop_input(...)`](../../../tf/nn/depthwise_conv2d_backprop_input.md): Computes the gradients of depthwise convolution with respect to the input.
+
+[`depthwise_conv2d_native(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/depthwise_conv2d_native.md): Computes a 2-D depthwise convolution given 4-D `input` and `filter` tensors.
+
+[`depthwise_conv2d_native_backprop_filter(...)`](../../../tf/nn/depthwise_conv2d_backprop_filter.md): Computes the gradients of depthwise convolution with respect to the filter.
+
+[`depthwise_conv2d_native_backprop_input(...)`](../../../tf/nn/depthwise_conv2d_backprop_input.md): Computes the gradients of depthwise convolution with respect to the input.
+
+[`dilation2d(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/dilation2d.md): Computes the grayscale dilation of 4-D `input` and 3-D `filter` tensors.
+
+[`dropout(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/dropout.md): Computes dropout. (deprecated arguments)
+
+[`dynamic_rnn(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/dynamic_rnn.md): Creates a recurrent neural network specified by RNNCell `cell`. (deprecated)
+
+[`elu(...)`](../../../tf/nn/elu.md): Computes exponential linear: `exp(features) - 1` if < 0, `features` otherwise.
+
+[`embedding_lookup(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/embedding_lookup.md): Looks up `ids` in a list of embedding tensors.
+
+[`embedding_lookup_sparse(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/embedding_lookup_sparse.md): Computes embeddings for the given ids and weights.
+
+[`erosion2d(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/erosion2d.md): Computes the grayscale erosion of 4-D `value` and 3-D `kernel` tensors.
+
+[`fixed_unigram_candidate_sampler(...)`](../../../tf/random/fixed_unigram_candidate_sampler.md): Samples a set of classes using the provided (fixed) base distribution.
+
+[`fractional_avg_pool(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/fractional_avg_pool.md): Performs fractional average pooling on the input. (deprecated)
+
+[`fractional_max_pool(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/fractional_max_pool.md): Performs fractional max pooling on the input. (deprecated)
+
+[`fused_batch_norm(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/fused_batch_norm.md): Batch normalization.
+
+[`in_top_k(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/math/in_top_k.md): Says whether the targets are in the top `K` predictions.
+
+[`l2_loss(...)`](../../../tf/nn/l2_loss.md): L2 Loss.
+
+[`l2_normalize(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/linalg/l2_normalize.md): Normalizes along dimension `axis` using an L2 norm. (deprecated arguments)
+
+[`leaky_relu(...)`](../../../tf/nn/leaky_relu.md): Compute the Leaky ReLU activation function.
+
+[`learned_unigram_candidate_sampler(...)`](../../../tf/random/learned_unigram_candidate_sampler.md): Samples a set of classes from a distribution learned during training.
+
+[`local_response_normalization(...)`](../../../tf/nn/local_response_normalization.md): Local Response Normalization.
+
+[`log_poisson_loss(...)`](../../../tf/nn/log_poisson_loss.md): Computes log Poisson loss given `log_input`.
+
+[`log_softmax(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/math/log_softmax.md): Computes log softmax activations. (deprecated arguments)
+
+[`log_uniform_candidate_sampler(...)`](../../../tf/random/log_uniform_candidate_sampler.md): Samples a set of classes using a log-uniform (Zipfian) base distribution.
+
+[`lrn(...)`](../../../tf/nn/local_response_normalization.md): Local Response Normalization.
+
+[`max_pool(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/max_pool.md): Performs the max pooling on the input.
+
+[`max_pool1d(...)`](../../../tf/nn/max_pool1d.md): Performs the max pooling on the input.
+
+[`max_pool2d(...)`](../../../tf/nn/max_pool2d.md): Performs the max pooling on the input.
+
+[`max_pool3d(...)`](../../../tf/nn/max_pool3d.md): Performs the max pooling on the input.
+
+[`max_pool_v2(...)`](../../../tf/nn/max_pool.md): Performs the max pooling on the input.
+
+[`max_pool_with_argmax(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/max_pool_with_argmax.md): Performs max pooling on the input and outputs both max values and indices.
+
+[`moments(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/moments.md): Calculate the mean and variance of `x`.
+
+[`nce_loss(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/nce_loss.md): Computes and returns the noise-contrastive estimation training loss.
+
+[`normalize_moments(...)`](../../../tf/nn/normalize_moments.md): Calculate the mean and variance of based on the sufficient statistics.
+
+[`pool(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/pool.md): Performs an N-D pooling operation.
+
+[`quantized_avg_pool(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/quantized_avg_pool.md): Produces the average pool of the input tensor for quantized types.
+
+[`quantized_conv2d(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/quantized_conv2d.md): Computes a 2D convolution given quantized 4D input and filter tensors.
+
+[`quantized_max_pool(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/quantized_max_pool.md): Produces the max pool of the input tensor for quantized types.
+
+[`quantized_relu_x(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/quantized_relu_x.md): Computes Quantized Rectified Linear X: `min(max(features, 0), max_value)`
+
+[`raw_rnn(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/raw_rnn.md): Creates an `RNN` specified by RNNCell `cell` and loop function `loop_fn`.
+
+[`relu(...)`](../../../tf/nn/relu.md): Computes rectified linear: `max(features, 0)`.
+
+[`relu6(...)`](../../../tf/nn/relu6.md): Computes Rectified Linear 6: `min(max(features, 0), 6)`.
+
+[`relu_layer(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/relu_layer.md): Computes Relu(x * weight + biases).
+
+[`safe_embedding_lookup_sparse(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/safe_embedding_lookup_sparse.md): Lookup embedding results, accounting for invalid IDs and empty features.
+
+[`sampled_softmax_loss(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/sampled_softmax_loss.md): Computes and returns the sampled softmax training loss.
+
+[`scale_regularization_loss(...)`](../../../tf/nn/scale_regularization_loss.md): Scales the sum of the given regularization losses by number of replicas.
+
+[`selu(...)`](../../../tf/nn/selu.md): Computes scaled exponential linear: `scale * alpha * (exp(features) - 1)`
+
+[`separable_conv2d(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/separable_conv2d.md): 2-D convolution with separable filters.
+
+[`sigmoid(...)`](../../../tf/math/sigmoid.md): Computes sigmoid of `x` element-wise.
+
+[`sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits.md): Computes sigmoid cross entropy given `logits`.
+
+[`softmax(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/math/softmax.md): Computes softmax activations. (deprecated arguments)
+
+[`softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits.md): Computes softmax cross entropy between `logits` and `labels`. (deprecated)
+
+[`softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2.md): Computes softmax cross entropy between `logits` and `labels`. (deprecated arguments)
+
+[`softplus(...)`](../../../tf/math/softplus.md): Computes softplus: `log(exp(features) + 1)`.
+
+[`softsign(...)`](../../../tf/nn/softsign.md): Computes softsign: `features / (abs(features) + 1)`.
+
+[`space_to_batch(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/space_to_batch.md): SpaceToBatch for 4-D tensors of type T.
+
+[`space_to_depth(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/space_to_depth.md): SpaceToDepth for tensors of type T.
+
+[`sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits.md): Computes sparse softmax cross entropy between `logits` and `labels`.
+
+[`static_bidirectional_rnn(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/static_bidirectional_rnn.md): Creates a bidirectional recurrent neural network. (deprecated)
+
+[`static_rnn(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/static_rnn.md): Creates a recurrent neural network specified by RNNCell `cell`. (deprecated)
+
+[`static_state_saving_rnn(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/static_state_saving_rnn.md): RNN that accepts a state saver for time-truncated RNN calculation. (deprecated)
+
+[`sufficient_statistics(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/sufficient_statistics.md): Calculate the sufficient statistics for the mean and variance of `x`.
+
+[`swish(...)`](../../../tf/nn/swish.md): Computes the Swish activation function: `x * sigmoid(x)`.
+
+[`tanh(...)`](../../../tf/math/tanh.md): Computes hyperbolic tangent of `x` element-wise.
+
+[`top_k(...)`](../../../tf/math/top_k.md): Finds values and indices of the `k` largest entries for the last dimension.
+
+[`uniform_candidate_sampler(...)`](../../../tf/random/uniform_candidate_sampler.md): Samples a set of classes using a uniform base distribution.
+
+[`weighted_cross_entropy_with_logits(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/weighted_cross_entropy_with_logits.md): Computes a weighted cross entropy. (deprecated arguments)
+
+[`weighted_moments(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/weighted_moments.md): Returns the frequency-weighted mean and variance of `x`.
+
+[`with_space_to_batch(...)`](../../../tf/nn/with_space_to_batch.md): Performs `op` on the space-to-batch representation of `input`.
+
+[`xw_plus_b(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/xw_plus_b.md): Computes matmul(x, weights) + biases.
+
+[`zero_fraction(...)`](../../../tf/math/zero_fraction.md): Returns the fraction of zeros in `value`.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/avg_pool.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/avg_pool.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..2373f316372
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/avg_pool.md
@@ -0,0 +1,123 @@
+description: Performs the average pooling on the input.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.avg_pool
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Performs the average pooling on the input.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.nn.avg_pool2d`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.avg_pool(
+ value, ksize, strides, padding, data_format='NHWC', name=None, input=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Each entry in `output` is the mean of the corresponding size `ksize`
+window in `value`.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+A 4-D `Tensor` of shape `[batch, height, width, channels]` and type
+`float32`, `float64`, `qint8`, `quint8`, or `qint32`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ksize`
+ |
+
+An int or list of `ints` that has length `1`, `2` or `4`. The size of
+the window for each dimension of the input tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+An int or list of `ints` that has length `1`, `2` or `4`. The
+stride of the sliding window for each dimension of the input tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+A string, either `'VALID'` or `'SAME'`. The padding algorithm.
+See the "returns" section of tf.nn.convolution for details.
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+A string. 'NHWC' and 'NCHW' are supported.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the operation.
+ |
+
+|
+`input`
+ |
+
+Alias for value.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` with the same type as `value`. The average pooled output tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/batch_norm_with_global_normalization.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/batch_norm_with_global_normalization.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..9888b3e9957
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/batch_norm_with_global_normalization.md
@@ -0,0 +1,152 @@
+description: Batch normalization.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.batch_norm_with_global_normalization
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Batch normalization.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.batch_norm_with_global_normalization(
+ t=None, m=None, v=None, beta=None, gamma=None, variance_epsilon=None,
+ scale_after_normalization=None, name=None, input=None, mean=None, variance=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This op is deprecated. See tf.nn.batch_normalization.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`t`
+ |
+
+A 4D input Tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`m`
+ |
+
+A 1D mean Tensor with size matching the last dimension of t.
+This is the first output from tf.nn.moments,
+or a saved moving average thereof.
+ |
+
+|
+`v`
+ |
+
+A 1D variance Tensor with size matching the last dimension of t.
+This is the second output from tf.nn.moments,
+or a saved moving average thereof.
+ |
+
+|
+`beta`
+ |
+
+A 1D beta Tensor with size matching the last dimension of t.
+An offset to be added to the normalized tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`gamma`
+ |
+
+A 1D gamma Tensor with size matching the last dimension of t.
+If "scale_after_normalization" is true, this tensor will be multiplied
+with the normalized tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`variance_epsilon`
+ |
+
+A small float number to avoid dividing by 0.
+ |
+
+|
+`scale_after_normalization`
+ |
+
+A bool indicating whether the resulted tensor
+needs to be multiplied with gamma.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for this operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`input`
+ |
+
+Alias for t.
+ |
+
+|
+`mean`
+ |
+
+Alias for m.
+ |
+
+|
+`variance`
+ |
+
+Alias for v.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A batch-normalized `t`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### References:
+
+Batch Normalization - Accelerating Deep Network Training by Reducing
+Internal Covariate Shift:
+ [Ioffe et al., 2015](http://proceedings.mlr.press/v37/ioffe15.html)
+ ([pdf](http://proceedings.mlr.press/v37/ioffe15.pdf))
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/bidirectional_dynamic_rnn.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/bidirectional_dynamic_rnn.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..ac00d377596
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/bidirectional_dynamic_rnn.md
@@ -0,0 +1,209 @@
+description: Creates a dynamic version of bidirectional recurrent neural network. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.bidirectional_dynamic_rnn
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Creates a dynamic version of bidirectional recurrent neural network. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.bidirectional_dynamic_rnn(
+ cell_fw, cell_bw, inputs, sequence_length=None, initial_state_fw=None,
+ initial_state_bw=None, dtype=None, parallel_iterations=None,
+ swap_memory=(False), time_major=(False), scope=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Please use `keras.layers.Bidirectional(keras.layers.RNN(cell))`, which is equivalent to this API
+
+Takes input and builds independent forward and backward RNNs. The input_size
+of forward and backward cell must match. The initial state for both directions
+is zero by default (but can be set optionally) and no intermediate states are
+ever returned -- the network is fully unrolled for the given (passed in)
+length(s) of the sequence(s) or completely unrolled if length(s) is not
+given.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cell_fw`
+ |
+
+An instance of RNNCell, to be used for forward direction.
+ |
+
+|
+`cell_bw`
+ |
+
+An instance of RNNCell, to be used for backward direction.
+ |
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+The RNN inputs.
+If time_major == False (default), this must be a tensor of shape:
+`[batch_size, max_time, ...]`, or a nested tuple of such elements.
+If time_major == True, this must be a tensor of shape: `[max_time,
+batch_size, ...]`, or a nested tuple of such elements.
+ |
+
+|
+`sequence_length`
+ |
+
+(optional) An int32/int64 vector, size `[batch_size]`,
+containing the actual lengths for each of the sequences in the batch. If
+not provided, all batch entries are assumed to be full sequences; and time
+reversal is applied from time `0` to `max_time` for each sequence.
+ |
+
+|
+`initial_state_fw`
+ |
+
+(optional) An initial state for the forward RNN. This must
+be a tensor of appropriate type and shape `[batch_size,
+cell_fw.state_size]`. If `cell_fw.state_size` is a tuple, this should be a
+tuple of tensors having shapes `[batch_size, s] for s in
+cell_fw.state_size`.
+ |
+
+|
+`initial_state_bw`
+ |
+
+(optional) Same as for `initial_state_fw`, but using the
+corresponding properties of `cell_bw`.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+(optional) The data type for the initial states and expected output.
+Required if initial_states are not provided or RNN states have a
+heterogeneous dtype.
+ |
+
+|
+`parallel_iterations`
+ |
+
+(Default: 32). The number of iterations to run in
+parallel. Those operations which do not have any temporal dependency and
+can be run in parallel, will be. This parameter trades off time for
+space. Values >> 1 use more memory but take less time, while smaller
+values use less memory but computations take longer.
+ |
+
+|
+`swap_memory`
+ |
+
+Transparently swap the tensors produced in forward inference
+but needed for back prop from GPU to CPU. This allows training RNNs which
+would typically not fit on a single GPU, with very minimal (or no)
+performance penalty.
+ |
+
+|
+`time_major`
+ |
+
+The shape format of the `inputs` and `outputs` Tensors. If true,
+these `Tensors` must be shaped `[max_time, batch_size, depth]`. If false,
+these `Tensors` must be shaped `[batch_size, max_time, depth]`. Using
+`time_major = True` is a bit more efficient because it avoids transposes
+at the beginning and end of the RNN calculation. However, most TensorFlow
+data is batch-major, so by default this function accepts input and emits
+output in batch-major form.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope`
+ |
+
+VariableScope for the created subgraph; defaults to
+"bidirectional_rnn"
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+A tuple (outputs, output_states) where:
+outputs: A tuple (output_fw, output_bw) containing the forward and
+the backward rnn output `Tensor`.
+If time_major == False (default),
+output_fw will be a `Tensor` shaped:
+`[batch_size, max_time, cell_fw.output_size]`
+and output_bw will be a `Tensor` shaped:
+`[batch_size, max_time, cell_bw.output_size]`.
+If time_major == True,
+output_fw will be a `Tensor` shaped:
+`[max_time, batch_size, cell_fw.output_size]`
+and output_bw will be a `Tensor` shaped:
+`[max_time, batch_size, cell_bw.output_size]`.
+It returns a tuple instead of a single concatenated `Tensor`, unlike
+in the `bidirectional_rnn`. If the concatenated one is preferred,
+the forward and backward outputs can be concatenated as
+tf.concat(outputs, 2).
+output_states: A tuple (output_state_fw, output_state_bw) containing
+the forward and the backward final states of bidirectional rnn.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `cell_fw` or `cell_bw` is not an instance of `RNNCell`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/conv1d.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/conv1d.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..44e8d96e2a9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/conv1d.md
@@ -0,0 +1,173 @@
+description: Computes a 1-D convolution given 3-D input and filter tensors. (deprecated argument values) (deprecated argument values)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.conv1d
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes a 1-D convolution given 3-D input and filter tensors. (deprecated argument values) (deprecated argument values)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.conv1d(
+ value=None, filters=None, stride=None, padding=None, use_cudnn_on_gpu=None,
+ data_format=None, name=None, input=None, dilations=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: SOME ARGUMENT VALUES ARE DEPRECATED: `(data_format='NCHW')`. They will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+`NCHW` for data_format is deprecated, use `NCW` instead
+
+Warning: SOME ARGUMENT VALUES ARE DEPRECATED: `(data_format='NHWC')`. They will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+`NHWC` for data_format is deprecated, use `NWC` instead
+
+Given an input tensor of shape
+ [batch, in_width, in_channels]
+if data_format is "NWC", or
+ [batch, in_channels, in_width]
+if data_format is "NCW",
+and a filter / kernel tensor of shape
+[filter_width, in_channels, out_channels], this op reshapes
+the arguments to pass them to conv2d to perform the equivalent
+convolution operation.
+
+Internally, this op reshapes the input tensors and invokes tf.nn.conv2d.
+For example, if `data_format` does not start with "NC", a tensor of shape
+ [batch, in_width, in_channels]
+is reshaped to
+ [batch, 1, in_width, in_channels],
+and the filter is reshaped to
+ [1, filter_width, in_channels, out_channels].
+The result is then reshaped back to
+ [batch, out_width, out_channels]
+\(where out_width is a function of the stride and padding as in conv2d\) and
+returned to the caller.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+A 3D `Tensor`. Must be of type `float16`, `float32`, or `float64`.
+ |
+
+|
+`filters`
+ |
+
+A 3D `Tensor`. Must have the same type as `value`.
+ |
+
+|
+`stride`
+ |
+
+An int or list of `ints` that has length `1` or `3`. The number of
+entries by which the filter is moved right at each step.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+'SAME' or 'VALID'
+ |
+
+|
+`use_cudnn_on_gpu`
+ |
+
+An optional `bool`. Defaults to `True`.
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+An optional `string` from `"NWC", "NCW"`. Defaults to `"NWC"`,
+the data is stored in the order of [batch, in_width, in_channels]. The
+`"NCW"` format stores data as [batch, in_channels, in_width].
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`input`
+ |
+
+Alias for value.
+ |
+
+|
+`dilations`
+ |
+
+An int or list of `ints` that has length `1` or `3` which
+defaults to 1. The dilation factor for each dimension of input. If set to
+k > 1, there will be k-1 skipped cells between each filter element on that
+dimension. Dilations in the batch and depth dimensions must be 1.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor`. Has the same type as input.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `data_format` is invalid.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/conv2d.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/conv2d.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..f0715ec3b97
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/conv2d.md
@@ -0,0 +1,170 @@
+description: Computes a 2-D convolution given 4-D input and filter tensors.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.conv2d
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes a 2-D convolution given 4-D `input` and `filter` tensors.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.conv2d(
+ input, filter=None, strides=None, padding=None, use_cudnn_on_gpu=(True),
+ data_format='NHWC', dilations=[1, 1, 1, 1], name=None, filters=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Given an input tensor of shape `[batch, in_height, in_width, in_channels]`
+and a filter / kernel tensor of shape
+`[filter_height, filter_width, in_channels, out_channels]`, this op
+performs the following:
+
+1. Flattens the filter to a 2-D matrix with shape
+ `[filter_height * filter_width * in_channels, output_channels]`.
+2. Extracts image patches from the input tensor to form a *virtual*
+ tensor of shape `[batch, out_height, out_width,
+ filter_height * filter_width * in_channels]`.
+3. For each patch, right-multiplies the filter matrix and the image patch
+ vector.
+
+In detail, with the default NHWC format,
+
+ output[b, i, j, k] =
+ sum_{di, dj, q} input[b, strides[1] * i + di, strides[2] * j + dj, q]
+ * filter[di, dj, q, k]
+
+Must have `strides[0] = strides[3] = 1`. For the most common case of the same
+horizontal and vertical strides, `strides = [1, stride, stride, 1]`.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types:
+`half`, `bfloat16`, `float32`, `float64`.
+A 4-D tensor. The dimension order is interpreted according to the value
+of `data_format`, see below for details.
+ |
+
+|
+`filter`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must have the same type as `input`.
+A 4-D tensor of shape
+`[filter_height, filter_width, in_channels, out_channels]`
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+An int or list of `ints` that has length `1`, `2` or `4`. The
+stride of the sliding window for each dimension of `input`. If a single
+value is given it is replicated in the `H` and `W` dimension. By default
+the `N` and `C` dimensions are set to 1. The dimension order is determined
+by the value of `data_format`, see below for details.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+Either the `string` `"SAME"` or `"VALID"` indicating the type of
+padding algorithm to use, or a list indicating the explicit paddings at
+the start and end of each dimension. When explicit padding is used and
+data_format is `"NHWC"`, this should be in the form `[[0, 0], [pad_top,
+pad_bottom], [pad_left, pad_right], [0, 0]]`. When explicit padding used
+and data_format is `"NCHW"`, this should be in the form `[[0, 0], [0, 0],
+[pad_top, pad_bottom], [pad_left, pad_right]]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_cudnn_on_gpu`
+ |
+
+An optional `bool`. Defaults to `True`.
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+An optional `string` from: `"NHWC", "NCHW"`.
+Defaults to `"NHWC"`.
+Specify the data format of the input and output data. With the
+default format "NHWC", the data is stored in the order of:
+[batch, height, width, channels].
+Alternatively, the format could be "NCHW", the data storage order of:
+[batch, channels, height, width].
+ |
+
+|
+`dilations`
+ |
+
+An int or list of `ints` that has length `1`, `2` or `4`,
+defaults to 1. The dilation factor for each dimension of`input`. If a
+single value is given it is replicated in the `H` and `W` dimension. By
+default the `N` and `C` dimensions are set to 1. If set to k > 1, there
+will be k-1 skipped cells between each filter element on that dimension.
+The dimension order is determined by the value of `data_format`, see above
+for details. Dilations in the batch and depth dimensions if a 4-d tensor
+must be 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`filters`
+ |
+
+Alias for filter.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `input`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/conv2d_backprop_filter.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/conv2d_backprop_filter.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..697919a260f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/conv2d_backprop_filter.md
@@ -0,0 +1,148 @@
+description: Computes the gradients of convolution with respect to the filter.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.conv2d_backprop_filter
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the gradients of convolution with respect to the filter.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.conv2d_backprop_filter(
+ input, filter_sizes, out_backprop, strides, padding, use_cudnn_on_gpu=(True),
+ data_format='NHWC', dilations=[1, 1, 1, 1], name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types:
+`half`, `bfloat16`, `float32`, `float64`.
+4-D with shape `[batch, in_height, in_width, in_channels]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`filter_sizes`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `int32`.
+An integer vector representing the tensor shape of `filter`,
+where `filter` is a 4-D
+`[filter_height, filter_width, in_channels, out_channels]` tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`out_backprop`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must have the same type as `input`.
+4-D with shape `[batch, out_height, out_width, out_channels]`.
+Gradients w.r.t. the output of the convolution.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+A list of `ints`.
+The stride of the sliding window for each dimension of the input
+of the convolution. Must be in the same order as the dimension specified
+with format.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+Either the `string `"SAME"` or `"VALID"` indicating the type of
+padding algorithm to use, or a list indicating the explicit paddings at
+the start and end of each dimension. When explicit padding is used and
+data_format is `"NHWC"`, this should be in the form `[[0, 0], [pad_top,
+pad_bottom], [pad_left, pad_right], [0, 0]]`. When explicit padding used
+and data_format is `"NCHW"`, this should be in the form `[[0, 0], [0, 0],
+[pad_top, pad_bottom], [pad_left, pad_right]]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_cudnn_on_gpu`
+ |
+
+An optional `bool`. Defaults to `True`.
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+An optional `string` from: `"NHWC", "NCHW"`.
+Defaults to `"NHWC"`.
+Specify the data format of the input and output data. With the
+default format "NHWC", the data is stored in the order of:
+[batch, in_height, in_width, in_channels].
+Alternatively, the format could be "NCHW", the data storage order of:
+[batch, in_channels, in_height, in_width].
+ |
+
+|
+`dilations`
+ |
+
+An optional list of `ints`. Defaults to `[1, 1, 1, 1]`.
+1-D tensor of length 4. The dilation factor for each dimension of
+`input`. If set to k > 1, there will be k-1 skipped cells between each
+filter element on that dimension. The dimension order is determined by
+the value of `data_format`, see above for details. Dilations in the batch
+and depth dimensions must be 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `input`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/conv2d_backprop_input.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/conv2d_backprop_input.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..2063b47784f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/conv2d_backprop_input.md
@@ -0,0 +1,156 @@
+description: Computes the gradients of convolution with respect to the input.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.conv2d_backprop_input
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the gradients of convolution with respect to the input.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.conv2d_backprop_input(
+ input_sizes, filter=None, out_backprop=None, strides=None, padding=None,
+ use_cudnn_on_gpu=(True), data_format='NHWC', dilations=[1, 1, 1, 1], name=None,
+ filters=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_sizes`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `int32`.
+An integer vector representing the shape of `input`,
+where `input` is a 4-D `[batch, height, width, channels]` tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`filter`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types:
+`half`, `bfloat16`, `float32`, `float64`.
+4-D with shape
+`[filter_height, filter_width, in_channels, out_channels]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`out_backprop`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must have the same type as `filter`.
+4-D with shape `[batch, out_height, out_width, out_channels]`.
+Gradients w.r.t. the output of the convolution.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+A list of `ints`.
+The stride of the sliding window for each dimension of the input
+of the convolution. Must be in the same order as the dimension specified
+with format.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+Either the `string `"SAME"` or `"VALID"` indicating the type of
+padding algorithm to use, or a list indicating the explicit paddings at
+the start and end of each dimension. When explicit padding is used and
+data_format is `"NHWC"`, this should be in the form `[[0, 0], [pad_top,
+pad_bottom], [pad_left, pad_right], [0, 0]]`. When explicit padding used
+and data_format is `"NCHW"`, this should be in the form `[[0, 0], [0, 0],
+[pad_top, pad_bottom], [pad_left, pad_right]]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_cudnn_on_gpu`
+ |
+
+An optional `bool`. Defaults to `True`.
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+An optional `string` from: `"NHWC", "NCHW"`.
+Defaults to `"NHWC"`.
+Specify the data format of the input and output data. With the
+default format "NHWC", the data is stored in the order of:
+[batch, in_height, in_width, in_channels].
+Alternatively, the format could be "NCHW", the data storage order of:
+[batch, in_channels, in_height, in_width].
+ |
+
+|
+`dilations`
+ |
+
+An optional list of `ints`. Defaults to `[1, 1, 1, 1]`.
+1-D tensor of length 4. The dilation factor for each dimension of
+`input`. If set to k > 1, there will be k-1 skipped cells between each
+filter element on that dimension. The dimension order is determined by
+the value of `data_format`, see above for details. Dilations in the batch
+and depth dimensions must be 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`filters`
+ |
+
+Alias for filter.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `filter`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/conv2d_transpose.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/conv2d_transpose.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..8a42139cf21
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/conv2d_transpose.md
@@ -0,0 +1,175 @@
+description: The transpose of conv2d.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.conv2d_transpose
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The transpose of `conv2d`.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.conv2d_transpose(
+ value=None, filter=None, output_shape=None, strides=None, padding='SAME',
+ data_format='NHWC', name=None, input=None, filters=None, dilations=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This operation is sometimes called "deconvolution" after
+(Zeiler et al., 2010), but is really the transpose (gradient) of `conv2d`
+rather than an actual deconvolution.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+A 4-D `Tensor` of type `float` and shape
+`[batch, height, width, in_channels]` for `NHWC` data format or
+`[batch, in_channels, height, width]` for `NCHW` data format.
+ |
+
+|
+`filter`
+ |
+
+A 4-D `Tensor` with the same type as `value` and shape
+`[height, width, output_channels, in_channels]`. `filter`'s
+`in_channels` dimension must match that of `value`.
+ |
+
+|
+`output_shape`
+ |
+
+A 1-D `Tensor` representing the output shape of the
+deconvolution op.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+An int or list of `ints` that has length `1`, `2` or `4`. The
+stride of the sliding window for each dimension of `input`. If a single
+value is given it is replicated in the `H` and `W` dimension. By default
+the `N` and `C` dimensions are set to 0. The dimension order is determined
+by the value of `data_format`, see below for details.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+A string, either `'VALID'` or `'SAME'`. The padding algorithm.
+See the "returns" section of tf.nn.convolution for details.
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+A string. 'NHWC' and 'NCHW' are supported.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the returned tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`input`
+ |
+
+Alias for value.
+ |
+
+|
+`filters`
+ |
+
+Alias for filter.
+ |
+
+|
+`dilations`
+ |
+
+An int or list of `ints` that has length `1`, `2` or `4`,
+defaults to 1. The dilation factor for each dimension of`input`. If a
+single value is given it is replicated in the `H` and `W` dimension. By
+default the `N` and `C` dimensions are set to 1. If set to k > 1, there
+will be k-1 skipped cells between each filter element on that dimension.
+The dimension order is determined by the value of `data_format`, see above
+for details. Dilations in the batch and depth dimensions if a 4-d tensor
+must be 1.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` with the same type as `value`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If input/output depth does not match `filter`'s shape, or if
+padding is other than `'VALID'` or `'SAME'`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### References:
+
+Deconvolutional Networks:
+ [Zeiler et al., 2010]
+ (https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/5539957)
+ ([pdf]
+ (http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.232.4023&rep=rep1&type=pdf))
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/conv3d.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/conv3d.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..425bf2cc363
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/conv3d.md
@@ -0,0 +1,128 @@
+description: Computes a 3-D convolution given 5-D input and filter tensors.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.conv3d
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes a 3-D convolution given 5-D `input` and `filter` tensors.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.conv3d(
+ input, filter=None, strides=None, padding=None, data_format='NDHWC',
+ dilations=[1, 1, 1, 1, 1], name=None, filters=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+In signal processing, cross-correlation is a measure of similarity of
+two waveforms as a function of a time-lag applied to one of them. This
+is also known as a sliding dot product or sliding inner-product.
+
+Our Conv3D implements a form of cross-correlation.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `half`, `bfloat16`, `float32`, `float64`.
+Shape `[batch, in_depth, in_height, in_width, in_channels]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`filter`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must have the same type as `input`.
+Shape `[filter_depth, filter_height, filter_width, in_channels,
+out_channels]`. `in_channels` must match between `input` and `filter`.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+A list of `ints` that has length `>= 5`.
+1-D tensor of length 5. The stride of the sliding window for each
+dimension of `input`. Must have `strides[0] = strides[4] = 1`.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+A `string` from: `"SAME", "VALID"`.
+The type of padding algorithm to use.
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+An optional `string` from: `"NDHWC", "NCDHW"`. Defaults to `"NDHWC"`.
+The data format of the input and output data. With the
+default format "NDHWC", the data is stored in the order of:
+[batch, in_depth, in_height, in_width, in_channels].
+Alternatively, the format could be "NCDHW", the data storage order is:
+[batch, in_channels, in_depth, in_height, in_width].
+ |
+
+|
+`dilations`
+ |
+
+An optional list of `ints`. Defaults to `[1, 1, 1, 1, 1]`.
+1-D tensor of length 5. The dilation factor for each dimension of
+`input`. If set to k > 1, there will be k-1 skipped cells between each
+filter element on that dimension. The dimension order is determined by the
+value of `data_format`, see above for details. Dilations in the batch and
+depth dimensions must be 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `input`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/conv3d_backprop_filter.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/conv3d_backprop_filter.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..4fd6908c2a8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/conv3d_backprop_filter.md
@@ -0,0 +1,140 @@
+description: Computes the gradients of 3-D convolution with respect to the filter.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.conv3d_backprop_filter
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the gradients of 3-D convolution with respect to the filter.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.nn.conv3d_backprop_filter_v2`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.conv3d_backprop_filter(
+ input, filter_sizes, out_backprop, strides, padding, data_format='NDHWC',
+ dilations=[1, 1, 1, 1, 1], name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `half`, `bfloat16`, `float32`, `float64`.
+Shape `[batch, depth, rows, cols, in_channels]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`filter_sizes`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `int32`.
+An integer vector representing the tensor shape of `filter`,
+where `filter` is a 5-D
+`[filter_depth, filter_height, filter_width, in_channels, out_channels]`
+tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`out_backprop`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must have the same type as `input`.
+Backprop signal of shape `[batch, out_depth, out_rows, out_cols,
+out_channels]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+A list of `ints` that has length `>= 5`.
+1-D tensor of length 5. The stride of the sliding window for each
+dimension of `input`. Must have `strides[0] = strides[4] = 1`.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+A `string` from: `"SAME", "VALID"`.
+The type of padding algorithm to use.
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+An optional `string` from: `"NDHWC", "NCDHW"`. Defaults to `"NDHWC"`.
+The data format of the input and output data. With the
+default format "NDHWC", the data is stored in the order of:
+[batch, in_depth, in_height, in_width, in_channels].
+Alternatively, the format could be "NCDHW", the data storage order is:
+[batch, in_channels, in_depth, in_height, in_width].
+ |
+
+|
+`dilations`
+ |
+
+An optional list of `ints`. Defaults to `[1, 1, 1, 1, 1]`.
+1-D tensor of length 5. The dilation factor for each dimension of
+`input`. If set to k > 1, there will be k-1 skipped cells between each
+filter element on that dimension. The dimension order is determined by the
+value of `data_format`, see above for details. Dilations in the batch and
+depth dimensions must be 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `input`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/conv3d_transpose.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/conv3d_transpose.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..36db8c5c303
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/conv3d_transpose.md
@@ -0,0 +1,172 @@
+description: The transpose of conv3d.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.conv3d_transpose
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The transpose of `conv3d`.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.conv3d_transpose(
+ value, filter=None, output_shape=None, strides=None, padding='SAME',
+ data_format='NDHWC', name=None, input=None, filters=None, dilations=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This operation is sometimes called "deconvolution" after
+(Zeiler et al., 2010), but is really the transpose (gradient) of `conv3d`
+rather than an actual deconvolution.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+A 5-D `Tensor` of type `float` and shape
+`[batch, depth, height, width, in_channels]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`filter`
+ |
+
+A 5-D `Tensor` with the same type as `value` and shape
+`[depth, height, width, output_channels, in_channels]`. `filter`'s
+`in_channels` dimension must match that of `value`.
+ |
+
+|
+`output_shape`
+ |
+
+A 1-D `Tensor` representing the output shape of the
+deconvolution op.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+A list of ints. The stride of the sliding window for each
+dimension of the input tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+A string, either `'VALID'` or `'SAME'`. The padding algorithm.
+See the "returns" section of tf.nn.convolution for details.
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+A string, either `'NDHWC'` or `'NCDHW`' specifying the layout
+of the input and output tensors. Defaults to `'NDHWC'`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the returned tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`input`
+ |
+
+Alias of value.
+ |
+
+|
+`filters`
+ |
+
+Alias of filter.
+ |
+
+|
+`dilations`
+ |
+
+An int or list of `ints` that has length `1`, `3` or `5`,
+defaults to 1. The dilation factor for each dimension of`input`. If a
+single value is given it is replicated in the `D`, `H` and `W` dimension.
+By default the `N` and `C` dimensions are set to 1. If set to k > 1, there
+will be k-1 skipped cells between each filter element on that dimension.
+The dimension order is determined by the value of `data_format`, see above
+for details. Dilations in the batch and depth dimensions if a 5-d tensor
+must be 1.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` with the same type as `value`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If input/output depth does not match `filter`'s shape, or if
+padding is other than `'VALID'` or `'SAME'`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### References:
+
+Deconvolutional Networks:
+ [Zeiler et al., 2010]
+ (https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/5539957)
+ ([pdf]
+ (http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.232.4023&rep=rep1&type=pdf))
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/convolution.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/convolution.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..8f03565ba0b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/convolution.md
@@ -0,0 +1,230 @@
+description: Computes sums of N-D convolutions (actually cross-correlation).
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.convolution
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes sums of N-D convolutions (actually cross-correlation).
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.convolution(
+ input, filter, padding, strides=None, dilation_rate=None, name=None,
+ data_format=None, filters=None, dilations=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This also supports either output striding via the optional `strides` parameter
+or atrous convolution (also known as convolution with holes or dilated
+convolution, based on the French word "trous" meaning holes in English) via
+the optional `dilation_rate` parameter. Currently, however, output striding
+is not supported for atrous convolutions.
+
+Specifically, in the case that `data_format` does not start with "NC", given
+a rank (N+2) `input` Tensor of shape
+
+ [num_batches,
+ input_spatial_shape[0],
+ ...,
+ input_spatial_shape[N-1],
+ num_input_channels],
+
+a rank (N+2) `filter` Tensor of shape
+
+ [spatial_filter_shape[0],
+ ...,
+ spatial_filter_shape[N-1],
+ num_input_channels,
+ num_output_channels],
+
+an optional `dilation_rate` tensor of shape [N] (defaulting to [1]*N)
+specifying the filter upsampling/input downsampling rate, and an optional list
+of N `strides` (defaulting [1]*N), this computes for each N-D spatial output
+position (x[0], ..., x[N-1]):
+
+```
+ output[b, x[0], ..., x[N-1], k] =
+ sum_{z[0], ..., z[N-1], q}
+ filter[z[0], ..., z[N-1], q, k] *
+ padded_input[b,
+ x[0]*strides[0] + dilation_rate[0]*z[0],
+ ...,
+ x[N-1]*strides[N-1] + dilation_rate[N-1]*z[N-1],
+ q]
+```
+where b is the index into the batch, k is the output channel number, q is the
+input channel number, and z is the N-D spatial offset within the filter. Here,
+`padded_input` is obtained by zero padding the input using an effective
+spatial filter shape of `(spatial_filter_shape-1) * dilation_rate + 1` and
+output striding `strides` as described in the
+[comment here](https://tensorflow.org/api_guides/python/nn#Convolution).
+
+In the case that `data_format` does start with `"NC"`, the `input` and output
+(but not the `filter`) are simply transposed as follows:
+
+ convolution(input, data_format, **kwargs) =
+ tf.transpose(convolution(tf.transpose(input, [0] + range(2,N+2) + [1]),
+ **kwargs),
+ [0, N+1] + range(1, N+1))
+
+It is required that 1 <= N <= 3.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input`
+ |
+
+An (N+2)-D `Tensor` of type `T`, of shape
+`[batch_size] + input_spatial_shape + [in_channels]` if data_format does
+not start with "NC" (default), or
+`[batch_size, in_channels] + input_spatial_shape` if data_format starts
+with "NC".
+ |
+
+|
+`filter`
+ |
+
+An (N+2)-D `Tensor` with the same type as `input` and shape
+`spatial_filter_shape + [in_channels, out_channels]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+A string, either `"VALID"` or `"SAME"`. The padding algorithm.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+Optional. Sequence of N ints >= 1. Specifies the output stride.
+Defaults to [1]*N. If any value of strides is > 1, then all values of
+dilation_rate must be 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`dilation_rate`
+ |
+
+Optional. Sequence of N ints >= 1. Specifies the filter
+upsampling/input downsampling rate. In the literature, the same parameter
+is sometimes called `input stride` or `dilation`. The effective filter
+size used for the convolution will be `spatial_filter_shape +
+(spatial_filter_shape - 1) * (rate - 1)`, obtained by inserting
+(dilation_rate[i]-1) zeros between consecutive elements of the original
+filter in each spatial dimension i. If any value of dilation_rate is > 1,
+then all values of strides must be 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the returned tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+A string or None. Specifies whether the channel dimension of
+the `input` and output is the last dimension (default, or if `data_format`
+does not start with "NC"), or the second dimension (if `data_format`
+starts with "NC"). For N=1, the valid values are "NWC" (default) and
+"NCW". For N=2, the valid values are "NHWC" (default) and "NCHW".
+For N=3, the valid values are "NDHWC" (default) and "NCDHW".
+ |
+
+|
+`filters`
+ |
+
+Alias of filter.
+ |
+
+|
+`dilations`
+ |
+
+Alias of dilation_rate.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` with the same type as `input` of shape
+
+`[batch_size] + output_spatial_shape + [out_channels]`
+
+if data_format is None or does not start with "NC", or
+
+`[batch_size, out_channels] + output_spatial_shape`
+
+if data_format starts with "NC",
+where `output_spatial_shape` depends on the value of `padding`.
+
+If padding == "SAME":
+output_spatial_shape[i] = ceil(input_spatial_shape[i] / strides[i])
+
+If padding == "VALID":
+output_spatial_shape[i] =
+ceil((input_spatial_shape[i] -
+(spatial_filter_shape[i]-1) * dilation_rate[i])
+/ strides[i]).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If input/output depth does not match `filter` shape, if padding
+is other than `"VALID"` or `"SAME"`, or if data_format is invalid.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/crelu.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/crelu.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..ae4f1282135
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/crelu.md
@@ -0,0 +1,93 @@
+description: Computes Concatenated ReLU.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.crelu
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes Concatenated ReLU.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.crelu(
+ features, name=None, axis=-1
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Concatenates a ReLU which selects only the positive part of the activation
+with a ReLU which selects only the *negative* part of the activation.
+Note that as a result this non-linearity doubles the depth of the activations.
+Source: [Understanding and Improving Convolutional Neural Networks via
+Concatenated Rectified Linear Units. W. Shang, et
+al.](https://arxiv.org/abs/1603.05201)
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`features`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` with type `float`, `double`, `int32`, `int64`, `uint8`,
+`int16`, or `int8`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`axis`
+ |
+
+The axis that the output values are concatenated along. Default is -1.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` with the same type as `features`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### References:
+
+Understanding and Improving Convolutional Neural Networks via Concatenated
+Rectified Linear Units:
+ [Shang et al., 2016](http://proceedings.mlr.press/v48/shang16)
+ ([pdf](http://proceedings.mlr.press/v48/shang16.pdf))
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/ctc_beam_search_decoder.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/ctc_beam_search_decoder.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..c78c650d898
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/ctc_beam_search_decoder.md
@@ -0,0 +1,130 @@
+description: Performs beam search decoding on the logits given in input.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.ctc_beam_search_decoder
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Performs beam search decoding on the logits given in input.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.ctc_beam_search_decoder(
+ inputs, sequence_length, beam_width=100, top_paths=1, merge_repeated=(True)
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+**Note** The `ctc_greedy_decoder` is a special case of the
+`ctc_beam_search_decoder` with `top_paths=1` and `beam_width=1` (but
+that decoder is faster for this special case).
+
+If `merge_repeated` is `True`, merge repeated classes in the output beams.
+This means that if consecutive entries in a beam are the same,
+only the first of these is emitted. That is, when the sequence is
+`A B B * B * B` (where '*' is the blank label), the return value is:
+
+ * `A B` if `merge_repeated = True`.
+ * `A B B B` if `merge_repeated = False`.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+3-D `float` `Tensor`, size `[max_time x batch_size x num_classes]`.
+The logits.
+ |
+
+|
+`sequence_length`
+ |
+
+1-D `int32` vector containing sequence lengths, having size
+`[batch_size]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`beam_width`
+ |
+
+An int scalar >= 0 (beam search beam width).
+ |
+
+|
+`top_paths`
+ |
+
+An int scalar >= 0, <= beam_width (controls output size).
+ |
+
+|
+`merge_repeated`
+ |
+
+Boolean. Default: True.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A tuple `(decoded, log_probabilities)` where
+ |
+
+
+|
+`decoded`
+ |
+
+A list of length top_paths, where `decoded[j]`
+is a `SparseTensor` containing the decoded outputs:
+
+`decoded[j].indices`: Indices matrix `(total_decoded_outputs[j] x 2)`
+The rows store: [batch, time].
+
+`decoded[j].values`: Values vector, size `(total_decoded_outputs[j])`.
+The vector stores the decoded classes for beam j.
+
+`decoded[j].dense_shape`: Shape vector, size `(2)`.
+The shape values are: `[batch_size, max_decoded_length[j]]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`log_probability`
+ |
+
+A `float` matrix `(batch_size x top_paths)` containing
+sequence log-probabilities.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/ctc_loss.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/ctc_loss.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..277eeb307f0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/ctc_loss.md
@@ -0,0 +1,222 @@
+description: Computes the CTC (Connectionist Temporal Classification) Loss.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.ctc_loss
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the CTC (Connectionist Temporal Classification) Loss.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.ctc_loss(
+ labels, inputs=None, sequence_length=None, preprocess_collapse_repeated=(False),
+ ctc_merge_repeated=(True), ignore_longer_outputs_than_inputs=(False),
+ time_major=(True), logits=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This op implements the CTC loss as presented in (Graves et al., 2016).
+
+#### Input requirements:
+
+
+
+```
+sequence_length(b) <= time for all b
+
+max(labels.indices(labels.indices[:, 1] == b, 2))
+ <= sequence_length(b) for all b.
+```
+
+#### Notes:
+
+
+
+This class performs the softmax operation for you, so inputs should
+be e.g. linear projections of outputs by an LSTM.
+
+The `inputs` Tensor's innermost dimension size, `num_classes`, represents
+`num_labels + 1` classes, where num_labels is the number of true labels, and
+the largest value `(num_classes - 1)` is reserved for the blank label.
+
+For example, for a vocabulary containing 3 labels `[a, b, c]`,
+`num_classes = 4` and the labels indexing is `{a: 0, b: 1, c: 2, blank: 3}`.
+
+Regarding the arguments `preprocess_collapse_repeated` and
+`ctc_merge_repeated`:
+
+If `preprocess_collapse_repeated` is True, then a preprocessing step runs
+before loss calculation, wherein repeated labels passed to the loss
+are merged into single labels. This is useful if the training labels come
+from, e.g., forced alignments and therefore have unnecessary repetitions.
+
+If `ctc_merge_repeated` is set False, then deep within the CTC calculation,
+repeated non-blank labels will not be merged and are interpreted
+as individual labels. This is a simplified (non-standard) version of CTC.
+
+Here is a table of the (roughly) expected first order behavior:
+
+* `preprocess_collapse_repeated=False`, `ctc_merge_repeated=True`
+
+ Classical CTC behavior: Outputs true repeated classes with blanks in
+ between, and can also output repeated classes with no blanks in
+ between that need to be collapsed by the decoder.
+
+* `preprocess_collapse_repeated=True`, `ctc_merge_repeated=False`
+
+ Never learns to output repeated classes, as they are collapsed
+ in the input labels before training.
+
+* `preprocess_collapse_repeated=False`, `ctc_merge_repeated=False`
+
+ Outputs repeated classes with blanks in between, but generally does not
+ require the decoder to collapse/merge repeated classes.
+
+* `preprocess_collapse_repeated=True`, `ctc_merge_repeated=True`
+
+ Untested. Very likely will not learn to output repeated classes.
+
+The `ignore_longer_outputs_than_inputs` option allows to specify the behavior
+of the CTCLoss when dealing with sequences that have longer outputs than
+inputs. If true, the CTCLoss will simply return zero gradient for those
+items, otherwise an InvalidArgument error is returned, stopping training.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+An `int32` `SparseTensor`.
+`labels.indices[i, :] == [b, t]` means `labels.values[i]` stores the id
+for (batch b, time t). `labels.values[i]` must take on values in `[0,
+num_labels)`. See `core/ops/ctc_ops.cc` for more details.
+ |
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+3-D `float` `Tensor`.
+If time_major == False, this will be a `Tensor` shaped: `[batch_size,
+max_time, num_classes]`.
+If time_major == True (default), this will be a `Tensor` shaped:
+`[max_time, batch_size, num_classes]`. The logits.
+ |
+
+|
+`sequence_length`
+ |
+
+1-D `int32` vector, size `[batch_size]`. The sequence
+lengths.
+ |
+
+|
+`preprocess_collapse_repeated`
+ |
+
+Boolean. Default: False. If True, repeated
+labels are collapsed prior to the CTC calculation.
+ |
+
+|
+`ctc_merge_repeated`
+ |
+
+Boolean. Default: True.
+ |
+
+|
+`ignore_longer_outputs_than_inputs`
+ |
+
+Boolean. Default: False. If True,
+sequences with longer outputs than inputs will be ignored.
+ |
+
+|
+`time_major`
+ |
+
+The shape format of the `inputs` Tensors. If True, these
+`Tensors` must be shaped `[max_time, batch_size, num_classes]`. If False,
+these `Tensors` must be shaped `[batch_size, max_time, num_classes]`.
+Using `time_major = True` (default) is a bit more efficient because it
+avoids transposes at the beginning of the ctc_loss calculation. However,
+most TensorFlow data is batch-major, so by this function also accepts
+inputs in batch-major form.
+ |
+
+|
+`logits`
+ |
+
+Alias for inputs.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A 1-D `float` `Tensor`, size `[batch]`, containing the negative log
+probabilities.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+if labels is not a `SparseTensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### References:
+
+Connectionist Temporal Classification - Labeling Unsegmented Sequence Data
+with Recurrent Neural Networks:
+ [Graves et al., 2016](https://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1143891)
+ ([pdf](http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~graves/icml_2006.pdf))
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/ctc_loss_v2.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/ctc_loss_v2.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..746b62d3126
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/ctc_loss_v2.md
@@ -0,0 +1,150 @@
+description: Computes CTC (Connectionist Temporal Classification) loss.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.ctc_loss_v2
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes CTC (Connectionist Temporal Classification) loss.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.ctc_loss_v2(
+ labels, logits, label_length, logit_length, logits_time_major=(True),
+ unique=None, blank_index=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This op implements the CTC loss as presented in (Graves et al., 2016).
+
+#### Notes:
+
+
+
+- Same as the "Classic CTC" in TensorFlow 1.x's tf.compat.v1.nn.ctc_loss
+ setting of preprocess_collapse_repeated=False, ctc_merge_repeated=True
+- Labels may be supplied as either a dense, zero-padded tensor with a
+ vector of label sequence lengths OR as a SparseTensor.
+- On TPU and GPU: Only dense padded labels are supported.
+- On CPU: Caller may use SparseTensor or dense padded labels but calling with
+ a SparseTensor will be significantly faster.
+- Default blank label is 0 rather num_classes - 1, unless overridden by
+ blank_index.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+tensor of shape [batch_size, max_label_seq_length] or SparseTensor
+ |
+
+|
+`logits`
+ |
+
+tensor of shape [frames, batch_size, num_labels], if
+logits_time_major == False, shape is [batch_size, frames, num_labels].
+ |
+
+|
+`label_length`
+ |
+
+tensor of shape [batch_size], None if labels is SparseTensor
+Length of reference label sequence in labels.
+ |
+
+|
+`logit_length`
+ |
+
+tensor of shape [batch_size] Length of input sequence in
+logits.
+ |
+
+|
+`logits_time_major`
+ |
+
+(optional) If True (default), logits is shaped [time,
+batch, logits]. If False, shape is [batch, time, logits]
+ |
+
+|
+`unique`
+ |
+
+(optional) Unique label indices as computed by
+ctc_unique_labels(labels). If supplied, enable a faster, memory efficient
+implementation on TPU.
+ |
+
+|
+`blank_index`
+ |
+
+(optional) Set the class index to use for the blank label.
+Negative values will start from num_classes, ie, -1 will reproduce the
+ctc_loss behavior of using num_classes - 1 for the blank symbol. There is
+some memory/performance overhead to switching from the default of 0 as an
+additional shifted copy of the logits may be created.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for this `Op`. Defaults to "ctc_loss_dense".
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`loss`
+ |
+
+tensor of shape [batch_size], negative log probabilities.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### References:
+
+Connectionist Temporal Classification - Labeling Unsegmented Sequence Data
+with Recurrent Neural Networks:
+ [Graves et al., 2016](https://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1143891)
+ ([pdf](http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~graves/icml_2006.pdf))
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/depthwise_conv2d.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/depthwise_conv2d.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..df3945175d3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/depthwise_conv2d.md
@@ -0,0 +1,140 @@
+description: Depthwise 2-D convolution.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.depthwise_conv2d
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Depthwise 2-D convolution.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.depthwise_conv2d(
+ input, filter, strides, padding, rate=None, name=None, data_format=None,
+ dilations=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Given a 4D input tensor ('NHWC' or 'NCHW' data formats)
+and a filter tensor of shape
+`[filter_height, filter_width, in_channels, channel_multiplier]`
+containing `in_channels` convolutional filters of depth 1, `depthwise_conv2d`
+applies a different filter to each input channel (expanding from 1 channel
+to `channel_multiplier` channels for each), then concatenates the results
+together. The output has `in_channels * channel_multiplier` channels.
+
+In detail, with the default NHWC format,
+
+ output[b, i, j, k * channel_multiplier + q] = sum_{di, dj}
+ filter[di, dj, k, q] * input[b, strides[1] * i + rate[0] * di,
+ strides[2] * j + rate[1] * dj, k]
+
+Must have `strides[0] = strides[3] = 1`. For the most common case of the
+same horizontal and vertical strides, `strides = [1, stride, stride, 1]`.
+If any value in `rate` is greater than 1, we perform atrous depthwise
+convolution, in which case all values in the `strides` tensor must be equal
+to 1.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input`
+ |
+
+4-D with shape according to `data_format`.
+ |
+
+|
+`filter`
+ |
+
+4-D with shape
+`[filter_height, filter_width, in_channels, channel_multiplier]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+1-D of size 4. The stride of the sliding window for each
+dimension of `input`.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+A string, either `'VALID'` or `'SAME'`. The padding algorithm.
+See the "returns" section of tf.nn.convolution for details.
+ |
+
+|
+`rate`
+ |
+
+1-D of size 2. The dilation rate in which we sample input values
+across the `height` and `width` dimensions in atrous convolution. If it is
+greater than 1, then all values of strides must be 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for this operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+The data format for input. Either "NHWC" (default) or "NCHW".
+ |
+
+|
+`dilations`
+ |
+
+Alias of rate.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A 4-D `Tensor` with shape according to `data_format`. E.g., for
+"NHWC" format, shape is
+`[batch, out_height, out_width, in_channels * channel_multiplier].`
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/depthwise_conv2d_native.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/depthwise_conv2d_native.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..f0568f2f3b5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/depthwise_conv2d_native.md
@@ -0,0 +1,133 @@
+description: Computes a 2-D depthwise convolution given 4-D input and filter tensors.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.depthwise_conv2d_native
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes a 2-D depthwise convolution given 4-D `input` and `filter` tensors.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.depthwise_conv2d_native(
+ input, filter, strides, padding, data_format='NHWC', dilations=[1, 1, 1, 1],
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Given an input tensor of shape `[batch, in_height, in_width, in_channels]`
+and a filter / kernel tensor of shape
+`[filter_height, filter_width, in_channels, channel_multiplier]`, containing
+`in_channels` convolutional filters of depth 1, `depthwise_conv2d` applies
+a different filter to each input channel (expanding from 1 channel to
+`channel_multiplier` channels for each), then concatenates the results
+together. Thus, the output has `in_channels * channel_multiplier` channels.
+
+```
+for k in 0..in_channels-1
+ for q in 0..channel_multiplier-1
+ output[b, i, j, k * channel_multiplier + q] =
+ sum_{di, dj} input[b, strides[1] * i + di, strides[2] * j + dj, k] *
+ filter[di, dj, k, q]
+```
+
+Must have `strides[0] = strides[3] = 1`. For the most common case of the same
+horizontal and vertices strides, `strides = [1, stride, stride, 1]`.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `half`, `bfloat16`, `float32`, `float64`.
+ |
+
+|
+`filter`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must have the same type as `input`.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+A list of `ints`.
+1-D of length 4. The stride of the sliding window for each dimension
+of `input`.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+A `string` from: `"SAME", "VALID"`.
+The type of padding algorithm to use.
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+An optional `string` from: `"NHWC", "NCHW"`. Defaults to `"NHWC"`.
+Specify the data format of the input and output data. With the
+default format "NHWC", the data is stored in the order of:
+[batch, height, width, channels].
+Alternatively, the format could be "NCHW", the data storage order of:
+[batch, channels, height, width].
+ |
+
+|
+`dilations`
+ |
+
+An optional list of `ints`. Defaults to `[1, 1, 1, 1]`.
+1-D tensor of length 4. The dilation factor for each dimension of
+`input`. If set to k > 1, there will be k-1 skipped cells between each filter
+element on that dimension. The dimension order is determined by the value of
+`data_format`, see above for details. Dilations in the batch and depth
+dimensions must be 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `input`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/dilation2d.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/dilation2d.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..b1f279a087c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/dilation2d.md
@@ -0,0 +1,130 @@
+description: Computes the grayscale dilation of 4-D input and 3-D filter tensors.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.dilation2d
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the grayscale dilation of 4-D `input` and 3-D `filter` tensors.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.dilation2d(
+ input, filter=None, strides=None, rates=None, padding=None, name=None,
+ filters=None, dilations=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The `input` tensor has shape `[batch, in_height, in_width, depth]` and the
+`filter` tensor has shape `[filter_height, filter_width, depth]`, i.e., each
+input channel is processed independently of the others with its own structuring
+function. The `output` tensor has shape
+`[batch, out_height, out_width, depth]`. The spatial dimensions of the output
+tensor depend on the `padding` algorithm. We currently only support the default
+"NHWC" `data_format`.
+
+In detail, the grayscale morphological 2-D dilation is the max-sum correlation
+(for consistency with `conv2d`, we use unmirrored filters):
+
+ output[b, y, x, c] =
+ max_{dy, dx} input[b,
+ strides[1] * y + rates[1] * dy,
+ strides[2] * x + rates[2] * dx,
+ c] +
+ filter[dy, dx, c]
+
+Max-pooling is a special case when the filter has size equal to the pooling
+kernel size and contains all zeros.
+
+Note on duality: The dilation of `input` by the `filter` is equal to the
+negation of the erosion of `-input` by the reflected `filter`.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `float32`, `float64`, `int32`, `uint8`, `int16`, `int8`, `int64`, `bfloat16`, `uint16`, `half`, `uint32`, `uint64`.
+4-D with shape `[batch, in_height, in_width, depth]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`filter`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must have the same type as `input`.
+3-D with shape `[filter_height, filter_width, depth]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+A list of `ints` that has length `>= 4`.
+The stride of the sliding window for each dimension of the input
+tensor. Must be: `[1, stride_height, stride_width, 1]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`rates`
+ |
+
+A list of `ints` that has length `>= 4`.
+The input stride for atrous morphological dilation. Must be:
+`[1, rate_height, rate_width, 1]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+A `string` from: `"SAME", "VALID"`.
+The type of padding algorithm to use.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `input`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/dropout.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/dropout.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..eed80bdb270
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/dropout.md
@@ -0,0 +1,135 @@
+description: Computes dropout. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.dropout
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes dropout. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.dropout(
+ x, keep_prob=None, noise_shape=None, seed=None, name=None, rate=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: SOME ARGUMENTS ARE DEPRECATED: `(keep_prob)`. They will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Please use `rate` instead of `keep_prob`. Rate should be set to `rate = 1 - keep_prob`.
+
+For each element of `x`, with probability `rate`, outputs `0`, and otherwise
+scales up the input by `1 / (1-rate)`. The scaling is such that the expected
+sum is unchanged.
+
+By default, each element is kept or dropped independently. If `noise_shape`
+is specified, it must be
+[broadcastable](http://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/user/basics.broadcasting.html)
+to the shape of `x`, and only dimensions with `noise_shape[i] == shape(x)[i]`
+will make independent decisions. For example, if `shape(x) = [k, l, m, n]`
+and `noise_shape = [k, 1, 1, n]`, each batch and channel component will be
+kept independently and each row and column will be kept or not kept together.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`x`
+ |
+
+A floating point tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`keep_prob`
+ |
+
+(deprecated) A deprecated alias for `(1-rate)`.
+ |
+
+|
+`noise_shape`
+ |
+
+A 1-D `Tensor` of type `int32`, representing the
+shape for randomly generated keep/drop flags.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+A Python integer. Used to create random seeds. See
+tf.random.set_seed for behavior.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for this operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`rate`
+ |
+
+A scalar `Tensor` with the same type as `x`. The probability that each
+element of `x` is discarded.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A Tensor of the same shape of `x`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `rate` is not in `[0, 1)` or if `x` is not a floating
+point tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/dynamic_rnn.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/dynamic_rnn.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..c83bd025476
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/dynamic_rnn.md
@@ -0,0 +1,248 @@
+description: Creates a recurrent neural network specified by RNNCell cell. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.dynamic_rnn
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Creates a recurrent neural network specified by RNNCell `cell`. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.dynamic_rnn(
+ cell, inputs, sequence_length=None, initial_state=None, dtype=None,
+ parallel_iterations=None, swap_memory=(False), time_major=(False), scope=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Please use `keras.layers.RNN(cell)`, which is equivalent to this API
+
+Performs fully dynamic unrolling of `inputs`.
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+# create a BasicRNNCell
+rnn_cell = tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.BasicRNNCell(hidden_size)
+
+# 'outputs' is a tensor of shape [batch_size, max_time, cell_state_size]
+
+# defining initial state
+initial_state = rnn_cell.zero_state(batch_size, dtype=tf.float32)
+
+# 'state' is a tensor of shape [batch_size, cell_state_size]
+outputs, state = tf.compat.v1.nn.dynamic_rnn(rnn_cell, input_data,
+ initial_state=initial_state,
+ dtype=tf.float32)
+```
+
+```python
+# create 2 LSTMCells
+rnn_layers = [tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.LSTMCell(size) for size in [128, 256]]
+
+# create a RNN cell composed sequentially of a number of RNNCells
+multi_rnn_cell = tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.MultiRNNCell(rnn_layers)
+
+# 'outputs' is a tensor of shape [batch_size, max_time, 256]
+# 'state' is a N-tuple where N is the number of LSTMCells containing a
+# tf.nn.rnn_cell.LSTMStateTuple for each cell
+outputs, state = tf.compat.v1.nn.dynamic_rnn(cell=multi_rnn_cell,
+ inputs=data,
+ dtype=tf.float32)
+```
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cell`
+ |
+
+An instance of RNNCell.
+ |
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+The RNN inputs.
+If `time_major == False` (default), this must be a `Tensor` of shape:
+`[batch_size, max_time, ...]`, or a nested tuple of such elements.
+If `time_major == True`, this must be a `Tensor` of shape: `[max_time,
+batch_size, ...]`, or a nested tuple of such elements. This may also be
+a (possibly nested) tuple of Tensors satisfying this property. The
+first two dimensions must match across all the inputs, but otherwise the
+ranks and other shape components may differ. In this case, input to
+`cell` at each time-step will replicate the structure of these tuples,
+except for the time dimension (from which the time is taken). The input
+to `cell` at each time step will be a `Tensor` or (possibly nested)
+tuple of Tensors each with dimensions `[batch_size, ...]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`sequence_length`
+ |
+
+(optional) An int32/int64 vector sized `[batch_size]`. Used
+to copy-through state and zero-out outputs when past a batch element's
+sequence length. This parameter enables users to extract the last valid
+state and properly padded outputs, so it is provided for correctness.
+ |
+
+|
+`initial_state`
+ |
+
+(optional) An initial state for the RNN. If `cell.state_size`
+is an integer, this must be a `Tensor` of appropriate type and shape
+`[batch_size, cell.state_size]`. If `cell.state_size` is a tuple, this
+should be a tuple of tensors having shapes `[batch_size, s] for s in
+cell.state_size`.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+(optional) The data type for the initial state and expected output.
+Required if initial_state is not provided or RNN state has a heterogeneous
+dtype.
+ |
+
+|
+`parallel_iterations`
+ |
+
+(Default: 32). The number of iterations to run in
+parallel. Those operations which do not have any temporal dependency and
+can be run in parallel, will be. This parameter trades off time for
+space. Values >> 1 use more memory but take less time, while smaller
+values use less memory but computations take longer.
+ |
+
+|
+`swap_memory`
+ |
+
+Transparently swap the tensors produced in forward inference
+but needed for back prop from GPU to CPU. This allows training RNNs which
+would typically not fit on a single GPU, with very minimal (or no)
+performance penalty.
+ |
+
+|
+`time_major`
+ |
+
+The shape format of the `inputs` and `outputs` Tensors. If true,
+these `Tensors` must be shaped `[max_time, batch_size, depth]`. If false,
+these `Tensors` must be shaped `[batch_size, max_time, depth]`. Using
+`time_major = True` is a bit more efficient because it avoids transposes
+at the beginning and end of the RNN calculation. However, most TensorFlow
+data is batch-major, so by default this function accepts input and emits
+output in batch-major form.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope`
+ |
+
+VariableScope for the created subgraph; defaults to "rnn".
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A pair (outputs, state) where:
+ |
+
+
+|
+`outputs`
+ |
+
+The RNN output `Tensor`.
+
+If time_major == False (default), this will be a `Tensor` shaped:
+`[batch_size, max_time, cell.output_size]`.
+
+If time_major == True, this will be a `Tensor` shaped:
+`[max_time, batch_size, cell.output_size]`.
+
+Note, if `cell.output_size` is a (possibly nested) tuple of integers
+or `TensorShape` objects, then `outputs` will be a tuple having the
+same structure as `cell.output_size`, containing Tensors having shapes
+corresponding to the shape data in `cell.output_size`.
+ |
+
+|
+`state`
+ |
+
+The final state. If `cell.state_size` is an int, this
+will be shaped `[batch_size, cell.state_size]`. If it is a
+`TensorShape`, this will be shaped `[batch_size] + cell.state_size`.
+If it is a (possibly nested) tuple of ints or `TensorShape`, this will
+be a tuple having the corresponding shapes. If cells are `LSTMCells`
+`state` will be a tuple containing a `LSTMStateTuple` for each cell.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `cell` is not an instance of RNNCell.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If inputs is None or an empty list.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/embedding_lookup.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/embedding_lookup.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a3849b3b62f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/embedding_lookup.md
@@ -0,0 +1,154 @@
+description: Looks up ids in a list of embedding tensors.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.embedding_lookup
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Looks up `ids` in a list of embedding tensors.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.embedding_lookup(
+ params, ids, partition_strategy='mod', name=None, validate_indices=(True),
+ max_norm=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This function is used to perform parallel lookups on the list of tensors in
+`params`. It is a generalization of tf.gather, where `params` is
+interpreted as a partitioning of a large embedding tensor. `params` may be
+a `PartitionedVariable` as returned by using tf.compat.v1.get_variable()
+with a partitioner.
+
+If `len(params) > 1`, each element `id` of `ids` is partitioned between
+the elements of `params` according to the `partition_strategy`.
+In all strategies, if the id space does not evenly divide the number of
+partitions, each of the first `(max_id + 1) % len(params)` partitions will
+be assigned one more id.
+
+If `partition_strategy` is `"mod"`, we assign each id to partition
+`p = id % len(params)`. For instance,
+13 ids are split across 5 partitions as:
+`[[0, 5, 10], [1, 6, 11], [2, 7, 12], [3, 8], [4, 9]]`
+
+If `partition_strategy` is `"div"`, we assign ids to partitions in a
+contiguous manner. In this case, 13 ids are split across 5 partitions as:
+`[[0, 1, 2], [3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8], [9, 10], [11, 12]]`
+
+If the input ids are ragged tensors, partition variables are not supported and
+the partition strategy and the max_norm are ignored.
+The results of the lookup are concatenated into a dense
+tensor. The returned tensor has shape `shape(ids) + shape(params)[1:]`.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`params`
+ |
+
+A single tensor representing the complete embedding tensor, or a
+list of P tensors all of same shape except for the first dimension,
+representing sharded embedding tensors. Alternatively, a
+`PartitionedVariable`, created by partitioning along dimension 0. Each
+element must be appropriately sized for the given `partition_strategy`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ids`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` or a 'RaggedTensor' with type `int32` or `int64` containing
+the ids to be looked up in `params`.
+ |
+
+|
+`partition_strategy`
+ |
+
+A string specifying the partitioning strategy, relevant
+if `len(params) > 1`. Currently `"div"` and `"mod"` are supported. Default
+is `"mod"`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`validate_indices`
+ |
+
+DEPRECATED. If this operation is assigned to CPU, values
+in `indices` are always validated to be within range. If assigned to GPU,
+out-of-bound indices result in safe but unspecified behavior, which may
+include raising an error.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_norm`
+ |
+
+If not `None`, each embedding is clipped if its l2-norm is larger
+than this value.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` or a 'RaggedTensor', depending on the input, with the same type
+as the tensors in `params`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `params` is empty.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/embedding_lookup_sparse.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/embedding_lookup_sparse.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..c82cf5c032e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/embedding_lookup_sparse.md
@@ -0,0 +1,184 @@
+description: Computes embeddings for the given ids and weights.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.embedding_lookup_sparse
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes embeddings for the given ids and weights.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.embedding_lookup_sparse(
+ params, sp_ids, sp_weights, partition_strategy='mod', name=None, combiner=None,
+ max_norm=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This op assumes that there is at least one id for each row in the dense tensor
+represented by sp_ids (i.e. there are no rows with empty features), and that
+all the indices of sp_ids are in canonical row-major order.
+
+It also assumes that all id values lie in the range [0, p0), where p0
+is the sum of the size of params along dimension 0.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`params`
+ |
+
+A single tensor representing the complete embedding tensor, or a
+list of P tensors all of same shape except for the first dimension,
+representing sharded embedding tensors. Alternatively, a
+`PartitionedVariable`, created by partitioning along dimension 0. Each
+element must be appropriately sized for the given `partition_strategy`.
+ |
+
+|
+`sp_ids`
+ |
+
+N x M `SparseTensor` of int64 ids where N is typically batch size
+and M is arbitrary.
+ |
+
+|
+`sp_weights`
+ |
+
+either a `SparseTensor` of float / double weights, or `None` to
+indicate all weights should be taken to be 1. If specified, `sp_weights`
+must have exactly the same shape and indices as `sp_ids`.
+ |
+
+|
+`partition_strategy`
+ |
+
+A string specifying the partitioning strategy, relevant
+if `len(params) > 1`. Currently `"div"` and `"mod"` are supported. Default
+is `"mod"`. See `tf.nn.embedding_lookup` for more details.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the op.
+ |
+
+|
+`combiner`
+ |
+
+A string specifying the reduction op. Currently "mean", "sqrtn"
+and "sum" are supported. "sum" computes the weighted sum of the embedding
+results for each row. "mean" is the weighted sum divided by the total
+weight. "sqrtn" is the weighted sum divided by the square root of the sum
+of the squares of the weights.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_norm`
+ |
+
+If not `None`, each embedding is clipped if its l2-norm is larger
+than this value, before combining.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A dense tensor representing the combined embeddings for the
+sparse ids. For each row in the dense tensor represented by `sp_ids`, the op
+looks up the embeddings for all ids in that row, multiplies them by the
+corresponding weight, and combines these embeddings as specified.
+
+In other words, if
+
+`shape(combined params) = [p0, p1, ..., pm]`
+
+and
+
+`shape(sp_ids) = shape(sp_weights) = [d0, d1, ..., dn]`
+
+then
+
+`shape(output) = [d0, d1, ..., dn-1, p1, ..., pm]`.
+
+For instance, if params is a 10x20 matrix, and sp_ids / sp_weights are
+
+```python
+[0, 0]: id 1, weight 2.0
+[0, 1]: id 3, weight 0.5
+[1, 0]: id 0, weight 1.0
+[2, 3]: id 1, weight 3.0
+```
+
+with `combiner`="mean", then the output will be a 3x20 matrix where
+
+```python
+output[0, :] = (params[1, :] * 2.0 + params[3, :] * 0.5) / (2.0 + 0.5)
+output[1, :] = (params[0, :] * 1.0) / 1.0
+output[2, :] = (params[1, :] * 3.0) / 3.0
+```
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `sp_ids` is not a `SparseTensor`, or if `sp_weights` is
+neither `None` nor `SparseTensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `combiner` is not one of {"mean", "sqrtn", "sum"}.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/erosion2d.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/erosion2d.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..515c5219525
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/erosion2d.md
@@ -0,0 +1,144 @@
+description: Computes the grayscale erosion of 4-D value and 3-D kernel tensors.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.erosion2d
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the grayscale erosion of 4-D `value` and 3-D `kernel` tensors.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.erosion2d(
+ value, kernel, strides, rates, padding, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The `value` tensor has shape `[batch, in_height, in_width, depth]` and the
+`kernel` tensor has shape `[kernel_height, kernel_width, depth]`, i.e.,
+each input channel is processed independently of the others with its own
+structuring function. The `output` tensor has shape
+`[batch, out_height, out_width, depth]`. The spatial dimensions of the
+output tensor depend on the `padding` algorithm. We currently only support the
+default "NHWC" `data_format`.
+
+In detail, the grayscale morphological 2-D erosion is given by:
+
+ output[b, y, x, c] =
+ min_{dy, dx} value[b,
+ strides[1] * y - rates[1] * dy,
+ strides[2] * x - rates[2] * dx,
+ c] -
+ kernel[dy, dx, c]
+
+Duality: The erosion of `value` by the `kernel` is equal to the negation of
+the dilation of `-value` by the reflected `kernel`.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. 4-D with shape `[batch, in_height, in_width, depth]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must have the same type as `value`.
+3-D with shape `[kernel_height, kernel_width, depth]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+A list of `ints` that has length `>= 4`.
+1-D of length 4. The stride of the sliding window for each dimension of
+the input tensor. Must be: `[1, stride_height, stride_width, 1]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`rates`
+ |
+
+A list of `ints` that has length `>= 4`.
+1-D of length 4. The input stride for atrous morphological dilation.
+Must be: `[1, rate_height, rate_width, 1]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+A `string` from: `"SAME", "VALID"`.
+The type of padding algorithm to use.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional). If not specified "erosion2d"
+is used.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `value`.
+4-D with shape `[batch, out_height, out_width, depth]`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `value` depth does not match `kernel`' shape, or if
+padding is other than `'VALID'` or `'SAME'`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/fractional_avg_pool.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/fractional_avg_pool.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..1cf8e1d86c2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/fractional_avg_pool.md
@@ -0,0 +1,150 @@
+description: Performs fractional average pooling on the input. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.fractional_avg_pool
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Performs fractional average pooling on the input. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.fractional_avg_pool(
+ value, pooling_ratio, pseudo_random=(False), overlapping=(False),
+ deterministic=(False), seed=0, seed2=0, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+`seed2` and `deterministic` args are deprecated. Use fractional_avg_pool_v2.
+
+This is a deprecated version of `fractional_avg_pool`.
+
+Fractional average pooling is similar to Fractional max pooling in the pooling
+region generation step. The only difference is that after pooling regions are
+generated, a mean operation is performed instead of a max operation in each
+pooling region.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. 4-D with shape `[batch, height, width, channels]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`pooling_ratio`
+ |
+
+A list of `floats` that has length >= 4. Pooling ratio for
+each dimension of `value`, currently only supports row and col dimension
+and should be >= 1.0. For example, a valid pooling ratio looks like [1.0,
+1.44, 1.73, 1.0]. The first and last elements must be 1.0 because we don't
+allow pooling on batch and channels dimensions. 1.44 and 1.73 are pooling
+ratio on height and width dimensions respectively.
+ |
+
+|
+`pseudo_random`
+ |
+
+An optional `bool`. Defaults to `False`. When set to `True`,
+generates the pooling sequence in a pseudorandom fashion, otherwise, in a
+random fashion. Check paper (Graham, 2015) for difference between
+pseudorandom and random.
+ |
+
+|
+`overlapping`
+ |
+
+An optional `bool`. Defaults to `False`. When set to `True`,
+it means when pooling, the values at the boundary of adjacent pooling
+cells are used by both cells. For example:
+`index 0 1 2 3 4`
+`value 20 5 16 3 7`
+If the pooling sequence is [0, 2, 4], then 16, at index 2 will be used
+twice. The result would be [20, 16] for fractional avg pooling.
+ |
+
+|
+`deterministic`
+ |
+
+An optional `bool`. Deprecated; use `fractional_avg_pool_v2`
+instead.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+An optional `int`. Defaults to `0`. If set to be non-zero, the
+random number generator is seeded by the given seed. Otherwise it is
+seeded by a random seed.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed2`
+ |
+
+An optional `int`. Deprecated; use `fractional_avg_pool_v2` instead.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A tuple of `Tensor` objects (`output`, `row_pooling_sequence`,
+`col_pooling_sequence`).
+ output: Output `Tensor` after fractional avg pooling. Has the same type as
+ `value`.
+ row_pooling_sequence: A `Tensor` of type `int64`.
+ col_pooling_sequence: A `Tensor` of type `int64`.
+
+#### References:
+
+Fractional Max-Pooling:
+ [Graham, 2015](https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6071)
+ ([pdf](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1412.6071.pdf))
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/fractional_max_pool.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/fractional_max_pool.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..22678fc47f4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/fractional_max_pool.md
@@ -0,0 +1,171 @@
+description: Performs fractional max pooling on the input. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.fractional_max_pool
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Performs fractional max pooling on the input. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.fractional_max_pool(
+ value, pooling_ratio, pseudo_random=(False), overlapping=(False),
+ deterministic=(False), seed=0, seed2=0, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+`seed2` and `deterministic` args are deprecated. Use fractional_max_pool_v2.
+
+This is a deprecated version of `fractional_max_pool`.
+
+Fractional max pooling is slightly different than regular max pooling. In
+regular max pooling, you downsize an input set by taking the maximum value of
+smaller N x N subsections of the set (often 2x2), and try to reduce the set by
+a factor of N, where N is an integer. Fractional max pooling, as you might
+expect from the word "fractional", means that the overall reduction ratio N
+does not have to be an integer.
+
+The sizes of the pooling regions are generated randomly but are fairly
+uniform. For example, let's look at the height dimension, and the constraints
+on the list of rows that will be pool boundaries.
+
+First we define the following:
+
+1. input_row_length : the number of rows from the input set
+2. output_row_length : which will be smaller than the input
+3. alpha = input_row_length / output_row_length : our reduction ratio
+4. K = floor(alpha)
+5. row_pooling_sequence : this is the result list of pool boundary rows
+
+Then, row_pooling_sequence should satisfy:
+
+1. a[0] = 0 : the first value of the sequence is 0
+2. a[end] = input_row_length : the last value of the sequence is the size
+3. K <= (a[i+1] - a[i]) <= K+1 : all intervals are K or K+1 size
+4. length(row_pooling_sequence) = output_row_length+1
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. 4-D with shape `[batch, height, width, channels]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`pooling_ratio`
+ |
+
+A list of `floats` that has length >= 4. Pooling ratio for
+each dimension of `value`, currently only supports row and col dimension
+and should be >= 1.0. For example, a valid pooling ratio looks like [1.0,
+1.44, 1.73, 1.0]. The first and last elements must be 1.0 because we don't
+allow pooling on batch and channels dimensions. 1.44 and 1.73 are pooling
+ratio on height and width dimensions respectively.
+ |
+
+|
+`pseudo_random`
+ |
+
+An optional `bool`. Defaults to `False`. When set to `True`,
+generates the pooling sequence in a pseudorandom fashion, otherwise, in a
+random fashion. Check (Graham, 2015) for difference between
+pseudorandom and random.
+ |
+
+|
+`overlapping`
+ |
+
+An optional `bool`. Defaults to `False`. When set to `True`,
+it means when pooling, the values at the boundary of adjacent pooling
+cells are used by both cells. For example:
+`index 0 1 2 3 4`
+`value 20 5 16 3 7`
+If the pooling sequence is [0, 2, 4], then 16, at index 2 will be used
+twice. The result would be [20, 16] for fractional max pooling.
+ |
+
+|
+`deterministic`
+ |
+
+An optional `bool`. Deprecated; use `fractional_max_pool_v2`
+instead.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+An optional `int`. Defaults to `0`. If set to be non-zero, the
+random number generator is seeded by the given seed. Otherwise it is
+seeded by a random seed.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed2`
+ |
+
+An optional `int`. Deprecated; use `fractional_max_pool_v2` instead.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A tuple of `Tensor` objects (`output`, `row_pooling_sequence`,
+`col_pooling_sequence`).
+ output: Output `Tensor` after fractional max pooling. Has the same type as
+ `value`.
+ row_pooling_sequence: A `Tensor` of type `int64`.
+ col_pooling_sequence: A `Tensor` of type `int64`.
+
+#### References:
+
+Fractional Max-Pooling:
+ [Graham, 2015](https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6071)
+ ([pdf](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1412.6071.pdf))
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/fused_batch_norm.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/fused_batch_norm.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a9662c75b0f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/fused_batch_norm.md
@@ -0,0 +1,188 @@
+description: Batch normalization.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.fused_batch_norm
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Batch normalization.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.fused_batch_norm(
+ x, scale, offset, mean=None, variance=None, epsilon=0.001, data_format='NHWC',
+ is_training=(True), name=None, exponential_avg_factor=1.0
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+See Source: [Batch Normalization: Accelerating Deep Network Training by
+Reducing Internal Covariate Shift; S. Ioffe, C. Szegedy]
+(http://arxiv.org/abs/1502.03167).
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`x`
+ |
+
+Input `Tensor` of 4 dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`scale`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of 1 dimension for scaling.
+ |
+
+|
+`offset`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of 1 dimension for bias.
+ |
+
+|
+`mean`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of 1 dimension for population mean. The shape and meaning
+of this argument depends on the value of is_training and
+exponential_avg_factor as follows:
+is_training==False (inference):
+Mean must be a `Tensor` of the same shape as scale containing the
+estimated population mean computed during training.
+is_training==True and exponential_avg_factor == 1.0:
+Mean must be None.
+is_training==True and exponential_avg_factor != 1.0:
+Mean must be a `Tensor` of the same shape as scale containing the
+exponential running mean.
+ |
+
+|
+`variance`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of 1 dimension for population variance. The shape and
+meaning of this argument depends on the value of is_training and
+exponential_avg_factor as follows:
+is_training==False (inference):
+Variance must be a `Tensor` of the same shape as scale containing
+the estimated population variance computed during training.
+is_training==True and exponential_avg_factor == 1.0:
+Variance must be None.
+is_training==True and exponential_avg_factor != 1.0:
+Variance must be a `Tensor` of the same shape as scale containing
+the exponential running variance.
+ |
+
+|
+`epsilon`
+ |
+
+A small float number added to the variance of x.
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+The data format for x. Either "NHWC" (default) or "NCHW".
+ |
+
+|
+`is_training`
+ |
+
+A bool value to specify if the operation is used for
+training or inference.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for this operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`exponential_avg_factor`
+ |
+
+A float number (usually between 0 and 1) used
+for controlling the decay of the running
+population average of mean and variance.
+If set to 1.0, the current batch average is
+returned.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`y`
+ |
+
+A 4D Tensor for the normalized, scaled, offsetted x.
+ |
+
+|
+`running_mean`
+ |
+
+A 1D Tensor for the exponential running mean of x.
+The output value is (1 - exponential_avg_factor) * mean +
+exponential_avg_factor * batch_mean), where batch_mean
+is the mean of the current batch in x.
+ |
+
+|
+`running_var`
+ |
+
+A 1D Tensor for the exponential running variance
+The output value is (1 - exponential_avg_factor) * variance +
+exponential_avg_factor * batch_variance), where batch_variance
+is the variance of the current batch in x.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### References:
+
+Batch Normalization - Accelerating Deep Network Training by Reducing
+Internal Covariate Shift:
+ [Ioffe et al., 2015](http://proceedings.mlr.press/v37/ioffe15.html)
+ ([pdf](http://proceedings.mlr.press/v37/ioffe15.pdf))
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/max_pool.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/max_pool.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..02e653a1d11
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/max_pool.md
@@ -0,0 +1,110 @@
+description: Performs the max pooling on the input.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.max_pool
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Performs the max pooling on the input.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.max_pool(
+ value, ksize, strides, padding, data_format='NHWC', name=None, input=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+A 4-D `Tensor` of the format specified by `data_format`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ksize`
+ |
+
+An int or list of `ints` that has length `1`, `2` or `4`.
+The size of the window for each dimension of the input tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+An int or list of `ints` that has length `1`, `2` or `4`.
+The stride of the sliding window for each dimension of the input tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+A string, either `'VALID'` or `'SAME'`. The padding algorithm.
+See the "returns" section of tf.nn.convolution for details.
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+A string. 'NHWC', 'NCHW' and 'NCHW_VECT_C' are supported.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the operation.
+ |
+
+|
+`input`
+ |
+
+Alias for value.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` of format specified by `data_format`.
+The max pooled output tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/max_pool_with_argmax.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/max_pool_with_argmax.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e04845faa52
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/max_pool_with_argmax.md
@@ -0,0 +1,136 @@
+description: Performs max pooling on the input and outputs both max values and indices.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.max_pool_with_argmax
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Performs max pooling on the input and outputs both max values and indices.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.max_pool_with_argmax(
+ input, ksize, strides, padding, data_format='NHWC', Targmax=None, name=None,
+ output_dtype=None, include_batch_in_index=(False)
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The indices in `argmax` are flattened, so that a maximum value at position
+`[b, y, x, c]` becomes flattened index:
+`(y * width + x) * channels + c` if `include_batch_in_index` is False;
+`((b * height + y) * width + x) * channels + c` if `include_batch_in_index` is True.
+
+The indices returned are always in `[0, height) x [0, width)` before flattening,
+even if padding is involved and the mathematically correct answer is outside
+(either negative or too large). This is a bug, but fixing it is difficult to do
+in a safe backwards compatible way, especially due to flattening.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `float32`, `float64`, `int32`, `uint8`, `int16`, `int8`, `int64`, `bfloat16`, `uint16`, `half`, `uint32`, `uint64`.
+4-D with shape `[batch, height, width, channels]`. Input to pool over.
+ |
+
+|
+`ksize`
+ |
+
+A list of `ints` that has length `>= 4`.
+The size of the window for each dimension of the input tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+A list of `ints` that has length `>= 4`.
+The stride of the sliding window for each dimension of the
+input tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+A `string` from: `"SAME", "VALID"`.
+The type of padding algorithm to use.
+ |
+
+|
+`Targmax`
+ |
+
+An optional tf.DType from: `tf.int32, tf.int64`. Defaults to tf.int64.
+ |
+
+|
+`include_batch_in_index`
+ |
+
+An optional `bool`. Defaults to `False`.
+Whether to include batch dimension in flattened index of `argmax`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A tuple of `Tensor` objects (output, argmax).
+ |
+
+
+|
+`output`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `input`.
+ |
+
+|
+`argmax`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `Targmax`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/moments.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/moments.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..16af284f3e0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/moments.md
@@ -0,0 +1,112 @@
+description: Calculate the mean and variance of x.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.moments
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Calculate the mean and variance of `x`.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.moments(
+ x, axes, shift=None, name=None, keep_dims=None, keepdims=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The mean and variance are calculated by aggregating the contents of `x`
+across `axes`. If `x` is 1-D and `axes = [0]` this is just the mean
+and variance of a vector.
+
+Note: shift is currently not used; the true mean is computed and used.
+
+When using these moments for batch normalization (see
+tf.nn.batch_normalization):
+
+ * for so-called "global normalization", used with convolutional filters with
+ shape `[batch, height, width, depth]`, pass `axes=[0, 1, 2]`.
+ * for simple batch normalization pass `axes=[0]` (batch only).
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`x`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`axes`
+ |
+
+Array of ints. Axes along which to compute mean and
+variance.
+ |
+
+|
+`shift`
+ |
+
+Not used in the current implementation
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name used to scope the operations that compute the moments.
+ |
+
+|
+`keep_dims`
+ |
+
+produce moments with the same dimensionality as the input.
+ |
+
+|
+`keepdims`
+ |
+
+Alias to keep_dims.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Two `Tensor` objects: `mean` and `variance`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/nce_loss.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/nce_loss.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3a343d81d62
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/nce_loss.md
@@ -0,0 +1,198 @@
+description: Computes and returns the noise-contrastive estimation training loss.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.nce_loss
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes and returns the noise-contrastive estimation training loss.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.nce_loss(
+ weights, biases, labels, inputs, num_sampled, num_classes, num_true=1,
+ sampled_values=None, remove_accidental_hits=(False), partition_strategy='mod',
+ name='nce_loss'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A common use case is to use this method for training, and calculate the full
+sigmoid loss for evaluation or inference. In this case, you must set
+`partition_strategy="div"` for the two losses to be consistent, as in the
+following example:
+
+```python
+if mode == "train":
+ loss = tf.nn.nce_loss(
+ weights=weights,
+ biases=biases,
+ labels=labels,
+ inputs=inputs,
+ ...,
+ partition_strategy="div")
+elif mode == "eval":
+ logits = tf.matmul(inputs, tf.transpose(weights))
+ logits = tf.nn.bias_add(logits, biases)
+ labels_one_hot = tf.one_hot(labels, n_classes)
+ loss = tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(
+ labels=labels_one_hot,
+ logits=logits)
+ loss = tf.reduce_sum(loss, axis=1)
+```
+
+Note: By default this uses a log-uniform (Zipfian) distribution for sampling,
+so your labels must be sorted in order of decreasing frequency to achieve
+good results. For more details, see
+tf.random.log_uniform_candidate_sampler.
+
+Note: In the case where `num_true` > 1, we assign to each target class
+the target probability 1 / `num_true` so that the target probabilities
+sum to 1 per-example.
+
+Note: It would be useful to allow a variable number of target classes per
+example. We hope to provide this functionality in a future release.
+For now, if you have a variable number of target classes, you can pad them
+out to a constant number by either repeating them or by padding
+with an otherwise unused class.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of shape `[num_classes, dim]`, or a list of `Tensor`
+objects whose concatenation along dimension 0 has shape
+[num_classes, dim]. The (possibly-partitioned) class embeddings.
+ |
+
+|
+`biases`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of shape `[num_classes]`. The class biases.
+ |
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `int64` and shape `[batch_size,
+num_true]`. The target classes.
+ |
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of shape `[batch_size, dim]`. The forward
+activations of the input network.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_sampled`
+ |
+
+An `int`. The number of negative classes to randomly sample
+per batch. This single sample of negative classes is evaluated for each
+element in the batch.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_classes`
+ |
+
+An `int`. The number of possible classes.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_true`
+ |
+
+An `int`. The number of target classes per training example.
+ |
+
+|
+`sampled_values`
+ |
+
+a tuple of (`sampled_candidates`, `true_expected_count`,
+`sampled_expected_count`) returned by a `*_candidate_sampler` function.
+(if None, we default to `log_uniform_candidate_sampler`)
+ |
+
+|
+`remove_accidental_hits`
+ |
+
+A `bool`. Whether to remove "accidental hits"
+where a sampled class equals one of the target classes. If set to
+`True`, this is a "Sampled Logistic" loss instead of NCE, and we are
+learning to generate log-odds instead of log probabilities. See
+our Candidate Sampling Algorithms Reference
+([pdf](https://www.tensorflow.org/extras/candidate_sampling.pdf)).
+Default is False.
+ |
+
+|
+`partition_strategy`
+ |
+
+A string specifying the partitioning strategy, relevant
+if `len(weights) > 1`. Currently `"div"` and `"mod"` are supported.
+Default is `"mod"`. See `tf.nn.embedding_lookup` for more details.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `batch_size` 1-D tensor of per-example NCE losses.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### References:
+
+Noise-contrastive estimation - A new estimation principle for unnormalized
+statistical models:
+ [Gutmann et al., 2010](http://proceedings.mlr.press/v9/gutmann10a)
+ ([pdf](http://proceedings.mlr.press/v9/gutmann10a/gutmann10a.pdf))
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/pool.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/pool.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a184ed341a4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/pool.md
@@ -0,0 +1,197 @@
+description: Performs an N-D pooling operation.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.pool
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Performs an N-D pooling operation.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.pool(
+ input, window_shape, pooling_type, padding, dilation_rate=None, strides=None,
+ name=None, data_format=None, dilations=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+In the case that `data_format` does not start with "NC", computes for
+ 0 <= b < batch_size,
+ 0 <= x[i] < output_spatial_shape[i],
+ 0 <= c < num_channels:
+
+```
+ output[b, x[0], ..., x[N-1], c] =
+ REDUCE_{z[0], ..., z[N-1]}
+ input[b,
+ x[0] * strides[0] - pad_before[0] + dilation_rate[0]*z[0],
+ ...
+ x[N-1]*strides[N-1] - pad_before[N-1] + dilation_rate[N-1]*z[N-1],
+ c],
+```
+
+where the reduction function REDUCE depends on the value of `pooling_type`,
+and pad_before is defined based on the value of `padding` as described in
+the "returns" section of tf.nn.convolution for details.
+The reduction never includes out-of-bounds positions.
+
+In the case that `data_format` starts with `"NC"`, the `input` and output are
+simply transposed as follows:
+
+```
+ pool(input, data_format, **kwargs) =
+ tf.transpose(pool(tf.transpose(input, [0] + range(2,N+2) + [1]),
+ **kwargs),
+ [0, N+1] + range(1, N+1))
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input`
+ |
+
+Tensor of rank N+2, of shape
+`[batch_size] + input_spatial_shape + [num_channels]` if data_format does
+not start with "NC" (default), or
+`[batch_size, num_channels] + input_spatial_shape` if data_format starts
+with "NC". Pooling happens over the spatial dimensions only.
+ |
+
+|
+`window_shape`
+ |
+
+Sequence of N ints >= 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`pooling_type`
+ |
+
+Specifies pooling operation, must be "AVG" or "MAX".
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+The padding algorithm, must be "SAME" or "VALID".
+See the "returns" section of tf.nn.convolution for details.
+ |
+
+|
+`dilation_rate`
+ |
+
+Optional. Dilation rate. List of N ints >= 1.
+Defaults to [1]*N. If any value of dilation_rate is > 1, then all values
+of strides must be 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+Optional. Sequence of N ints >= 1. Defaults to [1]*N.
+If any value of strides is > 1, then all values of dilation_rate must be
+1.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional. Name of the op.
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+A string or None. Specifies whether the channel dimension of
+the `input` and output is the last dimension (default, or if `data_format`
+does not start with "NC"), or the second dimension (if `data_format`
+starts with "NC"). For N=1, the valid values are "NWC" (default) and
+"NCW". For N=2, the valid values are "NHWC" (default) and "NCHW".
+For N=3, the valid values are "NDHWC" (default) and "NCDHW".
+ |
+
+|
+`dilations`
+ |
+
+Alias for dilation_rate
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Tensor of rank N+2, of shape
+[batch_size] + output_spatial_shape + [num_channels]
+
+if data_format is None or does not start with "NC", or
+
+[batch_size, num_channels] + output_spatial_shape
+
+if data_format starts with "NC",
+where `output_spatial_shape` depends on the value of padding:
+
+If padding = "SAME":
+output_spatial_shape[i] = ceil(input_spatial_shape[i] / strides[i])
+
+If padding = "VALID":
+output_spatial_shape[i] =
+ceil((input_spatial_shape[i] - (window_shape[i] - 1) * dilation_rate[i])
+/ strides[i]).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if arguments are invalid.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/quantized_avg_pool.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/quantized_avg_pool.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..0b8470a5811
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/quantized_avg_pool.md
@@ -0,0 +1,130 @@
+description: Produces the average pool of the input tensor for quantized types.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.quantized_avg_pool
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Produces the average pool of the input tensor for quantized types.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.quantized_avg_pool(
+ input, min_input, max_input, ksize, strides, padding, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `qint8`, `quint8`, `qint32`, `qint16`, `quint16`.
+4-D with shape `[batch, height, width, channels]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`min_input`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `float32`.
+The float value that the lowest quantized input value represents.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_input`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `float32`.
+The float value that the highest quantized input value represents.
+ |
+
+|
+`ksize`
+ |
+
+A list of `ints`.
+The size of the window for each dimension of the input tensor.
+The length must be 4 to match the number of dimensions of the input.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+A list of `ints`.
+The stride of the sliding window for each dimension of the input
+tensor. The length must be 4 to match the number of dimensions of the input.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+A `string` from: `"SAME", "VALID"`.
+The type of padding algorithm to use.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A tuple of `Tensor` objects (output, min_output, max_output).
+ |
+
+
+|
+`output`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `input`.
+ |
+
+|
+`min_output`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `float32`.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_output`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `float32`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/quantized_conv2d.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/quantized_conv2d.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..176b773b75e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/quantized_conv2d.md
@@ -0,0 +1,168 @@
+description: Computes a 2D convolution given quantized 4D input and filter tensors.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.quantized_conv2d
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes a 2D convolution given quantized 4D input and filter tensors.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.quantized_conv2d(
+ input, filter, min_input, max_input, min_filter, max_filter, strides, padding,
+ out_type=tf.dtypes.qint32, dilations=[1, 1, 1, 1], name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The inputs are quantized tensors where the lowest value represents the real
+number of the associated minimum, and the highest represents the maximum.
+This means that you can only interpret the quantized output in the same way, by
+taking the returned minimum and maximum values into account.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `qint8`, `quint8`, `qint32`, `qint16`, `quint16`.
+ |
+
+|
+`filter`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `qint8`, `quint8`, `qint32`, `qint16`, `quint16`.
+filter's input_depth dimension must match input's depth dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`min_input`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `float32`.
+The float value that the lowest quantized input value represents.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_input`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `float32`.
+The float value that the highest quantized input value represents.
+ |
+
+|
+`min_filter`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `float32`.
+The float value that the lowest quantized filter value represents.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_filter`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `float32`.
+The float value that the highest quantized filter value represents.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+A list of `ints`.
+The stride of the sliding window for each dimension of the input
+tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+A `string` from: `"SAME", "VALID"`.
+The type of padding algorithm to use.
+ |
+
+|
+`out_type`
+ |
+
+An optional tf.DType from: `tf.qint8, tf.quint8, tf.qint32, tf.qint16, tf.quint16`. Defaults to tf.qint32.
+ |
+
+|
+`dilations`
+ |
+
+An optional list of `ints`. Defaults to `[1, 1, 1, 1]`.
+1-D tensor of length 4. The dilation factor for each dimension of
+`input`. If set to k > 1, there will be k-1 skipped cells between each
+filter element on that dimension. The dimension order is determined by the
+value of `data_format`, see above for details. Dilations in the batch and
+depth dimensions must be 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A tuple of `Tensor` objects (output, min_output, max_output).
+ |
+
+
+|
+`output`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `out_type`.
+ |
+
+|
+`min_output`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `float32`.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_output`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `float32`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/quantized_max_pool.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/quantized_max_pool.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..ecb8fb8bc61
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/quantized_max_pool.md
@@ -0,0 +1,130 @@
+description: Produces the max pool of the input tensor for quantized types.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.quantized_max_pool
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Produces the max pool of the input tensor for quantized types.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.quantized_max_pool(
+ input, min_input, max_input, ksize, strides, padding, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `qint8`, `quint8`, `qint32`, `qint16`, `quint16`.
+The 4D (batch x rows x cols x depth) Tensor to MaxReduce over.
+ |
+
+|
+`min_input`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `float32`.
+The float value that the lowest quantized input value represents.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_input`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `float32`.
+The float value that the highest quantized input value represents.
+ |
+
+|
+`ksize`
+ |
+
+A list of `ints`.
+The size of the window for each dimension of the input tensor.
+The length must be 4 to match the number of dimensions of the input.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+A list of `ints`.
+The stride of the sliding window for each dimension of the input
+tensor. The length must be 4 to match the number of dimensions of the input.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+A `string` from: `"SAME", "VALID"`.
+The type of padding algorithm to use.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A tuple of `Tensor` objects (output, min_output, max_output).
+ |
+
+
+|
+`output`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `input`.
+ |
+
+|
+`min_output`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `float32`.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_output`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `float32`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/quantized_relu_x.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/quantized_relu_x.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..03e65d6ae13
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/quantized_relu_x.md
@@ -0,0 +1,118 @@
+description: Computes Quantized Rectified Linear X: min(max(features, 0), max_value)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.quantized_relu_x
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes Quantized Rectified Linear X: `min(max(features, 0), max_value)`
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.quantized_relu_x(
+ features, max_value, min_features, max_features, out_type=tf.dtypes.quint8,
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`features`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `qint8`, `quint8`, `qint32`, `qint16`, `quint16`.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_value`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `float32`.
+ |
+
+|
+`min_features`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `float32`.
+The float value that the lowest quantized value represents.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_features`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `float32`.
+The float value that the highest quantized value represents.
+ |
+
+|
+`out_type`
+ |
+
+An optional tf.DType from: `tf.qint8, tf.quint8, tf.qint32, tf.qint16, tf.quint16`. Defaults to tf.quint8.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A tuple of `Tensor` objects (activations, min_activations, max_activations).
+ |
+
+
+|
+`activations`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `out_type`.
+ |
+
+|
+`min_activations`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `float32`.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_activations`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `float32`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/raw_rnn.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/raw_rnn.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..1dc4140befb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/raw_rnn.md
@@ -0,0 +1,253 @@
+description: Creates an RNN specified by RNNCell cell and loop function loop_fn.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.raw_rnn
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Creates an `RNN` specified by RNNCell `cell` and loop function `loop_fn`.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.raw_rnn(
+ cell, loop_fn, parallel_iterations=None, swap_memory=(False), scope=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+**NOTE: This method is still in testing, and the API may change.**
+
+This function is a more primitive version of `dynamic_rnn` that provides
+more direct access to the inputs each iteration. It also provides more
+control over when to start and finish reading the sequence, and
+what to emit for the output.
+
+For example, it can be used to implement the dynamic decoder of a seq2seq
+model.
+
+Instead of working with `Tensor` objects, most operations work with
+`TensorArray` objects directly.
+
+The operation of `raw_rnn`, in pseudo-code, is basically the following:
+
+```python
+time = tf.constant(0, dtype=tf.int32)
+(finished, next_input, initial_state, emit_structure, loop_state) = loop_fn(
+ time=time, cell_output=None, cell_state=None, loop_state=None)
+emit_ta = TensorArray(dynamic_size=True, dtype=initial_state.dtype)
+state = initial_state
+while not all(finished):
+ (output, cell_state) = cell(next_input, state)
+ (next_finished, next_input, next_state, emit, loop_state) = loop_fn(
+ time=time + 1, cell_output=output, cell_state=cell_state,
+ loop_state=loop_state)
+ # Emit zeros and copy forward state for minibatch entries that are finished.
+ state = tf.where(finished, state, next_state)
+ emit = tf.where(finished, tf.zeros_like(emit_structure), emit)
+ emit_ta = emit_ta.write(time, emit)
+ # If any new minibatch entries are marked as finished, mark these.
+ finished = tf.logical_or(finished, next_finished)
+ time += 1
+return (emit_ta, state, loop_state)
+```
+
+with the additional properties that output and state may be (possibly nested)
+tuples, as determined by `cell.output_size` and `cell.state_size`, and
+as a result the final `state` and `emit_ta` may themselves be tuples.
+
+A simple implementation of `dynamic_rnn` via `raw_rnn` looks like this:
+
+```python
+inputs = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(shape=(max_time, batch_size, input_depth),
+ dtype=tf.float32)
+sequence_length = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(shape=(batch_size,),
+dtype=tf.int32)
+inputs_ta = tf.TensorArray(dtype=tf.float32, size=max_time)
+inputs_ta = inputs_ta.unstack(inputs)
+
+cell = tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.LSTMCell(num_units)
+
+def loop_fn(time, cell_output, cell_state, loop_state):
+ emit_output = cell_output # == None for time == 0
+ if cell_output is None: # time == 0
+ next_cell_state = cell.zero_state(batch_size, tf.float32)
+ else:
+ next_cell_state = cell_state
+ elements_finished = (time >= sequence_length)
+ finished = tf.reduce_all(elements_finished)
+ next_input = tf.cond(
+ finished,
+ lambda: tf.zeros([batch_size, input_depth], dtype=tf.float32),
+ lambda: inputs_ta.read(time))
+ next_loop_state = None
+ return (elements_finished, next_input, next_cell_state,
+ emit_output, next_loop_state)
+
+outputs_ta, final_state, _ = raw_rnn(cell, loop_fn)
+outputs = outputs_ta.stack()
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cell`
+ |
+
+An instance of RNNCell.
+ |
+
+|
+`loop_fn`
+ |
+
+A callable that takes inputs `(time, cell_output, cell_state,
+loop_state)` and returns the tuple `(finished, next_input,
+next_cell_state, emit_output, next_loop_state)`. Here `time` is an int32
+scalar `Tensor`, `cell_output` is a `Tensor` or (possibly nested) tuple of
+tensors as determined by `cell.output_size`, and `cell_state` is a
+`Tensor` or (possibly nested) tuple of tensors, as determined by the
+`loop_fn` on its first call (and should match `cell.state_size`).
+The outputs are: `finished`, a boolean `Tensor` of
+shape `[batch_size]`, `next_input`: the next input to feed to `cell`,
+`next_cell_state`: the next state to feed to `cell`,
+and `emit_output`: the output to store for this iteration. Note that
+`emit_output` should be a `Tensor` or (possibly nested) tuple of tensors
+which is aggregated in the `emit_ta` inside the `while_loop`. For the
+first call to `loop_fn`, the `emit_output` corresponds to the
+`emit_structure` which is then used to determine the size of the
+`zero_tensor` for the `emit_ta` (defaults to `cell.output_size`). For
+the subsequent calls to the `loop_fn`, the `emit_output` corresponds to
+the actual output tensor that is to be aggregated in the `emit_ta`. The
+parameter `cell_state` and output `next_cell_state` may be either a
+single or (possibly nested) tuple of tensors. The parameter
+`loop_state` and output `next_loop_state` may be either a single or
+(possibly nested) tuple of `Tensor` and `TensorArray` objects. This
+last parameter may be ignored by `loop_fn` and the return value may be
+`None`. If it is not `None`, then the `loop_state` will be propagated
+through the RNN loop, for use purely by `loop_fn` to keep track of its
+own state. The `next_loop_state` parameter returned may be `None`. The
+first call to `loop_fn` will be `time = 0`, `cell_output = None`,
+`cell_state = None`, and `loop_state = None`. For this call: The
+`next_cell_state` value should be the value with which to initialize the
+cell's state. It may be a final state from a previous RNN or it may be
+the output of `cell.zero_state()`. It should be a (possibly nested)
+tuple structure of tensors. If `cell.state_size` is an integer, this
+must be a `Tensor` of appropriate type and shape `[batch_size,
+cell.state_size]`. If `cell.state_size` is a `TensorShape`, this must be
+a `Tensor` of appropriate type and shape `[batch_size] +
+cell.state_size`. If `cell.state_size` is a (possibly nested) tuple of
+ints or `TensorShape`, this will be a tuple having the corresponding
+shapes. The `emit_output` value may be either `None` or a (possibly
+nested) tuple structure of tensors, e.g., `(tf.zeros(shape_0,
+dtype=dtype_0), tf.zeros(shape_1, dtype=dtype_1))`. If this first
+`emit_output` return value is `None`, then the `emit_ta` result of
+`raw_rnn` will have the same structure and dtypes as `cell.output_size`.
+Otherwise `emit_ta` will have the same structure, shapes (prepended with
+a `batch_size` dimension), and dtypes as `emit_output`. The actual
+values returned for `emit_output` at this initializing call are ignored.
+Note, this emit structure must be consistent across all time steps.
+ |
+
+|
+`parallel_iterations`
+ |
+
+(Default: 32). The number of iterations to run in
+parallel. Those operations which do not have any temporal dependency and
+can be run in parallel, will be. This parameter trades off time for
+space. Values >> 1 use more memory but take less time, while smaller
+values use less memory but computations take longer.
+ |
+
+|
+`swap_memory`
+ |
+
+Transparently swap the tensors produced in forward inference
+but needed for back prop from GPU to CPU. This allows training RNNs which
+would typically not fit on a single GPU, with very minimal (or no)
+performance penalty.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope`
+ |
+
+VariableScope for the created subgraph; defaults to "rnn".
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A tuple `(emit_ta, final_state, final_loop_state)` where:
+
+`emit_ta`: The RNN output `TensorArray`.
+If `loop_fn` returns a (possibly nested) set of Tensors for
+`emit_output` during initialization, (inputs `time = 0`,
+`cell_output = None`, and `loop_state = None`), then `emit_ta` will
+have the same structure, dtypes, and shapes as `emit_output` instead.
+If `loop_fn` returns `emit_output = None` during this call,
+the structure of `cell.output_size` is used:
+If `cell.output_size` is a (possibly nested) tuple of integers
+or `TensorShape` objects, then `emit_ta` will be a tuple having the
+same structure as `cell.output_size`, containing TensorArrays whose
+elements' shapes correspond to the shape data in `cell.output_size`.
+
+`final_state`: The final cell state. If `cell.state_size` is an int, this
+will be shaped `[batch_size, cell.state_size]`. If it is a
+`TensorShape`, this will be shaped `[batch_size] + cell.state_size`.
+If it is a (possibly nested) tuple of ints or `TensorShape`, this will
+be a tuple having the corresponding shapes.
+
+`final_loop_state`: The final loop state as returned by `loop_fn`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `cell` is not an instance of RNNCell, or `loop_fn` is not
+a `callable`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/relu_layer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/relu_layer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..344a3f45bca
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/relu_layer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,87 @@
+description: Computes Relu(x * weight + biases).
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.relu_layer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes Relu(x * weight + biases).
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.relu_layer(
+ x, weights, biases, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`x`
+ |
+
+a 2D tensor. Dimensions typically: batch, in_units
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+a 2D tensor. Dimensions typically: in_units, out_units
+ |
+
+|
+`biases`
+ |
+
+a 1D tensor. Dimensions: out_units
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional). If not specified
+"nn_relu_layer" is used.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A 2-D Tensor computing relu(matmul(x, weights) + biases).
+Dimensions typically: batch, out_units.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..838e6a01670
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell.md
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
+description: Module for constructing RNN Cells.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Module for constructing RNN Cells.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class BasicLSTMCell`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/BasicLSTMCell.md): DEPRECATED: Please use tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.LSTMCell instead.
+
+[`class BasicRNNCell`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/BasicRNNCell.md): The most basic RNN cell.
+
+[`class DeviceWrapper`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/DeviceWrapper.md): Operator that ensures an RNNCell runs on a particular device.
+
+[`class DropoutWrapper`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/DropoutWrapper.md): Operator adding dropout to inputs and outputs of the given cell.
+
+[`class GRUCell`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/GRUCell.md): Gated Recurrent Unit cell.
+
+[`class LSTMCell`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/LSTMCell.md): Long short-term memory unit (LSTM) recurrent network cell.
+
+[`class LSTMStateTuple`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/LSTMStateTuple.md): Tuple used by LSTM Cells for `state_size`, `zero_state`, and output state.
+
+[`class MultiRNNCell`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/MultiRNNCell.md): RNN cell composed sequentially of multiple simple cells.
+
+[`class RNNCell`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/RNNCell.md): Abstract object representing an RNN cell.
+
+[`class ResidualWrapper`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/ResidualWrapper.md): RNNCell wrapper that ensures cell inputs are added to the outputs.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/BasicLSTMCell.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/BasicLSTMCell.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..0cb993eaaea
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/BasicLSTMCell.md
@@ -0,0 +1,254 @@
+description: DEPRECATED: Please use tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.LSTMCell instead.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+DEPRECATED: Please use tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.LSTMCell instead.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell(
+ num_units, forget_bias=1.0, state_is_tuple=(True), activation=None, reuse=None,
+ name=None, dtype=None, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Basic LSTM recurrent network cell.
+
+The implementation is based on
+
+We add forget_bias (default: 1) to the biases of the forget gate in order to
+reduce the scale of forgetting in the beginning of the training.
+
+It does not allow cell clipping, a projection layer, and does not
+use peep-hole connections: it is the basic baseline.
+
+For advanced models, please use the full tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.LSTMCell
+that follows.
+
+Note that this cell is not optimized for performance. Please use
+`tf.contrib.cudnn_rnn.CudnnLSTM` for better performance on GPU, or
+`tf.contrib.rnn.LSTMBlockCell` and `tf.contrib.rnn.LSTMBlockFusedCell` for
+better performance on CPU.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`num_units`
+ |
+
+int, The number of units in the LSTM cell.
+ |
+
+|
+`forget_bias`
+ |
+
+float, The bias added to forget gates (see above). Must set
+to `0.0` manually when restoring from CudnnLSTM-trained checkpoints.
+ |
+
+|
+`state_is_tuple`
+ |
+
+If True, accepted and returned states are 2-tuples of the
+`c_state` and `m_state`. If False, they are concatenated along the
+column axis. The latter behavior will soon be deprecated.
+ |
+
+|
+`activation`
+ |
+
+Activation function of the inner states. Default: `tanh`. It
+could also be string that is within Keras activation function names.
+ |
+
+|
+`reuse`
+ |
+
+(optional) Python boolean describing whether to reuse variables in
+an existing scope. If not `True`, and the existing scope already has
+the given variables, an error is raised.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+String, the name of the layer. Layers with the same name will share
+weights, but to avoid mistakes we require reuse=True in such cases.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+Default dtype of the layer (default of `None` means use the type of
+the first input). Required when `build` is called before `call`.
+ |
+
+|
+`**kwargs`
+ |
+
+Dict, keyword named properties for common layer attributes, like
+`trainable` etc when constructing the cell from configs of get_config().
+When restoring from CudnnLSTM-trained checkpoints, must use
+`CudnnCompatibleLSTMCell` instead.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+DEPRECATED FUNCTION
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Stop using this property because tf.layers layers no longer track their graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`output_size`
+ |
+
+Integer or TensorShape: size of outputs produced by this cell.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope_name`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`state_size`
+ |
+
+size(s) of state(s) used by this cell.
+
+It can be represented by an Integer, a TensorShape or a tuple of Integers
+or TensorShapes.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+get_initial_state
+
+View source
+
+
+get_initial_state(
+ inputs=None, batch_size=None, dtype=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+zero_state
+
+View source
+
+
+zero_state(
+ batch_size, dtype
+)
+
+
+Return zero-filled state tensor(s).
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`batch_size`
+ |
+
+int, float, or unit Tensor representing the batch size.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+the data type to use for the state.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+If `state_size` is an int or TensorShape, then the return value is a
+`N-D` tensor of shape `[batch_size, state_size]` filled with zeros.
+
+If `state_size` is a nested list or tuple, then the return value is
+a nested list or tuple (of the same structure) of `2-D` tensors with
+the shapes `[batch_size, s]` for each s in `state_size`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/BasicRNNCell.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/BasicRNNCell.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..17d87abce0f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/BasicRNNCell.md
@@ -0,0 +1,219 @@
+description: The most basic RNN cell.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.BasicRNNCell
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The most basic RNN cell.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.BasicRNNCell(
+ num_units, activation=None, reuse=None, name=None, dtype=None, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Note that this cell is not optimized for performance. Please use
+`tf.contrib.cudnn_rnn.CudnnRNNTanh` for better performance on GPU.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`num_units`
+ |
+
+int, The number of units in the RNN cell.
+ |
+
+|
+`activation`
+ |
+
+Nonlinearity to use. Default: `tanh`. It could also be string
+that is within Keras activation function names.
+ |
+
+|
+`reuse`
+ |
+
+(optional) Python boolean describing whether to reuse variables in an
+existing scope. If not `True`, and the existing scope already has the
+given variables, an error is raised.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+String, the name of the layer. Layers with the same name will share
+weights, but to avoid mistakes we require reuse=True in such cases.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+Default dtype of the layer (default of `None` means use the type of
+the first input). Required when `build` is called before `call`.
+ |
+
+|
+`**kwargs`
+ |
+
+Dict, keyword named properties for common layer attributes, like
+`trainable` etc when constructing the cell from configs of get_config().
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+DEPRECATED FUNCTION
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Stop using this property because tf.layers layers no longer track their graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`output_size`
+ |
+
+Integer or TensorShape: size of outputs produced by this cell.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope_name`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`state_size`
+ |
+
+size(s) of state(s) used by this cell.
+
+It can be represented by an Integer, a TensorShape or a tuple of Integers
+or TensorShapes.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+get_initial_state
+
+View source
+
+
+get_initial_state(
+ inputs=None, batch_size=None, dtype=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+zero_state
+
+View source
+
+
+zero_state(
+ batch_size, dtype
+)
+
+
+Return zero-filled state tensor(s).
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`batch_size`
+ |
+
+int, float, or unit Tensor representing the batch size.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+the data type to use for the state.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+If `state_size` is an int or TensorShape, then the return value is a
+`N-D` tensor of shape `[batch_size, state_size]` filled with zeros.
+
+If `state_size` is a nested list or tuple, then the return value is
+a nested list or tuple (of the same structure) of `2-D` tensors with
+the shapes `[batch_size, s]` for each s in `state_size`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/DeviceWrapper.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/DeviceWrapper.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3a38a03bd04
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/DeviceWrapper.md
@@ -0,0 +1,144 @@
+description: Operator that ensures an RNNCell runs on a particular device.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.DeviceWrapper
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Operator that ensures an RNNCell runs on a particular device.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.DeviceWrapper(
+ *args, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cell`
+ |
+
+An instance of `RNNCell`.
+ |
+
+|
+`device`
+ |
+
+A device string or function, for passing to tf.device.
+ |
+
+|
+`**kwargs`
+ |
+
+dict of keyword arguments for base layer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+DEPRECATED FUNCTION
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Stop using this property because tf.layers layers no longer track their graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`output_size`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`scope_name`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`state_size`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+get_initial_state
+
+View source
+
+
+get_initial_state(
+ inputs=None, batch_size=None, dtype=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+zero_state
+
+View source
+
+
+zero_state(
+ batch_size, dtype
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/DropoutWrapper.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/DropoutWrapper.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e3fdda4a494
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/DropoutWrapper.md
@@ -0,0 +1,251 @@
+description: Operator adding dropout to inputs and outputs of the given cell.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.DropoutWrapper
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Operator adding dropout to inputs and outputs of the given cell.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.DropoutWrapper(
+ *args, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cell`
+ |
+
+an RNNCell, a projection to output_size is added to it.
+ |
+
+|
+`input_keep_prob`
+ |
+
+unit Tensor or float between 0 and 1, input keep
+probability; if it is constant and 1, no input dropout will be added.
+ |
+
+|
+`output_keep_prob`
+ |
+
+unit Tensor or float between 0 and 1, output keep
+probability; if it is constant and 1, no output dropout will be added.
+ |
+
+|
+`state_keep_prob`
+ |
+
+unit Tensor or float between 0 and 1, output keep
+probability; if it is constant and 1, no output dropout will be added.
+State dropout is performed on the outgoing states of the cell. **Note**
+the state components to which dropout is applied when `state_keep_prob`
+is in `(0, 1)` are also determined by the argument
+`dropout_state_filter_visitor` (e.g. by default dropout is never applied
+to the `c` component of an `LSTMStateTuple`).
+ |
+
+|
+`variational_recurrent`
+ |
+
+Python bool. If `True`, then the same dropout
+pattern is applied across all time steps per run call. If this parameter
+is set, `input_size` **must** be provided.
+ |
+
+|
+`input_size`
+ |
+
+(optional) (possibly nested tuple of) `TensorShape` objects
+containing the depth(s) of the input tensors expected to be passed in to
+the `DropoutWrapper`. Required and used **iff** `variational_recurrent
+= True` and `input_keep_prob < 1`.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+(optional) The `dtype` of the input, state, and output tensors.
+Required and used **iff** `variational_recurrent = True`.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+(optional) integer, the randomness seed.
+ |
+
+|
+`dropout_state_filter_visitor`
+ |
+
+(optional), default: (see below). Function
+that takes any hierarchical level of the state and returns a scalar or
+depth=1 structure of Python booleans describing which terms in the state
+should be dropped out. In addition, if the function returns `True`,
+dropout is applied across this sublevel. If the function returns
+`False`, dropout is not applied across this entire sublevel.
+Default behavior: perform dropout on all terms except the memory (`c`)
+state of `LSTMCellState` objects, and don't try to apply dropout to
+`TensorArray` objects: ```
+def dropout_state_filter_visitor(s):
+if isinstance(s, LSTMCellState): # Never perform dropout on the c
+state. return LSTMCellState(c=False, h=True)
+elif isinstance(s, TensorArray): return False return True ```
+ |
+
+|
+`**kwargs`
+ |
+
+dict of keyword arguments for base layer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+if `cell` is not an `RNNCell`, or `keep_state_fn` is provided
+but not `callable`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if any of the keep_probs are not between 0 and 1.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+DEPRECATED FUNCTION
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Stop using this property because tf.layers layers no longer track their graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`output_size`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`scope_name`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`state_size`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`wrapped_cell`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+get_initial_state
+
+View source
+
+
+get_initial_state(
+ inputs=None, batch_size=None, dtype=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+zero_state
+
+View source
+
+
+zero_state(
+ batch_size, dtype
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/GRUCell.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/GRUCell.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3d5640ce614
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/GRUCell.md
@@ -0,0 +1,242 @@
+description: Gated Recurrent Unit cell.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.GRUCell
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Gated Recurrent Unit cell.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.GRUCell(
+ num_units, activation=None, reuse=None, kernel_initializer=None,
+ bias_initializer=None, name=None, dtype=None, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Note that this cell is not optimized for performance. Please use
+`tf.contrib.cudnn_rnn.CudnnGRU` for better performance on GPU, or
+`tf.contrib.rnn.GRUBlockCellV2` for better performance on CPU.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`num_units`
+ |
+
+int, The number of units in the GRU cell.
+ |
+
+|
+`activation`
+ |
+
+Nonlinearity to use. Default: `tanh`.
+ |
+
+|
+`reuse`
+ |
+
+(optional) Python boolean describing whether to reuse variables in an
+existing scope. If not `True`, and the existing scope already has the
+given variables, an error is raised.
+ |
+
+|
+`kernel_initializer`
+ |
+
+(optional) The initializer to use for the weight and
+projection matrices.
+ |
+
+|
+`bias_initializer`
+ |
+
+(optional) The initializer to use for the bias.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+String, the name of the layer. Layers with the same name will share
+weights, but to avoid mistakes we require reuse=True in such cases.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+Default dtype of the layer (default of `None` means use the type of
+the first input). Required when `build` is called before `call`.
+ |
+
+|
+`**kwargs`
+ |
+
+Dict, keyword named properties for common layer attributes, like
+`trainable` etc when constructing the cell from configs of get_config().
+
+References:
+Learning Phrase Representations using RNN Encoder Decoder for Statistical
+Machine Translation:
+[Cho et al., 2014]
+(https://aclanthology.coli.uni-saarland.de/papers/D14-1179/d14-1179)
+([pdf](http://emnlp2014.org/papers/pdf/EMNLP2014179.pdf))
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+DEPRECATED FUNCTION
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Stop using this property because tf.layers layers no longer track their graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`output_size`
+ |
+
+Integer or TensorShape: size of outputs produced by this cell.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope_name`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`state_size`
+ |
+
+size(s) of state(s) used by this cell.
+
+It can be represented by an Integer, a TensorShape or a tuple of Integers
+or TensorShapes.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+get_initial_state
+
+View source
+
+
+get_initial_state(
+ inputs=None, batch_size=None, dtype=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+zero_state
+
+View source
+
+
+zero_state(
+ batch_size, dtype
+)
+
+
+Return zero-filled state tensor(s).
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`batch_size`
+ |
+
+int, float, or unit Tensor representing the batch size.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+the data type to use for the state.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+If `state_size` is an int or TensorShape, then the return value is a
+`N-D` tensor of shape `[batch_size, state_size]` filled with zeros.
+
+If `state_size` is a nested list or tuple, then the return value is
+a nested list or tuple (of the same structure) of `2-D` tensors with
+the shapes `[batch_size, s]` for each s in `state_size`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/LSTMCell.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/LSTMCell.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..288c6c24874
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/LSTMCell.md
@@ -0,0 +1,322 @@
+description: Long short-term memory unit (LSTM) recurrent network cell.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.LSTMCell
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Long short-term memory unit (LSTM) recurrent network cell.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.LSTMCell(
+ num_units, use_peepholes=(False), cell_clip=None, initializer=None,
+ num_proj=None, proj_clip=None, num_unit_shards=None, num_proj_shards=None,
+ forget_bias=1.0, state_is_tuple=(True), activation=None, reuse=None, name=None,
+ dtype=None, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The default non-peephole implementation is based on (Gers et al., 1999).
+The peephole implementation is based on (Sak et al., 2014).
+
+The class uses optional peep-hole connections, optional cell clipping, and
+an optional projection layer.
+
+Note that this cell is not optimized for performance. Please use
+`tf.contrib.cudnn_rnn.CudnnLSTM` for better performance on GPU, or
+`tf.contrib.rnn.LSTMBlockCell` and `tf.contrib.rnn.LSTMBlockFusedCell` for
+better performance on CPU.
+References:
+ Long short-term memory recurrent neural network architectures for large
+ scale acoustic modeling:
+ [Sak et al., 2014]
+ (https://www.isca-speech.org/archive/interspeech_2014/i14_0338.html)
+ ([pdf]
+ (https://www.isca-speech.org/archive/archive_papers/interspeech_2014/i14_0338.pdf))
+ Learning to forget:
+ [Gers et al., 1999]
+ (http://digital-library.theiet.org/content/conferences/10.1049/cp_19991218)
+ ([pdf](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1409.2329.pdf))
+ Long Short-Term Memory:
+ [Hochreiter et al., 1997]
+ (https://www.mitpressjournals.org/doi/abs/10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735)
+ ([pdf](http://ml.jku.at/publications/older/3504.pdf))
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`num_units`
+ |
+
+int, The number of units in the LSTM cell.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_peepholes`
+ |
+
+bool, set True to enable diagonal/peephole connections.
+ |
+
+|
+`cell_clip`
+ |
+
+(optional) A float value, if provided the cell state is clipped
+by this value prior to the cell output activation.
+ |
+
+|
+`initializer`
+ |
+
+(optional) The initializer to use for the weight and
+projection matrices.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_proj`
+ |
+
+(optional) int, The output dimensionality for the projection
+matrices. If None, no projection is performed.
+ |
+
+|
+`proj_clip`
+ |
+
+(optional) A float value. If `num_proj > 0` and `proj_clip` is
+provided, then the projected values are clipped elementwise to within
+`[-proj_clip, proj_clip]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_unit_shards`
+ |
+
+Deprecated, will be removed by Jan. 2017. Use a
+variable_scope partitioner instead.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_proj_shards`
+ |
+
+Deprecated, will be removed by Jan. 2017. Use a
+variable_scope partitioner instead.
+ |
+
+|
+`forget_bias`
+ |
+
+Biases of the forget gate are initialized by default to 1 in
+order to reduce the scale of forgetting at the beginning of the
+training. Must set it manually to `0.0` when restoring from CudnnLSTM
+trained checkpoints.
+ |
+
+|
+`state_is_tuple`
+ |
+
+If True, accepted and returned states are 2-tuples of the
+`c_state` and `m_state`. If False, they are concatenated along the
+column axis. This latter behavior will soon be deprecated.
+ |
+
+|
+`activation`
+ |
+
+Activation function of the inner states. Default: `tanh`. It
+could also be string that is within Keras activation function names.
+ |
+
+|
+`reuse`
+ |
+
+(optional) Python boolean describing whether to reuse variables in
+an existing scope. If not `True`, and the existing scope already has
+the given variables, an error is raised.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+String, the name of the layer. Layers with the same name will share
+weights, but to avoid mistakes we require reuse=True in such cases.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+Default dtype of the layer (default of `None` means use the type of
+the first input). Required when `build` is called before `call`.
+ |
+
+|
+`**kwargs`
+ |
+
+Dict, keyword named properties for common layer attributes, like
+`trainable` etc when constructing the cell from configs of get_config().
+When restoring from CudnnLSTM-trained checkpoints, use
+`CudnnCompatibleLSTMCell` instead.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+DEPRECATED FUNCTION
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Stop using this property because tf.layers layers no longer track their graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`output_size`
+ |
+
+Integer or TensorShape: size of outputs produced by this cell.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope_name`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`state_size`
+ |
+
+size(s) of state(s) used by this cell.
+
+It can be represented by an Integer, a TensorShape or a tuple of Integers
+or TensorShapes.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+get_initial_state
+
+View source
+
+
+get_initial_state(
+ inputs=None, batch_size=None, dtype=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+zero_state
+
+View source
+
+
+zero_state(
+ batch_size, dtype
+)
+
+
+Return zero-filled state tensor(s).
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`batch_size`
+ |
+
+int, float, or unit Tensor representing the batch size.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+the data type to use for the state.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+If `state_size` is an int or TensorShape, then the return value is a
+`N-D` tensor of shape `[batch_size, state_size]` filled with zeros.
+
+If `state_size` is a nested list or tuple, then the return value is
+a nested list or tuple (of the same structure) of `2-D` tensors with
+the shapes `[batch_size, s]` for each s in `state_size`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/LSTMStateTuple.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/LSTMStateTuple.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..526fa447c3e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/LSTMStateTuple.md
@@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
+description: Tuple used by LSTM Cells for state_size, zero_state, and output state.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.LSTMStateTuple
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Tuple used by LSTM Cells for `state_size`, `zero_state`, and output state.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.LSTMStateTuple(
+ c, h
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Stores two elements: `(c, h)`, in that order. Where `c` is the hidden state
+and `h` is the output.
+
+Only used when `state_is_tuple=True`.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`c`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`h`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `c`
+* `h`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/MultiRNNCell.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/MultiRNNCell.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..1b67b030e67
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/MultiRNNCell.md
@@ -0,0 +1,215 @@
+description: RNN cell composed sequentially of multiple simple cells.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.MultiRNNCell
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+RNN cell composed sequentially of multiple simple cells.
+
+Inherits From: [`RNNCell`](../../../../../tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/RNNCell.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.MultiRNNCell(
+ cells, state_is_tuple=(True)
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+num_units = [128, 64]
+cells = [BasicLSTMCell(num_units=n) for n in num_units]
+stacked_rnn_cell = MultiRNNCell(cells)
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cells`
+ |
+
+list of RNNCells that will be composed in this order.
+ |
+
+|
+`state_is_tuple`
+ |
+
+If True, accepted and returned states are n-tuples, where
+`n = len(cells)`. If False, the states are all concatenated along the
+column axis. This latter behavior will soon be deprecated.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if cells is empty (not allowed), or at least one of the cells
+returns a state tuple but the flag `state_is_tuple` is `False`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+DEPRECATED FUNCTION
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Stop using this property because tf.layers layers no longer track their graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`output_size`
+ |
+
+Integer or TensorShape: size of outputs produced by this cell.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope_name`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`state_size`
+ |
+
+size(s) of state(s) used by this cell.
+
+It can be represented by an Integer, a TensorShape or a tuple of Integers
+or TensorShapes.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+get_initial_state
+
+View source
+
+
+get_initial_state(
+ inputs=None, batch_size=None, dtype=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+zero_state
+
+View source
+
+
+zero_state(
+ batch_size, dtype
+)
+
+
+Return zero-filled state tensor(s).
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`batch_size`
+ |
+
+int, float, or unit Tensor representing the batch size.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+the data type to use for the state.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+If `state_size` is an int or TensorShape, then the return value is a
+`N-D` tensor of shape `[batch_size, state_size]` filled with zeros.
+
+If `state_size` is a nested list or tuple, then the return value is
+a nested list or tuple (of the same structure) of `2-D` tensors with
+the shapes `[batch_size, s]` for each s in `state_size`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/RNNCell.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/RNNCell.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..5e89cc4d74a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/RNNCell.md
@@ -0,0 +1,178 @@
+description: Abstract object representing an RNN cell.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.RNNCell
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Abstract object representing an RNN cell.
+
+Inherits From: [`Layer`](../../../../../tf/compat/v1/layers/Layer.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.RNNCell(
+ trainable=(True), name=None, dtype=None, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Every `RNNCell` must have the properties below and implement `call` with
+the signature `(output, next_state) = call(input, state)`. The optional
+third input argument, `scope`, is allowed for backwards compatibility
+purposes; but should be left off for new subclasses.
+
+This definition of cell differs from the definition used in the literature.
+In the literature, 'cell' refers to an object with a single scalar output.
+This definition refers to a horizontal array of such units.
+
+An RNN cell, in the most abstract setting, is anything that has
+a state and performs some operation that takes a matrix of inputs.
+This operation results in an output matrix with `self.output_size` columns.
+If `self.state_size` is an integer, this operation also results in a new
+state matrix with `self.state_size` columns. If `self.state_size` is a
+(possibly nested tuple of) TensorShape object(s), then it should return a
+matching structure of Tensors having shape `[batch_size].concatenate(s)`
+for each `s` in `self.batch_size`.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+DEPRECATED FUNCTION
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Stop using this property because tf.layers layers no longer track their graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`output_size`
+ |
+
+Integer or TensorShape: size of outputs produced by this cell.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope_name`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`state_size`
+ |
+
+size(s) of state(s) used by this cell.
+
+It can be represented by an Integer, a TensorShape or a tuple of Integers
+or TensorShapes.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+get_initial_state
+
+View source
+
+
+get_initial_state(
+ inputs=None, batch_size=None, dtype=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+zero_state
+
+View source
+
+
+zero_state(
+ batch_size, dtype
+)
+
+
+Return zero-filled state tensor(s).
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`batch_size`
+ |
+
+int, float, or unit Tensor representing the batch size.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+the data type to use for the state.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+If `state_size` is an int or TensorShape, then the return value is a
+`N-D` tensor of shape `[batch_size, state_size]` filled with zeros.
+
+If `state_size` is a nested list or tuple, then the return value is
+a nested list or tuple (of the same structure) of `2-D` tensors with
+the shapes `[batch_size, s]` for each s in `state_size`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/ResidualWrapper.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/ResidualWrapper.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..dad109900fd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/rnn_cell/ResidualWrapper.md
@@ -0,0 +1,147 @@
+description: RNNCell wrapper that ensures cell inputs are added to the outputs.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.ResidualWrapper
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+RNNCell wrapper that ensures cell inputs are added to the outputs.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.rnn_cell.ResidualWrapper(
+ *args, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cell`
+ |
+
+An instance of `RNNCell`.
+ |
+
+|
+`residual_fn`
+ |
+
+(Optional) The function to map raw cell inputs and raw cell
+outputs to the actual cell outputs of the residual network.
+Defaults to calling nest.map_structure on (lambda i, o: i + o), inputs
+and outputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`**kwargs`
+ |
+
+dict of keyword arguments for base layer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+DEPRECATED FUNCTION
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Stop using this property because tf.layers layers no longer track their graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`output_size`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`scope_name`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`state_size`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+get_initial_state
+
+View source
+
+
+get_initial_state(
+ inputs=None, batch_size=None, dtype=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+zero_state
+
+View source
+
+
+zero_state(
+ batch_size, dtype
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/safe_embedding_lookup_sparse.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/safe_embedding_lookup_sparse.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..05eb1d116b0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/safe_embedding_lookup_sparse.md
@@ -0,0 +1,155 @@
+description: Lookup embedding results, accounting for invalid IDs and empty features.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.safe_embedding_lookup_sparse
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Lookup embedding results, accounting for invalid IDs and empty features.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.safe_embedding_lookup_sparse(
+ embedding_weights, sparse_ids, sparse_weights=None, combiner='mean',
+ default_id=None, name=None, partition_strategy='div', max_norm=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The partitioned embedding in `embedding_weights` must all be the same shape
+except for the first dimension. The first dimension is allowed to vary as the
+vocabulary size is not necessarily a multiple of `P`. `embedding_weights`
+may be a `PartitionedVariable` as returned by using
+tf.compat.v1.get_variable() with a
+partitioner.
+
+Invalid IDs (< 0) are pruned from input IDs and weights, as well as any IDs
+with non-positive weight. For an entry with no features, the embedding vector
+for `default_id` is returned, or the 0-vector if `default_id` is not supplied.
+
+The ids and weights may be multi-dimensional. Embeddings are always aggregated
+along the last dimension.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`embedding_weights`
+ |
+
+A list of `P` float `Tensor`s or values representing
+partitioned embedding `Tensor`s. Alternatively, a `PartitionedVariable`
+created by partitioning along dimension 0. The total unpartitioned shape
+should be `[e_0, e_1, ..., e_m]`, where `e_0` represents the vocab size
+and `e_1, ..., e_m` are the embedding dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`sparse_ids`
+ |
+
+`SparseTensor` of shape `[d_0, d_1, ..., d_n]` containing the
+ids. `d_0` is typically batch size.
+ |
+
+|
+`sparse_weights`
+ |
+
+`SparseTensor` of same shape as `sparse_ids`, containing
+float weights corresponding to `sparse_ids`, or `None` if all weights are
+be assumed to be 1.0.
+ |
+
+|
+`combiner`
+ |
+
+A string specifying how to combine embedding results for each
+entry. Currently "mean", "sqrtn" and "sum" are supported, with "mean" the
+default.
+ |
+
+|
+`default_id`
+ |
+
+The id to use for an entry with no features.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for this operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`partition_strategy`
+ |
+
+A string specifying the partitioning strategy. Currently
+`"div"` and `"mod"` are supported. Default is `"div"`.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_norm`
+ |
+
+If not `None`, all embeddings are l2-normalized to max_norm before
+combining.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Dense `Tensor` of shape `[d_0, d_1, ..., d_{n-1}, e_1, ..., e_m]`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `embedding_weights` is empty.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/sampled_softmax_loss.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/sampled_softmax_loss.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..babac86dca3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/sampled_softmax_loss.md
@@ -0,0 +1,195 @@
+description: Computes and returns the sampled softmax training loss.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.sampled_softmax_loss
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes and returns the sampled softmax training loss.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.sampled_softmax_loss(
+ weights, biases, labels, inputs, num_sampled, num_classes, num_true=1,
+ sampled_values=None, remove_accidental_hits=(True), partition_strategy='mod',
+ name='sampled_softmax_loss', seed=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This is a faster way to train a softmax classifier over a huge number of
+classes.
+
+This operation is for training only. It is generally an underestimate of
+the full softmax loss.
+
+A common use case is to use this method for training, and calculate the full
+softmax loss for evaluation or inference. In this case, you must set
+`partition_strategy="div"` for the two losses to be consistent, as in the
+following example:
+
+```python
+if mode == "train":
+ loss = tf.nn.sampled_softmax_loss(
+ weights=weights,
+ biases=biases,
+ labels=labels,
+ inputs=inputs,
+ ...,
+ partition_strategy="div")
+elif mode == "eval":
+ logits = tf.matmul(inputs, tf.transpose(weights))
+ logits = tf.nn.bias_add(logits, biases)
+ labels_one_hot = tf.one_hot(labels, n_classes)
+ loss = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(
+ labels=labels_one_hot,
+ logits=logits)
+```
+
+See our Candidate Sampling Algorithms Reference
+([pdf](https://www.tensorflow.org/extras/candidate_sampling.pdf)).
+Also see Section 3 of (Jean et al., 2014) for the math.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of shape `[num_classes, dim]`, or a list of `Tensor`
+objects whose concatenation along dimension 0 has shape
+[num_classes, dim]. The (possibly-sharded) class embeddings.
+ |
+
+|
+`biases`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of shape `[num_classes]`. The class biases.
+ |
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `int64` and shape `[batch_size,
+num_true]`. The target classes. Note that this format differs from
+the `labels` argument of `nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits`.
+ |
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of shape `[batch_size, dim]`. The forward
+activations of the input network.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_sampled`
+ |
+
+An `int`. The number of classes to randomly sample per batch.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_classes`
+ |
+
+An `int`. The number of possible classes.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_true`
+ |
+
+An `int`. The number of target classes per training example.
+ |
+
+|
+`sampled_values`
+ |
+
+a tuple of (`sampled_candidates`, `true_expected_count`,
+`sampled_expected_count`) returned by a `*_candidate_sampler` function.
+(if None, we default to `log_uniform_candidate_sampler`)
+ |
+
+|
+`remove_accidental_hits`
+ |
+
+A `bool`. whether to remove "accidental hits"
+where a sampled class equals one of the target classes. Default is
+True.
+ |
+
+|
+`partition_strategy`
+ |
+
+A string specifying the partitioning strategy, relevant
+if `len(weights) > 1`. Currently `"div"` and `"mod"` are supported.
+Default is `"mod"`. See `tf.nn.embedding_lookup` for more details.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+random seed for candidate sampling. Default to None, which doesn't set
+the op-level random seed for candidate sampling.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `batch_size` 1-D tensor of per-example sampled softmax losses.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### References:
+
+On Using Very Large Target Vocabulary for Neural Machine Translation:
+ [Jean et al., 2014]
+ (https://aclanthology.coli.uni-saarland.de/papers/P15-1001/p15-1001)
+ ([pdf](http://aclweb.org/anthology/P15-1001))
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/separable_conv2d.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/separable_conv2d.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..0e06acbecfa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/separable_conv2d.md
@@ -0,0 +1,150 @@
+description: 2-D convolution with separable filters.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.separable_conv2d
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+2-D convolution with separable filters.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.separable_conv2d(
+ input, depthwise_filter, pointwise_filter, strides, padding, rate=None,
+ name=None, data_format=None, dilations=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Performs a depthwise convolution that acts separately on channels followed by
+a pointwise convolution that mixes channels. Note that this is separability
+between dimensions `[1, 2]` and `3`, not spatial separability between
+dimensions `1` and `2`.
+
+In detail, with the default NHWC format,
+
+ output[b, i, j, k] = sum_{di, dj, q, r}
+ input[b, strides[1] * i + di, strides[2] * j + dj, q] *
+ depthwise_filter[di, dj, q, r] *
+ pointwise_filter[0, 0, q * channel_multiplier + r, k]
+
+`strides` controls the strides for the depthwise convolution only, since
+the pointwise convolution has implicit strides of `[1, 1, 1, 1]`. Must have
+`strides[0] = strides[3] = 1`. For the most common case of the same
+horizontal and vertical strides, `strides = [1, stride, stride, 1]`.
+If any value in `rate` is greater than 1, we perform atrous depthwise
+convolution, in which case all values in the `strides` tensor must be equal
+to 1.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input`
+ |
+
+4-D `Tensor` with shape according to `data_format`.
+ |
+
+|
+`depthwise_filter`
+ |
+
+4-D `Tensor` with shape
+`[filter_height, filter_width, in_channels, channel_multiplier]`.
+Contains `in_channels` convolutional filters of depth 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`pointwise_filter`
+ |
+
+4-D `Tensor` with shape
+`[1, 1, channel_multiplier * in_channels, out_channels]`. Pointwise
+filter to mix channels after `depthwise_filter` has convolved spatially.
+ |
+
+|
+`strides`
+ |
+
+1-D of size 4. The strides for the depthwise convolution for
+each dimension of `input`.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding`
+ |
+
+A string, either `'VALID'` or `'SAME'`. The padding algorithm.
+See the "returns" section of tf.nn.convolution for details.
+ |
+
+|
+`rate`
+ |
+
+1-D of size 2. The dilation rate in which we sample input values
+across the `height` and `width` dimensions in atrous convolution. If it is
+greater than 1, then all values of strides must be 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for this operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+The data format for input. Either "NHWC" (default) or "NCHW".
+ |
+
+|
+`dilations`
+ |
+
+Alias of rate.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A 4-D `Tensor` with shape according to 'data_format'. For
+example, with data_format="NHWC", shape is [batch, out_height,
+out_width, out_channels].
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..9f0f8b42508
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits.md
@@ -0,0 +1,129 @@
+description: Computes sigmoid cross entropy given logits.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes sigmoid cross entropy given `logits`.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(
+ _sentinel=None, labels=None, logits=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Measures the probability error in discrete classification tasks in which each
+class is independent and not mutually exclusive. For instance, one could
+perform multilabel classification where a picture can contain both an elephant
+and a dog at the same time.
+
+For brevity, let `x = logits`, `z = labels`. The logistic loss is
+
+ z * -log(sigmoid(x)) + (1 - z) * -log(1 - sigmoid(x))
+ = z * -log(1 / (1 + exp(-x))) + (1 - z) * -log(exp(-x) / (1 + exp(-x)))
+ = z * log(1 + exp(-x)) + (1 - z) * (-log(exp(-x)) + log(1 + exp(-x)))
+ = z * log(1 + exp(-x)) + (1 - z) * (x + log(1 + exp(-x))
+ = (1 - z) * x + log(1 + exp(-x))
+ = x - x * z + log(1 + exp(-x))
+
+For x < 0, to avoid overflow in exp(-x), we reformulate the above
+
+ x - x * z + log(1 + exp(-x))
+ = log(exp(x)) - x * z + log(1 + exp(-x))
+ = - x * z + log(1 + exp(x))
+
+Hence, to ensure stability and avoid overflow, the implementation uses this
+equivalent formulation
+
+ max(x, 0) - x * z + log(1 + exp(-abs(x)))
+
+`logits` and `labels` must have the same type and shape.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`_sentinel`
+ |
+
+Used to prevent positional parameters. Internal, do not use.
+ |
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of the same type and shape as `logits`.
+ |
+
+|
+`logits`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `float32` or `float64`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` of the same shape as `logits` with the componentwise
+logistic losses.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `logits` and `labels` do not have the same shape.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..4038f50640f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits.md
@@ -0,0 +1,141 @@
+description: Computes softmax cross entropy between logits and labels. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes softmax cross entropy between `logits` and `labels`. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(
+ _sentinel=None, labels=None, logits=None, dim=-1, name=None, axis=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+
+Future major versions of TensorFlow will allow gradients to flow
+into the labels input on backprop by default.
+
+See `tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2`.
+
+
+Measures the probability error in discrete classification tasks in which the
+classes are mutually exclusive (each entry is in exactly one class). For
+example, each CIFAR-10 image is labeled with one and only one label: an image
+can be a dog or a truck, but not both.
+
+**NOTE:** While the classes are mutually exclusive, their probabilities
+need not be. All that is required is that each row of `labels` is
+a valid probability distribution. If they are not, the computation of the
+gradient will be incorrect.
+
+If using exclusive `labels` (wherein one and only
+one class is true at a time), see `sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits`.
+
+**WARNING:** This op expects unscaled logits, since it performs a `softmax`
+on `logits` internally for efficiency. Do not call this op with the
+output of `softmax`, as it will produce incorrect results.
+
+A common use case is to have logits and labels of shape
+`[batch_size, num_classes]`, but higher dimensions are supported, with
+the `dim` argument specifying the class dimension.
+
+Backpropagation will happen only into `logits`. To calculate a cross entropy
+loss that allows backpropagation into both `logits` and `labels`, see
+`tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2`.
+
+**Note that to avoid confusion, it is required to pass only named arguments to
+this function.**
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`_sentinel`
+ |
+
+Used to prevent positional parameters. Internal, do not use.
+ |
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+Each vector along the class dimension should hold a valid
+probability distribution e.g. for the case in which labels are of shape
+`[batch_size, num_classes]`, each row of `labels[i]` must be a valid
+probability distribution.
+ |
+
+|
+`logits`
+ |
+
+Per-label activations, typically a linear output. These activation
+energies are interpreted as unnormalized log probabilities.
+ |
+
+|
+`dim`
+ |
+
+The class dimension. Defaulted to -1 which is the last dimension.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`axis`
+ |
+
+Alias for dim.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` that contains the softmax cross entropy loss. Its type is the
+same as `logits` and its shape is the same as `labels` except that it does
+not have the last dimension of `labels`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..88fa8520f7f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2.md
@@ -0,0 +1,131 @@
+description: Computes softmax cross entropy between logits and labels. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes softmax cross entropy between `logits` and `labels`. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2(
+ labels, logits, axis=None, name=None, dim=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: SOME ARGUMENTS ARE DEPRECATED: `(dim)`. They will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+dim is deprecated, use axis instead
+
+Measures the probability error in discrete classification tasks in which the
+classes are mutually exclusive (each entry is in exactly one class). For
+example, each CIFAR-10 image is labeled with one and only one label: an image
+can be a dog or a truck, but not both.
+
+**NOTE:** While the classes are mutually exclusive, their probabilities
+need not be. All that is required is that each row of `labels` is
+a valid probability distribution. If they are not, the computation of the
+gradient will be incorrect.
+
+If using exclusive `labels` (wherein one and only
+one class is true at a time), see `sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits`.
+
+**WARNING:** This op expects unscaled logits, since it performs a `softmax`
+on `logits` internally for efficiency. Do not call this op with the
+output of `softmax`, as it will produce incorrect results.
+
+A common use case is to have logits and labels of shape
+`[batch_size, num_classes]`, but higher dimensions are supported, with
+the `axis` argument specifying the class dimension.
+
+`logits` and `labels` must have the same dtype (either `float16`, `float32`,
+or `float64`).
+
+Backpropagation will happen into both `logits` and `labels`. To disallow
+backpropagation into `labels`, pass label tensors through tf.stop_gradient
+before feeding it to this function.
+
+**Note that to avoid confusion, it is required to pass only named arguments to
+this function.**
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+Each vector along the class dimension should hold a valid
+probability distribution e.g. for the case in which labels are of shape
+`[batch_size, num_classes]`, each row of `labels[i]` must be a valid
+probability distribution.
+ |
+
+|
+`logits`
+ |
+
+Unscaled log probabilities.
+ |
+
+|
+`axis`
+ |
+
+The class dimension. Defaulted to -1 which is the last dimension.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`dim`
+ |
+
+Deprecated alias for axis.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` that contains the softmax cross entropy loss. Its type is the
+same as `logits` and its shape is the same as `labels` except that it does
+not have the last dimension of `labels`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..5ab223d6e42
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits.md
@@ -0,0 +1,136 @@
+description: Computes sparse softmax cross entropy between logits and labels.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes sparse softmax cross entropy between `logits` and `labels`.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(
+ _sentinel=None, labels=None, logits=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Measures the probability error in discrete classification tasks in which the
+classes are mutually exclusive (each entry is in exactly one class). For
+example, each CIFAR-10 image is labeled with one and only one label: an image
+can be a dog or a truck, but not both.
+
+**NOTE:** For this operation, the probability of a given label is considered
+exclusive. That is, soft classes are not allowed, and the `labels` vector
+must provide a single specific index for the true class for each row of
+`logits` (each minibatch entry). For soft softmax classification with
+a probability distribution for each entry, see
+`softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2`.
+
+**WARNING:** This op expects unscaled logits, since it performs a `softmax`
+on `logits` internally for efficiency. Do not call this op with the
+output of `softmax`, as it will produce incorrect results.
+
+A common use case is to have logits of shape
+`[batch_size, num_classes]` and have labels of shape
+`[batch_size]`, but higher dimensions are supported, in which
+case the `dim`-th dimension is assumed to be of size `num_classes`.
+`logits` must have the dtype of `float16`, `float32`, or `float64`, and
+`labels` must have the dtype of `int32` or `int64`.
+
+**Note that to avoid confusion, it is required to pass only named arguments to
+this function.**
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`_sentinel`
+ |
+
+Used to prevent positional parameters. Internal, do not use.
+ |
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+`Tensor` of shape `[d_0, d_1, ..., d_{r-1}]` (where `r` is rank of
+`labels` and result) and dtype `int32` or `int64`. Each entry in `labels`
+must be an index in `[0, num_classes)`. Other values will raise an
+exception when this op is run on CPU, and return `NaN` for corresponding
+loss and gradient rows on GPU.
+ |
+
+|
+`logits`
+ |
+
+Per-label activations (typically a linear output) of shape
+`[d_0, d_1, ..., d_{r-1}, num_classes]` and dtype `float16`, `float32`, or
+`float64`. These activation energies are interpreted as unnormalized log
+probabilities.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` of the same shape as `labels` and of the same type as `logits`
+with the softmax cross entropy loss.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If logits are scalars (need to have rank >= 1) or if the rank
+of the labels is not equal to the rank of the logits minus one.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/static_bidirectional_rnn.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/static_bidirectional_rnn.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..830485ee499
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/static_bidirectional_rnn.md
@@ -0,0 +1,163 @@
+description: Creates a bidirectional recurrent neural network. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.static_bidirectional_rnn
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Creates a bidirectional recurrent neural network. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.static_bidirectional_rnn(
+ cell_fw, cell_bw, inputs, initial_state_fw=None, initial_state_bw=None,
+ dtype=None, sequence_length=None, scope=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Please use `keras.layers.Bidirectional(keras.layers.RNN(cell, unroll=True))`, which is equivalent to this API
+
+Similar to the unidirectional case above (rnn) but takes input and builds
+independent forward and backward RNNs with the final forward and backward
+outputs depth-concatenated, such that the output will have the format
+[time][batch][cell_fw.output_size + cell_bw.output_size]. The input_size of
+forward and backward cell must match. The initial state for both directions
+is zero by default (but can be set optionally) and no intermediate states are
+ever returned -- the network is fully unrolled for the given (passed in)
+length(s) of the sequence(s) or completely unrolled if length(s) is not given.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cell_fw`
+ |
+
+An instance of RNNCell, to be used for forward direction.
+ |
+
+|
+`cell_bw`
+ |
+
+An instance of RNNCell, to be used for backward direction.
+ |
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+A length T list of inputs, each a tensor of shape [batch_size,
+input_size], or a nested tuple of such elements.
+ |
+
+|
+`initial_state_fw`
+ |
+
+(optional) An initial state for the forward RNN. This must
+be a tensor of appropriate type and shape `[batch_size,
+cell_fw.state_size]`. If `cell_fw.state_size` is a tuple, this should be a
+tuple of tensors having shapes `[batch_size, s] for s in
+cell_fw.state_size`.
+ |
+
+|
+`initial_state_bw`
+ |
+
+(optional) Same as for `initial_state_fw`, but using the
+corresponding properties of `cell_bw`.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+(optional) The data type for the initial state. Required if either
+of the initial states are not provided.
+ |
+
+|
+`sequence_length`
+ |
+
+(optional) An int32/int64 vector, size `[batch_size]`,
+containing the actual lengths for each of the sequences.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope`
+ |
+
+VariableScope for the created subgraph; defaults to
+"bidirectional_rnn"
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A tuple (outputs, output_state_fw, output_state_bw) where:
+outputs is a length `T` list of outputs (one for each input), which
+are depth-concatenated forward and backward outputs.
+output_state_fw is the final state of the forward rnn.
+output_state_bw is the final state of the backward rnn.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `cell_fw` or `cell_bw` is not an instance of `RNNCell`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If inputs is None or an empty list.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/static_rnn.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/static_rnn.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e33ab9fe749
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/static_rnn.md
@@ -0,0 +1,167 @@
+description: Creates a recurrent neural network specified by RNNCell cell. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.static_rnn
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Creates a recurrent neural network specified by RNNCell `cell`. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.static_rnn(
+ cell, inputs, initial_state=None, dtype=None, sequence_length=None, scope=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Please use `keras.layers.RNN(cell, unroll=True)`, which is equivalent to this API
+
+The simplest form of RNN network generated is:
+
+```python
+ state = cell.zero_state(...)
+ outputs = []
+ for input_ in inputs:
+ output, state = cell(input_, state)
+ outputs.append(output)
+ return (outputs, state)
+```
+However, a few other options are available:
+
+An initial state can be provided.
+If the sequence_length vector is provided, dynamic calculation is performed.
+This method of calculation does not compute the RNN steps past the maximum
+sequence length of the minibatch (thus saving computational time),
+and properly propagates the state at an example's sequence length
+to the final state output.
+
+The dynamic calculation performed is, at time `t` for batch row `b`,
+
+```python
+ (output, state)(b, t) =
+ (t >= sequence_length(b))
+ ? (zeros(cell.output_size), states(b, sequence_length(b) - 1))
+ : cell(input(b, t), state(b, t - 1))
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cell`
+ |
+
+An instance of RNNCell.
+ |
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+A length T list of inputs, each a `Tensor` of shape `[batch_size,
+input_size]`, or a nested tuple of such elements.
+ |
+
+|
+`initial_state`
+ |
+
+(optional) An initial state for the RNN. If `cell.state_size`
+is an integer, this must be a `Tensor` of appropriate type and shape
+`[batch_size, cell.state_size]`. If `cell.state_size` is a tuple, this
+should be a tuple of tensors having shapes `[batch_size, s] for s in
+cell.state_size`.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+(optional) The data type for the initial state and expected output.
+Required if initial_state is not provided or RNN state has a heterogeneous
+dtype.
+ |
+
+|
+`sequence_length`
+ |
+
+Specifies the length of each sequence in inputs. An int32
+or int64 vector (tensor) size `[batch_size]`, values in `[0, T)`.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope`
+ |
+
+VariableScope for the created subgraph; defaults to "rnn".
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A pair (outputs, state) where:
+
+- outputs is a length T list of outputs (one for each input), or a nested
+tuple of such elements.
+- state is the final state
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `cell` is not an instance of RNNCell.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `inputs` is `None` or an empty list, or if the input depth
+(column size) cannot be inferred from inputs via shape inference.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/static_state_saving_rnn.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/static_state_saving_rnn.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..74ba0f2dc2a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/static_state_saving_rnn.md
@@ -0,0 +1,134 @@
+description: RNN that accepts a state saver for time-truncated RNN calculation. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.static_state_saving_rnn
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+RNN that accepts a state saver for time-truncated RNN calculation. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.static_state_saving_rnn(
+ cell, inputs, state_saver, state_name, sequence_length=None, scope=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Please use `keras.layers.RNN(cell, stateful=True)`, which is equivalent to this API
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cell`
+ |
+
+An instance of `RNNCell`.
+ |
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+A length T list of inputs, each a `Tensor` of shape `[batch_size,
+input_size]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`state_saver`
+ |
+
+A state saver object with methods `state` and `save_state`.
+ |
+
+|
+`state_name`
+ |
+
+Python string or tuple of strings. The name to use with the
+state_saver. If the cell returns tuples of states (i.e., `cell.state_size`
+is a tuple) then `state_name` should be a tuple of strings having the same
+length as `cell.state_size`. Otherwise it should be a single string.
+ |
+
+|
+`sequence_length`
+ |
+
+(optional) An int32/int64 vector size [batch_size]. See the
+documentation for rnn() for more details about sequence_length.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope`
+ |
+
+VariableScope for the created subgraph; defaults to "rnn".
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A pair (outputs, state) where:
+outputs is a length T list of outputs (one for each input)
+states is the final state
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `cell` is not an instance of RNNCell.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `inputs` is `None` or an empty list, or if the arity and
+type of `state_name` does not match that of `cell.state_size`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/sufficient_statistics.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/sufficient_statistics.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..dc436718f2b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/sufficient_statistics.md
@@ -0,0 +1,109 @@
+description: Calculate the sufficient statistics for the mean and variance of x.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.sufficient_statistics
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Calculate the sufficient statistics for the mean and variance of `x`.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.sufficient_statistics(
+ x, axes, shift=None, keep_dims=None, name=None, keepdims=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+These sufficient statistics are computed using the one pass algorithm on
+an input that's optionally shifted. See:
+https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Algorithms_for_calculating_variance#Computing_shifted_data
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`x`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`axes`
+ |
+
+Array of ints. Axes along which to compute mean and variance.
+ |
+
+|
+`shift`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` containing the value by which to shift the data for
+numerical stability, or `None` if no shift is to be performed. A shift
+close to the true mean provides the most numerically stable results.
+ |
+
+|
+`keep_dims`
+ |
+
+produce statistics with the same dimensionality as the input.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name used to scope the operations that compute the sufficient stats.
+ |
+
+|
+`keepdims`
+ |
+
+Alias for keep_dims.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Four `Tensor` objects of the same type as `x`:
+
+* the count (number of elements to average over).
+* the (possibly shifted) sum of the elements in the array.
+* the (possibly shifted) sum of squares of the elements in the array.
+* the shift by which the mean must be corrected or None if `shift` is None.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/weighted_cross_entropy_with_logits.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/weighted_cross_entropy_with_logits.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..4968e74e37a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/weighted_cross_entropy_with_logits.md
@@ -0,0 +1,150 @@
+description: Computes a weighted cross entropy. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.weighted_cross_entropy_with_logits
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes a weighted cross entropy. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.weighted_cross_entropy_with_logits(
+ labels=None, logits=None, pos_weight=None, name=None, targets=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: SOME ARGUMENTS ARE DEPRECATED: `(targets)`. They will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+targets is deprecated, use labels instead
+
+This is like `sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits()` except that `pos_weight`,
+allows one to trade off recall and precision by up- or down-weighting the
+cost of a positive error relative to a negative error.
+
+The usual cross-entropy cost is defined as:
+
+ labels * -log(sigmoid(logits)) +
+ (1 - labels) * -log(1 - sigmoid(logits))
+
+A value `pos_weight > 1` decreases the false negative count, hence increasing
+the recall.
+Conversely setting `pos_weight < 1` decreases the false positive count and
+increases the precision.
+This can be seen from the fact that `pos_weight` is introduced as a
+multiplicative coefficient for the positive labels term
+in the loss expression:
+
+ labels * -log(sigmoid(logits)) * pos_weight +
+ (1 - labels) * -log(1 - sigmoid(logits))
+
+For brevity, let `x = logits`, `z = labels`, `q = pos_weight`.
+The loss is:
+
+ qz * -log(sigmoid(x)) + (1 - z) * -log(1 - sigmoid(x))
+ = qz * -log(1 / (1 + exp(-x))) + (1 - z) * -log(exp(-x) / (1 + exp(-x)))
+ = qz * log(1 + exp(-x)) + (1 - z) * (-log(exp(-x)) + log(1 + exp(-x)))
+ = qz * log(1 + exp(-x)) + (1 - z) * (x + log(1 + exp(-x))
+ = (1 - z) * x + (qz + 1 - z) * log(1 + exp(-x))
+ = (1 - z) * x + (1 + (q - 1) * z) * log(1 + exp(-x))
+
+Setting `l = (1 + (q - 1) * z)`, to ensure stability and avoid overflow,
+the implementation uses
+
+ (1 - z) * x + l * (log(1 + exp(-abs(x))) + max(-x, 0))
+
+`logits` and `labels` must have the same type and shape.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`labels`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of the same type and shape as `logits`.
+ |
+
+|
+`logits`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `float32` or `float64`.
+ |
+
+|
+`pos_weight`
+ |
+
+A coefficient to use on the positive examples.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`targets`
+ |
+
+Deprecated alias for labels.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` of the same shape as `logits` with the componentwise
+weighted logistic losses.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `logits` and `labels` do not have the same shape.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/weighted_moments.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/weighted_moments.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..d5dfcbd884d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/weighted_moments.md
@@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
+description: Returns the frequency-weighted mean and variance of x.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.weighted_moments
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns the frequency-weighted mean and variance of `x`.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.weighted_moments(
+ x, axes, frequency_weights, name=None, keep_dims=None, keepdims=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`x`
+ |
+
+A tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`axes`
+ |
+
+1-d tensor of int32 values; these are the axes along which
+to compute mean and variance.
+ |
+
+|
+`frequency_weights`
+ |
+
+A tensor of positive weights which can be
+broadcast with x.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Name used to scope the operation.
+ |
+
+|
+`keep_dims`
+ |
+
+Produce moments with the same dimensionality as the input.
+ |
+
+|
+`keepdims`
+ |
+
+Alias of keep_dims.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Two tensors: `weighted_mean` and `weighted_variance`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/xw_plus_b.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/xw_plus_b.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..318611bf63d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/nn/xw_plus_b.md
@@ -0,0 +1,87 @@
+description: Computes matmul(x, weights) + biases.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.nn.xw_plus_b
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes matmul(x, weights) + biases.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.nn.xw_plus_b(
+ x, weights, biases, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`x`
+ |
+
+a 2D tensor. Dimensions typically: batch, in_units
+ |
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+a 2D tensor. Dimensions typically: in_units, out_units
+ |
+
+|
+`biases`
+ |
+
+a 1D tensor. Dimensions: out_units
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional). If not specified
+"xw_plus_b" is used.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A 2-D Tensor computing matmul(x, weights) + biases.
+Dimensions typically: batch, out_units.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/no_regularizer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/no_regularizer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..312c2a45546
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/no_regularizer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+description: Use this function to prevent regularization of variables.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.no_regularizer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Use this function to prevent regularization of variables.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.no_regularizer(
+ _
+)
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/norm.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/norm.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3edd429880a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/norm.md
@@ -0,0 +1,177 @@
+description: Computes the norm of vectors, matrices, and tensors. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.norm
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the norm of vectors, matrices, and tensors. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.linalg.norm`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.norm(
+ tensor, ord='euclidean', axis=None, keepdims=None, name=None, keep_dims=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: SOME ARGUMENTS ARE DEPRECATED: `(keep_dims)`. They will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+keep_dims is deprecated, use keepdims instead
+
+This function can compute several different vector norms (the 1-norm, the
+Euclidean or 2-norm, the inf-norm, and in general the p-norm for p > 0) and
+matrix norms (Frobenius, 1-norm, 2-norm and inf-norm).
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`tensor`
+ |
+
+`Tensor` of types `float32`, `float64`, `complex64`, `complex128`
+ |
+
+|
+`ord`
+ |
+
+Order of the norm. Supported values are 'fro', 'euclidean',
+`1`, `2`, `np.inf` and any positive real number yielding the corresponding
+p-norm. Default is 'euclidean' which is equivalent to Frobenius norm if
+`tensor` is a matrix and equivalent to 2-norm for vectors.
+Some restrictions apply:
+a) The Frobenius norm `fro` is not defined for vectors,
+b) If axis is a 2-tuple (matrix norm), only 'euclidean', 'fro', `1`,
+`2`, `np.inf` are supported.
+See the description of `axis` on how to compute norms for a batch of
+vectors or matrices stored in a tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`axis`
+ |
+
+If `axis` is `None` (the default), the input is considered a vector
+and a single vector norm is computed over the entire set of values in the
+tensor, i.e. `norm(tensor, ord=ord)` is equivalent to
+`norm(reshape(tensor, [-1]), ord=ord)`.
+If `axis` is a Python integer, the input is considered a batch of vectors,
+and `axis` determines the axis in `tensor` over which to compute vector
+norms.
+If `axis` is a 2-tuple of Python integers it is considered a batch of
+matrices and `axis` determines the axes in `tensor` over which to compute
+a matrix norm.
+Negative indices are supported. Example: If you are passing a tensor that
+can be either a matrix or a batch of matrices at runtime, pass
+`axis=[-2,-1]` instead of `axis=None` to make sure that matrix norms are
+computed.
+ |
+
+|
+`keepdims`
+ |
+
+If True, the axis indicated in `axis` are kept with size 1.
+Otherwise, the dimensions in `axis` are removed from the output shape.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+The name of the op.
+ |
+
+|
+`keep_dims`
+ |
+
+Deprecated alias for `keepdims`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`output`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of the same type as tensor, containing the vector or
+matrix norms. If `keepdims` is True then the rank of output is equal to
+the rank of `tensor`. Otherwise, if `axis` is none the output is a scalar,
+if `axis` is an integer, the rank of `output` is one less than the rank
+of `tensor`, if `axis` is a 2-tuple the rank of `output` is two less
+than the rank of `tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `ord` or `axis` is invalid.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Numpy Compatibility
+Mostly equivalent to numpy.linalg.norm.
+Not supported: ord <= 0, 2-norm for matrices, nuclear norm.
+Other differences:
+ a) If axis is `None`, treats the flattened `tensor` as a vector
+ regardless of rank.
+ b) Explicitly supports 'euclidean' norm as the default, including for
+ higher order tensors.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/ones_like.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/ones_like.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..452b6416868
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/ones_like.md
@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
+description: Creates a tensor with all elements set to 1.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.ones_like
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Creates a tensor with all elements set to 1.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.ones_like(
+ tensor, dtype=None, name=None, optimize=(True)
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+See also tf.ones.
+
+Given a single tensor (`tensor`), this operation returns a tensor of the same
+type and shape as `tensor` with all elements set to 1. Optionally, you can
+specify a new type (`dtype`) for the returned tensor.
+
+#### For example:
+
+
+
+```python
+tensor = tf.constant([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
+tf.ones_like(tensor) # [[1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1]]
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`tensor`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+A type for the returned `Tensor`. Must be `float32`, `float64`,
+`int8`, `uint8`, `int16`, `uint16`, `int32`, `int64`, `complex64`,
+`complex128` or `bool`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`optimize`
+ |
+
+if true, attempt to statically determine the shape of 'tensor' and
+encode it as a constant.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` with all elements set to 1.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/op_scope.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/op_scope.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..387e88b5a84
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/op_scope.md
@@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
+description: DEPRECATED. Same as name_scope above, just different argument order.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.op_scope
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+DEPRECATED. Same as name_scope above, just different argument order.
+
+
+@tf_contextlib.contextmanager
+tf.compat.v1.op_scope(
+ values, name, default_name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/pad.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/pad.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..ccddbf8dd0f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/pad.md
@@ -0,0 +1,148 @@
+description: Pads a tensor.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.pad
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Pads a tensor.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.pad(
+ tensor, paddings, mode='CONSTANT', name=None, constant_values=0
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This operation pads a `tensor` according to the `paddings` you specify.
+`paddings` is an integer tensor with shape `[n, 2]`, where n is the rank of
+`tensor`. For each dimension D of `input`, `paddings[D, 0]` indicates how
+many values to add before the contents of `tensor` in that dimension, and
+`paddings[D, 1]` indicates how many values to add after the contents of
+`tensor` in that dimension. If `mode` is "REFLECT" then both `paddings[D, 0]`
+and `paddings[D, 1]` must be no greater than `tensor.dim_size(D) - 1`. If
+`mode` is "SYMMETRIC" then both `paddings[D, 0]` and `paddings[D, 1]` must be
+no greater than `tensor.dim_size(D)`.
+
+The padded size of each dimension D of the output is:
+
+`paddings[D, 0] + tensor.dim_size(D) + paddings[D, 1]`
+
+#### For example:
+
+
+
+```python
+t = tf.constant([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
+paddings = tf.constant([[1, 1,], [2, 2]])
+# 'constant_values' is 0.
+# rank of 't' is 2.
+tf.pad(t, paddings, "CONSTANT") # [[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
+ # [0, 0, 1, 2, 3, 0, 0],
+ # [0, 0, 4, 5, 6, 0, 0],
+ # [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]
+
+tf.pad(t, paddings, "REFLECT") # [[6, 5, 4, 5, 6, 5, 4],
+ # [3, 2, 1, 2, 3, 2, 1],
+ # [6, 5, 4, 5, 6, 5, 4],
+ # [3, 2, 1, 2, 3, 2, 1]]
+
+tf.pad(t, paddings, "SYMMETRIC") # [[2, 1, 1, 2, 3, 3, 2],
+ # [2, 1, 1, 2, 3, 3, 2],
+ # [5, 4, 4, 5, 6, 6, 5],
+ # [5, 4, 4, 5, 6, 6, 5]]
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`tensor`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`paddings`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `int32`.
+ |
+
+|
+`mode`
+ |
+
+One of "CONSTANT", "REFLECT", or "SYMMETRIC" (case-insensitive)
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`constant_values`
+ |
+
+In "CONSTANT" mode, the scalar pad value to use. Must be
+same type as `tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+When mode is not one of "CONSTANT", "REFLECT", or "SYMMETRIC".
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/parse_example.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/parse_example.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..4e9928b4425
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/parse_example.md
@@ -0,0 +1,324 @@
+description: Parses Example protos into a dict of tensors.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.parse_example
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Parses `Example` protos into a `dict` of tensors.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.io.parse_example`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.parse_example(
+ serialized, features, name=None, example_names=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Parses a number of serialized [`Example`](https://www.tensorflow.org/code/tensorflow/core/example/example.proto)
+protos given in `serialized`. We refer to `serialized` as a batch with
+`batch_size` many entries of individual `Example` protos.
+
+`example_names` may contain descriptive names for the corresponding serialized
+protos. These may be useful for debugging purposes, but they have no effect on
+the output. If not `None`, `example_names` must be the same length as
+`serialized`.
+
+This op parses serialized examples into a dictionary mapping keys to `Tensor`
+`SparseTensor`, and `RaggedTensor` objects. `features` is a dict from keys to
+`VarLenFeature`, `SparseFeature`, `RaggedFeature`, and `FixedLenFeature`
+objects. Each `VarLenFeature` and `SparseFeature` is mapped to a
+`SparseTensor`; each `FixedLenFeature` is mapped to a `Tensor`; and each
+`RaggedFeature` is mapped to a `RaggedTensor`.
+
+Each `VarLenFeature` maps to a `SparseTensor` of the specified type
+representing a ragged matrix. Its indices are `[batch, index]` where `batch`
+identifies the example in `serialized`, and `index` is the value's index in
+the list of values associated with that feature and example.
+
+Each `SparseFeature` maps to a `SparseTensor` of the specified type
+representing a Tensor of `dense_shape` `[batch_size] + SparseFeature.size`.
+Its `values` come from the feature in the examples with key `value_key`.
+A `values[i]` comes from a position `k` in the feature of an example at batch
+entry `batch`. This positional information is recorded in `indices[i]` as
+`[batch, index_0, index_1, ...]` where `index_j` is the `k-th` value of
+the feature in the example at with key `SparseFeature.index_key[j]`.
+In other words, we split the indices (except the first index indicating the
+batch entry) of a `SparseTensor` by dimension into different features of the
+`Example`. Due to its complexity a `VarLenFeature` should be preferred over a
+`SparseFeature` whenever possible.
+
+Each `FixedLenFeature` `df` maps to a `Tensor` of the specified type (or
+tf.float32 if not specified) and shape `(serialized.size(),) + df.shape`.
+
+`FixedLenFeature` entries with a `default_value` are optional. With no default
+value, we will fail if that `Feature` is missing from any example in
+`serialized`.
+
+Each `FixedLenSequenceFeature` `df` maps to a `Tensor` of the specified type
+(or tf.float32 if not specified) and shape
+`(serialized.size(), None) + df.shape`.
+All examples in `serialized` will be padded with `default_value` along the
+second dimension.
+
+Each `RaggedFeature` maps to a `RaggedTensor` of the specified type. It
+is formed by stacking the `RaggedTensor` for each example, where the
+`RaggedTensor` for each individual example is constructed using the tensors
+specified by `RaggedTensor.values_key` and `RaggedTensor.partition`. See
+the tf.io.RaggedFeature documentation for details and examples.
+
+#### Examples:
+
+
+
+For example, if one expects a tf.float32 `VarLenFeature` `ft` and three
+serialized `Example`s are provided:
+
+```
+serialized = [
+ features
+ { feature { key: "ft" value { float_list { value: [1.0, 2.0] } } } },
+ features
+ { feature []},
+ features
+ { feature { key: "ft" value { float_list { value: [3.0] } } }
+]
+```
+
+then the output will look like:
+
+```python
+{"ft": SparseTensor(indices=[[0, 0], [0, 1], [2, 0]],
+ values=[1.0, 2.0, 3.0],
+ dense_shape=(3, 2)) }
+```
+
+If instead a `FixedLenSequenceFeature` with `default_value = -1.0` and
+`shape=[]` is used then the output will look like:
+
+```python
+{"ft": [[1.0, 2.0], [3.0, -1.0]]}
+```
+
+Given two `Example` input protos in `serialized`:
+
+```
+[
+ features {
+ feature { key: "kw" value { bytes_list { value: [ "knit", "big" ] } } }
+ feature { key: "gps" value { float_list { value: [] } } }
+ },
+ features {
+ feature { key: "kw" value { bytes_list { value: [ "emmy" ] } } }
+ feature { key: "dank" value { int64_list { value: [ 42 ] } } }
+ feature { key: "gps" value { } }
+ }
+]
+```
+
+And arguments
+
+```
+example_names: ["input0", "input1"],
+features: {
+ "kw": VarLenFeature(tf.string),
+ "dank": VarLenFeature(tf.int64),
+ "gps": VarLenFeature(tf.float32),
+}
+```
+
+Then the output is a dictionary:
+
+```python
+{
+ "kw": SparseTensor(
+ indices=[[0, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0]],
+ values=["knit", "big", "emmy"]
+ dense_shape=[2, 2]),
+ "dank": SparseTensor(
+ indices=[[1, 0]],
+ values=[42],
+ dense_shape=[2, 1]),
+ "gps": SparseTensor(
+ indices=[],
+ values=[],
+ dense_shape=[2, 0]),
+}
+```
+
+For dense results in two serialized `Example`s:
+
+```
+[
+ features {
+ feature { key: "age" value { int64_list { value: [ 0 ] } } }
+ feature { key: "gender" value { bytes_list { value: [ "f" ] } } }
+ },
+ features {
+ feature { key: "age" value { int64_list { value: [] } } }
+ feature { key: "gender" value { bytes_list { value: [ "f" ] } } }
+ }
+]
+```
+
+#### We can use arguments:
+
+
+
+```
+example_names: ["input0", "input1"],
+features: {
+ "age": FixedLenFeature([], dtype=tf.int64, default_value=-1),
+ "gender": FixedLenFeature([], dtype=tf.string),
+}
+```
+
+And the expected output is:
+
+```python
+{
+ "age": [[0], [-1]],
+ "gender": [["f"], ["f"]],
+}
+```
+
+An alternative to `VarLenFeature` to obtain a `SparseTensor` is
+`SparseFeature`. For example, given two `Example` input protos in
+`serialized`:
+
+```
+[
+ features {
+ feature { key: "val" value { float_list { value: [ 0.5, -1.0 ] } } }
+ feature { key: "ix" value { int64_list { value: [ 3, 20 ] } } }
+ },
+ features {
+ feature { key: "val" value { float_list { value: [ 0.0 ] } } }
+ feature { key: "ix" value { int64_list { value: [ 42 ] } } }
+ }
+]
+```
+
+And arguments
+
+```
+example_names: ["input0", "input1"],
+features: {
+ "sparse": SparseFeature(
+ index_key="ix", value_key="val", dtype=tf.float32, size=100),
+}
+```
+
+Then the output is a dictionary:
+
+```python
+{
+ "sparse": SparseTensor(
+ indices=[[0, 3], [0, 20], [1, 42]],
+ values=[0.5, -1.0, 0.0]
+ dense_shape=[2, 100]),
+}
+```
+
+See the tf.io.RaggedFeature documentation for examples showing how
+`RaggedFeature` can be used to obtain `RaggedTensor`s.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`serialized`
+ |
+
+A vector (1-D Tensor) of strings, a batch of binary
+serialized `Example` protos.
+ |
+
+|
+`features`
+ |
+
+A `dict` mapping feature keys to `FixedLenFeature`,
+`VarLenFeature`, `SparseFeature`, and `RaggedFeature` values.
+ |
+
+|
+`example_names`
+ |
+
+A vector (1-D Tensor) of strings (optional), the names of
+the serialized protos in the batch.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for this operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `dict` mapping feature keys to `Tensor`, `SparseTensor`, and
+`RaggedTensor` values.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if any feature is invalid.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/parse_single_example.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/parse_single_example.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..76815363d1e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/parse_single_example.md
@@ -0,0 +1,127 @@
+description: Parses a single Example proto.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.parse_single_example
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Parses a single `Example` proto.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.io.parse_single_example`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.parse_single_example(
+ serialized, features, name=None, example_names=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Similar to `parse_example`, except:
+
+For dense tensors, the returned `Tensor` is identical to the output of
+`parse_example`, except there is no batch dimension, the output shape is the
+same as the shape given in `dense_shape`.
+
+For `SparseTensor`s, the first (batch) column of the indices matrix is removed
+(the indices matrix is a column vector), the values vector is unchanged, and
+the first (`batch_size`) entry of the shape vector is removed (it is now a
+single element vector).
+
+One might see performance advantages by batching `Example` protos with
+`parse_example` instead of using this function directly.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`serialized`
+ |
+
+A scalar string Tensor, a single serialized Example.
+ |
+
+|
+`features`
+ |
+
+A `dict` mapping feature keys to `FixedLenFeature` or
+`VarLenFeature` values.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for this operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`example_names`
+ |
+
+(Optional) A scalar string Tensor, the associated name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `dict` mapping feature keys to `Tensor` and `SparseTensor` values.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if any feature is invalid.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/placeholder.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/placeholder.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..2b9bb0efb96
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/placeholder.md
@@ -0,0 +1,122 @@
+description: Inserts a placeholder for a tensor that will be always fed.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.placeholder
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Inserts a placeholder for a tensor that will be always fed.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.placeholder(
+ dtype, shape=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+**Important**: This tensor will produce an error if evaluated. Its value must
+be fed using the `feed_dict` optional argument to `Session.run()`,
+`Tensor.eval()`, or `Operation.run()`.
+
+#### For example:
+
+
+
+```python
+x = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(1024, 1024))
+y = tf.matmul(x, x)
+
+with tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess:
+ print(sess.run(y)) # ERROR: will fail because x was not fed.
+
+ rand_array = np.random.rand(1024, 1024)
+ print(sess.run(y, feed_dict={x: rand_array})) # Will succeed.
+```
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+The type of elements in the tensor to be fed.
+ |
+
+|
+`shape`
+ |
+
+The shape of the tensor to be fed (optional). If the shape is not
+specified, you can feed a tensor of any shape.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` that may be used as a handle for feeding a value, but not
+evaluated directly.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+if eager execution is enabled
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+Placeholders are not compatible with eager execution.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/placeholder_with_default.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/placeholder_with_default.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..ac71a5ab336
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/placeholder_with_default.md
@@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
+description: A placeholder op that passes through input when its output is not fed.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.placeholder_with_default
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A placeholder op that passes through `input` when its output is not fed.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.placeholder_with_default(
+ input, shape, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. The default value to produce when output is not fed.
+ |
+
+|
+`shape`
+ |
+
+A tf.TensorShape or list of `int`s. The (possibly partial) shape of
+the tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `input`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..6246525bc1b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler.md
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
+description: Public API for tf.profiler namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.profiler
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.profiler namespace.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class AdviceProto`](../../../tf/compat/v1/profiler/AdviceProto.md): A ProtocolMessage
+
+[`class GraphNodeProto`](../../../tf/compat/v1/profiler/GraphNodeProto.md): A ProtocolMessage
+
+[`class MultiGraphNodeProto`](../../../tf/compat/v1/profiler/MultiGraphNodeProto.md): A ProtocolMessage
+
+[`class OpLogProto`](../../../tf/compat/v1/profiler/OpLogProto.md): A ProtocolMessage
+
+[`class ProfileOptionBuilder`](../../../tf/compat/v1/profiler/ProfileOptionBuilder.md): Option Builder for Profiling API.
+
+[`class Profiler`](../../../tf/compat/v1/profiler/Profiler.md): TensorFlow multi-step profiler.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`advise(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/profiler/advise.md): Auto profile and advise.
+
+[`profile(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/profiler/profile.md): Profile model.
+
+[`write_op_log(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/profiler/write_op_log.md): Log provided 'op_log', and add additional model information below.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/AdviceProto.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/AdviceProto.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..4c4d1433302
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/AdviceProto.md
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+description: A ProtocolMessage
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.profiler.AdviceProto
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A ProtocolMessage
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`checkers`
+ |
+
+`repeated CheckersEntry checkers`
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Child Classes
+[`class Checker`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/profiler/AdviceProto/Checker.md)
+
+[`class CheckersEntry`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/profiler/AdviceProto/CheckersEntry.md)
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/AdviceProto/Checker.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/AdviceProto/Checker.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..132357a7446
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/AdviceProto/Checker.md
@@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
+description: A ProtocolMessage
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.profiler.AdviceProto.Checker
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A ProtocolMessage
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`reports`
+ |
+
+`repeated string reports`
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/AdviceProto/CheckersEntry.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/AdviceProto/CheckersEntry.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..f3436fa92db
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/AdviceProto/CheckersEntry.md
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+description: A ProtocolMessage
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.profiler.AdviceProto.CheckersEntry
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A ProtocolMessage
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`key`
+ |
+
+`string key`
+ |
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`Checker value`
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/GraphNodeProto.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/GraphNodeProto.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..95016c68c1b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/GraphNodeProto.md
@@ -0,0 +1,232 @@
+description: A ProtocolMessage
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.profiler.GraphNodeProto
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A ProtocolMessage
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`accelerator_exec_micros`
+ |
+
+`int64 accelerator_exec_micros`
+ |
+
+|
+`children`
+ |
+
+`repeated GraphNodeProto children`
+ |
+
+|
+`cpu_exec_micros`
+ |
+
+`int64 cpu_exec_micros`
+ |
+
+|
+`devices`
+ |
+
+`repeated string devices`
+ |
+
+|
+`exec_micros`
+ |
+
+`int64 exec_micros`
+ |
+
+|
+`float_ops`
+ |
+
+`int64 float_ops`
+ |
+
+|
+`input_shapes`
+ |
+
+`repeated InputShapesEntry input_shapes`
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+`string name`
+ |
+
+|
+`output_bytes`
+ |
+
+`int64 output_bytes`
+ |
+
+|
+`parameters`
+ |
+
+`int64 parameters`
+ |
+
+|
+`peak_bytes`
+ |
+
+`int64 peak_bytes`
+ |
+
+|
+`requested_bytes`
+ |
+
+`int64 requested_bytes`
+ |
+
+|
+`residual_bytes`
+ |
+
+`int64 residual_bytes`
+ |
+
+|
+`run_count`
+ |
+
+`int64 run_count`
+ |
+
+|
+`shapes`
+ |
+
+`repeated TensorShapeProto shapes`
+ |
+
+|
+`tensor_value`
+ |
+
+`TFProfTensorProto tensor_value`
+ |
+
+|
+`total_accelerator_exec_micros`
+ |
+
+`int64 total_accelerator_exec_micros`
+ |
+
+|
+`total_cpu_exec_micros`
+ |
+
+`int64 total_cpu_exec_micros`
+ |
+
+|
+`total_definition_count`
+ |
+
+`int64 total_definition_count`
+ |
+
+|
+`total_exec_micros`
+ |
+
+`int64 total_exec_micros`
+ |
+
+|
+`total_float_ops`
+ |
+
+`int64 total_float_ops`
+ |
+
+|
+`total_output_bytes`
+ |
+
+`int64 total_output_bytes`
+ |
+
+|
+`total_parameters`
+ |
+
+`int64 total_parameters`
+ |
+
+|
+`total_peak_bytes`
+ |
+
+`int64 total_peak_bytes`
+ |
+
+|
+`total_requested_bytes`
+ |
+
+`int64 total_requested_bytes`
+ |
+
+|
+`total_residual_bytes`
+ |
+
+`int64 total_residual_bytes`
+ |
+
+|
+`total_run_count`
+ |
+
+`int64 total_run_count`
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Child Classes
+[`class InputShapesEntry`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/profiler/GraphNodeProto/InputShapesEntry.md)
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/GraphNodeProto/InputShapesEntry.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/GraphNodeProto/InputShapesEntry.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..19ccb9636b9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/GraphNodeProto/InputShapesEntry.md
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+description: A ProtocolMessage
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.profiler.GraphNodeProto.InputShapesEntry
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A ProtocolMessage
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`key`
+ |
+
+`int32 key`
+ |
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`TensorShapeProto value`
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/MultiGraphNodeProto.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/MultiGraphNodeProto.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..563e3633b44
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/MultiGraphNodeProto.md
@@ -0,0 +1,186 @@
+description: A ProtocolMessage
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.profiler.MultiGraphNodeProto
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A ProtocolMessage
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`accelerator_exec_micros`
+ |
+
+`int64 accelerator_exec_micros`
+ |
+
+|
+`children`
+ |
+
+`repeated MultiGraphNodeProto children`
+ |
+
+|
+`cpu_exec_micros`
+ |
+
+`int64 cpu_exec_micros`
+ |
+
+|
+`exec_micros`
+ |
+
+`int64 exec_micros`
+ |
+
+|
+`float_ops`
+ |
+
+`int64 float_ops`
+ |
+
+|
+`graph_nodes`
+ |
+
+`repeated GraphNodeProto graph_nodes`
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+`string name`
+ |
+
+|
+`output_bytes`
+ |
+
+`int64 output_bytes`
+ |
+
+|
+`parameters`
+ |
+
+`int64 parameters`
+ |
+
+|
+`peak_bytes`
+ |
+
+`int64 peak_bytes`
+ |
+
+|
+`requested_bytes`
+ |
+
+`int64 requested_bytes`
+ |
+
+|
+`residual_bytes`
+ |
+
+`int64 residual_bytes`
+ |
+
+|
+`total_accelerator_exec_micros`
+ |
+
+`int64 total_accelerator_exec_micros`
+ |
+
+|
+`total_cpu_exec_micros`
+ |
+
+`int64 total_cpu_exec_micros`
+ |
+
+|
+`total_exec_micros`
+ |
+
+`int64 total_exec_micros`
+ |
+
+|
+`total_float_ops`
+ |
+
+`int64 total_float_ops`
+ |
+
+|
+`total_output_bytes`
+ |
+
+`int64 total_output_bytes`
+ |
+
+|
+`total_parameters`
+ |
+
+`int64 total_parameters`
+ |
+
+|
+`total_peak_bytes`
+ |
+
+`int64 total_peak_bytes`
+ |
+
+|
+`total_requested_bytes`
+ |
+
+`int64 total_requested_bytes`
+ |
+
+|
+`total_residual_bytes`
+ |
+
+`int64 total_residual_bytes`
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/OpLogProto.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/OpLogProto.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..54ecaef74b2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/OpLogProto.md
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
+description: A ProtocolMessage
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.profiler.OpLogProto
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A ProtocolMessage
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`id_to_string`
+ |
+
+`repeated IdToStringEntry id_to_string`
+ |
+
+|
+`log_entries`
+ |
+
+`repeated OpLogEntry log_entries`
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Child Classes
+[`class IdToStringEntry`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/profiler/OpLogProto/IdToStringEntry.md)
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/OpLogProto/IdToStringEntry.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/OpLogProto/IdToStringEntry.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..b66500607be
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/OpLogProto/IdToStringEntry.md
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+description: A ProtocolMessage
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.profiler.OpLogProto.IdToStringEntry
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A ProtocolMessage
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`key`
+ |
+
+`int64 key`
+ |
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+`string value`
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/ProfileOptionBuilder.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/ProfileOptionBuilder.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e958f5c2fcf
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/ProfileOptionBuilder.md
@@ -0,0 +1,1020 @@
+description: Option Builder for Profiling API.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.profiler.ProfileOptionBuilder
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Option Builder for Profiling API.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.profiler.ProfileOptionBuilder(
+ options=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+For tutorial on the options, see
+https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/tree/master/tensorflow/core/profiler/g3doc/options.md
+
+```python
+# Users can use pre-built options:
+opts = (
+ tf.profiler.ProfileOptionBuilder.trainable_variables_parameter())
+
+# Or, build your own options:
+opts = (tf.compat.v1.profiler.ProfileOptionBuilder()
+ .with_max_depth(10)
+ .with_min_micros(1000)
+ .select(['accelerator_micros'])
+ .with_stdout_output()
+ .build()
+
+# Or customize the pre-built options:
+opts = (tf.compat.v1.profiler.ProfileOptionBuilder(
+ tf.profiler.ProfileOptionBuilder.time_and_memory())
+ .with_displaying_options(show_name_regexes=['.*rnn.*'])
+ .build())
+
+# Finally, profiling with the options:
+_ = tf.compat.v1.profiler.profile(tf.compat.v1.get_default_graph(),
+ run_meta=run_meta,
+ cmd='scope',
+ options=opts)
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`options`
+ |
+
+Optional initial option dict to start with.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+account_displayed_op_only
+
+View source
+
+
+account_displayed_op_only(
+ is_true
+)
+
+
+Whether only account the statistics of displayed profiler nodes.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`is_true`
+ |
+
+If true, only account statistics of nodes eventually
+displayed by the outputs.
+Otherwise, a node's statistics are accounted by its parents
+as long as it's types match 'account_type_regexes', even if
+it is hidden from the output, say, by hide_name_regexes.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+self
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+build
+
+View source
+
+
+build()
+
+
+Build a profiling option.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A dict of profiling options.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+float_operation
+
+View source
+
+
+@staticmethod
+float_operation()
+
+
+Options used to profile float operations.
+
+Please see https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/tree/master/tensorflow/core/profiler/g3doc/profile_model_architecture.md
+on the caveats of calculating float operations.
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A dict of profiling options.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+order_by
+
+View source
+
+
+order_by(
+ attribute
+)
+
+
+Order the displayed profiler nodes based on a attribute.
+
+Supported attribute includes micros, bytes, occurrence, params, etc.
+https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/tree/master/tensorflow/core/profiler/g3doc/options.md
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`attribute`
+ |
+
+An attribute the profiler node has.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+self
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+select
+
+View source
+
+
+select(
+ attributes
+)
+
+
+Select the attributes to display.
+
+See https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/tree/master/tensorflow/core/profiler/g3doc/options.md
+for supported attributes.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`attributes`
+ |
+
+A list of attribute the profiler node has.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+self
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+time_and_memory
+
+View source
+
+
+@staticmethod
+time_and_memory(
+ min_micros=1, min_bytes=1, min_accelerator_micros=0, min_cpu_micros=0,
+ min_peak_bytes=0, min_residual_bytes=0, min_output_bytes=0
+)
+
+
+Show operation time and memory consumptions.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`min_micros`
+ |
+
+Only show profiler nodes with execution time
+no less than this. It sums accelerator and cpu times.
+ |
+
+|
+`min_bytes`
+ |
+
+Only show profiler nodes requested to allocate no less bytes
+than this.
+ |
+
+|
+`min_accelerator_micros`
+ |
+
+Only show profiler nodes spend no less than
+this time on accelerator (e.g. GPU).
+ |
+
+|
+`min_cpu_micros`
+ |
+
+Only show profiler nodes spend no less than
+this time on cpu.
+ |
+
+|
+`min_peak_bytes`
+ |
+
+Only show profiler nodes using no less than this bytes
+at peak (high watermark). For profiler nodes consist of multiple
+graph nodes, it sums the graph nodes' peak_bytes.
+ |
+
+|
+`min_residual_bytes`
+ |
+
+Only show profiler nodes have no less than
+this bytes not being de-allocated after Compute() ends. For
+profiler nodes consist of multiple graph nodes, it sums the
+graph nodes' residual_bytes.
+ |
+
+|
+`min_output_bytes`
+ |
+
+Only show profiler nodes have no less than this bytes
+output. The output are not necessarily allocated by this profiler
+nodes.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A dict of profiling options.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+trainable_variables_parameter
+
+View source
+
+
+@staticmethod
+trainable_variables_parameter()
+
+
+Options used to profile trainable variable parameters.
+
+Normally used together with 'scope' view.
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A dict of profiling options.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+with_accounted_types
+
+View source
+
+
+with_accounted_types(
+ account_type_regexes
+)
+
+
+Selectively counting statistics based on node types.
+
+Here, 'types' means the profiler nodes' properties. Profiler by default
+consider device name (e.g. /job:xx/.../device:GPU:0) and operation type
+(e.g. MatMul) as profiler nodes' properties. User can also associate
+customized 'types' to profiler nodes through OpLogProto proto.
+
+For example, user can select profiler nodes placed on gpu:0 with:
+`account_type_regexes=['.*gpu:0.*']`
+
+If none of a node's properties match the specified regexes, the node is
+not displayed nor accounted.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`account_type_regexes`
+ |
+
+A list of regexes specifying the types.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+self.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+with_empty_output
+
+View source
+
+
+with_empty_output()
+
+
+Do not generate side-effect outputs.
+
+
+with_file_output
+
+View source
+
+
+with_file_output(
+ outfile
+)
+
+
+Print the result to a file.
+
+
+with_max_depth
+
+View source
+
+
+with_max_depth(
+ max_depth
+)
+
+
+Set the maximum depth of display.
+
+The depth depends on profiling view. For 'scope' view, it's the
+depth of name scope hierarchy (tree), for 'op' view, it's the number
+of operation types (list), etc.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`max_depth`
+ |
+
+Maximum depth of the data structure to display.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+self
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+with_min_execution_time
+
+View source
+
+
+with_min_execution_time(
+ min_micros=0, min_accelerator_micros=0, min_cpu_micros=0
+)
+
+
+Only show profiler nodes consuming no less than 'min_micros'.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`min_micros`
+ |
+
+Only show profiler nodes with execution time
+no less than this. It sums accelerator and cpu times.
+ |
+
+|
+`min_accelerator_micros`
+ |
+
+Only show profiler nodes spend no less than
+this time on accelerator (e.g. GPU).
+ |
+
+|
+`min_cpu_micros`
+ |
+
+Only show profiler nodes spend no less than
+this time on cpu.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+self
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+with_min_float_operations
+
+View source
+
+
+with_min_float_operations(
+ min_float_ops
+)
+
+
+Only show profiler nodes consuming no less than 'min_float_ops'.
+
+Please see https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/tree/master/tensorflow/core/profiler/g3doc/profile_model_architecture.md
+on the caveats of calculating float operations.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`min_float_ops`
+ |
+
+Only show profiler nodes with float operations
+no less than this.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+self
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+with_min_memory
+
+View source
+
+
+with_min_memory(
+ min_bytes=0, min_peak_bytes=0, min_residual_bytes=0, min_output_bytes=0
+)
+
+
+Only show profiler nodes consuming no less than 'min_bytes'.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`min_bytes`
+ |
+
+Only show profiler nodes requested to allocate no less bytes
+than this.
+ |
+
+|
+`min_peak_bytes`
+ |
+
+Only show profiler nodes using no less than this bytes
+at peak (high watermark). For profiler nodes consist of multiple
+graph nodes, it sums the graph nodes' peak_bytes.
+ |
+
+|
+`min_residual_bytes`
+ |
+
+Only show profiler nodes have no less than
+this bytes not being de-allocated after Compute() ends. For
+profiler nodes consist of multiple graph nodes, it sums the
+graph nodes' residual_bytes.
+ |
+
+|
+`min_output_bytes`
+ |
+
+Only show profiler nodes have no less than this bytes
+output. The output are not necessarily allocated by this profiler
+nodes.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+self
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+with_min_occurrence
+
+View source
+
+
+with_min_occurrence(
+ min_occurrence
+)
+
+
+Only show profiler nodes including no less than 'min_occurrence' graph nodes.
+
+A "node" means a profiler output node, which can be a python line
+(code view), an operation type (op view), or a graph node
+(graph/scope view). A python line includes all graph nodes created by that
+line, while an operation type includes all graph nodes of that type.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`min_occurrence`
+ |
+
+Only show nodes including no less than this.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+self
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+with_min_parameters
+
+View source
+
+
+with_min_parameters(
+ min_params
+)
+
+
+Only show profiler nodes holding no less than 'min_params' parameters.
+
+'Parameters' normally refers the weights of in TensorFlow variables.
+It reflects the 'capacity' of models.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`min_params`
+ |
+
+Only show profiler nodes holding number parameters
+no less than this.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+self
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+with_node_names
+
+View source
+
+
+with_node_names(
+ start_name_regexes=None, show_name_regexes=None, hide_name_regexes=None,
+ trim_name_regexes=None
+)
+
+
+Regular expressions used to select profiler nodes to display.
+
+After 'with_accounted_types' is evaluated, 'with_node_names' are
+evaluated as follows:
+
+ For a profile data structure, profiler first finds the profiler
+ nodes matching 'start_name_regexes', and starts displaying profiler
+ nodes from there. Then, if a node matches 'show_name_regexes' and
+ doesn't match 'hide_name_regexes', it's displayed. If a node matches
+ 'trim_name_regexes', profiler stops further searching that branch.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`start_name_regexes`
+ |
+
+list of node name regexes to start displaying.
+ |
+
+|
+`show_name_regexes`
+ |
+
+list of node names regexes to display.
+ |
+
+|
+`hide_name_regexes`
+ |
+
+list of node_names regexes that should be hidden.
+ |
+
+|
+`trim_name_regexes`
+ |
+
+list of node name regexes from where to stop.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+self
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+with_pprof_output
+
+View source
+
+
+with_pprof_output(
+ pprof_file
+)
+
+
+Generate a pprof profile gzip file.
+
+
+#### To use the pprof file:
+
+pprof -png --nodecount=100 --sample_index=1
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`pprof_file`
+ |
+
+filename for output, usually suffixed with .pb.gz.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+self.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+with_stdout_output
+
+View source
+
+
+with_stdout_output()
+
+
+Print the result to stdout.
+
+
+with_step
+
+View source
+
+
+with_step(
+ step
+)
+
+
+Which profile step to use for profiling.
+
+The 'step' here refers to the step defined by `Profiler.add_step()` API.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`step`
+ |
+
+When multiple steps of profiles are available, select which step's
+profile to use. If -1, use average of all available steps.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+self
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+with_timeline_output
+
+View source
+
+
+with_timeline_output(
+ timeline_file
+)
+
+
+Generate a timeline json file.
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/Profiler.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/Profiler.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..7151e688549
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/Profiler.md
@@ -0,0 +1,397 @@
+description: TensorFlow multi-step profiler.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.profiler.Profiler
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+TensorFlow multi-step profiler.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.profiler.Profiler(
+ graph=None, op_log=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/tree/master/tensorflow/core/profiler/README.md
+
+```python
+Typical use case:
+ # Currently we are only allowed to create 1 profiler per process.
+ profiler = Profiler(sess.graph)
+
+ for i in xrange(total_steps):
+ if i % 10000 == 0:
+ run_meta = tf.compat.v1.RunMetadata()
+ _ = sess.run(...,
+ options=tf.compat.v1.RunOptions(
+ trace_level=tf.RunOptions.FULL_TRACE),
+ run_metadata=run_meta)
+ profiler.add_step(i, run_meta)
+
+ # Profile the parameters of your model.
+ profiler.profile_name_scope(options=(option_builder.ProfileOptionBuilder
+ .trainable_variables_parameter()))
+
+ # Or profile the timing of your model operations.
+ opts = option_builder.ProfileOptionBuilder.time_and_memory()
+ profiler.profile_operations(options=opts)
+
+ # Or you can generate a timeline:
+ opts = (option_builder.ProfileOptionBuilder(
+ option_builder.ProfileOptionBuilder.time_and_memory())
+ .with_step(i)
+ .with_timeline_output(filename).build())
+ profiler.profile_graph(options=opts)
+ else:
+ _ = sess.run(...)
+ # Auto detect problems and generate advice.
+ profiler.advise()
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+tf.Graph. If None and eager execution is not enabled, use
+default graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`op_log`
+ |
+
+optional. tensorflow::tfprof::OpLogProto proto. Used to define
+extra op types.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+add_step
+
+View source
+
+
+add_step(
+ step, run_meta
+)
+
+
+Add statistics of a step.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`step`
+ |
+
+int, An id used to group one or more different `run_meta` together.
+When profiling with the profile_xxx APIs, user can use the `step`
+id in the `options` to profile these `run_meta` together.
+ |
+
+|
+`run_meta`
+ |
+
+RunMetadata proto that contains statistics of a session run.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+advise
+
+View source
+
+
+advise(
+ options
+)
+
+
+Automatically detect problems and generate reports.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`options`
+ |
+
+A dict of options. See ALL_ADVICE example above.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Advise proto that contains the reports from all checkers.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+profile_graph
+
+View source
+
+
+profile_graph(
+ options
+)
+
+
+Profile the statistics of graph nodes, organized by dataflow graph.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`options`
+ |
+
+A dict of options. See core/profiler/g3doc/options.md.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+a GraphNodeProto that records the results.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+profile_name_scope
+
+View source
+
+
+profile_name_scope(
+ options
+)
+
+
+Profile the statistics of graph nodes, organized by name scope.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`options`
+ |
+
+A dict of options. See core/profiler/g3doc/options.md.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+a GraphNodeProto that records the results.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+profile_operations
+
+View source
+
+
+profile_operations(
+ options
+)
+
+
+Profile the statistics of the Operation types (e.g. MatMul, Conv2D).
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`options`
+ |
+
+A dict of options. See core/profiler/g3doc/options.md.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+a MultiGraphNodeProto that records the results.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+profile_python
+
+View source
+
+
+profile_python(
+ options
+)
+
+
+Profile the statistics of the Python codes.
+
+ By default, it shows the call stack from root. To avoid
+ redundant output, you may use options to filter as below
+ options['show_name_regexes'] = ['.*my_code.py.*']
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`options`
+ |
+
+A dict of options. See core/profiler/g3doc/options.md.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+a MultiGraphNodeProto that records the results.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+serialize_to_string
+
+View source
+
+
+serialize_to_string()
+
+
+Serialize the ProfileProto to a binary string.
+
+ Users can write it to file for offline analysis by tfprof commandline
+ or graphical interface.
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+ProfileProto binary string.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/advise.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/advise.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..2027a6d6f92
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/advise.md
@@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
+description: Auto profile and advise.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.profiler.advise
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Auto profile and advise.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.profiler.advise(
+ graph=None, run_meta=None, options=_DEFAULT_ADVISE_OPTIONS
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ Builds profiles and automatically check anomalies of various
+ aspects. For more details:
+ https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/tree/master/tensorflow/core/profiler/README.md
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+tf.Graph. If None and eager execution is not enabled, use
+default graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`run_meta`
+ |
+
+optional tensorflow.RunMetadata proto. It is necessary to
+to support run time information profiling, such as time and memory.
+ |
+
+|
+`options`
+ |
+
+see ALL_ADVICE example above. Default checks everything.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Returns AdviceProto proto
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/profile.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/profile.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..c0caa949c5f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/profile.md
@@ -0,0 +1,105 @@
+description: Profile model.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.profiler.profile
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Profile model.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.profiler.profile(
+ graph=None, run_meta=None, op_log=None, cmd='scope',
+ options=_DEFAULT_PROFILE_OPTIONS
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ Tutorials and examples can be found in:
+ https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/master/tensorflow/core/profiler/g3doc/python_api.md
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+tf.Graph. If None and eager execution is not enabled, use
+default graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`run_meta`
+ |
+
+optional tensorflow.RunMetadata proto. It is necessary to
+to support run time information profiling, such as time and memory.
+ |
+
+|
+`op_log`
+ |
+
+tensorflow.tfprof.OpLogProto proto. User can assign "types" to
+graph nodes with op_log. "types" allow user to flexibly group and
+account profiles using options['accounted_type_regexes'].
+ |
+
+|
+`cmd`
+ |
+
+string. Either 'op', 'scope', 'graph' or 'code'.
+'op' view organizes profile using operation type. (e.g. MatMul)
+'scope' view organizes profile using graph node name scope.
+'graph' view organizes profile using graph node inputs/outputs.
+'code' view organizes profile using Python call stack.
+ |
+
+|
+`options`
+ |
+
+A dict of options. See core/profiler/g3doc/options.md.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+If cmd is 'scope' or 'graph', returns GraphNodeProto proto.
+If cmd is 'op' or 'code', returns MultiGraphNodeProto proto.
+Side effect: stdout/file/timeline.json depending on options['output']
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/write_op_log.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/write_op_log.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..123ec6ddb95
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/profiler/write_op_log.md
@@ -0,0 +1,88 @@
+description: Log provided 'op_log', and add additional model information below.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.profiler.write_op_log
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Log provided 'op_log', and add additional model information below.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.profiler.write_op_log(
+ graph, log_dir, op_log=None, run_meta=None, add_trace=(True)
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+ The API also assigns ops in tf.compat.v1.trainable_variables() an op type
+ called '_trainable_variables'.
+ The API also logs 'flops' statistics for ops with op.RegisterStatistics()
+ defined. flops calculation depends on Tensor shapes defined in 'graph',
+ which might not be complete. 'run_meta', if provided, completes the shape
+ information with best effort.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+tf.Graph. If None and eager execution is not enabled, use
+default graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`log_dir`
+ |
+
+directory to write the log file.
+ |
+
+|
+`op_log`
+ |
+
+(Optional) OpLogProto proto to be written. If not provided, an new
+one is created.
+ |
+
+|
+`run_meta`
+ |
+
+(Optional) RunMetadata proto that helps flops computation using
+run time shape information.
+ |
+
+|
+`add_trace`
+ |
+
+Whether to add python code trace information.
+Used to support "code" view.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/py_func.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/py_func.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..c6c9fa69fb2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/py_func.md
@@ -0,0 +1,134 @@
+description: Wraps a python function and uses it as a TensorFlow op.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.py_func
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Wraps a python function and uses it as a TensorFlow op.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.py_func(
+ func, inp, Tout, stateful=(True), name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Given a python function `func`, which takes numpy arrays as its
+arguments and returns numpy arrays as its outputs, wrap this function as an
+operation in a TensorFlow graph. The following snippet constructs a simple
+TensorFlow graph that invokes the `np.sinh()` NumPy function as a operation
+in the graph:
+
+```python
+def my_func(x):
+ # x will be a numpy array with the contents of the placeholder below
+ return np.sinh(x)
+input = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(tf.float32)
+y = tf.compat.v1.py_func(my_func, [input], tf.float32)
+```
+
+**N.B.** The tf.compat.v1.py_func() operation has the following known
+limitations:
+
+* The body of the function (i.e. `func`) will not be serialized in a
+ `GraphDef`. Therefore, you should not use this function if you need to
+ serialize your model and restore it in a different environment.
+
+* The operation must run in the same address space as the Python program
+ that calls tf.compat.v1.py_func(). If you are using distributed
+ TensorFlow, you
+ must run a tf.distribute.Server in the same process as the program that
+ calls
+ tf.compat.v1.py_func() and you must pin the created operation to a device
+ in that
+ server (e.g. using `with tf.device():`).
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`func`
+ |
+
+A Python function, which accepts `ndarray` objects as arguments and
+returns a list of `ndarray` objects (or a single `ndarray`). This function
+must accept as many arguments as there are tensors in `inp`, and these
+argument types will match the corresponding tf.Tensor objects in `inp`.
+The returns `ndarray`s must match the number and types defined `Tout`.
+Important Note: Input and output numpy `ndarray`s of `func` are not
+guaranteed to be copies. In some cases their underlying memory will be
+shared with the corresponding TensorFlow tensors. In-place modification
+or storing `func` input or return values in python datastructures
+without explicit (np.)copy can have non-deterministic consequences.
+ |
+
+|
+`inp`
+ |
+
+A list of `Tensor` objects.
+ |
+
+|
+`Tout`
+ |
+
+A list or tuple of tensorflow data types or a single tensorflow data
+type if there is only one, indicating what `func` returns.
+ |
+
+|
+`stateful`
+ |
+
+(Boolean.) If True, the function should be considered stateful. If
+a function is stateless, when given the same input it will return the same
+output and have no observable side effects. Optimizations such as common
+subexpression elimination are only performed on stateless operations.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of `Tensor` or a single `Tensor` which `func` computes.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/python_io.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/python_io.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..5b1c308c94c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/python_io.md
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+description: Python functions for directly manipulating TFRecord-formatted files.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.python_io
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Python functions for directly manipulating TFRecord-formatted files.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class TFRecordCompressionType`](../../../tf/compat/v1/io/TFRecordCompressionType.md): The type of compression for the record.
+
+[`class TFRecordOptions`](../../../tf/io/TFRecordOptions.md): Options used for manipulating TFRecord files.
+
+[`class TFRecordWriter`](../../../tf/io/TFRecordWriter.md): A class to write records to a TFRecords file.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`tf_record_iterator(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/io/tf_record_iterator.md): An iterator that read the records from a TFRecords file. (deprecated)
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/quantization.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/quantization.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..0834c0e4133
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/quantization.md
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
+description: Public API for tf.quantization namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.quantization
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.quantization namespace.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`dequantize(...)`](../../../tf/quantization/dequantize.md): Dequantize the 'input' tensor into a float or bfloat16 Tensor.
+
+[`fake_quant_with_min_max_args(...)`](../../../tf/quantization/fake_quant_with_min_max_args.md): Fake-quantize the 'inputs' tensor, type float to 'outputs' tensor of same type.
+
+[`fake_quant_with_min_max_args_gradient(...)`](../../../tf/quantization/fake_quant_with_min_max_args_gradient.md): Compute gradients for a FakeQuantWithMinMaxArgs operation.
+
+[`fake_quant_with_min_max_vars(...)`](../../../tf/quantization/fake_quant_with_min_max_vars.md): Fake-quantize the 'inputs' tensor of type float via global float scalars `min`
+
+[`fake_quant_with_min_max_vars_gradient(...)`](../../../tf/quantization/fake_quant_with_min_max_vars_gradient.md): Compute gradients for a FakeQuantWithMinMaxVars operation.
+
+[`fake_quant_with_min_max_vars_per_channel(...)`](../../../tf/quantization/fake_quant_with_min_max_vars_per_channel.md): Fake-quantize the 'inputs' tensor of type float and one of the shapes: `[d]`,
+
+[`fake_quant_with_min_max_vars_per_channel_gradient(...)`](../../../tf/quantization/fake_quant_with_min_max_vars_per_channel_gradient.md): Compute gradients for a FakeQuantWithMinMaxVarsPerChannel operation.
+
+[`quantize(...)`](../../../tf/quantization/quantize.md): Quantize the 'input' tensor of type float to 'output' tensor of type 'T'.
+
+[`quantize_and_dequantize(...)`](../../../tf/quantization/quantize_and_dequantize.md): Quantizes then dequantizes a tensor.
+
+[`quantized_concat(...)`](../../../tf/quantization/quantized_concat.md): Concatenates quantized tensors along one dimension.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/quantize_v2.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/quantize_v2.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..4c62b3bbfd8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/quantize_v2.md
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
+description: Please use tf.quantization.quantize instead.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.quantize_v2
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Please use tf.quantization.quantize instead.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.quantize_v2(
+ input, min_range, max_range, T, mode='MIN_COMBINED', name=None,
+ round_mode='HALF_AWAY_FROM_ZERO', narrow_range=(False), axis=None,
+ ensure_minimum_range=0.01
+)
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/queue.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/queue.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..16c9dbc84c6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/queue.md
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+description: Public API for tf.queue namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.queue
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.queue namespace.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class FIFOQueue`](../../../tf/queue/FIFOQueue.md): A queue implementation that dequeues elements in first-in first-out order.
+
+[`class PaddingFIFOQueue`](../../../tf/queue/PaddingFIFOQueue.md): A FIFOQueue that supports batching variable-sized tensors by padding.
+
+[`class PriorityQueue`](../../../tf/queue/PriorityQueue.md): A queue implementation that dequeues elements in prioritized order.
+
+[`class QueueBase`](../../../tf/queue/QueueBase.md): Base class for queue implementations.
+
+[`class RandomShuffleQueue`](../../../tf/queue/RandomShuffleQueue.md): A queue implementation that dequeues elements in a random order.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/ragged.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/ragged.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..8d47db5b063
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/ragged.md
@@ -0,0 +1,186 @@
+description: Ragged Tensors.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.ragged
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Ragged Tensors.
+
+
+This package defines ops for manipulating ragged tensors (tf.RaggedTensor),
+which are tensors with non-uniform shapes. In particular, each `RaggedTensor`
+has one or more *ragged dimensions*, which are dimensions whose slices may have
+different lengths. For example, the inner (column) dimension of
+`rt=[[3, 1, 4, 1], [], [5, 9, 2], [6], []]` is ragged, since the column slices
+(`rt[0, :]`, ..., `rt[4, :]`) have different lengths. For a more detailed
+description of ragged tensors, see the tf.RaggedTensor class documentation
+and the [Ragged Tensor Guide](/guide/ragged_tensors).
+
+
+### Additional ops that support `RaggedTensor`
+
+Arguments that accept `RaggedTensor`s are marked in **bold**.
+
+* `tf.batch_gather`(**params**, **indices**, name=`None`)
+* tf.bitwise.bitwise_and(**x**, **y**, name=`None`)
+* tf.bitwise.bitwise_or(**x**, **y**, name=`None`)
+* tf.bitwise.bitwise_xor(**x**, **y**, name=`None`)
+* tf.bitwise.invert(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.bitwise.left_shift(**x**, **y**, name=`None`)
+* tf.bitwise.right_shift(**x**, **y**, name=`None`)
+* tf.cast(**x**, dtype, name=`None`)
+* tf.clip_by_value(**t**, clip_value_min, clip_value_max, name=`None`)
+* tf.concat(**values**, axis, name=`'concat'`)
+* tf.debugging.check_numerics(**tensor**, message, name=`None`)
+* tf.dtypes.complex(**real**, **imag**, name=`None`)
+* tf.dtypes.saturate_cast(**value**, dtype, name=`None`)
+* tf.dynamic_partition(**data**, **partitions**, num_partitions, name=`None`)
+* tf.expand_dims(**input**, axis=`None`, name=`None`, dim=`None`)
+* tf.gather_nd(**params**, **indices**, name=`None`, batch_dims=`0`)
+* tf.gather(**params**, **indices**, validate_indices=`None`, name=`None`, axis=`None`, batch_dims=`0`)
+* tf.identity(**input**, name=`None`)
+* tf.io.decode_base64(**input**, name=`None`)
+* tf.io.decode_compressed(**bytes**, compression_type=`''`, name=`None`)
+* tf.io.encode_base64(**input**, pad=`False`, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.abs(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.acos(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.acosh(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.add_n(**inputs**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.add(**x**, **y**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.angle(**input**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.asin(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.asinh(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.atan2(**y**, **x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.atan(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.atanh(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.ceil(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.conj(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.cos(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.cosh(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.digamma(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.divide_no_nan(**x**, **y**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.divide(**x**, **y**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.equal(**x**, **y**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.erf(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.erfc(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.erfinv(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.exp(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.expm1(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.floor(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.floordiv(**x**, **y**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.floormod(**x**, **y**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.greater_equal(**x**, **y**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.greater(**x**, **y**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.imag(**input**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.is_finite(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.is_inf(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.is_nan(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.less_equal(**x**, **y**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.less(**x**, **y**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.lgamma(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.log1p(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.log_sigmoid(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.log(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.logical_and(**x**, **y**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.logical_not(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.logical_or(**x**, **y**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.logical_xor(**x**, **y**, name=`'LogicalXor'`)
+* tf.math.maximum(**x**, **y**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.minimum(**x**, **y**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.multiply(**x**, **y**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.ndtri(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.negative(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.not_equal(**x**, **y**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.pow(**x**, **y**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.real(**input**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.reciprocal(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.reduce_any(**input_tensor**, axis=`None`, keepdims=`False`, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.reduce_max(**input_tensor**, axis=`None`, keepdims=`False`, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.reduce_mean(**input_tensor**, axis=`None`, keepdims=`False`, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.reduce_min(**input_tensor**, axis=`None`, keepdims=`False`, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.reduce_prod(**input_tensor**, axis=`None`, keepdims=`False`, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.reduce_sum(**input_tensor**, axis=`None`, keepdims=`False`, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.rint(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.round(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.rsqrt(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.sign(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.sin(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.sinh(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.sqrt(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.square(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.squared_difference(**x**, **y**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.subtract(**x**, **y**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.tan(**x**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.truediv(**x**, **y**, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.unsorted_segment_max(**data**, **segment_ids**, num_segments, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.unsorted_segment_mean(**data**, **segment_ids**, num_segments, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.unsorted_segment_min(**data**, **segment_ids**, num_segments, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.unsorted_segment_prod(**data**, **segment_ids**, num_segments, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.unsorted_segment_sqrt_n(**data**, **segment_ids**, num_segments, name=`None`)
+* tf.math.unsorted_segment_sum(**data**, **segment_ids**, num_segments, name=`None`)
+* tf.one_hot(**indices**, depth, on_value=`None`, off_value=`None`, axis=`None`, dtype=`None`, name=`None`)
+* tf.ones_like(**tensor**, dtype=`None`, name=`None`, optimize=`True`)
+* tf.rank(**input**, name=`None`)
+* tf.realdiv(**x**, **y**, name=`None`)
+* tf.reduce_all(**input_tensor**, axis=`None`, keepdims=`False`, name=`None`)
+* tf.reverse(**tensor**, axis, name=`None`)
+* tf.size(**input**, name=`None`, out_type=tf.int32)
+* tf.squeeze(**input**, axis=`None`, name=`None`, squeeze_dims=`None`)
+* tf.stack(**values**, axis=`0`, name=`'stack'`)
+* tf.strings.as_string(**input**, precision=`-1`, scientific=`False`, shortest=`False`, width=`-1`, fill=`''`, name=`None`)
+* tf.strings.join(**inputs**, separator=`''`, name=`None`)
+* tf.strings.length(**input**, name=`None`, unit=`'BYTE'`)
+* tf.strings.reduce_join(**inputs**, axis=`None`, keepdims=`False`, separator=`''`, name=`None`)
+* tf.strings.regex_full_match(**input**, pattern, name=`None`)
+* tf.strings.regex_replace(**input**, pattern, rewrite, replace_global=`True`, name=`None`)
+* tf.strings.strip(**input**, name=`None`)
+* tf.strings.substr(**input**, pos, len, name=`None`, unit=`'BYTE'`)
+* tf.strings.to_hash_bucket_fast(**input**, num_buckets, name=`None`)
+* tf.strings.to_hash_bucket_strong(**input**, num_buckets, key, name=`None`)
+* tf.strings.to_hash_bucket(**input**, num_buckets, name=`None`)
+* tf.strings.to_hash_bucket(**input**, num_buckets, name=`None`)
+* tf.strings.to_number(**input**, out_type=tf.float32, name=`None`)
+* tf.strings.unicode_script(**input**, name=`None`)
+* tf.tile(**input**, multiples, name=`None`)
+* tf.truncatediv(**x**, **y**, name=`None`)
+* tf.truncatemod(**x**, **y**, name=`None`)
+* tf.where(**condition**, **x**=`None`, **y**=`None`, name=`None`)
+* tf.zeros_like(**tensor**, dtype=`None`, name=`None`, optimize=`True`)n
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class RaggedTensorValue`](../../../tf/compat/v1/ragged/RaggedTensorValue.md): Represents the value of a `RaggedTensor`.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`boolean_mask(...)`](../../../tf/ragged/boolean_mask.md): Applies a boolean mask to `data` without flattening the mask dimensions.
+
+[`constant(...)`](../../../tf/ragged/constant.md): Constructs a constant RaggedTensor from a nested Python list.
+
+[`constant_value(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/ragged/constant_value.md): Constructs a RaggedTensorValue from a nested Python list.
+
+[`map_flat_values(...)`](../../../tf/ragged/map_flat_values.md): Applies `op` to the values of one or more RaggedTensors.
+
+[`placeholder(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/ragged/placeholder.md): Creates a placeholder for a tf.RaggedTensor that will always be fed.
+
+[`range(...)`](../../../tf/ragged/range.md): Returns a `RaggedTensor` containing the specified sequences of numbers.
+
+[`row_splits_to_segment_ids(...)`](../../../tf/ragged/row_splits_to_segment_ids.md): Generates the segmentation corresponding to a RaggedTensor `row_splits`.
+
+[`segment_ids_to_row_splits(...)`](../../../tf/ragged/segment_ids_to_row_splits.md): Generates the RaggedTensor `row_splits` corresponding to a segmentation.
+
+[`stack(...)`](../../../tf/ragged/stack.md): Stacks a list of rank-`R` tensors into one rank-`(R+1)` `RaggedTensor`.
+
+[`stack_dynamic_partitions(...)`](../../../tf/ragged/stack_dynamic_partitions.md): Stacks dynamic partitions of a Tensor or RaggedTensor.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/ragged/RaggedTensorValue.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/ragged/RaggedTensorValue.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..70574033dae
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/ragged/RaggedTensorValue.md
@@ -0,0 +1,141 @@
+description: Represents the value of a RaggedTensor.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.ragged.RaggedTensorValue
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Represents the value of a `RaggedTensor`.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.ragged.RaggedTensorValue(
+ values, row_splits
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: `RaggedTensorValue` should only be used in graph mode; in
+eager mode, the tf.RaggedTensor class contains its value directly.
+
+See tf.RaggedTensor for a description of ragged tensors.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`values`
+ |
+
+A numpy array of any type and shape; or a RaggedTensorValue.
+ |
+
+|
+`row_splits`
+ |
+
+A 1-D int32 or int64 numpy array.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+The numpy dtype of values in this tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`flat_values`
+ |
+
+The innermost `values` array for this ragged tensor value.
+ |
+
+|
+`nested_row_splits`
+ |
+
+The row_splits for all ragged dimensions in this ragged tensor value.
+ |
+
+|
+`ragged_rank`
+ |
+
+The number of ragged dimensions in this ragged tensor value.
+ |
+
+|
+`row_splits`
+ |
+
+The split indices for the ragged tensor value.
+ |
+
+|
+`shape`
+ |
+
+A tuple indicating the shape of this RaggedTensorValue.
+ |
+
+|
+`values`
+ |
+
+The concatenated values for all rows in this tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+to_list
+
+View source
+
+
+to_list()
+
+
+Returns this ragged tensor value as a nested Python list.
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/ragged/constant_value.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/ragged/constant_value.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..8888eec42a9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/ragged/constant_value.md
@@ -0,0 +1,139 @@
+description: Constructs a RaggedTensorValue from a nested Python list.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.ragged.constant_value
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Constructs a RaggedTensorValue from a nested Python list.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.ragged.constant_value(
+ pylist, dtype=None, ragged_rank=None, inner_shape=None, row_splits_dtype='int64'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: This function returns a `RaggedTensorValue`, not a `RaggedTensor`.
+If you wish to construct a constant `RaggedTensor`, use
+[`ragged.constant(...)`](constant.md) instead.
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```
+>>> tf.compat.v1.ragged.constant_value([[1, 2], [3], [4, 5, 6]])
+tf.RaggedTensorValue(values=array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]),
+ row_splits=array([0, 2, 3, 6]))
+```
+
+All scalar values in `pylist` must have the same nesting depth `K`, and the
+returned `RaggedTensorValue` will have rank `K`. If `pylist` contains no
+scalar values, then `K` is one greater than the maximum depth of empty lists
+in `pylist`. All scalar values in `pylist` must be compatible with `dtype`.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`pylist`
+ |
+
+A nested `list`, `tuple` or `np.ndarray`. Any nested element that
+is not a `list` or `tuple` must be a scalar value compatible with `dtype`.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+`numpy.dtype`. The type of elements for the returned `RaggedTensor`.
+If not specified, then a default is chosen based on the scalar values in
+`pylist`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ragged_rank`
+ |
+
+An integer specifying the ragged rank of the returned
+`RaggedTensorValue`. Must be nonnegative and less than `K`. Defaults to
+`max(0, K - 1)` if `inner_shape` is not specified. Defaults to `max(0, K
+- 1 - len(inner_shape))` if `inner_shape` is specified.
+ |
+
+|
+`inner_shape`
+ |
+
+A tuple of integers specifying the shape for individual inner
+values in the returned `RaggedTensorValue`. Defaults to `()` if
+`ragged_rank` is not specified. If `ragged_rank` is specified, then a
+default is chosen based on the contents of `pylist`.
+ |
+
+|
+`row_splits_dtype`
+ |
+
+data type for the constructed `RaggedTensorValue`'s
+row_splits. One of `numpy.int32` or `numpy.int64`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `tf.RaggedTensorValue` or `numpy.array` with rank `K` and the specified
+`ragged_rank`, containing the values from `pylist`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the scalar values in `pylist` have inconsistent nesting
+depth; or if ragged_rank or inner_shape are incompatible with `pylist`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/ragged/placeholder.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/ragged/placeholder.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3813df682b3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/ragged/placeholder.md
@@ -0,0 +1,108 @@
+description: Creates a placeholder for a tf.RaggedTensor that will always be fed.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.ragged.placeholder
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Creates a placeholder for a tf.RaggedTensor that will always be fed.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.ragged.placeholder(
+ dtype, ragged_rank, value_shape=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+**Important**: This ragged tensor will produce an error if evaluated.
+Its value must be fed using the `feed_dict` optional argument to
+`Session.run()`, `Tensor.eval()`, or `Operation.run()`.
+
+@compatibility{eager} Placeholders are not compatible with eager execution.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+The data type for the `RaggedTensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ragged_rank`
+ |
+
+The ragged rank for the `RaggedTensor`
+ |
+
+|
+`value_shape`
+ |
+
+The shape for individual flat values in the `RaggedTensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `RaggedTensor` that may be used as a handle for feeding a value, but
+not evaluated directly.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+if eager execution is enabled
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/random.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/random.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..4c32ce48838
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/random.md
@@ -0,0 +1,85 @@
+description: Public API for tf.random namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.random
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.random namespace.
+
+
+
+## Modules
+
+[`experimental`](../../../tf/compat/v1/random/experimental.md) module: Public API for tf.random.experimental namespace.
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class Algorithm`](../../../tf/random/Algorithm.md): An enumeration.
+
+[`class Generator`](../../../tf/random/Generator.md): Random-number generator.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`all_candidate_sampler(...)`](../../../tf/random/all_candidate_sampler.md): Generate the set of all classes.
+
+[`categorical(...)`](../../../tf/random/categorical.md): Draws samples from a categorical distribution.
+
+[`create_rng_state(...)`](../../../tf/random/create_rng_state.md): Creates a RNG state from an integer or a vector.
+
+[`fixed_unigram_candidate_sampler(...)`](../../../tf/random/fixed_unigram_candidate_sampler.md): Samples a set of classes using the provided (fixed) base distribution.
+
+[`gamma(...)`](../../../tf/random/gamma.md): Draws `shape` samples from each of the given Gamma distribution(s).
+
+[`get_global_generator(...)`](../../../tf/random/get_global_generator.md): Retrieves the global generator.
+
+[`get_seed(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/get_seed.md): Returns the local seeds an operation should use given an op-specific seed.
+
+[`learned_unigram_candidate_sampler(...)`](../../../tf/random/learned_unigram_candidate_sampler.md): Samples a set of classes from a distribution learned during training.
+
+[`log_uniform_candidate_sampler(...)`](../../../tf/random/log_uniform_candidate_sampler.md): Samples a set of classes using a log-uniform (Zipfian) base distribution.
+
+[`multinomial(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/multinomial.md): Draws samples from a multinomial distribution. (deprecated)
+
+[`normal(...)`](../../../tf/random/normal.md): Outputs random values from a normal distribution.
+
+[`poisson(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/random_poisson.md): Draws `shape` samples from each of the given Poisson distribution(s).
+
+[`set_global_generator(...)`](../../../tf/random/set_global_generator.md): Replaces the global generator with another `Generator` object.
+
+[`set_random_seed(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/set_random_seed.md): Sets the graph-level random seed for the default graph.
+
+[`shuffle(...)`](../../../tf/random/shuffle.md): Randomly shuffles a tensor along its first dimension.
+
+[`stateless_binomial(...)`](../../../tf/random/stateless_binomial.md): Outputs deterministic pseudorandom values from a binomial distribution.
+
+[`stateless_categorical(...)`](../../../tf/random/stateless_categorical.md): Draws deterministic pseudorandom samples from a categorical distribution.
+
+[`stateless_gamma(...)`](../../../tf/random/stateless_gamma.md): Outputs deterministic pseudorandom values from a gamma distribution.
+
+[`stateless_multinomial(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/random/stateless_multinomial.md): Draws deterministic pseudorandom samples from a multinomial distribution. (deprecated)
+
+[`stateless_normal(...)`](../../../tf/random/stateless_normal.md): Outputs deterministic pseudorandom values from a normal distribution.
+
+[`stateless_poisson(...)`](../../../tf/random/stateless_poisson.md): Outputs deterministic pseudorandom values from a Poisson distribution.
+
+[`stateless_truncated_normal(...)`](../../../tf/random/stateless_truncated_normal.md): Outputs deterministic pseudorandom values, truncated normally distributed.
+
+[`stateless_uniform(...)`](../../../tf/random/stateless_uniform.md): Outputs deterministic pseudorandom values from a uniform distribution.
+
+[`truncated_normal(...)`](../../../tf/random/truncated_normal.md): Outputs random values from a truncated normal distribution.
+
+[`uniform(...)`](../../../tf/random/uniform.md): Outputs random values from a uniform distribution.
+
+[`uniform_candidate_sampler(...)`](../../../tf/random/uniform_candidate_sampler.md): Samples a set of classes using a uniform base distribution.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/random/experimental.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/random/experimental.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..9e9350507d7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/random/experimental.md
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
+description: Public API for tf.random.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.random.experimental
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.random.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class Algorithm`](../../../../tf/random/Algorithm.md): An enumeration.
+
+[`class Generator`](../../../../tf/random/Generator.md): Random-number generator.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`create_rng_state(...)`](../../../../tf/random/create_rng_state.md): Creates a RNG state from an integer or a vector.
+
+[`get_global_generator(...)`](../../../../tf/random/get_global_generator.md): Retrieves the global generator.
+
+[`set_global_generator(...)`](../../../../tf/random/set_global_generator.md): Replaces the global generator with another `Generator` object.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/random/stateless_multinomial.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/random/stateless_multinomial.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..9a233e40653
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/random/stateless_multinomial.md
@@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
+description: Draws deterministic pseudorandom samples from a multinomial distribution. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.random.stateless_multinomial
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Draws deterministic pseudorandom samples from a multinomial distribution. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.random.stateless_multinomial(
+ logits, num_samples, seed, output_dtype=tf.dtypes.int64, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use tf.random.stateless_categorical instead.
+
+This is a stateless version of tf.random.categorical: if run twice with the
+same seeds, it will produce the same pseudorandom numbers. The output is
+consistent across multiple runs on the same hardware (and between CPU
+and GPU), but may change between versions of TensorFlow or on non-CPU/GPU
+hardware.
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+# samples has shape [1, 5], where each value is either 0 or 1 with equal
+# probability.
+samples = tf.random.stateless_categorical(
+ tf.math.log([[0.5, 0.5]]), 5, seed=[7, 17])
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`logits`
+ |
+
+2-D Tensor with shape `[batch_size, num_classes]`. Each slice
+`[i, :]` represents the unnormalized log-probabilities for all classes.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_samples`
+ |
+
+0-D. Number of independent samples to draw for each row slice.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+A shape [2] integer Tensor of seeds to the random number generator.
+ |
+
+|
+`output_dtype`
+ |
+
+integer type to use for the output. Defaults to int64.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the operation.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The drawn samples of shape `[batch_size, num_samples]`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/random_normal_initializer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/random_normal_initializer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e3dec37efcd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/random_normal_initializer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,225 @@
+description: Initializer that generates tensors with a normal distribution.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.random_normal_initializer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Initializer that generates tensors with a normal distribution.
+
+Inherits From: [`Initializer`](../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Initializer.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.initializers.random_normal`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.random_normal_initializer(
+ mean=0.0, stddev=1.0, seed=None, dtype=tf.dtypes.float32
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`mean`
+ |
+
+a python scalar or a scalar tensor. Mean of the random values to
+generate.
+ |
+
+|
+`stddev`
+ |
+
+a python scalar or a scalar tensor. Standard deviation of the random
+values to generate.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+A Python integer. Used to create random seeds. See
+tf.compat.v1.set_random_seed for behavior.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+Default data type, used if no `dtype` argument is provided when
+calling the initializer. Only floating point types are supported.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+from_config
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+from_config(
+ config
+)
+
+
+Instantiates an initializer from a configuration dictionary.
+
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+initializer = RandomUniform(-1, 1)
+config = initializer.get_config()
+initializer = RandomUniform.from_config(config)
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+A Python dictionary. It will typically be the output of
+`get_config`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Initializer instance.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_config
+
+View source
+
+
+get_config()
+
+
+Returns the configuration of the initializer as a JSON-serializable dict.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A JSON-serializable Python dict.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+__call__
+
+View source
+
+
+__call__(
+ shape, dtype=None, partition_info=None
+)
+
+
+Returns a tensor object initialized as specified by the initializer.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of the tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+Optional dtype of the tensor. If not provided use the initializer
+dtype.
+ |
+
+|
+`partition_info`
+ |
+
+Optional information about the possible partitioning of a
+tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/random_poisson.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/random_poisson.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..9a783c721d6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/random_poisson.md
@@ -0,0 +1,129 @@
+description: Draws shape samples from each of the given Poisson distribution(s).
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.random_poisson
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Draws `shape` samples from each of the given Poisson distribution(s).
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.random.poisson`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.random_poisson(
+ lam, shape, dtype=tf.dtypes.float32, seed=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+`lam` is the rate parameter describing the distribution(s).
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+samples = tf.random.poisson([0.5, 1.5], [10])
+# samples has shape [10, 2], where each slice [:, 0] and [:, 1] represents
+# the samples drawn from each distribution
+
+samples = tf.random.poisson([12.2, 3.3], [7, 5])
+# samples has shape [7, 5, 2], where each slice [:, :, 0] and [:, :, 1]
+# represents the 7x5 samples drawn from each of the two distributions
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`lam`
+ |
+
+A Tensor or Python value or N-D array of type `dtype`.
+`lam` provides the rate parameter(s) describing the poisson
+distribution(s) to sample.
+ |
+
+|
+`shape`
+ |
+
+A 1-D integer Tensor or Python array. The shape of the output samples
+to be drawn per "rate"-parameterized distribution.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+The type of the output: `float16`, `float32`, `float64`, `int32` or
+`int64`.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+A Python integer. Used to create a random seed for the distributions.
+See
+tf.random.set_seed
+for behavior.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the operation.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`samples`
+ |
+
+a `Tensor` of shape `tf.concat([shape, tf.shape(lam)], axis=0)`
+with values of type `dtype`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/random_uniform_initializer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/random_uniform_initializer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..31b8012861d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/random_uniform_initializer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,225 @@
+description: Initializer that generates tensors with a uniform distribution.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.random_uniform_initializer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Initializer that generates tensors with a uniform distribution.
+
+Inherits From: [`Initializer`](../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Initializer.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.initializers.random_uniform`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.random_uniform_initializer(
+ minval=0, maxval=None, seed=None, dtype=tf.dtypes.float32
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`minval`
+ |
+
+A python scalar or a scalar tensor. Lower bound of the range of
+random values to generate.
+ |
+
+|
+`maxval`
+ |
+
+A python scalar or a scalar tensor. Upper bound of the range of
+random values to generate. Defaults to 1 for float types.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+A Python integer. Used to create random seeds. See
+tf.compat.v1.set_random_seed for behavior.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+Default data type, used if no `dtype` argument is provided when
+calling the initializer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+from_config
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+from_config(
+ config
+)
+
+
+Instantiates an initializer from a configuration dictionary.
+
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+initializer = RandomUniform(-1, 1)
+config = initializer.get_config()
+initializer = RandomUniform.from_config(config)
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+A Python dictionary. It will typically be the output of
+`get_config`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Initializer instance.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_config
+
+View source
+
+
+get_config()
+
+
+Returns the configuration of the initializer as a JSON-serializable dict.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A JSON-serializable Python dict.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+__call__
+
+View source
+
+
+__call__(
+ shape, dtype=None, partition_info=None
+)
+
+
+Returns a tensor object initialized as specified by the initializer.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of the tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+Optional dtype of the tensor. If not provided use the initializer
+dtype.
+ |
+
+|
+`partition_info`
+ |
+
+Optional information about the possible partitioning of a
+tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/raw_ops.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/raw_ops.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..bed30cd5e04
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/raw_ops.md
@@ -0,0 +1,2545 @@
+description: Public API for tf.raw_ops namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.raw_ops
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.raw_ops namespace.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`Abort(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Abort.md): Raise a exception to abort the process when called.
+
+[`Abs(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Abs.md): Computes the absolute value of a tensor.
+
+[`AccumulateNV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AccumulateNV2.md): Returns the element-wise sum of a list of tensors.
+
+[`AccumulatorApplyGradient(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AccumulatorApplyGradient.md): Applies a gradient to a given accumulator.
+
+[`AccumulatorNumAccumulated(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AccumulatorNumAccumulated.md): Returns the number of gradients aggregated in the given accumulators.
+
+[`AccumulatorSetGlobalStep(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AccumulatorSetGlobalStep.md): Updates the accumulator with a new value for global_step.
+
+[`AccumulatorTakeGradient(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AccumulatorTakeGradient.md): Extracts the average gradient in the given ConditionalAccumulator.
+
+[`Acos(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Acos.md): Computes acos of x element-wise.
+
+[`Acosh(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Acosh.md): Computes inverse hyperbolic cosine of x element-wise.
+
+[`Add(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Add.md): Returns x + y element-wise.
+
+[`AddManySparseToTensorsMap(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AddManySparseToTensorsMap.md): Add an `N`-minibatch `SparseTensor` to a `SparseTensorsMap`, return `N` handles.
+
+[`AddN(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AddN.md): Add all input tensors element wise.
+
+[`AddSparseToTensorsMap(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AddSparseToTensorsMap.md): Add a `SparseTensor` to a `SparseTensorsMap` return its handle.
+
+[`AddV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AddV2.md): Returns x + y element-wise.
+
+[`AdjustContrast(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AdjustContrast.md): Deprecated. Disallowed in GraphDef version >= 2.
+
+[`AdjustContrastv2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AdjustContrastv2.md): Adjust the contrast of one or more images.
+
+[`AdjustHue(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AdjustHue.md): Adjust the hue of one or more images.
+
+[`AdjustSaturation(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AdjustSaturation.md): Adjust the saturation of one or more images.
+
+[`All(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/All.md): Computes the "logical and" of elements across dimensions of a tensor.
+
+[`AllCandidateSampler(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AllCandidateSampler.md): Generates labels for candidate sampling with a learned unigram distribution.
+
+[`AllToAll(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AllToAll.md): An Op to exchange data across TPU replicas.
+
+[`Angle(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Angle.md): Returns the argument of a complex number.
+
+[`AnonymousIterator(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AnonymousIterator.md): A container for an iterator resource.
+
+[`AnonymousIteratorV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AnonymousIteratorV2.md): A container for an iterator resource.
+
+[`AnonymousMemoryCache(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AnonymousMemoryCache.md)
+
+[`AnonymousMultiDeviceIterator(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AnonymousMultiDeviceIterator.md): A container for a multi device iterator resource.
+
+[`AnonymousRandomSeedGenerator(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AnonymousRandomSeedGenerator.md)
+
+[`Any(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Any.md): Computes the "logical or" of elements across dimensions of a tensor.
+
+[`ApplyAdaMax(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ApplyAdaMax.md): Update '*var' according to the AdaMax algorithm.
+
+[`ApplyAdadelta(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ApplyAdadelta.md): Update '*var' according to the adadelta scheme.
+
+[`ApplyAdagrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ApplyAdagrad.md): Update '*var' according to the adagrad scheme.
+
+[`ApplyAdagradDA(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ApplyAdagradDA.md): Update '*var' according to the proximal adagrad scheme.
+
+[`ApplyAdagradV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ApplyAdagradV2.md): Update '*var' according to the adagrad scheme.
+
+[`ApplyAdam(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ApplyAdam.md): Update '*var' according to the Adam algorithm.
+
+[`ApplyAddSign(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ApplyAddSign.md): Update '*var' according to the AddSign update.
+
+[`ApplyCenteredRMSProp(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ApplyCenteredRMSProp.md): Update '*var' according to the centered RMSProp algorithm.
+
+[`ApplyFtrl(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ApplyFtrl.md): Update '*var' according to the Ftrl-proximal scheme.
+
+[`ApplyFtrlV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ApplyFtrlV2.md): Update '*var' according to the Ftrl-proximal scheme.
+
+[`ApplyGradientDescent(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ApplyGradientDescent.md): Update '*var' by subtracting 'alpha' * 'delta' from it.
+
+[`ApplyMomentum(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ApplyMomentum.md): Update '*var' according to the momentum scheme.
+
+[`ApplyPowerSign(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ApplyPowerSign.md): Update '*var' according to the AddSign update.
+
+[`ApplyProximalAdagrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ApplyProximalAdagrad.md): Update '*var' and '*accum' according to FOBOS with Adagrad learning rate.
+
+[`ApplyProximalGradientDescent(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ApplyProximalGradientDescent.md): Update '*var' as FOBOS algorithm with fixed learning rate.
+
+[`ApplyRMSProp(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ApplyRMSProp.md): Update '*var' according to the RMSProp algorithm.
+
+[`ApproximateEqual(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ApproximateEqual.md): Returns the truth value of abs(x-y) < tolerance element-wise.
+
+[`ArgMax(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ArgMax.md): Returns the index with the largest value across dimensions of a tensor.
+
+[`ArgMin(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ArgMin.md): Returns the index with the smallest value across dimensions of a tensor.
+
+[`AsString(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AsString.md): Converts each entry in the given tensor to strings.
+
+[`Asin(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Asin.md): Computes the trignometric inverse sine of x element-wise.
+
+[`Asinh(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Asinh.md): Computes inverse hyperbolic sine of x element-wise.
+
+[`Assert(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Assert.md): Asserts that the given condition is true.
+
+[`AssertCardinalityDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AssertCardinalityDataset.md)
+
+[`AssertNextDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AssertNextDataset.md): A transformation that asserts which transformations happen next.
+
+[`Assign(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Assign.md): Update 'ref' by assigning 'value' to it.
+
+[`AssignAdd(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AssignAdd.md): Update 'ref' by adding 'value' to it.
+
+[`AssignAddVariableOp(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AssignAddVariableOp.md): Adds a value to the current value of a variable.
+
+[`AssignSub(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AssignSub.md): Update 'ref' by subtracting 'value' from it.
+
+[`AssignSubVariableOp(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AssignSubVariableOp.md): Subtracts a value from the current value of a variable.
+
+[`AssignVariableOp(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AssignVariableOp.md): Assigns a new value to a variable.
+
+[`Atan(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Atan.md): Computes the trignometric inverse tangent of x element-wise.
+
+[`Atan2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Atan2.md): Computes arctangent of `y/x` element-wise, respecting signs of the arguments.
+
+[`Atanh(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Atanh.md): Computes inverse hyperbolic tangent of x element-wise.
+
+[`AudioSpectrogram(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AudioSpectrogram.md): Produces a visualization of audio data over time.
+
+[`AudioSummary(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AudioSummary.md): Outputs a `Summary` protocol buffer with audio.
+
+[`AudioSummaryV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AudioSummaryV2.md): Outputs a `Summary` protocol buffer with audio.
+
+[`AutoShardDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AutoShardDataset.md): Creates a dataset that shards the input dataset.
+
+[`AvgPool(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AvgPool.md): Performs average pooling on the input.
+
+[`AvgPool3D(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AvgPool3D.md): Performs 3D average pooling on the input.
+
+[`AvgPool3DGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AvgPool3DGrad.md): Computes gradients of average pooling function.
+
+[`AvgPoolGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/AvgPoolGrad.md): Computes gradients of the average pooling function.
+
+[`Barrier(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Barrier.md): Defines a barrier that persists across different graph executions.
+
+[`BarrierClose(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BarrierClose.md): Closes the given barrier.
+
+[`BarrierIncompleteSize(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BarrierIncompleteSize.md): Computes the number of incomplete elements in the given barrier.
+
+[`BarrierInsertMany(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BarrierInsertMany.md): For each key, assigns the respective value to the specified component.
+
+[`BarrierReadySize(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BarrierReadySize.md): Computes the number of complete elements in the given barrier.
+
+[`BarrierTakeMany(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BarrierTakeMany.md): Takes the given number of completed elements from a barrier.
+
+[`Batch(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Batch.md): Batches all input tensors nondeterministically.
+
+[`BatchCholesky(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BatchCholesky.md)
+
+[`BatchCholeskyGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BatchCholeskyGrad.md)
+
+[`BatchDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BatchDataset.md): Creates a dataset that batches `batch_size` elements from `input_dataset`.
+
+[`BatchDatasetV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BatchDatasetV2.md): Creates a dataset that batches `batch_size` elements from `input_dataset`.
+
+[`BatchFFT(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BatchFFT.md)
+
+[`BatchFFT2D(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BatchFFT2D.md)
+
+[`BatchFFT3D(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BatchFFT3D.md)
+
+[`BatchFunction(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BatchFunction.md): Batches all the inputs tensors to the computation done by the function.
+
+[`BatchIFFT(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BatchIFFT.md)
+
+[`BatchIFFT2D(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BatchIFFT2D.md)
+
+[`BatchIFFT3D(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BatchIFFT3D.md)
+
+[`BatchMatMul(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BatchMatMul.md): Multiplies slices of two tensors in batches.
+
+[`BatchMatMulV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BatchMatMulV2.md): Multiplies slices of two tensors in batches.
+
+[`BatchMatrixBandPart(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BatchMatrixBandPart.md)
+
+[`BatchMatrixDeterminant(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BatchMatrixDeterminant.md)
+
+[`BatchMatrixDiag(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BatchMatrixDiag.md)
+
+[`BatchMatrixDiagPart(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BatchMatrixDiagPart.md)
+
+[`BatchMatrixInverse(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BatchMatrixInverse.md)
+
+[`BatchMatrixSetDiag(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BatchMatrixSetDiag.md)
+
+[`BatchMatrixSolve(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BatchMatrixSolve.md)
+
+[`BatchMatrixSolveLs(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BatchMatrixSolveLs.md)
+
+[`BatchMatrixTriangularSolve(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BatchMatrixTriangularSolve.md)
+
+[`BatchNormWithGlobalNormalization(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BatchNormWithGlobalNormalization.md): Batch normalization.
+
+[`BatchNormWithGlobalNormalizationGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BatchNormWithGlobalNormalizationGrad.md): Gradients for batch normalization.
+
+[`BatchSelfAdjointEig(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BatchSelfAdjointEig.md)
+
+[`BatchSelfAdjointEigV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BatchSelfAdjointEigV2.md)
+
+[`BatchSvd(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BatchSvd.md)
+
+[`BatchToSpace(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BatchToSpace.md): BatchToSpace for 4-D tensors of type T.
+
+[`BatchToSpaceND(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BatchToSpaceND.md): BatchToSpace for N-D tensors of type T.
+
+[`BesselI0e(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BesselI0e.md): Computes the Bessel i0e function of `x` element-wise.
+
+[`BesselI1e(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BesselI1e.md): Computes the Bessel i1e function of `x` element-wise.
+
+[`Betainc(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Betainc.md): Compute the regularized incomplete beta integral \\(I_x(a, b)\\).
+
+[`BiasAdd(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BiasAdd.md): Adds `bias` to `value`.
+
+[`BiasAddGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BiasAddGrad.md): The backward operation for "BiasAdd" on the "bias" tensor.
+
+[`BiasAddV1(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BiasAddV1.md): Adds `bias` to `value`.
+
+[`Bincount(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Bincount.md): Counts the number of occurrences of each value in an integer array.
+
+[`Bitcast(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Bitcast.md): Bitcasts a tensor from one type to another without copying data.
+
+[`BitwiseAnd(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BitwiseAnd.md): Elementwise computes the bitwise AND of `x` and `y`.
+
+[`BitwiseOr(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BitwiseOr.md): Elementwise computes the bitwise OR of `x` and `y`.
+
+[`BitwiseXor(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BitwiseXor.md): Elementwise computes the bitwise XOR of `x` and `y`.
+
+[`BlockLSTM(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BlockLSTM.md): Computes the LSTM cell forward propagation for all the time steps.
+
+[`BlockLSTMGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BlockLSTMGrad.md): Computes the LSTM cell backward propagation for the entire time sequence.
+
+[`BlockLSTMGradV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BlockLSTMGradV2.md): Computes the LSTM cell backward propagation for the entire time sequence.
+
+[`BlockLSTMV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BlockLSTMV2.md): Computes the LSTM cell forward propagation for all the time steps.
+
+[`BoostedTreesAggregateStats(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BoostedTreesAggregateStats.md): Aggregates the summary of accumulated stats for the batch.
+
+[`BoostedTreesBucketize(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BoostedTreesBucketize.md): Bucketize each feature based on bucket boundaries.
+
+[`BoostedTreesCalculateBestFeatureSplit(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BoostedTreesCalculateBestFeatureSplit.md): Calculates gains for each feature and returns the best possible split information for the feature.
+
+[`BoostedTreesCalculateBestFeatureSplitV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BoostedTreesCalculateBestFeatureSplitV2.md): Calculates gains for each feature and returns the best possible split information for each node. However, if no split is found, then no split information is returned for that node.
+
+[`BoostedTreesCalculateBestGainsPerFeature(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BoostedTreesCalculateBestGainsPerFeature.md): Calculates gains for each feature and returns the best possible split information for the feature.
+
+[`BoostedTreesCenterBias(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BoostedTreesCenterBias.md): Calculates the prior from the training data (the bias) and fills in the first node with the logits' prior. Returns a boolean indicating whether to continue centering.
+
+[`BoostedTreesCreateEnsemble(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BoostedTreesCreateEnsemble.md): Creates a tree ensemble model and returns a handle to it.
+
+[`BoostedTreesCreateQuantileStreamResource(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BoostedTreesCreateQuantileStreamResource.md): Create the Resource for Quantile Streams.
+
+[`BoostedTreesDeserializeEnsemble(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BoostedTreesDeserializeEnsemble.md): Deserializes a serialized tree ensemble config and replaces current tree
+
+[`BoostedTreesEnsembleResourceHandleOp(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BoostedTreesEnsembleResourceHandleOp.md): Creates a handle to a BoostedTreesEnsembleResource
+
+[`BoostedTreesExampleDebugOutputs(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BoostedTreesExampleDebugOutputs.md): Debugging/model interpretability outputs for each example.
+
+[`BoostedTreesFlushQuantileSummaries(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BoostedTreesFlushQuantileSummaries.md): Flush the quantile summaries from each quantile stream resource.
+
+[`BoostedTreesGetEnsembleStates(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BoostedTreesGetEnsembleStates.md): Retrieves the tree ensemble resource stamp token, number of trees and growing statistics.
+
+[`BoostedTreesMakeQuantileSummaries(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BoostedTreesMakeQuantileSummaries.md): Makes the summary of quantiles for the batch.
+
+[`BoostedTreesMakeStatsSummary(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BoostedTreesMakeStatsSummary.md): Makes the summary of accumulated stats for the batch.
+
+[`BoostedTreesPredict(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BoostedTreesPredict.md): Runs multiple additive regression ensemble predictors on input instances and
+
+[`BoostedTreesQuantileStreamResourceAddSummaries(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BoostedTreesQuantileStreamResourceAddSummaries.md): Add the quantile summaries to each quantile stream resource.
+
+[`BoostedTreesQuantileStreamResourceDeserialize(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BoostedTreesQuantileStreamResourceDeserialize.md): Deserialize bucket boundaries and ready flag into current QuantileAccumulator.
+
+[`BoostedTreesQuantileStreamResourceFlush(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BoostedTreesQuantileStreamResourceFlush.md): Flush the summaries for a quantile stream resource.
+
+[`BoostedTreesQuantileStreamResourceGetBucketBoundaries(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BoostedTreesQuantileStreamResourceGetBucketBoundaries.md): Generate the bucket boundaries for each feature based on accumulated summaries.
+
+[`BoostedTreesQuantileStreamResourceHandleOp(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BoostedTreesQuantileStreamResourceHandleOp.md): Creates a handle to a BoostedTreesQuantileStreamResource.
+
+[`BoostedTreesSerializeEnsemble(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BoostedTreesSerializeEnsemble.md): Serializes the tree ensemble to a proto.
+
+[`BoostedTreesSparseAggregateStats(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BoostedTreesSparseAggregateStats.md): Aggregates the summary of accumulated stats for the batch.
+
+[`BoostedTreesSparseCalculateBestFeatureSplit(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BoostedTreesSparseCalculateBestFeatureSplit.md): Calculates gains for each feature and returns the best possible split information for the feature.
+
+[`BoostedTreesTrainingPredict(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BoostedTreesTrainingPredict.md): Runs multiple additive regression ensemble predictors on input instances and
+
+[`BoostedTreesUpdateEnsemble(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BoostedTreesUpdateEnsemble.md): Updates the tree ensemble by either adding a layer to the last tree being grown
+
+[`BoostedTreesUpdateEnsembleV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BoostedTreesUpdateEnsembleV2.md): Updates the tree ensemble by adding a layer to the last tree being grown
+
+[`BroadcastArgs(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BroadcastArgs.md): Return the shape of s0 op s1 with broadcast.
+
+[`BroadcastGradientArgs(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BroadcastGradientArgs.md): Return the reduction indices for computing gradients of s0 op s1 with broadcast.
+
+[`BroadcastTo(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BroadcastTo.md): Broadcast an array for a compatible shape.
+
+[`Bucketize(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Bucketize.md): Bucketizes 'input' based on 'boundaries'.
+
+[`BytesProducedStatsDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/BytesProducedStatsDataset.md): Records the bytes size of each element of `input_dataset` in a StatsAggregator.
+
+[`CSRSparseMatrixComponents(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CSRSparseMatrixComponents.md): Reads out the CSR components at batch `index`.
+
+[`CSRSparseMatrixToDense(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CSRSparseMatrixToDense.md): Convert a (possibly batched) CSRSparseMatrix to dense.
+
+[`CSRSparseMatrixToSparseTensor(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CSRSparseMatrixToSparseTensor.md): Converts a (possibly batched) CSRSparesMatrix to a SparseTensor.
+
+[`CSVDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CSVDataset.md)
+
+[`CTCBeamSearchDecoder(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CTCBeamSearchDecoder.md): Performs beam search decoding on the logits given in input.
+
+[`CTCGreedyDecoder(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CTCGreedyDecoder.md): Performs greedy decoding on the logits given in inputs.
+
+[`CTCLoss(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CTCLoss.md): Calculates the CTC Loss (log probability) for each batch entry. Also calculates
+
+[`CTCLossV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CTCLossV2.md): Calculates the CTC Loss (log probability) for each batch entry. Also calculates
+
+[`CacheDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CacheDataset.md): Creates a dataset that caches elements from `input_dataset`.
+
+[`CacheDatasetV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CacheDatasetV2.md)
+
+[`Case(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Case.md): An n-way switch statement which calls a single branch function.
+
+[`Cast(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Cast.md): Cast x of type SrcT to y of DstT.
+
+[`Ceil(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Ceil.md): Returns element-wise smallest integer not less than x.
+
+[`CheckNumerics(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CheckNumerics.md): Checks a tensor for NaN and Inf values.
+
+[`CheckNumericsV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CheckNumericsV2.md): Checks a tensor for NaN, -Inf and +Inf values.
+
+[`Cholesky(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Cholesky.md): Computes the Cholesky decomposition of one or more square matrices.
+
+[`CholeskyGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CholeskyGrad.md): Computes the reverse mode backpropagated gradient of the Cholesky algorithm.
+
+[`ChooseFastestBranchDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ChooseFastestBranchDataset.md)
+
+[`ChooseFastestDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ChooseFastestDataset.md)
+
+[`ClipByValue(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ClipByValue.md): Clips tensor values to a specified min and max.
+
+[`CloseSummaryWriter(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CloseSummaryWriter.md)
+
+[`CollectiveBcastRecv(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CollectiveBcastRecv.md): Receives a tensor value broadcast from another device.
+
+[`CollectiveBcastSend(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CollectiveBcastSend.md): Broadcasts a tensor value to one or more other devices.
+
+[`CollectiveGather(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CollectiveGather.md): Mutually accumulates multiple tensors of identical type and shape.
+
+[`CollectivePermute(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CollectivePermute.md): An Op to permute tensors across replicated TPU instances.
+
+[`CollectiveReduce(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CollectiveReduce.md): Mutually reduces multiple tensors of identical type and shape.
+
+[`CombinedNonMaxSuppression(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CombinedNonMaxSuppression.md): Greedily selects a subset of bounding boxes in descending order of score,
+
+[`CompareAndBitpack(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CompareAndBitpack.md): Compare values of `input` to `threshold` and pack resulting bits into a `uint8`.
+
+[`Complex(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Complex.md): Converts two real numbers to a complex number.
+
+[`ComplexAbs(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ComplexAbs.md): Computes the complex absolute value of a tensor.
+
+[`ComputeAccidentalHits(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ComputeAccidentalHits.md): Computes the ids of the positions in sampled_candidates that match true_labels.
+
+[`Concat(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Concat.md): Concatenates tensors along one dimension.
+
+[`ConcatOffset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ConcatOffset.md): Computes offsets of concat inputs within its output.
+
+[`ConcatV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ConcatV2.md): Concatenates tensors along one dimension.
+
+[`ConcatenateDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ConcatenateDataset.md): Creates a dataset that concatenates `input_dataset` with `another_dataset`.
+
+[`ConditionalAccumulator(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ConditionalAccumulator.md): A conditional accumulator for aggregating gradients.
+
+[`ConfigureDistributedTPU(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ConfigureDistributedTPU.md): Sets up the centralized structures for a distributed TPU system.
+
+[`ConfigureTPUEmbedding(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ConfigureTPUEmbedding.md): Sets up TPUEmbedding in a distributed TPU system.
+
+[`Conj(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Conj.md): Returns the complex conjugate of a complex number.
+
+[`ConjugateTranspose(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ConjugateTranspose.md): Shuffle dimensions of x according to a permutation and conjugate the result.
+
+[`Const(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Const.md): Returns a constant tensor.
+
+[`ConsumeMutexLock(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ConsumeMutexLock.md): This op consumes a lock created by `MutexLock`.
+
+[`ControlTrigger(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ControlTrigger.md): Does nothing. Serves as a control trigger for scheduling.
+
+[`Conv2D(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Conv2D.md): Computes a 2-D convolution given 4-D `input` and `filter` tensors.
+
+[`Conv2DBackpropFilter(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Conv2DBackpropFilter.md): Computes the gradients of convolution with respect to the filter.
+
+[`Conv2DBackpropInput(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Conv2DBackpropInput.md): Computes the gradients of convolution with respect to the input.
+
+[`Conv3D(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Conv3D.md): Computes a 3-D convolution given 5-D `input` and `filter` tensors.
+
+[`Conv3DBackpropFilter(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Conv3DBackpropFilter.md): Computes the gradients of 3-D convolution with respect to the filter.
+
+[`Conv3DBackpropFilterV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Conv3DBackpropFilterV2.md): Computes the gradients of 3-D convolution with respect to the filter.
+
+[`Conv3DBackpropInput(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Conv3DBackpropInput.md): Computes the gradients of 3-D convolution with respect to the input.
+
+[`Conv3DBackpropInputV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Conv3DBackpropInputV2.md): Computes the gradients of 3-D convolution with respect to the input.
+
+[`Copy(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Copy.md): Copy a tensor from CPU-to-CPU or GPU-to-GPU.
+
+[`CopyHost(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CopyHost.md): Copy a tensor to host.
+
+[`Cos(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Cos.md): Computes cos of x element-wise.
+
+[`Cosh(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Cosh.md): Computes hyperbolic cosine of x element-wise.
+
+[`CountUpTo(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CountUpTo.md): Increments 'ref' until it reaches 'limit'.
+
+[`CreateSummaryDbWriter(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CreateSummaryDbWriter.md)
+
+[`CreateSummaryFileWriter(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CreateSummaryFileWriter.md)
+
+[`CropAndResize(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CropAndResize.md): Extracts crops from the input image tensor and resizes them.
+
+[`CropAndResizeGradBoxes(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CropAndResizeGradBoxes.md): Computes the gradient of the crop_and_resize op wrt the input boxes tensor.
+
+[`CropAndResizeGradImage(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CropAndResizeGradImage.md): Computes the gradient of the crop_and_resize op wrt the input image tensor.
+
+[`Cross(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Cross.md): Compute the pairwise cross product.
+
+[`CrossReplicaSum(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CrossReplicaSum.md): An Op to sum inputs across replicated TPU instances.
+
+[`CudnnRNN(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CudnnRNN.md): A RNN backed by cuDNN.
+
+[`CudnnRNNBackprop(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CudnnRNNBackprop.md): Backprop step of CudnnRNN.
+
+[`CudnnRNNBackpropV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CudnnRNNBackpropV2.md): Backprop step of CudnnRNN.
+
+[`CudnnRNNBackpropV3(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CudnnRNNBackpropV3.md): Backprop step of CudnnRNNV3.
+
+[`CudnnRNNCanonicalToParams(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CudnnRNNCanonicalToParams.md): Converts CudnnRNN params from canonical form to usable form.
+
+[`CudnnRNNCanonicalToParamsV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CudnnRNNCanonicalToParamsV2.md): Converts CudnnRNN params from canonical form to usable form. It supports the projection in LSTM.
+
+[`CudnnRNNParamsSize(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CudnnRNNParamsSize.md): Computes size of weights that can be used by a Cudnn RNN model.
+
+[`CudnnRNNParamsToCanonical(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CudnnRNNParamsToCanonical.md): Retrieves CudnnRNN params in canonical form.
+
+[`CudnnRNNParamsToCanonicalV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CudnnRNNParamsToCanonicalV2.md): Retrieves CudnnRNN params in canonical form. It supports the projection in LSTM.
+
+[`CudnnRNNV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CudnnRNNV2.md): A RNN backed by cuDNN.
+
+[`CudnnRNNV3(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CudnnRNNV3.md): A RNN backed by cuDNN.
+
+[`Cumprod(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Cumprod.md): Compute the cumulative product of the tensor `x` along `axis`.
+
+[`Cumsum(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Cumsum.md): Compute the cumulative sum of the tensor `x` along `axis`.
+
+[`CumulativeLogsumexp(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/CumulativeLogsumexp.md): Compute the cumulative product of the tensor `x` along `axis`.
+
+[`DataFormatDimMap(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DataFormatDimMap.md): Returns the dimension index in the destination data format given the one in
+
+[`DataFormatVecPermute(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DataFormatVecPermute.md): Returns the permuted vector/tensor in the destination data format given the
+
+[`DatasetCardinality(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DatasetCardinality.md): Returns the cardinality of `input_dataset`.
+
+[`DatasetFromGraph(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DatasetFromGraph.md): Creates a dataset from the given `graph_def`.
+
+[`DatasetToGraph(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DatasetToGraph.md): Returns a serialized GraphDef representing `input_dataset`.
+
+[`DatasetToGraphV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DatasetToGraphV2.md): Returns a serialized GraphDef representing `input_dataset`.
+
+[`DatasetToSingleElement(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DatasetToSingleElement.md): Outputs the single element from the given dataset.
+
+[`DatasetToTFRecord(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DatasetToTFRecord.md): Writes the given dataset to the given file using the TFRecord format.
+
+[`Dawsn(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Dawsn.md)
+
+[`DebugGradientIdentity(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DebugGradientIdentity.md): Identity op for gradient debugging.
+
+[`DebugGradientRefIdentity(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DebugGradientRefIdentity.md): Identity op for gradient debugging.
+
+[`DebugIdentity(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DebugIdentity.md): Provides an identity mapping of the non-Ref type input tensor for debugging.
+
+[`DebugIdentityV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DebugIdentityV2.md): Debug Identity V2 Op.
+
+[`DebugNanCount(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DebugNanCount.md): Debug NaN Value Counter Op.
+
+[`DebugNumericSummary(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DebugNumericSummary.md): Debug Numeric Summary Op.
+
+[`DebugNumericSummaryV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DebugNumericSummaryV2.md): Debug Numeric Summary V2 Op.
+
+[`DecodeAndCropJpeg(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DecodeAndCropJpeg.md): Decode and Crop a JPEG-encoded image to a uint8 tensor.
+
+[`DecodeBase64(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DecodeBase64.md): Decode web-safe base64-encoded strings.
+
+[`DecodeBmp(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DecodeBmp.md): Decode the first frame of a BMP-encoded image to a uint8 tensor.
+
+[`DecodeCSV(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DecodeCSV.md): Convert CSV records to tensors. Each column maps to one tensor.
+
+[`DecodeCompressed(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DecodeCompressed.md): Decompress strings.
+
+[`DecodeGif(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DecodeGif.md): Decode the frame(s) of a GIF-encoded image to a uint8 tensor.
+
+[`DecodeJSONExample(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DecodeJSONExample.md): Convert JSON-encoded Example records to binary protocol buffer strings.
+
+[`DecodeJpeg(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DecodeJpeg.md): Decode a JPEG-encoded image to a uint8 tensor.
+
+[`DecodePaddedRaw(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DecodePaddedRaw.md): Reinterpret the bytes of a string as a vector of numbers.
+
+[`DecodePng(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DecodePng.md): Decode a PNG-encoded image to a uint8 or uint16 tensor.
+
+[`DecodeProtoV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DecodeProtoV2.md): The op extracts fields from a serialized protocol buffers message into tensors.
+
+[`DecodeRaw(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DecodeRaw.md): Reinterpret the bytes of a string as a vector of numbers.
+
+[`DecodeWav(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DecodeWav.md): Decode a 16-bit PCM WAV file to a float tensor.
+
+[`DeepCopy(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DeepCopy.md): Makes a copy of `x`.
+
+[`DeleteIterator(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DeleteIterator.md): A container for an iterator resource.
+
+[`DeleteMemoryCache(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DeleteMemoryCache.md)
+
+[`DeleteMultiDeviceIterator(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DeleteMultiDeviceIterator.md): A container for an iterator resource.
+
+[`DeleteRandomSeedGenerator(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DeleteRandomSeedGenerator.md)
+
+[`DeleteSessionTensor(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DeleteSessionTensor.md): Delete the tensor specified by its handle in the session.
+
+[`DenseToCSRSparseMatrix(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DenseToCSRSparseMatrix.md): Converts a dense tensor to a (possibly batched) CSRSparseMatrix.
+
+[`DenseToDenseSetOperation(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DenseToDenseSetOperation.md): Applies set operation along last dimension of 2 `Tensor` inputs.
+
+[`DenseToSparseBatchDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DenseToSparseBatchDataset.md): Creates a dataset that batches input elements into a SparseTensor.
+
+[`DenseToSparseSetOperation(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DenseToSparseSetOperation.md): Applies set operation along last dimension of `Tensor` and `SparseTensor`.
+
+[`DepthToSpace(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DepthToSpace.md): DepthToSpace for tensors of type T.
+
+[`DepthwiseConv2dNative(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DepthwiseConv2dNative.md): Computes a 2-D depthwise convolution given 4-D `input` and `filter` tensors.
+
+[`DepthwiseConv2dNativeBackpropFilter(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DepthwiseConv2dNativeBackpropFilter.md): Computes the gradients of depthwise convolution with respect to the filter.
+
+[`DepthwiseConv2dNativeBackpropInput(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DepthwiseConv2dNativeBackpropInput.md): Computes the gradients of depthwise convolution with respect to the input.
+
+[`Dequantize(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Dequantize.md): Dequantize the 'input' tensor into a float or bfloat16 Tensor.
+
+[`DeserializeIterator(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DeserializeIterator.md): Converts the given variant tensor to an iterator and stores it in the given resource.
+
+[`DeserializeManySparse(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DeserializeManySparse.md): Deserialize and concatenate `SparseTensors` from a serialized minibatch.
+
+[`DeserializeSparse(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DeserializeSparse.md): Deserialize `SparseTensor` objects.
+
+[`DestroyResourceOp(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DestroyResourceOp.md): Deletes the resource specified by the handle.
+
+[`DestroyTemporaryVariable(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DestroyTemporaryVariable.md): Destroys the temporary variable and returns its final value.
+
+[`Diag(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Diag.md): Returns a diagonal tensor with a given diagonal values.
+
+[`DiagPart(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DiagPart.md): Returns the diagonal part of the tensor.
+
+[`Digamma(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Digamma.md): Computes Psi, the derivative of Lgamma (the log of the absolute value of
+
+[`Dilation2D(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Dilation2D.md): Computes the grayscale dilation of 4-D `input` and 3-D `filter` tensors.
+
+[`Dilation2DBackpropFilter(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Dilation2DBackpropFilter.md): Computes the gradient of morphological 2-D dilation with respect to the filter.
+
+[`Dilation2DBackpropInput(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Dilation2DBackpropInput.md): Computes the gradient of morphological 2-D dilation with respect to the input.
+
+[`DirectedInterleaveDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DirectedInterleaveDataset.md): A substitute for `InterleaveDataset` on a fixed list of `N` datasets.
+
+[`Div(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Div.md): Returns x / y element-wise.
+
+[`DivNoNan(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DivNoNan.md): Returns 0 if the denominator is zero.
+
+[`DrawBoundingBoxes(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DrawBoundingBoxes.md): Draw bounding boxes on a batch of images.
+
+[`DrawBoundingBoxesV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DrawBoundingBoxesV2.md): Draw bounding boxes on a batch of images.
+
+[`DummyMemoryCache(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DummyMemoryCache.md)
+
+[`DynamicPartition(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DynamicPartition.md): Partitions `data` into `num_partitions` tensors using indices from `partitions`.
+
+[`DynamicStitch(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/DynamicStitch.md): Interleave the values from the `data` tensors into a single tensor.
+
+[`EagerPyFunc(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/EagerPyFunc.md): Eagerly executes a python function to compute func(input)->output. The
+
+[`EditDistance(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/EditDistance.md): Computes the (possibly normalized) Levenshtein Edit Distance.
+
+[`Eig(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Eig.md): Computes the eigen decomposition of one or more square matrices.
+
+[`Einsum(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Einsum.md): Tensor contraction according to Einstein summation convention.
+
+[`Elu(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Elu.md): Computes exponential linear: `exp(features) - 1` if < 0, `features` otherwise.
+
+[`EluGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/EluGrad.md): Computes gradients for the exponential linear (Elu) operation.
+
+[`Empty(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Empty.md): Creates a tensor with the given shape.
+
+[`EmptyTensorList(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/EmptyTensorList.md): Creates and returns an empty tensor list.
+
+[`EncodeBase64(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/EncodeBase64.md): Encode strings into web-safe base64 format.
+
+[`EncodeJpeg(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/EncodeJpeg.md): JPEG-encode an image.
+
+[`EncodeJpegVariableQuality(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/EncodeJpegVariableQuality.md): JPEG encode input image with provided compression quality.
+
+[`EncodePng(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/EncodePng.md): PNG-encode an image.
+
+[`EncodeProto(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/EncodeProto.md): The op serializes protobuf messages provided in the input tensors.
+
+[`EncodeWav(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/EncodeWav.md): Encode audio data using the WAV file format.
+
+[`EnqueueTPUEmbeddingIntegerBatch(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/EnqueueTPUEmbeddingIntegerBatch.md): An op that enqueues a list of input batch tensors to TPUEmbedding.
+
+[`EnqueueTPUEmbeddingSparseBatch(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/EnqueueTPUEmbeddingSparseBatch.md): An op that enqueues TPUEmbedding input indices from a SparseTensor.
+
+[`EnqueueTPUEmbeddingSparseTensorBatch(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/EnqueueTPUEmbeddingSparseTensorBatch.md): Eases the porting of code that uses tf.nn.embedding_lookup_sparse().
+
+[`EnsureShape(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/EnsureShape.md): Ensures that the tensor's shape matches the expected shape.
+
+[`Enter(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Enter.md): Creates or finds a child frame, and makes `data` available to the child frame.
+
+[`Equal(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Equal.md): Returns the truth value of (x == y) element-wise.
+
+[`Erf(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Erf.md): Computes the Gauss error function of `x` element-wise.
+
+[`Erfc(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Erfc.md): Computes the complementary error function of `x` element-wise.
+
+[`Erfinv(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Erfinv.md)
+
+[`EuclideanNorm(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/EuclideanNorm.md): Computes the euclidean norm of elements across dimensions of a tensor.
+
+[`Exit(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Exit.md): Exits the current frame to its parent frame.
+
+[`Exp(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Exp.md): Computes exponential of x element-wise. \\(y = e^x\\).
+
+[`ExpandDims(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExpandDims.md): Inserts a dimension of 1 into a tensor's shape.
+
+[`ExperimentalAssertNextDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalAssertNextDataset.md)
+
+[`ExperimentalAutoShardDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalAutoShardDataset.md): Creates a dataset that shards the input dataset.
+
+[`ExperimentalBytesProducedStatsDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalBytesProducedStatsDataset.md): Records the bytes size of each element of `input_dataset` in a StatsAggregator.
+
+[`ExperimentalCSVDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalCSVDataset.md)
+
+[`ExperimentalChooseFastestDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalChooseFastestDataset.md)
+
+[`ExperimentalDatasetCardinality(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalDatasetCardinality.md): Returns the cardinality of `input_dataset`.
+
+[`ExperimentalDatasetToTFRecord(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalDatasetToTFRecord.md): Writes the given dataset to the given file using the TFRecord format.
+
+[`ExperimentalDenseToSparseBatchDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalDenseToSparseBatchDataset.md): Creates a dataset that batches input elements into a SparseTensor.
+
+[`ExperimentalDirectedInterleaveDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalDirectedInterleaveDataset.md): A substitute for `InterleaveDataset` on a fixed list of `N` datasets.
+
+[`ExperimentalGroupByReducerDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalGroupByReducerDataset.md): Creates a dataset that computes a group-by on `input_dataset`.
+
+[`ExperimentalGroupByWindowDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalGroupByWindowDataset.md): Creates a dataset that computes a windowed group-by on `input_dataset`.
+
+[`ExperimentalIgnoreErrorsDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalIgnoreErrorsDataset.md): Creates a dataset that contains the elements of `input_dataset` ignoring errors.
+
+[`ExperimentalIteratorGetDevice(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalIteratorGetDevice.md): Returns the name of the device on which `resource` has been placed.
+
+[`ExperimentalLMDBDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalLMDBDataset.md)
+
+[`ExperimentalLatencyStatsDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalLatencyStatsDataset.md): Records the latency of producing `input_dataset` elements in a StatsAggregator.
+
+[`ExperimentalMapAndBatchDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalMapAndBatchDataset.md): Creates a dataset that fuses mapping with batching.
+
+[`ExperimentalMapDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalMapDataset.md): Creates a dataset that applies `f` to the outputs of `input_dataset`.
+
+[`ExperimentalMatchingFilesDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalMatchingFilesDataset.md)
+
+[`ExperimentalMaxIntraOpParallelismDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalMaxIntraOpParallelismDataset.md): Creates a dataset that overrides the maximum intra-op parallelism.
+
+[`ExperimentalNonSerializableDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalNonSerializableDataset.md)
+
+[`ExperimentalParallelInterleaveDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalParallelInterleaveDataset.md): Creates a dataset that applies `f` to the outputs of `input_dataset`.
+
+[`ExperimentalParseExampleDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalParseExampleDataset.md): Transforms `input_dataset` containing `Example` protos as vectors of DT_STRING into a dataset of `Tensor` or `SparseTensor` objects representing the parsed features.
+
+[`ExperimentalPrivateThreadPoolDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalPrivateThreadPoolDataset.md): Creates a dataset that uses a custom thread pool to compute `input_dataset`.
+
+[`ExperimentalRandomDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalRandomDataset.md): Creates a Dataset that returns pseudorandom numbers.
+
+[`ExperimentalRebatchDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalRebatchDataset.md): Creates a dataset that changes the batch size.
+
+[`ExperimentalScanDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalScanDataset.md): Creates a dataset successively reduces `f` over the elements of `input_dataset`.
+
+[`ExperimentalSetStatsAggregatorDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalSetStatsAggregatorDataset.md)
+
+[`ExperimentalSleepDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalSleepDataset.md)
+
+[`ExperimentalSlidingWindowDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalSlidingWindowDataset.md): Creates a dataset that passes a sliding window over `input_dataset`.
+
+[`ExperimentalSqlDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalSqlDataset.md): Creates a dataset that executes a SQL query and emits rows of the result set.
+
+[`ExperimentalStatsAggregatorHandle(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalStatsAggregatorHandle.md): Creates a statistics manager resource.
+
+[`ExperimentalStatsAggregatorSummary(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalStatsAggregatorSummary.md): Produces a summary of any statistics recorded by the given statistics manager.
+
+[`ExperimentalTakeWhileDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalTakeWhileDataset.md): Creates a dataset that stops iteration when predicate` is false.
+
+[`ExperimentalThreadPoolDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalThreadPoolDataset.md): Creates a dataset that uses a custom thread pool to compute `input_dataset`.
+
+[`ExperimentalThreadPoolHandle(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalThreadPoolHandle.md): Creates a dataset that uses a custom thread pool to compute `input_dataset`.
+
+[`ExperimentalUnbatchDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalUnbatchDataset.md): A dataset that splits the elements of its input into multiple elements.
+
+[`ExperimentalUniqueDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExperimentalUniqueDataset.md): Creates a dataset that contains the unique elements of `input_dataset`.
+
+[`Expint(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Expint.md)
+
+[`Expm1(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Expm1.md): Computes `exp(x) - 1` element-wise.
+
+[`ExtractGlimpse(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExtractGlimpse.md): Extracts a glimpse from the input tensor.
+
+[`ExtractImagePatches(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExtractImagePatches.md): Extract `patches` from `images` and put them in the "depth" output dimension.
+
+[`ExtractJpegShape(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExtractJpegShape.md): Extract the shape information of a JPEG-encoded image.
+
+[`ExtractVolumePatches(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ExtractVolumePatches.md): Extract `patches` from `input` and put them in the "depth" output dimension. 3D extension of `extract_image_patches`.
+
+[`FFT(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FFT.md): Fast Fourier transform.
+
+[`FFT2D(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FFT2D.md): 2D fast Fourier transform.
+
+[`FFT3D(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FFT3D.md): 3D fast Fourier transform.
+
+[`FIFOQueue(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FIFOQueue.md): A queue that produces elements in first-in first-out order.
+
+[`FIFOQueueV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FIFOQueueV2.md): A queue that produces elements in first-in first-out order.
+
+[`Fact(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Fact.md): Output a fact about factorials.
+
+[`FakeParam(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FakeParam.md): This op is used as a placeholder in If branch functions. It doesn't provide a
+
+[`FakeQuantWithMinMaxArgs(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FakeQuantWithMinMaxArgs.md): Fake-quantize the 'inputs' tensor, type float to 'outputs' tensor of same type.
+
+[`FakeQuantWithMinMaxArgsGradient(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FakeQuantWithMinMaxArgsGradient.md): Compute gradients for a FakeQuantWithMinMaxArgs operation.
+
+[`FakeQuantWithMinMaxVars(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FakeQuantWithMinMaxVars.md): Fake-quantize the 'inputs' tensor of type float via global float scalars `min`
+
+[`FakeQuantWithMinMaxVarsGradient(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FakeQuantWithMinMaxVarsGradient.md): Compute gradients for a FakeQuantWithMinMaxVars operation.
+
+[`FakeQuantWithMinMaxVarsPerChannel(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FakeQuantWithMinMaxVarsPerChannel.md): Fake-quantize the 'inputs' tensor of type float and one of the shapes: `[d]`,
+
+[`FakeQuantWithMinMaxVarsPerChannelGradient(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FakeQuantWithMinMaxVarsPerChannelGradient.md): Compute gradients for a FakeQuantWithMinMaxVarsPerChannel operation.
+
+[`FakeQueue(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FakeQueue.md): Deprecated. Do not use.
+
+[`Fill(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Fill.md): Creates a tensor filled with a scalar value.
+
+[`FilterByLastComponentDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FilterByLastComponentDataset.md): Creates a dataset containing elements of first component of `input_dataset` having true in the last component.
+
+[`FilterDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FilterDataset.md): Creates a dataset containing elements of `input_dataset` matching `predicate`.
+
+[`Fingerprint(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Fingerprint.md): Generates fingerprint values.
+
+[`FixedLengthRecordDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FixedLengthRecordDataset.md): Creates a dataset that emits the records from one or more binary files.
+
+[`FixedLengthRecordDatasetV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FixedLengthRecordDatasetV2.md)
+
+[`FixedLengthRecordReader(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FixedLengthRecordReader.md): A Reader that outputs fixed-length records from a file.
+
+[`FixedLengthRecordReaderV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FixedLengthRecordReaderV2.md): A Reader that outputs fixed-length records from a file.
+
+[`FixedUnigramCandidateSampler(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FixedUnigramCandidateSampler.md): Generates labels for candidate sampling with a learned unigram distribution.
+
+[`FlatMapDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FlatMapDataset.md): Creates a dataset that applies `f` to the outputs of `input_dataset`.
+
+[`Floor(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Floor.md): Returns element-wise largest integer not greater than x.
+
+[`FloorDiv(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FloorDiv.md): Returns x // y element-wise.
+
+[`FloorMod(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FloorMod.md): Returns element-wise remainder of division. When `x < 0` xor `y < 0` is
+
+[`FlushSummaryWriter(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FlushSummaryWriter.md)
+
+[`For(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/For.md): ```python
+
+[`FractionalAvgPool(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FractionalAvgPool.md): Performs fractional average pooling on the input.
+
+[`FractionalAvgPoolGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FractionalAvgPoolGrad.md): Computes gradient of the FractionalAvgPool function.
+
+[`FractionalMaxPool(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FractionalMaxPool.md): Performs fractional max pooling on the input.
+
+[`FractionalMaxPoolGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FractionalMaxPoolGrad.md): Computes gradient of the FractionalMaxPool function.
+
+[`FresnelCos(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FresnelCos.md)
+
+[`FresnelSin(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FresnelSin.md)
+
+[`FusedBatchNorm(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FusedBatchNorm.md): Batch normalization.
+
+[`FusedBatchNormGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FusedBatchNormGrad.md): Gradient for batch normalization.
+
+[`FusedBatchNormGradV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FusedBatchNormGradV2.md): Gradient for batch normalization.
+
+[`FusedBatchNormGradV3(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FusedBatchNormGradV3.md): Gradient for batch normalization.
+
+[`FusedBatchNormV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FusedBatchNormV2.md): Batch normalization.
+
+[`FusedBatchNormV3(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FusedBatchNormV3.md): Batch normalization.
+
+[`FusedPadConv2D(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FusedPadConv2D.md): Performs a padding as a preprocess during a convolution.
+
+[`FusedResizeAndPadConv2D(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/FusedResizeAndPadConv2D.md): Performs a resize and padding as a preprocess during a convolution.
+
+[`GRUBlockCell(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/GRUBlockCell.md): Computes the GRU cell forward propagation for 1 time step.
+
+[`GRUBlockCellGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/GRUBlockCellGrad.md): Computes the GRU cell back-propagation for 1 time step.
+
+[`Gather(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Gather.md): Gather slices from `params` according to `indices`.
+
+[`GatherNd(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/GatherNd.md): Gather slices from `params` into a Tensor with shape specified by `indices`.
+
+[`GatherV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/GatherV2.md): Gather slices from `params` axis `axis` according to `indices`.
+
+[`GenerateBoundingBoxProposals(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/GenerateBoundingBoxProposals.md): This op produces Region of Interests from given bounding boxes(bbox_deltas) encoded wrt anchors according to eq.2 in arXiv:1506.01497
+
+[`GenerateVocabRemapping(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/GenerateVocabRemapping.md): Given a path to new and old vocabulary files, returns a remapping Tensor of
+
+[`GeneratorDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/GeneratorDataset.md): Creates a dataset that invokes a function to generate elements.
+
+[`GetSessionHandle(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/GetSessionHandle.md): Store the input tensor in the state of the current session.
+
+[`GetSessionHandleV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/GetSessionHandleV2.md): Store the input tensor in the state of the current session.
+
+[`GetSessionTensor(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/GetSessionTensor.md): Get the value of the tensor specified by its handle.
+
+[`Greater(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Greater.md): Returns the truth value of (x > y) element-wise.
+
+[`GreaterEqual(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/GreaterEqual.md): Returns the truth value of (x >= y) element-wise.
+
+[`GroupByReducerDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/GroupByReducerDataset.md): Creates a dataset that computes a group-by on `input_dataset`.
+
+[`GroupByWindowDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/GroupByWindowDataset.md): Creates a dataset that computes a windowed group-by on `input_dataset`.
+
+[`GuaranteeConst(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/GuaranteeConst.md): Gives a guarantee to the TF runtime that the input tensor is a constant.
+
+[`HSVToRGB(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/HSVToRGB.md): Convert one or more images from HSV to RGB.
+
+[`HashTable(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/HashTable.md): Creates a non-initialized hash table.
+
+[`HashTableV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/HashTableV2.md): Creates a non-initialized hash table.
+
+[`HistogramFixedWidth(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/HistogramFixedWidth.md): Return histogram of values.
+
+[`HistogramSummary(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/HistogramSummary.md): Outputs a `Summary` protocol buffer with a histogram.
+
+[`IFFT(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/IFFT.md): Inverse fast Fourier transform.
+
+[`IFFT2D(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/IFFT2D.md): Inverse 2D fast Fourier transform.
+
+[`IFFT3D(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/IFFT3D.md): Inverse 3D fast Fourier transform.
+
+[`IRFFT(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/IRFFT.md): Inverse real-valued fast Fourier transform.
+
+[`IRFFT2D(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/IRFFT2D.md): Inverse 2D real-valued fast Fourier transform.
+
+[`IRFFT3D(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/IRFFT3D.md): Inverse 3D real-valued fast Fourier transform.
+
+[`Identity(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Identity.md): Return a tensor with the same shape and contents as the input tensor or value.
+
+[`IdentityN(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/IdentityN.md): Returns a list of tensors with the same shapes and contents as the input
+
+[`IdentityReader(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/IdentityReader.md): A Reader that outputs the queued work as both the key and value.
+
+[`IdentityReaderV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/IdentityReaderV2.md): A Reader that outputs the queued work as both the key and value.
+
+[`If(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/If.md): output = cond ? then_branch(input) : else_branch(input)
+
+[`Igamma(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Igamma.md): Compute the lower regularized incomplete Gamma function `P(a, x)`.
+
+[`IgammaGradA(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/IgammaGradA.md): Computes the gradient of `igamma(a, x)` wrt `a`.
+
+[`Igammac(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Igammac.md): Compute the upper regularized incomplete Gamma function `Q(a, x)`.
+
+[`IgnoreErrorsDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/IgnoreErrorsDataset.md): Creates a dataset that contains the elements of `input_dataset` ignoring errors.
+
+[`Imag(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Imag.md): Returns the imaginary part of a complex number.
+
+[`ImageProjectiveTransformV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ImageProjectiveTransformV2.md): Applies the given transform to each of the images.
+
+[`ImageSummary(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ImageSummary.md): Outputs a `Summary` protocol buffer with images.
+
+[`ImmutableConst(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ImmutableConst.md): Returns immutable tensor from memory region.
+
+[`ImportEvent(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ImportEvent.md)
+
+[`InTopK(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/InTopK.md): Says whether the targets are in the top `K` predictions.
+
+[`InTopKV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/InTopKV2.md): Says whether the targets are in the top `K` predictions.
+
+[`InfeedDequeue(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/InfeedDequeue.md): A placeholder op for a value that will be fed into the computation.
+
+[`InfeedDequeueTuple(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/InfeedDequeueTuple.md): Fetches multiple values from infeed as an XLA tuple.
+
+[`InfeedEnqueue(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/InfeedEnqueue.md): An op which feeds a single Tensor value into the computation.
+
+[`InfeedEnqueuePrelinearizedBuffer(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/InfeedEnqueuePrelinearizedBuffer.md): An op which enqueues prelinearized buffer into TPU infeed.
+
+[`InfeedEnqueueTuple(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/InfeedEnqueueTuple.md): Feeds multiple Tensor values into the computation as an XLA tuple.
+
+[`InitializeTable(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/InitializeTable.md): Table initializer that takes two tensors for keys and values respectively.
+
+[`InitializeTableFromTextFile(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/InitializeTableFromTextFile.md): Initializes a table from a text file.
+
+[`InitializeTableFromTextFileV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/InitializeTableFromTextFileV2.md): Initializes a table from a text file.
+
+[`InitializeTableV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/InitializeTableV2.md): Table initializer that takes two tensors for keys and values respectively.
+
+[`InplaceAdd(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/InplaceAdd.md): Adds v into specified rows of x.
+
+[`InplaceSub(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/InplaceSub.md): Subtracts `v` into specified rows of `x`.
+
+[`InplaceUpdate(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/InplaceUpdate.md): Updates specified rows with values in `v`.
+
+[`InterleaveDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/InterleaveDataset.md): Creates a dataset that applies `f` to the outputs of `input_dataset`.
+
+[`Inv(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Inv.md): Computes the reciprocal of x element-wise.
+
+[`InvGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/InvGrad.md): Computes the gradient for the inverse of `x` wrt its input.
+
+[`Invert(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Invert.md): Invert (flip) each bit of supported types; for example, type `uint8` value 01010101 becomes 10101010.
+
+[`InvertPermutation(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/InvertPermutation.md): Computes the inverse permutation of a tensor.
+
+[`IsBoostedTreesEnsembleInitialized(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/IsBoostedTreesEnsembleInitialized.md): Checks whether a tree ensemble has been initialized.
+
+[`IsBoostedTreesQuantileStreamResourceInitialized(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/IsBoostedTreesQuantileStreamResourceInitialized.md): Checks whether a quantile stream has been initialized.
+
+[`IsFinite(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/IsFinite.md): Returns which elements of x are finite.
+
+[`IsInf(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/IsInf.md): Returns which elements of x are Inf.
+
+[`IsNan(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/IsNan.md): Returns which elements of x are NaN.
+
+[`IsVariableInitialized(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/IsVariableInitialized.md): Checks whether a tensor has been initialized.
+
+[`Iterator(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Iterator.md): A container for an iterator resource.
+
+[`IteratorFromStringHandle(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/IteratorFromStringHandle.md): Converts the given string representing a handle to an iterator to a resource.
+
+[`IteratorFromStringHandleV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/IteratorFromStringHandleV2.md)
+
+[`IteratorGetDevice(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/IteratorGetDevice.md): Returns the name of the device on which `resource` has been placed.
+
+[`IteratorGetNext(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/IteratorGetNext.md): Gets the next output from the given iterator .
+
+[`IteratorGetNextAsOptional(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/IteratorGetNextAsOptional.md): Gets the next output from the given iterator as an Optional variant.
+
+[`IteratorGetNextSync(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/IteratorGetNextSync.md): Gets the next output from the given iterator.
+
+[`IteratorToStringHandle(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/IteratorToStringHandle.md): Converts the given `resource_handle` representing an iterator to a string.
+
+[`IteratorV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/IteratorV2.md)
+
+[`L2Loss(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/L2Loss.md): L2 Loss.
+
+[`LMDBDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LMDBDataset.md): Creates a dataset that emits the key-value pairs in one or more LMDB files.
+
+[`LMDBReader(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LMDBReader.md): A Reader that outputs the records from a LMDB file.
+
+[`LRN(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LRN.md): Local Response Normalization.
+
+[`LRNGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LRNGrad.md): Gradients for Local Response Normalization.
+
+[`LSTMBlockCell(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LSTMBlockCell.md): Computes the LSTM cell forward propagation for 1 time step.
+
+[`LSTMBlockCellGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LSTMBlockCellGrad.md): Computes the LSTM cell backward propagation for 1 timestep.
+
+[`LatencyStatsDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LatencyStatsDataset.md): Records the latency of producing `input_dataset` elements in a StatsAggregator.
+
+[`LeakyRelu(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LeakyRelu.md): Computes rectified linear: `max(features, features * alpha)`.
+
+[`LeakyReluGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LeakyReluGrad.md): Computes rectified linear gradients for a LeakyRelu operation.
+
+[`LearnedUnigramCandidateSampler(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LearnedUnigramCandidateSampler.md): Generates labels for candidate sampling with a learned unigram distribution.
+
+[`LeftShift(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LeftShift.md): Elementwise computes the bitwise left-shift of `x` and `y`.
+
+[`LegacyParallelInterleaveDatasetV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LegacyParallelInterleaveDatasetV2.md): Creates a dataset that applies `f` to the outputs of `input_dataset`.
+
+[`Less(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Less.md): Returns the truth value of (x < y) element-wise.
+
+[`LessEqual(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LessEqual.md): Returns the truth value of (x <= y) element-wise.
+
+[`Lgamma(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Lgamma.md): Computes the log of the absolute value of `Gamma(x)` element-wise.
+
+[`LinSpace(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LinSpace.md): Generates values in an interval.
+
+[`ListDiff(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ListDiff.md): Computes the difference between two lists of numbers or strings.
+
+[`LoadAndRemapMatrix(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LoadAndRemapMatrix.md): Loads a 2-D (matrix) `Tensor` with name `old_tensor_name` from the checkpoint
+
+[`LoadTPUEmbeddingADAMParameters(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LoadTPUEmbeddingADAMParameters.md): Load ADAM embedding parameters.
+
+[`LoadTPUEmbeddingADAMParametersGradAccumDebug(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LoadTPUEmbeddingADAMParametersGradAccumDebug.md): Load ADAM embedding parameters with debug support.
+
+[`LoadTPUEmbeddingAdadeltaParameters(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LoadTPUEmbeddingAdadeltaParameters.md): Load Adadelta embedding parameters.
+
+[`LoadTPUEmbeddingAdadeltaParametersGradAccumDebug(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LoadTPUEmbeddingAdadeltaParametersGradAccumDebug.md): Load Adadelta parameters with debug support.
+
+[`LoadTPUEmbeddingAdagradParameters(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LoadTPUEmbeddingAdagradParameters.md): Load Adagrad embedding parameters.
+
+[`LoadTPUEmbeddingAdagradParametersGradAccumDebug(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LoadTPUEmbeddingAdagradParametersGradAccumDebug.md): Load Adagrad embedding parameters with debug support.
+
+[`LoadTPUEmbeddingCenteredRMSPropParameters(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LoadTPUEmbeddingCenteredRMSPropParameters.md): Load centered RMSProp embedding parameters.
+
+[`LoadTPUEmbeddingFTRLParameters(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LoadTPUEmbeddingFTRLParameters.md): Load FTRL embedding parameters.
+
+[`LoadTPUEmbeddingFTRLParametersGradAccumDebug(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LoadTPUEmbeddingFTRLParametersGradAccumDebug.md): Load FTRL embedding parameters with debug support.
+
+[`LoadTPUEmbeddingMDLAdagradLightParameters(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LoadTPUEmbeddingMDLAdagradLightParameters.md): Load MDL Adagrad Light embedding parameters.
+
+[`LoadTPUEmbeddingMomentumParameters(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LoadTPUEmbeddingMomentumParameters.md): Load Momentum embedding parameters.
+
+[`LoadTPUEmbeddingMomentumParametersGradAccumDebug(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LoadTPUEmbeddingMomentumParametersGradAccumDebug.md): Load Momentum embedding parameters with debug support.
+
+[`LoadTPUEmbeddingProximalAdagradParameters(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LoadTPUEmbeddingProximalAdagradParameters.md): Load proximal Adagrad embedding parameters.
+
+[`LoadTPUEmbeddingProximalAdagradParametersGradAccumDebug(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LoadTPUEmbeddingProximalAdagradParametersGradAccumDebug.md): Load proximal Adagrad embedding parameters with debug support.
+
+[`LoadTPUEmbeddingRMSPropParameters(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LoadTPUEmbeddingRMSPropParameters.md): Load RMSProp embedding parameters.
+
+[`LoadTPUEmbeddingRMSPropParametersGradAccumDebug(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LoadTPUEmbeddingRMSPropParametersGradAccumDebug.md): Load RMSProp embedding parameters with debug support.
+
+[`LoadTPUEmbeddingStochasticGradientDescentParameters(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LoadTPUEmbeddingStochasticGradientDescentParameters.md): Load SGD embedding parameters.
+
+[`Log(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Log.md): Computes natural logarithm of x element-wise.
+
+[`Log1p(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Log1p.md): Computes natural logarithm of (1 + x) element-wise.
+
+[`LogMatrixDeterminant(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LogMatrixDeterminant.md): Computes the sign and the log of the absolute value of the determinant of
+
+[`LogSoftmax(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LogSoftmax.md): Computes log softmax activations.
+
+[`LogUniformCandidateSampler(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LogUniformCandidateSampler.md): Generates labels for candidate sampling with a log-uniform distribution.
+
+[`LogicalAnd(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LogicalAnd.md): Returns the truth value of x AND y element-wise.
+
+[`LogicalNot(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LogicalNot.md): Returns the truth value of `NOT x` element-wise.
+
+[`LogicalOr(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LogicalOr.md): Returns the truth value of x OR y element-wise.
+
+[`LookupTableExport(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LookupTableExport.md): Outputs all keys and values in the table.
+
+[`LookupTableExportV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LookupTableExportV2.md): Outputs all keys and values in the table.
+
+[`LookupTableFind(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LookupTableFind.md): Looks up keys in a table, outputs the corresponding values.
+
+[`LookupTableFindV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LookupTableFindV2.md): Looks up keys in a table, outputs the corresponding values.
+
+[`LookupTableImport(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LookupTableImport.md): Replaces the contents of the table with the specified keys and values.
+
+[`LookupTableImportV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LookupTableImportV2.md): Replaces the contents of the table with the specified keys and values.
+
+[`LookupTableInsert(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LookupTableInsert.md): Updates the table to associates keys with values.
+
+[`LookupTableInsertV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LookupTableInsertV2.md): Updates the table to associates keys with values.
+
+[`LookupTableRemoveV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LookupTableRemoveV2.md): Removes keys and its associated values from a table.
+
+[`LookupTableSize(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LookupTableSize.md): Computes the number of elements in the given table.
+
+[`LookupTableSizeV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LookupTableSizeV2.md): Computes the number of elements in the given table.
+
+[`LoopCond(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LoopCond.md): Forwards the input to the output.
+
+[`LowerBound(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/LowerBound.md): Applies lower_bound(sorted_search_values, values) along each row.
+
+[`Lu(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Lu.md): Computes the LU decomposition of one or more square matrices.
+
+[`MakeIterator(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MakeIterator.md): Makes a new iterator from the given `dataset` and stores it in `iterator`.
+
+[`MapAndBatchDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MapAndBatchDataset.md): Creates a dataset that fuses mapping with batching.
+
+[`MapClear(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MapClear.md): Op removes all elements in the underlying container.
+
+[`MapDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MapDataset.md): Creates a dataset that applies `f` to the outputs of `input_dataset`.
+
+[`MapDefun(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MapDefun.md): Maps a function on the list of tensors unpacked from arguments on dimension 0.
+
+[`MapIncompleteSize(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MapIncompleteSize.md): Op returns the number of incomplete elements in the underlying container.
+
+[`MapPeek(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MapPeek.md): Op peeks at the values at the specified key. If the
+
+[`MapSize(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MapSize.md): Op returns the number of elements in the underlying container.
+
+[`MapStage(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MapStage.md): Stage (key, values) in the underlying container which behaves like a hashtable.
+
+[`MapUnstage(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MapUnstage.md): Op removes and returns the values associated with the key
+
+[`MapUnstageNoKey(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MapUnstageNoKey.md): Op removes and returns a random (key, value)
+
+[`MatMul(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MatMul.md): Multiply the matrix "a" by the matrix "b".
+
+[`MatchingFiles(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MatchingFiles.md): Returns the set of files matching one or more glob patterns.
+
+[`MatchingFilesDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MatchingFilesDataset.md)
+
+[`MatrixBandPart(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MatrixBandPart.md): Copy a tensor setting everything outside a central band in each innermost matrix
+
+[`MatrixDeterminant(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MatrixDeterminant.md): Computes the determinant of one or more square matrices.
+
+[`MatrixDiag(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MatrixDiag.md): Returns a batched diagonal tensor with a given batched diagonal values.
+
+[`MatrixDiagPart(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MatrixDiagPart.md): Returns the batched diagonal part of a batched tensor.
+
+[`MatrixDiagPartV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MatrixDiagPartV2.md): Returns the batched diagonal part of a batched tensor.
+
+[`MatrixDiagPartV3(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MatrixDiagPartV3.md): Returns the batched diagonal part of a batched tensor.
+
+[`MatrixDiagV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MatrixDiagV2.md): Returns a batched diagonal tensor with given batched diagonal values.
+
+[`MatrixDiagV3(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MatrixDiagV3.md): Returns a batched diagonal tensor with given batched diagonal values.
+
+[`MatrixExponential(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MatrixExponential.md): Deprecated, use python implementation tf.linalg.matrix_exponential.
+
+[`MatrixInverse(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MatrixInverse.md): Computes the inverse of one or more square invertible matrices or their
+
+[`MatrixLogarithm(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MatrixLogarithm.md): Computes the matrix logarithm of one or more square matrices:
+
+[`MatrixSetDiag(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MatrixSetDiag.md): Returns a batched matrix tensor with new batched diagonal values.
+
+[`MatrixSetDiagV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MatrixSetDiagV2.md): Returns a batched matrix tensor with new batched diagonal values.
+
+[`MatrixSetDiagV3(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MatrixSetDiagV3.md): Returns a batched matrix tensor with new batched diagonal values.
+
+[`MatrixSolve(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MatrixSolve.md): Solves systems of linear equations.
+
+[`MatrixSolveLs(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MatrixSolveLs.md): Solves one or more linear least-squares problems.
+
+[`MatrixSquareRoot(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MatrixSquareRoot.md): Computes the matrix square root of one or more square matrices:
+
+[`MatrixTriangularSolve(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MatrixTriangularSolve.md): Solves systems of linear equations with upper or lower triangular matrices by backsubstitution.
+
+[`Max(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Max.md): Computes the maximum of elements across dimensions of a tensor.
+
+[`MaxIntraOpParallelismDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MaxIntraOpParallelismDataset.md): Creates a dataset that overrides the maximum intra-op parallelism.
+
+[`MaxPool(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MaxPool.md): Performs max pooling on the input.
+
+[`MaxPool3D(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MaxPool3D.md): Performs 3D max pooling on the input.
+
+[`MaxPool3DGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MaxPool3DGrad.md): Computes gradients of max pooling function.
+
+[`MaxPool3DGradGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MaxPool3DGradGrad.md): Computes second-order gradients of the maxpooling function.
+
+[`MaxPoolGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MaxPoolGrad.md): Computes gradients of the maxpooling function.
+
+[`MaxPoolGradGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MaxPoolGradGrad.md): Computes second-order gradients of the maxpooling function.
+
+[`MaxPoolGradGradV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MaxPoolGradGradV2.md): Computes second-order gradients of the maxpooling function.
+
+[`MaxPoolGradGradWithArgmax(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MaxPoolGradGradWithArgmax.md): Computes second-order gradients of the maxpooling function.
+
+[`MaxPoolGradV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MaxPoolGradV2.md): Computes gradients of the maxpooling function.
+
+[`MaxPoolGradWithArgmax(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MaxPoolGradWithArgmax.md): Computes gradients of the maxpooling function.
+
+[`MaxPoolV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MaxPoolV2.md): Performs max pooling on the input.
+
+[`MaxPoolWithArgmax(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MaxPoolWithArgmax.md): Performs max pooling on the input and outputs both max values and indices.
+
+[`Maximum(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Maximum.md): Returns the max of x and y (i.e. x > y ? x : y) element-wise.
+
+[`Mean(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Mean.md): Computes the mean of elements across dimensions of a tensor.
+
+[`Merge(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Merge.md): Forwards the value of an available tensor from `inputs` to `output`.
+
+[`MergeSummary(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MergeSummary.md): Merges summaries.
+
+[`MergeV2Checkpoints(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MergeV2Checkpoints.md): V2 format specific: merges the metadata files of sharded checkpoints. The
+
+[`Mfcc(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Mfcc.md): Transforms a spectrogram into a form that's useful for speech recognition.
+
+[`Min(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Min.md): Computes the minimum of elements across dimensions of a tensor.
+
+[`Minimum(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Minimum.md): Returns the min of x and y (i.e. x < y ? x : y) element-wise.
+
+[`MirrorPad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MirrorPad.md): Pads a tensor with mirrored values.
+
+[`MirrorPadGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MirrorPadGrad.md): Gradient op for `MirrorPad` op. This op folds a mirror-padded tensor.
+
+[`Mod(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Mod.md): Returns element-wise remainder of division. This emulates C semantics in that
+
+[`ModelDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ModelDataset.md): Identity transformation that models performance.
+
+[`Mul(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Mul.md): Returns x * y element-wise.
+
+[`MulNoNan(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MulNoNan.md): Returns x * y element-wise. Returns zero if y is zero, even if x if infinite or NaN.
+
+[`MultiDeviceIterator(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MultiDeviceIterator.md): Creates a MultiDeviceIterator resource.
+
+[`MultiDeviceIteratorFromStringHandle(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MultiDeviceIteratorFromStringHandle.md): Generates a MultiDeviceIterator resource from its provided string handle.
+
+[`MultiDeviceIteratorGetNextFromShard(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MultiDeviceIteratorGetNextFromShard.md): Gets next element for the provided shard number.
+
+[`MultiDeviceIteratorInit(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MultiDeviceIteratorInit.md): Initializes the multi device iterator with the given dataset.
+
+[`MultiDeviceIteratorToStringHandle(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MultiDeviceIteratorToStringHandle.md): Produces a string handle for the given MultiDeviceIterator.
+
+[`Multinomial(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Multinomial.md): Draws samples from a multinomial distribution.
+
+[`MutableDenseHashTable(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MutableDenseHashTable.md): Creates an empty hash table that uses tensors as the backing store.
+
+[`MutableDenseHashTableV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MutableDenseHashTableV2.md): Creates an empty hash table that uses tensors as the backing store.
+
+[`MutableHashTable(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MutableHashTable.md): Creates an empty hash table.
+
+[`MutableHashTableOfTensors(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MutableHashTableOfTensors.md): Creates an empty hash table.
+
+[`MutableHashTableOfTensorsV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MutableHashTableOfTensorsV2.md): Creates an empty hash table.
+
+[`MutableHashTableV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MutableHashTableV2.md): Creates an empty hash table.
+
+[`MutexLock(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MutexLock.md): Locks a mutex resource. The output is the lock. So long as the lock tensor
+
+[`MutexV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/MutexV2.md): Creates a Mutex resource that can be locked by `MutexLock`.
+
+[`NcclAllReduce(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/NcclAllReduce.md): Outputs a tensor containing the reduction across all input tensors.
+
+[`NcclBroadcast(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/NcclBroadcast.md): Sends `input` to all devices that are connected to the output.
+
+[`NcclReduce(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/NcclReduce.md): Reduces `input` from `num_devices` using `reduction` to a single device.
+
+[`Ndtri(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Ndtri.md)
+
+[`Neg(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Neg.md): Computes numerical negative value element-wise.
+
+[`NextAfter(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/NextAfter.md): Returns the next representable value of `x1` in the direction of `x2`, element-wise.
+
+[`NextIteration(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/NextIteration.md): Makes its input available to the next iteration.
+
+[`NoOp(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/NoOp.md): Does nothing. Only useful as a placeholder for control edges.
+
+[`NonDeterministicInts(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/NonDeterministicInts.md): Non-deterministically generates some integers.
+
+[`NonMaxSuppression(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/NonMaxSuppression.md): Greedily selects a subset of bounding boxes in descending order of score,
+
+[`NonMaxSuppressionV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/NonMaxSuppressionV2.md): Greedily selects a subset of bounding boxes in descending order of score,
+
+[`NonMaxSuppressionV3(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/NonMaxSuppressionV3.md): Greedily selects a subset of bounding boxes in descending order of score,
+
+[`NonMaxSuppressionV4(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/NonMaxSuppressionV4.md): Greedily selects a subset of bounding boxes in descending order of score,
+
+[`NonMaxSuppressionV5(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/NonMaxSuppressionV5.md): Greedily selects a subset of bounding boxes in descending order of score,
+
+[`NonMaxSuppressionWithOverlaps(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/NonMaxSuppressionWithOverlaps.md): Greedily selects a subset of bounding boxes in descending order of score,
+
+[`NonSerializableDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/NonSerializableDataset.md)
+
+[`NotEqual(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/NotEqual.md): Returns the truth value of (x != y) element-wise.
+
+[`NthElement(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/NthElement.md): Finds values of the `n`-th order statistic for the last dimension.
+
+[`OneHot(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/OneHot.md): Returns a one-hot tensor.
+
+[`OneShotIterator(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/OneShotIterator.md): Makes a "one-shot" iterator that can be iterated only once.
+
+[`OnesLike(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/OnesLike.md): Returns a tensor of ones with the same shape and type as x.
+
+[`OptimizeDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/OptimizeDataset.md): Creates a dataset by applying optimizations to `input_dataset`.
+
+[`OptionalFromValue(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/OptionalFromValue.md): Constructs an Optional variant from a tuple of tensors.
+
+[`OptionalGetValue(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/OptionalGetValue.md): Returns the value stored in an Optional variant or raises an error if none exists.
+
+[`OptionalHasValue(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/OptionalHasValue.md): Returns true if and only if the given Optional variant has a value.
+
+[`OptionalNone(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/OptionalNone.md): Creates an Optional variant with no value.
+
+[`OrderedMapClear(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/OrderedMapClear.md): Op removes all elements in the underlying container.
+
+[`OrderedMapIncompleteSize(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/OrderedMapIncompleteSize.md): Op returns the number of incomplete elements in the underlying container.
+
+[`OrderedMapPeek(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/OrderedMapPeek.md): Op peeks at the values at the specified key. If the
+
+[`OrderedMapSize(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/OrderedMapSize.md): Op returns the number of elements in the underlying container.
+
+[`OrderedMapStage(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/OrderedMapStage.md): Stage (key, values) in the underlying container which behaves like a ordered
+
+[`OrderedMapUnstage(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/OrderedMapUnstage.md): Op removes and returns the values associated with the key
+
+[`OrderedMapUnstageNoKey(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/OrderedMapUnstageNoKey.md): Op removes and returns the (key, value) element with the smallest
+
+[`OutfeedDequeue(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/OutfeedDequeue.md): Retrieves a single tensor from the computation outfeed.
+
+[`OutfeedDequeueTuple(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/OutfeedDequeueTuple.md): Retrieve multiple values from the computation outfeed.
+
+[`OutfeedEnqueue(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/OutfeedEnqueue.md): Enqueue a Tensor on the computation outfeed.
+
+[`OutfeedEnqueueTuple(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/OutfeedEnqueueTuple.md): Enqueue multiple Tensor values on the computation outfeed.
+
+[`Pack(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Pack.md): Packs a list of `N` rank-`R` tensors into one rank-`(R+1)` tensor.
+
+[`Pad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Pad.md): Pads a tensor with zeros.
+
+[`PadV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/PadV2.md): Pads a tensor.
+
+[`PaddedBatchDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/PaddedBatchDataset.md): Creates a dataset that batches and pads `batch_size` elements from the input.
+
+[`PaddedBatchDatasetV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/PaddedBatchDatasetV2.md): Creates a dataset that batches and pads `batch_size` elements from the input.
+
+[`PaddingFIFOQueue(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/PaddingFIFOQueue.md): A queue that produces elements in first-in first-out order.
+
+[`PaddingFIFOQueueV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/PaddingFIFOQueueV2.md): A queue that produces elements in first-in first-out order.
+
+[`ParallelConcat(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ParallelConcat.md): Concatenates a list of `N` tensors along the first dimension.
+
+[`ParallelDynamicStitch(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ParallelDynamicStitch.md): Interleave the values from the `data` tensors into a single tensor.
+
+[`ParallelInterleaveDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ParallelInterleaveDataset.md): Creates a dataset that applies `f` to the outputs of `input_dataset`.
+
+[`ParallelInterleaveDatasetV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ParallelInterleaveDatasetV2.md): Creates a dataset that applies `f` to the outputs of `input_dataset`.
+
+[`ParallelInterleaveDatasetV3(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ParallelInterleaveDatasetV3.md): Creates a dataset that applies `f` to the outputs of `input_dataset`.
+
+[`ParallelInterleaveDatasetV4(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ParallelInterleaveDatasetV4.md): Creates a dataset that applies `f` to the outputs of `input_dataset`.
+
+[`ParallelMapDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ParallelMapDataset.md): Creates a dataset that applies `f` to the outputs of `input_dataset`.
+
+[`ParallelMapDatasetV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ParallelMapDatasetV2.md): Creates a dataset that applies `f` to the outputs of `input_dataset`.
+
+[`ParameterizedTruncatedNormal(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ParameterizedTruncatedNormal.md): Outputs random values from a normal distribution. The parameters may each be a
+
+[`ParseExample(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ParseExample.md): Transforms a vector of brain.Example protos (as strings) into typed tensors.
+
+[`ParseExampleDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ParseExampleDataset.md): Transforms `input_dataset` containing `Example` protos as vectors of DT_STRING into a dataset of `Tensor` or `SparseTensor` objects representing the parsed features.
+
+[`ParseExampleDatasetV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ParseExampleDatasetV2.md): Transforms `input_dataset` containing `Example` protos as vectors of DT_STRING into a dataset of `Tensor` or `SparseTensor` objects representing the parsed features.
+
+[`ParseExampleV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ParseExampleV2.md): Transforms a vector of tf.Example protos (as strings) into typed tensors.
+
+[`ParseSequenceExample(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ParseSequenceExample.md): Transforms a vector of brain.SequenceExample protos (as strings) into typed tensors.
+
+[`ParseSequenceExampleV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ParseSequenceExampleV2.md): Transforms a vector of tf.io.SequenceExample protos (as strings) into
+
+[`ParseSingleExample(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ParseSingleExample.md): Transforms a tf.Example proto (as a string) into typed tensors.
+
+[`ParseSingleSequenceExample(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ParseSingleSequenceExample.md): Transforms a scalar brain.SequenceExample proto (as strings) into typed tensors.
+
+[`ParseTensor(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ParseTensor.md): Transforms a serialized tensorflow.TensorProto proto into a Tensor.
+
+[`PartitionedCall(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/PartitionedCall.md): returns `f(inputs)`, where `f`'s body is placed and partitioned.
+
+[`Placeholder(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Placeholder.md): A placeholder op for a value that will be fed into the computation.
+
+[`PlaceholderV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/PlaceholderV2.md): A placeholder op for a value that will be fed into the computation.
+
+[`PlaceholderWithDefault(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/PlaceholderWithDefault.md): A placeholder op that passes through `input` when its output is not fed.
+
+[`Polygamma(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Polygamma.md): Compute the polygamma function \\(\psi^{(n)}(x)\\).
+
+[`PopulationCount(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/PopulationCount.md): Computes element-wise population count (a.k.a. popcount, bitsum, bitcount).
+
+[`Pow(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Pow.md): Computes the power of one value to another.
+
+[`PrefetchDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/PrefetchDataset.md): Creates a dataset that asynchronously prefetches elements from `input_dataset`.
+
+[`Prelinearize(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Prelinearize.md): An op which linearizes one Tensor value to an opaque variant tensor.
+
+[`PrelinearizeTuple(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/PrelinearizeTuple.md): An op which linearizes multiple Tensor values to an opaque variant tensor.
+
+[`PreventGradient(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/PreventGradient.md): An identity op that triggers an error if a gradient is requested.
+
+[`Print(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Print.md): Prints a list of tensors.
+
+[`PrintV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/PrintV2.md): Prints a string scalar.
+
+[`PriorityQueue(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/PriorityQueue.md): A queue that produces elements sorted by the first component value.
+
+[`PriorityQueueV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/PriorityQueueV2.md): A queue that produces elements sorted by the first component value.
+
+[`PrivateThreadPoolDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/PrivateThreadPoolDataset.md): Creates a dataset that uses a custom thread pool to compute `input_dataset`.
+
+[`Prod(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Prod.md): Computes the product of elements across dimensions of a tensor.
+
+[`PyFunc(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/PyFunc.md): Invokes a python function to compute func(input)->output.
+
+[`PyFuncStateless(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/PyFuncStateless.md): A stateless version of PyFunc.
+
+[`Qr(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Qr.md): Computes the QR decompositions of one or more matrices.
+
+[`QuantizeAndDequantize(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizeAndDequantize.md): Use QuantizeAndDequantizeV2 instead.
+
+[`QuantizeAndDequantizeV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizeAndDequantizeV2.md): Quantizes then dequantizes a tensor.
+
+[`QuantizeAndDequantizeV3(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizeAndDequantizeV3.md): Quantizes then dequantizes a tensor.
+
+[`QuantizeDownAndShrinkRange(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizeDownAndShrinkRange.md): Convert the quantized 'input' tensor into a lower-precision 'output', using the
+
+[`QuantizeV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizeV2.md): Quantize the 'input' tensor of type float to 'output' tensor of type 'T'.
+
+[`QuantizedAdd(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizedAdd.md): Returns x + y element-wise, working on quantized buffers.
+
+[`QuantizedAvgPool(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizedAvgPool.md): Produces the average pool of the input tensor for quantized types.
+
+[`QuantizedBatchNormWithGlobalNormalization(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizedBatchNormWithGlobalNormalization.md): Quantized Batch normalization.
+
+[`QuantizedBiasAdd(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizedBiasAdd.md): Adds Tensor 'bias' to Tensor 'input' for Quantized types.
+
+[`QuantizedConcat(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizedConcat.md): Concatenates quantized tensors along one dimension.
+
+[`QuantizedConv2D(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizedConv2D.md): Computes a 2D convolution given quantized 4D input and filter tensors.
+
+[`QuantizedConv2DAndRelu(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizedConv2DAndRelu.md)
+
+[`QuantizedConv2DAndReluAndRequantize(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizedConv2DAndReluAndRequantize.md)
+
+[`QuantizedConv2DAndRequantize(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizedConv2DAndRequantize.md)
+
+[`QuantizedConv2DPerChannel(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizedConv2DPerChannel.md): Computes QuantizedConv2D per channel.
+
+[`QuantizedConv2DWithBias(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizedConv2DWithBias.md)
+
+[`QuantizedConv2DWithBiasAndRelu(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizedConv2DWithBiasAndRelu.md)
+
+[`QuantizedConv2DWithBiasAndReluAndRequantize(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizedConv2DWithBiasAndReluAndRequantize.md)
+
+[`QuantizedConv2DWithBiasAndRequantize(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizedConv2DWithBiasAndRequantize.md)
+
+[`QuantizedConv2DWithBiasSignedSumAndReluAndRequantize(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizedConv2DWithBiasSignedSumAndReluAndRequantize.md)
+
+[`QuantizedConv2DWithBiasSumAndRelu(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizedConv2DWithBiasSumAndRelu.md)
+
+[`QuantizedConv2DWithBiasSumAndReluAndRequantize(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizedConv2DWithBiasSumAndReluAndRequantize.md)
+
+[`QuantizedDepthwiseConv2D(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizedDepthwiseConv2D.md): Computes quantized depthwise Conv2D.
+
+[`QuantizedDepthwiseConv2DWithBias(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizedDepthwiseConv2DWithBias.md): Computes quantized depthwise Conv2D with Bias.
+
+[`QuantizedDepthwiseConv2DWithBiasAndRelu(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizedDepthwiseConv2DWithBiasAndRelu.md): Computes quantized depthwise Conv2D with Bias and Relu.
+
+[`QuantizedDepthwiseConv2DWithBiasAndReluAndRequantize(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizedDepthwiseConv2DWithBiasAndReluAndRequantize.md): Computes quantized depthwise Conv2D with Bias, Relu and Requantize.
+
+[`QuantizedInstanceNorm(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizedInstanceNorm.md): Quantized Instance normalization.
+
+[`QuantizedMatMul(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizedMatMul.md): Perform a quantized matrix multiplication of `a` by the matrix `b`.
+
+[`QuantizedMatMulWithBias(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizedMatMulWithBias.md): Performs a quantized matrix multiplication of `a` by the matrix `b` with bias
+
+[`QuantizedMatMulWithBiasAndDequantize(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizedMatMulWithBiasAndDequantize.md)
+
+[`QuantizedMatMulWithBiasAndRelu(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizedMatMulWithBiasAndRelu.md): Perform a quantized matrix multiplication of `a` by the matrix `b` with bias
+
+[`QuantizedMatMulWithBiasAndReluAndRequantize(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizedMatMulWithBiasAndReluAndRequantize.md): Perform a quantized matrix multiplication of `a` by the matrix `b` with bias
+
+[`QuantizedMatMulWithBiasAndRequantize(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizedMatMulWithBiasAndRequantize.md)
+
+[`QuantizedMaxPool(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizedMaxPool.md): Produces the max pool of the input tensor for quantized types.
+
+[`QuantizedMul(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizedMul.md): Returns x * y element-wise, working on quantized buffers.
+
+[`QuantizedRelu(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizedRelu.md): Computes Quantized Rectified Linear: `max(features, 0)`
+
+[`QuantizedRelu6(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizedRelu6.md): Computes Quantized Rectified Linear 6: `min(max(features, 0), 6)`
+
+[`QuantizedReluX(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizedReluX.md): Computes Quantized Rectified Linear X: `min(max(features, 0), max_value)`
+
+[`QuantizedReshape(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizedReshape.md): Reshapes a quantized tensor as per the Reshape op.
+
+[`QuantizedResizeBilinear(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QuantizedResizeBilinear.md): Resize quantized `images` to `size` using quantized bilinear interpolation.
+
+[`QueueClose(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QueueClose.md): Closes the given queue.
+
+[`QueueCloseV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QueueCloseV2.md): Closes the given queue.
+
+[`QueueDequeue(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QueueDequeue.md): Dequeues a tuple of one or more tensors from the given queue.
+
+[`QueueDequeueMany(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QueueDequeueMany.md): Dequeues `n` tuples of one or more tensors from the given queue.
+
+[`QueueDequeueManyV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QueueDequeueManyV2.md): Dequeues `n` tuples of one or more tensors from the given queue.
+
+[`QueueDequeueUpTo(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QueueDequeueUpTo.md): Dequeues `n` tuples of one or more tensors from the given queue.
+
+[`QueueDequeueUpToV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QueueDequeueUpToV2.md): Dequeues `n` tuples of one or more tensors from the given queue.
+
+[`QueueDequeueV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QueueDequeueV2.md): Dequeues a tuple of one or more tensors from the given queue.
+
+[`QueueEnqueue(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QueueEnqueue.md): Enqueues a tuple of one or more tensors in the given queue.
+
+[`QueueEnqueueMany(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QueueEnqueueMany.md): Enqueues zero or more tuples of one or more tensors in the given queue.
+
+[`QueueEnqueueManyV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QueueEnqueueManyV2.md): Enqueues zero or more tuples of one or more tensors in the given queue.
+
+[`QueueEnqueueV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QueueEnqueueV2.md): Enqueues a tuple of one or more tensors in the given queue.
+
+[`QueueIsClosed(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QueueIsClosed.md): Returns true if queue is closed.
+
+[`QueueIsClosedV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QueueIsClosedV2.md): Returns true if queue is closed.
+
+[`QueueSize(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QueueSize.md): Computes the number of elements in the given queue.
+
+[`QueueSizeV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/QueueSizeV2.md): Computes the number of elements in the given queue.
+
+[`RFFT(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RFFT.md): Real-valued fast Fourier transform.
+
+[`RFFT2D(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RFFT2D.md): 2D real-valued fast Fourier transform.
+
+[`RFFT3D(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RFFT3D.md): 3D real-valued fast Fourier transform.
+
+[`RGBToHSV(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RGBToHSV.md): Converts one or more images from RGB to HSV.
+
+[`RaggedGather(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RaggedGather.md): Gather ragged slices from `params` axis `0` according to `indices`.
+
+[`RaggedRange(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RaggedRange.md): Returns a `RaggedTensor` containing the specified sequences of numbers.
+
+[`RaggedTensorFromVariant(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RaggedTensorFromVariant.md): Decodes a `variant` Tensor into a `RaggedTensor`.
+
+[`RaggedTensorToSparse(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RaggedTensorToSparse.md): Converts a `RaggedTensor` into a `SparseTensor` with the same values.
+
+[`RaggedTensorToTensor(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RaggedTensorToTensor.md): Create a dense tensor from a ragged tensor, possibly altering its shape.
+
+[`RaggedTensorToVariant(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RaggedTensorToVariant.md): Encodes a `RaggedTensor` into a `variant` Tensor.
+
+[`RandomCrop(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RandomCrop.md): Randomly crop `image`.
+
+[`RandomDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RandomDataset.md): Creates a Dataset that returns pseudorandom numbers.
+
+[`RandomGamma(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RandomGamma.md): Outputs random values from the Gamma distribution(s) described by alpha.
+
+[`RandomGammaGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RandomGammaGrad.md): Computes the derivative of a Gamma random sample w.r.t. `alpha`.
+
+[`RandomPoisson(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RandomPoisson.md): Use RandomPoissonV2 instead.
+
+[`RandomPoissonV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RandomPoissonV2.md): Outputs random values from the Poisson distribution(s) described by rate.
+
+[`RandomShuffle(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RandomShuffle.md): Randomly shuffles a tensor along its first dimension.
+
+[`RandomShuffleQueue(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RandomShuffleQueue.md): A queue that randomizes the order of elements.
+
+[`RandomShuffleQueueV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RandomShuffleQueueV2.md): A queue that randomizes the order of elements.
+
+[`RandomStandardNormal(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RandomStandardNormal.md): Outputs random values from a normal distribution.
+
+[`RandomUniform(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RandomUniform.md): Outputs random values from a uniform distribution.
+
+[`RandomUniformInt(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RandomUniformInt.md): Outputs random integers from a uniform distribution.
+
+[`Range(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Range.md): Creates a sequence of numbers.
+
+[`RangeDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RangeDataset.md): Creates a dataset with a range of values. Corresponds to python's xrange.
+
+[`Rank(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Rank.md): Returns the rank of a tensor.
+
+[`ReadFile(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ReadFile.md): Reads and outputs the entire contents of the input filename.
+
+[`ReadVariableOp(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ReadVariableOp.md): Reads the value of a variable.
+
+[`ReaderNumRecordsProduced(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ReaderNumRecordsProduced.md): Returns the number of records this Reader has produced.
+
+[`ReaderNumRecordsProducedV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ReaderNumRecordsProducedV2.md): Returns the number of records this Reader has produced.
+
+[`ReaderNumWorkUnitsCompleted(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ReaderNumWorkUnitsCompleted.md): Returns the number of work units this Reader has finished processing.
+
+[`ReaderNumWorkUnitsCompletedV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ReaderNumWorkUnitsCompletedV2.md): Returns the number of work units this Reader has finished processing.
+
+[`ReaderRead(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ReaderRead.md): Returns the next record (key, value pair) produced by a Reader.
+
+[`ReaderReadUpTo(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ReaderReadUpTo.md): Returns up to `num_records` (key, value) pairs produced by a Reader.
+
+[`ReaderReadUpToV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ReaderReadUpToV2.md): Returns up to `num_records` (key, value) pairs produced by a Reader.
+
+[`ReaderReadV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ReaderReadV2.md): Returns the next record (key, value pair) produced by a Reader.
+
+[`ReaderReset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ReaderReset.md): Restore a Reader to its initial clean state.
+
+[`ReaderResetV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ReaderResetV2.md): Restore a Reader to its initial clean state.
+
+[`ReaderRestoreState(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ReaderRestoreState.md): Restore a reader to a previously saved state.
+
+[`ReaderRestoreStateV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ReaderRestoreStateV2.md): Restore a reader to a previously saved state.
+
+[`ReaderSerializeState(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ReaderSerializeState.md): Produce a string tensor that encodes the state of a Reader.
+
+[`ReaderSerializeStateV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ReaderSerializeStateV2.md): Produce a string tensor that encodes the state of a Reader.
+
+[`Real(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Real.md): Returns the real part of a complex number.
+
+[`RealDiv(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RealDiv.md): Returns x / y element-wise for real types.
+
+[`RebatchDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RebatchDataset.md): Creates a dataset that changes the batch size.
+
+[`Reciprocal(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Reciprocal.md): Computes the reciprocal of x element-wise.
+
+[`ReciprocalGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ReciprocalGrad.md): Computes the gradient for the inverse of `x` wrt its input.
+
+[`RecordInput(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RecordInput.md): Emits randomized records.
+
+[`Recv(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Recv.md): Receives the named tensor from send_device on recv_device.
+
+[`RecvTPUEmbeddingActivations(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RecvTPUEmbeddingActivations.md): An op that receives embedding activations on the TPU.
+
+[`ReduceDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ReduceDataset.md): Reduces the input dataset to a singleton using a reduce function.
+
+[`ReduceJoin(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ReduceJoin.md): Joins a string Tensor across the given dimensions.
+
+[`RefEnter(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RefEnter.md): Creates or finds a child frame, and makes `data` available to the child frame.
+
+[`RefExit(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RefExit.md): Exits the current frame to its parent frame.
+
+[`RefIdentity(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RefIdentity.md): Return the same ref tensor as the input ref tensor.
+
+[`RefMerge(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RefMerge.md): Forwards the value of an available tensor from `inputs` to `output`.
+
+[`RefNextIteration(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RefNextIteration.md): Makes its input available to the next iteration.
+
+[`RefSelect(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RefSelect.md): Forwards the `index`th element of `inputs` to `output`.
+
+[`RefSwitch(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RefSwitch.md): Forwards the ref tensor `data` to the output port determined by `pred`.
+
+[`RegexFullMatch(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RegexFullMatch.md): Check if the input matches the regex pattern.
+
+[`RegexReplace(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RegexReplace.md): Replaces matches of the `pattern` regular expression in `input` with the
+
+[`Relu(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Relu.md): Computes rectified linear: `max(features, 0)`.
+
+[`Relu6(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Relu6.md): Computes rectified linear 6: `min(max(features, 0), 6)`.
+
+[`Relu6Grad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Relu6Grad.md): Computes rectified linear 6 gradients for a Relu6 operation.
+
+[`ReluGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ReluGrad.md): Computes rectified linear gradients for a Relu operation.
+
+[`RemoteCall(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RemoteCall.md): Runs function `f` on a remote device indicated by `target`.
+
+[`RepeatDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RepeatDataset.md): Creates a dataset that emits the outputs of `input_dataset` `count` times.
+
+[`RequantizationRange(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RequantizationRange.md): Computes a range that covers the actual values present in a quantized tensor.
+
+[`RequantizationRangePerChannel(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RequantizationRangePerChannel.md): Computes requantization range per channel.
+
+[`Requantize(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Requantize.md): Converts the quantized `input` tensor into a lower-precision `output`.
+
+[`RequantizePerChannel(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RequantizePerChannel.md): Requantizes input with min and max values known per channel.
+
+[`Reshape(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Reshape.md): Reshapes a tensor.
+
+[`ResizeArea(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResizeArea.md): Resize `images` to `size` using area interpolation.
+
+[`ResizeBicubic(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResizeBicubic.md): Resize `images` to `size` using bicubic interpolation.
+
+[`ResizeBicubicGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResizeBicubicGrad.md): Computes the gradient of bicubic interpolation.
+
+[`ResizeBilinear(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResizeBilinear.md): Resize `images` to `size` using bilinear interpolation.
+
+[`ResizeBilinearGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResizeBilinearGrad.md): Computes the gradient of bilinear interpolation.
+
+[`ResizeNearestNeighbor(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResizeNearestNeighbor.md): Resize `images` to `size` using nearest neighbor interpolation.
+
+[`ResizeNearestNeighborGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResizeNearestNeighborGrad.md): Computes the gradient of nearest neighbor interpolation.
+
+[`ResourceAccumulatorApplyGradient(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceAccumulatorApplyGradient.md): Applies a gradient to a given accumulator.
+
+[`ResourceAccumulatorNumAccumulated(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceAccumulatorNumAccumulated.md): Returns the number of gradients aggregated in the given accumulators.
+
+[`ResourceAccumulatorSetGlobalStep(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceAccumulatorSetGlobalStep.md): Updates the accumulator with a new value for global_step.
+
+[`ResourceAccumulatorTakeGradient(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceAccumulatorTakeGradient.md): Extracts the average gradient in the given ConditionalAccumulator.
+
+[`ResourceApplyAdaMax(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceApplyAdaMax.md): Update '*var' according to the AdaMax algorithm.
+
+[`ResourceApplyAdadelta(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceApplyAdadelta.md): Update '*var' according to the adadelta scheme.
+
+[`ResourceApplyAdagrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceApplyAdagrad.md): Update '*var' according to the adagrad scheme.
+
+[`ResourceApplyAdagradDA(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceApplyAdagradDA.md): Update '*var' according to the proximal adagrad scheme.
+
+[`ResourceApplyAdagradV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceApplyAdagradV2.md): Update '*var' according to the adagrad scheme.
+
+[`ResourceApplyAdam(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceApplyAdam.md): Update '*var' according to the Adam algorithm.
+
+[`ResourceApplyAdamWithAmsgrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceApplyAdamWithAmsgrad.md): Update '*var' according to the Adam algorithm.
+
+[`ResourceApplyAddSign(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceApplyAddSign.md): Update '*var' according to the AddSign update.
+
+[`ResourceApplyCenteredRMSProp(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceApplyCenteredRMSProp.md): Update '*var' according to the centered RMSProp algorithm.
+
+[`ResourceApplyFtrl(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceApplyFtrl.md): Update '*var' according to the Ftrl-proximal scheme.
+
+[`ResourceApplyFtrlV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceApplyFtrlV2.md): Update '*var' according to the Ftrl-proximal scheme.
+
+[`ResourceApplyGradientDescent(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceApplyGradientDescent.md): Update '*var' by subtracting 'alpha' * 'delta' from it.
+
+[`ResourceApplyKerasMomentum(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceApplyKerasMomentum.md): Update '*var' according to the momentum scheme.
+
+[`ResourceApplyMomentum(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceApplyMomentum.md): Update '*var' according to the momentum scheme. Set use_nesterov = True if you
+
+[`ResourceApplyPowerSign(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceApplyPowerSign.md): Update '*var' according to the AddSign update.
+
+[`ResourceApplyProximalAdagrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceApplyProximalAdagrad.md): Update '*var' and '*accum' according to FOBOS with Adagrad learning rate.
+
+[`ResourceApplyProximalGradientDescent(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceApplyProximalGradientDescent.md): Update '*var' as FOBOS algorithm with fixed learning rate.
+
+[`ResourceApplyRMSProp(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceApplyRMSProp.md): Update '*var' according to the RMSProp algorithm.
+
+[`ResourceConditionalAccumulator(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceConditionalAccumulator.md): A conditional accumulator for aggregating gradients.
+
+[`ResourceCountUpTo(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceCountUpTo.md): Increments variable pointed to by 'resource' until it reaches 'limit'.
+
+[`ResourceGather(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceGather.md): Gather slices from the variable pointed to by `resource` according to `indices`.
+
+[`ResourceGatherNd(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceGatherNd.md)
+
+[`ResourceScatterAdd(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceScatterAdd.md): Adds sparse updates to the variable referenced by `resource`.
+
+[`ResourceScatterDiv(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceScatterDiv.md): Divides sparse updates into the variable referenced by `resource`.
+
+[`ResourceScatterMax(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceScatterMax.md): Reduces sparse updates into the variable referenced by `resource` using the `max` operation.
+
+[`ResourceScatterMin(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceScatterMin.md): Reduces sparse updates into the variable referenced by `resource` using the `min` operation.
+
+[`ResourceScatterMul(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceScatterMul.md): Multiplies sparse updates into the variable referenced by `resource`.
+
+[`ResourceScatterNdAdd(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceScatterNdAdd.md): Applies sparse addition to individual values or slices in a Variable.
+
+[`ResourceScatterNdSub(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceScatterNdSub.md): Applies sparse subtraction to individual values or slices in a Variable.
+
+[`ResourceScatterNdUpdate(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceScatterNdUpdate.md): Applies sparse `updates` to individual values or slices within a given
+
+[`ResourceScatterSub(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceScatterSub.md): Subtracts sparse updates from the variable referenced by `resource`.
+
+[`ResourceScatterUpdate(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceScatterUpdate.md): Assigns sparse updates to the variable referenced by `resource`.
+
+[`ResourceSparseApplyAdadelta(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceSparseApplyAdadelta.md): var: Should be from a Variable().
+
+[`ResourceSparseApplyAdagrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceSparseApplyAdagrad.md): Update relevant entries in '*var' and '*accum' according to the adagrad scheme.
+
+[`ResourceSparseApplyAdagradDA(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceSparseApplyAdagradDA.md): Update entries in '*var' and '*accum' according to the proximal adagrad scheme.
+
+[`ResourceSparseApplyAdagradV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceSparseApplyAdagradV2.md): Update relevant entries in '*var' and '*accum' according to the adagrad scheme.
+
+[`ResourceSparseApplyCenteredRMSProp(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceSparseApplyCenteredRMSProp.md): Update '*var' according to the centered RMSProp algorithm.
+
+[`ResourceSparseApplyFtrl(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceSparseApplyFtrl.md): Update relevant entries in '*var' according to the Ftrl-proximal scheme.
+
+[`ResourceSparseApplyFtrlV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceSparseApplyFtrlV2.md): Update relevant entries in '*var' according to the Ftrl-proximal scheme.
+
+[`ResourceSparseApplyKerasMomentum(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceSparseApplyKerasMomentum.md): Update relevant entries in '*var' and '*accum' according to the momentum scheme.
+
+[`ResourceSparseApplyMomentum(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceSparseApplyMomentum.md): Update relevant entries in '*var' and '*accum' according to the momentum scheme.
+
+[`ResourceSparseApplyProximalAdagrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceSparseApplyProximalAdagrad.md): Sparse update entries in '*var' and '*accum' according to FOBOS algorithm.
+
+[`ResourceSparseApplyProximalGradientDescent(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceSparseApplyProximalGradientDescent.md): Sparse update '*var' as FOBOS algorithm with fixed learning rate.
+
+[`ResourceSparseApplyRMSProp(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceSparseApplyRMSProp.md): Update '*var' according to the RMSProp algorithm.
+
+[`ResourceStridedSliceAssign(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ResourceStridedSliceAssign.md): Assign `value` to the sliced l-value reference of `ref`.
+
+[`Restore(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Restore.md): Restores a tensor from checkpoint files.
+
+[`RestoreSlice(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RestoreSlice.md): Restores a tensor from checkpoint files.
+
+[`RestoreV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RestoreV2.md): Restores tensors from a V2 checkpoint.
+
+[`RetrieveTPUEmbeddingADAMParameters(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RetrieveTPUEmbeddingADAMParameters.md): Retrieve ADAM embedding parameters.
+
+[`RetrieveTPUEmbeddingADAMParametersGradAccumDebug(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RetrieveTPUEmbeddingADAMParametersGradAccumDebug.md): Retrieve ADAM embedding parameters with debug support.
+
+[`RetrieveTPUEmbeddingAdadeltaParameters(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RetrieveTPUEmbeddingAdadeltaParameters.md): Retrieve Adadelta embedding parameters.
+
+[`RetrieveTPUEmbeddingAdadeltaParametersGradAccumDebug(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RetrieveTPUEmbeddingAdadeltaParametersGradAccumDebug.md): Retrieve Adadelta embedding parameters with debug support.
+
+[`RetrieveTPUEmbeddingAdagradParameters(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RetrieveTPUEmbeddingAdagradParameters.md): Retrieve Adagrad embedding parameters.
+
+[`RetrieveTPUEmbeddingAdagradParametersGradAccumDebug(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RetrieveTPUEmbeddingAdagradParametersGradAccumDebug.md): Retrieve Adagrad embedding parameters with debug support.
+
+[`RetrieveTPUEmbeddingCenteredRMSPropParameters(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RetrieveTPUEmbeddingCenteredRMSPropParameters.md): Retrieve centered RMSProp embedding parameters.
+
+[`RetrieveTPUEmbeddingFTRLParameters(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RetrieveTPUEmbeddingFTRLParameters.md): Retrieve FTRL embedding parameters.
+
+[`RetrieveTPUEmbeddingFTRLParametersGradAccumDebug(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RetrieveTPUEmbeddingFTRLParametersGradAccumDebug.md): Retrieve FTRL embedding parameters with debug support.
+
+[`RetrieveTPUEmbeddingMDLAdagradLightParameters(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RetrieveTPUEmbeddingMDLAdagradLightParameters.md): Retrieve MDL Adagrad Light embedding parameters.
+
+[`RetrieveTPUEmbeddingMomentumParameters(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RetrieveTPUEmbeddingMomentumParameters.md): Retrieve Momentum embedding parameters.
+
+[`RetrieveTPUEmbeddingMomentumParametersGradAccumDebug(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RetrieveTPUEmbeddingMomentumParametersGradAccumDebug.md): Retrieve Momentum embedding parameters with debug support.
+
+[`RetrieveTPUEmbeddingProximalAdagradParameters(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RetrieveTPUEmbeddingProximalAdagradParameters.md): Retrieve proximal Adagrad embedding parameters.
+
+[`RetrieveTPUEmbeddingProximalAdagradParametersGradAccumDebug(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RetrieveTPUEmbeddingProximalAdagradParametersGradAccumDebug.md): Retrieve proximal Adagrad embedding parameters with debug support.
+
+[`RetrieveTPUEmbeddingRMSPropParameters(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RetrieveTPUEmbeddingRMSPropParameters.md): Retrieve RMSProp embedding parameters.
+
+[`RetrieveTPUEmbeddingRMSPropParametersGradAccumDebug(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RetrieveTPUEmbeddingRMSPropParametersGradAccumDebug.md): Retrieve RMSProp embedding parameters with debug support.
+
+[`RetrieveTPUEmbeddingStochasticGradientDescentParameters(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RetrieveTPUEmbeddingStochasticGradientDescentParameters.md): Retrieve SGD embedding parameters.
+
+[`Reverse(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Reverse.md): Reverses specific dimensions of a tensor.
+
+[`ReverseSequence(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ReverseSequence.md): Reverses variable length slices.
+
+[`ReverseV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ReverseV2.md): Reverses specific dimensions of a tensor.
+
+[`RightShift(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RightShift.md): Elementwise computes the bitwise right-shift of `x` and `y`.
+
+[`Rint(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Rint.md): Returns element-wise integer closest to x.
+
+[`RngSkip(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RngSkip.md): Advance the counter of a counter-based RNG.
+
+[`Roll(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Roll.md): Rolls the elements of a tensor along an axis.
+
+[`Round(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Round.md): Rounds the values of a tensor to the nearest integer, element-wise.
+
+[`Rsqrt(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Rsqrt.md): Computes reciprocal of square root of x element-wise.
+
+[`RsqrtGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/RsqrtGrad.md): Computes the gradient for the rsqrt of `x` wrt its input.
+
+[`SampleDistortedBoundingBox(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SampleDistortedBoundingBox.md): Generate a single randomly distorted bounding box for an image.
+
+[`SampleDistortedBoundingBoxV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SampleDistortedBoundingBoxV2.md): Generate a single randomly distorted bounding box for an image.
+
+[`SamplingDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SamplingDataset.md): Creates a dataset that takes a Bernoulli sample of the contents of another dataset.
+
+[`Save(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Save.md): Saves the input tensors to disk.
+
+[`SaveSlices(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SaveSlices.md): Saves input tensors slices to disk.
+
+[`SaveV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SaveV2.md): Saves tensors in V2 checkpoint format.
+
+[`ScalarSummary(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ScalarSummary.md): Outputs a `Summary` protocol buffer with scalar values.
+
+[`ScaleAndTranslate(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ScaleAndTranslate.md)
+
+[`ScaleAndTranslateGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ScaleAndTranslateGrad.md)
+
+[`ScanDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ScanDataset.md): Creates a dataset successively reduces `f` over the elements of `input_dataset`.
+
+[`ScatterAdd(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ScatterAdd.md): Adds sparse updates to a variable reference.
+
+[`ScatterDiv(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ScatterDiv.md): Divides a variable reference by sparse updates.
+
+[`ScatterMax(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ScatterMax.md): Reduces sparse updates into a variable reference using the `max` operation.
+
+[`ScatterMin(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ScatterMin.md): Reduces sparse updates into a variable reference using the `min` operation.
+
+[`ScatterMul(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ScatterMul.md): Multiplies sparse updates into a variable reference.
+
+[`ScatterNd(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ScatterNd.md): Scatter `updates` into a new tensor according to `indices`.
+
+[`ScatterNdAdd(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ScatterNdAdd.md): Applies sparse addition to individual values or slices in a Variable.
+
+[`ScatterNdNonAliasingAdd(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ScatterNdNonAliasingAdd.md): Applies sparse addition to `input` using individual values or slices
+
+[`ScatterNdSub(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ScatterNdSub.md): Applies sparse subtraction to individual values or slices in a Variable.
+
+[`ScatterNdUpdate(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ScatterNdUpdate.md): Applies sparse `updates` to individual values or slices within a given
+
+[`ScatterSub(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ScatterSub.md): Subtracts sparse updates to a variable reference.
+
+[`ScatterUpdate(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ScatterUpdate.md): Applies sparse updates to a variable reference.
+
+[`SdcaFprint(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SdcaFprint.md): Computes fingerprints of the input strings.
+
+[`SdcaOptimizer(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SdcaOptimizer.md): Distributed version of Stochastic Dual Coordinate Ascent (SDCA) optimizer for
+
+[`SdcaOptimizerV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SdcaOptimizerV2.md): Distributed version of Stochastic Dual Coordinate Ascent (SDCA) optimizer for
+
+[`SdcaShrinkL1(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SdcaShrinkL1.md): Applies L1 regularization shrink step on the parameters.
+
+[`SegmentMax(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SegmentMax.md): Computes the maximum along segments of a tensor.
+
+[`SegmentMean(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SegmentMean.md): Computes the mean along segments of a tensor.
+
+[`SegmentMin(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SegmentMin.md): Computes the minimum along segments of a tensor.
+
+[`SegmentProd(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SegmentProd.md): Computes the product along segments of a tensor.
+
+[`SegmentSum(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SegmentSum.md): Computes the sum along segments of a tensor.
+
+[`Select(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Select.md): Selects elements from `x` or `y`, depending on `condition`.
+
+[`SelectV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SelectV2.md)
+
+[`SelfAdjointEig(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SelfAdjointEig.md): Computes the Eigen Decomposition of a batch of square self-adjoint matrices.
+
+[`SelfAdjointEigV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SelfAdjointEigV2.md): Computes the eigen decomposition of one or more square self-adjoint matrices.
+
+[`Selu(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Selu.md): Computes scaled exponential linear: `scale * alpha * (exp(features) - 1)`
+
+[`SeluGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SeluGrad.md): Computes gradients for the scaled exponential linear (Selu) operation.
+
+[`Send(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Send.md): Sends the named tensor from send_device to recv_device.
+
+[`SendTPUEmbeddingGradients(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SendTPUEmbeddingGradients.md): Performs gradient updates of embedding tables.
+
+[`SerializeIterator(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SerializeIterator.md): Converts the given `resource_handle` representing an iterator to a variant tensor.
+
+[`SerializeManySparse(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SerializeManySparse.md): Serialize an `N`-minibatch `SparseTensor` into an `[N, 3]` `Tensor` object.
+
+[`SerializeSparse(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SerializeSparse.md): Serialize a `SparseTensor` into a `[3]` `Tensor` object.
+
+[`SerializeTensor(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SerializeTensor.md): Transforms a Tensor into a serialized TensorProto proto.
+
+[`SetSize(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SetSize.md): Number of unique elements along last dimension of input `set`.
+
+[`SetStatsAggregatorDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SetStatsAggregatorDataset.md)
+
+[`Shape(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Shape.md): Returns the shape of a tensor.
+
+[`ShapeN(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ShapeN.md): Returns shape of tensors.
+
+[`ShardDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ShardDataset.md): Creates a `Dataset` that includes only 1/`num_shards` of this dataset.
+
+[`ShardedFilename(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ShardedFilename.md): Generate a sharded filename. The filename is printf formatted as
+
+[`ShardedFilespec(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ShardedFilespec.md): Generate a glob pattern matching all sharded file names.
+
+[`ShuffleAndRepeatDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ShuffleAndRepeatDataset.md): Creates a dataset that shuffles and repeats elements from `input_dataset`
+
+[`ShuffleDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ShuffleDataset.md): Creates a dataset that shuffles elements from `input_dataset` pseudorandomly.
+
+[`ShuffleDatasetV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ShuffleDatasetV2.md)
+
+[`ShutdownDistributedTPU(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ShutdownDistributedTPU.md): Shuts down a running distributed TPU system.
+
+[`Sigmoid(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Sigmoid.md): Computes sigmoid of `x` element-wise.
+
+[`SigmoidGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SigmoidGrad.md): Computes the gradient of the sigmoid of `x` wrt its input.
+
+[`Sign(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Sign.md): Returns an element-wise indication of the sign of a number.
+
+[`Sin(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Sin.md): Computes sine of x element-wise.
+
+[`Sinh(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Sinh.md): Computes hyperbolic sine of x element-wise.
+
+[`Size(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Size.md): Returns the size of a tensor.
+
+[`SkipDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SkipDataset.md): Creates a dataset that skips `count` elements from the `input_dataset`.
+
+[`SleepDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SleepDataset.md)
+
+[`Slice(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Slice.md): Return a slice from 'input'.
+
+[`SlidingWindowDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SlidingWindowDataset.md): Creates a dataset that passes a sliding window over `input_dataset`.
+
+[`Snapshot(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Snapshot.md): Returns a copy of the input tensor.
+
+[`SnapshotDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SnapshotDataset.md): Creates a dataset that will write to / read from a snapshot.
+
+[`SobolSample(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SobolSample.md): Generates points from the Sobol sequence.
+
+[`Softmax(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Softmax.md): Computes softmax activations.
+
+[`SoftmaxCrossEntropyWithLogits(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SoftmaxCrossEntropyWithLogits.md): Computes softmax cross entropy cost and gradients to backpropagate.
+
+[`Softplus(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Softplus.md): Computes softplus: `log(exp(features) + 1)`.
+
+[`SoftplusGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SoftplusGrad.md): Computes softplus gradients for a softplus operation.
+
+[`Softsign(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Softsign.md): Computes softsign: `features / (abs(features) + 1)`.
+
+[`SoftsignGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SoftsignGrad.md): Computes softsign gradients for a softsign operation.
+
+[`SpaceToBatch(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SpaceToBatch.md): SpaceToBatch for 4-D tensors of type T.
+
+[`SpaceToBatchND(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SpaceToBatchND.md): SpaceToBatch for N-D tensors of type T.
+
+[`SpaceToDepth(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SpaceToDepth.md): SpaceToDepth for tensors of type T.
+
+[`SparseAccumulatorApplyGradient(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseAccumulatorApplyGradient.md): Applies a sparse gradient to a given accumulator.
+
+[`SparseAccumulatorTakeGradient(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseAccumulatorTakeGradient.md): Extracts the average sparse gradient in a SparseConditionalAccumulator.
+
+[`SparseAdd(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseAdd.md): Adds two `SparseTensor` objects to produce another `SparseTensor`.
+
+[`SparseAddGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseAddGrad.md): The gradient operator for the SparseAdd op.
+
+[`SparseApplyAdadelta(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseApplyAdadelta.md): var: Should be from a Variable().
+
+[`SparseApplyAdagrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseApplyAdagrad.md): Update relevant entries in '*var' and '*accum' according to the adagrad scheme.
+
+[`SparseApplyAdagradDA(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseApplyAdagradDA.md): Update entries in '*var' and '*accum' according to the proximal adagrad scheme.
+
+[`SparseApplyAdagradV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseApplyAdagradV2.md): Update relevant entries in '*var' and '*accum' according to the adagrad scheme.
+
+[`SparseApplyCenteredRMSProp(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseApplyCenteredRMSProp.md): Update '*var' according to the centered RMSProp algorithm.
+
+[`SparseApplyFtrl(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseApplyFtrl.md): Update relevant entries in '*var' according to the Ftrl-proximal scheme.
+
+[`SparseApplyFtrlV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseApplyFtrlV2.md): Update relevant entries in '*var' according to the Ftrl-proximal scheme.
+
+[`SparseApplyMomentum(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseApplyMomentum.md): Update relevant entries in '*var' and '*accum' according to the momentum scheme.
+
+[`SparseApplyProximalAdagrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseApplyProximalAdagrad.md): Sparse update entries in '*var' and '*accum' according to FOBOS algorithm.
+
+[`SparseApplyProximalGradientDescent(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseApplyProximalGradientDescent.md): Sparse update '*var' as FOBOS algorithm with fixed learning rate.
+
+[`SparseApplyRMSProp(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseApplyRMSProp.md): Update '*var' according to the RMSProp algorithm.
+
+[`SparseConcat(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseConcat.md): Concatenates a list of `SparseTensor` along the specified dimension.
+
+[`SparseConditionalAccumulator(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseConditionalAccumulator.md): A conditional accumulator for aggregating sparse gradients.
+
+[`SparseCross(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseCross.md): Generates sparse cross from a list of sparse and dense tensors.
+
+[`SparseDenseCwiseAdd(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseDenseCwiseAdd.md): Adds up a SparseTensor and a dense Tensor, using these special rules:
+
+[`SparseDenseCwiseDiv(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseDenseCwiseDiv.md): Component-wise divides a SparseTensor by a dense Tensor.
+
+[`SparseDenseCwiseMul(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseDenseCwiseMul.md): Component-wise multiplies a SparseTensor by a dense Tensor.
+
+[`SparseFillEmptyRows(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseFillEmptyRows.md): Fills empty rows in the input 2-D `SparseTensor` with a default value.
+
+[`SparseFillEmptyRowsGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseFillEmptyRowsGrad.md): The gradient of SparseFillEmptyRows.
+
+[`SparseMatMul(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseMatMul.md): Multiply matrix "a" by matrix "b".
+
+[`SparseMatrixAdd(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseMatrixAdd.md): Sparse addition of two CSR matrices, C = alpha * A + beta * B.
+
+[`SparseMatrixMatMul(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseMatrixMatMul.md): Matrix-multiplies a sparse matrix with a dense matrix.
+
+[`SparseMatrixMul(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseMatrixMul.md): Element-wise multiplication of a sparse matrix with a dense tensor.
+
+[`SparseMatrixNNZ(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseMatrixNNZ.md): Returns the number of nonzeroes of `sparse_matrix`.
+
+[`SparseMatrixOrderingAMD(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseMatrixOrderingAMD.md): Computes the Approximate Minimum Degree (AMD) ordering of `input`.
+
+[`SparseMatrixSoftmax(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseMatrixSoftmax.md): Calculates the softmax of a CSRSparseMatrix.
+
+[`SparseMatrixSoftmaxGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseMatrixSoftmaxGrad.md): Calculates the gradient of the SparseMatrixSoftmax op.
+
+[`SparseMatrixSparseCholesky(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseMatrixSparseCholesky.md): Computes the sparse Cholesky decomposition of `input`.
+
+[`SparseMatrixSparseMatMul(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseMatrixSparseMatMul.md): Sparse-matrix-multiplies two CSR matrices `a` and `b`.
+
+[`SparseMatrixTranspose(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseMatrixTranspose.md): Transposes the inner (matrix) dimensions of a CSRSparseMatrix.
+
+[`SparseMatrixZeros(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseMatrixZeros.md): Creates an all-zeros CSRSparseMatrix with shape `dense_shape`.
+
+[`SparseReduceMax(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseReduceMax.md): Computes the max of elements across dimensions of a SparseTensor.
+
+[`SparseReduceMaxSparse(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseReduceMaxSparse.md): Computes the max of elements across dimensions of a SparseTensor.
+
+[`SparseReduceSum(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseReduceSum.md): Computes the sum of elements across dimensions of a SparseTensor.
+
+[`SparseReduceSumSparse(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseReduceSumSparse.md): Computes the sum of elements across dimensions of a SparseTensor.
+
+[`SparseReorder(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseReorder.md): Reorders a SparseTensor into the canonical, row-major ordering.
+
+[`SparseReshape(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseReshape.md): Reshapes a SparseTensor to represent values in a new dense shape.
+
+[`SparseSegmentMean(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseSegmentMean.md): Computes the mean along sparse segments of a tensor.
+
+[`SparseSegmentMeanGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseSegmentMeanGrad.md): Computes gradients for SparseSegmentMean.
+
+[`SparseSegmentMeanWithNumSegments(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseSegmentMeanWithNumSegments.md): Computes the mean along sparse segments of a tensor.
+
+[`SparseSegmentSqrtN(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseSegmentSqrtN.md): Computes the sum along sparse segments of a tensor divided by the sqrt of N.
+
+[`SparseSegmentSqrtNGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseSegmentSqrtNGrad.md): Computes gradients for SparseSegmentSqrtN.
+
+[`SparseSegmentSqrtNWithNumSegments(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseSegmentSqrtNWithNumSegments.md): Computes the sum along sparse segments of a tensor divided by the sqrt of N.
+
+[`SparseSegmentSum(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseSegmentSum.md): Computes the sum along sparse segments of a tensor.
+
+[`SparseSegmentSumWithNumSegments(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseSegmentSumWithNumSegments.md): Computes the sum along sparse segments of a tensor.
+
+[`SparseSlice(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseSlice.md): Slice a `SparseTensor` based on the `start` and `size`.
+
+[`SparseSliceGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseSliceGrad.md): The gradient operator for the SparseSlice op.
+
+[`SparseSoftmax(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseSoftmax.md): Applies softmax to a batched N-D `SparseTensor`.
+
+[`SparseSoftmaxCrossEntropyWithLogits(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseSoftmaxCrossEntropyWithLogits.md): Computes softmax cross entropy cost and gradients to backpropagate.
+
+[`SparseSparseMaximum(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseSparseMaximum.md): Returns the element-wise max of two SparseTensors.
+
+[`SparseSparseMinimum(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseSparseMinimum.md): Returns the element-wise min of two SparseTensors.
+
+[`SparseSplit(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseSplit.md): Split a `SparseTensor` into `num_split` tensors along one dimension.
+
+[`SparseTensorDenseAdd(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseTensorDenseAdd.md): Adds up a `SparseTensor` and a dense `Tensor`, producing a dense `Tensor`.
+
+[`SparseTensorDenseMatMul(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseTensorDenseMatMul.md): Multiply SparseTensor (of rank 2) "A" by dense matrix "B".
+
+[`SparseTensorSliceDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseTensorSliceDataset.md): Creates a dataset that splits a SparseTensor into elements row-wise.
+
+[`SparseTensorToCSRSparseMatrix(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseTensorToCSRSparseMatrix.md): Converts a SparseTensor to a (possibly batched) CSRSparseMatrix.
+
+[`SparseToDense(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseToDense.md): Converts a sparse representation into a dense tensor.
+
+[`SparseToSparseSetOperation(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SparseToSparseSetOperation.md): Applies set operation along last dimension of 2 `SparseTensor` inputs.
+
+[`Spence(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Spence.md)
+
+[`Split(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Split.md): Splits a tensor into `num_split` tensors along one dimension.
+
+[`SplitV(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SplitV.md): Splits a tensor into `num_split` tensors along one dimension.
+
+[`SqlDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SqlDataset.md): Creates a dataset that executes a SQL query and emits rows of the result set.
+
+[`Sqrt(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Sqrt.md): Computes square root of x element-wise.
+
+[`SqrtGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SqrtGrad.md): Computes the gradient for the sqrt of `x` wrt its input.
+
+[`Square(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Square.md): Computes square of x element-wise.
+
+[`SquaredDifference(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SquaredDifference.md): Returns (x - y)(x - y) element-wise.
+
+[`Squeeze(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Squeeze.md): Removes dimensions of size 1 from the shape of a tensor.
+
+[`Stack(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Stack.md): Deprecated, use StackV2.
+
+[`StackClose(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StackClose.md): Deprecated, use StackCloseV2.
+
+[`StackCloseV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StackCloseV2.md): Delete the stack from its resource container.
+
+[`StackPop(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StackPop.md): Deprecated, use StackPopV2.
+
+[`StackPopV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StackPopV2.md): Pop the element at the top of the stack.
+
+[`StackPush(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StackPush.md): Deprecated, use StackPushV2.
+
+[`StackPushV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StackPushV2.md): Push an element onto the stack.
+
+[`StackV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StackV2.md): A stack that produces elements in first-in last-out order.
+
+[`Stage(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Stage.md): Stage values similar to a lightweight Enqueue.
+
+[`StageClear(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StageClear.md): Op removes all elements in the underlying container.
+
+[`StagePeek(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StagePeek.md): Op peeks at the values at the specified index. If the
+
+[`StageSize(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StageSize.md): Op returns the number of elements in the underlying container.
+
+[`StatefulPartitionedCall(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StatefulPartitionedCall.md): returns `f(inputs)`, where `f`'s body is placed and partitioned.
+
+[`StatefulRandomBinomial(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StatefulRandomBinomial.md)
+
+[`StatefulStandardNormal(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StatefulStandardNormal.md): Outputs random values from a normal distribution. This op is deprecated in favor of op 'StatefulStandardNormalV2'
+
+[`StatefulStandardNormalV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StatefulStandardNormalV2.md): Outputs random values from a normal distribution.
+
+[`StatefulTruncatedNormal(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StatefulTruncatedNormal.md): Outputs random values from a truncated normal distribution.
+
+[`StatefulUniform(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StatefulUniform.md): Outputs random values from a uniform distribution.
+
+[`StatefulUniformFullInt(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StatefulUniformFullInt.md): Outputs random integers from a uniform distribution.
+
+[`StatefulUniformInt(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StatefulUniformInt.md): Outputs random integers from a uniform distribution.
+
+[`StatelessIf(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StatelessIf.md): output = cond ? then_branch(input) : else_branch(input)
+
+[`StatelessMultinomial(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StatelessMultinomial.md): Draws samples from a multinomial distribution.
+
+[`StatelessRandomBinomial(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StatelessRandomBinomial.md): Outputs deterministic pseudorandom random numbers from a binomial distribution.
+
+[`StatelessRandomGammaV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StatelessRandomGammaV2.md): Outputs deterministic pseudorandom random numbers from a gamma distribution.
+
+[`StatelessRandomNormal(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StatelessRandomNormal.md): Outputs deterministic pseudorandom values from a normal distribution.
+
+[`StatelessRandomPoisson(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StatelessRandomPoisson.md): Outputs deterministic pseudorandom random numbers from a Poisson distribution.
+
+[`StatelessRandomUniform(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StatelessRandomUniform.md): Outputs deterministic pseudorandom random values from a uniform distribution.
+
+[`StatelessRandomUniformFullInt(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StatelessRandomUniformFullInt.md): Outputs deterministic pseudorandom random integers from a uniform distribution.
+
+[`StatelessRandomUniformInt(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StatelessRandomUniformInt.md): Outputs deterministic pseudorandom random integers from a uniform distribution.
+
+[`StatelessTruncatedNormal(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StatelessTruncatedNormal.md): Outputs deterministic pseudorandom values from a truncated normal distribution.
+
+[`StatelessWhile(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StatelessWhile.md): output = input; While (Cond(output)) { output = Body(output) }
+
+[`StaticRegexFullMatch(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StaticRegexFullMatch.md): Check if the input matches the regex pattern.
+
+[`StaticRegexReplace(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StaticRegexReplace.md): Replaces the match of pattern in input with rewrite.
+
+[`StatsAggregatorHandle(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StatsAggregatorHandle.md): Creates a statistics manager resource.
+
+[`StatsAggregatorHandleV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StatsAggregatorHandleV2.md)
+
+[`StatsAggregatorSetSummaryWriter(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StatsAggregatorSetSummaryWriter.md): Set a summary_writer_interface to record statistics using given stats_aggregator.
+
+[`StatsAggregatorSummary(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StatsAggregatorSummary.md): Produces a summary of any statistics recorded by the given statistics manager.
+
+[`StopGradient(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StopGradient.md): Stops gradient computation.
+
+[`StridedSlice(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StridedSlice.md): Return a strided slice from `input`.
+
+[`StridedSliceAssign(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StridedSliceAssign.md): Assign `value` to the sliced l-value reference of `ref`.
+
+[`StridedSliceGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StridedSliceGrad.md): Returns the gradient of `StridedSlice`.
+
+[`StringFormat(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StringFormat.md): Formats a string template using a list of tensors.
+
+[`StringJoin(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StringJoin.md): Joins the strings in the given list of string tensors into one tensor;
+
+[`StringLength(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StringLength.md): String lengths of `input`.
+
+[`StringLower(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StringLower.md): Converts all uppercase characters into their respective lowercase replacements.
+
+[`StringNGrams(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StringNGrams.md): Creates ngrams from ragged string data.
+
+[`StringSplit(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StringSplit.md): Split elements of `input` based on `delimiter` into a `SparseTensor`.
+
+[`StringSplitV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StringSplitV2.md): Split elements of `source` based on `sep` into a `SparseTensor`.
+
+[`StringStrip(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StringStrip.md): Strip leading and trailing whitespaces from the Tensor.
+
+[`StringToHashBucket(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StringToHashBucket.md): Converts each string in the input Tensor to its hash mod by a number of buckets.
+
+[`StringToHashBucketFast(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StringToHashBucketFast.md): Converts each string in the input Tensor to its hash mod by a number of buckets.
+
+[`StringToHashBucketStrong(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StringToHashBucketStrong.md): Converts each string in the input Tensor to its hash mod by a number of buckets.
+
+[`StringToNumber(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StringToNumber.md): Converts each string in the input Tensor to the specified numeric type.
+
+[`StringUpper(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/StringUpper.md): Converts all lowercase characters into their respective uppercase replacements.
+
+[`Sub(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Sub.md): Returns x - y element-wise.
+
+[`Substr(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Substr.md): Return substrings from `Tensor` of strings.
+
+[`Sum(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Sum.md): Computes the sum of elements across dimensions of a tensor.
+
+[`SummaryWriter(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SummaryWriter.md)
+
+[`Svd(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Svd.md): Computes the singular value decompositions of one or more matrices.
+
+[`Switch(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Switch.md): Forwards `data` to the output port determined by `pred`.
+
+[`SymbolicGradient(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/SymbolicGradient.md): Computes the gradient function for function f via backpropagation.
+
+[`TFRecordDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TFRecordDataset.md): Creates a dataset that emits the records from one or more TFRecord files.
+
+[`TFRecordReader(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TFRecordReader.md): A Reader that outputs the records from a TensorFlow Records file.
+
+[`TFRecordReaderV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TFRecordReaderV2.md): A Reader that outputs the records from a TensorFlow Records file.
+
+[`TPUCompilationResult(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TPUCompilationResult.md): Returns the result of a TPU compilation.
+
+[`TPUEmbeddingActivations(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TPUEmbeddingActivations.md): An op enabling differentiation of TPU Embeddings.
+
+[`TPUOrdinalSelector(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TPUOrdinalSelector.md): A TPU core selector Op.
+
+[`TPUPartitionedCall(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TPUPartitionedCall.md): Calls a function placed on a specified TPU device.
+
+[`TPUReplicateMetadata(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TPUReplicateMetadata.md): Metadata indicating how the TPU computation should be replicated.
+
+[`TPUReplicatedInput(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TPUReplicatedInput.md): Connects N inputs to an N-way replicated TPU computation.
+
+[`TPUReplicatedOutput(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TPUReplicatedOutput.md): Connects N outputs from an N-way replicated TPU computation.
+
+[`TakeDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TakeDataset.md): Creates a dataset that contains `count` elements from the `input_dataset`.
+
+[`TakeManySparseFromTensorsMap(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TakeManySparseFromTensorsMap.md): Read `SparseTensors` from a `SparseTensorsMap` and concatenate them.
+
+[`TakeWhileDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TakeWhileDataset.md): Creates a dataset that stops iteration when predicate` is false.
+
+[`Tan(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Tan.md): Computes tan of x element-wise.
+
+[`Tanh(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Tanh.md): Computes hyperbolic tangent of `x` element-wise.
+
+[`TanhGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TanhGrad.md): Computes the gradient for the tanh of `x` wrt its input.
+
+[`TemporaryVariable(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TemporaryVariable.md): Returns a tensor that may be mutated, but only persists within a single step.
+
+[`TensorArray(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorArray.md)
+
+[`TensorArrayClose(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorArrayClose.md)
+
+[`TensorArrayCloseV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorArrayCloseV2.md): Deprecated. Use TensorArrayCloseV3
+
+[`TensorArrayCloseV3(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorArrayCloseV3.md): Delete the TensorArray from its resource container.
+
+[`TensorArrayConcat(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorArrayConcat.md)
+
+[`TensorArrayConcatV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorArrayConcatV2.md): Deprecated. Use TensorArrayConcatV3
+
+[`TensorArrayConcatV3(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorArrayConcatV3.md): Concat the elements from the TensorArray into value `value`.
+
+[`TensorArrayGather(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorArrayGather.md)
+
+[`TensorArrayGatherV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorArrayGatherV2.md): Deprecated. Use TensorArrayGatherV3
+
+[`TensorArrayGatherV3(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorArrayGatherV3.md): Gather specific elements from the TensorArray into output `value`.
+
+[`TensorArrayGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorArrayGrad.md)
+
+[`TensorArrayGradV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorArrayGradV2.md): Deprecated. Use TensorArrayGradV3
+
+[`TensorArrayGradV3(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorArrayGradV3.md): Creates a TensorArray for storing the gradients of values in the given handle.
+
+[`TensorArrayGradWithShape(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorArrayGradWithShape.md): Creates a TensorArray for storing multiple gradients of values in the given handle.
+
+[`TensorArrayPack(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorArrayPack.md)
+
+[`TensorArrayRead(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorArrayRead.md)
+
+[`TensorArrayReadV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorArrayReadV2.md): Deprecated. Use TensorArrayReadV3
+
+[`TensorArrayReadV3(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorArrayReadV3.md): Read an element from the TensorArray into output `value`.
+
+[`TensorArrayScatter(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorArrayScatter.md)
+
+[`TensorArrayScatterV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorArrayScatterV2.md): Deprecated. Use TensorArrayScatterV3
+
+[`TensorArrayScatterV3(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorArrayScatterV3.md): Scatter the data from the input value into specific TensorArray elements.
+
+[`TensorArraySize(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorArraySize.md)
+
+[`TensorArraySizeV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorArraySizeV2.md): Deprecated. Use TensorArraySizeV3
+
+[`TensorArraySizeV3(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorArraySizeV3.md): Get the current size of the TensorArray.
+
+[`TensorArraySplit(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorArraySplit.md)
+
+[`TensorArraySplitV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorArraySplitV2.md): Deprecated. Use TensorArraySplitV3
+
+[`TensorArraySplitV3(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorArraySplitV3.md): Split the data from the input value into TensorArray elements.
+
+[`TensorArrayUnpack(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorArrayUnpack.md)
+
+[`TensorArrayV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorArrayV2.md): Deprecated. Use TensorArrayV3
+
+[`TensorArrayV3(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorArrayV3.md): An array of Tensors of given size.
+
+[`TensorArrayWrite(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorArrayWrite.md)
+
+[`TensorArrayWriteV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorArrayWriteV2.md): Deprecated. Use TensorArrayGradV3
+
+[`TensorArrayWriteV3(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorArrayWriteV3.md): Push an element onto the tensor_array.
+
+[`TensorDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorDataset.md): Creates a dataset that emits `components` as a tuple of tensors once.
+
+[`TensorListConcat(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorListConcat.md): Concats all tensors in the list along the 0th dimension.
+
+[`TensorListConcatLists(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorListConcatLists.md)
+
+[`TensorListConcatV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorListConcatV2.md): Concats all tensors in the list along the 0th dimension.
+
+[`TensorListElementShape(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorListElementShape.md): The shape of the elements of the given list, as a tensor.
+
+[`TensorListFromTensor(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorListFromTensor.md): Creates a TensorList which, when stacked, has the value of `tensor`.
+
+[`TensorListGather(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorListGather.md): Creates a Tensor by indexing into the TensorList.
+
+[`TensorListGetItem(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorListGetItem.md): Returns the item in the list with the given index.
+
+[`TensorListLength(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorListLength.md): Returns the number of tensors in the input tensor list.
+
+[`TensorListPopBack(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorListPopBack.md): Returns the last element of the input list as well as a list with all but that element.
+
+[`TensorListPushBack(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorListPushBack.md): Returns a list which has the passed-in `Tensor` as last element and the other elements of the given list in `input_handle`.
+
+[`TensorListPushBackBatch(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorListPushBackBatch.md)
+
+[`TensorListReserve(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorListReserve.md): List of the given size with empty elements.
+
+[`TensorListResize(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorListResize.md): Resizes the list.
+
+[`TensorListScatter(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorListScatter.md): Creates a TensorList by indexing into a Tensor.
+
+[`TensorListScatterIntoExistingList(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorListScatterIntoExistingList.md): Scatters tensor at indices in an input list.
+
+[`TensorListScatterV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorListScatterV2.md): Creates a TensorList by indexing into a Tensor.
+
+[`TensorListSetItem(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorListSetItem.md): Sets the index-th position of the list to contain the given tensor.
+
+[`TensorListSplit(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorListSplit.md): Splits a tensor into a list.
+
+[`TensorListStack(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorListStack.md): Stacks all tensors in the list.
+
+[`TensorScatterAdd(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorScatterAdd.md): Adds sparse `updates` to an existing tensor according to `indices`.
+
+[`TensorScatterSub(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorScatterSub.md): Subtracts sparse `updates` from an existing tensor according to `indices`.
+
+[`TensorScatterUpdate(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorScatterUpdate.md): Scatter `updates` into an existing tensor according to `indices`.
+
+[`TensorSliceDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorSliceDataset.md): Creates a dataset that emits each dim-0 slice of `components` once.
+
+[`TensorStridedSliceUpdate(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorStridedSliceUpdate.md): Assign `value` to the sliced l-value reference of `input`.
+
+[`TensorSummary(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorSummary.md): Outputs a `Summary` protocol buffer with a tensor.
+
+[`TensorSummaryV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TensorSummaryV2.md): Outputs a `Summary` protocol buffer with a tensor and per-plugin data.
+
+[`TextLineDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TextLineDataset.md): Creates a dataset that emits the lines of one or more text files.
+
+[`TextLineReader(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TextLineReader.md): A Reader that outputs the lines of a file delimited by '\n'.
+
+[`TextLineReaderV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TextLineReaderV2.md): A Reader that outputs the lines of a file delimited by '\n'.
+
+[`ThreadPoolDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ThreadPoolDataset.md): Creates a dataset that uses a custom thread pool to compute `input_dataset`.
+
+[`ThreadPoolHandle(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ThreadPoolHandle.md): Creates a dataset that uses a custom thread pool to compute `input_dataset`.
+
+[`ThreadUnsafeUnigramCandidateSampler(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ThreadUnsafeUnigramCandidateSampler.md): Generates labels for candidate sampling with a learned unigram distribution.
+
+[`Tile(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Tile.md): Constructs a tensor by tiling a given tensor.
+
+[`TileGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TileGrad.md): Returns the gradient of `Tile`.
+
+[`Timestamp(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Timestamp.md): Provides the time since epoch in seconds.
+
+[`ToBool(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ToBool.md): Converts a tensor to a scalar predicate.
+
+[`TopK(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TopK.md): Finds values and indices of the `k` largest elements for the last dimension.
+
+[`TopKV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TopKV2.md): Finds values and indices of the `k` largest elements for the last dimension.
+
+[`Transpose(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Transpose.md): Shuffle dimensions of x according to a permutation.
+
+[`TridiagonalMatMul(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TridiagonalMatMul.md): Calculate product with tridiagonal matrix.
+
+[`TridiagonalSolve(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TridiagonalSolve.md): Solves tridiagonal systems of equations.
+
+[`TruncateDiv(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TruncateDiv.md): Returns x / y element-wise for integer types.
+
+[`TruncateMod(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TruncateMod.md): Returns element-wise remainder of division. This emulates C semantics in that
+
+[`TruncatedNormal(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/TruncatedNormal.md): Outputs random values from a truncated normal distribution.
+
+[`Unbatch(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Unbatch.md): Reverses the operation of Batch for a single output Tensor.
+
+[`UnbatchDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/UnbatchDataset.md): A dataset that splits the elements of its input into multiple elements.
+
+[`UnbatchGrad(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/UnbatchGrad.md): Gradient of Unbatch.
+
+[`UnicodeDecode(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/UnicodeDecode.md): Decodes each string in `input` into a sequence of Unicode code points.
+
+[`UnicodeDecodeWithOffsets(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/UnicodeDecodeWithOffsets.md): Decodes each string in `input` into a sequence of Unicode code points.
+
+[`UnicodeEncode(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/UnicodeEncode.md): Encode a tensor of ints into unicode strings.
+
+[`UnicodeScript(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/UnicodeScript.md): Determine the script codes of a given tensor of Unicode integer code points.
+
+[`UnicodeTranscode(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/UnicodeTranscode.md): Transcode the input text from a source encoding to a destination encoding.
+
+[`UniformCandidateSampler(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/UniformCandidateSampler.md): Generates labels for candidate sampling with a uniform distribution.
+
+[`Unique(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Unique.md): Finds unique elements in a 1-D tensor.
+
+[`UniqueDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/UniqueDataset.md): Creates a dataset that contains the unique elements of `input_dataset`.
+
+[`UniqueV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/UniqueV2.md): Finds unique elements along an axis of a tensor.
+
+[`UniqueWithCounts(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/UniqueWithCounts.md): Finds unique elements in a 1-D tensor.
+
+[`UniqueWithCountsV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/UniqueWithCountsV2.md): Finds unique elements along an axis of a tensor.
+
+[`Unpack(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Unpack.md): Unpacks a given dimension of a rank-`R` tensor into `num` rank-`(R-1)` tensors.
+
+[`UnravelIndex(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/UnravelIndex.md): Converts an array of flat indices into a tuple of coordinate arrays.
+
+[`UnsortedSegmentJoin(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/UnsortedSegmentJoin.md): Joins the elements of `inputs` based on `segment_ids`.
+
+[`UnsortedSegmentMax(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/UnsortedSegmentMax.md): Computes the maximum along segments of a tensor.
+
+[`UnsortedSegmentMin(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/UnsortedSegmentMin.md): Computes the minimum along segments of a tensor.
+
+[`UnsortedSegmentProd(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/UnsortedSegmentProd.md): Computes the product along segments of a tensor.
+
+[`UnsortedSegmentSum(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/UnsortedSegmentSum.md): Computes the sum along segments of a tensor.
+
+[`Unstage(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Unstage.md): Op is similar to a lightweight Dequeue.
+
+[`UnwrapDatasetVariant(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/UnwrapDatasetVariant.md)
+
+[`UpperBound(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/UpperBound.md): Applies upper_bound(sorted_search_values, values) along each row.
+
+[`VarHandleOp(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/VarHandleOp.md): Creates a handle to a Variable resource.
+
+[`VarIsInitializedOp(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/VarIsInitializedOp.md): Checks whether a resource handle-based variable has been initialized.
+
+[`Variable(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Variable.md): Use VariableV2 instead.
+
+[`VariableShape(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/VariableShape.md): Returns the shape of the variable pointed to by `resource`.
+
+[`VariableV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/VariableV2.md): Holds state in the form of a tensor that persists across steps.
+
+[`Where(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Where.md): Returns locations of nonzero / true values in a tensor.
+
+[`While(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/While.md): output = input; While (Cond(output)) { output = Body(output) }
+
+[`WholeFileReader(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/WholeFileReader.md): A Reader that outputs the entire contents of a file as a value.
+
+[`WholeFileReaderV2(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/WholeFileReaderV2.md): A Reader that outputs the entire contents of a file as a value.
+
+[`WindowDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/WindowDataset.md): Combines (nests of) input elements into a dataset of (nests of) windows.
+
+[`WorkerHeartbeat(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/WorkerHeartbeat.md): Worker heartbeat op.
+
+[`WrapDatasetVariant(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/WrapDatasetVariant.md)
+
+[`WriteAudioSummary(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/WriteAudioSummary.md)
+
+[`WriteFile(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/WriteFile.md): Writes contents to the file at input filename. Creates file and recursively
+
+[`WriteGraphSummary(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/WriteGraphSummary.md)
+
+[`WriteHistogramSummary(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/WriteHistogramSummary.md)
+
+[`WriteImageSummary(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/WriteImageSummary.md)
+
+[`WriteRawProtoSummary(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/WriteRawProtoSummary.md)
+
+[`WriteScalarSummary(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/WriteScalarSummary.md)
+
+[`WriteSummary(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/WriteSummary.md)
+
+[`Xdivy(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Xdivy.md): Returns 0 if x == 0, and x / y otherwise, elementwise.
+
+[`Xlog1py(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Xlog1py.md): Returns 0 if x == 0, and x * log1p(y) otherwise, elementwise.
+
+[`Xlogy(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Xlogy.md): Returns 0 if x == 0, and x * log(y) otherwise, elementwise.
+
+[`ZerosLike(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ZerosLike.md): Returns a tensor of zeros with the same shape and type as x.
+
+[`Zeta(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/Zeta.md): Compute the Hurwitz zeta function \\(\zeta(x, q)\\).
+
+[`ZipDataset(...)`](../../../tf/raw_ops/ZipDataset.md): Creates a dataset that zips together `input_datasets`.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/reduce_all.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/reduce_all.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..febee24d2c1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/reduce_all.md
@@ -0,0 +1,141 @@
+description: Computes the "logical and" of elements across dimensions of a tensor. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.reduce_all
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the "logical and" of elements across dimensions of a tensor. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.math.reduce_all`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.reduce_all(
+ input_tensor, axis=None, keepdims=None, name=None, reduction_indices=None,
+ keep_dims=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: SOME ARGUMENTS ARE DEPRECATED: `(keep_dims)`. They will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+keep_dims is deprecated, use keepdims instead
+
+Reduces `input_tensor` along the dimensions given in `axis`.
+Unless `keepdims` is true, the rank of the tensor is reduced by 1 for each
+entry in `axis`. If `keepdims` is true, the reduced dimensions
+are retained with length 1.
+
+If `axis` is None, all dimensions are reduced, and a
+tensor with a single element is returned.
+
+#### For example:
+
+
+
+```python
+x = tf.constant([[True, True], [False, False]])
+tf.reduce_all(x) # False
+tf.reduce_all(x, 0) # [False, False]
+tf.reduce_all(x, 1) # [True, False]
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_tensor`
+ |
+
+The boolean tensor to reduce.
+ |
+
+|
+`axis`
+ |
+
+The dimensions to reduce. If `None` (the default), reduces all
+dimensions. Must be in the range `[-rank(input_tensor),
+rank(input_tensor))`.
+ |
+
+|
+`keepdims`
+ |
+
+If true, retains reduced dimensions with length 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`reduction_indices`
+ |
+
+The old (deprecated) name for axis.
+ |
+
+|
+`keep_dims`
+ |
+
+Deprecated alias for `keepdims`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The reduced tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Numpy Compatibility
+Equivalent to np.all
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/reduce_any.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/reduce_any.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..576db1ddab8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/reduce_any.md
@@ -0,0 +1,141 @@
+description: Computes the "logical or" of elements across dimensions of a tensor. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.reduce_any
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the "logical or" of elements across dimensions of a tensor. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.math.reduce_any`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.reduce_any(
+ input_tensor, axis=None, keepdims=None, name=None, reduction_indices=None,
+ keep_dims=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: SOME ARGUMENTS ARE DEPRECATED: `(keep_dims)`. They will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+keep_dims is deprecated, use keepdims instead
+
+Reduces `input_tensor` along the dimensions given in `axis`.
+Unless `keepdims` is true, the rank of the tensor is reduced by 1 for each
+entry in `axis`. If `keepdims` is true, the reduced dimensions
+are retained with length 1.
+
+If `axis` is None, all dimensions are reduced, and a
+tensor with a single element is returned.
+
+#### For example:
+
+
+
+```python
+x = tf.constant([[True, True], [False, False]])
+tf.reduce_any(x) # True
+tf.reduce_any(x, 0) # [True, True]
+tf.reduce_any(x, 1) # [True, False]
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_tensor`
+ |
+
+The boolean tensor to reduce.
+ |
+
+|
+`axis`
+ |
+
+The dimensions to reduce. If `None` (the default), reduces all
+dimensions. Must be in the range `[-rank(input_tensor),
+rank(input_tensor))`.
+ |
+
+|
+`keepdims`
+ |
+
+If true, retains reduced dimensions with length 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`reduction_indices`
+ |
+
+The old (deprecated) name for axis.
+ |
+
+|
+`keep_dims`
+ |
+
+Deprecated alias for `keepdims`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The reduced tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Numpy Compatibility
+Equivalent to np.any
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/reduce_join.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/reduce_join.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..ecdd7f20b75
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/reduce_join.md
@@ -0,0 +1,118 @@
+description: Joins all strings into a single string, or joins along an axis.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.reduce_join
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Joins all strings into a single string, or joins along an axis.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.strings.reduce_join`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.reduce_join(
+ inputs, axis=None, keep_dims=None, separator='', name=None,
+ reduction_indices=None, keepdims=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+```
+>>> tf.strings.reduce_join([['abc','123'],
+... ['def','456']]).numpy()
+b'abc123def456'
+>>> tf.strings.reduce_join([['abc','123'],
+... ['def','456']], axis=-1).numpy()
+array([b'abc123', b'def456'], dtype=object)
+>>> tf.strings.reduce_join([['abc','123'],
+... ['def','456']],
+... axis=-1,
+... separator=" ").numpy()
+array([b'abc 123', b'def 456'], dtype=object)
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+A tf.string tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`axis`
+ |
+
+Which axis to join along. The default behavior is to join all
+elements, producing a scalar.
+ |
+
+|
+`keepdims`
+ |
+
+If true, retains reduced dimensions with length 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`separator`
+ |
+
+a string added between each string being joined.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/reduce_logsumexp.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/reduce_logsumexp.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..cdb0ffd8c11
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/reduce_logsumexp.md
@@ -0,0 +1,141 @@
+description: Computes log(sum(exp(elements across dimensions of a tensor))). (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.reduce_logsumexp
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes log(sum(exp(elements across dimensions of a tensor))). (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.math.reduce_logsumexp`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.reduce_logsumexp(
+ input_tensor, axis=None, keepdims=None, name=None, reduction_indices=None,
+ keep_dims=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: SOME ARGUMENTS ARE DEPRECATED: `(keep_dims)`. They will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+keep_dims is deprecated, use keepdims instead
+
+Reduces `input_tensor` along the dimensions given in `axis`.
+Unless `keepdims` is true, the rank of the tensor is reduced by 1 for each
+entry in `axis`. If `keepdims` is true, the reduced dimensions
+are retained with length 1.
+
+If `axis` has no entries, all dimensions are reduced, and a
+tensor with a single element is returned.
+
+This function is more numerically stable than log(sum(exp(input))). It avoids
+overflows caused by taking the exp of large inputs and underflows caused by
+taking the log of small inputs.
+
+#### For example:
+
+
+
+```python
+x = tf.constant([[0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0.]])
+tf.reduce_logsumexp(x) # log(6)
+tf.reduce_logsumexp(x, 0) # [log(2), log(2), log(2)]
+tf.reduce_logsumexp(x, 1) # [log(3), log(3)]
+tf.reduce_logsumexp(x, 1, keepdims=True) # [[log(3)], [log(3)]]
+tf.reduce_logsumexp(x, [0, 1]) # log(6)
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_tensor`
+ |
+
+The tensor to reduce. Should have numeric type.
+ |
+
+|
+`axis`
+ |
+
+The dimensions to reduce. If `None` (the default), reduces all
+dimensions. Must be in the range `[-rank(input_tensor),
+rank(input_tensor))`.
+ |
+
+|
+`keepdims`
+ |
+
+If true, retains reduced dimensions with length 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`reduction_indices`
+ |
+
+The old (deprecated) name for axis.
+ |
+
+|
+`keep_dims`
+ |
+
+Deprecated alias for `keepdims`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The reduced tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/reduce_max.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/reduce_max.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..45d39fdfad2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/reduce_max.md
@@ -0,0 +1,130 @@
+description: Computes the maximum of elements across dimensions of a tensor. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.reduce_max
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the maximum of elements across dimensions of a tensor. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.math.reduce_max`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.reduce_max(
+ input_tensor, axis=None, keepdims=None, name=None, reduction_indices=None,
+ keep_dims=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: SOME ARGUMENTS ARE DEPRECATED: `(keep_dims)`. They will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+keep_dims is deprecated, use keepdims instead
+
+Reduces `input_tensor` along the dimensions given in `axis`.
+Unless `keepdims` is true, the rank of the tensor is reduced by 1 for each
+entry in `axis`. If `keepdims` is true, the reduced dimensions
+are retained with length 1.
+
+If `axis` is None, all dimensions are reduced, and a
+tensor with a single element is returned.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_tensor`
+ |
+
+The tensor to reduce. Should have real numeric type.
+ |
+
+|
+`axis`
+ |
+
+The dimensions to reduce. If `None` (the default), reduces all
+dimensions. Must be in the range `[-rank(input_tensor),
+rank(input_tensor))`.
+ |
+
+|
+`keepdims`
+ |
+
+If true, retains reduced dimensions with length 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`reduction_indices`
+ |
+
+The old (deprecated) name for axis.
+ |
+
+|
+`keep_dims`
+ |
+
+Deprecated alias for `keepdims`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The reduced tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Numpy Compatibility
+Equivalent to np.max
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/reduce_mean.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/reduce_mean.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..c0e8b570bbb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/reduce_mean.md
@@ -0,0 +1,156 @@
+description: Computes the mean of elements across dimensions of a tensor.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.reduce_mean
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the mean of elements across dimensions of a tensor.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.math.reduce_mean`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.reduce_mean(
+ input_tensor, axis=None, keepdims=None, name=None, reduction_indices=None,
+ keep_dims=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Reduces `input_tensor` along the dimensions given in `axis` by computing the
+mean of elements across the dimensions in `axis`.
+Unless `keepdims` is true, the rank of the tensor is reduced by 1 for each
+entry in `axis`. If `keepdims` is true, the reduced dimensions
+are retained with length 1.
+
+If `axis` is None, all dimensions are reduced, and a tensor with a single
+element is returned.
+
+#### For example:
+
+
+
+```
+>>> x = tf.constant([[1., 1.], [2., 2.]])
+>>> tf.reduce_mean(x)
+
+>>> tf.reduce_mean(x, 0)
+
+>>> tf.reduce_mean(x, 1)
+
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_tensor`
+ |
+
+The tensor to reduce. Should have numeric type.
+ |
+
+|
+`axis`
+ |
+
+The dimensions to reduce. If `None` (the default), reduces all
+dimensions. Must be in the range `[-rank(input_tensor),
+rank(input_tensor))`.
+ |
+
+|
+`keepdims`
+ |
+
+If true, retains reduced dimensions with length 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`reduction_indices`
+ |
+
+The old (deprecated) name for axis.
+ |
+
+|
+`keep_dims`
+ |
+
+Deprecated alias for `keepdims`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The reduced tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Numpy Compatibility
+Equivalent to np.mean
+
+Please note that `np.mean` has a `dtype` parameter that could be used to
+specify the output type. By default this is `dtype=float64`. On the other
+hand, tf.reduce_mean has an aggressive type inference from `input_tensor`,
+for example:
+
+```
+>>> x = tf.constant([1, 0, 1, 0])
+>>> tf.reduce_mean(x)
+
+>>> y = tf.constant([1., 0., 1., 0.])
+>>> tf.reduce_mean(y)
+
+```
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/reduce_min.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/reduce_min.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..62d6b18f2c4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/reduce_min.md
@@ -0,0 +1,130 @@
+description: Computes the minimum of elements across dimensions of a tensor. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.reduce_min
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the minimum of elements across dimensions of a tensor. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.math.reduce_min`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.reduce_min(
+ input_tensor, axis=None, keepdims=None, name=None, reduction_indices=None,
+ keep_dims=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: SOME ARGUMENTS ARE DEPRECATED: `(keep_dims)`. They will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+keep_dims is deprecated, use keepdims instead
+
+Reduces `input_tensor` along the dimensions given in `axis`.
+Unless `keepdims` is true, the rank of the tensor is reduced by 1 for each
+entry in `axis`. If `keepdims` is true, the reduced dimensions
+are retained with length 1.
+
+If `axis` is None, all dimensions are reduced, and a
+tensor with a single element is returned.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_tensor`
+ |
+
+The tensor to reduce. Should have real numeric type.
+ |
+
+|
+`axis`
+ |
+
+The dimensions to reduce. If `None` (the default), reduces all
+dimensions. Must be in the range `[-rank(input_tensor),
+rank(input_tensor))`.
+ |
+
+|
+`keepdims`
+ |
+
+If true, retains reduced dimensions with length 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`reduction_indices`
+ |
+
+The old (deprecated) name for axis.
+ |
+
+|
+`keep_dims`
+ |
+
+Deprecated alias for `keepdims`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The reduced tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Numpy Compatibility
+Equivalent to np.min
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/reduce_prod.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/reduce_prod.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..5dc806d3863
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/reduce_prod.md
@@ -0,0 +1,130 @@
+description: Computes the product of elements across dimensions of a tensor. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.reduce_prod
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the product of elements across dimensions of a tensor. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.math.reduce_prod`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.reduce_prod(
+ input_tensor, axis=None, keepdims=None, name=None, reduction_indices=None,
+ keep_dims=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: SOME ARGUMENTS ARE DEPRECATED: `(keep_dims)`. They will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+keep_dims is deprecated, use keepdims instead
+
+Reduces `input_tensor` along the dimensions given in `axis`.
+Unless `keepdims` is true, the rank of the tensor is reduced by 1 for each
+entry in `axis`. If `keepdims` is true, the reduced dimensions
+are retained with length 1.
+
+If `axis` is None, all dimensions are reduced, and a
+tensor with a single element is returned.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_tensor`
+ |
+
+The tensor to reduce. Should have numeric type.
+ |
+
+|
+`axis`
+ |
+
+The dimensions to reduce. If `None` (the default), reduces all
+dimensions. Must be in the range `[-rank(input_tensor),
+rank(input_tensor))`.
+ |
+
+|
+`keepdims`
+ |
+
+If true, retains reduced dimensions with length 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`reduction_indices`
+ |
+
+The old (deprecated) name for axis.
+ |
+
+|
+`keep_dims`
+ |
+
+Deprecated alias for `keepdims`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The reduced tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Numpy Compatibility
+Equivalent to np.prod
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/reduce_sum.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/reduce_sum.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..9d560ae3e66
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/reduce_sum.md
@@ -0,0 +1,144 @@
+description: Computes the sum of elements across dimensions of a tensor. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.reduce_sum
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the sum of elements across dimensions of a tensor. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.math.reduce_sum`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.reduce_sum(
+ input_tensor, axis=None, keepdims=None, name=None, reduction_indices=None,
+ keep_dims=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: SOME ARGUMENTS ARE DEPRECATED: `(keep_dims)`. They will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+keep_dims is deprecated, use keepdims instead
+
+Reduces `input_tensor` along the dimensions given in `axis`.
+Unless `keepdims` is true, the rank of the tensor is reduced by 1 for each
+entry in `axis`. If `keepdims` is true, the reduced dimensions
+are retained with length 1.
+
+If `axis` is None, all dimensions are reduced, and a
+tensor with a single element is returned.
+
+#### For example:
+
+
+
+```python
+x = tf.constant([[1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1]])
+tf.reduce_sum(x) # 6
+tf.reduce_sum(x, 0) # [2, 2, 2]
+tf.reduce_sum(x, 1) # [3, 3]
+tf.reduce_sum(x, 1, keepdims=True) # [[3], [3]]
+tf.reduce_sum(x, [0, 1]) # 6
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_tensor`
+ |
+
+The tensor to reduce. Should have numeric type.
+ |
+
+|
+`axis`
+ |
+
+The dimensions to reduce. If `None` (the default), reduces all
+dimensions. Must be in the range `[-rank(input_tensor),
+rank(input_tensor))`.
+ |
+
+|
+`keepdims`
+ |
+
+If true, retains reduced dimensions with length 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`reduction_indices`
+ |
+
+The old (deprecated) name for axis.
+ |
+
+|
+`keep_dims`
+ |
+
+Deprecated alias for `keepdims`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The reduced tensor, of the same dtype as the input_tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Numpy Compatibility
+Equivalent to np.sum apart the fact that numpy upcast uint8 and int32 to
+int64 while tensorflow returns the same dtype as the input.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/report_uninitialized_variables.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/report_uninitialized_variables.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..21e9c7bec92
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/report_uninitialized_variables.md
@@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
+description: Adds ops to list the names of uninitialized variables.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.report_uninitialized_variables
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Adds ops to list the names of uninitialized variables.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.report_uninitialized_variables(
+ var_list=None, name='report_uninitialized_variables'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+When run, it returns a 1-D tensor containing the names of uninitialized
+variables if there are any, or an empty array if there are none.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`var_list`
+ |
+
+List of `Variable` objects to check. Defaults to the value of
+`global_variables() + local_variables()`
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name of the `Operation`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A 1-D tensor containing names of the uninitialized variables, or an empty
+1-D tensor if there are no variables or no uninitialized variables.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+**NOTE** The output of this function should be used. If it is not, a warning will be logged or an error may be raised. To mark the output as used, call its .mark_used() method.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/reset_default_graph.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/reset_default_graph.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..7258dac3374
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/reset_default_graph.md
@@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
+description: Clears the default graph stack and resets the global default graph.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.reset_default_graph
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Clears the default graph stack and resets the global default graph.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.reset_default_graph()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+NOTE: The default graph is a property of the current thread. This
+function applies only to the current thread. Calling this function while
+a tf.compat.v1.Session or tf.compat.v1.InteractiveSession is active will
+result in undefined
+behavior. Using any previously created tf.Operation or tf.Tensor objects
+after calling this function will result in undefined behavior.
+Raises:
+ AssertionError: If this function is called within a nested graph.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/resource_loader.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/resource_loader.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..f17b5c27e96
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/resource_loader.md
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+description: Resource management library.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.resource_loader
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Resource management library.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`get_data_files_path(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/resource_loader/get_data_files_path.md): Get a direct path to the data files colocated with the script.
+
+[`get_path_to_datafile(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/resource_loader/get_path_to_datafile.md): Get the path to the specified file in the data dependencies.
+
+[`get_root_dir_with_all_resources(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/resource_loader/get_root_dir_with_all_resources.md): Get a root directory containing all the data attributes in the build rule.
+
+[`load_resource(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/resource_loader/load_resource.md): Load the resource at given path, where path is relative to tensorflow/.
+
+[`readahead_file_path(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/resource_loader/readahead_file_path.md): Readahead files not implemented; simply returns given path.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/resource_loader/get_data_files_path.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/resource_loader/get_data_files_path.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..f8046c20300
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/resource_loader/get_data_files_path.md
@@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
+description: Get a direct path to the data files colocated with the script.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.resource_loader.get_data_files_path
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Get a direct path to the data files colocated with the script.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.resource_loader.get_data_files_path()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The directory where files specified in data attribute of py_test
+and py_binary are stored.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/resource_loader/get_path_to_datafile.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/resource_loader/get_path_to_datafile.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..cf657deabb2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/resource_loader/get_path_to_datafile.md
@@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
+description: Get the path to the specified file in the data dependencies.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.resource_loader.get_path_to_datafile
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Get the path to the specified file in the data dependencies.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.resource_loader.get_path_to_datafile(
+ path
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The path is relative to tensorflow/
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`path`
+ |
+
+a string resource path relative to tensorflow/
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the specified file present in the data attribute of py_test
+or py_binary.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`IOError`
+ |
+
+If the path is not found, or the resource can't be opened.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/resource_loader/get_root_dir_with_all_resources.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/resource_loader/get_root_dir_with_all_resources.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..96a360f2f7f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/resource_loader/get_root_dir_with_all_resources.md
@@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
+description: Get a root directory containing all the data attributes in the build rule.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.resource_loader.get_root_dir_with_all_resources
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Get a root directory containing all the data attributes in the build rule.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.resource_loader.get_root_dir_with_all_resources()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to the specified file present in the data attribute of py_test
+or py_binary. Falls back to returning the same as get_data_files_path if it
+fails to detect a bazel runfiles directory.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/resource_loader/load_resource.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/resource_loader/load_resource.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..6791951b3eb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/resource_loader/load_resource.md
@@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
+description: Load the resource at given path, where path is relative to tensorflow/.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.resource_loader.load_resource
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Load the resource at given path, where path is relative to tensorflow/.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.resource_loader.load_resource(
+ path
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`path`
+ |
+
+a string resource path relative to tensorflow/.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The contents of that resource.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`IOError`
+ |
+
+If the path is not found, or the resource can't be opened.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/resource_loader/readahead_file_path.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/resource_loader/readahead_file_path.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..93328594b60
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/resource_loader/readahead_file_path.md
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+description: Readahead files not implemented; simply returns given path.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.resource_loader.readahead_file_path
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Readahead files not implemented; simply returns given path.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.resource_loader.readahead_file_path(
+ path, readahead='128M'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/resource_variables_enabled.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/resource_variables_enabled.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..c4fa814ed51
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/resource_variables_enabled.md
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
+description: Returns True if resource variables are enabled.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.resource_variables_enabled
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns `True` if resource variables are enabled.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.resource_variables_enabled()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Resource variables are improved versions of TensorFlow variables with a
+well-defined memory model. Accessing a resource variable reads its value, and
+all ops which access a specific read value of the variable are guaranteed to
+see the same value for that tensor. Writes which happen after a read (by
+having a control or data dependency on the read) are guaranteed not to affect
+the value of the read tensor, and similarly writes which happen before a read
+are guaranteed to affect the value. No guarantees are made about unordered
+read/write pairs.
+
+Calling tf.enable_resource_variables() lets you opt-in to this TensorFlow 2.0
+feature.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/reverse_sequence.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/reverse_sequence.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..d2875c7898c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/reverse_sequence.md
@@ -0,0 +1,105 @@
+description: Reverses variable length slices. (deprecated arguments) (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.reverse_sequence
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Reverses variable length slices. (deprecated arguments) (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.reverse_sequence(
+ input, seq_lengths, seq_axis=None, batch_axis=None, name=None, seq_dim=None,
+ batch_dim=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: SOME ARGUMENTS ARE DEPRECATED: `(seq_dim)`. They will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+seq_dim is deprecated, use seq_axis instead
+
+Warning: SOME ARGUMENTS ARE DEPRECATED: `(batch_dim)`. They will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+batch_dim is deprecated, use batch_axis instead
+
+This op first slices `input` along the dimension `batch_axis`, and for
+each slice `i`, reverses the first `seq_lengths[i]` elements along the
+dimension `seq_axis`.
+
+The elements of `seq_lengths` must obey `seq_lengths[i] <=
+input.dims[seq_dim]`, and `seq_lengths` must be a vector of length
+`input.dims[batch_dim]`.
+
+The output slice `i` along dimension `batch_axis` is then given by
+input slice `i`, with the first `seq_lengths[i]` slices along
+dimension `seq_axis` reversed.
+
+#### Example usage:
+
+
+
+```
+>>> seq_lengths = [7, 2, 3, 5]
+>>> input = [[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 0, 0, 0], [1, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
+... [1, 2, 3, 4, 0, 0, 0, 0], [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]]
+>>> output = tf.reverse_sequence(input, seq_lengths, seq_axis=1, batch_axis=0)
+>>> output
+
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+|
+`input`: A `Tensor`. The input to reverse.
+`seq_lengths`: A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `int32`,
+`int64`. 1-D with length `input.dims(batch_dim)` and `max(seq_lengths) <=
+input.dims(seq_dim)`
+`seq_axis`: An `int`. The dimension which is partially reversed.
+`batch_axis`: An optional `int`. Defaults to `0`. The dimension along which
+reversal is performed.
+`name`: A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A Tensor. Has the same type as input.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..17ec716f299
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model.md
@@ -0,0 +1,133 @@
+description: Public API for tf.saved_model namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.saved_model
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.saved_model namespace.
+
+
+
+## Modules
+
+[`builder`](../../../tf/compat/v1/saved_model/builder.md) module: SavedModel builder.
+
+[`constants`](../../../tf/compat/v1/saved_model/constants.md) module: Constants for SavedModel save and restore operations.
+
+[`experimental`](../../../tf/compat/v1/saved_model/experimental.md) module: Public API for tf.saved_model.experimental namespace.
+
+[`loader`](../../../tf/compat/v1/saved_model/loader.md) module: Loader functionality for SavedModel with hermetic, language-neutral exports.
+
+[`main_op`](../../../tf/compat/v1/saved_model/main_op.md) module: SavedModel main op.
+
+[`signature_constants`](../../../tf/compat/v1/saved_model/signature_constants.md) module: Signature constants for SavedModel save and restore operations.
+
+[`signature_def_utils`](../../../tf/compat/v1/saved_model/signature_def_utils.md) module: SignatureDef utility functions.
+
+[`tag_constants`](../../../tf/compat/v1/saved_model/tag_constants.md) module: Common tags used for graphs in SavedModel.
+
+[`utils`](../../../tf/compat/v1/saved_model/utils.md) module: SavedModel utility functions.
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class Asset`](../../../tf/saved_model/Asset.md): Represents a file asset to hermetically include in a SavedModel.
+
+[`class Builder`](../../../tf/compat/v1/saved_model/Builder.md): Builds the `SavedModel` protocol buffer and saves variables and assets.
+
+[`class SaveOptions`](../../../tf/saved_model/SaveOptions.md): Options for saving to SavedModel.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`build_signature_def(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/saved_model/build_signature_def.md): Utility function to build a SignatureDef protocol buffer.
+
+[`build_tensor_info(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/saved_model/build_tensor_info.md): Utility function to build TensorInfo proto from a Tensor. (deprecated)
+
+[`classification_signature_def(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/saved_model/classification_signature_def.md): Creates classification signature from given examples and predictions.
+
+[`contains_saved_model(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/saved_model/contains_saved_model.md): Checks whether the provided export directory could contain a SavedModel.
+
+[`get_tensor_from_tensor_info(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/saved_model/get_tensor_from_tensor_info.md): Returns the Tensor or CompositeTensor described by a TensorInfo proto. (deprecated)
+
+[`is_valid_signature(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/saved_model/is_valid_signature.md): Determine whether a SignatureDef can be served by TensorFlow Serving.
+
+[`load(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/saved_model/load.md): Loads the model from a SavedModel as specified by tags. (deprecated)
+
+[`load_v2(...)`](../../../tf/saved_model/load.md): Load a SavedModel from `export_dir`.
+
+[`main_op_with_restore(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/saved_model/main_op_with_restore.md): Returns a main op to init variables, tables and restore the graph. (deprecated)
+
+[`maybe_saved_model_directory(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/saved_model/contains_saved_model.md): Checks whether the provided export directory could contain a SavedModel.
+
+[`predict_signature_def(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/saved_model/predict_signature_def.md): Creates prediction signature from given inputs and outputs.
+
+[`regression_signature_def(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/saved_model/regression_signature_def.md): Creates regression signature from given examples and predictions.
+
+[`save(...)`](../../../tf/saved_model/save.md): Exports the Trackable object `obj` to [SavedModel format](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/master/tensorflow/python/saved_model/README.md).
+
+[`simple_save(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/saved_model/simple_save.md): Convenience function to build a SavedModel suitable for serving. (deprecated)
+
+## Other Members
+
+* `ASSETS_DIRECTORY = 'assets'`
+* `ASSETS_KEY = 'saved_model_assets'`
+* `CLASSIFY_INPUTS = 'inputs'`
+* `CLASSIFY_METHOD_NAME = 'tensorflow/serving/classify'`
+* `CLASSIFY_OUTPUT_CLASSES = 'classes'`
+* `CLASSIFY_OUTPUT_SCORES = 'scores'`
+* `DEBUG_DIRECTORY = 'debug'`
+* `DEBUG_INFO_FILENAME_PB = 'saved_model_debug_info.pb'`
+* `DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY = 'serving_default'`
+* `GPU = 'gpu'`
+* `LEGACY_INIT_OP_KEY = 'legacy_init_op'`
+* `MAIN_OP_KEY = 'saved_model_main_op'`
+* `PREDICT_INPUTS = 'inputs'`
+* `PREDICT_METHOD_NAME = 'tensorflow/serving/predict'`
+* `PREDICT_OUTPUTS = 'outputs'`
+* `REGRESS_INPUTS = 'inputs'`
+* `REGRESS_METHOD_NAME = 'tensorflow/serving/regress'`
+* `REGRESS_OUTPUTS = 'outputs'`
+* `SAVED_MODEL_FILENAME_PB = 'saved_model.pb'`
+* `SAVED_MODEL_FILENAME_PBTXT = 'saved_model.pbtxt'`
+* `SAVED_MODEL_SCHEMA_VERSION = 1`
+* `SERVING = 'serve'`
+* `TPU = 'tpu'`
+* `TRAINING = 'train'`
+* `VARIABLES_DIRECTORY = 'variables'`
+* `VARIABLES_FILENAME = 'variables'`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/Builder.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/Builder.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..fed747c53c4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/Builder.md
@@ -0,0 +1,353 @@
+description: Builds the SavedModel protocol buffer and saves variables and assets.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.saved_model.Builder
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Builds the `SavedModel` protocol buffer and saves variables and assets.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.saved_model.builder.SavedModelBuilder`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.saved_model.Builder(
+ export_dir
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The `SavedModelBuilder` class provides the functionality to build a
+`SavedModel` protocol buffer. Specifically, this allows multiple meta
+graphs to be saved as part of a single language-neutral `SavedModel`,
+while sharing variables and assets.
+
+To build a SavedModel, the first meta graph must be saved with variables.
+Subsequent meta graphs will simply be saved with their graph definitions. If
+assets need to be saved and written or copied to disk, they can be provided
+when the meta graph def is added. If multiple meta graph defs are associated
+an asset of the same name, only the first version is retained.
+
+Each meta graph added to the SavedModel must be annotated with tags. The tags
+provide a means to identify the specific meta graph to load and restore, along
+with the shared set of variables and assets.
+
+Typical usage for the `SavedModelBuilder`:
+
+```python
+...
+builder = tf.compat.v1.saved_model.Builder(export_dir)
+
+with tf.compat.v1.Session(graph=tf.Graph()) as sess:
+ ...
+ builder.add_meta_graph_and_variables(sess,
+ ["foo-tag"],
+ signature_def_map=foo_signatures,
+ assets_collection=foo_assets)
+...
+
+with tf.compat.v1.Session(graph=tf.Graph()) as sess:
+ ...
+ builder.add_meta_graph(["bar-tag", "baz-tag"])
+...
+
+builder.save()
+```
+
+Note: This function will only be available through the v1 compatibility
+library as tf.compat.v1.saved_model.builder.SavedModelBuilder or
+tf.compat.v1.saved_model.Builder. Tensorflow 2.0 will introduce a new
+object-based method of creating SavedModels.
+
+## Methods
+
+
+
+View source
+
+
+add_meta_graph(
+ tags, signature_def_map=None, assets_collection=None, legacy_init_op=None,
+ clear_devices=(False), main_op=None, strip_default_attrs=(False), saver=None
+)
+
+
+Adds the current meta graph to the SavedModel.
+
+Creates a Saver in the current scope and uses the Saver to export the meta
+graph def. Invoking this API requires the `add_meta_graph_and_variables()`
+API to have been invoked before.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`tags`
+ |
+
+The set of tags to annotate the meta graph def with.
+ |
+
+|
+`signature_def_map`
+ |
+
+The map of signature defs to be added to the meta graph
+def.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_collection`
+ |
+
+Assets to be saved with SavedModel. Note
+that this list should be a subset of the assets saved as part of
+the first meta graph in the SavedModel.
+ |
+
+|
+`clear_devices`
+ |
+
+Set to true if the device info on the default graph should
+be cleared.
+ |
+
+|
+`init_op`
+ |
+
+Op or group of ops to execute when the graph is loaded. Note
+that when the init_op is specified it is run after the restore op at
+load-time.
+ |
+
+|
+`train_op`
+ |
+
+Op or group of opts that trains the model when run. This will
+not be run automatically when the graph is loaded, instead saved in
+a SignatureDef accessible through the exported MetaGraph.
+ |
+
+|
+`saver`
+ |
+
+An instance of tf.compat.v1.train.Saver that will be used to export
+the metagraph. If None, a sharded Saver that restores all variables will
+be used.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`AssertionError`
+ |
+
+If the variables for the SavedModel have not been saved
+yet, or if the graph already contains one or more legacy init ops.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+View source
+
+
+add_meta_graph_and_variables(
+ sess, tags, signature_def_map=None, assets_collection=None, legacy_init_op=None,
+ clear_devices=(False), main_op=None, strip_default_attrs=(False), saver=None
+)
+
+
+Adds the current meta graph to the SavedModel and saves variables.
+
+Creates a Saver to save the variables from the provided session. Exports the
+corresponding meta graph def. This function assumes that the variables to be
+saved have been initialized. For a given `SavedModelBuilder`, this API must
+be called exactly once and for the first meta graph to save. For subsequent
+meta graph defs to be added, the `add_meta_graph()` API must be used.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sess`
+ |
+
+The TensorFlow session from which to save the meta graph and
+variables.
+ |
+
+|
+`tags`
+ |
+
+The set of tags with which to save the meta graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`signature_def_map`
+ |
+
+The map of signature def map to add to the meta graph
+def.
+ |
+
+|
+`assets_collection`
+ |
+
+Assets to be saved with SavedModel.
+ |
+
+|
+`clear_devices`
+ |
+
+Set to true if the device info on the default graph should
+be cleared.
+ |
+
+|
+`init_op`
+ |
+
+Op or group of ops to execute when the graph is loaded. Note
+that when the init_op is specified it is run after the restore op at
+load-time.
+ |
+
+|
+`train_op`
+ |
+
+Op or group of ops that trains the model when run. This will
+not be run automatically when the graph is loaded, instead saved in
+a SignatureDef accessible through the exported MetaGraph.
+ |
+
+|
+`strip_default_attrs`
+ |
+
+Boolean. If `True`, default-valued attributes will be
+removed from the NodeDefs. For a detailed guide, see
+[Stripping Default-Valued Attributes](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/master/tensorflow/python/saved_model/README.md#stripping-default-valued-attributes).
+ |
+
+|
+`saver`
+ |
+
+An instance of tf.compat.v1.train.Saver that will be used to export the
+metagraph and save variables. If None, a sharded Saver that restores
+all variables will be used.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+save
+
+View source
+
+
+save(
+ as_text=(False)
+)
+
+
+Writes a `SavedModel` protocol buffer to disk.
+
+The function writes the SavedModel protocol buffer to the export directory
+in a serialized format.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+Writes the SavedModel protocol buffer in text format to
+disk. Protocol buffers in text format are useful for debugging, but
+parsing fails when it encounters an unknown field and so is not forward
+compatible. This means changes to TensorFlow may prevent deployment of
+new text format SavedModels to existing serving binaries. Do not deploy
+`as_text` SavedModels to production.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The path to which the SavedModel protocol buffer was written.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/build_signature_def.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/build_signature_def.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..728e8b124a1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/build_signature_def.md
@@ -0,0 +1,91 @@
+description: Utility function to build a SignatureDef protocol buffer.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.saved_model.build_signature_def
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Utility function to build a SignatureDef protocol buffer.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.saved_model.signature_def_utils.build_signature_def`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.saved_model.build_signature_def(
+ inputs=None, outputs=None, method_name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+Inputs of the SignatureDef defined as a proto map of string to
+tensor info.
+ |
+
+|
+`outputs`
+ |
+
+Outputs of the SignatureDef defined as a proto map of string to
+tensor info.
+ |
+
+|
+`method_name`
+ |
+
+Method name of the SignatureDef as a string.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A SignatureDef protocol buffer constructed based on the supplied arguments.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/build_tensor_info.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/build_tensor_info.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..801521bce1b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/build_tensor_info.md
@@ -0,0 +1,97 @@
+description: Utility function to build TensorInfo proto from a Tensor. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.saved_model.build_tensor_info
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Utility function to build TensorInfo proto from a Tensor. (deprecated)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.saved_model.utils.build_tensor_info`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.saved_model.build_tensor_info(
+ tensor
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+This function will only be available through the v1 compatibility library as tf.compat.v1.saved_model.utils.build_tensor_info or tf.compat.v1.saved_model.build_tensor_info.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`tensor`
+ |
+
+Tensor or SparseTensor whose name, dtype and shape are used to
+build the TensorInfo. For SparseTensors, the names of the three
+constituent Tensors are used.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A TensorInfo protocol buffer constructed based on the supplied argument.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/builder.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/builder.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..eb5dee34cc7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/builder.md
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
+description: SavedModel builder.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.saved_model.builder
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+SavedModel builder.
+
+
+Builds a SavedModel that can be saved to storage, is language neutral, and
+enables systems to produce, consume, or transform TensorFlow Models.
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class SavedModelBuilder`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/saved_model/Builder.md): Builds the `SavedModel` protocol buffer and saves variables and assets.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/classification_signature_def.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/classification_signature_def.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..8c34b39cd6c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/classification_signature_def.md
@@ -0,0 +1,110 @@
+description: Creates classification signature from given examples and predictions.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.saved_model.classification_signature_def
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Creates classification signature from given examples and predictions.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.saved_model.signature_def_utils.classification_signature_def`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.saved_model.classification_signature_def(
+ examples, classes, scores
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This function produces signatures intended for use with the TensorFlow Serving
+Classify API (tensorflow_serving/apis/prediction_service.proto), and so
+constrains the input and output types to those allowed by TensorFlow Serving.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`examples`
+ |
+
+A string `Tensor`, expected to accept serialized tf.Examples.
+ |
+
+|
+`classes`
+ |
+
+A string `Tensor`. Note that the ClassificationResponse message
+requires that class labels are strings, not integers or anything else.
+ |
+
+|
+`scores`
+ |
+
+a float `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A classification-flavored signature_def.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If examples is `None`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/constants.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/constants.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..ed00464329c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/constants.md
@@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
+description: Constants for SavedModel save and restore operations.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.saved_model.constants
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Constants for SavedModel save and restore operations.
+
+
+
+## Other Members
+
+* `ASSETS_DIRECTORY = 'assets'`
+* `ASSETS_KEY = 'saved_model_assets'`
+* `DEBUG_DIRECTORY = 'debug'`
+* `DEBUG_INFO_FILENAME_PB = 'saved_model_debug_info.pb'`
+* `LEGACY_INIT_OP_KEY = 'legacy_init_op'`
+* `MAIN_OP_KEY = 'saved_model_main_op'`
+* `SAVED_MODEL_FILENAME_PB = 'saved_model.pb'`
+* `SAVED_MODEL_FILENAME_PBTXT = 'saved_model.pbtxt'`
+* `SAVED_MODEL_SCHEMA_VERSION = 1`
+* `VARIABLES_DIRECTORY = 'variables'`
+* `VARIABLES_FILENAME = 'variables'`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/contains_saved_model.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/contains_saved_model.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..4f3691f1bef
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/contains_saved_model.md
@@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
+description: Checks whether the provided export directory could contain a SavedModel.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.saved_model.contains_saved_model
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Checks whether the provided export directory could contain a SavedModel.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.saved_model.loader.maybe_saved_model_directory`, `tf.compat.v1.saved_model.maybe_saved_model_directory`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.saved_model.contains_saved_model(
+ export_dir
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Note that the method does not load any data by itself. If the method returns
+`false`, the export directory definitely does not contain a SavedModel. If the
+method returns `true`, the export directory may contain a SavedModel but
+provides no guarantee that it can be loaded.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir`
+ |
+
+Absolute string path to possible export location. For example,
+'/my/foo/model'.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+True if the export directory contains SavedModel files, False otherwise.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/experimental.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/experimental.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..2aa0e4e0e3d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/experimental.md
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+description: Public API for tf.saved_model.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.saved_model.experimental
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.saved_model.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`save(...)`](../../../../tf/saved_model/save.md): Exports the Trackable object `obj` to [SavedModel format](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/master/tensorflow/python/saved_model/README.md).
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/get_tensor_from_tensor_info.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/get_tensor_from_tensor_info.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..130c4df5310
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/get_tensor_from_tensor_info.md
@@ -0,0 +1,120 @@
+description: Returns the Tensor or CompositeTensor described by a TensorInfo proto. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.saved_model.get_tensor_from_tensor_info
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns the Tensor or CompositeTensor described by a TensorInfo proto. (deprecated)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.saved_model.utils.get_tensor_from_tensor_info`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.saved_model.get_tensor_from_tensor_info(
+ tensor_info, graph=None, import_scope=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+This function will only be available through the v1 compatibility library as tf.compat.v1.saved_model.utils.get_tensor_from_tensor_info or tf.compat.v1.saved_model.get_tensor_from_tensor_info.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`tensor_info`
+ |
+
+A TensorInfo proto describing a Tensor or SparseTensor or
+CompositeTensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+The tf.Graph in which tensors are looked up. If None, the
+current default graph is used.
+ |
+
+|
+`import_scope`
+ |
+
+If not None, names in `tensor_info` are prefixed with this
+string before lookup.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The Tensor or SparseTensor or CompositeTensor in `graph` described by
+`tensor_info`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`KeyError`
+ |
+
+If `tensor_info` does not correspond to a tensor in `graph`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `tensor_info` is malformed.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/is_valid_signature.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/is_valid_signature.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..f1eda7274c3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/is_valid_signature.md
@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
+description: Determine whether a SignatureDef can be served by TensorFlow Serving.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.saved_model.is_valid_signature
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Determine whether a SignatureDef can be served by TensorFlow Serving.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.saved_model.signature_def_utils.is_valid_signature`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.saved_model.is_valid_signature(
+ signature_def
+)
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/load.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/load.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..0317b62e04a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/load.md
@@ -0,0 +1,130 @@
+description: Loads the model from a SavedModel as specified by tags. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.saved_model.load
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Loads the model from a SavedModel as specified by tags. (deprecated)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.saved_model.loader.load`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.saved_model.load(
+ sess, tags, export_dir, import_scope=None, **saver_kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+This function will only be available through the v1 compatibility library as tf.compat.v1.saved_model.loader.load or tf.compat.v1.saved_model.load. There will be a new function for importing SavedModels in Tensorflow 2.0.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sess`
+ |
+
+The TensorFlow session to restore the variables.
+ |
+
+|
+`tags`
+ |
+
+Set of string tags to identify the required MetaGraphDef. These should
+correspond to the tags used when saving the variables using the
+SavedModel `save()` API.
+ |
+
+|
+`export_dir`
+ |
+
+Directory in which the SavedModel protocol buffer and variables
+to be loaded are located.
+ |
+
+|
+`import_scope`
+ |
+
+Optional `string` -- if specified, prepend this string
+followed by '/' to all loaded tensor names. This scope is applied to
+tensor instances loaded into the passed session, but it is *not* written
+through to the static `MetaGraphDef` protocol buffer that is returned.
+ |
+
+|
+`**saver_kwargs`
+ |
+
+Optional keyword arguments passed through to Saver.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The `MetaGraphDef` protocol buffer loaded in the provided session. This
+can be used to further extract signature-defs, collection-defs, etc.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+MetaGraphDef associated with the tags cannot be found.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/loader.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/loader.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..50b9866f3bd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/loader.md
@@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
+description: Loader functionality for SavedModel with hermetic, language-neutral exports.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.saved_model.loader
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Loader functionality for SavedModel with hermetic, language-neutral exports.
+
+
+Load and restore capability for a SavedModel, which may include multiple meta
+graph defs. Each SavedModel is associated with a single checkpoint. Each meta
+graph def is saved with one or more tags, which are used to identify the exact
+meta graph def to load.
+
+The `load` operation requires the session in which to restore the graph
+definition and variables, the tags used to identify the meta graph def to
+load and the location of the SavedModel.
+
+Upon a load, the subset of variables and assets supplied as part of the specific
+meta graph def, will be restored into the supplied session. The values of the
+variables though will correspond to the saved values from the first meta graph
+added to the SavedModel using `add_meta_graph_and_variables(...)` in
+`builder.py`.
+
+#### Typical usage:
+
+
+
+```python
+...
+builder = tf.compat.v1.saved_model.builder.SavedModelBuilder(export_dir)
+
+with tf.compat.v1.Session(graph=tf.Graph()) as sess:
+ ...
+ builder.add_meta_graph_and_variables(sess,
+ ["foo-tag"],
+ signature_def_map=foo_signatures,
+ assets_collection=foo_assets)
+...
+
+with tf.compat.v1.Session(graph=tf.Graph()) as sess:
+ ...
+ builder.add_meta_graph(["bar-tag", "baz-tag"],
+ assets_collection=bar_baz_assets)
+...
+
+builder.save()
+
+...
+with tf.compat.v1.Session(graph=tf.Graph()) as sess:
+ tf.compat.v1.saved_model.loader.load(sess, ["foo-tag"], export_dir)
+ ...
+
+```
+
+## Functions
+
+[`load(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/saved_model/load.md): Loads the model from a SavedModel as specified by tags. (deprecated)
+
+[`maybe_saved_model_directory(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/saved_model/contains_saved_model.md): Checks whether the provided export directory could contain a SavedModel.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/main_op.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/main_op.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..f8082cab66a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/main_op.md
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
+description: SavedModel main op.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.saved_model.main_op
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+SavedModel main op.
+
+
+Builds a main op that defines the sequence of ops to be run as part of the
+SavedModel load/restore operations.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`main_op(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/saved_model/main_op/main_op.md): Returns a main op to init variables and tables. (deprecated)
+
+[`main_op_with_restore(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/saved_model/main_op_with_restore.md): Returns a main op to init variables, tables and restore the graph. (deprecated)
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/main_op/main_op.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/main_op/main_op.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..64e0c8134fb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/main_op/main_op.md
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
+description: Returns a main op to init variables and tables. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.saved_model.main_op.main_op
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns a main op to init variables and tables. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.saved_model.main_op.main_op()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+This function will only be available through the v1 compatibility library as tf.compat.v1.saved_model.main_op.main_op.
+
+Returns the main op including the group of ops that initializes all
+variables, initializes local variables and initialize all tables.
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The set of ops to be run as part of the main op upon the load operation.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/main_op_with_restore.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/main_op_with_restore.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..2707862c612
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/main_op_with_restore.md
@@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
+description: Returns a main op to init variables, tables and restore the graph. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.saved_model.main_op_with_restore
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns a main op to init variables, tables and restore the graph. (deprecated)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.saved_model.main_op.main_op_with_restore`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.saved_model.main_op_with_restore(
+ restore_op_name
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+This function will only be available through the v1 compatibility library as tf.compat.v1.saved_model.main_op_with_restore or tf.compat.v1.saved_model.main_op.main_op_with_restore.
+
+Returns the main op including the group of ops that initializes all
+variables, initialize local variables, initialize all tables and the restore
+op name.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`restore_op_name`
+ |
+
+Name of the op to use to restore the graph.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The set of ops to be run as part of the main op upon the load operation.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/predict_signature_def.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/predict_signature_def.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..cefcf65ff37
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/predict_signature_def.md
@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
+description: Creates prediction signature from given inputs and outputs.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.saved_model.predict_signature_def
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Creates prediction signature from given inputs and outputs.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.saved_model.signature_def_utils.predict_signature_def`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.saved_model.predict_signature_def(
+ inputs, outputs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This function produces signatures intended for use with the TensorFlow Serving
+Predict API (tensorflow_serving/apis/prediction_service.proto). This API
+imposes no constraints on the input and output types.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+dict of string to `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`outputs`
+ |
+
+dict of string to `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A prediction-flavored signature_def.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If inputs or outputs is `None`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/regression_signature_def.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/regression_signature_def.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..255f4626af8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/regression_signature_def.md
@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
+description: Creates regression signature from given examples and predictions.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.saved_model.regression_signature_def
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Creates regression signature from given examples and predictions.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.saved_model.signature_def_utils.regression_signature_def`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.saved_model.regression_signature_def(
+ examples, predictions
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This function produces signatures intended for use with the TensorFlow Serving
+Regress API (tensorflow_serving/apis/prediction_service.proto), and so
+constrains the input and output types to those allowed by TensorFlow Serving.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`examples`
+ |
+
+A string `Tensor`, expected to accept serialized tf.Examples.
+ |
+
+|
+`predictions`
+ |
+
+A float `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A regression-flavored signature_def.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If examples is `None`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/signature_constants.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/signature_constants.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..924f09ec525
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/signature_constants.md
@@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
+description: Signature constants for SavedModel save and restore operations.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.saved_model.signature_constants
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Signature constants for SavedModel save and restore operations.
+
+
+
+## Other Members
+
+* `CLASSIFY_INPUTS = 'inputs'`
+* `CLASSIFY_METHOD_NAME = 'tensorflow/serving/classify'`
+* `CLASSIFY_OUTPUT_CLASSES = 'classes'`
+* `CLASSIFY_OUTPUT_SCORES = 'scores'`
+* `DEFAULT_SERVING_SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY = 'serving_default'`
+* `PREDICT_INPUTS = 'inputs'`
+* `PREDICT_METHOD_NAME = 'tensorflow/serving/predict'`
+* `PREDICT_OUTPUTS = 'outputs'`
+* `REGRESS_INPUTS = 'inputs'`
+* `REGRESS_METHOD_NAME = 'tensorflow/serving/regress'`
+* `REGRESS_OUTPUTS = 'outputs'`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/signature_def_utils.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/signature_def_utils.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..5db0740831a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/signature_def_utils.md
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
+description: SignatureDef utility functions.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.saved_model.signature_def_utils
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+SignatureDef utility functions.
+
+
+Utility functions for building and inspecting SignatureDef protos.
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class MethodNameUpdater`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/saved_model/signature_def_utils/MethodNameUpdater.md): Updates the method name(s) of the SavedModel stored in the given path.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`build_signature_def(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/saved_model/build_signature_def.md): Utility function to build a SignatureDef protocol buffer.
+
+[`classification_signature_def(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/saved_model/classification_signature_def.md): Creates classification signature from given examples and predictions.
+
+[`is_valid_signature(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/saved_model/is_valid_signature.md): Determine whether a SignatureDef can be served by TensorFlow Serving.
+
+[`predict_signature_def(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/saved_model/predict_signature_def.md): Creates prediction signature from given inputs and outputs.
+
+[`regression_signature_def(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/saved_model/regression_signature_def.md): Creates regression signature from given examples and predictions.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/signature_def_utils/MethodNameUpdater.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/signature_def_utils/MethodNameUpdater.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..840e568984a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/signature_def_utils/MethodNameUpdater.md
@@ -0,0 +1,212 @@
+description: Updates the method name(s) of the SavedModel stored in the given path.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.saved_model.signature_def_utils.MethodNameUpdater
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Updates the method name(s) of the SavedModel stored in the given path.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.saved_model.signature_def_utils.MethodNameUpdater(
+ export_dir
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The `MethodNameUpdater` class provides the functionality to update the method
+name field in the signature_defs of the given SavedModel. For example, it
+can be used to replace the `predict` `method_name` to `regress`.
+
+Typical usages of the `MethodNameUpdater`
+```python
+...
+updater = tf.compat.v1.saved_model.MethodNameUpdater(export_dir)
+# Update all signature_defs with key "foo" in all meta graph defs.
+updater.replace_method_name(signature_key="foo", method_name="regress")
+# Update a single signature_def with key "bar" in the meta graph def with
+# tags ["serve"]
+updater.replace_method_name(signature_key="bar", method_name="classify",
+ tags="serve")
+updater.save(new_export_dir)
+```
+
+Note: This function will only be available through the v1 compatibility
+library as tf.compat.v1.saved_model.builder.MethodNameUpdater.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_dir`
+ |
+
+Directory containing the SavedModel files.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`IOError`
+ |
+
+If the saved model file does not exist, or cannot be successfully
+parsed.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+replace_method_name
+
+View source
+
+
+replace_method_name(
+ signature_key, method_name, tags=None
+)
+
+
+Replaces the method_name in the specified signature_def.
+
+This will match and replace multiple sig defs iff tags is None (i.e when
+multiple `MetaGraph`s have a signature_def with the same key).
+If tags is not None, this will only replace a single signature_def in the
+`MetaGraph` with matching tags.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`signature_key`
+ |
+
+Key of the signature_def to be updated.
+ |
+
+|
+`method_name`
+ |
+
+new method_name to replace the existing one.
+ |
+
+|
+`tags`
+ |
+
+A tag or sequence of tags identifying the `MetaGraph` to update. If
+None, all meta graphs will be updated.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if signature_key or method_name are not defined or
+if no metagraphs were found with the associated tags or
+if no meta graph has a signature_def that matches signature_key.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+save
+
+View source
+
+
+save(
+ new_export_dir=None
+)
+
+
+Saves the updated `SavedModel`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`new_export_dir`
+ |
+
+Path where the updated `SavedModel` will be saved. If
+None, the input `SavedModel` will be overriden with the updates.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`errors.OpError`
+ |
+
+If there are errors during the file save operation.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/simple_save.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/simple_save.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..399d84e864e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/simple_save.md
@@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
+description: Convenience function to build a SavedModel suitable for serving. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.saved_model.simple_save
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Convenience function to build a SavedModel suitable for serving. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.saved_model.simple_save(
+ session, export_dir, inputs, outputs, legacy_init_op=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+This function will only be available through the v1 compatibility library as tf.compat.v1.saved_model.simple_save.
+
+In many common cases, saving models for serving will be as simple as:
+
+ simple_save(session,
+ export_dir,
+ inputs={"x": x, "y": y},
+ outputs={"z": z})
+
+Although in many cases it's not necessary to understand all of the many ways
+ to configure a SavedModel, this method has a few practical implications:
+ - It will be treated as a graph for inference / serving (i.e. uses the tag
+ `saved_model.SERVING`)
+ - The SavedModel will load in TensorFlow Serving and supports the
+ [Predict
+ API](https://github.com/tensorflow/serving/blob/master/tensorflow_serving/apis/predict.proto).
+ To use the Classify, Regress, or MultiInference APIs, please
+ use either
+ [tf.Estimator](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/estimator/Estimator)
+ or the lower level
+ [SavedModel
+ APIs](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/master/tensorflow/python/saved_model/README.md).
+ - Some TensorFlow ops depend on information on disk or other information
+ called "assets". These are generally handled automatically by adding the
+ assets to the `GraphKeys.ASSET_FILEPATHS` collection. Only assets in that
+ collection are exported; if you need more custom behavior, you'll need to
+ use the
+ [SavedModelBuilder](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/master/tensorflow/python/saved_model/builder.py).
+
+More information about SavedModel and signatures can be found here:
+https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/master/tensorflow/python/saved_model/README.md.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`session`
+ |
+
+The TensorFlow session from which to save the meta graph and
+variables.
+ |
+
+|
+`export_dir`
+ |
+
+The path to which the SavedModel will be stored.
+ |
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+dict mapping string input names to tensors. These are added
+to the SignatureDef as the inputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`outputs`
+ |
+
+dict mapping string output names to tensors. These are added
+to the SignatureDef as the outputs.
+ |
+
+|
+`legacy_init_op`
+ |
+
+Legacy support for op or group of ops to execute after the
+restore op upon a load.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/tag_constants.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/tag_constants.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..4040aa58a2b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/tag_constants.md
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+description: Common tags used for graphs in SavedModel.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.saved_model.tag_constants
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Common tags used for graphs in SavedModel.
+
+
+
+## Other Members
+
+* `GPU = 'gpu'`
+* `SERVING = 'serve'`
+* `TPU = 'tpu'`
+* `TRAINING = 'train'`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/utils.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/utils.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..9a821634dea
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/saved_model/utils.md
@@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
+description: SavedModel utility functions.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.saved_model.utils
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+SavedModel utility functions.
+
+
+Utility functions to assist with setup and construction of the SavedModel proto.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`build_tensor_info(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/saved_model/build_tensor_info.md): Utility function to build TensorInfo proto from a Tensor. (deprecated)
+
+[`get_tensor_from_tensor_info(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/saved_model/get_tensor_from_tensor_info.md): Returns the Tensor or CompositeTensor described by a TensorInfo proto. (deprecated)
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scalar_mul.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scalar_mul.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a67ed0c757a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scalar_mul.md
@@ -0,0 +1,109 @@
+description: Multiplies a scalar times a Tensor or IndexedSlices object.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.scalar_mul
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Multiplies a scalar times a `Tensor` or `IndexedSlices` object.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.math.scalar_mul`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.scalar_mul(
+ scalar, x, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Intended for use in gradient code which might deal with `IndexedSlices`
+objects, which are easy to multiply by a scalar but more expensive to
+multiply with arbitrary tensors.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`scalar`
+ |
+
+A 0-D scalar `Tensor`. Must have known shape.
+ |
+
+|
+`x`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` or `IndexedSlices` to be scaled.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`scalar * x` of the same type (`Tensor` or `IndexedSlices`) as `x`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if scalar is not a 0-D `scalar`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scan.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scan.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..b34c57a415b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scan.md
@@ -0,0 +1,217 @@
+description: scan on the list of tensors unpacked from elems on dimension 0.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.scan
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+scan on the list of tensors unpacked from `elems` on dimension 0.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.scan(
+ fn, elems, initializer=None, parallel_iterations=10, back_prop=(True),
+ swap_memory=(False), infer_shape=(True), reverse=(False), name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The simplest version of `scan` repeatedly applies the callable `fn` to a
+sequence of elements from first to last. The elements are made of the tensors
+unpacked from `elems` on dimension 0. The callable fn takes two tensors as
+arguments. The first argument is the accumulated value computed from the
+preceding invocation of fn, and the second is the value at the current
+position of `elems`. If `initializer` is None, `elems` must contain at least
+one element, and its first element is used as the initializer.
+
+Suppose that `elems` is unpacked into `values`, a list of tensors. The shape
+of the result tensor is `[len(values)] + fn(initializer, values[0]).shape`.
+If reverse=True, it's fn(initializer, values[-1]).shape.
+
+This method also allows multi-arity `elems` and accumulator. If `elems`
+is a (possibly nested) list or tuple of tensors, then each of these tensors
+must have a matching first (unpack) dimension. The second argument of
+`fn` must match the structure of `elems`.
+
+If no `initializer` is provided, the output structure and dtypes of `fn`
+are assumed to be the same as its input; and in this case, the first
+argument of `fn` must match the structure of `elems`.
+
+If an `initializer` is provided, then the output of `fn` must have the same
+structure as `initializer`; and the first argument of `fn` must match
+this structure.
+
+For example, if `elems` is `(t1, [t2, t3])` and `initializer` is
+`[i1, i2]` then an appropriate signature for `fn` in `python2` is:
+`fn = lambda (acc_p1, acc_p2), (t1, [t2, t3]):` and `fn` must return a list,
+`[acc_n1, acc_n2]`. An alternative correct signature for `fn`, and the
+ one that works in `python3`, is:
+`fn = lambda a, t:`, where `a` and `t` correspond to the input tuples.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`fn`
+ |
+
+The callable to be performed. It accepts two arguments. The first will
+have the same structure as `initializer` if one is provided, otherwise it
+will have the same structure as `elems`. The second will have the same
+(possibly nested) structure as `elems`. Its output must have the same
+structure as `initializer` if one is provided, otherwise it must have the
+same structure as `elems`.
+ |
+
+|
+`elems`
+ |
+
+A tensor or (possibly nested) sequence of tensors, each of which will
+be unpacked along their first dimension. The nested sequence of the
+resulting slices will be the first argument to `fn`.
+ |
+
+|
+`initializer`
+ |
+
+(optional) A tensor or (possibly nested) sequence of tensors,
+initial value for the accumulator, and the expected output type of `fn`.
+ |
+
+|
+`parallel_iterations`
+ |
+
+(optional) The number of iterations allowed to run in
+parallel.
+ |
+
+|
+`back_prop`
+ |
+
+(optional) True enables support for back propagation.
+ |
+
+|
+`swap_memory`
+ |
+
+(optional) True enables GPU-CPU memory swapping.
+ |
+
+|
+`infer_shape`
+ |
+
+(optional) False disables tests for consistent output shapes.
+ |
+
+|
+`reverse`
+ |
+
+(optional) True scans the tensor last to first (instead of first to
+last).
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+(optional) Name prefix for the returned tensors.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A tensor or (possibly nested) sequence of tensors. Each tensor packs the
+results of applying `fn` to tensors unpacked from `elems` along the first
+dimension, and the previous accumulator value(s), from first to last (or
+last to first, if `reverse=True`).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+if `fn` is not callable or the structure of the output of
+`fn` and `initializer` do not match.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if the lengths of the output of `fn` and `initializer`
+do not match.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Examples:
+
+```python
+elems = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
+sum = scan(lambda a, x: a + x, elems)
+# sum == [1, 3, 6, 10, 15, 21]
+sum = scan(lambda a, x: a + x, elems, reverse=True)
+# sum == [21, 20, 18, 15, 11, 6]
+```
+
+```python
+elems = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
+initializer = np.array(0)
+sum_one = scan(
+ lambda a, x: x[0] - x[1] + a, (elems + 1, elems), initializer)
+# sum_one == [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
+```
+
+```python
+elems = np.array([1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0])
+initializer = (np.array(0), np.array(1))
+fibonaccis = scan(lambda a, _: (a[1], a[0] + a[1]), elems, initializer)
+# fibonaccis == ([1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8], [1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13])
+```
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scatter_add.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scatter_add.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..88c515d9012
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scatter_add.md
@@ -0,0 +1,120 @@
+description: Adds sparse updates to the variable referenced by resource.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.scatter_add
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Adds sparse updates to the variable referenced by `resource`.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.scatter_add(
+ ref, indices, updates, use_locking=(False), name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This operation computes
+
+```python
+ # Scalar indices
+ ref[indices, ...] += updates[...]
+
+ # Vector indices (for each i)
+ ref[indices[i], ...] += updates[i, ...]
+
+ # High rank indices (for each i, ..., j)
+ ref[indices[i, ..., j], ...] += updates[i, ..., j, ...]
+```
+
+This operation outputs `ref` after the update is done.
+This makes it easier to chain operations that need to use the updated value.
+Duplicate entries are handled correctly: if multiple `indices` reference
+the same location, their contributions add.
+
+Requires `updates.shape = indices.shape + ref.shape[1:]`.
+
+
+
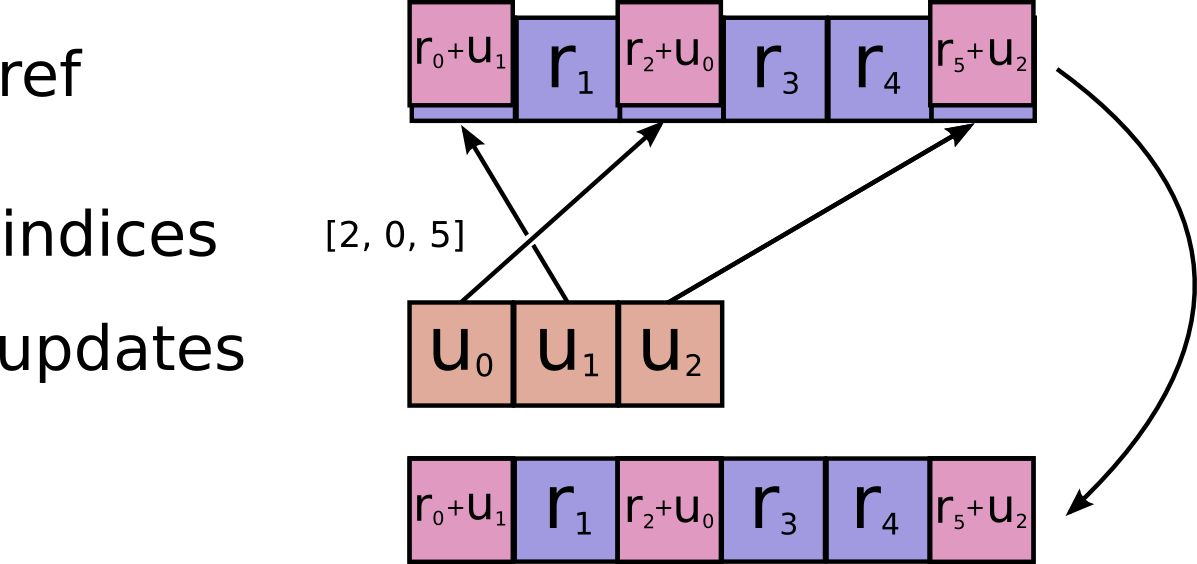
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ref`
+ |
+
+A `Variable`.
+ |
+
+|
+`indices`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `int32`, `int64`.
+A tensor of indices into the first dimension of `ref`.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must have the same type as `ref`.
+A tensor of updated values to store in `ref`.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_locking`
+ |
+
+An optional `bool`. Defaults to `False`.
+If True, the assignment will be protected by a lock;
+otherwise the behavior is undefined, but may exhibit less contention.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Same as `ref`. Returned as a convenience for operations that want
+to use the updated values after the update is done.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scatter_div.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scatter_div.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..4708206c8ef
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scatter_div.md
@@ -0,0 +1,120 @@
+description: Divides a variable reference by sparse updates.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.scatter_div
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Divides a variable reference by sparse updates.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.scatter_div(
+ ref, indices, updates, use_locking=(False), name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This operation computes
+
+```python
+ # Scalar indices
+ ref[indices, ...] /= updates[...]
+
+ # Vector indices (for each i)
+ ref[indices[i], ...] /= updates[i, ...]
+
+ # High rank indices (for each i, ..., j)
+ ref[indices[i, ..., j], ...] /= updates[i, ..., j, ...]
+```
+
+This operation outputs `ref` after the update is done.
+This makes it easier to chain operations that need to use the reset value.
+
+Duplicate entries are handled correctly: if multiple `indices` reference
+the same location, their contributions divide.
+
+Requires `updates.shape = indices.shape + ref.shape[1:]` or `updates.shape =
+[]`.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ref`
+ |
+
+A mutable `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `float32`,
+`float64`, `int32`, `uint8`, `int16`, `int8`, `complex64`, `int64`,
+`qint8`, `quint8`, `qint32`, `bfloat16`, `uint16`, `complex128`, `half`,
+`uint32`, `uint64`. Should be from a `Variable` node.
+ |
+
+|
+`indices`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `int32`, `int64`. A
+tensor of indices into the first dimension of `ref`.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must have the same type as `ref`. A tensor of values
+that `ref` is divided by.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_locking`
+ |
+
+An optional `bool`. Defaults to `False`. If True, the operation
+will be protected by a lock; otherwise the behavior is undefined, but may
+exhibit less contention.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A mutable `Tensor`. Has the same type as `ref`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scatter_max.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scatter_max.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..507503b58be
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scatter_max.md
@@ -0,0 +1,123 @@
+description: Reduces sparse updates into a variable reference using the max operation.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.scatter_max
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Reduces sparse updates into a variable reference using the `max` operation.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.scatter_max(
+ ref, indices, updates, use_locking=(False), name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This operation computes
+
+ # Scalar indices
+ ref[indices, ...] = max(ref[indices, ...], updates[...])
+
+ # Vector indices (for each i)
+ ref[indices[i], ...] = max(ref[indices[i], ...], updates[i, ...])
+
+ # High rank indices (for each i, ..., j)
+ ref[indices[i, ..., j], ...] = max(ref[indices[i, ..., j], ...],
+ updates[i, ..., j, ...])
+
+This operation outputs `ref` after the update is done.
+This makes it easier to chain operations that need to use the reset value.
+
+Duplicate entries are handled correctly: if multiple `indices` reference
+the same location, their contributions combine.
+
+Requires `updates.shape = indices.shape + ref.shape[1:]` or `updates.shape =
+[]`.
+
+
+
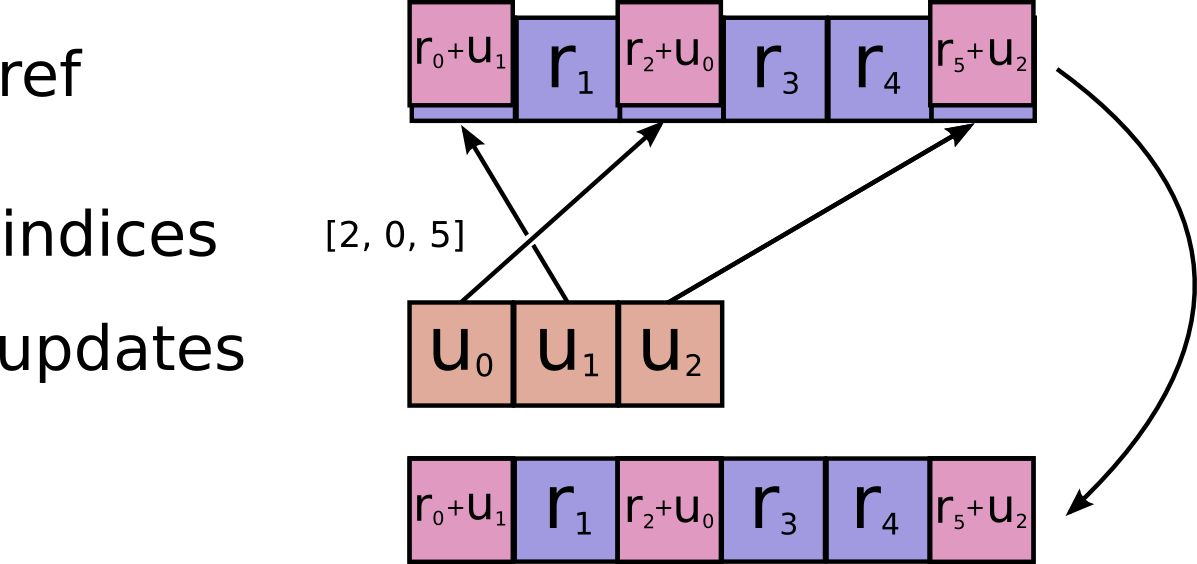
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ref`
+ |
+
+A mutable `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `half`,
+`bfloat16`, `float32`, `float64`, `int32`, `int64`. Should be from a
+`Variable` node.
+ |
+
+|
+`indices`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `int32`, `int64`. A
+tensor of indices into the first dimension of `ref`.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must have the same type as `ref`. A tensor of updated
+values to reduce into `ref`.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_locking`
+ |
+
+An optional `bool`. Defaults to `False`. If True, the update
+will be protected by a lock; otherwise the behavior is undefined, but may
+exhibit less contention.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A mutable `Tensor`. Has the same type as `ref`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scatter_min.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scatter_min.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..d398c7c15f6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scatter_min.md
@@ -0,0 +1,123 @@
+description: Reduces sparse updates into a variable reference using the min operation.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.scatter_min
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Reduces sparse updates into a variable reference using the `min` operation.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.scatter_min(
+ ref, indices, updates, use_locking=(False), name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This operation computes
+
+ # Scalar indices
+ ref[indices, ...] = min(ref[indices, ...], updates[...])
+
+ # Vector indices (for each i)
+ ref[indices[i], ...] = min(ref[indices[i], ...], updates[i, ...])
+
+ # High rank indices (for each i, ..., j)
+ ref[indices[i, ..., j], ...] = min(ref[indices[i, ..., j], ...],
+ updates[i, ..., j, ...])
+
+This operation outputs `ref` after the update is done.
+This makes it easier to chain operations that need to use the reset value.
+
+Duplicate entries are handled correctly: if multiple `indices` reference
+the same location, their contributions combine.
+
+Requires `updates.shape = indices.shape + ref.shape[1:]` or `updates.shape =
+[]`.
+
+
+
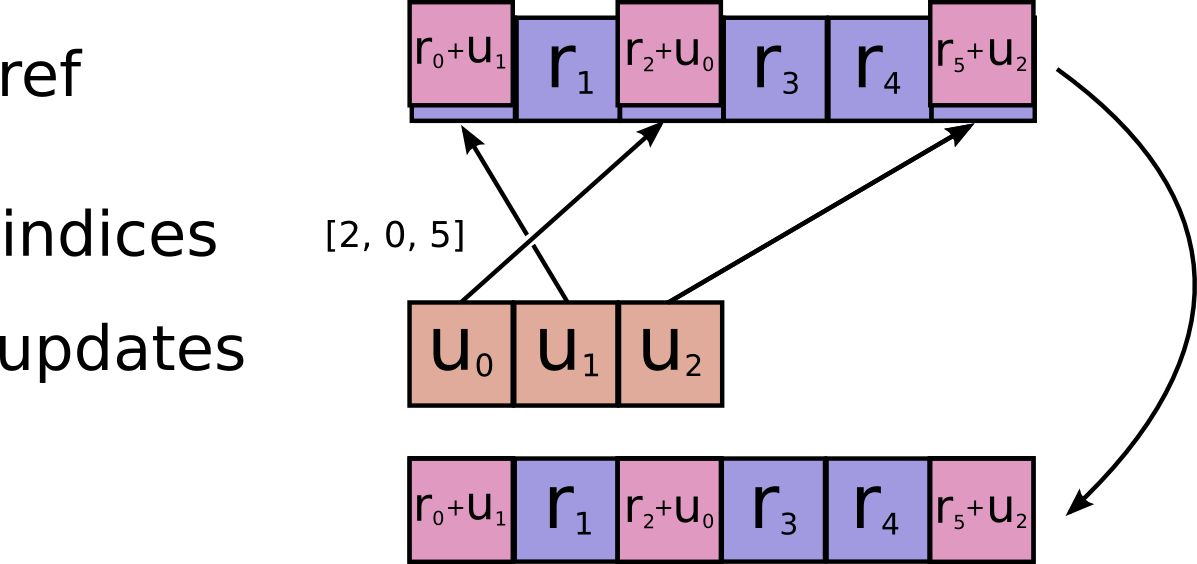
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ref`
+ |
+
+A mutable `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `half`,
+`bfloat16`, `float32`, `float64`, `int32`, `int64`. Should be from a
+`Variable` node.
+ |
+
+|
+`indices`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `int32`, `int64`. A
+tensor of indices into the first dimension of `ref`.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must have the same type as `ref`. A tensor of updated
+values to reduce into `ref`.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_locking`
+ |
+
+An optional `bool`. Defaults to `False`. If True, the update
+will be protected by a lock; otherwise the behavior is undefined, but may
+exhibit less contention.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A mutable `Tensor`. Has the same type as `ref`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scatter_mul.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scatter_mul.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..83136c36d70
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scatter_mul.md
@@ -0,0 +1,120 @@
+description: Multiplies sparse updates into a variable reference.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.scatter_mul
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Multiplies sparse updates into a variable reference.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.scatter_mul(
+ ref, indices, updates, use_locking=(False), name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This operation computes
+
+```python
+ # Scalar indices
+ ref[indices, ...] *= updates[...]
+
+ # Vector indices (for each i)
+ ref[indices[i], ...] *= updates[i, ...]
+
+ # High rank indices (for each i, ..., j)
+ ref[indices[i, ..., j], ...] *= updates[i, ..., j, ...]
+```
+
+This operation outputs `ref` after the update is done.
+This makes it easier to chain operations that need to use the reset value.
+
+Duplicate entries are handled correctly: if multiple `indices` reference
+the same location, their contributions multiply.
+
+Requires `updates.shape = indices.shape + ref.shape[1:]` or `updates.shape =
+[]`.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ref`
+ |
+
+A mutable `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `float32`,
+`float64`, `int32`, `uint8`, `int16`, `int8`, `complex64`, `int64`,
+`qint8`, `quint8`, `qint32`, `bfloat16`, `uint16`, `complex128`, `half`,
+`uint32`, `uint64`. Should be from a `Variable` node.
+ |
+
+|
+`indices`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `int32`, `int64`. A
+tensor of indices into the first dimension of `ref`.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must have the same type as `ref`. A tensor of updated
+values to multiply to `ref`.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_locking`
+ |
+
+An optional `bool`. Defaults to `False`. If True, the operation
+will be protected by a lock; otherwise the behavior is undefined, but may
+exhibit less contention.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A mutable `Tensor`. Has the same type as `ref`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scatter_nd_add.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scatter_nd_add.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..65fab970ed2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scatter_nd_add.md
@@ -0,0 +1,132 @@
+description: Applies sparse addition to individual values or slices in a Variable.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.scatter_nd_add
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Applies sparse addition to individual values or slices in a Variable.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.scatter_nd_add(
+ ref, indices, updates, use_locking=(False), name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+`ref` is a `Tensor` with rank `P` and `indices` is a `Tensor` of rank `Q`.
+
+`indices` must be integer tensor, containing indices into `ref`.
+It must be shape `[d_0, ..., d_{Q-2}, K]` where `0 < K <= P`.
+
+The innermost dimension of `indices` (with length `K`) corresponds to
+indices into elements (if `K = P`) or slices (if `K < P`) along the `K`th
+dimension of `ref`.
+
+`updates` is `Tensor` of rank `Q-1+P-K` with shape:
+
+```
+[d_0, ..., d_{Q-2}, ref.shape[K], ..., ref.shape[P-1]]
+```
+
+For example, say we want to add 4 scattered elements to a rank-1 tensor to
+8 elements. In Python, that addition would look like this:
+
+```python
+ref = tf.Variable([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8])
+indices = tf.constant([[4], [3], [1], [7]])
+updates = tf.constant([9, 10, 11, 12])
+add = tf.compat.v1.scatter_nd_add(ref, indices, updates)
+with tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess:
+ print sess.run(add)
+```
+
+The resulting update to ref would look like this:
+
+ [1, 13, 3, 14, 14, 6, 7, 20]
+
+See tf.scatter_nd for more details about how to make updates to
+slices.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ref`
+ |
+
+A mutable `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `float32`,
+`float64`, `int32`, `uint8`, `int16`, `int8`, `complex64`, `int64`,
+`qint8`, `quint8`, `qint32`, `bfloat16`, `uint16`, `complex128`, `half`,
+`uint32`, `uint64`. A mutable Tensor. Should be from a Variable node.
+ |
+
+|
+`indices`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `int32`, `int64`.
+A tensor of indices into ref.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must have the same type as `ref`.
+A tensor of updated values to add to ref.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_locking`
+ |
+
+An optional `bool`. Defaults to `False`.
+If True, the assignment will be protected by a lock;
+otherwise the behavior is undefined, but may exhibit less contention.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A mutable `Tensor`. Has the same type as `ref`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scatter_nd_sub.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scatter_nd_sub.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..5ce09c0ced5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scatter_nd_sub.md
@@ -0,0 +1,133 @@
+description: Applies sparse subtraction to individual values or slices in a Variable.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.scatter_nd_sub
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Applies sparse subtraction to individual values or slices in a Variable.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.scatter_nd_sub(
+ ref, indices, updates, use_locking=(False), name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+`ref` is a `Tensor` with rank `P` and `indices` is a `Tensor` of rank `Q`.
+
+`indices` must be integer tensor, containing indices into `ref`.
+It must be shape `[d_0, ..., d_{Q-2}, K]` where `0 < K <= P`.
+
+The innermost dimension of `indices` (with length `K`) corresponds to
+indices into elements (if `K = P`) or slices (if `K < P`) along the `K`th
+dimension of `ref`.
+
+`updates` is `Tensor` of rank `Q-1+P-K` with shape:
+
+```
+[d_0, ..., d_{Q-2}, ref.shape[K], ..., ref.shape[P-1]]
+```
+
+For example, say we want to subtract 4 scattered elements from a rank-1 tensor
+with 8 elements. In Python, that update would look like this:
+
+```python
+ref = tf.Variable([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8])
+indices = tf.constant([[4], [3], [1] ,[7]])
+updates = tf.constant([9, 10, 11, 12])
+op = tf.compat.v1.scatter_nd_sub(ref, indices, updates)
+with tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess:
+ print sess.run(op)
+```
+
+The resulting update to ref would look like this:
+
+ [1, -9, 3, -6, -6, 6, 7, -4]
+
+See tf.scatter_nd for more details about how to make updates to
+slices.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ref`
+ |
+
+A mutable `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `float32`,
+`float64`, `int32`, `uint8`, `int16`, `int8`, `complex64`, `int64`,
+`qint8`, `quint8`, `qint32`, `bfloat16`, `uint16`, `complex128`, `half`,
+`uint32`, `uint64`. A mutable Tensor. Should be from a Variable node.
+ |
+
+|
+`indices`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `int32`, `int64`.
+A tensor of indices into ref.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must have the same type as `ref`.
+A tensor of updated values to add to ref.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_locking`
+ |
+
+An optional `bool`. Defaults to `False`.
+An optional bool. Defaults to True. If True, the assignment will
+be protected by a lock; otherwise the behavior is undefined,
+but may exhibit less contention.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A mutable `Tensor`. Has the same type as `ref`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scatter_nd_update.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scatter_nd_update.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..6a9b82b2b95
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scatter_nd_update.md
@@ -0,0 +1,131 @@
+description: Applies sparse updates to individual values or slices in a Variable.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.scatter_nd_update
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Applies sparse `updates` to individual values or slices in a Variable.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.scatter_nd_update(
+ ref, indices, updates, use_locking=(True), name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+`ref` is a `Tensor` with rank `P` and `indices` is a `Tensor` of rank `Q`.
+
+`indices` must be integer tensor, containing indices into `ref`.
+It must be shape `[d_0, ..., d_{Q-2}, K]` where `0 < K <= P`.
+
+The innermost dimension of `indices` (with length `K`) corresponds to
+indices into elements (if `K = P`) or slices (if `K < P`) along the `K`th
+dimension of `ref`.
+
+`updates` is `Tensor` of rank `Q-1+P-K` with shape:
+
+```
+[d_0, ..., d_{Q-2}, ref.shape[K], ..., ref.shape[P-1]].
+```
+
+For example, say we want to update 4 scattered elements to a rank-1 tensor to
+8 elements. In Python, that update would look like this:
+
+```python
+ ref = tf.Variable([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8])
+ indices = tf.constant([[4], [3], [1] ,[7]])
+ updates = tf.constant([9, 10, 11, 12])
+ update = tf.compat.v1.scatter_nd_update(ref, indices, updates)
+ with tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess:
+ print sess.run(update)
+```
+
+The resulting update to ref would look like this:
+
+ [1, 11, 3, 10, 9, 6, 7, 12]
+
+See tf.scatter_nd for more details about how to make updates to
+slices.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ref`
+ |
+
+A Variable.
+ |
+
+|
+`indices`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `int32`, `int64`.
+A tensor of indices into ref.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must have the same type as `ref`.
+A Tensor. Must have the same type as ref. A tensor of updated
+values to add to ref.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_locking`
+ |
+
+An optional `bool`. Defaults to `True`.
+An optional bool. Defaults to True. If True, the assignment will
+be protected by a lock; otherwise the behavior is undefined,
+but may exhibit less contention.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The value of the variable after the update.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scatter_sub.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scatter_sub.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..4ef76f03595
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scatter_sub.md
@@ -0,0 +1,123 @@
+description: Subtracts sparse updates to a variable reference.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.scatter_sub
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Subtracts sparse updates to a variable reference.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.scatter_sub(
+ ref, indices, updates, use_locking=(False), name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+```python
+ # Scalar indices
+ ref[indices, ...] -= updates[...]
+
+ # Vector indices (for each i)
+ ref[indices[i], ...] -= updates[i, ...]
+
+ # High rank indices (for each i, ..., j)
+ ref[indices[i, ..., j], ...] -= updates[i, ..., j, ...]
+```
+
+This operation outputs `ref` after the update is done.
+This makes it easier to chain operations that need to use the reset value.
+
+Duplicate entries are handled correctly: if multiple `indices` reference
+the same location, their (negated) contributions add.
+
+Requires `updates.shape = indices.shape + ref.shape[1:]` or
+`updates.shape = []`.
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ref`
+ |
+
+A mutable `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `float32`,
+`float64`, `int32`, `uint8`, `int16`, `int8`, `complex64`, `int64`,
+`qint8`, `quint8`, `qint32`, `bfloat16`, `uint16`, `complex128`, `half`,
+`uint32`, `uint64`. Should be from a `Variable` node.
+ |
+
+|
+`indices`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `int32`, `int64`.
+A tensor of indices into the first dimension of `ref`.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must have the same type as `ref`.
+A tensor of updated values to subtract from `ref`.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_locking`
+ |
+
+An optional `bool`. Defaults to `False`.
+If True, the subtraction will be protected by a lock;
+otherwise the behavior is undefined, but may exhibit less contention.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A mutable `Tensor`. Has the same type as `ref`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scatter_update.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scatter_update.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..dcd029b31d1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/scatter_update.md
@@ -0,0 +1,122 @@
+description: Applies sparse updates to a variable reference.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.scatter_update
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Applies sparse updates to a variable reference.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.scatter_update(
+ ref, indices, updates, use_locking=(True), name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This operation computes
+
+```python
+ # Scalar indices
+ ref[indices, ...] = updates[...]
+
+ # Vector indices (for each i)
+ ref[indices[i], ...] = updates[i, ...]
+
+ # High rank indices (for each i, ..., j)
+ ref[indices[i, ..., j], ...] = updates[i, ..., j, ...]
+```
+
+This operation outputs `ref` after the update is done.
+This makes it easier to chain operations that need to use the reset value.
+
+If values in `ref` is to be updated more than once, because there are
+duplicate entries in `indices`, the order at which the updates happen
+for each value is undefined.
+
+Requires `updates.shape = indices.shape + ref.shape[1:]`.
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ref`
+ |
+
+A `Variable`.
+ |
+
+|
+`indices`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `int32`, `int64`.
+A tensor of indices into the first dimension of `ref`.
+ |
+
+|
+`updates`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must have the same type as `ref`.
+A tensor of updated values to store in `ref`.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_locking`
+ |
+
+An optional `bool`. Defaults to `True`.
+If True, the assignment will be protected by a lock;
+otherwise the behavior is undefined, but may exhibit less contention.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Same as `ref`. Returned as a convenience for operations that want
+to use the updated values after the update is done.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/serialize_many_sparse.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/serialize_many_sparse.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..7f86b5ccdda
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/serialize_many_sparse.md
@@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
+description: Serialize N-minibatch SparseTensor into an [N, 3] Tensor.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.serialize_many_sparse
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Serialize `N`-minibatch `SparseTensor` into an `[N, 3]` `Tensor`.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.io.serialize_many_sparse`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.serialize_many_sparse(
+ sp_input, name=None, out_type=tf.dtypes.string
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The `SparseTensor` must have rank `R` greater than 1, and the first dimension
+is treated as the minibatch dimension. Elements of the `SparseTensor`
+must be sorted in increasing order of this first dimension. The serialized
+`SparseTensor` objects going into each row of the output `Tensor` will have
+rank `R-1`.
+
+The minibatch size `N` is extracted from `sparse_shape[0]`.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sp_input`
+ |
+
+The input rank `R` `SparseTensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name prefix for the returned tensors (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`out_type`
+ |
+
+The `dtype` to use for serialization.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A matrix (2-D `Tensor`) with `N` rows and `3` columns. Each column
+represents serialized `SparseTensor`'s indices, values, and shape
+(respectively).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `sp_input` is not a `SparseTensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/serialize_sparse.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/serialize_sparse.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..5bf602e8801
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/serialize_sparse.md
@@ -0,0 +1,107 @@
+description: Serialize a SparseTensor into a 3-vector (1-D Tensor) object.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.serialize_sparse
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Serialize a `SparseTensor` into a 3-vector (1-D `Tensor`) object.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.io.serialize_sparse`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.serialize_sparse(
+ sp_input, name=None, out_type=tf.dtypes.string
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sp_input`
+ |
+
+The input `SparseTensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name prefix for the returned tensors (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`out_type`
+ |
+
+The `dtype` to use for serialization.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A 3-vector (1-D `Tensor`), with each column representing the serialized
+`SparseTensor`'s indices, values, and shape (respectively).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `sp_input` is not a `SparseTensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/set_random_seed.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/set_random_seed.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..6bd57230099
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/set_random_seed.md
@@ -0,0 +1,153 @@
+description: Sets the graph-level random seed for the default graph.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.set_random_seed
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Sets the graph-level random seed for the default graph.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.random.set_random_seed`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.set_random_seed(
+ seed
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Operations that rely on a random seed actually derive it from two seeds:
+the graph-level and operation-level seeds. This sets the graph-level seed.
+
+Its interactions with operation-level seeds is as follows:
+
+ 1. If neither the graph-level nor the operation seed is set:
+ A random seed is used for this op.
+ 2. If the graph-level seed is set, but the operation seed is not:
+ The system deterministically picks an operation seed in conjunction with
+ the graph-level seed so that it gets a unique random sequence. Within the
+ same version of tensorflow and user code, this sequence is deterministic.
+ However across different versions, this sequence might change. If the
+ code depends on particular seeds to work, specify both graph-level
+ and operation-level seeds explicitly.
+ 3. If the graph-level seed is not set, but the operation seed is set:
+ A default graph-level seed and the specified operation seed are used to
+ determine the random sequence.
+ 4. If both the graph-level and the operation seed are set:
+ Both seeds are used in conjunction to determine the random sequence.
+
+To illustrate the user-visible effects, consider these examples:
+
+To generate different sequences across sessions, set neither
+graph-level nor op-level seeds:
+
+```python
+a = tf.random.uniform([1])
+b = tf.random.normal([1])
+
+print("Session 1")
+with tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess1:
+ print(sess1.run(a)) # generates 'A1'
+ print(sess1.run(a)) # generates 'A2'
+ print(sess1.run(b)) # generates 'B1'
+ print(sess1.run(b)) # generates 'B2'
+
+print("Session 2")
+with tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess2:
+ print(sess2.run(a)) # generates 'A3'
+ print(sess2.run(a)) # generates 'A4'
+ print(sess2.run(b)) # generates 'B3'
+ print(sess2.run(b)) # generates 'B4'
+```
+
+To generate the same repeatable sequence for an op across sessions, set the
+seed for the op:
+
+```python
+a = tf.random.uniform([1], seed=1)
+b = tf.random.normal([1])
+
+# Repeatedly running this block with the same graph will generate the same
+# sequence of values for 'a', but different sequences of values for 'b'.
+print("Session 1")
+with tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess1:
+ print(sess1.run(a)) # generates 'A1'
+ print(sess1.run(a)) # generates 'A2'
+ print(sess1.run(b)) # generates 'B1'
+ print(sess1.run(b)) # generates 'B2'
+
+print("Session 2")
+with tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess2:
+ print(sess2.run(a)) # generates 'A1'
+ print(sess2.run(a)) # generates 'A2'
+ print(sess2.run(b)) # generates 'B3'
+ print(sess2.run(b)) # generates 'B4'
+```
+
+To make the random sequences generated by all ops be repeatable across
+sessions, set a graph-level seed:
+
+```python
+tf.compat.v1.random.set_random_seed(1234)
+a = tf.random.uniform([1])
+b = tf.random.normal([1])
+
+# Repeatedly running this block with the same graph will generate the same
+# sequences of 'a' and 'b'.
+print("Session 1")
+with tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess1:
+ print(sess1.run(a)) # generates 'A1'
+ print(sess1.run(a)) # generates 'A2'
+ print(sess1.run(b)) # generates 'B1'
+ print(sess1.run(b)) # generates 'B2'
+
+print("Session 2")
+with tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess2:
+ print(sess2.run(a)) # generates 'A1'
+ print(sess2.run(a)) # generates 'A2'
+ print(sess2.run(b)) # generates 'B1'
+ print(sess2.run(b)) # generates 'B2'
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+integer.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/setdiff1d.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/setdiff1d.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..79c7bb50c83
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/setdiff1d.md
@@ -0,0 +1,120 @@
+description: Computes the difference between two lists of numbers or strings.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.setdiff1d
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the difference between two lists of numbers or strings.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.setdiff1d(
+ x, y, index_dtype=tf.dtypes.int32, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Given a list `x` and a list `y`, this operation returns a list `out` that
+represents all values that are in `x` but not in `y`. The returned list `out`
+is sorted in the same order that the numbers appear in `x` (duplicates are
+preserved). This operation also returns a list `idx` that represents the
+position of each `out` element in `x`. In other words:
+
+`out[i] = x[idx[i]] for i in [0, 1, ..., len(out) - 1]`
+
+For example, given this input:
+
+```
+x = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
+y = [1, 3, 5]
+```
+
+This operation would return:
+
+```
+out ==> [2, 4, 6]
+idx ==> [1, 3, 5]
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`x`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. 1-D. Values to keep.
+ |
+
+|
+`y`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must have the same type as `x`. 1-D. Values to remove.
+ |
+
+|
+`out_idx`
+ |
+
+An optional tf.DType from: `tf.int32, tf.int64`. Defaults to tf.int32.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A tuple of `Tensor` objects (out, idx).
+ |
+
+
+|
+`out`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `x`.
+ |
+
+|
+`idx`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `out_idx`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sets.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sets.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..8e6f70efb85
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sets.md
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
+description: Tensorflow set operations.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.sets
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Tensorflow set operations.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`difference(...)`](../../../tf/sets/difference.md): Compute set difference of elements in last dimension of `a` and `b`.
+
+[`intersection(...)`](../../../tf/sets/intersection.md): Compute set intersection of elements in last dimension of `a` and `b`.
+
+[`set_difference(...)`](../../../tf/sets/difference.md): Compute set difference of elements in last dimension of `a` and `b`.
+
+[`set_intersection(...)`](../../../tf/sets/intersection.md): Compute set intersection of elements in last dimension of `a` and `b`.
+
+[`set_size(...)`](../../../tf/sets/size.md): Compute number of unique elements along last dimension of `a`.
+
+[`set_union(...)`](../../../tf/sets/union.md): Compute set union of elements in last dimension of `a` and `b`.
+
+[`size(...)`](../../../tf/sets/size.md): Compute number of unique elements along last dimension of `a`.
+
+[`union(...)`](../../../tf/sets/union.md): Compute set union of elements in last dimension of `a` and `b`.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/shape.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/shape.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..c1c6bdf3736
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/shape.md
@@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
+description: Returns the shape of a tensor.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.shape
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns the shape of a tensor.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.shape(
+ input, name=None, out_type=tf.dtypes.int32
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This operation returns a 1-D integer tensor representing the shape of `input`.
+
+#### For example:
+
+
+
+```python
+t = tf.constant([[[1, 1, 1], [2, 2, 2]], [[3, 3, 3], [4, 4, 4]]])
+tf.shape(t) # [2, 2, 3]
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` or `SparseTensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`out_type`
+ |
+
+(Optional) The specified output type of the operation (`int32`
+or `int64`). Defaults to tf.int32.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` of type `out_type`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/signal.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/signal.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e25735363c9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/signal.md
@@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
+description: Signal processing operations.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.signal
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Signal processing operations.
+
+
+See the [tf.signal](https://tensorflow.org/api_guides/python/contrib.signal)
+guide.
+
+
+[hamming]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Window_function#Hamming_window
+[hann]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Window_function#Hann_window
+[mel]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mel_scale
+[mfcc]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mel-frequency_cepstrum
+[stft]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Short-time_Fourier_transform
+
+## Functions
+
+[`dct(...)`](../../../tf/signal/dct.md): Computes the 1D [Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT)][dct] of `input`.
+
+[`fft(...)`](../../../tf/signal/fft.md): Fast Fourier transform.
+
+[`fft2d(...)`](../../../tf/signal/fft2d.md): 2D fast Fourier transform.
+
+[`fft3d(...)`](../../../tf/signal/fft3d.md): 3D fast Fourier transform.
+
+[`fftshift(...)`](../../../tf/signal/fftshift.md): Shift the zero-frequency component to the center of the spectrum.
+
+[`frame(...)`](../../../tf/signal/frame.md): Expands `signal`'s `axis` dimension into frames of `frame_length`.
+
+[`hamming_window(...)`](../../../tf/signal/hamming_window.md): Generate a [Hamming][hamming] window.
+
+[`hann_window(...)`](../../../tf/signal/hann_window.md): Generate a [Hann window][hann].
+
+[`idct(...)`](../../../tf/signal/idct.md): Computes the 1D [Inverse Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT)][idct] of `input`.
+
+[`ifft(...)`](../../../tf/signal/ifft.md): Inverse fast Fourier transform.
+
+[`ifft2d(...)`](../../../tf/signal/ifft2d.md): Inverse 2D fast Fourier transform.
+
+[`ifft3d(...)`](../../../tf/signal/ifft3d.md): Inverse 3D fast Fourier transform.
+
+[`ifftshift(...)`](../../../tf/signal/ifftshift.md): The inverse of fftshift.
+
+[`inverse_mdct(...)`](../../../tf/signal/inverse_mdct.md): Computes the inverse modified DCT of `mdcts`.
+
+[`inverse_stft(...)`](../../../tf/signal/inverse_stft.md): Computes the inverse [Short-time Fourier Transform][stft] of `stfts`.
+
+[`inverse_stft_window_fn(...)`](../../../tf/signal/inverse_stft_window_fn.md): Generates a window function that can be used in `inverse_stft`.
+
+[`irfft(...)`](../../../tf/signal/irfft.md): Inverse real-valued fast Fourier transform.
+
+[`irfft2d(...)`](../../../tf/signal/irfft2d.md): Inverse 2D real-valued fast Fourier transform.
+
+[`irfft3d(...)`](../../../tf/signal/irfft3d.md): Inverse 3D real-valued fast Fourier transform.
+
+[`kaiser_bessel_derived_window(...)`](../../../tf/signal/kaiser_bessel_derived_window.md): Generate a [Kaiser Bessel derived window][kbd].
+
+[`kaiser_window(...)`](../../../tf/signal/kaiser_window.md): Generate a [Kaiser window][kaiser].
+
+[`linear_to_mel_weight_matrix(...)`](../../../tf/signal/linear_to_mel_weight_matrix.md): Returns a matrix to warp linear scale spectrograms to the [mel scale][mel].
+
+[`mdct(...)`](../../../tf/signal/mdct.md): Computes the [Modified Discrete Cosine Transform][mdct] of `signals`.
+
+[`mfccs_from_log_mel_spectrograms(...)`](../../../tf/signal/mfccs_from_log_mel_spectrograms.md): Computes [MFCCs][mfcc] of `log_mel_spectrograms`.
+
+[`overlap_and_add(...)`](../../../tf/signal/overlap_and_add.md): Reconstructs a signal from a framed representation.
+
+[`rfft(...)`](../../../tf/signal/rfft.md): Real-valued fast Fourier transform.
+
+[`rfft2d(...)`](../../../tf/signal/rfft2d.md): 2D real-valued fast Fourier transform.
+
+[`rfft3d(...)`](../../../tf/signal/rfft3d.md): 3D real-valued fast Fourier transform.
+
+[`stft(...)`](../../../tf/signal/stft.md): Computes the [Short-time Fourier Transform][stft] of `signals`.
+
+[`vorbis_window(...)`](../../../tf/signal/vorbis_window.md): Generate a [Vorbis power complementary window][vorbis].
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/size.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/size.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..f02dceb78e1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/size.md
@@ -0,0 +1,96 @@
+description: Returns the size of a tensor.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.size
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns the size of a tensor.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.size(
+ input, name=None, out_type=tf.dtypes.int32
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns a 0-D `Tensor` representing the number of elements in `input`
+of type `out_type`. Defaults to tf.int32.
+
+#### For example:
+
+
+
+```python
+t = tf.constant([[[1, 1, 1], [2, 2, 2]], [[3, 3, 3], [4, 4, 4]]])
+tf.size(t) # 12
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` or `SparseTensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`out_type`
+ |
+
+(Optional) The specified non-quantized numeric output type of the
+operation. Defaults to tf.int32.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+A `Tensor` of type `out_type`. Defaults to tf.int32.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Numpy Compatibility
+Equivalent to np.size()
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/space_to_batch.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/space_to_batch.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..971edde5ee5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/space_to_batch.md
@@ -0,0 +1,188 @@
+description: SpaceToBatch for 4-D tensors of type T.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.space_to_batch
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+SpaceToBatch for 4-D tensors of type T.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.nn.space_to_batch`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.space_to_batch(
+ input, paddings, block_size=None, name=None, block_shape=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This is a legacy version of the more general SpaceToBatchND.
+
+Zero-pads and then rearranges (permutes) blocks of spatial data into batch.
+More specifically, this op outputs a copy of the input tensor where values from
+the `height` and `width` dimensions are moved to the `batch` dimension. After
+the zero-padding, both `height` and `width` of the input must be divisible by the
+block size.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. 4-D with shape `[batch, height, width, depth]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`paddings`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `int32`, `int64`.
+2-D tensor of non-negative integers with shape `[2, 2]`. It specifies
+the padding of the input with zeros across the spatial dimensions as follows:
+
+paddings = [[pad_top, pad_bottom], [pad_left, pad_right]]
+
+The effective spatial dimensions of the zero-padded input tensor will be:
+
+height_pad = pad_top + height + pad_bottom
+width_pad = pad_left + width + pad_right
+
+The attr `block_size` must be greater than one. It indicates the block size.
+
+* Non-overlapping blocks of size `block_size x block size` in the height and
+width dimensions are rearranged into the batch dimension at each location.
+* The batch of the output tensor is `batch * block_size * block_size`.
+* Both height_pad and width_pad must be divisible by block_size.
+
+The shape of the output will be:
+
+[batch*block_size*block_size, height_pad/block_size, width_pad/block_size,
+depth]
+
+Some examples:
+
+(1) For the following input of shape `[1, 2, 2, 1]` and block_size of 2:
+
+```
+x = [[[[1], [2]], [[3], [4]]]]
+```
+
+The output tensor has shape `[4, 1, 1, 1]` and value:
+
+```
+[[[[1]]], [[[2]]], [[[3]]], [[[4]]]]
+```
+
+(2) For the following input of shape `[1, 2, 2, 3]` and block_size of 2:
+
+```
+x = [[[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]],
+[[7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 12]]]]
+```
+
+The output tensor has shape `[4, 1, 1, 3]` and value:
+
+```
+[[[[1, 2, 3]]], [[[4, 5, 6]]], [[[7, 8, 9]]], [[[10, 11, 12]]]]
+```
+
+(3) For the following input of shape `[1, 4, 4, 1]` and block_size of 2:
+
+```
+x = [[[[1], [2], [3], [4]],
+[[5], [6], [7], [8]],
+[[9], [10], [11], [12]],
+[[13], [14], [15], [16]]]]
+```
+
+The output tensor has shape `[4, 2, 2, 1]` and value:
+
+```
+x = [[[[1], [3]], [[9], [11]]],
+[[[2], [4]], [[10], [12]]],
+[[[5], [7]], [[13], [15]]],
+[[[6], [8]], [[14], [16]]]]
+```
+
+(4) For the following input of shape `[2, 2, 4, 1]` and block_size of 2:
+
+```
+x = [[[[1], [2], [3], [4]],
+[[5], [6], [7], [8]]],
+[[[9], [10], [11], [12]],
+[[13], [14], [15], [16]]]]
+```
+
+The output tensor has shape `[8, 1, 2, 1]` and value:
+
+```
+x = [[[[1], [3]]], [[[9], [11]]], [[[2], [4]]], [[[10], [12]]],
+[[[5], [7]]], [[[13], [15]]], [[[6], [8]]], [[[14], [16]]]]
+```
+
+Among others, this operation is useful for reducing atrous convolution into
+regular convolution.
+ |
+
+|
+`block_size`
+ |
+
+An `int` that is `>= 2`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `input`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/space_to_depth.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/space_to_depth.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..c33b260b86b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/space_to_depth.md
@@ -0,0 +1,179 @@
+description: SpaceToDepth for tensors of type T.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.space_to_depth
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+SpaceToDepth for tensors of type T.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.nn.space_to_depth`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.space_to_depth(
+ input, block_size, name=None, data_format='NHWC'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Rearranges blocks of spatial data, into depth. More specifically,
+this op outputs a copy of the input tensor where values from the `height`
+and `width` dimensions are moved to the `depth` dimension.
+The attr `block_size` indicates the input block size.
+
+ * Non-overlapping blocks of size `block_size x block size` are rearranged
+ into depth at each location.
+ * The depth of the output tensor is `block_size * block_size * input_depth`.
+ * The Y, X coordinates within each block of the input become the high order
+ component of the output channel index.
+ * The input tensor's height and width must be divisible by block_size.
+
+The `data_format` attr specifies the layout of the input and output tensors
+with the following options:
+ "NHWC": `[ batch, height, width, channels ]`
+ "NCHW": `[ batch, channels, height, width ]`
+ "NCHW_VECT_C":
+ `qint8 [ batch, channels / 4, height, width, 4 ]`
+
+It is useful to consider the operation as transforming a 6-D Tensor.
+e.g. for data_format = NHWC,
+ Each element in the input tensor can be specified via 6 coordinates,
+ ordered by decreasing memory layout significance as:
+ n,oY,bY,oX,bX,iC (where n=batch index, oX, oY means X or Y coordinates
+ within the output image, bX, bY means coordinates
+ within the input block, iC means input channels).
+ The output would be a transpose to the following layout:
+ n,oY,oX,bY,bX,iC
+
+This operation is useful for resizing the activations between convolutions
+(but keeping all data), e.g. instead of pooling. It is also useful for training
+purely convolutional models.
+
+For example, given an input of shape `[1, 2, 2, 1]`, data_format = "NHWC" and
+block_size = 2:
+
+```
+x = [[[[1], [2]],
+ [[3], [4]]]]
+```
+
+This operation will output a tensor of shape `[1, 1, 1, 4]`:
+
+```
+[[[[1, 2, 3, 4]]]]
+```
+
+Here, the input has a batch of 1 and each batch element has shape `[2, 2, 1]`,
+the corresponding output will have a single element (i.e. width and height are
+both 1) and will have a depth of 4 channels (1 * block_size * block_size).
+The output element shape is `[1, 1, 4]`.
+
+For an input tensor with larger depth, here of shape `[1, 2, 2, 3]`, e.g.
+
+```
+x = [[[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]],
+ [[7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 12]]]]
+```
+
+This operation, for block_size of 2, will return the following tensor of shape
+`[1, 1, 1, 12]`
+
+```
+[[[[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12]]]]
+```
+
+Similarly, for the following input of shape `[1 4 4 1]`, and a block size of 2:
+
+```
+x = [[[[1], [2], [5], [6]],
+ [[3], [4], [7], [8]],
+ [[9], [10], [13], [14]],
+ [[11], [12], [15], [16]]]]
+```
+
+the operator will return the following tensor of shape `[1 2 2 4]`:
+
+```
+x = [[[[1, 2, 3, 4],
+ [5, 6, 7, 8]],
+ [[9, 10, 11, 12],
+ [13, 14, 15, 16]]]]
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`block_size`
+ |
+
+An `int` that is `>= 2`. The size of the spatial block.
+ |
+
+|
+`data_format`
+ |
+
+An optional `string` from: `"NHWC", "NCHW", "NCHW_VECT_C"`. Defaults to `"NHWC"`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `input`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3c068f847dc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse.md
@@ -0,0 +1,94 @@
+description: Sparse Tensor Representation.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.sparse
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Sparse Tensor Representation.
+
+
+See also tf.SparseTensor.
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class SparseConditionalAccumulator`](../../../tf/compat/v1/SparseConditionalAccumulator.md): A conditional accumulator for aggregating sparse gradients.
+
+[`class SparseTensor`](../../../tf/sparse/SparseTensor.md): Represents a sparse tensor.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`add(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/sparse_add.md): Adds two tensors, at least one of each is a `SparseTensor`. (deprecated arguments)
+
+[`concat(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/sparse_concat.md): Concatenates a list of `SparseTensor` along the specified dimension. (deprecated arguments)
+
+[`cross(...)`](../../../tf/sparse/cross.md): Generates sparse cross from a list of sparse and dense tensors.
+
+[`cross_hashed(...)`](../../../tf/sparse/cross_hashed.md): Generates hashed sparse cross from a list of sparse and dense tensors.
+
+[`expand_dims(...)`](../../../tf/sparse/expand_dims.md): Inserts a dimension of 1 into a tensor's shape.
+
+[`eye(...)`](../../../tf/sparse/eye.md): Creates a two-dimensional sparse tensor with ones along the diagonal.
+
+[`fill_empty_rows(...)`](../../../tf/sparse/fill_empty_rows.md): Fills empty rows in the input 2-D `SparseTensor` with a default value.
+
+[`from_dense(...)`](../../../tf/sparse/from_dense.md): Converts a dense tensor into a sparse tensor.
+
+[`mask(...)`](../../../tf/sparse/mask.md): Masks elements of `IndexedSlices`.
+
+[`matmul(...)`](../../../tf/sparse/sparse_dense_matmul.md): Multiply SparseTensor (or dense Matrix) (of rank 2) "A" by dense matrix
+
+[`maximum(...)`](../../../tf/sparse/maximum.md): Returns the element-wise max of two SparseTensors.
+
+[`merge(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/sparse_merge.md): Combines a batch of feature ids and values into a single `SparseTensor`. (deprecated)
+
+[`minimum(...)`](../../../tf/sparse/minimum.md): Returns the element-wise min of two SparseTensors.
+
+[`placeholder(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/sparse_placeholder.md): Inserts a placeholder for a sparse tensor that will be always fed.
+
+[`reduce_max(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/sparse_reduce_max.md): Computes the max of elements across dimensions of a SparseTensor. (deprecated arguments) (deprecated arguments)
+
+[`reduce_max_sparse(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/sparse_reduce_max_sparse.md): Computes the max of elements across dimensions of a SparseTensor. (deprecated arguments)
+
+[`reduce_sum(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/sparse_reduce_sum.md): Computes the sum of elements across dimensions of a SparseTensor. (deprecated arguments) (deprecated arguments)
+
+[`reduce_sum_sparse(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/sparse_reduce_sum_sparse.md): Computes the sum of elements across dimensions of a SparseTensor. (deprecated arguments)
+
+[`reorder(...)`](../../../tf/sparse/reorder.md): Reorders a `SparseTensor` into the canonical, row-major ordering.
+
+[`reset_shape(...)`](../../../tf/sparse/reset_shape.md): Resets the shape of a `SparseTensor` with indices and values unchanged.
+
+[`reshape(...)`](../../../tf/sparse/reshape.md): Reshapes a `SparseTensor` to represent values in a new dense shape.
+
+[`retain(...)`](../../../tf/sparse/retain.md): Retains specified non-empty values within a `SparseTensor`.
+
+[`segment_mean(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/sparse_segment_mean.md): Computes the mean along sparse segments of a tensor.
+
+[`segment_sqrt_n(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/sparse_segment_sqrt_n.md): Computes the sum along sparse segments of a tensor divided by the sqrt(N).
+
+[`segment_sum(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/sparse_segment_sum.md): Computes the sum along sparse segments of a tensor.
+
+[`slice(...)`](../../../tf/sparse/slice.md): Slice a `SparseTensor` based on the `start` and `size.
+
+[`softmax(...)`](../../../tf/sparse/softmax.md): Applies softmax to a batched N-D `SparseTensor`.
+
+[`sparse_dense_matmul(...)`](../../../tf/sparse/sparse_dense_matmul.md): Multiply SparseTensor (or dense Matrix) (of rank 2) "A" by dense matrix
+
+[`split(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/sparse_split.md): Split a `SparseTensor` into `num_split` tensors along `axis`. (deprecated arguments)
+
+[`to_dense(...)`](../../../tf/sparse/to_dense.md): Converts a `SparseTensor` into a dense tensor.
+
+[`to_indicator(...)`](../../../tf/sparse/to_indicator.md): Converts a `SparseTensor` of ids into a dense bool indicator tensor.
+
+[`transpose(...)`](../../../tf/sparse/transpose.md): Transposes a `SparseTensor`
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_add.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_add.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a799ca22a74
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_add.md
@@ -0,0 +1,154 @@
+description: Adds two tensors, at least one of each is a SparseTensor. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.sparse_add
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Adds two tensors, at least one of each is a `SparseTensor`. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.sparse.add`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.sparse_add(
+ a, b, threshold=None, thresh=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: SOME ARGUMENTS ARE DEPRECATED: `(thresh)`. They will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+thresh is deprecated, use threshold instead
+
+If one `SparseTensor` and one `Tensor` are passed in, returns a `Tensor`. If
+both arguments are `SparseTensor`s, this returns a `SparseTensor`. The order
+of arguments does not matter. Use vanilla tf.add() for adding two dense
+`Tensor`s.
+
+The shapes of the two operands must match: broadcasting is not supported.
+
+The indices of any input `SparseTensor` are assumed ordered in standard
+lexicographic order. If this is not the case, before this step run
+`SparseReorder` to restore index ordering.
+
+If both arguments are sparse, we perform "clipping" as follows. By default,
+if two values sum to zero at some index, the output `SparseTensor` would still
+include that particular location in its index, storing a zero in the
+corresponding value slot. To override this, callers can specify `thresh`,
+indicating that if the sum has a magnitude strictly smaller than `thresh`, its
+corresponding value and index would then not be included. In particular,
+`thresh == 0.0` (default) means everything is kept and actual thresholding
+happens only for a positive value.
+
+For example, suppose the logical sum of two sparse operands is (densified):
+
+ [ 2]
+ [.1 0]
+ [ 6 -.2]
+
+Then,
+
+* `thresh == 0` (the default): all 5 index/value pairs will be returned.
+* `thresh == 0.11`: only .1 and 0 will vanish, and the remaining three
+ index/value pairs will be returned.
+* `thresh == 0.21`: .1, 0, and -.2 will vanish.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`a`
+ |
+
+The first operand; `SparseTensor` or `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`b`
+ |
+
+The second operand; `SparseTensor` or `Tensor`. At least one operand
+must be sparse.
+ |
+
+|
+`threshold`
+ |
+
+An optional 0-D `Tensor` (defaults to `0`). The magnitude
+threshold that determines if an output value/index pair takes space. Its
+dtype should match that of the values if they are real; if the latter are
+complex64/complex128, then the dtype should be float32/float64,
+correspondingly.
+ |
+
+|
+`thresh`
+ |
+
+Deprecated alias for `threshold`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `SparseTensor` or a `Tensor`, representing the sum.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If both `a` and `b` are `Tensor`s. Use tf.add() instead.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_concat.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_concat.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..f6155965b5a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_concat.md
@@ -0,0 +1,211 @@
+description: Concatenates a list of SparseTensor along the specified dimension. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.sparse_concat
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Concatenates a list of `SparseTensor` along the specified dimension. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.sparse.concat`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.sparse_concat(
+ axis, sp_inputs, name=None, expand_nonconcat_dim=(False), concat_dim=None,
+ expand_nonconcat_dims=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: SOME ARGUMENTS ARE DEPRECATED: `(concat_dim)`. They will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+concat_dim is deprecated, use axis instead
+
+Concatenation is with respect to the dense versions of each sparse input.
+It is assumed that each inputs is a `SparseTensor` whose elements are ordered
+along increasing dimension number.
+
+If expand_nonconcat_dim is False, all inputs' shapes must match, except for
+the concat dimension. If expand_nonconcat_dim is True, then inputs' shapes are
+allowed to vary among all inputs.
+
+The `indices`, `values`, and `shapes` lists must have the same length.
+
+If expand_nonconcat_dim is False, then the output shape is identical to the
+inputs', except along the concat dimension, where it is the sum of the inputs'
+sizes along that dimension.
+
+If expand_nonconcat_dim is True, then the output shape along the non-concat
+dimensions will be expand to be the largest among all inputs, and it is the
+sum of the inputs sizes along the concat dimension.
+
+The output elements will be resorted to preserve the sort order along
+increasing dimension number.
+
+This op runs in `O(M log M)` time, where `M` is the total number of non-empty
+values across all inputs. This is due to the need for an internal sort in
+order to concatenate efficiently across an arbitrary dimension.
+
+For example, if `axis = 1` and the inputs are
+
+ sp_inputs[0]: shape = [2, 3]
+ [0, 2]: "a"
+ [1, 0]: "b"
+ [1, 1]: "c"
+
+ sp_inputs[1]: shape = [2, 4]
+ [0, 1]: "d"
+ [0, 2]: "e"
+
+then the output will be
+
+ shape = [2, 7]
+ [0, 2]: "a"
+ [0, 4]: "d"
+ [0, 5]: "e"
+ [1, 0]: "b"
+ [1, 1]: "c"
+
+Graphically this is equivalent to doing
+
+ [ a] concat [ d e ] = [ a d e ]
+ [b c ] [ ] [b c ]
+
+Another example, if 'axis = 1' and the inputs are
+
+ sp_inputs[0]: shape = [3, 3]
+ [0, 2]: "a"
+ [1, 0]: "b"
+ [2, 1]: "c"
+
+ sp_inputs[1]: shape = [2, 4]
+ [0, 1]: "d"
+ [0, 2]: "e"
+
+if expand_nonconcat_dim = False, this will result in an error. But if
+expand_nonconcat_dim = True, this will result in:
+
+ shape = [3, 7]
+ [0, 2]: "a"
+ [0, 4]: "d"
+ [0, 5]: "e"
+ [1, 0]: "b"
+ [2, 1]: "c"
+
+Graphically this is equivalent to doing
+
+ [ a] concat [ d e ] = [ a d e ]
+ [b ] [ ] [b ]
+ [ c ] [ c ]
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`axis`
+ |
+
+Dimension to concatenate along. Must be in range [-rank, rank),
+where rank is the number of dimensions in each input `SparseTensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`sp_inputs`
+ |
+
+List of `SparseTensor` to concatenate.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name prefix for the returned tensors (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`expand_nonconcat_dim`
+ |
+
+Whether to allow the expansion in the non-concat
+dimensions. Defaulted to False.
+ |
+
+|
+`concat_dim`
+ |
+
+The old (deprecated) name for axis.
+ |
+
+|
+`expand_nonconcat_dims`
+ |
+
+alias for expand_nonconcat_dim
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `SparseTensor` with the concatenated output.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `sp_inputs` is not a list of `SparseTensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_matmul.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_matmul.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..cf87e6a4394
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_matmul.md
@@ -0,0 +1,111 @@
+description: Multiply matrix "a" by matrix "b".
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.sparse_matmul
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Multiply matrix "a" by matrix "b".
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.sparse_matmul(
+ a, b, transpose_a=(False), transpose_b=(False), a_is_sparse=(False),
+ b_is_sparse=(False), name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The inputs must be two-dimensional matrices and the inner dimension of "a" must
+match the outer dimension of "b". Both "a" and "b" must be `Tensor`s not
+`SparseTensor`s. This op is optimized for the case where at least one of "a" or
+"b" is sparse, in the sense that they have a large proportion of zero values.
+The breakeven for using this versus a dense matrix multiply on one platform was
+30% zero values in the sparse matrix.
+
+The gradient computation of this operation will only take advantage of sparsity
+in the input gradient when that gradient comes from a Relu.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`a`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `float32`, `bfloat16`.
+ |
+
+|
+`b`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `float32`, `bfloat16`.
+ |
+
+|
+`transpose_a`
+ |
+
+An optional `bool`. Defaults to `False`.
+ |
+
+|
+`transpose_b`
+ |
+
+An optional `bool`. Defaults to `False`.
+ |
+
+|
+`a_is_sparse`
+ |
+
+An optional `bool`. Defaults to `False`.
+ |
+
+|
+`b_is_sparse`
+ |
+
+An optional `bool`. Defaults to `False`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` of type `float32`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_merge.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_merge.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..30aa5226154
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_merge.md
@@ -0,0 +1,205 @@
+description: Combines a batch of feature ids and values into a single SparseTensor. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.sparse_merge
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Combines a batch of feature ids and values into a single `SparseTensor`. (deprecated)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.sparse.merge`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.sparse_merge(
+ sp_ids, sp_values, vocab_size, name=None, already_sorted=(False)
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+No similar op available at this time.
+
+The most common use case for this function occurs when feature ids and
+their corresponding values are stored in `Example` protos on disk.
+`parse_example` will return a batch of ids and a batch of values, and this
+function joins them into a single logical `SparseTensor` for use in
+functions such as `sparse_tensor_dense_matmul`, `sparse_to_dense`, etc.
+
+The `SparseTensor` returned by this function has the following properties:
+
+ - `indices` is equivalent to `sp_ids.indices` with the last
+ dimension discarded and replaced with `sp_ids.values`.
+ - `values` is simply `sp_values.values`.
+ - If `sp_ids.dense_shape = [D0, D1, ..., Dn, K]`, then
+ `output.shape = [D0, D1, ..., Dn, vocab_size]`.
+
+For example, consider the following feature vectors:
+
+```python
+ vector1 = [-3, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
+ vector2 = [ 0, 1, 0, 4, 1, 0]
+ vector3 = [ 5, 0, 0, 9, 0, 0]
+```
+
+These might be stored sparsely in the following Example protos by storing
+only the feature ids (column number if the vectors are treated as a matrix)
+of the non-zero elements and the corresponding values:
+
+```python
+ examples = [Example(features={
+ "ids": Feature(int64_list=Int64List(value=[0])),
+ "values": Feature(float_list=FloatList(value=[-3]))}),
+ Example(features={
+ "ids": Feature(int64_list=Int64List(value=[1, 4, 3])),
+ "values": Feature(float_list=FloatList(value=[1, 1, 4]))}),
+ Example(features={
+ "ids": Feature(int64_list=Int64List(value=[0, 3])),
+ "values": Feature(float_list=FloatList(value=[5, 9]))})]
+```
+
+The result of calling parse_example on these examples will produce a
+dictionary with entries for "ids" and "values". Passing those two objects
+to this function along with vocab_size=6, will produce a `SparseTensor` that
+sparsely represents all three instances. Namely, the `indices` property will
+contain the coordinates of the non-zero entries in the feature matrix (the
+first dimension is the row number in the matrix, i.e., the index within the
+batch, and the second dimension is the column number, i.e., the feature id);
+`values` will contain the actual values. `shape` will be the shape of the
+original matrix, i.e., (3, 6). For our example above, the output will be
+equal to:
+
+```python
+ SparseTensor(indices=[[0, 0], [1, 1], [1, 3], [1, 4], [2, 0], [2, 3]],
+ values=[-3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9],
+ dense_shape=[3, 6])
+```
+
+This method generalizes to higher-dimensions by simply providing a list for
+both the sp_ids as well as the vocab_size.
+In this case the resulting `SparseTensor` has the following properties:
+ - `indices` is equivalent to `sp_ids[0].indices` with the last
+ dimension discarded and concatenated with
+ `sp_ids[0].values, sp_ids[1].values, ...`.
+ - `values` is simply `sp_values.values`.
+ - If `sp_ids.dense_shape = [D0, D1, ..., Dn, K]`, then
+ `output.shape = [D0, D1, ..., Dn] + vocab_size`.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sp_ids`
+ |
+
+A single `SparseTensor` with `values` property of type `int32`
+or `int64` or a Python list of such `SparseTensor`s or a list thereof.
+ |
+
+|
+`sp_values`
+ |
+
+A `SparseTensor` of any type.
+ |
+
+|
+`vocab_size`
+ |
+
+A scalar `int64` Tensor (or Python int) containing the new size
+of the last dimension, `all(0 <= sp_ids.values < vocab_size)`.
+Or a list thereof with `all(0 <= sp_ids[i].values < vocab_size[i])` for
+all `i`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name prefix for the returned tensors (optional)
+ |
+
+|
+`already_sorted`
+ |
+
+A boolean to specify whether the per-batch values in
+`sp_values` are already sorted. If so skip sorting, False by default
+(optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `SparseTensor` compactly representing a batch of feature ids and values,
+useful for passing to functions that expect such a `SparseTensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `sp_values` is not a `SparseTensor`. Or if `sp_ids` is neither
+a `SparseTensor` nor a list thereof. Or if `vocab_size` is not a
+`Tensor` or a Python int and `sp_ids` is a `SparseTensor`. Or if
+`vocab_size` is not a or list thereof and `sp_ids` is a list.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `sp_ids` and `vocab_size` are lists of different lengths.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_placeholder.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_placeholder.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..64f98f4f576
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_placeholder.md
@@ -0,0 +1,138 @@
+description: Inserts a placeholder for a sparse tensor that will be always fed.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.sparse_placeholder
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Inserts a placeholder for a sparse tensor that will be always fed.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.sparse.placeholder`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.sparse_placeholder(
+ dtype, shape=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+**Important**: This sparse tensor will produce an error if evaluated.
+Its value must be fed using the `feed_dict` optional argument to
+`Session.run()`, `Tensor.eval()`, or `Operation.run()`.
+
+#### For example:
+
+
+
+```python
+x = tf.compat.v1.sparse.placeholder(tf.float32)
+y = tf.sparse.reduce_sum(x)
+
+with tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess:
+ print(sess.run(y)) # ERROR: will fail because x was not fed.
+
+ indices = np.array([[3, 2, 0], [4, 5, 1]], dtype=np.int64)
+ values = np.array([1.0, 2.0], dtype=np.float32)
+ shape = np.array([7, 9, 2], dtype=np.int64)
+ print(sess.run(y, feed_dict={
+ x: tf.compat.v1.SparseTensorValue(indices, values, shape)})) # Will
+ succeed.
+ print(sess.run(y, feed_dict={
+ x: (indices, values, shape)})) # Will succeed.
+
+ sp = tf.SparseTensor(indices=indices, values=values, dense_shape=shape)
+ sp_value = sp.eval(session=sess)
+ print(sess.run(y, feed_dict={x: sp_value})) # Will succeed.
+```
+
+@compatibility{eager} Placeholders are not compatible with eager execution.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+The type of `values` elements in the tensor to be fed.
+ |
+
+|
+`shape`
+ |
+
+The shape of the tensor to be fed (optional). If the shape is not
+specified, you can feed a sparse tensor of any shape.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for prefixing the operations (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `SparseTensor` that may be used as a handle for feeding a value, but not
+evaluated directly.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+if eager execution is enabled
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_reduce_max.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_reduce_max.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e50e06649b6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_reduce_max.md
@@ -0,0 +1,152 @@
+description: Computes the max of elements across dimensions of a SparseTensor. (deprecated arguments) (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.sparse_reduce_max
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the max of elements across dimensions of a SparseTensor. (deprecated arguments) (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.sparse.reduce_max`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.sparse_reduce_max(
+ sp_input, axis=None, keepdims=None, reduction_axes=None, keep_dims=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: SOME ARGUMENTS ARE DEPRECATED: `(keep_dims)`. They will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+keep_dims is deprecated, use keepdims instead
+
+Warning: SOME ARGUMENTS ARE DEPRECATED: `(reduction_axes)`. They will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+reduction_axes is deprecated, use axis instead
+
+This Op takes a SparseTensor and is the sparse counterpart to
+tf.reduce_max(). In particular, this Op also returns a dense `Tensor`
+instead of a sparse one.
+
+Note: A gradient is not defined for this function, so it can't be used
+in training models that need gradient descent.
+
+Reduces `sp_input` along the dimensions given in `reduction_axes`. Unless
+`keepdims` is true, the rank of the tensor is reduced by 1 for each entry in
+`reduction_axes`. If `keepdims` is true, the reduced dimensions are retained
+with length 1.
+
+If `reduction_axes` has no entries, all dimensions are reduced, and a tensor
+with a single element is returned. Additionally, the axes can be negative,
+similar to the indexing rules in Python.
+
+The values not defined in `sp_input` don't participate in the reduce max,
+as opposed to be implicitly assumed 0 -- hence it can return negative values
+for sparse `reduction_axes`. But, in case there are no values in
+`reduction_axes`, it will reduce to 0. See second example below.
+
+#### For example:
+
+
+
+```python
+# 'x' represents [[1, ?, 2]
+# [?, 3, ?]]
+# where ? is implicitly-zero.
+tf.sparse.reduce_max(x) ==> 3
+tf.sparse.reduce_max(x, 0) ==> [1, 3, 2]
+tf.sparse.reduce_max(x, 1) ==> [2, 3] # Can also use -1 as the axis.
+tf.sparse.reduce_max(x, 1, keepdims=True) ==> [[2], [3]]
+tf.sparse.reduce_max(x, [0, 1]) ==> 3
+
+# 'y' represents [[-7, ?]
+# [ 4, 3]
+# [ ?, ?]
+tf.sparse.reduce_max(x, 1) ==> [-7, 4, 0]
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sp_input`
+ |
+
+The SparseTensor to reduce. Should have numeric type.
+ |
+
+|
+`axis`
+ |
+
+The dimensions to reduce; list or scalar. If `None` (the
+default), reduces all dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`keepdims`
+ |
+
+If true, retain reduced dimensions with length 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`reduction_axes`
+ |
+
+Deprecated name of `axis`.
+ |
+
+|
+`keep_dims`
+ |
+
+Deprecated alias for `keepdims`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The reduced Tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_reduce_max_sparse.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_reduce_max_sparse.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..2a1a78680a9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_reduce_max_sparse.md
@@ -0,0 +1,123 @@
+description: Computes the max of elements across dimensions of a SparseTensor. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.sparse_reduce_max_sparse
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the max of elements across dimensions of a SparseTensor. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.sparse.reduce_max_sparse`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.sparse_reduce_max_sparse(
+ sp_input, axis=None, keepdims=None, reduction_axes=None, keep_dims=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: SOME ARGUMENTS ARE DEPRECATED: `(keep_dims)`. They will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+keep_dims is deprecated, use keepdims instead
+
+This Op takes a SparseTensor and is the sparse counterpart to
+tf.reduce_max(). In contrast to SparseReduceSum, this Op returns a
+SparseTensor.
+
+Note: A gradient is not defined for this function, so it can't be used
+in training models that need gradient descent.
+
+Reduces `sp_input` along the dimensions given in `reduction_axes`. Unless
+`keepdims` is true, the rank of the tensor is reduced by 1 for each entry in
+`reduction_axes`. If `keepdims` is true, the reduced dimensions are retained
+with length 1.
+
+If `reduction_axes` has no entries, all dimensions are reduced, and a tensor
+with a single element is returned. Additionally, the axes can be negative,
+which are interpreted according to the indexing rules in Python.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sp_input`
+ |
+
+The SparseTensor to reduce. Should have numeric type.
+ |
+
+|
+`axis`
+ |
+
+The dimensions to reduce; list or scalar. If `None` (the
+default), reduces all dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`keepdims`
+ |
+
+If true, retain reduced dimensions with length 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`reduction_axes`
+ |
+
+Deprecated name of axis.
+ |
+
+|
+`keep_dims`
+ |
+
+Deprecated alias for `keepdims`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The reduced SparseTensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_reduce_sum.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_reduce_sum.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..fef30e5ff45
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_reduce_sum.md
@@ -0,0 +1,139 @@
+description: Computes the sum of elements across dimensions of a SparseTensor. (deprecated arguments) (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.sparse_reduce_sum
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the sum of elements across dimensions of a SparseTensor. (deprecated arguments) (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.sparse.reduce_sum`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.sparse_reduce_sum(
+ sp_input, axis=None, keepdims=None, reduction_axes=None, keep_dims=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: SOME ARGUMENTS ARE DEPRECATED: `(keep_dims)`. They will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+keep_dims is deprecated, use keepdims instead
+
+Warning: SOME ARGUMENTS ARE DEPRECATED: `(reduction_axes)`. They will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+reduction_axes is deprecated, use axis instead
+
+This Op takes a SparseTensor and is the sparse counterpart to
+tf.reduce_sum(). In particular, this Op also returns a dense `Tensor`
+instead of a sparse one.
+
+Reduces `sp_input` along the dimensions given in `reduction_axes`. Unless
+`keepdims` is true, the rank of the tensor is reduced by 1 for each entry in
+`reduction_axes`. If `keepdims` is true, the reduced dimensions are retained
+with length 1.
+
+If `reduction_axes` has no entries, all dimensions are reduced, and a tensor
+with a single element is returned. Additionally, the axes can be negative,
+similar to the indexing rules in Python.
+
+#### For example:
+
+
+
+```python
+# 'x' represents [[1, ?, 1]
+# [?, 1, ?]]
+# where ? is implicitly-zero.
+tf.sparse.reduce_sum(x) ==> 3
+tf.sparse.reduce_sum(x, 0) ==> [1, 1, 1]
+tf.sparse.reduce_sum(x, 1) ==> [2, 1] # Can also use -1 as the axis.
+tf.sparse.reduce_sum(x, 1, keepdims=True) ==> [[2], [1]]
+tf.sparse.reduce_sum(x, [0, 1]) ==> 3
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sp_input`
+ |
+
+The SparseTensor to reduce. Should have numeric type.
+ |
+
+|
+`axis`
+ |
+
+The dimensions to reduce; list or scalar. If `None` (the
+default), reduces all dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`keepdims`
+ |
+
+If true, retain reduced dimensions with length 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`reduction_axes`
+ |
+
+Deprecated name of `axis`.
+ |
+
+|
+`keep_dims`
+ |
+
+Deprecated alias for `keepdims`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The reduced Tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_reduce_sum_sparse.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_reduce_sum_sparse.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..0d5920ccc99
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_reduce_sum_sparse.md
@@ -0,0 +1,123 @@
+description: Computes the sum of elements across dimensions of a SparseTensor. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.sparse_reduce_sum_sparse
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the sum of elements across dimensions of a SparseTensor. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.sparse.reduce_sum_sparse`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.sparse_reduce_sum_sparse(
+ sp_input, axis=None, keepdims=None, reduction_axes=None, keep_dims=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: SOME ARGUMENTS ARE DEPRECATED: `(keep_dims)`. They will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+keep_dims is deprecated, use keepdims instead
+
+This Op takes a SparseTensor and is the sparse counterpart to
+tf.reduce_sum(). In contrast to SparseReduceSum, this Op returns a
+SparseTensor.
+
+Note: A gradient is not defined for this function, so it can't be used
+in training models that need gradient descent.
+
+Reduces `sp_input` along the dimensions given in `reduction_axes`. Unless
+`keepdims` is true, the rank of the tensor is reduced by 1 for each entry in
+`reduction_axes`. If `keepdims` is true, the reduced dimensions are retained
+with length 1.
+
+If `reduction_axes` has no entries, all dimensions are reduced, and a tensor
+with a single element is returned. Additionally, the axes can be negative,
+which are interpreted according to the indexing rules in Python.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sp_input`
+ |
+
+The SparseTensor to reduce. Should have numeric type.
+ |
+
+|
+`axis`
+ |
+
+The dimensions to reduce; list or scalar. If `None` (the
+default), reduces all dimensions.
+ |
+
+|
+`keepdims`
+ |
+
+If true, retain reduced dimensions with length 1.
+ |
+
+|
+`reduction_axes`
+ |
+
+Deprecated name of axis.
+ |
+
+|
+`keep_dims`
+ |
+
+Deprecated alias for `keepdims`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The reduced SparseTensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_segment_mean.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_segment_mean.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..7bf0f1f355c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_segment_mean.md
@@ -0,0 +1,118 @@
+description: Computes the mean along sparse segments of a tensor.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.sparse_segment_mean
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the mean along sparse segments of a tensor.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.sparse.segment_mean`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.sparse_segment_mean(
+ data, indices, segment_ids, name=None, num_segments=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Read [the section on
+segmentation](https://www.tensorflow.org/versions/r2.0/api_docs/python/tf/math#about_segmentation)
+for an explanation of segments.
+
+Like tf.math.segment_mean, but `segment_ids` can have rank less than
+`data`'s first dimension, selecting a subset of dimension 0, specified by
+`indices`.
+`segment_ids` is allowed to have missing ids, in which case the output will
+be zeros at those indices. In those cases `num_segments` is used to determine
+the size of the output.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`data`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` with data that will be assembled in the output.
+ |
+
+|
+`indices`
+ |
+
+A 1-D `Tensor` with indices into `data`. Has same rank as
+`segment_ids`.
+ |
+
+|
+`segment_ids`
+ |
+
+A 1-D `Tensor` with indices into the output `Tensor`. Values
+should be sorted and can be repeated.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`num_segments`
+ |
+
+An optional int32 scalar. Indicates the size of the output
+`Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `tensor` of the shape as data, except for dimension 0 which
+has size `k`, the number of segments specified via `num_segments` or
+inferred for the last element in `segments_ids`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_segment_sqrt_n.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_segment_sqrt_n.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..cc0035ab177
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_segment_sqrt_n.md
@@ -0,0 +1,109 @@
+description: Computes the sum along sparse segments of a tensor divided by the sqrt(N).
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.sparse_segment_sqrt_n
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the sum along sparse segments of a tensor divided by the sqrt(N).
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.sparse.segment_sqrt_n`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.sparse_segment_sqrt_n(
+ data, indices, segment_ids, name=None, num_segments=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+`N` is the size of the segment being reduced.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`data`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` with data that will be assembled in the output.
+ |
+
+|
+`indices`
+ |
+
+A 1-D `Tensor` with indices into `data`. Has same rank as
+`segment_ids`.
+ |
+
+|
+`segment_ids`
+ |
+
+A 1-D `Tensor` with indices into the output `Tensor`. Values
+should be sorted and can be repeated.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`num_segments`
+ |
+
+An optional int32 scalar. Indicates the size of the output
+`Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `tensor` of the shape as data, except for dimension 0 which
+has size `k`, the number of segments specified via `num_segments` or
+inferred for the last element in `segments_ids`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_segment_sum.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_segment_sum.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..40642c12a81
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_segment_sum.md
@@ -0,0 +1,150 @@
+description: Computes the sum along sparse segments of a tensor.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.sparse_segment_sum
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the sum along sparse segments of a tensor.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.sparse.segment_sum`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.sparse_segment_sum(
+ data, indices, segment_ids, name=None, num_segments=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Read [the section on
+segmentation](https://www.tensorflow.org/versions/r2.0/api_docs/python/tf/math#about_segmentation)
+for an explanation of segments.
+
+Like tf.math.segment_sum, but `segment_ids` can have rank less than `data`'s
+first dimension, selecting a subset of dimension 0, specified by `indices`.
+`segment_ids` is allowed to have missing ids, in which case the output will
+be zeros at those indices. In those cases `num_segments` is used to determine
+the size of the output.
+
+#### For example:
+
+
+
+```python
+c = tf.constant([[1,2,3,4], [-1,-2,-3,-4], [5,6,7,8]])
+
+# Select two rows, one segment.
+tf.sparse.segment_sum(c, tf.constant([0, 1]), tf.constant([0, 0]))
+# => [[0 0 0 0]]
+
+# Select two rows, two segment.
+tf.sparse.segment_sum(c, tf.constant([0, 1]), tf.constant([0, 1]))
+# => [[ 1 2 3 4]
+# [-1 -2 -3 -4]]
+
+# With missing segment ids.
+tf.sparse.segment_sum(c, tf.constant([0, 1]), tf.constant([0, 2]),
+ num_segments=4)
+# => [[ 1 2 3 4]
+# [ 0 0 0 0]
+# [-1 -2 -3 -4]
+# [ 0 0 0 0]]
+
+# Select all rows, two segments.
+tf.sparse.segment_sum(c, tf.constant([0, 1, 2]), tf.constant([0, 0, 1]))
+# => [[0 0 0 0]
+# [5 6 7 8]]
+
+# Which is equivalent to:
+tf.math.segment_sum(c, tf.constant([0, 0, 1]))
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`data`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` with data that will be assembled in the output.
+ |
+
+|
+`indices`
+ |
+
+A 1-D `Tensor` with indices into `data`. Has same rank as
+`segment_ids`.
+ |
+
+|
+`segment_ids`
+ |
+
+A 1-D `Tensor` with indices into the output `Tensor`. Values
+should be sorted and can be repeated.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`num_segments`
+ |
+
+An optional int32 scalar. Indicates the size of the output
+`Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `tensor` of the shape as data, except for dimension 0 which
+has size `k`, the number of segments specified via `num_segments` or
+inferred for the last element in `segments_ids`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_split.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_split.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..433891a7d48
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_split.md
@@ -0,0 +1,157 @@
+description: Split a SparseTensor into num_split tensors along axis. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.sparse_split
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Split a `SparseTensor` into `num_split` tensors along `axis`. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.sparse.split`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.sparse_split(
+ keyword_required=KeywordRequired(), sp_input=None, num_split=None, axis=None,
+ name=None, split_dim=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: SOME ARGUMENTS ARE DEPRECATED: `(split_dim)`. They will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+split_dim is deprecated, use axis instead
+
+If the `sp_input.dense_shape[axis]` is not an integer multiple of `num_split`
+each slice starting from 0:`shape[axis] % num_split` gets extra one
+dimension. For example, if `axis = 1` and `num_split = 2` and the
+input is:
+
+ input_tensor = shape = [2, 7]
+ [ a d e ]
+ [b c ]
+
+Graphically the output tensors are:
+
+ output_tensor[0] =
+ [ a ]
+ [b c ]
+
+ output_tensor[1] =
+ [ d e ]
+ [ ]
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`keyword_required`
+ |
+
+Python 2 standin for * (temporary for argument reorder)
+ |
+
+|
+`sp_input`
+ |
+
+The `SparseTensor` to split.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_split`
+ |
+
+A Python integer. The number of ways to split.
+ |
+
+|
+`axis`
+ |
+
+A 0-D `int32` `Tensor`. The dimension along which to split.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`split_dim`
+ |
+
+Deprecated old name for axis.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+`num_split` `SparseTensor` objects resulting from splitting `value`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `sp_input` is not a `SparseTensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the deprecated `split_dim` and `axis` are both non None.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_to_dense.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_to_dense.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..331227540e3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sparse_to_dense.md
@@ -0,0 +1,130 @@
+description: Converts a sparse representation into a dense tensor. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.sparse_to_dense
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Converts a sparse representation into a dense tensor. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.sparse_to_dense(
+ sparse_indices, output_shape, sparse_values, default_value=0,
+ validate_indices=(True), name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Create a tf.sparse.SparseTensor and use tf.sparse.to_dense instead.
+
+Builds an array `dense` with shape `output_shape` such that
+
+```python
+# If sparse_indices is scalar
+dense[i] = (i == sparse_indices ? sparse_values : default_value)
+
+# If sparse_indices is a vector, then for each i
+dense[sparse_indices[i]] = sparse_values[i]
+
+# If sparse_indices is an n by d matrix, then for each i in [0, n)
+dense[sparse_indices[i][0], ..., sparse_indices[i][d-1]] = sparse_values[i]
+```
+
+All other values in `dense` are set to `default_value`. If `sparse_values`
+is a scalar, all sparse indices are set to this single value.
+
+Indices should be sorted in lexicographic order, and indices must not
+contain any repeats. If `validate_indices` is True, these properties
+are checked during execution.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sparse_indices`
+ |
+
+A 0-D, 1-D, or 2-D `Tensor` of type `int32` or `int64`.
+`sparse_indices[i]` contains the complete index where `sparse_values[i]`
+will be placed.
+ |
+
+|
+`output_shape`
+ |
+
+A 1-D `Tensor` of the same type as `sparse_indices`. Shape
+of the dense output tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`sparse_values`
+ |
+
+A 0-D or 1-D `Tensor`. Values corresponding to each row of
+`sparse_indices`, or a scalar value to be used for all sparse indices.
+ |
+
+|
+`default_value`
+ |
+
+A 0-D `Tensor` of the same type as `sparse_values`. Value
+to set for indices not specified in `sparse_indices`. Defaults to zero.
+ |
+
+|
+`validate_indices`
+ |
+
+A boolean value. If True, indices are checked to make
+sure they are sorted in lexicographic order and that there are no repeats.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Dense `Tensor` of shape `output_shape`. Has the same type as
+`sparse_values`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/spectral.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/spectral.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..0c72845c954
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/spectral.md
@@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
+description: Public API for tf.spectral namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.spectral
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.spectral namespace.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`dct(...)`](../../../tf/signal/dct.md): Computes the 1D [Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT)][dct] of `input`.
+
+[`fft(...)`](../../../tf/signal/fft.md): Fast Fourier transform.
+
+[`fft2d(...)`](../../../tf/signal/fft2d.md): 2D fast Fourier transform.
+
+[`fft3d(...)`](../../../tf/signal/fft3d.md): 3D fast Fourier transform.
+
+[`idct(...)`](../../../tf/signal/idct.md): Computes the 1D [Inverse Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT)][idct] of `input`.
+
+[`ifft(...)`](../../../tf/signal/ifft.md): Inverse fast Fourier transform.
+
+[`ifft2d(...)`](../../../tf/signal/ifft2d.md): Inverse 2D fast Fourier transform.
+
+[`ifft3d(...)`](../../../tf/signal/ifft3d.md): Inverse 3D fast Fourier transform.
+
+[`irfft(...)`](../../../tf/signal/irfft.md): Inverse real-valued fast Fourier transform.
+
+[`irfft2d(...)`](../../../tf/signal/irfft2d.md): Inverse 2D real-valued fast Fourier transform.
+
+[`irfft3d(...)`](../../../tf/signal/irfft3d.md): Inverse 3D real-valued fast Fourier transform.
+
+[`rfft(...)`](../../../tf/signal/rfft.md): Real-valued fast Fourier transform.
+
+[`rfft2d(...)`](../../../tf/signal/rfft2d.md): 2D real-valued fast Fourier transform.
+
+[`rfft3d(...)`](../../../tf/signal/rfft3d.md): 3D real-valued fast Fourier transform.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/squeeze.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/squeeze.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..cfd3010e058
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/squeeze.md
@@ -0,0 +1,139 @@
+description: Removes dimensions of size 1 from the shape of a tensor. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.squeeze
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Removes dimensions of size 1 from the shape of a tensor. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.squeeze(
+ input, axis=None, name=None, squeeze_dims=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: SOME ARGUMENTS ARE DEPRECATED: `(squeeze_dims)`. They will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use the `axis` argument instead
+
+Given a tensor `input`, this operation returns a tensor of the same type with
+all dimensions of size 1 removed. If you don't want to remove all size 1
+dimensions, you can remove specific size 1 dimensions by specifying
+`axis`.
+
+#### For example:
+
+
+
+```
+>>> # 't' is a tensor of shape [1, 2, 1, 3, 1, 1]
+>>> t = tf.ones([1, 2, 1, 3, 1, 1])
+>>> print(tf.shape(tf.squeeze(t)).numpy())
+[2 3]
+```
+
+Or, to remove specific size 1 dimensions:
+
+```
+>>> # 't' is a tensor of shape [1, 2, 1, 3, 1, 1]
+>>> t = tf.ones([1, 2, 1, 3, 1, 1])
+>>> print(tf.shape(tf.squeeze(t, [2, 4])).numpy())
+[1 2 3 1]
+```
+
+Note: if `input` is a tf.RaggedTensor, then this operation takes `O(N)`
+time, where `N` is the number of elements in the squeezed dimensions.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. The `input` to squeeze.
+ |
+
+|
+`axis`
+ |
+
+An optional list of `ints`. Defaults to `[]`. If specified, only
+squeezes the dimensions listed. The dimension index starts at 0. It is an
+error to squeeze a dimension that is not 1. Must be in the range
+`[-rank(input), rank(input))`. Must be specified if `input` is a
+`RaggedTensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`squeeze_dims`
+ |
+
+Deprecated keyword argument that is now axis.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `input`.
+Contains the same data as `input`, but has one or more dimensions of
+size 1 removed.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+When both `squeeze_dims` and `axis` are specified.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/string_split.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/string_split.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..bcbd226e50c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/string_split.md
@@ -0,0 +1,151 @@
+description: Split elements of source based on delimiter. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.string_split
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Split elements of `source` based on `delimiter`. (deprecated arguments)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.string_split(
+ source, sep=None, skip_empty=(True), delimiter=None, result_type='SparseTensor',
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: SOME ARGUMENTS ARE DEPRECATED: `(delimiter)`. They will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+delimiter is deprecated, please use sep instead.
+
+Let N be the size of `source` (typically N will be the batch size). Split each
+element of `source` based on `delimiter` and return a `SparseTensor`
+or `RaggedTensor` containing the split tokens. Empty tokens are ignored.
+
+If `sep` is an empty string, each element of the `source` is split
+into individual strings, each containing one byte. (This includes splitting
+multibyte sequences of UTF-8.) If delimiter contains multiple bytes, it is
+treated as a set of delimiters with each considered a potential split point.
+
+#### Examples:
+
+
+
+```
+>>> print(tf.compat.v1.string_split(['hello world', 'a b c']))
+SparseTensor(indices=tf.Tensor( [[0 0] [0 1] [1 0] [1 1] [1 2]], ...),
+ values=tf.Tensor([b'hello' b'world' b'a' b'b' b'c'], ...),
+ dense_shape=tf.Tensor([2 3], shape=(2,), dtype=int64))
+```
+
+```
+>>> print(tf.compat.v1.string_split(['hello world', 'a b c'],
+... result_type="RaggedTensor"))
+
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`source`
+ |
+
+`1-D` string `Tensor`, the strings to split.
+ |
+
+|
+`sep`
+ |
+
+`0-D` string `Tensor`, the delimiter character, the string should
+be length 0 or 1. Default is ' '.
+ |
+
+|
+`skip_empty`
+ |
+
+A `bool`. If `True`, skip the empty strings from the result.
+ |
+
+|
+`delimiter`
+ |
+
+deprecated alias for `sep`.
+ |
+
+|
+`result_type`
+ |
+
+The tensor type for the result: one of `"RaggedTensor"` or
+`"SparseTensor"`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If delimiter is not a string.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `SparseTensor` or `RaggedTensor` of rank `2`, the strings split according
+to the delimiter. The first column of the indices corresponds to the row
+in `source` and the second column corresponds to the index of the split
+component in this row.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/string_to_hash_bucket.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/string_to_hash_bucket.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..b3bbd0ed7d4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/string_to_hash_bucket.md
@@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
+description: Converts each string in the input Tensor to its hash mod by a number of buckets.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.string_to_hash_bucket
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Converts each string in the input Tensor to its hash mod by a number of buckets.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.strings.to_hash_bucket`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.string_to_hash_bucket(
+ string_tensor=None, num_buckets=None, name=None, input=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The hash function is deterministic on the content of the string within the
+process.
+
+Note that the hash function may change from time to time.
+This functionality will be deprecated and it's recommended to use
+`tf.string_to_hash_bucket_fast()` or `tf.string_to_hash_bucket_strong()`.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`string_tensor`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `string`.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_buckets`
+ |
+
+An `int` that is `>= 1`. The number of buckets.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` of type `int64`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/string_to_number.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/string_to_number.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e5284196975
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/string_to_number.md
@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
+description: Converts each string in the input Tensor to the specified numeric type.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.string_to_number
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Converts each string in the input Tensor to the specified numeric type.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.strings.to_number`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.string_to_number(
+ string_tensor=None, out_type=tf.dtypes.float32, name=None, input=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+(Note that int32 overflow results in an error while float overflow
+results in a rounded value.)
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```
+>>> strings = ["5.0", "3.0", "7.0"]
+>>> tf.strings.to_number(strings)
+
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`string_tensor`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `string`.
+ |
+
+|
+`out_type`
+ |
+
+An optional tf.DType from: `tf.float32, tf.float64, tf.int32, tf.int64`. Defaults to tf.float32.
+The numeric type to interpret each string in `string_tensor` as.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` of type `out_type`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/strings.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/strings.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..f8985a38048
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/strings.md
@@ -0,0 +1,75 @@
+description: Operations for working with string Tensors.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.strings
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Operations for working with string Tensors.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`as_string(...)`](../../../tf/strings/as_string.md): Converts each entry in the given tensor to strings.
+
+[`bytes_split(...)`](../../../tf/strings/bytes_split.md): Split string elements of `input` into bytes.
+
+[`format(...)`](../../../tf/strings/format.md): Formats a string template using a list of tensors.
+
+[`join(...)`](../../../tf/strings/join.md): Perform element-wise concatenation of a list of string tensors.
+
+[`length(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/strings/length.md): Computes the length of each string given in the input tensor.
+
+[`lower(...)`](../../../tf/strings/lower.md): Converts all uppercase characters into their respective lowercase replacements.
+
+[`ngrams(...)`](../../../tf/strings/ngrams.md): Create a tensor of n-grams based on `data`.
+
+[`reduce_join(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/reduce_join.md): Joins all strings into a single string, or joins along an axis.
+
+[`regex_full_match(...)`](../../../tf/strings/regex_full_match.md): Check if the input matches the regex pattern.
+
+[`regex_replace(...)`](../../../tf/strings/regex_replace.md): Replace elements of `input` matching regex `pattern` with `rewrite`.
+
+[`split(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/strings/split.md): Split elements of `input` based on `sep`.
+
+[`strip(...)`](../../../tf/strings/strip.md): Strip leading and trailing whitespaces from the Tensor.
+
+[`substr(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/strings/substr.md): Return substrings from `Tensor` of strings.
+
+[`to_hash_bucket(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/string_to_hash_bucket.md): Converts each string in the input Tensor to its hash mod by a number of buckets.
+
+[`to_hash_bucket_fast(...)`](../../../tf/strings/to_hash_bucket_fast.md): Converts each string in the input Tensor to its hash mod by a number of buckets.
+
+[`to_hash_bucket_strong(...)`](../../../tf/strings/to_hash_bucket_strong.md): Converts each string in the input Tensor to its hash mod by a number of buckets.
+
+[`to_number(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/string_to_number.md): Converts each string in the input Tensor to the specified numeric type.
+
+[`unicode_decode(...)`](../../../tf/strings/unicode_decode.md): Decodes each string in `input` into a sequence of Unicode code points.
+
+[`unicode_decode_with_offsets(...)`](../../../tf/strings/unicode_decode_with_offsets.md): Decodes each string into a sequence of code points with start offsets.
+
+[`unicode_encode(...)`](../../../tf/strings/unicode_encode.md): Encodes each sequence of Unicode code points in `input` into a string.
+
+[`unicode_script(...)`](../../../tf/strings/unicode_script.md): Determine the script codes of a given tensor of Unicode integer code points.
+
+[`unicode_split(...)`](../../../tf/strings/unicode_split.md): Splits each string in `input` into a sequence of Unicode code points.
+
+[`unicode_split_with_offsets(...)`](../../../tf/strings/unicode_split_with_offsets.md): Splits each string into a sequence of code points with start offsets.
+
+[`unicode_transcode(...)`](../../../tf/strings/unicode_transcode.md): Transcode the input text from a source encoding to a destination encoding.
+
+[`unsorted_segment_join(...)`](../../../tf/strings/unsorted_segment_join.md): Joins the elements of `inputs` based on `segment_ids`.
+
+[`upper(...)`](../../../tf/strings/upper.md): Converts all lowercase characters into their respective uppercase replacements.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/strings/length.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/strings/length.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..f4a089b4104
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/strings/length.md
@@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
+description: Computes the length of each string given in the input tensor.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.strings.length
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the length of each string given in the input tensor.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.strings.length(
+ input, name=None, unit='BYTE'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+```
+>>> strings = tf.constant(['Hello','TensorFlow', '🙂'])
+>>> tf.strings.length(strings).numpy() # default counts bytes
+array([ 5, 10, 4], dtype=int32)
+>>> tf.strings.length(strings, unit="UTF8_CHAR").numpy()
+array([ 5, 10, 1], dtype=int32)
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `string`. The strings for which to compute the
+length for each element.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`unit`
+ |
+
+An optional `string` from: `"BYTE", "UTF8_CHAR"`. Defaults to
+`"BYTE"`. The unit that is counted to compute string length. One of:
+`"BYTE"` (for the number of bytes in each string) or `"UTF8_CHAR"` (for
+the number of UTF-8 encoded Unicode code points in each string). Results
+are undefined if `unit=UTF8_CHAR` and the `input` strings do not contain
+structurally valid UTF-8.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` of type `int32`, containing the length of the input string in
+the same element of the input tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/strings/split.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/strings/split.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..07c2d5a337b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/strings/split.md
@@ -0,0 +1,149 @@
+description: Split elements of input based on sep.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.strings.split
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Split elements of `input` based on `sep`.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.strings.split(
+ input=None, sep=None, maxsplit=-1, result_type='SparseTensor', source=None,
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Let N be the size of `input` (typically N will be the batch size). Split each
+element of `input` based on `sep` and return a `SparseTensor` or
+`RaggedTensor` containing the split tokens. Empty tokens are ignored.
+
+#### Examples:
+
+
+
+```
+>>> print(tf.compat.v1.strings.split(['hello world', 'a b c']))
+SparseTensor(indices=tf.Tensor( [[0 0] [0 1] [1 0] [1 1] [1 2]], ...),
+ values=tf.Tensor([b'hello' b'world' b'a' b'b' b'c'], ...),
+ dense_shape=tf.Tensor([2 3], shape=(2,), dtype=int64))
+```
+
+```
+>>> print(tf.compat.v1.strings.split(['hello world', 'a b c'],
+... result_type="RaggedTensor"))
+
+```
+
+If `sep` is given, consecutive delimiters are not grouped together and are
+deemed to delimit empty strings. For example, `input` of `"1<>2<><>3"` and
+`sep` of `"<>"` returns `["1", "2", "", "3"]`. If `sep` is None or an empty
+string, consecutive whitespace are regarded as a single separator, and the
+result will contain no empty strings at the start or end if the string has
+leading or trailing whitespace.
+
+Note that the above mentioned behavior matches python's str.split.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input`
+ |
+
+A string `Tensor` of rank `N`, the strings to split. If
+`rank(input)` is not known statically, then it is assumed to be `1`.
+ |
+
+|
+`sep`
+ |
+
+`0-D` string `Tensor`, the delimiter character.
+ |
+
+|
+`maxsplit`
+ |
+
+An `int`. If `maxsplit > 0`, limit of the split of the result.
+ |
+
+|
+`result_type`
+ |
+
+The tensor type for the result: one of `"RaggedTensor"` or
+`"SparseTensor"`.
+ |
+
+|
+`source`
+ |
+
+alias for "input" argument.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If sep is not a string.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `SparseTensor` or `RaggedTensor` of rank `N+1`, the strings split
+according to the delimiter.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/strings/substr.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/strings/substr.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..dd71d143730
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/strings/substr.md
@@ -0,0 +1,191 @@
+description: Return substrings from Tensor of strings.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.strings.substr
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Return substrings from `Tensor` of strings.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.strings.substr(
+ input, pos, len, name=None, unit='BYTE'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+For each string in the input `Tensor`, creates a substring starting at index
+`pos` with a total length of `len`.
+
+If `len` defines a substring that would extend beyond the length of the input
+string, or if `len` is negative, then as many characters as possible are used.
+
+A negative `pos` indicates distance within the string backwards from the end.
+
+If `pos` specifies an index which is out of range for any of the input strings,
+then an `InvalidArgumentError` is thrown.
+
+`pos` and `len` must have the same shape, otherwise a `ValueError` is thrown on
+Op creation.
+
+*NOTE*: `Substr` supports broadcasting up to two dimensions. More about
+broadcasting
+[here](http://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/user/basics.broadcasting.html)
+
+---
+
+Examples
+
+Using scalar `pos` and `len`:
+
+```python
+input = [b'Hello', b'World']
+position = 1
+length = 3
+
+output = [b'ell', b'orl']
+```
+
+Using `pos` and `len` with same shape as `input`:
+
+```python
+input = [[b'ten', b'eleven', b'twelve'],
+ [b'thirteen', b'fourteen', b'fifteen'],
+ [b'sixteen', b'seventeen', b'eighteen']]
+position = [[1, 2, 3],
+ [1, 2, 3],
+ [1, 2, 3]]
+length = [[2, 3, 4],
+ [4, 3, 2],
+ [5, 5, 5]]
+
+output = [[b'en', b'eve', b'lve'],
+ [b'hirt', b'urt', b'te'],
+ [b'ixtee', b'vente', b'hteen']]
+```
+
+Broadcasting `pos` and `len` onto `input`:
+
+```
+input = [[b'ten', b'eleven', b'twelve'],
+ [b'thirteen', b'fourteen', b'fifteen'],
+ [b'sixteen', b'seventeen', b'eighteen'],
+ [b'nineteen', b'twenty', b'twentyone']]
+position = [1, 2, 3]
+length = [1, 2, 3]
+
+output = [[b'e', b'ev', b'lve'],
+ [b'h', b'ur', b'tee'],
+ [b'i', b've', b'hte'],
+ [b'i', b'en', b'nty']]
+```
+
+Broadcasting `input` onto `pos` and `len`:
+
+```
+input = b'thirteen'
+position = [1, 5, 7]
+length = [3, 2, 1]
+
+output = [b'hir', b'ee', b'n']
+```
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+|
+* `ValueError`: If the first argument cannot be converted to a
+Tensor of `dtype string`.
+* `InvalidArgumentError`: If indicies are out of range.
+* `ValueError`: If `pos` and `len` are not the same shape.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `string`. Tensor of strings
+ |
+
+|
+`pos`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `int32`, `int64`.
+Scalar defining the position of first character in each substring
+ |
+
+|
+`len`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must have the same type as `pos`.
+Scalar defining the number of characters to include in each substring
+ |
+
+|
+`unit`
+ |
+
+An optional `string` from: `"BYTE", "UTF8_CHAR"`. Defaults to `"BYTE"`.
+The unit that is used to create the substring. One of: `"BYTE"` (for
+defining position and length by bytes) or `"UTF8_CHAR"` (for the UTF-8
+encoded Unicode code points). The default is `"BYTE"`. Results are undefined if
+`unit=UTF8_CHAR` and the `input` strings do not contain structurally valid
+UTF-8.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` of type `string`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/substr.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/substr.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..2c0af7af6d2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/substr.md
@@ -0,0 +1,191 @@
+description: Return substrings from Tensor of strings.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.substr
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Return substrings from `Tensor` of strings.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.substr(
+ input, pos, len, name=None, unit='BYTE'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+For each string in the input `Tensor`, creates a substring starting at index
+`pos` with a total length of `len`.
+
+If `len` defines a substring that would extend beyond the length of the input
+string, or if `len` is negative, then as many characters as possible are used.
+
+A negative `pos` indicates distance within the string backwards from the end.
+
+If `pos` specifies an index which is out of range for any of the input strings,
+then an `InvalidArgumentError` is thrown.
+
+`pos` and `len` must have the same shape, otherwise a `ValueError` is thrown on
+Op creation.
+
+*NOTE*: `Substr` supports broadcasting up to two dimensions. More about
+broadcasting
+[here](http://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/user/basics.broadcasting.html)
+
+---
+
+Examples
+
+Using scalar `pos` and `len`:
+
+```python
+input = [b'Hello', b'World']
+position = 1
+length = 3
+
+output = [b'ell', b'orl']
+```
+
+Using `pos` and `len` with same shape as `input`:
+
+```python
+input = [[b'ten', b'eleven', b'twelve'],
+ [b'thirteen', b'fourteen', b'fifteen'],
+ [b'sixteen', b'seventeen', b'eighteen']]
+position = [[1, 2, 3],
+ [1, 2, 3],
+ [1, 2, 3]]
+length = [[2, 3, 4],
+ [4, 3, 2],
+ [5, 5, 5]]
+
+output = [[b'en', b'eve', b'lve'],
+ [b'hirt', b'urt', b'te'],
+ [b'ixtee', b'vente', b'hteen']]
+```
+
+Broadcasting `pos` and `len` onto `input`:
+
+```
+input = [[b'ten', b'eleven', b'twelve'],
+ [b'thirteen', b'fourteen', b'fifteen'],
+ [b'sixteen', b'seventeen', b'eighteen'],
+ [b'nineteen', b'twenty', b'twentyone']]
+position = [1, 2, 3]
+length = [1, 2, 3]
+
+output = [[b'e', b'ev', b'lve'],
+ [b'h', b'ur', b'tee'],
+ [b'i', b've', b'hte'],
+ [b'i', b'en', b'nty']]
+```
+
+Broadcasting `input` onto `pos` and `len`:
+
+```
+input = b'thirteen'
+position = [1, 5, 7]
+length = [3, 2, 1]
+
+output = [b'hir', b'ee', b'n']
+```
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+|
+* `ValueError`: If the first argument cannot be converted to a
+Tensor of `dtype string`.
+* `InvalidArgumentError`: If indicies are out of range.
+* `ValueError`: If `pos` and `len` are not the same shape.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `string`. Tensor of strings
+ |
+
+|
+`pos`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `int32`, `int64`.
+Scalar defining the position of first character in each substring
+ |
+
+|
+`len`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`. Must have the same type as `pos`.
+Scalar defining the number of characters to include in each substring
+ |
+
+|
+`unit`
+ |
+
+An optional `string` from: `"BYTE", "UTF8_CHAR"`. Defaults to `"BYTE"`.
+The unit that is used to create the substring. One of: `"BYTE"` (for
+defining position and length by bytes) or `"UTF8_CHAR"` (for the UTF-8
+encoded Unicode code points). The default is `"BYTE"`. Results are undefined if
+`unit=UTF8_CHAR` and the `input` strings do not contain structurally valid
+UTF-8.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` of type `string`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..9d38954978a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary.md
@@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
+description: Operations for writing summary data, for use in analysis and visualization.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.summary
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Operations for writing summary data, for use in analysis and visualization.
+
+
+See the [Summaries and
+TensorBoard](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/summaries_and_tensorboard) guide.
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class Event`](../../../tf/compat/v1/Event.md): A ProtocolMessage
+
+[`class FileWriter`](../../../tf/compat/v1/summary/FileWriter.md): Writes `Summary` protocol buffers to event files.
+
+[`class FileWriterCache`](../../../tf/compat/v1/summary/FileWriterCache.md): Cache for file writers.
+
+[`class SessionLog`](../../../tf/compat/v1/SessionLog.md): A ProtocolMessage
+
+[`class Summary`](../../../tf/compat/v1/Summary.md): A ProtocolMessage
+
+[`class SummaryDescription`](../../../tf/compat/v1/summary/SummaryDescription.md): A ProtocolMessage
+
+[`class TaggedRunMetadata`](../../../tf/compat/v1/summary/TaggedRunMetadata.md): A ProtocolMessage
+
+## Functions
+
+[`all_v2_summary_ops(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/summary/all_v2_summary_ops.md): Returns all V2-style summary ops defined in the current default graph.
+
+[`audio(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/summary/audio.md): Outputs a `Summary` protocol buffer with audio.
+
+[`get_summary_description(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/summary/get_summary_description.md): Given a TensorSummary node_def, retrieve its SummaryDescription.
+
+[`histogram(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/summary/histogram.md): Outputs a `Summary` protocol buffer with a histogram.
+
+[`image(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/summary/image.md): Outputs a `Summary` protocol buffer with images.
+
+[`initialize(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/summary/initialize.md): Initializes summary writing for graph execution mode.
+
+[`merge(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/summary/merge.md): Merges summaries.
+
+[`merge_all(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/summary/merge_all.md): Merges all summaries collected in the default graph.
+
+[`scalar(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/summary/scalar.md): Outputs a `Summary` protocol buffer containing a single scalar value.
+
+[`tensor_summary(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/summary/tensor_summary.md): Outputs a `Summary` protocol buffer with a serialized tensor.proto.
+
+[`text(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/summary/text.md): Summarizes textual data.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/FileWriter.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/FileWriter.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..4793edd3388
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/FileWriter.md
@@ -0,0 +1,519 @@
+description: Writes Summary protocol buffers to event files.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.summary.FileWriter
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Writes `Summary` protocol buffers to event files.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.summary.FileWriter(
+ logdir, graph=None, max_queue=10, flush_secs=120, graph_def=None,
+ filename_suffix=None, session=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The `FileWriter` class provides a mechanism to create an event file in a
+given directory and add summaries and events to it. The class updates the
+file contents asynchronously. This allows a training program to call methods
+to add data to the file directly from the training loop, without slowing down
+training.
+
+When constructed with a tf.compat.v1.Session parameter, a `FileWriter`
+instead forms a compatibility layer over new graph-based summaries
+(`tf.contrib.summary`) to facilitate the use of new summary writing with
+pre-existing code that expects a `FileWriter` instance.
+
+This class is not thread-safe.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`logdir`
+ |
+
+A string. Directory where event file will be written.
+ |
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+A `Graph` object, such as `sess.graph`.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_queue`
+ |
+
+Integer. Size of the queue for pending events and summaries.
+ |
+
+|
+`flush_secs`
+ |
+
+Number. How often, in seconds, to flush the
+pending events and summaries to disk.
+ |
+
+|
+`graph_def`
+ |
+
+DEPRECATED: Use the `graph` argument instead.
+ |
+
+|
+`filename_suffix`
+ |
+
+A string. Every event file's name is suffixed with
+`suffix`.
+ |
+
+|
+`session`
+ |
+
+A tf.compat.v1.Session object. See details above.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If called with eager execution enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+add_event
+
+View source
+
+
+add_event(
+ event
+)
+
+
+Adds an event to the event file.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`event`
+ |
+
+An `Event` protocol buffer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+add_graph
+
+View source
+
+
+add_graph(
+ graph, global_step=None, graph_def=None
+)
+
+
+Adds a `Graph` to the event file.
+
+The graph described by the protocol buffer will be displayed by
+TensorBoard. Most users pass a graph in the constructor instead.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+A `Graph` object, such as `sess.graph`.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Number. Optional global step counter to record with the
+graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`graph_def`
+ |
+
+DEPRECATED. Use the `graph` parameter instead.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If both graph and graph_def are passed to the method.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+View source
+
+
+add_meta_graph(
+ meta_graph_def, global_step=None
+)
+
+
+Adds a `MetaGraphDef` to the event file.
+
+The `MetaGraphDef` allows running the given graph via
+`saver.import_meta_graph()`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`meta_graph_def`
+ |
+
+A `MetaGraphDef` object, often as returned by
+`saver.export_meta_graph()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Number. Optional global step counter to record with the
+graph.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If both `meta_graph_def` is not an instance of `MetaGraphDef`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+View source
+
+
+add_run_metadata(
+ run_metadata, tag, global_step=None
+)
+
+
+Adds a metadata information for a single session.run() call.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`run_metadata`
+ |
+
+A `RunMetadata` protobuf object.
+ |
+
+|
+`tag`
+ |
+
+The tag name for this metadata.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Number. Optional global step counter to record with the
+StepStats.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the provided tag was already used for this type of event.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+add_session_log
+
+View source
+
+
+add_session_log(
+ session_log, global_step=None
+)
+
+
+Adds a `SessionLog` protocol buffer to the event file.
+
+This method wraps the provided session in an `Event` protocol buffer
+and adds it to the event file.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`session_log`
+ |
+
+A `SessionLog` protocol buffer.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Number. Optional global step value to record with the
+summary.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+add_summary
+
+View source
+
+
+add_summary(
+ summary, global_step=None
+)
+
+
+Adds a `Summary` protocol buffer to the event file.
+
+This method wraps the provided summary in an `Event` protocol buffer
+and adds it to the event file.
+
+You can pass the result of evaluating any summary op, using
+`tf.Session.run` or
+tf.Tensor.eval, to this
+function. Alternatively, you can pass a tf.compat.v1.Summary protocol
+buffer that you populate with your own data. The latter is
+commonly done to report evaluation results in event files.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`summary`
+ |
+
+A `Summary` protocol buffer, optionally serialized as a string.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Number. Optional global step value to record with the
+summary.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+close
+
+View source
+
+
+close()
+
+
+Flushes the event file to disk and close the file.
+
+Call this method when you do not need the summary writer anymore.
+
+flush
+
+View source
+
+
+flush()
+
+
+Flushes the event file to disk.
+
+Call this method to make sure that all pending events have been written to
+disk.
+
+get_logdir
+
+View source
+
+
+get_logdir()
+
+
+Returns the directory where event file will be written.
+
+
+reopen
+
+View source
+
+
+reopen()
+
+
+Reopens the EventFileWriter.
+
+Can be called after `close()` to add more events in the same directory.
+The events will go into a new events file.
+
+Does nothing if the EventFileWriter was not closed.
+
+__enter__
+
+View source
+
+
+__enter__()
+
+
+Make usable with "with" statement.
+
+
+__exit__
+
+View source
+
+
+__exit__(
+ unused_type, unused_value, unused_traceback
+)
+
+
+Make usable with "with" statement.
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/FileWriterCache.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/FileWriterCache.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..7cecca1da88
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/FileWriterCache.md
@@ -0,0 +1,91 @@
+description: Cache for file writers.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.summary.FileWriterCache
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Cache for file writers.
+
+
+
+This class caches file writers, one per directory.
+
+## Methods
+
+clear
+
+View source
+
+
+@staticmethod
+clear()
+
+
+Clear cached summary writers. Currently only used for unit tests.
+
+
+get
+
+View source
+
+
+@staticmethod
+get(
+ logdir
+)
+
+
+Returns the FileWriter for the specified directory.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`logdir`
+ |
+
+str, name of the directory.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `FileWriter`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/SummaryDescription.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/SummaryDescription.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..055cee86fa0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/SummaryDescription.md
@@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
+description: A ProtocolMessage
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.summary.SummaryDescription
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A ProtocolMessage
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`type_hint`
+ |
+
+`string type_hint`
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/TaggedRunMetadata.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/TaggedRunMetadata.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..4a979a31977
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/TaggedRunMetadata.md
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+description: A ProtocolMessage
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.summary.TaggedRunMetadata
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A ProtocolMessage
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`run_metadata`
+ |
+
+`bytes run_metadata`
+ |
+
+|
+`tag`
+ |
+
+`string tag`
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/all_v2_summary_ops.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/all_v2_summary_ops.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3e9d229c919
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/all_v2_summary_ops.md
@@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
+description: Returns all V2-style summary ops defined in the current default graph.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.summary.all_v2_summary_ops
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns all V2-style summary ops defined in the current default graph.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.summary.all_v2_summary_ops()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This includes ops from TF 2.0 tf.summary and TF 1.x tf.contrib.summary (except
+for `tf.contrib.summary.graph` and `tf.contrib.summary.import_event`), but
+does *not* include TF 1.x tf.summary ops.
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+List of summary ops, or None if called under eager execution.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/audio.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/audio.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..7ade8d13dde
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/audio.md
@@ -0,0 +1,117 @@
+description: Outputs a Summary protocol buffer with audio.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.summary.audio
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Outputs a `Summary` protocol buffer with audio.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.summary.audio(
+ name, tensor, sample_rate, max_outputs=3, collections=None, family=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The summary has up to `max_outputs` summary values containing audio. The
+audio is built from `tensor` which must be 3-D with shape `[batch_size,
+frames, channels]` or 2-D with shape `[batch_size, frames]`. The values are
+assumed to be in the range of `[-1.0, 1.0]` with a sample rate of
+`sample_rate`.
+
+The `tag` in the outputted Summary.Value protobufs is generated based on the
+name, with a suffix depending on the max_outputs setting:
+
+* If `max_outputs` is 1, the summary value tag is '*name*/audio'.
+* If `max_outputs` is greater than 1, the summary value tags are
+ generated sequentially as '*name*/audio/0', '*name*/audio/1', etc
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the generated node. Will also serve as a series name in
+TensorBoard.
+ |
+
+|
+`tensor`
+ |
+
+A 3-D `float32` `Tensor` of shape `[batch_size, frames, channels]`
+or a 2-D `float32` `Tensor` of shape `[batch_size, frames]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`sample_rate`
+ |
+
+A Scalar `float32` `Tensor` indicating the sample rate of the
+signal in hertz.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_outputs`
+ |
+
+Max number of batch elements to generate audio for.
+ |
+
+|
+`collections`
+ |
+
+Optional list of ops.GraphKeys. The collections to add the
+summary to. Defaults to [_ops.GraphKeys.SUMMARIES]
+ |
+
+|
+`family`
+ |
+
+Optional; if provided, used as the prefix of the summary tag name,
+which controls the tab name used for display on Tensorboard.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A scalar `Tensor` of type `string`. The serialized `Summary` protocol
+buffer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/get_summary_description.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/get_summary_description.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..b6706f1e823
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/get_summary_description.md
@@ -0,0 +1,90 @@
+description: Given a TensorSummary node_def, retrieve its SummaryDescription.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.summary.get_summary_description
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Given a TensorSummary node_def, retrieve its SummaryDescription.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.summary.get_summary_description(
+ node_def
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+When a Summary op is instantiated, a SummaryDescription of associated
+metadata is stored in its NodeDef. This method retrieves the description.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`node_def`
+ |
+
+the node_def_pb2.NodeDef of a TensorSummary op
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+a summary_pb2.SummaryDescription
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if the node is not a summary op.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+Not compatible with eager execution. To write TensorBoard
+summaries under eager execution, use `tf.contrib.summary` instead.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/histogram.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/histogram.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..657c96cbaf9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/histogram.md
@@ -0,0 +1,100 @@
+description: Outputs a Summary protocol buffer with a histogram.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.summary.histogram
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Outputs a `Summary` protocol buffer with a histogram.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.summary.histogram(
+ name, values, collections=None, family=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Adding a histogram summary makes it possible to visualize your data's
+distribution in TensorBoard. You can see a detailed explanation of the
+TensorBoard histogram dashboard
+[here](https://www.tensorflow.org/get_started/tensorboard_histograms).
+
+The generated
+[`Summary`](https://www.tensorflow.org/code/tensorflow/core/framework/summary.proto)
+has one summary value containing a histogram for `values`.
+
+This op reports an `InvalidArgument` error if any value is not finite.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the generated node. Will also serve as a series name in
+TensorBoard.
+ |
+
+|
+`values`
+ |
+
+A real numeric `Tensor`. Any shape. Values to use to
+build the histogram.
+ |
+
+|
+`collections`
+ |
+
+Optional list of graph collections keys. The new summary op is
+added to these collections. Defaults to `[GraphKeys.SUMMARIES]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`family`
+ |
+
+Optional; if provided, used as the prefix of the summary tag name,
+which controls the tab name used for display on Tensorboard.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A scalar `Tensor` of type `string`. The serialized `Summary` protocol
+buffer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/image.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/image.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..1eebfb02678
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/image.md
@@ -0,0 +1,123 @@
+description: Outputs a Summary protocol buffer with images.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.summary.image
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Outputs a `Summary` protocol buffer with images.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.summary.image(
+ name, tensor, max_outputs=3, collections=None, family=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The summary has up to `max_outputs` summary values containing images. The
+images are built from `tensor` which must be 4-D with shape `[batch_size,
+height, width, channels]` and where `channels` can be:
+
+* 1: `tensor` is interpreted as Grayscale.
+* 3: `tensor` is interpreted as RGB.
+* 4: `tensor` is interpreted as RGBA.
+
+The images have the same number of channels as the input tensor. For float
+input, the values are normalized one image at a time to fit in the range
+`[0, 255]`. `uint8` values are unchanged. The op uses two different
+normalization algorithms:
+
+* If the input values are all positive, they are rescaled so the largest one
+ is 255.
+
+* If any input value is negative, the values are shifted so input value 0.0
+ is at 127. They are then rescaled so that either the smallest value is 0,
+ or the largest one is 255.
+
+The `tag` in the outputted Summary.Value protobufs is generated based on the
+name, with a suffix depending on the max_outputs setting:
+
+* If `max_outputs` is 1, the summary value tag is '*name*/image'.
+* If `max_outputs` is greater than 1, the summary value tags are
+ generated sequentially as '*name*/image/0', '*name*/image/1', etc.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the generated node. Will also serve as a series name in
+TensorBoard.
+ |
+
+|
+`tensor`
+ |
+
+A 4-D `uint8` or `float32` `Tensor` of shape `[batch_size, height,
+width, channels]` where `channels` is 1, 3, or 4.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_outputs`
+ |
+
+Max number of batch elements to generate images for.
+ |
+
+|
+`collections`
+ |
+
+Optional list of ops.GraphKeys. The collections to add the
+summary to. Defaults to [_ops.GraphKeys.SUMMARIES]
+ |
+
+|
+`family`
+ |
+
+Optional; if provided, used as the prefix of the summary tag name,
+which controls the tab name used for display on Tensorboard.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A scalar `Tensor` of type `string`. The serialized `Summary` protocol
+buffer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/initialize.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/initialize.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..86f8a48f500
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/initialize.md
@@ -0,0 +1,93 @@
+description: Initializes summary writing for graph execution mode.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.summary.initialize
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Initializes summary writing for graph execution mode.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.summary.initialize(
+ graph=None, session=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This operation is a no-op when executing eagerly.
+
+This helper method provides a higher-level alternative to using
+`tf.contrib.summary.summary_writer_initializer_op` and
+`tf.contrib.summary.graph`.
+
+Most users will also want to call tf.compat.v1.train.create_global_step
+which can happen before or after this function is called.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+A tf.Graph or tf.compat.v1.GraphDef to output to the writer.
+This function will not write the default graph by default. When
+writing to an event log file, the associated step will be zero.
+ |
+
+|
+`session`
+ |
+
+So this method can call `tf.Session.run`. This defaults
+to tf.compat.v1.get_default_session.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If the current thread has no default
+`tf.contrib.summary.SummaryWriter`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If session wasn't passed and no default session.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/merge.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/merge.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..010fd5dd0b6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/merge.md
@@ -0,0 +1,112 @@
+description: Merges summaries.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.summary.merge
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Merges summaries.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.summary.merge(
+ inputs, collections=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This op creates a
+[`Summary`](https://www.tensorflow.org/code/tensorflow/core/framework/summary.proto)
+protocol buffer that contains the union of all the values in the input
+summaries.
+
+When the Op is run, it reports an `InvalidArgument` error if multiple values
+in the summaries to merge use the same tag.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+A list of `string` `Tensor` objects containing serialized `Summary`
+protocol buffers.
+ |
+
+|
+`collections`
+ |
+
+Optional list of graph collections keys. The new summary op is
+added to these collections. Defaults to `[]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A scalar `Tensor` of type `string`. The serialized `Summary` protocol
+buffer resulting from the merging.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If called with eager mode enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+Not compatible with eager execution. To write TensorBoard
+summaries under eager execution, use `tf.contrib.summary` instead.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/merge_all.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/merge_all.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..083eef4cdd2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/merge_all.md
@@ -0,0 +1,98 @@
+description: Merges all summaries collected in the default graph.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.summary.merge_all
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Merges all summaries collected in the default graph.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.summary.merge_all(
+ key=tf.GraphKeys.SUMMARIES, scope=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`key`
+ |
+
+`GraphKey` used to collect the summaries. Defaults to
+`GraphKeys.SUMMARIES`.
+ |
+
+|
+`scope`
+ |
+
+Optional scope used to filter the summary ops, using `re.match`
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+If no summaries were collected, returns None. Otherwise returns a scalar
+`Tensor` of type `string` containing the serialized `Summary` protocol
+buffer resulting from the merging.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If called with eager execution enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+Not compatible with eager execution. To write TensorBoard
+summaries under eager execution, use `tf.contrib.summary` instead.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/scalar.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/scalar.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..d98f69359fa
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/scalar.md
@@ -0,0 +1,106 @@
+description: Outputs a Summary protocol buffer containing a single scalar value.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.summary.scalar
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Outputs a `Summary` protocol buffer containing a single scalar value.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.summary.scalar(
+ name, tensor, collections=None, family=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The generated Summary has a Tensor.proto containing the input Tensor.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the generated node. Will also serve as the series name in
+TensorBoard.
+ |
+
+|
+`tensor`
+ |
+
+A real numeric Tensor containing a single value.
+ |
+
+|
+`collections`
+ |
+
+Optional list of graph collections keys. The new summary op is
+added to these collections. Defaults to `[GraphKeys.SUMMARIES]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`family`
+ |
+
+Optional; if provided, used as the prefix of the summary tag name,
+which controls the tab name used for display on Tensorboard.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A scalar `Tensor` of type `string`. Which contains a `Summary` protobuf.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If tensor has the wrong shape or type.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/tensor_summary.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/tensor_summary.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..34b791f5e0f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/tensor_summary.md
@@ -0,0 +1,116 @@
+description: Outputs a Summary protocol buffer with a serialized tensor.proto.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.summary.tensor_summary
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Outputs a `Summary` protocol buffer with a serialized tensor.proto.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.summary.tensor_summary(
+ name, tensor, summary_description=None, collections=None, summary_metadata=None,
+ family=None, display_name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the generated node. If display_name is not set, it will
+also serve as the tag name in TensorBoard. (In that case, the tag
+name will inherit tf name scopes.)
+ |
+
+|
+`tensor`
+ |
+
+A tensor of any type and shape to serialize.
+ |
+
+|
+`summary_description`
+ |
+
+A long description of the summary sequence. Markdown
+is supported.
+ |
+
+|
+`collections`
+ |
+
+Optional list of graph collections keys. The new summary op is
+added to these collections. Defaults to `[GraphKeys.SUMMARIES]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`summary_metadata`
+ |
+
+Optional SummaryMetadata proto (which describes which
+plugins may use the summary value).
+ |
+
+|
+`family`
+ |
+
+Optional; if provided, used as the prefix of the summary tag,
+which controls the name used for display on TensorBoard when
+display_name is not set.
+ |
+
+|
+`display_name`
+ |
+
+A string used to name this data in TensorBoard. If this is
+not set, then the node name will be used instead.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A scalar `Tensor` of type `string`. The serialized `Summary` protocol
+buffer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/text.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/text.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..358b80f937d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/summary/text.md
@@ -0,0 +1,106 @@
+description: Summarizes textual data.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.summary.text
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Summarizes textual data.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.summary.text(
+ name, tensor, collections=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Text data summarized via this plugin will be visible in the Text Dashboard
+in TensorBoard. The standard TensorBoard Text Dashboard will render markdown
+in the strings, and will automatically organize 1d and 2d tensors into tables.
+If a tensor with more than 2 dimensions is provided, a 2d subarray will be
+displayed along with a warning message. (Note that this behavior is not
+intrinsic to the text summary api, but rather to the default TensorBoard text
+plugin.)
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the generated node. Will also serve as a series name in
+TensorBoard.
+ |
+
+|
+`tensor`
+ |
+
+a string-type Tensor to summarize.
+ |
+
+|
+`collections`
+ |
+
+Optional list of ops.GraphKeys. The collections to add the
+summary to. Defaults to [_ops.GraphKeys.SUMMARIES]
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A TensorSummary op that is configured so that TensorBoard will recognize
+that it contains textual data. The TensorSummary is a scalar `Tensor` of
+type `string` which contains `Summary` protobufs.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If tensor has the wrong type.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sysconfig.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sysconfig.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e749a8ca8ad
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/sysconfig.md
@@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
+description: System configuration library.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.sysconfig
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+System configuration library.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`get_compile_flags(...)`](../../../tf/sysconfig/get_compile_flags.md): Get the compilation flags for custom operators.
+
+[`get_include(...)`](../../../tf/sysconfig/get_include.md): Get the directory containing the TensorFlow C++ header files.
+
+[`get_lib(...)`](../../../tf/sysconfig/get_lib.md): Get the directory containing the TensorFlow framework library.
+
+[`get_link_flags(...)`](../../../tf/sysconfig/get_link_flags.md): Get the link flags for custom operators.
+
+## Other Members
+
+* `CXX11_ABI_FLAG = 0`
+* `MONOLITHIC_BUILD = 0`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tables_initializer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tables_initializer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..23dc4e4c586
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tables_initializer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
+description: Returns an Op that initializes all tables of the default graph.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.tables_initializer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns an Op that initializes all tables of the default graph.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.initializers.tables_initializer`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.tables_initializer(
+ name='init_all_tables'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+See the [Low Level
+Intro](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/low_level_intro#feature_columns)
+guide, for an example of usage.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the initialization op.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Op that initializes all tables. Note that if there are
+not tables the returned Op is a NoOp.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/test.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/test.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e1621b8c0c2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/test.md
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
+description: Testing.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.test
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Testing.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class Benchmark`](../../../tf/test/Benchmark.md): Abstract class that provides helpers for TensorFlow benchmarks.
+
+[`class StubOutForTesting`](../../../tf/compat/v1/test/StubOutForTesting.md): Support class for stubbing methods out for unit testing.
+
+[`class TestCase`](../../../tf/test/TestCase.md): Base class for tests that need to test TensorFlow.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`assert_equal_graph_def(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/test/assert_equal_graph_def.md): Asserts that two `GraphDef`s are (mostly) the same.
+
+[`benchmark_config(...)`](../../../tf/test/benchmark_config.md): Returns a tf.compat.v1.ConfigProto for disabling the dependency optimizer.
+
+[`compute_gradient(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/test/compute_gradient.md): Computes and returns the theoretical and numerical Jacobian. (deprecated)
+
+[`compute_gradient_error(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/test/compute_gradient_error.md): Computes the gradient error. (deprecated)
+
+[`create_local_cluster(...)`](../../../tf/test/create_local_cluster.md): Create and start local servers and return the associated `Server` objects.
+
+[`get_temp_dir(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/test/get_temp_dir.md): Returns a temporary directory for use during tests.
+
+[`gpu_device_name(...)`](../../../tf/test/gpu_device_name.md): Returns the name of a GPU device if available or the empty string.
+
+[`is_built_with_cuda(...)`](../../../tf/test/is_built_with_cuda.md): Returns whether TensorFlow was built with CUDA (GPU) support.
+
+[`is_built_with_gpu_support(...)`](../../../tf/test/is_built_with_gpu_support.md): Returns whether TensorFlow was built with GPU (i.e. CUDA or ROCm) support.
+
+[`is_built_with_rocm(...)`](../../../tf/test/is_built_with_rocm.md): Returns whether TensorFlow was built with ROCm (GPU) support.
+
+[`is_built_with_xla(...)`](../../../tf/test/is_built_with_xla.md): Returns whether TensorFlow was built with XLA support.
+
+[`is_gpu_available(...)`](../../../tf/test/is_gpu_available.md): Returns whether TensorFlow can access a GPU. (deprecated)
+
+[`main(...)`](../../../tf/test/main.md): Runs all unit tests.
+
+[`test_src_dir_path(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/test/test_src_dir_path.md): Creates an absolute test srcdir path given a relative path.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/test/StubOutForTesting.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/test/StubOutForTesting.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..52560a7e102
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/test/StubOutForTesting.md
@@ -0,0 +1,258 @@
+description: Support class for stubbing methods out for unit testing.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.test.StubOutForTesting
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Support class for stubbing methods out for unit testing.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.test.StubOutForTesting()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Sample Usage:
+
+
+
+You want os.path.exists() to always return true during testing.
+
+ stubs = StubOutForTesting()
+ stubs.Set(os.path, 'exists', lambda x: 1)
+ ...
+ stubs.CleanUp()
+
+The above changes os.path.exists into a lambda that returns 1. Once
+the ... part of the code finishes, the CleanUp() looks up the old
+value of os.path.exists and restores it.
+
+## Methods
+
+CleanUp
+
+View source
+
+
+CleanUp()
+
+
+Undoes all SmartSet() & Set() calls, restoring original definitions.
+
+
+Set
+
+View source
+
+
+Set(
+ parent, child_name, new_child
+)
+
+
+In parent, replace child_name's old definition with new_child.
+
+The parent could be a module when the child is a function at
+module scope. Or the parent could be a class when a class' method
+is being replaced. The named child is set to new_child, while the
+prior definition is saved away for later, when UnsetAll() is
+called.
+
+This method supports the case where child_name is a staticmethod or a
+classmethod of parent.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`parent`
+ |
+
+The context in which the attribute child_name is to be changed.
+ |
+
+|
+`child_name`
+ |
+
+The name of the attribute to change.
+ |
+
+|
+`new_child`
+ |
+
+The new value of the attribute.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+SmartSet
+
+View source
+
+
+SmartSet(
+ obj, attr_name, new_attr
+)
+
+
+Replace obj.attr_name with new_attr.
+
+This method is smart and works at the module, class, and instance level
+while preserving proper inheritance. It will not stub out C types however
+unless that has been explicitly allowed by the type.
+
+This method supports the case where attr_name is a staticmethod or a
+classmethod of obj.
+
+#### Notes:
+
+- If obj is an instance, then it is its class that will actually be
+ stubbed. Note that the method Set() does not do that: if obj is
+ an instance, it (and not its class) will be stubbed.
+- The stubbing is using the builtin getattr and setattr. So, the __get__
+ and __set__ will be called when stubbing (
+ probably be to manipulate obj.__dict__ instead of getattr() and
+ setattr()).
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`obj`
+ |
+
+The object whose attributes we want to modify.
+ |
+
+|
+`attr_name`
+ |
+
+The name of the attribute to modify.
+ |
+
+|
+`new_attr`
+ |
+
+The new value for the attribute.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`AttributeError`
+ |
+
+If the attribute cannot be found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+SmartUnsetAll
+
+View source
+
+
+SmartUnsetAll()
+
+
+Reverses SmartSet() calls, restoring things to original definitions.
+
+This method is automatically called when the StubOutForTesting()
+object is deleted; there is no need to call it explicitly.
+
+It is okay to call SmartUnsetAll() repeatedly, as later calls have
+no effect if no SmartSet() calls have been made.
+
+UnsetAll
+
+View source
+
+
+UnsetAll()
+
+
+Reverses Set() calls, restoring things to their original definitions.
+
+This method is automatically called when the StubOutForTesting()
+object is deleted; there is no need to call it explicitly.
+
+It is okay to call UnsetAll() repeatedly, as later calls have no
+effect if no Set() calls have been made.
+
+__enter__
+
+View source
+
+
+__enter__()
+
+
+
+
+
+__exit__
+
+View source
+
+
+__exit__(
+ unused_exc_type, unused_exc_value, unused_tb
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/test/assert_equal_graph_def.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/test/assert_equal_graph_def.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e9564c46cd0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/test/assert_equal_graph_def.md
@@ -0,0 +1,100 @@
+description: Asserts that two GraphDefs are (mostly) the same.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.test.assert_equal_graph_def
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Asserts that two `GraphDef`s are (mostly) the same.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.test.assert_equal_graph_def(
+ actual, expected, checkpoint_v2=(False), hash_table_shared_name=(False)
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Compares two `GraphDef` protos for equality, ignoring versions and ordering of
+nodes, attrs, and control inputs. Node names are used to match up nodes
+between the graphs, so the naming of nodes must be consistent.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`actual`
+ |
+
+The `GraphDef` we have.
+ |
+
+|
+`expected`
+ |
+
+The `GraphDef` we expected.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_v2`
+ |
+
+boolean determining whether to ignore randomized attribute
+values that appear in V2 checkpoints.
+ |
+
+|
+`hash_table_shared_name`
+ |
+
+boolean determining whether to ignore randomized
+shared_names that appear in HashTableV2 op defs.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`AssertionError`
+ |
+
+If the `GraphDef`s do not match.
+ |
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If either argument is not a `GraphDef`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/test/compute_gradient.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/test/compute_gradient.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..4f7fa2d4e04
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/test/compute_gradient.md
@@ -0,0 +1,137 @@
+description: Computes and returns the theoretical and numerical Jacobian. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.test.compute_gradient
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes and returns the theoretical and numerical Jacobian. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.test.compute_gradient(
+ x, x_shape, y, y_shape, x_init_value=None, delta=0.001, init_targets=None,
+ extra_feed_dict=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use tf.test.compute_gradient in 2.0, which has better support for functions. Note that the two versions have different usage, so code change is needed.
+
+If `x` or `y` is complex, the Jacobian will still be real but the
+corresponding Jacobian dimension(s) will be twice as large. This is required
+even if both input and output is complex since TensorFlow graphs are not
+necessarily holomorphic, and may have gradients not expressible as complex
+numbers. For example, if `x` is complex with shape `[m]` and `y` is complex
+with shape `[n]`, each Jacobian `J` will have shape `[m * 2, n * 2]` with
+
+ J[:m, :n] = d(Re y)/d(Re x)
+ J[:m, n:] = d(Im y)/d(Re x)
+ J[m:, :n] = d(Re y)/d(Im x)
+ J[m:, n:] = d(Im y)/d(Im x)
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`x`
+ |
+
+a tensor or list of tensors
+ |
+
+|
+`x_shape`
+ |
+
+the dimensions of x as a tuple or an array of ints. If x is a list,
+then this is the list of shapes.
+ |
+
+|
+`y`
+ |
+
+a tensor
+ |
+
+|
+`y_shape`
+ |
+
+the dimensions of y as a tuple or an array of ints.
+ |
+
+|
+`x_init_value`
+ |
+
+(optional) a numpy array of the same shape as "x"
+representing the initial value of x. If x is a list, this should be a list
+of numpy arrays. If this is none, the function will pick a random tensor
+as the initial value.
+ |
+
+|
+`delta`
+ |
+
+(optional) the amount of perturbation.
+ |
+
+|
+`init_targets`
+ |
+
+list of targets to run to initialize model params.
+ |
+
+|
+`extra_feed_dict`
+ |
+
+dict that allows fixing specified tensor values
+during the Jacobian calculation.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Two 2-d numpy arrays representing the theoretical and numerical
+Jacobian for dy/dx. Each has "x_size" rows and "y_size" columns
+where "x_size" is the number of elements in x and "y_size" is the
+number of elements in y. If x is a list, returns a list of two numpy arrays.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/test/compute_gradient_error.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/test/compute_gradient_error.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..b92023ab1df
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/test/compute_gradient_error.md
@@ -0,0 +1,133 @@
+description: Computes the gradient error. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.test.compute_gradient_error
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes the gradient error. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.test.compute_gradient_error(
+ x, x_shape, y, y_shape, x_init_value=None, delta=0.001, init_targets=None,
+ extra_feed_dict=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use tf.test.compute_gradient in 2.0, which has better support for functions. Note that the two versions have different usage, so code change is needed.
+
+Computes the maximum error for dy/dx between the computed Jacobian and the
+numerically estimated Jacobian.
+
+This function will modify the tensors passed in as it adds more operations
+and hence changing the consumers of the operations of the input tensors.
+
+This function adds operations to the current session. To compute the error
+using a particular device, such as a GPU, use the standard methods for
+setting a device (e.g. using with sess.graph.device() or setting a device
+function in the session constructor).
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`x`
+ |
+
+a tensor or list of tensors
+ |
+
+|
+`x_shape`
+ |
+
+the dimensions of x as a tuple or an array of ints. If x is a list,
+then this is the list of shapes.
+ |
+
+|
+`y`
+ |
+
+a tensor
+ |
+
+|
+`y_shape`
+ |
+
+the dimensions of y as a tuple or an array of ints.
+ |
+
+|
+`x_init_value`
+ |
+
+(optional) a numpy array of the same shape as "x"
+representing the initial value of x. If x is a list, this should be a list
+of numpy arrays. If this is none, the function will pick a random tensor
+as the initial value.
+ |
+
+|
+`delta`
+ |
+
+(optional) the amount of perturbation.
+ |
+
+|
+`init_targets`
+ |
+
+list of targets to run to initialize model params.
+ |
+
+|
+`extra_feed_dict`
+ |
+
+dict that allows fixing specified tensor values
+during the Jacobian calculation.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The maximum error in between the two Jacobians.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/test/get_temp_dir.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/test/get_temp_dir.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..4dd7d893145
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/test/get_temp_dir.md
@@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
+description: Returns a temporary directory for use during tests.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.test.get_temp_dir
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns a temporary directory for use during tests.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.test.get_temp_dir()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+There is no need to delete the directory after the test.
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The temporary directory.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/test/test_src_dir_path.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/test/test_src_dir_path.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..590185f880e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/test/test_src_dir_path.md
@@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
+description: Creates an absolute test srcdir path given a relative path.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.test.test_src_dir_path
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Creates an absolute test srcdir path given a relative path.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.test.test_src_dir_path(
+ relative_path
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`relative_path`
+ |
+
+a path relative to tensorflow root.
+e.g. "core/platform".
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An absolute path to the linked in runfiles.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/to_bfloat16.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/to_bfloat16.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..4c48d6a3e45
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/to_bfloat16.md
@@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
+description: Casts a tensor to type bfloat16. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.to_bfloat16
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Casts a tensor to type `bfloat16`. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.to_bfloat16(
+ x, name='ToBFloat16'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use tf.cast instead.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`x`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` or `SparseTensor` or `IndexedSlices`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` or `SparseTensor` or `IndexedSlices` with same shape as `x` with
+type `bfloat16`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `x` cannot be cast to the `bfloat16`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/to_complex128.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/to_complex128.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..7407095b5ac
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/to_complex128.md
@@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
+description: Casts a tensor to type complex128. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.to_complex128
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Casts a tensor to type `complex128`. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.to_complex128(
+ x, name='ToComplex128'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use tf.cast instead.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`x`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` or `SparseTensor` or `IndexedSlices`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` or `SparseTensor` or `IndexedSlices` with same shape as `x` with
+type `complex128`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `x` cannot be cast to the `complex128`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/to_complex64.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/to_complex64.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..2db34a2b56c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/to_complex64.md
@@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
+description: Casts a tensor to type complex64. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.to_complex64
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Casts a tensor to type `complex64`. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.to_complex64(
+ x, name='ToComplex64'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use tf.cast instead.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`x`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` or `SparseTensor` or `IndexedSlices`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` or `SparseTensor` or `IndexedSlices` with same shape as `x` with
+type `complex64`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `x` cannot be cast to the `complex64`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/to_double.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/to_double.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e38ca8ad951
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/to_double.md
@@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
+description: Casts a tensor to type float64. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.to_double
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Casts a tensor to type `float64`. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.to_double(
+ x, name='ToDouble'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use tf.cast instead.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`x`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` or `SparseTensor` or `IndexedSlices`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` or `SparseTensor` or `IndexedSlices` with same shape as `x` with
+type `float64`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `x` cannot be cast to the `float64`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/to_float.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/to_float.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..882161732cc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/to_float.md
@@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
+description: Casts a tensor to type float32. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.to_float
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Casts a tensor to type `float32`. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.to_float(
+ x, name='ToFloat'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use tf.cast instead.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`x`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` or `SparseTensor` or `IndexedSlices`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` or `SparseTensor` or `IndexedSlices` with same shape as `x` with
+type `float32`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `x` cannot be cast to the `float32`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/to_int32.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/to_int32.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..c546a48b9a3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/to_int32.md
@@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
+description: Casts a tensor to type int32. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.to_int32
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Casts a tensor to type `int32`. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.to_int32(
+ x, name='ToInt32'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use tf.cast instead.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`x`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` or `SparseTensor` or `IndexedSlices`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` or `SparseTensor` or `IndexedSlices` with same shape as `x` with
+type `int32`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `x` cannot be cast to the `int32`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/to_int64.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/to_int64.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..9b6f931d5f9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/to_int64.md
@@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
+description: Casts a tensor to type int64. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.to_int64
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Casts a tensor to type `int64`. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.to_int64(
+ x, name='ToInt64'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use tf.cast instead.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`x`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` or `SparseTensor` or `IndexedSlices`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` or `SparseTensor` or `IndexedSlices` with same shape as `x` with
+type `int64`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `x` cannot be cast to the `int64`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e32a7db5a6d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu.md
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+description: Ops related to Tensor Processing Units.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.tpu
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Ops related to Tensor Processing Units.
+
+
+
+## Modules
+
+[`experimental`](../../../tf/compat/v1/tpu/experimental.md) module: Public API for tf.tpu.experimental namespace.
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class CrossShardOptimizer`](../../../tf/compat/v1/tpu/CrossShardOptimizer.md): An optimizer that averages gradients across TPU shards.
+
+[`class PaddingSpec`](../../../tf/compat/v1/tpu/PaddingSpec.md): Represents the type of padding policies for tpu.replicate.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`batch_parallel(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/tpu/batch_parallel.md): Shards `computation` along the batch dimension for parallel execution.
+
+[`bfloat16_scope(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/tpu/bfloat16_scope.md): Scope class for bfloat16 variables so that the model uses custom getter.
+
+[`core(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/tpu/core.md): Returns the device name for a core in a replicated TPU computation.
+
+[`cross_replica_sum(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/tpu/cross_replica_sum.md): Sum the input tensor across replicas according to group_assignment.
+
+[`initialize_system(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/tpu/initialize_system.md): Initializes a distributed TPU system for use with TensorFlow.
+
+[`outside_compilation(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/tpu/outside_compilation.md): Builds part of a computation outside any current TPU replicate scope.
+
+[`replicate(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/tpu/replicate.md): Builds a graph operator that runs a replicated TPU computation.
+
+[`rewrite(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/tpu/rewrite.md): Rewrites `computation` for execution on a TPU system.
+
+[`shard(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/tpu/shard.md): Shards `computation` for parallel execution.
+
+[`shutdown_system(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/tpu/shutdown_system.md): Shuts down a running a distributed TPU system.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/CrossShardOptimizer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/CrossShardOptimizer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..f0cd0631011
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/CrossShardOptimizer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,551 @@
+description: An optimizer that averages gradients across TPU shards.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.tpu.CrossShardOptimizer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+An optimizer that averages gradients across TPU shards.
+
+Inherits From: [`Optimizer`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/train/Optimizer.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.tpu.CrossShardOptimizer(
+ opt, reduction=losses.Reduction.MEAN, name='CrossShardOptimizer',
+ group_assignment=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`opt`
+ |
+
+An existing `Optimizer` to encapsulate.
+ |
+
+|
+`reduction`
+ |
+
+The reduction to apply to the shard losses.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name prefix for the operations created when applying
+gradients. Defaults to "CrossShardOptimizer".
+ |
+
+|
+`group_assignment`
+ |
+
+Optional 2d int32 lists with shape
+[num_groups, num_replicas_per_group] which describles how to apply
+optimizer to subgroups.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If reduction is not a valid cross-shard reduction.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+apply_gradients
+
+View source
+
+
+apply_gradients(
+ grads_and_vars, global_step=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+Apply gradients to variables.
+
+Calls tpu_ops.cross_replica_sum() to sum gradient contributions across
+replicas, and then applies the real optimizer.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`grads_and_vars`
+ |
+
+List of (gradient, variable) pairs as returned by
+compute_gradients().
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Optional Variable to increment by one after the
+variables have been updated.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the returned operation. Default to the
+name passed to the Optimizer constructor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An `Operation` that applies the gradients. If `global_step` was not None,
+that operation also increments `global_step`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the grads_and_vars is malformed.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+compute_gradients
+
+View source
+
+
+compute_gradients(
+ loss, var_list=None, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+Compute gradients of "loss" for the variables in "var_list".
+
+This simply wraps `compute_gradients()` from the real optimizer. The
+gradients will be aggregated in `apply_gradients()` so that user can
+modify the gradients like clipping with per replica global norm if needed.
+The global norm with aggregated gradients can be bad as one replica's huge
+gradients can hurt the gradients from other replicas.
+
+When the CrossShardOptimizer is constructed with
+`reduction == losses.Reduction.MEAN` (default), this function scales the
+loss by `1.0 / num_shards` before computing the gradients. Assuming the
+optimizer uses the default implementation of `compute_gradients()`, the
+gradients of the scaled loss are scaled by `1.0 / num_shards` compared to
+the gradients of the original loss. This scaling factor is important because
+`apply_gradients()` sums gradients across shards, rather than averaging
+them. However, the scaling factor must be taken into account when clipping
+the norm of the gradients or performing other postprocessing.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`loss`
+ |
+
+A Tensor containing the value to minimize.
+ |
+
+|
+`var_list`
+ |
+
+Optional list or tuple of tf.Variable to update to minimize
+`loss`. Defaults to the list of variables collected in the graph
+under the key `GraphKey.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES`.
+ |
+
+|
+`**kwargs`
+ |
+
+Keyword arguments for compute_gradients().
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of (gradient, variable) pairs.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If not within a tpu_shard_context or group_assignment is
+invalid.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+get_name
+
+View source
+
+
+get_name()
+
+
+
+
+
+get_slot
+
+View source
+
+
+get_slot(
+ *args, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+Return a slot named "name" created for "var" by the Optimizer.
+
+This simply wraps the get_slot() from the actual optimizer.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`*args`
+ |
+
+Arguments for get_slot().
+ |
+
+|
+`**kwargs`
+ |
+
+Keyword arguments for get_slot().
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The `Variable` for the slot if it was created, `None` otherwise.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_slot_names
+
+View source
+
+
+get_slot_names(
+ *args, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+Return a list of the names of slots created by the `Optimizer`.
+
+This simply wraps the get_slot_names() from the actual optimizer.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`*args`
+ |
+
+Arguments for get_slot().
+ |
+
+|
+`**kwargs`
+ |
+
+Keyword arguments for get_slot().
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of strings.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+minimize
+
+View source
+
+
+minimize(
+ loss, global_step=None, var_list=None, gate_gradients=GATE_OP,
+ aggregation_method=None, colocate_gradients_with_ops=(False), name=None,
+ grad_loss=None
+)
+
+
+Add operations to minimize `loss` by updating `var_list`.
+
+This method simply combines calls `compute_gradients()` and
+`apply_gradients()`. If you want to process the gradient before applying
+them call `compute_gradients()` and `apply_gradients()` explicitly instead
+of using this function.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`loss`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` containing the value to minimize.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Optional `Variable` to increment by one after the
+variables have been updated.
+ |
+
+|
+`var_list`
+ |
+
+Optional list or tuple of `Variable` objects to update to
+minimize `loss`. Defaults to the list of variables collected in
+the graph under the key `GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES`.
+ |
+
+|
+`gate_gradients`
+ |
+
+How to gate the computation of gradients. Can be
+`GATE_NONE`, `GATE_OP`, or `GATE_GRAPH`.
+ |
+
+|
+`aggregation_method`
+ |
+
+Specifies the method used to combine gradient terms.
+Valid values are defined in the class `AggregationMethod`.
+ |
+
+|
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops`
+ |
+
+If True, try colocating gradients with
+the corresponding op.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the returned operation.
+ |
+
+|
+`grad_loss`
+ |
+
+Optional. A `Tensor` holding the gradient computed for `loss`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Operation that updates the variables in `var_list`. If `global_step`
+was not `None`, that operation also increments `global_step`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If some of the variables are not `Variable` objects.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+When eager execution is enabled, `loss` should be a Python function that
+takes no arguments and computes the value to be minimized. Minimization (and
+gradient computation) is done with respect to the elements of `var_list` if
+not None, else with respect to any trainable variables created during the
+execution of the `loss` function. `gate_gradients`, `aggregation_method`,
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops` and `grad_loss` are ignored when eager
+execution is enabled.
+
+
+
+variables
+
+View source
+
+
+variables()
+
+
+Forwarding the variables from the underlying optimizer.
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `GATE_GRAPH = 2`
+* `GATE_NONE = 0`
+* `GATE_OP = 1`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/PaddingSpec.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/PaddingSpec.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3de7413e5f1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/PaddingSpec.md
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+description: Represents the type of padding policies for tpu.replicate.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.tpu.PaddingSpec
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Represents the type of padding policies for tpu.replicate.
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `AUTO = `
+* `POWER_OF_TWO = `
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/batch_parallel.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/batch_parallel.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..604c8c51ed2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/batch_parallel.md
@@ -0,0 +1,143 @@
+description: Shards computation along the batch dimension for parallel execution.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.tpu.batch_parallel
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Shards `computation` along the batch dimension for parallel execution.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.tpu.batch_parallel(
+ computation, inputs=None, num_shards=1, infeed_queue=None,
+ device_assignment=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Convenience wrapper around shard().
+
+`inputs` must be a list of Tensors or None (equivalent to an empty list).
+Each input is split into `num_shards` pieces along the 0-th dimension, and
+computation is applied to each shard in parallel.
+
+Tensors are broadcast to all shards if they are lexically captured by
+`computation`. e.g.,
+
+x = tf.constant(7)
+def computation():
+ return x + 3
+... = shard(computation, ...)
+
+The outputs from all shards are concatenated back together along their 0-th
+dimension.
+
+Inputs and outputs of the computation must be at least rank-1 Tensors.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`computation`
+ |
+
+A Python function that builds a computation to apply to each
+shard of the input.
+ |
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+A list of input tensors or None (equivalent to an empty list). The
+0-th dimension of each Tensor must have size divisible by `num_shards`.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_shards`
+ |
+
+The number of shards.
+ |
+
+|
+`infeed_queue`
+ |
+
+If not `None`, the `InfeedQueue` from which to append a tuple
+of arguments as inputs to `computation`.
+ |
+
+|
+`device_assignment`
+ |
+
+If not `None`, a `DeviceAssignment` describing the
+mapping between logical cores in the computation with physical cores in
+the TPU topology. Uses a default device assignment if `None`. The
+`DeviceAssignment` may be omitted if each shard of the computation uses
+only one core, and there is either only one shard, or the number of shards
+is equal to the number of cores in the TPU system.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+(Deprecated) Does nothing.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of output tensors.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `num_shards <= 0`
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/bfloat16_scope.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/bfloat16_scope.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..0a2b62d70e3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/bfloat16_scope.md
@@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
+description: Scope class for bfloat16 variables so that the model uses custom getter.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.tpu.bfloat16_scope
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Scope class for bfloat16 variables so that the model uses custom getter.
+
+
+@tf_contextlib.contextmanager
+tf.compat.v1.tpu.bfloat16_scope()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This enables variables to be read as bfloat16 type when using get_variable.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/core.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/core.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..dda97da5b4c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/core.md
@@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
+description: Returns the device name for a core in a replicated TPU computation.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.tpu.core
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns the device name for a core in a replicated TPU computation.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.tpu.core(
+ num
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`num`
+ |
+
+the virtual core number within each replica to which operators should
+be assigned.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+A device name, suitable for passing to tf.device().
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/cross_replica_sum.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/cross_replica_sum.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..0d6b917fb2c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/cross_replica_sum.md
@@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
+description: Sum the input tensor across replicas according to group_assignment.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.tpu.cross_replica_sum
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Sum the input tensor across replicas according to group_assignment.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.tpu.cross_replica_sum(
+ x, group_assignment=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`x`
+ |
+
+The local tensor to the sum.
+ |
+
+|
+`group_assignment`
+ |
+
+Optional 2d int32 lists with shape [num_groups,
+num_replicas_per_group]. `group_assignment[i]` represents the replica
+ids in the ith subgroup.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional op name.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` which is summed across replicas.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/experimental.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/experimental.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..39999c36b88
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/experimental.md
@@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
+description: Public API for tf.tpu.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.tpu.experimental
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.tpu.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class AdagradParameters`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/tpu/experimental/AdagradParameters.md): Optimization parameters for Adagrad with TPU embeddings.
+
+[`class AdamParameters`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/tpu/experimental/AdamParameters.md): Optimization parameters for Adam with TPU embeddings.
+
+[`class DeviceAssignment`](../../../../tf/tpu/experimental/DeviceAssignment.md): Mapping from logical cores in a computation to the physical TPU topology.
+
+[`class FtrlParameters`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/tpu/experimental/FtrlParameters.md): Optimization parameters for Ftrl with TPU embeddings.
+
+[`class StochasticGradientDescentParameters`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/tpu/experimental/StochasticGradientDescentParameters.md): Optimization parameters for stochastic gradient descent for TPU embeddings.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`embedding_column(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/tpu/experimental/embedding_column.md): TPU version of tf.compat.v1.feature_column.embedding_column.
+
+[`initialize_tpu_system(...)`](../../../../tf/tpu/experimental/initialize_tpu_system.md): Initialize the TPU devices.
+
+[`shared_embedding_columns(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/tpu/experimental/shared_embedding_columns.md): TPU version of tf.compat.v1.feature_column.shared_embedding_columns.
+
+[`shutdown_tpu_system(...)`](../../../../tf/tpu/experimental/shutdown_tpu_system.md): Shuts down the TPU devices.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/experimental/AdagradParameters.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/experimental/AdagradParameters.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3ee28fc97c6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/experimental/AdagradParameters.md
@@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
+description: Optimization parameters for Adagrad with TPU embeddings.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.tpu.experimental.AdagradParameters
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Optimization parameters for Adagrad with TPU embeddings.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.tpu.experimental.AdagradParameters(
+ learning_rate, initial_accumulator=0.1, use_gradient_accumulation=(True),
+ clip_weight_min=None, clip_weight_max=None, weight_decay_factor=None,
+ multiply_weight_decay_factor_by_learning_rate=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Pass this to `tf.estimator.tpu.experimental.EmbeddingConfigSpec` via the
+`optimization_parameters` argument to set the optimizer and its parameters.
+See the documentation for `tf.estimator.tpu.experimental.EmbeddingConfigSpec`
+for more details.
+
+```
+estimator = tf.estimator.tpu.TPUEstimator(
+ ...
+ embedding_spec=tf.estimator.tpu.experimental.EmbeddingConfigSpec(
+ ...
+ optimization_parameters=tf.tpu.experimental.AdagradParameters(0.1),
+ ...))
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`learning_rate`
+ |
+
+used for updating embedding table.
+ |
+
+|
+`initial_accumulator`
+ |
+
+initial accumulator for Adagrad.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_gradient_accumulation`
+ |
+
+setting this to `False` makes embedding
+gradients calculation less accurate but faster. Please see
+`optimization_parameters.proto` for details.
+for details.
+ |
+
+|
+`clip_weight_min`
+ |
+
+the minimum value to clip by; None means -infinity.
+ |
+
+|
+`clip_weight_max`
+ |
+
+the maximum value to clip by; None means +infinity.
+ |
+
+|
+`weight_decay_factor`
+ |
+
+amount of weight decay to apply; None means that the
+weights are not decayed.
+ |
+
+|
+`multiply_weight_decay_factor_by_learning_rate`
+ |
+
+if true,
+`weight_decay_factor` is multiplied by the current learning rate.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/experimental/AdamParameters.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/experimental/AdamParameters.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..693524ab25b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/experimental/AdamParameters.md
@@ -0,0 +1,148 @@
+description: Optimization parameters for Adam with TPU embeddings.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.tpu.experimental.AdamParameters
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Optimization parameters for Adam with TPU embeddings.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.tpu.experimental.AdamParameters(
+ learning_rate, beta1=0.9, beta2=0.999, epsilon=1e-08, lazy_adam=(True),
+ sum_inside_sqrt=(True), use_gradient_accumulation=(True), clip_weight_min=None,
+ clip_weight_max=None, weight_decay_factor=None,
+ multiply_weight_decay_factor_by_learning_rate=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Pass this to `tf.estimator.tpu.experimental.EmbeddingConfigSpec` via the
+`optimization_parameters` argument to set the optimizer and its parameters.
+See the documentation for `tf.estimator.tpu.experimental.EmbeddingConfigSpec`
+for more details.
+
+```
+estimator = tf.estimator.tpu.TPUEstimator(
+ ...
+ embedding_config_spec=tf.estimator.tpu.experimental.EmbeddingConfigSpec(
+ ...
+ optimization_parameters=tf.tpu.experimental.AdamParameters(0.1),
+ ...))
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`learning_rate`
+ |
+
+a floating point value. The learning rate.
+ |
+
+|
+`beta1`
+ |
+
+A float value.
+The exponential decay rate for the 1st moment estimates.
+ |
+
+|
+`beta2`
+ |
+
+A float value.
+The exponential decay rate for the 2nd moment estimates.
+ |
+
+|
+`epsilon`
+ |
+
+A small constant for numerical stability.
+ |
+
+|
+`lazy_adam`
+ |
+
+Use lazy Adam instead of Adam. Lazy Adam trains faster.
+Please see `optimization_parameters.proto` for details.
+ |
+
+|
+`sum_inside_sqrt`
+ |
+
+This improves training speed. Please see
+`optimization_parameters.proto` for details.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_gradient_accumulation`
+ |
+
+setting this to `False` makes embedding
+gradients calculation less accurate but faster. Please see
+`optimization_parameters.proto` for details.
+for details.
+ |
+
+|
+`clip_weight_min`
+ |
+
+the minimum value to clip by; None means -infinity.
+ |
+
+|
+`clip_weight_max`
+ |
+
+the maximum value to clip by; None means +infinity.
+ |
+
+|
+`weight_decay_factor`
+ |
+
+amount of weight decay to apply; None means that the
+weights are not decayed.
+ |
+
+|
+`multiply_weight_decay_factor_by_learning_rate`
+ |
+
+if true,
+`weight_decay_factor` is multiplied by the current learning rate.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/experimental/FtrlParameters.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/experimental/FtrlParameters.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..92d8111730c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/experimental/FtrlParameters.md
@@ -0,0 +1,143 @@
+description: Optimization parameters for Ftrl with TPU embeddings.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.tpu.experimental.FtrlParameters
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Optimization parameters for Ftrl with TPU embeddings.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.tpu.experimental.FtrlParameters(
+ learning_rate, learning_rate_power=-0.5, initial_accumulator_value=0.1,
+ l1_regularization_strength=0.0, l2_regularization_strength=0.0,
+ use_gradient_accumulation=(True), clip_weight_min=None, clip_weight_max=None,
+ weight_decay_factor=None, multiply_weight_decay_factor_by_learning_rate=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Pass this to `tf.estimator.tpu.experimental.EmbeddingConfigSpec` via the
+`optimization_parameters` argument to set the optimizer and its parameters.
+See the documentation for `tf.estimator.tpu.experimental.EmbeddingConfigSpec`
+for more details.
+
+```
+estimator = tf.estimator.tpu.TPUEstimator(
+ ...
+ embedding_config_spec=tf.estimator.tpu.experimental.EmbeddingConfigSpec(
+ ...
+ optimization_parameters=tf.tpu.experimental.FtrlParameters(0.1),
+ ...))
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`learning_rate`
+ |
+
+a floating point value. The learning rate.
+ |
+
+|
+`learning_rate_power`
+ |
+
+A float value, must be less or equal to zero.
+Controls how the learning rate decreases during training. Use zero for
+a fixed learning rate. See section 3.1 in the
+[paper](https://www.eecs.tufts.edu/~dsculley/papers/ad-click-prediction.pdf).
+ |
+
+|
+`initial_accumulator_value`
+ |
+
+The starting value for accumulators.
+Only zero or positive values are allowed.
+ |
+
+|
+`l1_regularization_strength`
+ |
+
+A float value, must be greater than or
+equal to zero.
+ |
+
+|
+`l2_regularization_strength`
+ |
+
+A float value, must be greater than or
+equal to zero.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_gradient_accumulation`
+ |
+
+setting this to `False` makes embedding
+gradients calculation less accurate but faster. Please see
+`optimization_parameters.proto` for details.
+for details.
+ |
+
+|
+`clip_weight_min`
+ |
+
+the minimum value to clip by; None means -infinity.
+ |
+
+|
+`clip_weight_max`
+ |
+
+the maximum value to clip by; None means +infinity.
+ |
+
+|
+`weight_decay_factor`
+ |
+
+amount of weight decay to apply; None means that the
+weights are not decayed.
+ |
+
+|
+`multiply_weight_decay_factor_by_learning_rate`
+ |
+
+if true,
+`weight_decay_factor` is multiplied by the current learning rate.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/experimental/StochasticGradientDescentParameters.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/experimental/StochasticGradientDescentParameters.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..f7b19f452c7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/experimental/StochasticGradientDescentParameters.md
@@ -0,0 +1,97 @@
+description: Optimization parameters for stochastic gradient descent for TPU embeddings.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.tpu.experimental.StochasticGradientDescentParameters
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Optimization parameters for stochastic gradient descent for TPU embeddings.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.tpu.experimental.StochasticGradientDescentParameters(
+ learning_rate, clip_weight_min=None, clip_weight_max=None,
+ weight_decay_factor=None, multiply_weight_decay_factor_by_learning_rate=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Pass this to `tf.estimator.tpu.experimental.EmbeddingConfigSpec` via the
+`optimization_parameters` argument to set the optimizer and its parameters.
+See the documentation for `tf.estimator.tpu.experimental.EmbeddingConfigSpec`
+for more details.
+
+```
+estimator = tf.estimator.tpu.TPUEstimator(
+ ...
+ embedding_config_spec=tf.estimator.tpu.experimental.EmbeddingConfigSpec(
+ ...
+ optimization_parameters=(
+ tf.tpu.experimental.StochasticGradientDescentParameters(0.1))))
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`learning_rate`
+ |
+
+a floating point value. The learning rate.
+ |
+
+|
+`clip_weight_min`
+ |
+
+the minimum value to clip by; None means -infinity.
+ |
+
+|
+`clip_weight_max`
+ |
+
+the maximum value to clip by; None means +infinity.
+ |
+
+|
+`weight_decay_factor`
+ |
+
+amount of weight decay to apply; None means that the
+weights are not decayed.
+ |
+
+|
+`multiply_weight_decay_factor_by_learning_rate`
+ |
+
+if true,
+`weight_decay_factor` is multiplied by the current learning rate.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/experimental/embedding_column.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/experimental/embedding_column.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e7fc8005c81
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/experimental/embedding_column.md
@@ -0,0 +1,205 @@
+description: TPU version of tf.compat.v1.feature_column.embedding_column.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.tpu.experimental.embedding_column
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+TPU version of tf.compat.v1.feature_column.embedding_column.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.tpu.experimental.embedding_column(
+ categorical_column, dimension, combiner='mean', initializer=None,
+ max_sequence_length=0, learning_rate_fn=None, embedding_lookup_device=None,
+ tensor_core_shape=None, use_safe_embedding_lookup=(True)
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Note that the interface for `tf.tpu.experimental.embedding_column` is
+different from that of tf.compat.v1.feature_column.embedding_column: The
+following arguments are NOT supported: `ckpt_to_load_from`,
+`tensor_name_in_ckpt`, `max_norm` and `trainable`.
+
+Use this function in place of tf.compat.v1.feature_column.embedding_column
+when you want to use the TPU to accelerate your embedding lookups via TPU
+embeddings.
+
+```
+column = tf.feature_column.categorical_column_with_identity(...)
+tpu_column = tf.tpu.experimental.embedding_column(column, 10)
+...
+def model_fn(features):
+ dense_feature = tf.keras.layers.DenseFeature(tpu_column)
+ embedded_feature = dense_feature(features)
+ ...
+
+estimator = tf.estimator.tpu.TPUEstimator(
+ model_fn=model_fn,
+ ...
+ embedding_config_spec=tf.estimator.tpu.experimental.EmbeddingConfigSpec(
+ column=[tpu_column],
+ ...))
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`categorical_column`
+ |
+
+A categorical column returned from
+`categorical_column_with_identity`, `weighted_categorical_column`,
+`categorical_column_with_vocabulary_file`,
+`categorical_column_with_vocabulary_list`,
+`sequence_categorical_column_with_identity`,
+`sequence_categorical_column_with_vocabulary_file`,
+`sequence_categorical_column_with_vocabulary_list`
+ |
+
+|
+`dimension`
+ |
+
+An integer specifying dimension of the embedding, must be > 0.
+ |
+
+|
+`combiner`
+ |
+
+A string specifying how to reduce if there are multiple entries
+in a single row for a non-sequence column. For more information, see
+tf.feature_column.embedding_column.
+ |
+
+|
+`initializer`
+ |
+
+A variable initializer function to be used in embedding
+variable initialization. If not specified, defaults to
+tf.compat.v1.truncated_normal_initializer with mean `0.0` and
+standard deviation `1/sqrt(dimension)`.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_sequence_length`
+ |
+
+An non-negative integer specifying the max sequence
+length. Any sequence shorter then this will be padded with 0 embeddings
+and any sequence longer will be truncated. This must be positive for
+sequence features and 0 for non-sequence features.
+ |
+
+|
+`learning_rate_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that takes global step and returns learning
+rate for the embedding table.
+ |
+
+|
+`embedding_lookup_device`
+ |
+
+The device on which to run the embedding lookup.
+Valid options are "cpu", "tpu_tensor_core", and "tpu_embedding_core".
+If specifying "tpu_tensor_core", a tensor_core_shape must be supplied.
+If not specified, the default behavior is embedding lookup on
+"tpu_embedding_core" for training and "cpu" for inference.
+Valid options for training : ["tpu_embedding_core", "tpu_tensor_core"]
+Valid options for serving : ["cpu", "tpu_tensor_core"]
+For training, tpu_embedding_core is good for large embedding vocab (>1M),
+otherwise, tpu_tensor_core is often sufficient.
+For serving, doing embedding lookup on tpu_tensor_core during serving is
+a way to reduce host cpu usage in cases where that is a bottleneck.
+ |
+
+|
+`tensor_core_shape`
+ |
+
+If supplied, a list of integers which specifies
+the intended dense shape to run embedding lookup for this feature on
+TensorCore. The batch dimension can be left None or -1 to indicate
+a dynamic shape. Only rank 2 shapes currently supported.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_safe_embedding_lookup`
+ |
+
+If true, uses safe_embedding_lookup_sparse
+instead of embedding_lookup_sparse. safe_embedding_lookup_sparse ensures
+there are no empty rows and all weights and ids are positive at the
+expense of extra compute cost. This only applies to rank 2 (NxM) shaped
+input tensors. Defaults to true, consider turning off if the above checks
+are not needed. Note that having empty rows will not trigger any error
+though the output result might be 0 or omitted.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `_TPUEmbeddingColumnV2`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `dimension` not > 0.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `initializer` is specified but not callable.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/experimental/shared_embedding_columns.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/experimental/shared_embedding_columns.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3b8d6397f82
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/experimental/shared_embedding_columns.md
@@ -0,0 +1,236 @@
+description: TPU version of tf.compat.v1.feature_column.shared_embedding_columns.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.tpu.experimental.shared_embedding_columns
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+TPU version of tf.compat.v1.feature_column.shared_embedding_columns.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.tpu.experimental.shared_embedding_columns(
+ categorical_columns, dimension, combiner='mean', initializer=None,
+ shared_embedding_collection_name=None, max_sequence_lengths=None,
+ learning_rate_fn=None, embedding_lookup_device=None, tensor_core_shape=None,
+ use_safe_embedding_lookup=(True)
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Note that the interface for `tf.tpu.experimental.shared_embedding_columns` is
+different from that of tf.compat.v1.feature_column.shared_embedding_columns:
+The following arguments are NOT supported: `ckpt_to_load_from`,
+`tensor_name_in_ckpt`, `max_norm` and `trainable`.
+
+Use this function in place of
+tf.compat.v1.feature_column.shared_embedding_columns` when you want to use the
+TPU to accelerate your embedding lookups via TPU embeddings.
+
+```
+column_a = tf.feature_column.categorical_column_with_identity(...)
+column_b = tf.feature_column.categorical_column_with_identity(...)
+tpu_columns = tf.tpu.experimental.shared_embedding_columns(
+ [column_a, column_b], 10)
+...
+def model_fn(features):
+ dense_feature = tf.keras.layers.DenseFeature(tpu_columns)
+ embedded_feature = dense_feature(features)
+ ...
+
+estimator = tf.estimator.tpu.TPUEstimator(
+ model_fn=model_fn,
+ ...
+ embedding_config_spec=tf.estimator.tpu.experimental.EmbeddingConfigSpec(
+ column=tpu_columns,
+ ...))
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`categorical_columns`
+ |
+
+A list of categorical columns returned from
+`categorical_column_with_identity`, `weighted_categorical_column`,
+`categorical_column_with_vocabulary_file`,
+`categorical_column_with_vocabulary_list`,
+`sequence_categorical_column_with_identity`,
+`sequence_categorical_column_with_vocabulary_file`,
+`sequence_categorical_column_with_vocabulary_list`
+ |
+
+|
+`dimension`
+ |
+
+An integer specifying dimension of the embedding, must be > 0.
+ |
+
+|
+`combiner`
+ |
+
+A string specifying how to reduce if there are multiple entries in
+a single row for a non-sequence column. For more information, see
+tf.feature_column.embedding_column.
+ |
+
+|
+`initializer`
+ |
+
+A variable initializer function to be used in embedding
+variable initialization. If not specified, defaults to
+`tf.truncated_normal_initializer` with mean `0.0` and standard deviation
+`1/sqrt(dimension)`.
+ |
+
+|
+`shared_embedding_collection_name`
+ |
+
+Optional name of the collection where
+shared embedding weights are added. If not given, a reasonable name will
+be chosen based on the names of `categorical_columns`. This is also used
+in `variable_scope` when creating shared embedding weights.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_sequence_lengths`
+ |
+
+An list of non-negative integers, either None or empty
+or the same length as the argument categorical_columns. Entries
+corresponding to non-sequence columns must be 0 and entries corresponding
+to sequence columns specify the max sequence length for the column. Any
+sequence shorter then this will be padded with 0 embeddings and any
+sequence longer will be truncated.
+ |
+
+|
+`learning_rate_fn`
+ |
+
+A function that takes global step and returns learning
+rate for the embedding table.
+ |
+
+|
+`embedding_lookup_device`
+ |
+
+The device on which to run the embedding lookup.
+Valid options are "cpu", "tpu_tensor_core", and "tpu_embedding_core". If
+specifying "tpu_tensor_core", a tensor_core_shape must be supplied.
+Defaults to "cpu". If not specified, the default behavior is embedding
+lookup on "tpu_embedding_core" for training and "cpu" for inference.
+Valid options for training : ["tpu_embedding_core", "tpu_tensor_core"]
+Valid options for serving : ["cpu", "tpu_tensor_core"]
+For training, tpu_embedding_core is good for large embedding vocab (>1M),
+otherwise, tpu_tensor_core is often sufficient.
+For serving, doing embedding lookup on tpu_tensor_core during serving is
+a way to reduce host cpu usage in cases where that is a bottleneck.
+ |
+
+|
+`tensor_core_shape`
+ |
+
+If supplied, a list of integers which specifies the
+intended dense shape to run embedding lookup for this feature on
+TensorCore. The batch dimension can be left None or -1 to indicate a
+dynamic shape. Only rank 2 shapes currently supported.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_safe_embedding_lookup`
+ |
+
+If true, uses safe_embedding_lookup_sparse
+instead of embedding_lookup_sparse. safe_embedding_lookup_sparse ensures
+there are no empty rows and all weights and ids are positive at the
+expense of extra compute cost. This only applies to rank 2 (NxM) shaped
+input tensors. Defaults to true, consider turning off if the above checks
+are not needed. Note that having empty rows will not trigger any error
+though the output result might be 0 or omitted.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of `_TPUSharedEmbeddingColumnV2`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `dimension` not > 0.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `initializer` is specified but not callable.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `max_sequence_lengths` is specified and not the same length
+as `categorical_columns`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `max_sequence_lengths` is positive for a non sequence column
+or 0 for a sequence column.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/initialize_system.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/initialize_system.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..df527703963
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/initialize_system.md
@@ -0,0 +1,85 @@
+description: Initializes a distributed TPU system for use with TensorFlow.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.tpu.initialize_system
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Initializes a distributed TPU system for use with TensorFlow.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.tpu.initialize_system(
+ embedding_config=None, job=None, compilation_failure_closes_chips=(True)
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`embedding_config`
+ |
+
+If not None, a `TPUEmbeddingConfiguration` proto
+describing the desired configuration of the hardware embedding lookup
+tables. If embedding_config is None, no hardware embeddings can be used.
+ |
+
+|
+`job`
+ |
+
+The job (the XXX in TensorFlow device specification /job:XXX) that
+contains the TPU devices that will be initialized. If job=None it is
+assumed there is only one job in the TensorFlow flock, and an error will
+be returned if this assumption does not hold.
+ |
+
+|
+`compilation_failure_closes_chips`
+ |
+
+Set the configuration whether
+we want to close TPU chips when there is a compilation failure.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A serialized `TopologyProto` that describes the TPU system. Note:
+the topology must be evaluated using `Session.run` before it can be used.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/outside_compilation.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/outside_compilation.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..5fe66671a61
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/outside_compilation.md
@@ -0,0 +1,132 @@
+description: Builds part of a computation outside any current TPU replicate scope.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.tpu.outside_compilation
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Builds part of a computation outside any current TPU replicate scope.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.tpu.outside_compilation(
+ computation, *args, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+`tf.tpu.outside_compilation()` is used to run ops in `computation` on CPU
+instead of running on TPU. For example, users can run ops that are not
+supported on TPU's (e.g. tf.summary.write()) by explicitly placing those
+ops on CPU's. Below usage of outside compilation will place ops in
+`computation_with_string_ops` on CPU.
+
+#### Example usage:
+
+
+
+```python
+def computation_with_string_ops(x):
+ # strings types are not supported on TPU's and below ops must
+ # run on CPU instead.
+ output = tf.strings.format('1{}', x)
+ return tf.strings.to_number(output)
+
+def tpu_computation():
+ # Expected output is 11.
+ output = tf.tpu.outside_compilation(computation_with_string_ops, 1)
+```
+
+Outside compilation should be called inside TPUReplicateContext. That is,
+`tf.tpu.outside_compilation()` should be called inside a function that is
+passed to `tpu.split_compile_and_replicate()` -- this is implied when
+outside compilation is invoked inside a function passed to TPUStrategy
+`run()`. If invoked outside of TPUReplicateContext,
+then this simply returns the result of `computation`, and therefore,
+would be a no-op. Note that outside compilation is different from
+`tf.distribute.experimental.TPUStrategy.merge_call()` as logic in
+outside compilation is replicated and executed separately for each
+replica. On the other hand, `merge_call()` requires a `merge_fn`
+to aggregate the inputs from different replicas and is executed only
+once.
+
+For variables placed in TPU device, which includes variables created inside
+TPUStrategy scope, outside compilation logic must not include variable
+read/write. For variables placed on host, which is the case when variables
+created via TPUEstimator, variable read/write is only allowed if the variable
+is not accessed by any other ops in the TPU computation. Variable read/write
+from outside compilation cluster is not visible from TPU computation and
+vice versa. Therefore, if outside compilation logic contains such host
+variables read/write ops and if the variables are accessed by TPU
+computation as well, then this may lead to deadlock.
+
+Internally, `tf.tpu.outside_compilation()` adds outside compilation
+attributes to all ops in `computation`. During later graph pass, these
+ops with outside compilation attribute is extracted out and replicated
+into a host-side graph. Inputs to this extract host-side graph is sent
+from TPU computation graph to host graph via a pair of XlaSendToHost and
+XlaRecvFromHost ops. Note that using `tf.tpu.outside_compilation()`
+may result in tensor transfer between TPU and CPU, leading to non-trivial
+performance impact.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`computation`
+ |
+
+A Python function that builds the computation to
+place on the host.
+ |
+
+|
+`*args`
+ |
+
+the positional arguments for the computation.
+ |
+
+|
+`**kwargs`
+ |
+
+the keyword arguments for the computation.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The Tensors returned by computation.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/replicate.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/replicate.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..8666e7639b1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/replicate.md
@@ -0,0 +1,209 @@
+description: Builds a graph operator that runs a replicated TPU computation.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.tpu.replicate
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Builds a graph operator that runs a replicated TPU computation.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.tpu.replicate(
+ computation, inputs=None, infeed_queue=None, device_assignment=None, name=None,
+ maximum_shapes=None, padding_spec=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Example for the basic usage that `inputs` has static shape:
+
+```python
+
+def computation(x):
+ x = x + 1
+ return tf.math.reduce_mean(x)
+
+x = tf.convert_to_tensor([1., 2., 3.])
+y = tf.convert_to_tensor([4., 5., 6.])
+tf.compat.v1.tpu.replicate(computation, inputs=[[x], [y]])
+```
+
+If the `inputs` has dynamic shapes and you would like to automatically
+bucketize the inputs to avoid XLA recompilation. See the advanced example
+below:
+
+```python
+
+def computation(x):
+ x = x + 1
+ return tf.math.reduce_mean(x)
+
+# Assume input tensors in two replicas `x` and `y` both have dynamic shape
+# ([None, 2]).
+tf.compat.v1.tpu.replicate(
+ computation,
+ inputs=[x, y],
+ maximum_shapes=[tf.TensorShape([None, None])],
+ padding_spec=tf.compat.v1.tpu.PaddingSpec.POWER_OF_TWO)
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`computation`
+ |
+
+A Python function that builds the computation to replicate.
+ |
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+A list of lists of input tensors or `None` (equivalent to
+`[[]]`), indexed by `[replica_num][input_num]`. All replicas must
+have the same number of inputs. Each input can be a nested structure
+containing values that are convertible to tensors. Note that passing an
+N-dimension list of compatible values will result in a N-dimension list of
+scalar tensors rather than a single Rank-N tensors. If you need different
+behavior, convert part of inputs to tensors with tf.convert_to_tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`infeed_queue`
+ |
+
+If not `None`, the `InfeedQueue` from which to append a tuple
+of arguments as inputs to computation.
+ |
+
+|
+`device_assignment`
+ |
+
+If not `None`, a `DeviceAssignment` describing the
+mapping between logical cores in the computation with physical cores in
+the TPU topology. Uses a default device assignment if `None`. The
+`DeviceAssignment` may be omitted if each replica of the computation uses
+only one core, and there is either only one replica, or the number of
+replicas is equal to the number of cores in the TPU system.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+(Deprecated) Does nothing.
+ |
+
+|
+`maximum_shapes`
+ |
+
+A nested structure of tf.TensorShape representing the shape
+to which the respective component of each input element in each replica
+should be padded. Any unknown dimensions (e.g.
+tf.compat.v1.Dimension(None) in a tf.TensorShape or -1 in a tensor-like
+object) will be padded to the maximum size of that dimension over all
+replicas. The structure of `maximum_shapes` needs to be the same as
+`inputs[0]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`padding_spec`
+ |
+
+An enum specified by `tpu.PaddingSpec`. This describes the
+padding policy when the `inputs` to `tpu.replicate` is dynamic.
+One usage is to enable automatic bucketizing on the inputs by setting the
+value to `tpu.PaddingSpec.POWER_OF_TWO`, which can help to reduce the
+recompilation in the XLA side.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of outputs, indexed by `[replica_num]` each output can be a nested
+structure same as what computation() returns with a few exceptions.
+
+Exceptions include:
+1) None output: a NoOp would be returned which control-depends on
+computation.
+2) Single value output: A tuple containing the value would be returned.
+3) Operation-only outputs: a NoOp would be returned which
+control-depends on computation.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If all replicas do not have equal numbers of input tensors.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the number of inputs per replica does not match
+the number of formal parameters to `computation`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the static `inputs` dimensions don't match with the values
+given in `maximum_shapes`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the structure of inputs per replica does not match
+the structure of `maximum_shapes`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/rewrite.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/rewrite.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..be7d4de7e18
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/rewrite.md
@@ -0,0 +1,118 @@
+description: Rewrites computation for execution on a TPU system.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.tpu.rewrite
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Rewrites `computation` for execution on a TPU system.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.tpu.rewrite(
+ computation, inputs=None, infeed_queue=None, device_assignment=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`computation`
+ |
+
+A Python function that builds a computation to apply to the
+input. If the function takes n inputs, 'inputs' should be a list of n
+tensors.
+
+`computation` may return a list of operations and tensors. Tensors must
+come before operations in the returned list. The return value of
+`rewrite` is a list of tensors corresponding to the tensors from the
+output of `computation`.
+
+All `Operation`s constructed during `computation` will be executed when
+evaluating any of the returned output tensors, not just the ones returned.
+ |
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+A list of input tensors or `None` (equivalent to an empty list).
+Each input can be a nested structure containing values that are
+convertible to tensors. Note that passing an N-dimension list of
+compatible values will result in a N-dimension list of scalar tensors
+rather than a single Rank-N tensors. If you need different behavior,
+convert part of inputs to tensors with tf.convert_to_tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`infeed_queue`
+ |
+
+If not `None`, the `InfeedQueue` from which to append a tuple
+of arguments as inputs to `computation`.
+ |
+
+|
+`device_assignment`
+ |
+
+if not `None`, a `DeviceAssignment` describing the
+mapping between logical cores in the computation with physical cores in
+the TPU topology. May be omitted for a single-core computation, in which
+case the core attached to task 0, TPU device 0 is used.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+(Deprecated) Does nothing.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Same data structure as if computation(*inputs) is called directly with some
+exceptions for correctness. Exceptions include:
+1) None output: a NoOp would be returned which control-depends on
+computation.
+2) Single value output: A tuple containing the value would be returned.
+3) Operation-only outputs: a NoOp would be returned which
+control-depends on computation.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/shard.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/shard.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..f0fba5c4c64
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/shard.md
@@ -0,0 +1,192 @@
+description: Shards computation for parallel execution.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.tpu.shard
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Shards `computation` for parallel execution.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.tpu.shard(
+ computation, inputs=None, num_shards=1, input_shard_axes=None,
+ outputs_from_all_shards=(True), output_shard_axes=None, infeed_queue=None,
+ device_assignment=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+`inputs` must be a list of Tensors or None (equivalent to an empty list), each
+of which has a corresponding split axis (from `input_shard_axes`). Each input
+is split into `num_shards` pieces along the corresponding axis, and
+computation is applied to each shard in parallel.
+
+Tensors are broadcast to all shards if they are lexically captured by
+`computation`. e.g.,
+
+x = tf.constant(7)
+def computation():
+ return x + 3
+... = shard(computation, ...)
+
+
+as inputs.
+
+If `outputs_from_all_shards` is true, the outputs from all shards of
+`computation` are concatenated back together along their `output_shard_axes`.
+Otherwise, each output is taken from an arbitrary shard.
+
+Inputs and outputs of the computation must be at least rank-1 Tensors.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`computation`
+ |
+
+A Python function that builds a computation to apply to each
+shard of the input.
+ |
+
+|
+`inputs`
+ |
+
+A list of input tensors or None (equivalent to an empty list). Each
+input tensor has a corresponding shard axes, given by `input_shard_axes`,
+which must have size divisible by `num_shards`.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_shards`
+ |
+
+The number of shards.
+ |
+
+|
+`input_shard_axes`
+ |
+
+A list of dimensions along which to shard `inputs`, or
+`None`. `None` means "shard all inputs along dimension 0". If not `None`,
+there must be one dimension per input.
+ |
+
+|
+`outputs_from_all_shards`
+ |
+
+Boolean or list of boolean. For each output, if
+`True`, outputs from all shards are concatenated along the corresponding
+`output_shard_axes` entry. Otherwise, each output is taken
+from an arbitrary shard. If the argument is a boolean, the argument's
+value is used for each output.
+ |
+
+|
+`output_shard_axes`
+ |
+
+A list of dimensions along which to concatenate the
+outputs of `computation`, or `None`. `None` means "concatenate all outputs
+along dimension 0". If not `None`, there must be one dimension per output.
+Ignored if `outputs_from_all_shards` is False.
+ |
+
+|
+`infeed_queue`
+ |
+
+If not `None`, the `InfeedQueue` to use to augment the inputs
+of `computation`.
+ |
+
+|
+`device_assignment`
+ |
+
+If not `None`, a `DeviceAssignment` describing the
+mapping between logical cores in the computation with physical cores in
+the TPU topology. Uses a default device assignment if `None`. The
+`DeviceAssignment` may be omitted if each shard of the computation uses
+only one core, and there is either only one shard, or the number of shards
+is equal to the number of cores in the TPU system.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+(Deprecated) Does nothing.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of output tensors.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If num_shards <= 0
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If len(input_shard_axes) != len(inputs)
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If len(output_shard_axes) != len(outputs from `computation`)
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/shutdown_system.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/shutdown_system.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..671d120460d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tpu/shutdown_system.md
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+description: Shuts down a running a distributed TPU system.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.tpu.shutdown_system
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Shuts down a running a distributed TPU system.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.tpu.shutdown_system(
+ job=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`job`
+ |
+
+The job (the XXX in TensorFlow device specification /job:XXX) that
+contains the TPU devices that will be shutdown. If job=None it is
+assumed there is only one job in the TensorFlow flock, and an error will
+be returned if this assumption does not hold.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..475473bab80
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train.md
@@ -0,0 +1,264 @@
+description: Support for training models.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.train
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Support for training models.
+
+
+See the [Training](https://tensorflow.org/api_guides/python/train) guide.
+
+## Modules
+
+[`experimental`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/experimental.md) module: Public API for tf.train.experimental namespace.
+
+[`queue_runner`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/queue_runner.md) module: Public API for tf.train.queue_runner namespace.
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class AdadeltaOptimizer`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/AdadeltaOptimizer.md): Optimizer that implements the Adadelta algorithm.
+
+[`class AdagradDAOptimizer`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/AdagradDAOptimizer.md): Adagrad Dual Averaging algorithm for sparse linear models.
+
+[`class AdagradOptimizer`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/AdagradOptimizer.md): Optimizer that implements the Adagrad algorithm.
+
+[`class AdamOptimizer`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/AdamOptimizer.md): Optimizer that implements the Adam algorithm.
+
+[`class BytesList`](../../../tf/train/BytesList.md): A ProtocolMessage
+
+[`class Checkpoint`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/Checkpoint.md): Groups trackable objects, saving and restoring them.
+
+[`class CheckpointManager`](../../../tf/train/CheckpointManager.md): Deletes old checkpoints.
+
+[`class CheckpointSaverHook`](../../../tf/estimator/CheckpointSaverHook.md): Saves checkpoints every N steps or seconds.
+
+[`class CheckpointSaverListener`](../../../tf/estimator/CheckpointSaverListener.md): Interface for listeners that take action before or after checkpoint save.
+
+[`class ChiefSessionCreator`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/ChiefSessionCreator.md): Creates a tf.compat.v1.Session for a chief.
+
+[`class ClusterDef`](../../../tf/train/ClusterDef.md): A ProtocolMessage
+
+[`class ClusterSpec`](../../../tf/train/ClusterSpec.md): Represents a cluster as a set of "tasks", organized into "jobs".
+
+[`class Coordinator`](../../../tf/train/Coordinator.md): A coordinator for threads.
+
+[`class Example`](../../../tf/train/Example.md): A ProtocolMessage
+
+[`class ExponentialMovingAverage`](../../../tf/train/ExponentialMovingAverage.md): Maintains moving averages of variables by employing an exponential decay.
+
+[`class Feature`](../../../tf/train/Feature.md): A ProtocolMessage
+
+[`class FeatureList`](../../../tf/train/FeatureList.md): A ProtocolMessage
+
+[`class FeatureLists`](../../../tf/train/FeatureLists.md): A ProtocolMessage
+
+[`class Features`](../../../tf/train/Features.md): A ProtocolMessage
+
+[`class FeedFnHook`](../../../tf/estimator/FeedFnHook.md): Runs `feed_fn` and sets the `feed_dict` accordingly.
+
+[`class FinalOpsHook`](../../../tf/estimator/FinalOpsHook.md): A hook which evaluates `Tensors` at the end of a session.
+
+[`class FloatList`](../../../tf/train/FloatList.md): A ProtocolMessage
+
+[`class FtrlOptimizer`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/FtrlOptimizer.md): Optimizer that implements the FTRL algorithm.
+
+[`class GlobalStepWaiterHook`](../../../tf/estimator/GlobalStepWaiterHook.md): Delays execution until global step reaches `wait_until_step`.
+
+[`class GradientDescentOptimizer`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/GradientDescentOptimizer.md): Optimizer that implements the gradient descent algorithm.
+
+[`class Int64List`](../../../tf/train/Int64List.md): A ProtocolMessage
+
+[`class JobDef`](../../../tf/train/JobDef.md): A ProtocolMessage
+
+[`class LoggingTensorHook`](../../../tf/estimator/LoggingTensorHook.md): Prints the given tensors every N local steps, every N seconds, or at end.
+
+[`class LooperThread`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/LooperThread.md): A thread that runs code repeatedly, optionally on a timer.
+
+[`class MomentumOptimizer`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/MomentumOptimizer.md): Optimizer that implements the Momentum algorithm.
+
+[`class MonitoredSession`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/MonitoredSession.md): Session-like object that handles initialization, recovery and hooks.
+
+[`class NanLossDuringTrainingError`](../../../tf/estimator/NanLossDuringTrainingError.md): Unspecified run-time error.
+
+[`class NanTensorHook`](../../../tf/estimator/NanTensorHook.md): Monitors the loss tensor and stops training if loss is NaN.
+
+[`class Optimizer`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/Optimizer.md): Base class for optimizers.
+
+[`class ProfilerHook`](../../../tf/estimator/ProfilerHook.md): Captures CPU/GPU profiling information every N steps or seconds.
+
+[`class ProximalAdagradOptimizer`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/ProximalAdagradOptimizer.md): Optimizer that implements the Proximal Adagrad algorithm.
+
+[`class ProximalGradientDescentOptimizer`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/ProximalGradientDescentOptimizer.md): Optimizer that implements the proximal gradient descent algorithm.
+
+[`class QueueRunner`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/QueueRunner.md): Holds a list of enqueue operations for a queue, each to be run in a thread.
+
+[`class RMSPropOptimizer`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/RMSPropOptimizer.md): Optimizer that implements the RMSProp algorithm (Tielemans et al.
+
+[`class Saver`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/Saver.md): Saves and restores variables.
+
+[`class SaverDef`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/SaverDef.md): A ProtocolMessage
+
+[`class Scaffold`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/Scaffold.md): Structure to create or gather pieces commonly needed to train a model.
+
+[`class SecondOrStepTimer`](../../../tf/estimator/SecondOrStepTimer.md): Timer that triggers at most once every N seconds or once every N steps.
+
+[`class SequenceExample`](../../../tf/train/SequenceExample.md): A ProtocolMessage
+
+[`class Server`](../../../tf/distribute/Server.md): An in-process TensorFlow server, for use in distributed training.
+
+[`class ServerDef`](../../../tf/train/ServerDef.md): A ProtocolMessage
+
+[`class SessionCreator`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/SessionCreator.md): A factory for tf.Session.
+
+[`class SessionManager`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/SessionManager.md): Training helper that restores from checkpoint and creates session.
+
+[`class SessionRunArgs`](../../../tf/estimator/SessionRunArgs.md): Represents arguments to be added to a `Session.run()` call.
+
+[`class SessionRunContext`](../../../tf/estimator/SessionRunContext.md): Provides information about the `session.run()` call being made.
+
+[`class SessionRunHook`](../../../tf/estimator/SessionRunHook.md): Hook to extend calls to MonitoredSession.run().
+
+[`class SessionRunValues`](../../../tf/estimator/SessionRunValues.md): Contains the results of `Session.run()`.
+
+[`class SingularMonitoredSession`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/SingularMonitoredSession.md): Session-like object that handles initialization, restoring, and hooks.
+
+[`class StepCounterHook`](../../../tf/estimator/StepCounterHook.md): Hook that counts steps per second.
+
+[`class StopAtStepHook`](../../../tf/estimator/StopAtStepHook.md): Hook that requests stop at a specified step.
+
+[`class SummarySaverHook`](../../../tf/estimator/SummarySaverHook.md): Saves summaries every N steps.
+
+[`class Supervisor`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/Supervisor.md): A training helper that checkpoints models and computes summaries.
+
+[`class SyncReplicasOptimizer`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/SyncReplicasOptimizer.md): Class to synchronize, aggregate gradients and pass them to the optimizer.
+
+[`class VocabInfo`](../../../tf/estimator/VocabInfo.md): Vocabulary information for warm-starting.
+
+[`class WorkerSessionCreator`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/WorkerSessionCreator.md): Creates a tf.compat.v1.Session for a worker.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`MonitoredTrainingSession(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/MonitoredTrainingSession.md): Creates a `MonitoredSession` for training.
+
+[`NewCheckpointReader(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/NewCheckpointReader.md): A function that returns a CheckPointReader.
+
+[`add_queue_runner(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/add_queue_runner.md): Adds a `QueueRunner` to a collection in the graph. (deprecated)
+
+[`assert_global_step(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/assert_global_step.md): Asserts `global_step_tensor` is a scalar int `Variable` or `Tensor`.
+
+[`basic_train_loop(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/basic_train_loop.md): Basic loop to train a model.
+
+[`batch(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/batch.md): Creates batches of tensors in `tensors`. (deprecated)
+
+[`batch_join(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/batch_join.md): Runs a list of tensors to fill a queue to create batches of examples. (deprecated)
+
+[`checkpoint_exists(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/checkpoint_exists.md): Checks whether a V1 or V2 checkpoint exists with the specified prefix. (deprecated)
+
+[`checkpoints_iterator(...)`](../../../tf/train/checkpoints_iterator.md): Continuously yield new checkpoint files as they appear.
+
+[`cosine_decay(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/cosine_decay.md): Applies cosine decay to the learning rate.
+
+[`cosine_decay_restarts(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/cosine_decay_restarts.md): Applies cosine decay with restarts to the learning rate.
+
+[`create_global_step(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/create_global_step.md): Create global step tensor in graph.
+
+[`do_quantize_training_on_graphdef(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/do_quantize_training_on_graphdef.md): A general quantization scheme is being developed in `tf.contrib.quantize`. (deprecated)
+
+[`exponential_decay(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/exponential_decay.md): Applies exponential decay to the learning rate.
+
+[`export_meta_graph(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/export_meta_graph.md): Returns `MetaGraphDef` proto.
+
+[`generate_checkpoint_state_proto(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/generate_checkpoint_state_proto.md): Generates a checkpoint state proto.
+
+[`get_checkpoint_mtimes(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/get_checkpoint_mtimes.md): Returns the mtimes (modification timestamps) of the checkpoints. (deprecated)
+
+[`get_checkpoint_state(...)`](../../../tf/train/get_checkpoint_state.md): Returns CheckpointState proto from the "checkpoint" file.
+
+[`get_global_step(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/get_global_step.md): Get the global step tensor.
+
+[`get_or_create_global_step(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/get_or_create_global_step.md): Returns and create (if necessary) the global step tensor.
+
+[`global_step(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/global_step.md): Small helper to get the global step.
+
+[`import_meta_graph(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/import_meta_graph.md): Recreates a Graph saved in a `MetaGraphDef` proto.
+
+[`init_from_checkpoint(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/init_from_checkpoint.md): Replaces tf.Variable initializers so they load from a checkpoint file.
+
+[`input_producer(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/input_producer.md): Output the rows of `input_tensor` to a queue for an input pipeline. (deprecated)
+
+[`inverse_time_decay(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/inverse_time_decay.md): Applies inverse time decay to the initial learning rate.
+
+[`latest_checkpoint(...)`](../../../tf/train/latest_checkpoint.md): Finds the filename of latest saved checkpoint file.
+
+[`limit_epochs(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/limit_epochs.md): Returns tensor `num_epochs` times and then raises an `OutOfRange` error. (deprecated)
+
+[`linear_cosine_decay(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/linear_cosine_decay.md): Applies linear cosine decay to the learning rate.
+
+[`list_variables(...)`](../../../tf/train/list_variables.md): Returns list of all variables in the checkpoint.
+
+[`load_checkpoint(...)`](../../../tf/train/load_checkpoint.md): Returns `CheckpointReader` for checkpoint found in `ckpt_dir_or_file`.
+
+[`load_variable(...)`](../../../tf/train/load_variable.md): Returns the tensor value of the given variable in the checkpoint.
+
+[`match_filenames_once(...)`](../../../tf/io/match_filenames_once.md): Save the list of files matching pattern, so it is only computed once.
+
+[`maybe_batch(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/maybe_batch.md): Conditionally creates batches of tensors based on `keep_input`. (deprecated)
+
+[`maybe_batch_join(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/maybe_batch_join.md): Runs a list of tensors to conditionally fill a queue to create batches. (deprecated)
+
+[`maybe_shuffle_batch(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/maybe_shuffle_batch.md): Creates batches by randomly shuffling conditionally-enqueued tensors. (deprecated)
+
+[`maybe_shuffle_batch_join(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/maybe_shuffle_batch_join.md): Create batches by randomly shuffling conditionally-enqueued tensors. (deprecated)
+
+[`natural_exp_decay(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/natural_exp_decay.md): Applies natural exponential decay to the initial learning rate.
+
+[`noisy_linear_cosine_decay(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/noisy_linear_cosine_decay.md): Applies noisy linear cosine decay to the learning rate.
+
+[`piecewise_constant(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/piecewise_constant.md): Piecewise constant from boundaries and interval values.
+
+[`piecewise_constant_decay(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/piecewise_constant.md): Piecewise constant from boundaries and interval values.
+
+[`polynomial_decay(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/polynomial_decay.md): Applies a polynomial decay to the learning rate.
+
+[`range_input_producer(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/range_input_producer.md): Produces the integers from 0 to limit-1 in a queue. (deprecated)
+
+[`remove_checkpoint(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/remove_checkpoint.md): Removes a checkpoint given by `checkpoint_prefix`. (deprecated)
+
+[`replica_device_setter(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/replica_device_setter.md): Return a `device function` to use when building a Graph for replicas.
+
+[`sdca_fprint(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/sdca_fprint.md): Computes fingerprints of the input strings.
+
+[`sdca_optimizer(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/sdca_optimizer.md): Distributed version of Stochastic Dual Coordinate Ascent (SDCA) optimizer for
+
+[`sdca_shrink_l1(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/sdca_shrink_l1.md): Applies L1 regularization shrink step on the parameters.
+
+[`shuffle_batch(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/shuffle_batch.md): Creates batches by randomly shuffling tensors. (deprecated)
+
+[`shuffle_batch_join(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/shuffle_batch_join.md): Create batches by randomly shuffling tensors. (deprecated)
+
+[`slice_input_producer(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/slice_input_producer.md): Produces a slice of each `Tensor` in `tensor_list`. (deprecated)
+
+[`start_queue_runners(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/start_queue_runners.md): Starts all queue runners collected in the graph. (deprecated)
+
+[`string_input_producer(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/string_input_producer.md): Output strings (e.g. filenames) to a queue for an input pipeline. (deprecated)
+
+[`summary_iterator(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/summary_iterator.md): An iterator for reading `Event` protocol buffers from an event file.
+
+[`update_checkpoint_state(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/update_checkpoint_state.md): Updates the content of the 'checkpoint' file. (deprecated)
+
+[`warm_start(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/train/warm_start.md): Warm-starts a model using the given settings.
+
+[`write_graph(...)`](../../../tf/io/write_graph.md): Writes a graph proto to a file.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/AdadeltaOptimizer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/AdadeltaOptimizer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..19e56a2e28b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/AdadeltaOptimizer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,596 @@
+description: Optimizer that implements the Adadelta algorithm.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.AdadeltaOptimizer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Optimizer that implements the Adadelta algorithm.
+
+Inherits From: [`Optimizer`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/train/Optimizer.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.AdadeltaOptimizer(
+ learning_rate=0.001, rho=0.95, epsilon=1e-08, use_locking=(False),
+ name='Adadelta'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### References:
+
+ADADELTA - An Adaptive Learning Rate Method:
+ [Zeiler, 2012](http://arxiv.org/abs/1212.5701)
+ ([pdf](http://arxiv.org/pdf/1212.5701v1.pdf))
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`learning_rate`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` or a floating point value. The learning rate.
+To match the exact form in the original paper use 1.0.
+ |
+
+|
+`rho`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` or a floating point value. The decay rate.
+ |
+
+|
+`epsilon`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` or a floating point value. A constant epsilon used
+to better conditioning the grad update.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_locking`
+ |
+
+If `True` use locks for update operations.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name prefix for the operations created when applying
+gradients. Defaults to "Adadelta".
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+apply_gradients
+
+View source
+
+
+apply_gradients(
+ grads_and_vars, global_step=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+Apply gradients to variables.
+
+This is the second part of `minimize()`. It returns an `Operation` that
+applies gradients.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`grads_and_vars`
+ |
+
+List of (gradient, variable) pairs as returned by
+`compute_gradients()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Optional `Variable` to increment by one after the
+variables have been updated.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the returned operation. Default to the
+name passed to the `Optimizer` constructor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An `Operation` that applies the specified gradients. If `global_step`
+was not None, that operation also increments `global_step`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `grads_and_vars` is malformed.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If none of the variables have gradients.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If you should use `_distributed_apply()` instead.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+compute_gradients
+
+View source
+
+
+compute_gradients(
+ loss, var_list=None, gate_gradients=GATE_OP, aggregation_method=None,
+ colocate_gradients_with_ops=(False), grad_loss=None
+)
+
+
+Compute gradients of `loss` for the variables in `var_list`.
+
+This is the first part of `minimize()`. It returns a list
+of (gradient, variable) pairs where "gradient" is the gradient
+for "variable". Note that "gradient" can be a `Tensor`, an
+`IndexedSlices`, or `None` if there is no gradient for the
+given variable.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`loss`
+ |
+
+A Tensor containing the value to minimize or a callable taking
+no arguments which returns the value to minimize. When eager execution
+is enabled it must be a callable.
+ |
+
+|
+`var_list`
+ |
+
+Optional list or tuple of tf.Variable to update to minimize
+`loss`. Defaults to the list of variables collected in the graph
+under the key `GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES`.
+ |
+
+|
+`gate_gradients`
+ |
+
+How to gate the computation of gradients. Can be
+`GATE_NONE`, `GATE_OP`, or `GATE_GRAPH`.
+ |
+
+|
+`aggregation_method`
+ |
+
+Specifies the method used to combine gradient terms.
+Valid values are defined in the class `AggregationMethod`.
+ |
+
+|
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops`
+ |
+
+If True, try colocating gradients with
+the corresponding op.
+ |
+
+|
+`grad_loss`
+ |
+
+Optional. A `Tensor` holding the gradient computed for `loss`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of (gradient, variable) pairs. Variable is always present, but
+gradient can be `None`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `var_list` contains anything else than `Variable` objects.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If some arguments are invalid.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If called with eager execution enabled and `loss` is
+not callable.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+When eager execution is enabled, `gate_gradients`, `aggregation_method`,
+and `colocate_gradients_with_ops` are ignored.
+
+
+
+get_name
+
+View source
+
+
+get_name()
+
+
+
+
+
+get_slot
+
+View source
+
+
+get_slot(
+ var, name
+)
+
+
+Return a slot named `name` created for `var` by the Optimizer.
+
+Some `Optimizer` subclasses use additional variables. For example
+`Momentum` and `Adagrad` use variables to accumulate updates. This method
+gives access to these `Variable` objects if for some reason you need them.
+
+Use `get_slot_names()` to get the list of slot names created by the
+`Optimizer`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`var`
+ |
+
+A variable passed to `minimize()` or `apply_gradients()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The `Variable` for the slot if it was created, `None` otherwise.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_slot_names
+
+View source
+
+
+get_slot_names()
+
+
+Return a list of the names of slots created by the `Optimizer`.
+
+See `get_slot()`.
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of strings.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+minimize
+
+View source
+
+
+minimize(
+ loss, global_step=None, var_list=None, gate_gradients=GATE_OP,
+ aggregation_method=None, colocate_gradients_with_ops=(False), name=None,
+ grad_loss=None
+)
+
+
+Add operations to minimize `loss` by updating `var_list`.
+
+This method simply combines calls `compute_gradients()` and
+`apply_gradients()`. If you want to process the gradient before applying
+them call `compute_gradients()` and `apply_gradients()` explicitly instead
+of using this function.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`loss`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` containing the value to minimize.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Optional `Variable` to increment by one after the
+variables have been updated.
+ |
+
+|
+`var_list`
+ |
+
+Optional list or tuple of `Variable` objects to update to
+minimize `loss`. Defaults to the list of variables collected in
+the graph under the key `GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES`.
+ |
+
+|
+`gate_gradients`
+ |
+
+How to gate the computation of gradients. Can be
+`GATE_NONE`, `GATE_OP`, or `GATE_GRAPH`.
+ |
+
+|
+`aggregation_method`
+ |
+
+Specifies the method used to combine gradient terms.
+Valid values are defined in the class `AggregationMethod`.
+ |
+
+|
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops`
+ |
+
+If True, try colocating gradients with
+the corresponding op.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the returned operation.
+ |
+
+|
+`grad_loss`
+ |
+
+Optional. A `Tensor` holding the gradient computed for `loss`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Operation that updates the variables in `var_list`. If `global_step`
+was not `None`, that operation also increments `global_step`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If some of the variables are not `Variable` objects.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+When eager execution is enabled, `loss` should be a Python function that
+takes no arguments and computes the value to be minimized. Minimization (and
+gradient computation) is done with respect to the elements of `var_list` if
+not None, else with respect to any trainable variables created during the
+execution of the `loss` function. `gate_gradients`, `aggregation_method`,
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops` and `grad_loss` are ignored when eager
+execution is enabled.
+
+
+
+variables
+
+View source
+
+
+variables()
+
+
+A list of variables which encode the current state of `Optimizer`.
+
+Includes slot variables and additional global variables created by the
+optimizer in the current default graph.
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of variables.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `GATE_GRAPH = 2`
+* `GATE_NONE = 0`
+* `GATE_OP = 1`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/AdagradDAOptimizer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/AdagradDAOptimizer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..f8b7dcabae8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/AdagradDAOptimizer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,638 @@
+description: Adagrad Dual Averaging algorithm for sparse linear models.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.AdagradDAOptimizer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Adagrad Dual Averaging algorithm for sparse linear models.
+
+Inherits From: [`Optimizer`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/train/Optimizer.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.AdagradDAOptimizer(
+ learning_rate, global_step, initial_gradient_squared_accumulator_value=0.1,
+ l1_regularization_strength=0.0, l2_regularization_strength=0.0,
+ use_locking=(False), name='AdagradDA'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This optimizer takes care of regularization of unseen features in a mini batch
+by updating them when they are seen with a closed form update rule that is
+equivalent to having updated them on every mini-batch.
+
+AdagradDA is typically used when there is a need for large sparsity in the
+trained model. This optimizer only guarantees sparsity for linear models. Be
+careful when using AdagradDA for deep networks as it will require careful
+initialization of the gradient accumulators for it to train.
+
+#### References:
+
+Adaptive Subgradient Methods for Online Learning and Stochastic Optimization
+ :[Duchi et al., 2011](http://jmlr.org/papers/v12/duchi11a.html)
+ ([pdf](http://www.jmlr.org/papers/volume12/duchi11a/duchi11a.pdf))
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`learning_rate`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` or a floating point value. The learning rate.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` containing the current training step number.
+ |
+
+|
+`initial_gradient_squared_accumulator_value`
+ |
+
+A floating point value.
+Starting value for the accumulators, must be positive.
+ |
+
+|
+`l1_regularization_strength`
+ |
+
+A float value, must be greater than or
+equal to zero.
+ |
+
+|
+`l2_regularization_strength`
+ |
+
+A float value, must be greater than or
+equal to zero.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_locking`
+ |
+
+If `True` use locks for update operations.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name prefix for the operations created when applying
+gradients. Defaults to "AdagradDA".
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `initial_gradient_squared_accumulator_value` is
+invalid.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+apply_gradients
+
+View source
+
+
+apply_gradients(
+ grads_and_vars, global_step=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+Apply gradients to variables.
+
+This is the second part of `minimize()`. It returns an `Operation` that
+applies gradients.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`grads_and_vars`
+ |
+
+List of (gradient, variable) pairs as returned by
+`compute_gradients()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Optional `Variable` to increment by one after the
+variables have been updated.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the returned operation. Default to the
+name passed to the `Optimizer` constructor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An `Operation` that applies the specified gradients. If `global_step`
+was not None, that operation also increments `global_step`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `grads_and_vars` is malformed.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If none of the variables have gradients.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If you should use `_distributed_apply()` instead.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+compute_gradients
+
+View source
+
+
+compute_gradients(
+ loss, var_list=None, gate_gradients=GATE_OP, aggregation_method=None,
+ colocate_gradients_with_ops=(False), grad_loss=None
+)
+
+
+Compute gradients of `loss` for the variables in `var_list`.
+
+This is the first part of `minimize()`. It returns a list
+of (gradient, variable) pairs where "gradient" is the gradient
+for "variable". Note that "gradient" can be a `Tensor`, an
+`IndexedSlices`, or `None` if there is no gradient for the
+given variable.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`loss`
+ |
+
+A Tensor containing the value to minimize or a callable taking
+no arguments which returns the value to minimize. When eager execution
+is enabled it must be a callable.
+ |
+
+|
+`var_list`
+ |
+
+Optional list or tuple of tf.Variable to update to minimize
+`loss`. Defaults to the list of variables collected in the graph
+under the key `GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES`.
+ |
+
+|
+`gate_gradients`
+ |
+
+How to gate the computation of gradients. Can be
+`GATE_NONE`, `GATE_OP`, or `GATE_GRAPH`.
+ |
+
+|
+`aggregation_method`
+ |
+
+Specifies the method used to combine gradient terms.
+Valid values are defined in the class `AggregationMethod`.
+ |
+
+|
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops`
+ |
+
+If True, try colocating gradients with
+the corresponding op.
+ |
+
+|
+`grad_loss`
+ |
+
+Optional. A `Tensor` holding the gradient computed for `loss`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of (gradient, variable) pairs. Variable is always present, but
+gradient can be `None`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `var_list` contains anything else than `Variable` objects.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If some arguments are invalid.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If called with eager execution enabled and `loss` is
+not callable.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+When eager execution is enabled, `gate_gradients`, `aggregation_method`,
+and `colocate_gradients_with_ops` are ignored.
+
+
+
+get_name
+
+View source
+
+
+get_name()
+
+
+
+
+
+get_slot
+
+View source
+
+
+get_slot(
+ var, name
+)
+
+
+Return a slot named `name` created for `var` by the Optimizer.
+
+Some `Optimizer` subclasses use additional variables. For example
+`Momentum` and `Adagrad` use variables to accumulate updates. This method
+gives access to these `Variable` objects if for some reason you need them.
+
+Use `get_slot_names()` to get the list of slot names created by the
+`Optimizer`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`var`
+ |
+
+A variable passed to `minimize()` or `apply_gradients()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The `Variable` for the slot if it was created, `None` otherwise.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_slot_names
+
+View source
+
+
+get_slot_names()
+
+
+Return a list of the names of slots created by the `Optimizer`.
+
+See `get_slot()`.
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of strings.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+minimize
+
+View source
+
+
+minimize(
+ loss, global_step=None, var_list=None, gate_gradients=GATE_OP,
+ aggregation_method=None, colocate_gradients_with_ops=(False), name=None,
+ grad_loss=None
+)
+
+
+Add operations to minimize `loss` by updating `var_list`.
+
+This method simply combines calls `compute_gradients()` and
+`apply_gradients()`. If you want to process the gradient before applying
+them call `compute_gradients()` and `apply_gradients()` explicitly instead
+of using this function.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`loss`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` containing the value to minimize.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Optional `Variable` to increment by one after the
+variables have been updated.
+ |
+
+|
+`var_list`
+ |
+
+Optional list or tuple of `Variable` objects to update to
+minimize `loss`. Defaults to the list of variables collected in
+the graph under the key `GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES`.
+ |
+
+|
+`gate_gradients`
+ |
+
+How to gate the computation of gradients. Can be
+`GATE_NONE`, `GATE_OP`, or `GATE_GRAPH`.
+ |
+
+|
+`aggregation_method`
+ |
+
+Specifies the method used to combine gradient terms.
+Valid values are defined in the class `AggregationMethod`.
+ |
+
+|
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops`
+ |
+
+If True, try colocating gradients with
+the corresponding op.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the returned operation.
+ |
+
+|
+`grad_loss`
+ |
+
+Optional. A `Tensor` holding the gradient computed for `loss`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Operation that updates the variables in `var_list`. If `global_step`
+was not `None`, that operation also increments `global_step`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If some of the variables are not `Variable` objects.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+When eager execution is enabled, `loss` should be a Python function that
+takes no arguments and computes the value to be minimized. Minimization (and
+gradient computation) is done with respect to the elements of `var_list` if
+not None, else with respect to any trainable variables created during the
+execution of the `loss` function. `gate_gradients`, `aggregation_method`,
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops` and `grad_loss` are ignored when eager
+execution is enabled.
+
+
+
+variables
+
+View source
+
+
+variables()
+
+
+A list of variables which encode the current state of `Optimizer`.
+
+Includes slot variables and additional global variables created by the
+optimizer in the current default graph.
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of variables.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `GATE_GRAPH = 2`
+* `GATE_NONE = 0`
+* `GATE_OP = 1`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/AdagradOptimizer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/AdagradOptimizer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e630d460bf9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/AdagradOptimizer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,605 @@
+description: Optimizer that implements the Adagrad algorithm.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.AdagradOptimizer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Optimizer that implements the Adagrad algorithm.
+
+Inherits From: [`Optimizer`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/train/Optimizer.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.AdagradOptimizer(
+ learning_rate, initial_accumulator_value=0.1, use_locking=(False),
+ name='Adagrad'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### References:
+
+Adaptive Subgradient Methods for Online Learning and Stochastic Optimization
+ :[Duchi et al., 2011](http://jmlr.org/papers/v12/duchi11a.html)
+ ([pdf](http://www.jmlr.org/papers/volume12/duchi11a/duchi11a.pdf))
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`learning_rate`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` or a floating point value. The learning rate.
+ |
+
+|
+`initial_accumulator_value`
+ |
+
+A floating point value.
+Starting value for the accumulators, must be positive.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_locking`
+ |
+
+If `True` use locks for update operations.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name prefix for the operations created when applying
+gradients. Defaults to "Adagrad".
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `initial_accumulator_value` is invalid.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+apply_gradients
+
+View source
+
+
+apply_gradients(
+ grads_and_vars, global_step=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+Apply gradients to variables.
+
+This is the second part of `minimize()`. It returns an `Operation` that
+applies gradients.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`grads_and_vars`
+ |
+
+List of (gradient, variable) pairs as returned by
+`compute_gradients()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Optional `Variable` to increment by one after the
+variables have been updated.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the returned operation. Default to the
+name passed to the `Optimizer` constructor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An `Operation` that applies the specified gradients. If `global_step`
+was not None, that operation also increments `global_step`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `grads_and_vars` is malformed.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If none of the variables have gradients.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If you should use `_distributed_apply()` instead.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+compute_gradients
+
+View source
+
+
+compute_gradients(
+ loss, var_list=None, gate_gradients=GATE_OP, aggregation_method=None,
+ colocate_gradients_with_ops=(False), grad_loss=None
+)
+
+
+Compute gradients of `loss` for the variables in `var_list`.
+
+This is the first part of `minimize()`. It returns a list
+of (gradient, variable) pairs where "gradient" is the gradient
+for "variable". Note that "gradient" can be a `Tensor`, an
+`IndexedSlices`, or `None` if there is no gradient for the
+given variable.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`loss`
+ |
+
+A Tensor containing the value to minimize or a callable taking
+no arguments which returns the value to minimize. When eager execution
+is enabled it must be a callable.
+ |
+
+|
+`var_list`
+ |
+
+Optional list or tuple of tf.Variable to update to minimize
+`loss`. Defaults to the list of variables collected in the graph
+under the key `GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES`.
+ |
+
+|
+`gate_gradients`
+ |
+
+How to gate the computation of gradients. Can be
+`GATE_NONE`, `GATE_OP`, or `GATE_GRAPH`.
+ |
+
+|
+`aggregation_method`
+ |
+
+Specifies the method used to combine gradient terms.
+Valid values are defined in the class `AggregationMethod`.
+ |
+
+|
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops`
+ |
+
+If True, try colocating gradients with
+the corresponding op.
+ |
+
+|
+`grad_loss`
+ |
+
+Optional. A `Tensor` holding the gradient computed for `loss`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of (gradient, variable) pairs. Variable is always present, but
+gradient can be `None`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `var_list` contains anything else than `Variable` objects.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If some arguments are invalid.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If called with eager execution enabled and `loss` is
+not callable.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+When eager execution is enabled, `gate_gradients`, `aggregation_method`,
+and `colocate_gradients_with_ops` are ignored.
+
+
+
+get_name
+
+View source
+
+
+get_name()
+
+
+
+
+
+get_slot
+
+View source
+
+
+get_slot(
+ var, name
+)
+
+
+Return a slot named `name` created for `var` by the Optimizer.
+
+Some `Optimizer` subclasses use additional variables. For example
+`Momentum` and `Adagrad` use variables to accumulate updates. This method
+gives access to these `Variable` objects if for some reason you need them.
+
+Use `get_slot_names()` to get the list of slot names created by the
+`Optimizer`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`var`
+ |
+
+A variable passed to `minimize()` or `apply_gradients()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The `Variable` for the slot if it was created, `None` otherwise.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_slot_names
+
+View source
+
+
+get_slot_names()
+
+
+Return a list of the names of slots created by the `Optimizer`.
+
+See `get_slot()`.
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of strings.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+minimize
+
+View source
+
+
+minimize(
+ loss, global_step=None, var_list=None, gate_gradients=GATE_OP,
+ aggregation_method=None, colocate_gradients_with_ops=(False), name=None,
+ grad_loss=None
+)
+
+
+Add operations to minimize `loss` by updating `var_list`.
+
+This method simply combines calls `compute_gradients()` and
+`apply_gradients()`. If you want to process the gradient before applying
+them call `compute_gradients()` and `apply_gradients()` explicitly instead
+of using this function.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`loss`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` containing the value to minimize.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Optional `Variable` to increment by one after the
+variables have been updated.
+ |
+
+|
+`var_list`
+ |
+
+Optional list or tuple of `Variable` objects to update to
+minimize `loss`. Defaults to the list of variables collected in
+the graph under the key `GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES`.
+ |
+
+|
+`gate_gradients`
+ |
+
+How to gate the computation of gradients. Can be
+`GATE_NONE`, `GATE_OP`, or `GATE_GRAPH`.
+ |
+
+|
+`aggregation_method`
+ |
+
+Specifies the method used to combine gradient terms.
+Valid values are defined in the class `AggregationMethod`.
+ |
+
+|
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops`
+ |
+
+If True, try colocating gradients with
+the corresponding op.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the returned operation.
+ |
+
+|
+`grad_loss`
+ |
+
+Optional. A `Tensor` holding the gradient computed for `loss`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Operation that updates the variables in `var_list`. If `global_step`
+was not `None`, that operation also increments `global_step`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If some of the variables are not `Variable` objects.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+When eager execution is enabled, `loss` should be a Python function that
+takes no arguments and computes the value to be minimized. Minimization (and
+gradient computation) is done with respect to the elements of `var_list` if
+not None, else with respect to any trainable variables created during the
+execution of the `loss` function. `gate_gradients`, `aggregation_method`,
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops` and `grad_loss` are ignored when eager
+execution is enabled.
+
+
+
+variables
+
+View source
+
+
+variables()
+
+
+A list of variables which encode the current state of `Optimizer`.
+
+Includes slot variables and additional global variables created by the
+optimizer in the current default graph.
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of variables.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `GATE_GRAPH = 2`
+* `GATE_NONE = 0`
+* `GATE_OP = 1`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/AdamOptimizer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/AdamOptimizer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..057350c3701
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/AdamOptimizer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,609 @@
+description: Optimizer that implements the Adam algorithm.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.AdamOptimizer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Optimizer that implements the Adam algorithm.
+
+Inherits From: [`Optimizer`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/train/Optimizer.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.AdamOptimizer(
+ learning_rate=0.001, beta1=0.9, beta2=0.999, epsilon=1e-08, use_locking=(False),
+ name='Adam'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### References:
+
+Adam - A Method for Stochastic Optimization:
+ [Kingma et al., 2015](https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980)
+ ([pdf](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1412.6980.pdf))
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`learning_rate`
+ |
+
+A Tensor or a floating point value. The learning rate.
+ |
+
+|
+`beta1`
+ |
+
+A float value or a constant float tensor. The exponential decay
+rate for the 1st moment estimates.
+ |
+
+|
+`beta2`
+ |
+
+A float value or a constant float tensor. The exponential decay
+rate for the 2nd moment estimates.
+ |
+
+|
+`epsilon`
+ |
+
+A small constant for numerical stability. This epsilon is
+"epsilon hat" in the Kingma and Ba paper (in the formula just before
+Section 2.1), not the epsilon in Algorithm 1 of the paper.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_locking`
+ |
+
+If True use locks for update operations.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the operations created when applying gradients.
+Defaults to "Adam". @compatibility(eager) When eager execution is
+enabled, `learning_rate`, `beta1`, `beta2`, and `epsilon` can each be a
+callable that takes no arguments and returns the actual value to use.
+This can be useful for changing these values across different
+invocations of optimizer functions. @end_compatibility
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+apply_gradients
+
+View source
+
+
+apply_gradients(
+ grads_and_vars, global_step=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+Apply gradients to variables.
+
+This is the second part of `minimize()`. It returns an `Operation` that
+applies gradients.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`grads_and_vars`
+ |
+
+List of (gradient, variable) pairs as returned by
+`compute_gradients()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Optional `Variable` to increment by one after the
+variables have been updated.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the returned operation. Default to the
+name passed to the `Optimizer` constructor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An `Operation` that applies the specified gradients. If `global_step`
+was not None, that operation also increments `global_step`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `grads_and_vars` is malformed.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If none of the variables have gradients.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If you should use `_distributed_apply()` instead.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+compute_gradients
+
+View source
+
+
+compute_gradients(
+ loss, var_list=None, gate_gradients=GATE_OP, aggregation_method=None,
+ colocate_gradients_with_ops=(False), grad_loss=None
+)
+
+
+Compute gradients of `loss` for the variables in `var_list`.
+
+This is the first part of `minimize()`. It returns a list
+of (gradient, variable) pairs where "gradient" is the gradient
+for "variable". Note that "gradient" can be a `Tensor`, an
+`IndexedSlices`, or `None` if there is no gradient for the
+given variable.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`loss`
+ |
+
+A Tensor containing the value to minimize or a callable taking
+no arguments which returns the value to minimize. When eager execution
+is enabled it must be a callable.
+ |
+
+|
+`var_list`
+ |
+
+Optional list or tuple of tf.Variable to update to minimize
+`loss`. Defaults to the list of variables collected in the graph
+under the key `GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES`.
+ |
+
+|
+`gate_gradients`
+ |
+
+How to gate the computation of gradients. Can be
+`GATE_NONE`, `GATE_OP`, or `GATE_GRAPH`.
+ |
+
+|
+`aggregation_method`
+ |
+
+Specifies the method used to combine gradient terms.
+Valid values are defined in the class `AggregationMethod`.
+ |
+
+|
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops`
+ |
+
+If True, try colocating gradients with
+the corresponding op.
+ |
+
+|
+`grad_loss`
+ |
+
+Optional. A `Tensor` holding the gradient computed for `loss`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of (gradient, variable) pairs. Variable is always present, but
+gradient can be `None`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `var_list` contains anything else than `Variable` objects.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If some arguments are invalid.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If called with eager execution enabled and `loss` is
+not callable.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+When eager execution is enabled, `gate_gradients`, `aggregation_method`,
+and `colocate_gradients_with_ops` are ignored.
+
+
+
+get_name
+
+View source
+
+
+get_name()
+
+
+
+
+
+get_slot
+
+View source
+
+
+get_slot(
+ var, name
+)
+
+
+Return a slot named `name` created for `var` by the Optimizer.
+
+Some `Optimizer` subclasses use additional variables. For example
+`Momentum` and `Adagrad` use variables to accumulate updates. This method
+gives access to these `Variable` objects if for some reason you need them.
+
+Use `get_slot_names()` to get the list of slot names created by the
+`Optimizer`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`var`
+ |
+
+A variable passed to `minimize()` or `apply_gradients()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The `Variable` for the slot if it was created, `None` otherwise.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_slot_names
+
+View source
+
+
+get_slot_names()
+
+
+Return a list of the names of slots created by the `Optimizer`.
+
+See `get_slot()`.
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of strings.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+minimize
+
+View source
+
+
+minimize(
+ loss, global_step=None, var_list=None, gate_gradients=GATE_OP,
+ aggregation_method=None, colocate_gradients_with_ops=(False), name=None,
+ grad_loss=None
+)
+
+
+Add operations to minimize `loss` by updating `var_list`.
+
+This method simply combines calls `compute_gradients()` and
+`apply_gradients()`. If you want to process the gradient before applying
+them call `compute_gradients()` and `apply_gradients()` explicitly instead
+of using this function.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`loss`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` containing the value to minimize.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Optional `Variable` to increment by one after the
+variables have been updated.
+ |
+
+|
+`var_list`
+ |
+
+Optional list or tuple of `Variable` objects to update to
+minimize `loss`. Defaults to the list of variables collected in
+the graph under the key `GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES`.
+ |
+
+|
+`gate_gradients`
+ |
+
+How to gate the computation of gradients. Can be
+`GATE_NONE`, `GATE_OP`, or `GATE_GRAPH`.
+ |
+
+|
+`aggregation_method`
+ |
+
+Specifies the method used to combine gradient terms.
+Valid values are defined in the class `AggregationMethod`.
+ |
+
+|
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops`
+ |
+
+If True, try colocating gradients with
+the corresponding op.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the returned operation.
+ |
+
+|
+`grad_loss`
+ |
+
+Optional. A `Tensor` holding the gradient computed for `loss`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Operation that updates the variables in `var_list`. If `global_step`
+was not `None`, that operation also increments `global_step`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If some of the variables are not `Variable` objects.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+When eager execution is enabled, `loss` should be a Python function that
+takes no arguments and computes the value to be minimized. Minimization (and
+gradient computation) is done with respect to the elements of `var_list` if
+not None, else with respect to any trainable variables created during the
+execution of the `loss` function. `gate_gradients`, `aggregation_method`,
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops` and `grad_loss` are ignored when eager
+execution is enabled.
+
+
+
+variables
+
+View source
+
+
+variables()
+
+
+A list of variables which encode the current state of `Optimizer`.
+
+Includes slot variables and additional global variables created by the
+optimizer in the current default graph.
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of variables.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `GATE_GRAPH = 2`
+* `GATE_NONE = 0`
+* `GATE_OP = 1`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/Checkpoint.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/Checkpoint.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..21ed858b289
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/Checkpoint.md
@@ -0,0 +1,459 @@
+description: Groups trackable objects, saving and restoring them.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.Checkpoint
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Groups trackable objects, saving and restoring them.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.Checkpoint(
+ **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+`Checkpoint`'s constructor accepts keyword arguments whose values are types
+that contain trackable state, such as tf.compat.v1.train.Optimizer
+implementations, tf.Variable, `tf.keras.Layer` implementations, or
+tf.keras.Model implementations. It saves these values with a checkpoint, and
+maintains a `save_counter` for numbering checkpoints.
+
+Example usage when graph building:
+
+```python
+import tensorflow as tf
+import os
+
+checkpoint_directory = "/tmp/training_checkpoints"
+checkpoint_prefix = os.path.join(checkpoint_directory, "ckpt")
+
+checkpoint = tf.train.Checkpoint(optimizer=optimizer, model=model)
+status = checkpoint.restore(tf.train.latest_checkpoint(checkpoint_directory))
+train_op = optimizer.minimize( ... )
+status.assert_consumed() # Optional sanity checks.
+with tf.compat.v1.Session() as session:
+ # Use the Session to restore variables, or initialize them if
+ # tf.train.latest_checkpoint returned None.
+ status.initialize_or_restore(session)
+ for _ in range(num_training_steps):
+ session.run(train_op)
+ checkpoint.save(file_prefix=checkpoint_prefix)
+```
+
+Example usage with eager execution enabled:
+
+```python
+import tensorflow as tf
+import os
+
+tf.compat.v1.enable_eager_execution()
+
+checkpoint_directory = "/tmp/training_checkpoints"
+checkpoint_prefix = os.path.join(checkpoint_directory, "ckpt")
+
+checkpoint = tf.train.Checkpoint(optimizer=optimizer, model=model)
+status = checkpoint.restore(tf.train.latest_checkpoint(checkpoint_directory))
+for _ in range(num_training_steps):
+ optimizer.minimize( ... ) # Variables will be restored on creation.
+status.assert_consumed() # Optional sanity checks.
+checkpoint.save(file_prefix=checkpoint_prefix)
+```
+
+`Checkpoint.save` and `Checkpoint.restore` write and read object-based
+checkpoints, in contrast to tf.compat.v1.train.Saver which writes and reads
+`variable.name` based checkpoints. Object-based checkpointing saves a graph of
+dependencies between Python objects (`Layer`s, `Optimizer`s, `Variable`s,
+etc.) with named edges, and this graph is used to match variables when
+restoring a checkpoint. It can be more robust to changes in the Python
+program, and helps to support restore-on-create for variables when executing
+eagerly. Prefer tf.train.Checkpoint over tf.compat.v1.train.Saver for new
+code.
+
+`Checkpoint` objects have dependencies on the objects passed as keyword
+arguments to their constructors, and each dependency is given a name that is
+identical to the name of the keyword argument for which it was created.
+TensorFlow classes like `Layer`s and `Optimizer`s will automatically add
+dependencies on their variables (e.g. "kernel" and "bias" for
+tf.keras.layers.Dense). Inheriting from tf.keras.Model makes managing
+dependencies easy in user-defined classes, since `Model` hooks into attribute
+assignment. For example:
+
+```python
+class Regress(tf.keras.Model):
+
+ def __init__(self):
+ super(Regress, self).__init__()
+ self.input_transform = tf.keras.layers.Dense(10)
+ # ...
+
+ def call(self, inputs):
+ x = self.input_transform(inputs)
+ # ...
+```
+
+This `Model` has a dependency named "input_transform" on its `Dense` layer,
+which in turn depends on its variables. As a result, saving an instance of
+`Regress` using tf.train.Checkpoint will also save all the variables created
+by the `Dense` layer.
+
+When variables are assigned to multiple workers, each worker writes its own
+section of the checkpoint. These sections are then merged/re-indexed to behave
+as a single checkpoint. This avoids copying all variables to one worker, but
+does require that all workers see a common filesystem.
+
+While tf.keras.Model.save_weights and tf.train.Checkpoint.save save in the
+same format, note that the root of the resulting checkpoint is the object the
+save method is attached to. This means saving a tf.keras.Model using
+`save_weights` and loading into a tf.train.Checkpoint with a `Model`
+attached (or vice versa) will not match the `Model`'s variables. See the
+[guide to training
+checkpoints](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/checkpoint) for
+details. Prefer tf.train.Checkpoint over tf.keras.Model.save_weights for
+training checkpoints.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`**kwargs`
+ |
+
+Keyword arguments are set as attributes of this object, and are
+saved with the checkpoint. Values must be trackable objects.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If objects in `kwargs` are not trackable.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`save_counter`
+ |
+
+Incremented when `save()` is called. Used to number
+checkpoints.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+restore
+
+View source
+
+
+restore(
+ save_path
+)
+
+
+Restore a training checkpoint.
+
+Restores this `Checkpoint` and any objects it depends on.
+
+When executing eagerly, either assigns values immediately if variables to
+restore have been created already, or defers restoration until the variables
+are created. Dependencies added after this call will be matched if they have
+a corresponding object in the checkpoint (the restore request will queue in
+any trackable object waiting for the expected dependency to be added).
+
+When graph building, restoration ops are added to the graph but not run
+immediately.
+
+To ensure that loading is complete and no more assignments will take place,
+use the `assert_consumed()` method of the status object returned by
+`restore`:
+
+```python
+checkpoint = tf.train.Checkpoint( ... )
+checkpoint.restore(path).assert_consumed()
+```
+
+An exception will be raised if any Python objects in the dependency graph
+were not found in the checkpoint, or if any checkpointed values do not have
+a matching Python object.
+
+When graph building, `assert_consumed()` indicates that all of the restore
+ops that will be created for this checkpoint have been created. They can be
+run via the `run_restore_ops()` method of the status object:
+
+```python
+checkpoint.restore(path).assert_consumed().run_restore_ops()
+```
+
+If the checkpoint has not been consumed completely, then the list of restore
+ops will grow as more objects are added to the dependency graph.
+
+Name-based tf.compat.v1.train.Saver checkpoints can be loaded using this
+method. Names are used to match variables. No restore ops are created/run
+until `run_restore_ops()` or `initialize_or_restore()` are called on the
+returned status object when graph building, but there is restore-on-creation
+when executing eagerly. Re-encode name-based checkpoints using
+tf.train.Checkpoint.save as soon as possible.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`save_path`
+ |
+
+The path to the checkpoint, as returned by `save` or
+tf.train.latest_checkpoint. If None (as when there is no latest
+checkpoint for tf.train.latest_checkpoint to return), returns an
+object which may run initializers for objects in the dependency graph.
+If the checkpoint was written by the name-based
+tf.compat.v1.train.Saver, names are used to match variables.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+A load status object, which can be used to make assertions about the
+status of a checkpoint restoration and run initialization/restore ops.
+
+The returned status object has the following methods:
+
+* `assert_consumed()`:
+Raises an exception if any variables are unmatched: either
+checkpointed values which don't have a matching Python object or
+Python objects in the dependency graph with no values in the
+checkpoint. This method returns the status object, and so may be
+chained with `initialize_or_restore` or `run_restore_ops`.
+
+* `assert_existing_objects_matched()`:
+Raises an exception if any existing Python objects in the dependency
+graph are unmatched. Unlike `assert_consumed`, this assertion will
+pass if values in the checkpoint have no corresponding Python
+objects. For example a `tf.keras.Layer` object which has not yet been
+built, and so has not created any variables, will pass this assertion
+but fail `assert_consumed`. Useful when loading part of a larger
+checkpoint into a new Python program, e.g. a training checkpoint with
+a tf.compat.v1.train.Optimizer was saved but only the state required
+for
+inference is being loaded. This method returns the status object, and
+so may be chained with `initialize_or_restore` or `run_restore_ops`.
+
+* `assert_nontrivial_match()`: Asserts that something aside from the root
+object was matched. This is a very weak assertion, but is useful for
+sanity checking in library code where objects may exist in the
+checkpoint which haven't been created in Python and some Python
+objects may not have a checkpointed value.
+
+* `expect_partial()`: Silence warnings about incomplete checkpoint
+restores. Warnings are otherwise printed for unused parts of the
+checkpoint file or object when the `Checkpoint` object is deleted
+(often at program shutdown).
+
+* `initialize_or_restore(session=None)`:
+When graph building, runs variable initializers if `save_path` is
+`None`, but otherwise runs restore operations. If no `session` is
+explicitly specified, the default session is used. No effect when
+executing eagerly (variables are initialized or restored eagerly).
+
+* `run_restore_ops(session=None)`:
+When graph building, runs restore operations. If no `session` is
+explicitly specified, the default session is used. No effect when
+executing eagerly (restore operations are run eagerly). May only be
+called when `save_path` is not `None`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+save
+
+View source
+
+
+save(
+ file_prefix, session=None
+)
+
+
+Saves a training checkpoint and provides basic checkpoint management.
+
+The saved checkpoint includes variables created by this object and any
+trackable objects it depends on at the time `Checkpoint.save()` is
+called.
+
+`save` is a basic convenience wrapper around the `write` method,
+sequentially numbering checkpoints using `save_counter` and updating the
+metadata used by tf.train.latest_checkpoint. More advanced checkpoint
+management, for example garbage collection and custom numbering, may be
+provided by other utilities which also wrap `write`
+(tf.train.CheckpointManager for example).
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`file_prefix`
+ |
+
+A prefix to use for the checkpoint filenames
+(/path/to/directory/and_a_prefix). Names are generated based on this
+prefix and `Checkpoint.save_counter`.
+ |
+
+|
+`session`
+ |
+
+The session to evaluate variables in. Ignored when executing
+eagerly. If not provided when graph building, the default session is
+used.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The full path to the checkpoint.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+write
+
+View source
+
+
+write(
+ file_prefix, session=None
+)
+
+
+Writes a training checkpoint.
+
+The checkpoint includes variables created by this object and any
+trackable objects it depends on at the time `Checkpoint.write()` is
+called.
+
+`write` does not number checkpoints, increment `save_counter`, or update the
+metadata used by tf.train.latest_checkpoint. It is primarily intended for
+use by higher level checkpoint management utilities. `save` provides a very
+basic implementation of these features.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`file_prefix`
+ |
+
+A prefix to use for the checkpoint filenames
+(/path/to/directory/and_a_prefix).
+ |
+
+|
+`session`
+ |
+
+The session to evaluate variables in. Ignored when executing
+eagerly. If not provided when graph building, the default session is
+used.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The full path to the checkpoint (i.e. `file_prefix`).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/ChiefSessionCreator.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/ChiefSessionCreator.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..f9c68119544
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/ChiefSessionCreator.md
@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
+description: Creates a tf.compat.v1.Session for a chief.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.ChiefSessionCreator
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Creates a tf.compat.v1.Session for a chief.
+
+Inherits From: [`SessionCreator`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/train/SessionCreator.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.ChiefSessionCreator(
+ scaffold=None, master='', config=None, checkpoint_dir=None,
+ checkpoint_filename_with_path=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`scaffold`
+ |
+
+A `Scaffold` used for gathering or building supportive ops. If
+not specified a default one is created. It's used to finalize the graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`master`
+ |
+
+`String` representation of the TensorFlow master to use.
+ |
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+`ConfigProto` proto used to configure the session.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_dir`
+ |
+
+A string. Optional path to a directory where to restore
+variables.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_filename_with_path`
+ |
+
+Full file name path to the checkpoint file.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+create_session
+
+View source
+
+
+create_session()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/FtrlOptimizer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/FtrlOptimizer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..887670b431e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/FtrlOptimizer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,670 @@
+description: Optimizer that implements the FTRL algorithm.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.FtrlOptimizer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Optimizer that implements the FTRL algorithm.
+
+Inherits From: [`Optimizer`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/train/Optimizer.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.FtrlOptimizer(
+ learning_rate, learning_rate_power=-0.5, initial_accumulator_value=0.1,
+ l1_regularization_strength=0.0, l2_regularization_strength=0.0,
+ use_locking=(False), name='Ftrl', accum_name=None, linear_name=None,
+ l2_shrinkage_regularization_strength=0.0
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This version has support for both online L2 (McMahan et al., 2013) and
+shrinkage-type L2, which is the addition of an L2 penalty
+to the loss function.
+
+#### References:
+
+Ad-click prediction:
+ [McMahan et al., 2013](https://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2488200)
+ ([pdf](https://dl.acm.org/ft_gateway.cfm?id=2488200&ftid=1388399&dwn=1&CFID=32233078&CFTOKEN=d60fe57a294c056a-CB75C374-F915-E7A6-1573FBBC7BF7D526))
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`learning_rate`
+ |
+
+A float value or a constant float `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`learning_rate_power`
+ |
+
+A float value, must be less or equal to zero.
+Controls how the learning rate decreases during training. Use zero for
+a fixed learning rate. See section 3.1 in (McMahan et al., 2013).
+ |
+
+|
+`initial_accumulator_value`
+ |
+
+The starting value for accumulators.
+Only zero or positive values are allowed.
+ |
+
+|
+`l1_regularization_strength`
+ |
+
+A float value, must be greater than or
+equal to zero.
+ |
+
+|
+`l2_regularization_strength`
+ |
+
+A float value, must be greater than or
+equal to zero.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_locking`
+ |
+
+If `True` use locks for update operations.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name prefix for the operations created when applying
+gradients. Defaults to "Ftrl".
+ |
+
+|
+`accum_name`
+ |
+
+The suffix for the variable that keeps the gradient squared
+accumulator. If not present, defaults to name.
+ |
+
+|
+`linear_name`
+ |
+
+The suffix for the variable that keeps the linear gradient
+accumulator. If not present, defaults to name + "_1".
+ |
+
+|
+`l2_shrinkage_regularization_strength`
+ |
+
+A float value, must be greater than
+or equal to zero. This differs from L2 above in that the L2 above is a
+stabilization penalty, whereas this L2 shrinkage is a magnitude penalty.
+The FTRL formulation can be written as:
+w_{t+1} = argmin_w(\hat{g}_{1:t}w + L1*||w||_1 + L2*||w||_2^2), where
+\hat{g} = g + (2*L2_shrinkage*w), and g is the gradient of the loss
+function w.r.t. the weights w.
+Specifically, in the absence of L1 regularization, it is equivalent to
+the following update rule:
+w_{t+1} = w_t - lr_t / (1 + 2*L2*lr_t) * g_t -
+2*L2_shrinkage*lr_t / (1 + 2*L2*lr_t) * w_t
+where lr_t is the learning rate at t.
+When input is sparse shrinkage will only happen on the active weights.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If one of the arguments is invalid.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+apply_gradients
+
+View source
+
+
+apply_gradients(
+ grads_and_vars, global_step=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+Apply gradients to variables.
+
+This is the second part of `minimize()`. It returns an `Operation` that
+applies gradients.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`grads_and_vars`
+ |
+
+List of (gradient, variable) pairs as returned by
+`compute_gradients()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Optional `Variable` to increment by one after the
+variables have been updated.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the returned operation. Default to the
+name passed to the `Optimizer` constructor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An `Operation` that applies the specified gradients. If `global_step`
+was not None, that operation also increments `global_step`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `grads_and_vars` is malformed.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If none of the variables have gradients.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If you should use `_distributed_apply()` instead.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+compute_gradients
+
+View source
+
+
+compute_gradients(
+ loss, var_list=None, gate_gradients=GATE_OP, aggregation_method=None,
+ colocate_gradients_with_ops=(False), grad_loss=None
+)
+
+
+Compute gradients of `loss` for the variables in `var_list`.
+
+This is the first part of `minimize()`. It returns a list
+of (gradient, variable) pairs where "gradient" is the gradient
+for "variable". Note that "gradient" can be a `Tensor`, an
+`IndexedSlices`, or `None` if there is no gradient for the
+given variable.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`loss`
+ |
+
+A Tensor containing the value to minimize or a callable taking
+no arguments which returns the value to minimize. When eager execution
+is enabled it must be a callable.
+ |
+
+|
+`var_list`
+ |
+
+Optional list or tuple of tf.Variable to update to minimize
+`loss`. Defaults to the list of variables collected in the graph
+under the key `GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES`.
+ |
+
+|
+`gate_gradients`
+ |
+
+How to gate the computation of gradients. Can be
+`GATE_NONE`, `GATE_OP`, or `GATE_GRAPH`.
+ |
+
+|
+`aggregation_method`
+ |
+
+Specifies the method used to combine gradient terms.
+Valid values are defined in the class `AggregationMethod`.
+ |
+
+|
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops`
+ |
+
+If True, try colocating gradients with
+the corresponding op.
+ |
+
+|
+`grad_loss`
+ |
+
+Optional. A `Tensor` holding the gradient computed for `loss`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of (gradient, variable) pairs. Variable is always present, but
+gradient can be `None`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `var_list` contains anything else than `Variable` objects.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If some arguments are invalid.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If called with eager execution enabled and `loss` is
+not callable.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+When eager execution is enabled, `gate_gradients`, `aggregation_method`,
+and `colocate_gradients_with_ops` are ignored.
+
+
+
+get_name
+
+View source
+
+
+get_name()
+
+
+
+
+
+get_slot
+
+View source
+
+
+get_slot(
+ var, name
+)
+
+
+Return a slot named `name` created for `var` by the Optimizer.
+
+Some `Optimizer` subclasses use additional variables. For example
+`Momentum` and `Adagrad` use variables to accumulate updates. This method
+gives access to these `Variable` objects if for some reason you need them.
+
+Use `get_slot_names()` to get the list of slot names created by the
+`Optimizer`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`var`
+ |
+
+A variable passed to `minimize()` or `apply_gradients()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The `Variable` for the slot if it was created, `None` otherwise.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_slot_names
+
+View source
+
+
+get_slot_names()
+
+
+Return a list of the names of slots created by the `Optimizer`.
+
+See `get_slot()`.
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of strings.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+minimize
+
+View source
+
+
+minimize(
+ loss, global_step=None, var_list=None, gate_gradients=GATE_OP,
+ aggregation_method=None, colocate_gradients_with_ops=(False), name=None,
+ grad_loss=None
+)
+
+
+Add operations to minimize `loss` by updating `var_list`.
+
+This method simply combines calls `compute_gradients()` and
+`apply_gradients()`. If you want to process the gradient before applying
+them call `compute_gradients()` and `apply_gradients()` explicitly instead
+of using this function.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`loss`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` containing the value to minimize.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Optional `Variable` to increment by one after the
+variables have been updated.
+ |
+
+|
+`var_list`
+ |
+
+Optional list or tuple of `Variable` objects to update to
+minimize `loss`. Defaults to the list of variables collected in
+the graph under the key `GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES`.
+ |
+
+|
+`gate_gradients`
+ |
+
+How to gate the computation of gradients. Can be
+`GATE_NONE`, `GATE_OP`, or `GATE_GRAPH`.
+ |
+
+|
+`aggregation_method`
+ |
+
+Specifies the method used to combine gradient terms.
+Valid values are defined in the class `AggregationMethod`.
+ |
+
+|
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops`
+ |
+
+If True, try colocating gradients with
+the corresponding op.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the returned operation.
+ |
+
+|
+`grad_loss`
+ |
+
+Optional. A `Tensor` holding the gradient computed for `loss`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Operation that updates the variables in `var_list`. If `global_step`
+was not `None`, that operation also increments `global_step`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If some of the variables are not `Variable` objects.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+When eager execution is enabled, `loss` should be a Python function that
+takes no arguments and computes the value to be minimized. Minimization (and
+gradient computation) is done with respect to the elements of `var_list` if
+not None, else with respect to any trainable variables created during the
+execution of the `loss` function. `gate_gradients`, `aggregation_method`,
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops` and `grad_loss` are ignored when eager
+execution is enabled.
+
+
+
+variables
+
+View source
+
+
+variables()
+
+
+A list of variables which encode the current state of `Optimizer`.
+
+Includes slot variables and additional global variables created by the
+optimizer in the current default graph.
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of variables.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `GATE_GRAPH = 2`
+* `GATE_NONE = 0`
+* `GATE_OP = 1`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/GradientDescentOptimizer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/GradientDescentOptimizer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a47e8765e92
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/GradientDescentOptimizer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,573 @@
+description: Optimizer that implements the gradient descent algorithm.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.GradientDescentOptimizer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Optimizer that implements the gradient descent algorithm.
+
+Inherits From: [`Optimizer`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/train/Optimizer.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(
+ learning_rate, use_locking=(False), name='GradientDescent'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`learning_rate`
+ |
+
+A Tensor or a floating point value. The learning
+rate to use.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_locking`
+ |
+
+If True use locks for update operations.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name prefix for the operations created when applying
+gradients. Defaults to "GradientDescent".
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+apply_gradients
+
+View source
+
+
+apply_gradients(
+ grads_and_vars, global_step=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+Apply gradients to variables.
+
+This is the second part of `minimize()`. It returns an `Operation` that
+applies gradients.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`grads_and_vars`
+ |
+
+List of (gradient, variable) pairs as returned by
+`compute_gradients()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Optional `Variable` to increment by one after the
+variables have been updated.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the returned operation. Default to the
+name passed to the `Optimizer` constructor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An `Operation` that applies the specified gradients. If `global_step`
+was not None, that operation also increments `global_step`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `grads_and_vars` is malformed.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If none of the variables have gradients.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If you should use `_distributed_apply()` instead.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+compute_gradients
+
+View source
+
+
+compute_gradients(
+ loss, var_list=None, gate_gradients=GATE_OP, aggregation_method=None,
+ colocate_gradients_with_ops=(False), grad_loss=None
+)
+
+
+Compute gradients of `loss` for the variables in `var_list`.
+
+This is the first part of `minimize()`. It returns a list
+of (gradient, variable) pairs where "gradient" is the gradient
+for "variable". Note that "gradient" can be a `Tensor`, an
+`IndexedSlices`, or `None` if there is no gradient for the
+given variable.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`loss`
+ |
+
+A Tensor containing the value to minimize or a callable taking
+no arguments which returns the value to minimize. When eager execution
+is enabled it must be a callable.
+ |
+
+|
+`var_list`
+ |
+
+Optional list or tuple of tf.Variable to update to minimize
+`loss`. Defaults to the list of variables collected in the graph
+under the key `GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES`.
+ |
+
+|
+`gate_gradients`
+ |
+
+How to gate the computation of gradients. Can be
+`GATE_NONE`, `GATE_OP`, or `GATE_GRAPH`.
+ |
+
+|
+`aggregation_method`
+ |
+
+Specifies the method used to combine gradient terms.
+Valid values are defined in the class `AggregationMethod`.
+ |
+
+|
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops`
+ |
+
+If True, try colocating gradients with
+the corresponding op.
+ |
+
+|
+`grad_loss`
+ |
+
+Optional. A `Tensor` holding the gradient computed for `loss`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of (gradient, variable) pairs. Variable is always present, but
+gradient can be `None`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `var_list` contains anything else than `Variable` objects.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If some arguments are invalid.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If called with eager execution enabled and `loss` is
+not callable.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+When eager execution is enabled, `gate_gradients`, `aggregation_method`,
+and `colocate_gradients_with_ops` are ignored.
+
+
+
+get_name
+
+View source
+
+
+get_name()
+
+
+
+
+
+get_slot
+
+View source
+
+
+get_slot(
+ var, name
+)
+
+
+Return a slot named `name` created for `var` by the Optimizer.
+
+Some `Optimizer` subclasses use additional variables. For example
+`Momentum` and `Adagrad` use variables to accumulate updates. This method
+gives access to these `Variable` objects if for some reason you need them.
+
+Use `get_slot_names()` to get the list of slot names created by the
+`Optimizer`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`var`
+ |
+
+A variable passed to `minimize()` or `apply_gradients()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The `Variable` for the slot if it was created, `None` otherwise.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_slot_names
+
+View source
+
+
+get_slot_names()
+
+
+Return a list of the names of slots created by the `Optimizer`.
+
+See `get_slot()`.
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of strings.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+minimize
+
+View source
+
+
+minimize(
+ loss, global_step=None, var_list=None, gate_gradients=GATE_OP,
+ aggregation_method=None, colocate_gradients_with_ops=(False), name=None,
+ grad_loss=None
+)
+
+
+Add operations to minimize `loss` by updating `var_list`.
+
+This method simply combines calls `compute_gradients()` and
+`apply_gradients()`. If you want to process the gradient before applying
+them call `compute_gradients()` and `apply_gradients()` explicitly instead
+of using this function.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`loss`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` containing the value to minimize.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Optional `Variable` to increment by one after the
+variables have been updated.
+ |
+
+|
+`var_list`
+ |
+
+Optional list or tuple of `Variable` objects to update to
+minimize `loss`. Defaults to the list of variables collected in
+the graph under the key `GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES`.
+ |
+
+|
+`gate_gradients`
+ |
+
+How to gate the computation of gradients. Can be
+`GATE_NONE`, `GATE_OP`, or `GATE_GRAPH`.
+ |
+
+|
+`aggregation_method`
+ |
+
+Specifies the method used to combine gradient terms.
+Valid values are defined in the class `AggregationMethod`.
+ |
+
+|
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops`
+ |
+
+If True, try colocating gradients with
+the corresponding op.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the returned operation.
+ |
+
+|
+`grad_loss`
+ |
+
+Optional. A `Tensor` holding the gradient computed for `loss`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Operation that updates the variables in `var_list`. If `global_step`
+was not `None`, that operation also increments `global_step`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If some of the variables are not `Variable` objects.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+When eager execution is enabled, `loss` should be a Python function that
+takes no arguments and computes the value to be minimized. Minimization (and
+gradient computation) is done with respect to the elements of `var_list` if
+not None, else with respect to any trainable variables created during the
+execution of the `loss` function. `gate_gradients`, `aggregation_method`,
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops` and `grad_loss` are ignored when eager
+execution is enabled.
+
+
+
+variables
+
+View source
+
+
+variables()
+
+
+A list of variables which encode the current state of `Optimizer`.
+
+Includes slot variables and additional global variables created by the
+optimizer in the current default graph.
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of variables.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `GATE_GRAPH = 2`
+* `GATE_NONE = 0`
+* `GATE_OP = 1`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/LooperThread.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/LooperThread.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..091db942fe1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/LooperThread.md
@@ -0,0 +1,416 @@
+description: A thread that runs code repeatedly, optionally on a timer.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.LooperThread
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A thread that runs code repeatedly, optionally on a timer.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.LooperThread(
+ coord, timer_interval_secs, target=None, args=None, kwargs=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This thread class is intended to be used with a `Coordinator`. It repeatedly
+runs code specified either as `target` and `args` or by the `run_loop()`
+method.
+
+Before each run the thread checks if the coordinator has requested stop. In
+that case the looper thread terminates immediately.
+
+If the code being run raises an exception, that exception is reported to the
+coordinator and the thread terminates. The coordinator will then request all
+the other threads it coordinates to stop.
+
+You typically pass looper threads to the supervisor `Join()` method.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`coord`
+ |
+
+A Coordinator.
+ |
+
+|
+`timer_interval_secs`
+ |
+
+Time boundaries at which to call Run(), or None
+if it should be called back to back.
+ |
+
+|
+`target`
+ |
+
+Optional callable object that will be executed in the thread.
+ |
+
+|
+`args`
+ |
+
+Optional arguments to pass to `target` when calling it.
+ |
+
+|
+`kwargs`
+ |
+
+Optional keyword arguments to pass to `target` when calling it.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If one of the arguments is invalid.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`daemon`
+ |
+
+A boolean value indicating whether this thread is a daemon thread.
+
+This must be set before start() is called, otherwise RuntimeError is
+raised. Its initial value is inherited from the creating thread; the
+main thread is not a daemon thread and therefore all threads created in
+the main thread default to daemon = False.
+
+The entire Python program exits when only daemon threads are left.
+ |
+
+|
+`ident`
+ |
+
+Thread identifier of this thread or None if it has not been started.
+
+This is a nonzero integer. See the get_ident() function. Thread
+identifiers may be recycled when a thread exits and another thread is
+created. The identifier is available even after the thread has exited.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string used for identification purposes only.
+
+It has no semantics. Multiple threads may be given the same name. The
+initial name is set by the constructor.
+ |
+
+|
+`native_id`
+ |
+
+Native integral thread ID of this thread, or None if it has not been started.
+
+This is a non-negative integer. See the get_native_id() function.
+This represents the Thread ID as reported by the kernel.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+getName
+
+
+getName()
+
+
+
+
+
+isAlive
+
+
+isAlive()
+
+
+Return whether the thread is alive.
+
+This method is deprecated, use is_alive() instead.
+
+isDaemon
+
+
+isDaemon()
+
+
+
+
+
+is_alive
+
+
+is_alive()
+
+
+Return whether the thread is alive.
+
+This method returns True just before the run() method starts until just
+after the run() method terminates. The module function enumerate()
+returns a list of all alive threads.
+
+join
+
+
+join(
+ timeout=None
+)
+
+
+Wait until the thread terminates.
+
+This blocks the calling thread until the thread whose join() method is
+called terminates -- either normally or through an unhandled exception
+or until the optional timeout occurs.
+
+When the timeout argument is present and not None, it should be a
+floating point number specifying a timeout for the operation in seconds
+(or fractions thereof). As join() always returns None, you must call
+is_alive() after join() to decide whether a timeout happened -- if the
+thread is still alive, the join() call timed out.
+
+When the timeout argument is not present or None, the operation will
+block until the thread terminates.
+
+A thread can be join()ed many times.
+
+join() raises a RuntimeError if an attempt is made to join the current
+thread as that would cause a deadlock. It is also an error to join() a
+thread before it has been started and attempts to do so raises the same
+exception.
+
+loop
+
+View source
+
+
+@staticmethod
+loop(
+ coord, timer_interval_secs, target, args=None, kwargs=None
+)
+
+
+Start a LooperThread that calls a function periodically.
+
+If `timer_interval_secs` is None the thread calls `target(args)`
+repeatedly. Otherwise `target(args)` is called every `timer_interval_secs`
+seconds. The thread terminates when a stop of the coordinator is
+requested.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`coord`
+ |
+
+A Coordinator.
+ |
+
+|
+`timer_interval_secs`
+ |
+
+Number. Time boundaries at which to call `target`.
+ |
+
+|
+`target`
+ |
+
+A callable object.
+ |
+
+|
+`args`
+ |
+
+Optional arguments to pass to `target` when calling it.
+ |
+
+|
+`kwargs`
+ |
+
+Optional keyword arguments to pass to `target` when calling it.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The started thread.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+run
+
+View source
+
+
+run()
+
+
+Method representing the thread's activity.
+
+You may override this method in a subclass. The standard run() method
+invokes the callable object passed to the object's constructor as the
+target argument, if any, with sequential and keyword arguments taken
+from the args and kwargs arguments, respectively.
+
+run_loop
+
+View source
+
+
+run_loop()
+
+
+Called at 'timer_interval_secs' boundaries.
+
+
+setDaemon
+
+
+setDaemon(
+ daemonic
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+setName
+
+
+setName(
+ name
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+start
+
+
+start()
+
+
+Start the thread's activity.
+
+It must be called at most once per thread object. It arranges for the
+object's run() method to be invoked in a separate thread of control.
+
+This method will raise a RuntimeError if called more than once on the
+same thread object.
+
+start_loop
+
+View source
+
+
+start_loop()
+
+
+Called when the thread starts.
+
+
+stop_loop
+
+View source
+
+
+stop_loop()
+
+
+Called when the thread stops.
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/MomentumOptimizer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/MomentumOptimizer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..0ce3a74473c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/MomentumOptimizer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,608 @@
+description: Optimizer that implements the Momentum algorithm.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.MomentumOptimizer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Optimizer that implements the Momentum algorithm.
+
+Inherits From: [`Optimizer`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/train/Optimizer.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.MomentumOptimizer(
+ learning_rate, momentum, use_locking=(False), name='Momentum',
+ use_nesterov=(False)
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes (if `use_nesterov = False`):
+
+```
+accumulation = momentum * accumulation + gradient
+variable -= learning_rate * accumulation
+```
+
+Note that in the dense version of this algorithm, `accumulation` is updated
+and applied regardless of a gradient's value, whereas the sparse version (when
+the gradient is an `IndexedSlices`, typically because of tf.gather or an
+embedding) only updates variable slices and corresponding `accumulation` terms
+when that part of the variable was used in the forward pass.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`learning_rate`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` or a floating point value. The learning rate.
+ |
+
+|
+`momentum`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` or a floating point value. The momentum.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_locking`
+ |
+
+If `True` use locks for update operations.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name prefix for the operations created when applying
+gradients. Defaults to "Momentum".
+ |
+
+|
+`use_nesterov`
+ |
+
+If `True` use Nesterov Momentum.
+See (Sutskever et al., 2013).
+This implementation always computes gradients at the value of the
+variable(s) passed to the optimizer. Using Nesterov Momentum makes the
+variable(s) track the values called `theta_t + mu*v_t` in the paper.
+This implementation is an approximation of the original formula, valid
+for high values of momentum. It will compute the "adjusted gradient"
+in NAG by assuming that the new gradient will be estimated by the
+current average gradient plus the product of momentum and the change
+in the average gradient.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+apply_gradients
+
+View source
+
+
+apply_gradients(
+ grads_and_vars, global_step=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+Apply gradients to variables.
+
+This is the second part of `minimize()`. It returns an `Operation` that
+applies gradients.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`grads_and_vars`
+ |
+
+List of (gradient, variable) pairs as returned by
+`compute_gradients()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Optional `Variable` to increment by one after the
+variables have been updated.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the returned operation. Default to the
+name passed to the `Optimizer` constructor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An `Operation` that applies the specified gradients. If `global_step`
+was not None, that operation also increments `global_step`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `grads_and_vars` is malformed.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If none of the variables have gradients.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If you should use `_distributed_apply()` instead.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+compute_gradients
+
+View source
+
+
+compute_gradients(
+ loss, var_list=None, gate_gradients=GATE_OP, aggregation_method=None,
+ colocate_gradients_with_ops=(False), grad_loss=None
+)
+
+
+Compute gradients of `loss` for the variables in `var_list`.
+
+This is the first part of `minimize()`. It returns a list
+of (gradient, variable) pairs where "gradient" is the gradient
+for "variable". Note that "gradient" can be a `Tensor`, an
+`IndexedSlices`, or `None` if there is no gradient for the
+given variable.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`loss`
+ |
+
+A Tensor containing the value to minimize or a callable taking
+no arguments which returns the value to minimize. When eager execution
+is enabled it must be a callable.
+ |
+
+|
+`var_list`
+ |
+
+Optional list or tuple of tf.Variable to update to minimize
+`loss`. Defaults to the list of variables collected in the graph
+under the key `GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES`.
+ |
+
+|
+`gate_gradients`
+ |
+
+How to gate the computation of gradients. Can be
+`GATE_NONE`, `GATE_OP`, or `GATE_GRAPH`.
+ |
+
+|
+`aggregation_method`
+ |
+
+Specifies the method used to combine gradient terms.
+Valid values are defined in the class `AggregationMethod`.
+ |
+
+|
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops`
+ |
+
+If True, try colocating gradients with
+the corresponding op.
+ |
+
+|
+`grad_loss`
+ |
+
+Optional. A `Tensor` holding the gradient computed for `loss`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of (gradient, variable) pairs. Variable is always present, but
+gradient can be `None`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `var_list` contains anything else than `Variable` objects.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If some arguments are invalid.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If called with eager execution enabled and `loss` is
+not callable.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+When eager execution is enabled, `gate_gradients`, `aggregation_method`,
+and `colocate_gradients_with_ops` are ignored.
+
+
+
+get_name
+
+View source
+
+
+get_name()
+
+
+
+
+
+get_slot
+
+View source
+
+
+get_slot(
+ var, name
+)
+
+
+Return a slot named `name` created for `var` by the Optimizer.
+
+Some `Optimizer` subclasses use additional variables. For example
+`Momentum` and `Adagrad` use variables to accumulate updates. This method
+gives access to these `Variable` objects if for some reason you need them.
+
+Use `get_slot_names()` to get the list of slot names created by the
+`Optimizer`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`var`
+ |
+
+A variable passed to `minimize()` or `apply_gradients()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The `Variable` for the slot if it was created, `None` otherwise.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_slot_names
+
+View source
+
+
+get_slot_names()
+
+
+Return a list of the names of slots created by the `Optimizer`.
+
+See `get_slot()`.
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of strings.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+minimize
+
+View source
+
+
+minimize(
+ loss, global_step=None, var_list=None, gate_gradients=GATE_OP,
+ aggregation_method=None, colocate_gradients_with_ops=(False), name=None,
+ grad_loss=None
+)
+
+
+Add operations to minimize `loss` by updating `var_list`.
+
+This method simply combines calls `compute_gradients()` and
+`apply_gradients()`. If you want to process the gradient before applying
+them call `compute_gradients()` and `apply_gradients()` explicitly instead
+of using this function.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`loss`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` containing the value to minimize.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Optional `Variable` to increment by one after the
+variables have been updated.
+ |
+
+|
+`var_list`
+ |
+
+Optional list or tuple of `Variable` objects to update to
+minimize `loss`. Defaults to the list of variables collected in
+the graph under the key `GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES`.
+ |
+
+|
+`gate_gradients`
+ |
+
+How to gate the computation of gradients. Can be
+`GATE_NONE`, `GATE_OP`, or `GATE_GRAPH`.
+ |
+
+|
+`aggregation_method`
+ |
+
+Specifies the method used to combine gradient terms.
+Valid values are defined in the class `AggregationMethod`.
+ |
+
+|
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops`
+ |
+
+If True, try colocating gradients with
+the corresponding op.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the returned operation.
+ |
+
+|
+`grad_loss`
+ |
+
+Optional. A `Tensor` holding the gradient computed for `loss`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Operation that updates the variables in `var_list`. If `global_step`
+was not `None`, that operation also increments `global_step`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If some of the variables are not `Variable` objects.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+When eager execution is enabled, `loss` should be a Python function that
+takes no arguments and computes the value to be minimized. Minimization (and
+gradient computation) is done with respect to the elements of `var_list` if
+not None, else with respect to any trainable variables created during the
+execution of the `loss` function. `gate_gradients`, `aggregation_method`,
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops` and `grad_loss` are ignored when eager
+execution is enabled.
+
+
+
+variables
+
+View source
+
+
+variables()
+
+
+A list of variables which encode the current state of `Optimizer`.
+
+Includes slot variables and additional global variables created by the
+optimizer in the current default graph.
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of variables.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `GATE_GRAPH = 2`
+* `GATE_NONE = 0`
+* `GATE_OP = 1`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/MonitoredSession.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/MonitoredSession.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..0167d748675
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/MonitoredSession.md
@@ -0,0 +1,421 @@
+description: Session-like object that handles initialization, recovery and hooks.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.MonitoredSession
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Session-like object that handles initialization, recovery and hooks.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.MonitoredSession(
+ session_creator=None, hooks=None, stop_grace_period_secs=120
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Example usage:
+
+
+
+```python
+saver_hook = CheckpointSaverHook(...)
+summary_hook = SummarySaverHook(...)
+with MonitoredSession(session_creator=ChiefSessionCreator(...),
+ hooks=[saver_hook, summary_hook]) as sess:
+ while not sess.should_stop():
+ sess.run(train_op)
+```
+
+Initialization: At creation time the monitored session does following things
+in given order:
+
+* calls `hook.begin()` for each given hook
+* finalizes the graph via `scaffold.finalize()`
+* create session
+* initializes the model via initialization ops provided by `Scaffold`
+* restores variables if a checkpoint exists
+* launches queue runners
+* calls `hook.after_create_session()`
+
+Run: When `run()` is called, the monitored session does following things:
+
+* calls `hook.before_run()`
+* calls TensorFlow `session.run()` with merged fetches and feed_dict
+* calls `hook.after_run()`
+* returns result of `session.run()` asked by user
+* if `AbortedError` or `UnavailableError` occurs, it recovers or
+ reinitializes the session before executing the run() call again
+
+
+Exit: At the `close()`, the monitored session does following things in order:
+
+* calls `hook.end()`
+* closes the queue runners and the session
+* suppresses `OutOfRange` error which indicates that all inputs have been
+ processed if the monitored_session is used as a context
+
+How to set tf.compat.v1.Session arguments:
+
+* In most cases you can set session arguments as follows:
+
+```python
+MonitoredSession(
+ session_creator=ChiefSessionCreator(master=..., config=...))
+```
+
+* In distributed setting for a non-chief worker, you can use following:
+
+```python
+MonitoredSession(
+ session_creator=WorkerSessionCreator(master=..., config=...))
+```
+
+See `MonitoredTrainingSession` for an example usage based on chief or worker.
+
+Note: This is not a tf.compat.v1.Session. For example, it cannot do
+following:
+
+* it cannot be set as default session.
+* it cannot be sent to saver.save.
+* it cannot be sent to tf.train.start_queue_runners.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`session_creator`
+ |
+
+A factory object to create session. Typically a
+`ChiefSessionCreator` which is the default one.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+An iterable of `SessionRunHook' objects.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A MonitoredSession object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`session_creator`
+ |
+
+A factory object to create session. Typically a
+`ChiefSessionCreator` or a `WorkerSessionCreator`.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+An iterable of `SessionRunHook' objects.
+ |
+
+|
+`should_recover`
+ |
+
+A bool. Indicates whether to recover from `AbortedError`
+and `UnavailableError` or not.
+ |
+
+|
+`stop_grace_period_secs`
+ |
+
+Number of seconds given to threads to stop after
+`close()` has been called.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+The graph that was launched in this session.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Child Classes
+[`class StepContext`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/train/MonitoredSession/StepContext.md)
+
+## Methods
+
+close
+
+View source
+
+
+close()
+
+
+
+
+
+run
+
+View source
+
+
+run(
+ fetches, feed_dict=None, options=None, run_metadata=None
+)
+
+
+Run ops in the monitored session.
+
+This method is completely compatible with the `tf.Session.run()` method.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`fetches`
+ |
+
+Same as `tf.Session.run()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`feed_dict`
+ |
+
+Same as `tf.Session.run()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`options`
+ |
+
+Same as `tf.Session.run()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`run_metadata`
+ |
+
+Same as `tf.Session.run()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Same as `tf.Session.run()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+run_step_fn
+
+View source
+
+
+run_step_fn(
+ step_fn
+)
+
+
+Run ops using a step function.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`step_fn`
+ |
+
+A function or a method with a single argument of type
+`StepContext`. The function may use methods of the argument to perform
+computations with access to a raw session. The returned value of the
+`step_fn` will be returned from `run_step_fn`, unless a stop is
+requested. In that case, the next `should_stop` call will return True.
+Example usage:
+```python
+with tf.Graph().as_default():
+c = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(dtypes.float32)
+v = tf.add(c, 4.0)
+w = tf.add(c, 0.5)
+def step_fn(step_context):
+a = step_context.session.run(fetches=v, feed_dict={c: 0.5})
+if a <= 4.5:
+step_context.request_stop()
+return step_context.run_with_hooks(fetches=w,
+feed_dict={c: 0.1})
+
+with tf.MonitoredSession() as session:
+while not session.should_stop():
+a = session.run_step_fn(step_fn)
+```
+Hooks interact with the `run_with_hooks()` call inside the
+`step_fn` as they do with a `MonitoredSession.run` call.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Returns the returned value of `step_fn`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`StopIteration`
+ |
+
+if `step_fn` has called `request_stop()`. It may be
+caught by `with tf.MonitoredSession()` to close the session.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `step_fn` doesn't have a single argument called
+`step_context`. It may also optionally have `self` for cases when it
+belongs to an object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+should_stop
+
+View source
+
+
+should_stop()
+
+
+
+
+
+__enter__
+
+View source
+
+
+__enter__()
+
+
+
+
+
+__exit__
+
+View source
+
+
+__exit__(
+ exception_type, exception_value, traceback
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/MonitoredSession/StepContext.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/MonitoredSession/StepContext.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..55cd006f36d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/MonitoredSession/StepContext.md
@@ -0,0 +1,139 @@
+description: Control flow instrument for the step_fn from run_step_fn().
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.MonitoredSession.StepContext
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Control flow instrument for the `step_fn` from `run_step_fn()`.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.train.SingularMonitoredSession.StepContext`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.MonitoredSession.StepContext(
+ session, run_with_hooks_fn
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Users of `step_fn` may perform `run()` calls without running hooks
+by accessing the `session`. A `run()` call with hooks may be performed
+using `run_with_hooks()`. Computation flow can be interrupted using
+`request_stop()`.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`session`
+ |
+
+An instance of tf.compat.v1.Session.
+ |
+
+|
+`run_with_hooks_fn`
+ |
+
+A function for running fetches and hooks.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`session`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+request_stop
+
+View source
+
+
+request_stop()
+
+
+Exit the training loop by causing `should_stop()` to return `True`.
+
+ Causes `step_fn` to exit by raising an exception.
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+|
+StopIteration
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+run_with_hooks
+
+View source
+
+
+run_with_hooks(
+ *args, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+Same as `MonitoredSession.run`. Accepts the same arguments.
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/MonitoredTrainingSession.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/MonitoredTrainingSession.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..40bd66340fd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/MonitoredTrainingSession.md
@@ -0,0 +1,210 @@
+description: Creates a MonitoredSession for training.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.MonitoredTrainingSession
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Creates a `MonitoredSession` for training.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.MonitoredTrainingSession(
+ master='', is_chief=(True), checkpoint_dir=None, scaffold=None, hooks=None,
+ chief_only_hooks=None, save_checkpoint_secs=USE_DEFAULT,
+ save_summaries_steps=USE_DEFAULT, save_summaries_secs=USE_DEFAULT, config=None,
+ stop_grace_period_secs=120, log_step_count_steps=100, max_wait_secs=7200,
+ save_checkpoint_steps=USE_DEFAULT, summary_dir=None, save_graph_def=(True)
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+For a chief, this utility sets proper session initializer/restorer. It also
+creates hooks related to checkpoint and summary saving. For workers, this
+utility sets proper session creator which waits for the chief to
+initialize/restore. Please check tf.compat.v1.train.MonitoredSession for
+more
+information.
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`master`
+ |
+
+`String` the TensorFlow master to use.
+ |
+
+|
+`is_chief`
+ |
+
+If `True`, it will take care of initialization and recovery the
+underlying TensorFlow session. If `False`, it will wait on a chief to
+initialize or recover the TensorFlow session.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_dir`
+ |
+
+A string. Optional path to a directory where to restore
+variables.
+ |
+
+|
+`scaffold`
+ |
+
+A `Scaffold` used for gathering or building supportive ops. If not
+specified, a default one is created. It's used to finalize the graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+Optional list of `SessionRunHook` objects.
+ |
+
+|
+`chief_only_hooks`
+ |
+
+list of `SessionRunHook` objects. Activate these hooks if
+`is_chief==True`, ignore otherwise.
+ |
+
+|
+`save_checkpoint_secs`
+ |
+
+The frequency, in seconds, that a checkpoint is saved
+using a default checkpoint saver. If both `save_checkpoint_steps` and
+`save_checkpoint_secs` are set to `None`, then the default checkpoint
+saver isn't used. If both are provided, then only `save_checkpoint_secs`
+is used. Default 600.
+ |
+
+|
+`save_summaries_steps`
+ |
+
+The frequency, in number of global steps, that the
+summaries are written to disk using a default summary saver. If both
+`save_summaries_steps` and `save_summaries_secs` are set to `None`, then
+the default summary saver isn't used. Default 100.
+ |
+
+|
+`save_summaries_secs`
+ |
+
+The frequency, in secs, that the summaries are written
+to disk using a default summary saver. If both `save_summaries_steps` and
+`save_summaries_secs` are set to `None`, then the default summary saver
+isn't used. Default not enabled.
+ |
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+an instance of tf.compat.v1.ConfigProto proto used to configure
+the session. It's the `config` argument of constructor of
+tf.compat.v1.Session.
+ |
+
+|
+`stop_grace_period_secs`
+ |
+
+Number of seconds given to threads to stop after
+`close()` has been called.
+ |
+
+|
+`log_step_count_steps`
+ |
+
+The frequency, in number of global steps, that the
+global step/sec is logged.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_wait_secs`
+ |
+
+Maximum time workers should wait for the session to become
+available. This should be kept relatively short to help detect incorrect
+code, but sometimes may need to be increased if the chief takes a while to
+start up.
+ |
+
+|
+`save_checkpoint_steps`
+ |
+
+The frequency, in number of global steps, that a
+checkpoint is saved using a default checkpoint saver. If both
+`save_checkpoint_steps` and `save_checkpoint_secs` are set to `None`, then
+the default checkpoint saver isn't used. If both are provided, then only
+`save_checkpoint_secs` is used. Default not enabled.
+ |
+
+|
+`summary_dir`
+ |
+
+A string. Optional path to a directory where to save
+summaries. If None, checkpoint_dir is used instead.
+ |
+
+|
+`save_graph_def`
+ |
+
+Whether to save the GraphDef and MetaGraphDef to
+`checkpoint_dir`. The GraphDef is saved after the session is created as
+`graph.pbtxt`. MetaGraphDefs are saved out for every checkpoint as
+`model.ckpt-*.meta`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `MonitoredSession` object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/NewCheckpointReader.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/NewCheckpointReader.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a5814e265df
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/NewCheckpointReader.md
@@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
+description: A function that returns a CheckPointReader.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.NewCheckpointReader
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A function that returns a CheckPointReader.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.NewCheckpointReader(
+ filepattern
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`filepattern`
+ |
+
+The filename.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A CheckpointReader object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/Optimizer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/Optimizer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..ebbaa468d5e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/Optimizer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,665 @@
+description: Base class for optimizers.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.Optimizer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Base class for optimizers.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.Optimizer(
+ use_locking, name
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This class defines the API to add Ops to train a model. You never use this
+class directly, but instead instantiate one of its subclasses such as
+`GradientDescentOptimizer`, `AdagradOptimizer`, or `MomentumOptimizer`.
+
+### Usage
+
+```python
+# Create an optimizer with the desired parameters.
+opt = GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.1)
+# Add Ops to the graph to minimize a cost by updating a list of variables.
+# "cost" is a Tensor, and the list of variables contains tf.Variable
+# objects.
+opt_op = opt.minimize(cost, var_list=)
+```
+
+In the training program you will just have to run the returned Op.
+
+```python
+# Execute opt_op to do one step of training:
+opt_op.run()
+```
+
+### Processing gradients before applying them.
+
+Calling `minimize()` takes care of both computing the gradients and
+applying them to the variables. If you want to process the gradients
+before applying them you can instead use the optimizer in three steps:
+
+1. Compute the gradients with `compute_gradients()`.
+2. Process the gradients as you wish.
+3. Apply the processed gradients with `apply_gradients()`.
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+# Create an optimizer.
+opt = GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.1)
+
+# Compute the gradients for a list of variables.
+grads_and_vars = opt.compute_gradients(loss, )
+
+# grads_and_vars is a list of tuples (gradient, variable). Do whatever you
+# need to the 'gradient' part, for example cap them, etc.
+capped_grads_and_vars = [(MyCapper(gv[0]), gv[1]) for gv in grads_and_vars]
+
+# Ask the optimizer to apply the capped gradients.
+opt.apply_gradients(capped_grads_and_vars)
+```
+
+### Gating Gradients
+
+Both `minimize()` and `compute_gradients()` accept a `gate_gradients`
+argument that controls the degree of parallelism during the application of
+the gradients.
+
+The possible values are: `GATE_NONE`, `GATE_OP`, and `GATE_GRAPH`.
+
+`GATE_NONE`: Compute and apply gradients in parallel. This provides
+the maximum parallelism in execution, at the cost of some non-reproducibility
+in the results. For example the two gradients of `matmul` depend on the input
+values: With `GATE_NONE` one of the gradients could be applied to one of the
+inputs _before_ the other gradient is computed resulting in non-reproducible
+results.
+
+`GATE_OP`: For each Op, make sure all gradients are computed before
+they are used. This prevents race conditions for Ops that generate gradients
+for multiple inputs where the gradients depend on the inputs.
+
+`GATE_GRAPH`: Make sure all gradients for all variables are computed
+before any one of them is used. This provides the least parallelism but can
+be useful if you want to process all gradients before applying any of them.
+
+### Slots
+
+Some optimizer subclasses, such as `MomentumOptimizer` and `AdagradOptimizer`
+allocate and manage additional variables associated with the variables to
+train. These are called Slots. Slots have names and you can ask the
+optimizer for the names of the slots that it uses. Once you have a slot name
+you can ask the optimizer for the variable it created to hold the slot value.
+
+This can be useful if you want to log debug a training algorithm, report stats
+about the slots, etc.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`use_locking`
+ |
+
+Bool. If True apply use locks to prevent concurrent updates
+to variables.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A non-empty string. The name to use for accumulators created
+for the optimizer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If name is malformed.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+apply_gradients
+
+View source
+
+
+apply_gradients(
+ grads_and_vars, global_step=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+Apply gradients to variables.
+
+This is the second part of `minimize()`. It returns an `Operation` that
+applies gradients.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`grads_and_vars`
+ |
+
+List of (gradient, variable) pairs as returned by
+`compute_gradients()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Optional `Variable` to increment by one after the
+variables have been updated.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the returned operation. Default to the
+name passed to the `Optimizer` constructor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An `Operation` that applies the specified gradients. If `global_step`
+was not None, that operation also increments `global_step`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `grads_and_vars` is malformed.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If none of the variables have gradients.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If you should use `_distributed_apply()` instead.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+compute_gradients
+
+View source
+
+
+compute_gradients(
+ loss, var_list=None, gate_gradients=GATE_OP, aggregation_method=None,
+ colocate_gradients_with_ops=(False), grad_loss=None
+)
+
+
+Compute gradients of `loss` for the variables in `var_list`.
+
+This is the first part of `minimize()`. It returns a list
+of (gradient, variable) pairs where "gradient" is the gradient
+for "variable". Note that "gradient" can be a `Tensor`, an
+`IndexedSlices`, or `None` if there is no gradient for the
+given variable.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`loss`
+ |
+
+A Tensor containing the value to minimize or a callable taking
+no arguments which returns the value to minimize. When eager execution
+is enabled it must be a callable.
+ |
+
+|
+`var_list`
+ |
+
+Optional list or tuple of tf.Variable to update to minimize
+`loss`. Defaults to the list of variables collected in the graph
+under the key `GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES`.
+ |
+
+|
+`gate_gradients`
+ |
+
+How to gate the computation of gradients. Can be
+`GATE_NONE`, `GATE_OP`, or `GATE_GRAPH`.
+ |
+
+|
+`aggregation_method`
+ |
+
+Specifies the method used to combine gradient terms.
+Valid values are defined in the class `AggregationMethod`.
+ |
+
+|
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops`
+ |
+
+If True, try colocating gradients with
+the corresponding op.
+ |
+
+|
+`grad_loss`
+ |
+
+Optional. A `Tensor` holding the gradient computed for `loss`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of (gradient, variable) pairs. Variable is always present, but
+gradient can be `None`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `var_list` contains anything else than `Variable` objects.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If some arguments are invalid.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If called with eager execution enabled and `loss` is
+not callable.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+When eager execution is enabled, `gate_gradients`, `aggregation_method`,
+and `colocate_gradients_with_ops` are ignored.
+
+
+
+get_name
+
+View source
+
+
+get_name()
+
+
+
+
+
+get_slot
+
+View source
+
+
+get_slot(
+ var, name
+)
+
+
+Return a slot named `name` created for `var` by the Optimizer.
+
+Some `Optimizer` subclasses use additional variables. For example
+`Momentum` and `Adagrad` use variables to accumulate updates. This method
+gives access to these `Variable` objects if for some reason you need them.
+
+Use `get_slot_names()` to get the list of slot names created by the
+`Optimizer`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`var`
+ |
+
+A variable passed to `minimize()` or `apply_gradients()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The `Variable` for the slot if it was created, `None` otherwise.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_slot_names
+
+View source
+
+
+get_slot_names()
+
+
+Return a list of the names of slots created by the `Optimizer`.
+
+See `get_slot()`.
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of strings.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+minimize
+
+View source
+
+
+minimize(
+ loss, global_step=None, var_list=None, gate_gradients=GATE_OP,
+ aggregation_method=None, colocate_gradients_with_ops=(False), name=None,
+ grad_loss=None
+)
+
+
+Add operations to minimize `loss` by updating `var_list`.
+
+This method simply combines calls `compute_gradients()` and
+`apply_gradients()`. If you want to process the gradient before applying
+them call `compute_gradients()` and `apply_gradients()` explicitly instead
+of using this function.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`loss`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` containing the value to minimize.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Optional `Variable` to increment by one after the
+variables have been updated.
+ |
+
+|
+`var_list`
+ |
+
+Optional list or tuple of `Variable` objects to update to
+minimize `loss`. Defaults to the list of variables collected in
+the graph under the key `GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES`.
+ |
+
+|
+`gate_gradients`
+ |
+
+How to gate the computation of gradients. Can be
+`GATE_NONE`, `GATE_OP`, or `GATE_GRAPH`.
+ |
+
+|
+`aggregation_method`
+ |
+
+Specifies the method used to combine gradient terms.
+Valid values are defined in the class `AggregationMethod`.
+ |
+
+|
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops`
+ |
+
+If True, try colocating gradients with
+the corresponding op.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the returned operation.
+ |
+
+|
+`grad_loss`
+ |
+
+Optional. A `Tensor` holding the gradient computed for `loss`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Operation that updates the variables in `var_list`. If `global_step`
+was not `None`, that operation also increments `global_step`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If some of the variables are not `Variable` objects.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+When eager execution is enabled, `loss` should be a Python function that
+takes no arguments and computes the value to be minimized. Minimization (and
+gradient computation) is done with respect to the elements of `var_list` if
+not None, else with respect to any trainable variables created during the
+execution of the `loss` function. `gate_gradients`, `aggregation_method`,
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops` and `grad_loss` are ignored when eager
+execution is enabled.
+
+
+
+variables
+
+View source
+
+
+variables()
+
+
+A list of variables which encode the current state of `Optimizer`.
+
+Includes slot variables and additional global variables created by the
+optimizer in the current default graph.
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of variables.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `GATE_GRAPH = 2`
+* `GATE_NONE = 0`
+* `GATE_OP = 1`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/ProximalAdagradOptimizer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/ProximalAdagradOptimizer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..30a46742daf
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/ProximalAdagradOptimizer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,624 @@
+description: Optimizer that implements the Proximal Adagrad algorithm.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.ProximalAdagradOptimizer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Optimizer that implements the Proximal Adagrad algorithm.
+
+Inherits From: [`Optimizer`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/train/Optimizer.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.ProximalAdagradOptimizer(
+ learning_rate, initial_accumulator_value=0.1, l1_regularization_strength=0.0,
+ l2_regularization_strength=0.0, use_locking=(False), name='ProximalAdagrad'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### References:
+
+Adaptive Subgradient Methods for Online Learning and Stochastic Optimization:
+ [Duchi et al., 2011](http://jmlr.org/papers/v12/duchi11a.html)
+ ([pdf](http://www.jmlr.org/papers/volume12/duchi11a/duchi11a.pdf))
+Efficient Learning using Forward-Backward Splitting:
+ [Duchi et al., 2009](http://papers.nips.cc/paper/3793-efficient-learning-using-forward-backward-splitting)
+ ([pdf](http://papers.nips.cc/paper/3793-efficient-learning-using-forward-backward-splitting.pdf))
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`learning_rate`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` or a floating point value. The learning rate.
+ |
+
+|
+`initial_accumulator_value`
+ |
+
+A floating point value.
+Starting value for the accumulators, must be positive.
+ |
+
+|
+`l1_regularization_strength`
+ |
+
+A float value, must be greater than or
+equal to zero.
+ |
+
+|
+`l2_regularization_strength`
+ |
+
+A float value, must be greater than or
+equal to zero.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_locking`
+ |
+
+If `True` use locks for update operations.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name prefix for the operations created when applying
+gradients. Defaults to "Adagrad".
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `initial_accumulator_value` is invalid.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+apply_gradients
+
+View source
+
+
+apply_gradients(
+ grads_and_vars, global_step=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+Apply gradients to variables.
+
+This is the second part of `minimize()`. It returns an `Operation` that
+applies gradients.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`grads_and_vars`
+ |
+
+List of (gradient, variable) pairs as returned by
+`compute_gradients()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Optional `Variable` to increment by one after the
+variables have been updated.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the returned operation. Default to the
+name passed to the `Optimizer` constructor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An `Operation` that applies the specified gradients. If `global_step`
+was not None, that operation also increments `global_step`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `grads_and_vars` is malformed.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If none of the variables have gradients.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If you should use `_distributed_apply()` instead.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+compute_gradients
+
+View source
+
+
+compute_gradients(
+ loss, var_list=None, gate_gradients=GATE_OP, aggregation_method=None,
+ colocate_gradients_with_ops=(False), grad_loss=None
+)
+
+
+Compute gradients of `loss` for the variables in `var_list`.
+
+This is the first part of `minimize()`. It returns a list
+of (gradient, variable) pairs where "gradient" is the gradient
+for "variable". Note that "gradient" can be a `Tensor`, an
+`IndexedSlices`, or `None` if there is no gradient for the
+given variable.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`loss`
+ |
+
+A Tensor containing the value to minimize or a callable taking
+no arguments which returns the value to minimize. When eager execution
+is enabled it must be a callable.
+ |
+
+|
+`var_list`
+ |
+
+Optional list or tuple of tf.Variable to update to minimize
+`loss`. Defaults to the list of variables collected in the graph
+under the key `GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES`.
+ |
+
+|
+`gate_gradients`
+ |
+
+How to gate the computation of gradients. Can be
+`GATE_NONE`, `GATE_OP`, or `GATE_GRAPH`.
+ |
+
+|
+`aggregation_method`
+ |
+
+Specifies the method used to combine gradient terms.
+Valid values are defined in the class `AggregationMethod`.
+ |
+
+|
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops`
+ |
+
+If True, try colocating gradients with
+the corresponding op.
+ |
+
+|
+`grad_loss`
+ |
+
+Optional. A `Tensor` holding the gradient computed for `loss`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of (gradient, variable) pairs. Variable is always present, but
+gradient can be `None`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `var_list` contains anything else than `Variable` objects.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If some arguments are invalid.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If called with eager execution enabled and `loss` is
+not callable.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+When eager execution is enabled, `gate_gradients`, `aggregation_method`,
+and `colocate_gradients_with_ops` are ignored.
+
+
+
+get_name
+
+View source
+
+
+get_name()
+
+
+
+
+
+get_slot
+
+View source
+
+
+get_slot(
+ var, name
+)
+
+
+Return a slot named `name` created for `var` by the Optimizer.
+
+Some `Optimizer` subclasses use additional variables. For example
+`Momentum` and `Adagrad` use variables to accumulate updates. This method
+gives access to these `Variable` objects if for some reason you need them.
+
+Use `get_slot_names()` to get the list of slot names created by the
+`Optimizer`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`var`
+ |
+
+A variable passed to `minimize()` or `apply_gradients()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The `Variable` for the slot if it was created, `None` otherwise.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_slot_names
+
+View source
+
+
+get_slot_names()
+
+
+Return a list of the names of slots created by the `Optimizer`.
+
+See `get_slot()`.
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of strings.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+minimize
+
+View source
+
+
+minimize(
+ loss, global_step=None, var_list=None, gate_gradients=GATE_OP,
+ aggregation_method=None, colocate_gradients_with_ops=(False), name=None,
+ grad_loss=None
+)
+
+
+Add operations to minimize `loss` by updating `var_list`.
+
+This method simply combines calls `compute_gradients()` and
+`apply_gradients()`. If you want to process the gradient before applying
+them call `compute_gradients()` and `apply_gradients()` explicitly instead
+of using this function.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`loss`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` containing the value to minimize.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Optional `Variable` to increment by one after the
+variables have been updated.
+ |
+
+|
+`var_list`
+ |
+
+Optional list or tuple of `Variable` objects to update to
+minimize `loss`. Defaults to the list of variables collected in
+the graph under the key `GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES`.
+ |
+
+|
+`gate_gradients`
+ |
+
+How to gate the computation of gradients. Can be
+`GATE_NONE`, `GATE_OP`, or `GATE_GRAPH`.
+ |
+
+|
+`aggregation_method`
+ |
+
+Specifies the method used to combine gradient terms.
+Valid values are defined in the class `AggregationMethod`.
+ |
+
+|
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops`
+ |
+
+If True, try colocating gradients with
+the corresponding op.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the returned operation.
+ |
+
+|
+`grad_loss`
+ |
+
+Optional. A `Tensor` holding the gradient computed for `loss`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Operation that updates the variables in `var_list`. If `global_step`
+was not `None`, that operation also increments `global_step`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If some of the variables are not `Variable` objects.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+When eager execution is enabled, `loss` should be a Python function that
+takes no arguments and computes the value to be minimized. Minimization (and
+gradient computation) is done with respect to the elements of `var_list` if
+not None, else with respect to any trainable variables created during the
+execution of the `loss` function. `gate_gradients`, `aggregation_method`,
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops` and `grad_loss` are ignored when eager
+execution is enabled.
+
+
+
+variables
+
+View source
+
+
+variables()
+
+
+A list of variables which encode the current state of `Optimizer`.
+
+Includes slot variables and additional global variables created by the
+optimizer in the current default graph.
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of variables.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `GATE_GRAPH = 2`
+* `GATE_NONE = 0`
+* `GATE_OP = 1`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/ProximalGradientDescentOptimizer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/ProximalGradientDescentOptimizer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..6817bf9ccbd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/ProximalGradientDescentOptimizer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,597 @@
+description: Optimizer that implements the proximal gradient descent algorithm.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.ProximalGradientDescentOptimizer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Optimizer that implements the proximal gradient descent algorithm.
+
+Inherits From: [`Optimizer`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/train/Optimizer.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.ProximalGradientDescentOptimizer(
+ learning_rate, l1_regularization_strength=0.0, l2_regularization_strength=0.0,
+ use_locking=(False), name='ProximalGradientDescent'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### References:
+
+Efficient Learning using Forward-Backward Splitting:
+ [Duchi et al., 2009](http://papers.nips.cc/paper/3793-efficient-learning-using-forward-backward-splitting)
+ ([pdf](http://papers.nips.cc/paper/3793-efficient-learning-using-forward-backward-splitting.pdf))
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`learning_rate`
+ |
+
+A Tensor or a floating point value. The learning
+rate to use.
+ |
+
+|
+`l1_regularization_strength`
+ |
+
+A float value, must be greater than or
+equal to zero.
+ |
+
+|
+`l2_regularization_strength`
+ |
+
+A float value, must be greater than or
+equal to zero.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_locking`
+ |
+
+If True use locks for update operations.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name prefix for the operations created when applying
+gradients. Defaults to "GradientDescent".
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+apply_gradients
+
+View source
+
+
+apply_gradients(
+ grads_and_vars, global_step=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+Apply gradients to variables.
+
+This is the second part of `minimize()`. It returns an `Operation` that
+applies gradients.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`grads_and_vars`
+ |
+
+List of (gradient, variable) pairs as returned by
+`compute_gradients()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Optional `Variable` to increment by one after the
+variables have been updated.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the returned operation. Default to the
+name passed to the `Optimizer` constructor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An `Operation` that applies the specified gradients. If `global_step`
+was not None, that operation also increments `global_step`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `grads_and_vars` is malformed.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If none of the variables have gradients.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If you should use `_distributed_apply()` instead.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+compute_gradients
+
+View source
+
+
+compute_gradients(
+ loss, var_list=None, gate_gradients=GATE_OP, aggregation_method=None,
+ colocate_gradients_with_ops=(False), grad_loss=None
+)
+
+
+Compute gradients of `loss` for the variables in `var_list`.
+
+This is the first part of `minimize()`. It returns a list
+of (gradient, variable) pairs where "gradient" is the gradient
+for "variable". Note that "gradient" can be a `Tensor`, an
+`IndexedSlices`, or `None` if there is no gradient for the
+given variable.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`loss`
+ |
+
+A Tensor containing the value to minimize or a callable taking
+no arguments which returns the value to minimize. When eager execution
+is enabled it must be a callable.
+ |
+
+|
+`var_list`
+ |
+
+Optional list or tuple of tf.Variable to update to minimize
+`loss`. Defaults to the list of variables collected in the graph
+under the key `GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES`.
+ |
+
+|
+`gate_gradients`
+ |
+
+How to gate the computation of gradients. Can be
+`GATE_NONE`, `GATE_OP`, or `GATE_GRAPH`.
+ |
+
+|
+`aggregation_method`
+ |
+
+Specifies the method used to combine gradient terms.
+Valid values are defined in the class `AggregationMethod`.
+ |
+
+|
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops`
+ |
+
+If True, try colocating gradients with
+the corresponding op.
+ |
+
+|
+`grad_loss`
+ |
+
+Optional. A `Tensor` holding the gradient computed for `loss`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of (gradient, variable) pairs. Variable is always present, but
+gradient can be `None`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `var_list` contains anything else than `Variable` objects.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If some arguments are invalid.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If called with eager execution enabled and `loss` is
+not callable.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+When eager execution is enabled, `gate_gradients`, `aggregation_method`,
+and `colocate_gradients_with_ops` are ignored.
+
+
+
+get_name
+
+View source
+
+
+get_name()
+
+
+
+
+
+get_slot
+
+View source
+
+
+get_slot(
+ var, name
+)
+
+
+Return a slot named `name` created for `var` by the Optimizer.
+
+Some `Optimizer` subclasses use additional variables. For example
+`Momentum` and `Adagrad` use variables to accumulate updates. This method
+gives access to these `Variable` objects if for some reason you need them.
+
+Use `get_slot_names()` to get the list of slot names created by the
+`Optimizer`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`var`
+ |
+
+A variable passed to `minimize()` or `apply_gradients()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The `Variable` for the slot if it was created, `None` otherwise.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_slot_names
+
+View source
+
+
+get_slot_names()
+
+
+Return a list of the names of slots created by the `Optimizer`.
+
+See `get_slot()`.
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of strings.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+minimize
+
+View source
+
+
+minimize(
+ loss, global_step=None, var_list=None, gate_gradients=GATE_OP,
+ aggregation_method=None, colocate_gradients_with_ops=(False), name=None,
+ grad_loss=None
+)
+
+
+Add operations to minimize `loss` by updating `var_list`.
+
+This method simply combines calls `compute_gradients()` and
+`apply_gradients()`. If you want to process the gradient before applying
+them call `compute_gradients()` and `apply_gradients()` explicitly instead
+of using this function.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`loss`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` containing the value to minimize.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Optional `Variable` to increment by one after the
+variables have been updated.
+ |
+
+|
+`var_list`
+ |
+
+Optional list or tuple of `Variable` objects to update to
+minimize `loss`. Defaults to the list of variables collected in
+the graph under the key `GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES`.
+ |
+
+|
+`gate_gradients`
+ |
+
+How to gate the computation of gradients. Can be
+`GATE_NONE`, `GATE_OP`, or `GATE_GRAPH`.
+ |
+
+|
+`aggregation_method`
+ |
+
+Specifies the method used to combine gradient terms.
+Valid values are defined in the class `AggregationMethod`.
+ |
+
+|
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops`
+ |
+
+If True, try colocating gradients with
+the corresponding op.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the returned operation.
+ |
+
+|
+`grad_loss`
+ |
+
+Optional. A `Tensor` holding the gradient computed for `loss`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Operation that updates the variables in `var_list`. If `global_step`
+was not `None`, that operation also increments `global_step`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If some of the variables are not `Variable` objects.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+When eager execution is enabled, `loss` should be a Python function that
+takes no arguments and computes the value to be minimized. Minimization (and
+gradient computation) is done with respect to the elements of `var_list` if
+not None, else with respect to any trainable variables created during the
+execution of the `loss` function. `gate_gradients`, `aggregation_method`,
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops` and `grad_loss` are ignored when eager
+execution is enabled.
+
+
+
+variables
+
+View source
+
+
+variables()
+
+
+A list of variables which encode the current state of `Optimizer`.
+
+Includes slot variables and additional global variables created by the
+optimizer in the current default graph.
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of variables.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `GATE_GRAPH = 2`
+* `GATE_NONE = 0`
+* `GATE_OP = 1`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/QueueRunner.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/QueueRunner.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..72a59434b89
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/QueueRunner.md
@@ -0,0 +1,380 @@
+description: Holds a list of enqueue operations for a queue, each to be run in a thread.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.QueueRunner
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Holds a list of enqueue operations for a queue, each to be run in a thread.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.train.queue_runner.QueueRunner`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.QueueRunner(
+ queue=None, enqueue_ops=None, close_op=None, cancel_op=None,
+ queue_closed_exception_types=None, queue_runner_def=None, import_scope=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Queues are a convenient TensorFlow mechanism to compute tensors
+asynchronously using multiple threads. For example in the canonical 'Input
+Reader' setup one set of threads generates filenames in a queue; a second set
+of threads read records from the files, processes them, and enqueues tensors
+on a second queue; a third set of threads dequeues these input records to
+construct batches and runs them through training operations.
+
+There are several delicate issues when running multiple threads that way:
+closing the queues in sequence as the input is exhausted, correctly catching
+and reporting exceptions, etc.
+
+The `QueueRunner`, combined with the `Coordinator`, helps handle these issues.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`queue`
+ |
+
+A `Queue`.
+ |
+
+|
+`enqueue_ops`
+ |
+
+List of enqueue ops to run in threads later.
+ |
+
+|
+`close_op`
+ |
+
+Op to close the queue. Pending enqueue ops are preserved.
+ |
+
+|
+`cancel_op`
+ |
+
+Op to close the queue and cancel pending enqueue ops.
+ |
+
+|
+`queue_closed_exception_types`
+ |
+
+Optional tuple of Exception types that
+indicate that the queue has been closed when raised during an enqueue
+operation. Defaults to `(tf.errors.OutOfRangeError,)`. Another common
+case includes `(tf.errors.OutOfRangeError, tf.errors.CancelledError)`,
+when some of the enqueue ops may dequeue from other Queues.
+ |
+
+|
+`queue_runner_def`
+ |
+
+Optional `QueueRunnerDef` protocol buffer. If specified,
+recreates the QueueRunner from its contents. `queue_runner_def` and the
+other arguments are mutually exclusive.
+ |
+
+|
+`import_scope`
+ |
+
+Optional `string`. Name scope to add. Only used when
+initializing from protocol buffer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If both `queue_runner_def` and `queue` are both specified.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `queue` or `enqueue_ops` are not provided when not
+restoring from `queue_runner_def`.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If eager execution is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+QueueRunners are not compatible with eager execution. Instead, please
+use tf.data to get data into your model.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cancel_op`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`close_op`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`enqueue_ops`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`exceptions_raised`
+ |
+
+Exceptions raised but not handled by the `QueueRunner` threads.
+
+Exceptions raised in queue runner threads are handled in one of two ways
+depending on whether or not a `Coordinator` was passed to
+`create_threads()`:
+
+* With a `Coordinator`, exceptions are reported to the coordinator and
+forgotten by the `QueueRunner`.
+* Without a `Coordinator`, exceptions are captured by the `QueueRunner` and
+made available in this `exceptions_raised` property.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+The string name of the underlying Queue.
+ |
+
+|
+`queue`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`queue_closed_exception_types`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+create_threads
+
+View source
+
+
+create_threads(
+ sess, coord=None, daemon=(False), start=(False)
+)
+
+
+Create threads to run the enqueue ops for the given session.
+
+This method requires a session in which the graph was launched. It creates
+a list of threads, optionally starting them. There is one thread for each
+op passed in `enqueue_ops`.
+
+The `coord` argument is an optional coordinator that the threads will use
+to terminate together and report exceptions. If a coordinator is given,
+this method starts an additional thread to close the queue when the
+coordinator requests a stop.
+
+If previously created threads for the given session are still running, no
+new threads will be created.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sess`
+ |
+
+A `Session`.
+ |
+
+|
+`coord`
+ |
+
+Optional `Coordinator` object for reporting errors and checking
+stop conditions.
+ |
+
+|
+`daemon`
+ |
+
+Boolean. If `True` make the threads daemon threads.
+ |
+
+|
+`start`
+ |
+
+Boolean. If `True` starts the threads. If `False` the
+caller must call the `start()` method of the returned threads.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of threads.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+from_proto
+
+View source
+
+
+@staticmethod
+from_proto(
+ queue_runner_def, import_scope=None
+)
+
+
+Returns a `QueueRunner` object created from `queue_runner_def`.
+
+
+to_proto
+
+View source
+
+
+to_proto(
+ export_scope=None
+)
+
+
+Converts this `QueueRunner` to a `QueueRunnerDef` protocol buffer.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_scope`
+ |
+
+Optional `string`. Name scope to remove.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `QueueRunnerDef` protocol buffer, or `None` if the `Variable` is not in
+the specified name scope.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/RMSPropOptimizer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/RMSPropOptimizer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..db11e84cd49
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/RMSPropOptimizer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,612 @@
+description: Optimizer that implements the RMSProp algorithm (Tielemans et al.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.RMSPropOptimizer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Optimizer that implements the RMSProp algorithm (Tielemans et al.
+
+Inherits From: [`Optimizer`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/train/Optimizer.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.RMSPropOptimizer(
+ learning_rate, decay=0.9, momentum=0.0, epsilon=1e-10, use_locking=(False),
+ centered=(False), name='RMSProp'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+2012).
+
+#### References:
+
+Coursera slide 29:
+Hinton, 2012
+([pdf](http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~tijmen/csc321/slides/lecture_slides_lec6.pdf))
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`learning_rate`
+ |
+
+A Tensor or a floating point value. The learning rate.
+ |
+
+|
+`decay`
+ |
+
+Discounting factor for the history/coming gradient
+ |
+
+|
+`momentum`
+ |
+
+A scalar tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`epsilon`
+ |
+
+Small value to avoid zero denominator.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_locking`
+ |
+
+If True use locks for update operation.
+ |
+
+|
+`centered`
+ |
+
+If True, gradients are normalized by the estimated variance of
+the gradient; if False, by the uncentered second moment. Setting this to
+True may help with training, but is slightly more expensive in terms of
+computation and memory. Defaults to False.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name prefix for the operations created when applying
+gradients. Defaults to "RMSProp".
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+apply_gradients
+
+View source
+
+
+apply_gradients(
+ grads_and_vars, global_step=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+Apply gradients to variables.
+
+This is the second part of `minimize()`. It returns an `Operation` that
+applies gradients.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`grads_and_vars`
+ |
+
+List of (gradient, variable) pairs as returned by
+`compute_gradients()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Optional `Variable` to increment by one after the
+variables have been updated.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the returned operation. Default to the
+name passed to the `Optimizer` constructor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An `Operation` that applies the specified gradients. If `global_step`
+was not None, that operation also increments `global_step`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `grads_and_vars` is malformed.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If none of the variables have gradients.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If you should use `_distributed_apply()` instead.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+compute_gradients
+
+View source
+
+
+compute_gradients(
+ loss, var_list=None, gate_gradients=GATE_OP, aggregation_method=None,
+ colocate_gradients_with_ops=(False), grad_loss=None
+)
+
+
+Compute gradients of `loss` for the variables in `var_list`.
+
+This is the first part of `minimize()`. It returns a list
+of (gradient, variable) pairs where "gradient" is the gradient
+for "variable". Note that "gradient" can be a `Tensor`, an
+`IndexedSlices`, or `None` if there is no gradient for the
+given variable.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`loss`
+ |
+
+A Tensor containing the value to minimize or a callable taking
+no arguments which returns the value to minimize. When eager execution
+is enabled it must be a callable.
+ |
+
+|
+`var_list`
+ |
+
+Optional list or tuple of tf.Variable to update to minimize
+`loss`. Defaults to the list of variables collected in the graph
+under the key `GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES`.
+ |
+
+|
+`gate_gradients`
+ |
+
+How to gate the computation of gradients. Can be
+`GATE_NONE`, `GATE_OP`, or `GATE_GRAPH`.
+ |
+
+|
+`aggregation_method`
+ |
+
+Specifies the method used to combine gradient terms.
+Valid values are defined in the class `AggregationMethod`.
+ |
+
+|
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops`
+ |
+
+If True, try colocating gradients with
+the corresponding op.
+ |
+
+|
+`grad_loss`
+ |
+
+Optional. A `Tensor` holding the gradient computed for `loss`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of (gradient, variable) pairs. Variable is always present, but
+gradient can be `None`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `var_list` contains anything else than `Variable` objects.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If some arguments are invalid.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If called with eager execution enabled and `loss` is
+not callable.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+When eager execution is enabled, `gate_gradients`, `aggregation_method`,
+and `colocate_gradients_with_ops` are ignored.
+
+
+
+get_name
+
+View source
+
+
+get_name()
+
+
+
+
+
+get_slot
+
+View source
+
+
+get_slot(
+ var, name
+)
+
+
+Return a slot named `name` created for `var` by the Optimizer.
+
+Some `Optimizer` subclasses use additional variables. For example
+`Momentum` and `Adagrad` use variables to accumulate updates. This method
+gives access to these `Variable` objects if for some reason you need them.
+
+Use `get_slot_names()` to get the list of slot names created by the
+`Optimizer`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`var`
+ |
+
+A variable passed to `minimize()` or `apply_gradients()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The `Variable` for the slot if it was created, `None` otherwise.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_slot_names
+
+View source
+
+
+get_slot_names()
+
+
+Return a list of the names of slots created by the `Optimizer`.
+
+See `get_slot()`.
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of strings.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+minimize
+
+View source
+
+
+minimize(
+ loss, global_step=None, var_list=None, gate_gradients=GATE_OP,
+ aggregation_method=None, colocate_gradients_with_ops=(False), name=None,
+ grad_loss=None
+)
+
+
+Add operations to minimize `loss` by updating `var_list`.
+
+This method simply combines calls `compute_gradients()` and
+`apply_gradients()`. If you want to process the gradient before applying
+them call `compute_gradients()` and `apply_gradients()` explicitly instead
+of using this function.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`loss`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` containing the value to minimize.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Optional `Variable` to increment by one after the
+variables have been updated.
+ |
+
+|
+`var_list`
+ |
+
+Optional list or tuple of `Variable` objects to update to
+minimize `loss`. Defaults to the list of variables collected in
+the graph under the key `GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES`.
+ |
+
+|
+`gate_gradients`
+ |
+
+How to gate the computation of gradients. Can be
+`GATE_NONE`, `GATE_OP`, or `GATE_GRAPH`.
+ |
+
+|
+`aggregation_method`
+ |
+
+Specifies the method used to combine gradient terms.
+Valid values are defined in the class `AggregationMethod`.
+ |
+
+|
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops`
+ |
+
+If True, try colocating gradients with
+the corresponding op.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the returned operation.
+ |
+
+|
+`grad_loss`
+ |
+
+Optional. A `Tensor` holding the gradient computed for `loss`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Operation that updates the variables in `var_list`. If `global_step`
+was not `None`, that operation also increments `global_step`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If some of the variables are not `Variable` objects.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+When eager execution is enabled, `loss` should be a Python function that
+takes no arguments and computes the value to be minimized. Minimization (and
+gradient computation) is done with respect to the elements of `var_list` if
+not None, else with respect to any trainable variables created during the
+execution of the `loss` function. `gate_gradients`, `aggregation_method`,
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops` and `grad_loss` are ignored when eager
+execution is enabled.
+
+
+
+variables
+
+View source
+
+
+variables()
+
+
+A list of variables which encode the current state of `Optimizer`.
+
+Includes slot variables and additional global variables created by the
+optimizer in the current default graph.
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of variables.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `GATE_GRAPH = 2`
+* `GATE_NONE = 0`
+* `GATE_OP = 1`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/Saver.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/Saver.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..5115824415a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/Saver.md
@@ -0,0 +1,897 @@
+description: Saves and restores variables.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.Saver
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Saves and restores variables.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.Saver(
+ var_list=None, reshape=(False), sharded=(False), max_to_keep=5,
+ keep_checkpoint_every_n_hours=10000.0, name=None, restore_sequentially=(False),
+ saver_def=None, builder=None, defer_build=(False), allow_empty=(False),
+ write_version=tf.train.SaverDef.V2, pad_step_number=(False),
+ save_relative_paths=(False), filename=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+See [Variables](https://tensorflow.org/guide/variables)
+for an overview of variables, saving and restoring.
+
+The `Saver` class adds ops to save and restore variables to and from
+*checkpoints*. It also provides convenience methods to run these ops.
+
+Checkpoints are binary files in a proprietary format which map variable names
+to tensor values. The best way to examine the contents of a checkpoint is to
+load it using a `Saver`.
+
+Savers can automatically number checkpoint filenames with a provided counter.
+This lets you keep multiple checkpoints at different steps while training a
+model. For example you can number the checkpoint filenames with the training
+step number. To avoid filling up disks, savers manage checkpoint files
+automatically. For example, they can keep only the N most recent files, or
+one checkpoint for every N hours of training.
+
+You number checkpoint filenames by passing a value to the optional
+`global_step` argument to `save()`:
+
+```python
+saver.save(sess, 'my-model', global_step=0) ==> filename: 'my-model-0'
+...
+saver.save(sess, 'my-model', global_step=1000) ==> filename: 'my-model-1000'
+```
+
+Additionally, optional arguments to the `Saver()` constructor let you control
+the proliferation of checkpoint files on disk:
+
+* `max_to_keep` indicates the maximum number of recent checkpoint files to
+ keep. As new files are created, older files are deleted. If None or 0,
+ no checkpoints are deleted from the filesystem but only the last one is
+ kept in the `checkpoint` file. Defaults to 5 (that is, the 5 most recent
+ checkpoint files are kept.)
+
+* `keep_checkpoint_every_n_hours`: In addition to keeping the most recent
+ `max_to_keep` checkpoint files, you might want to keep one checkpoint file
+ for every N hours of training. This can be useful if you want to later
+ analyze how a model progressed during a long training session. For
+ example, passing `keep_checkpoint_every_n_hours=2` ensures that you keep
+ one checkpoint file for every 2 hours of training. The default value of
+ 10,000 hours effectively disables the feature.
+
+Note that you still have to call the `save()` method to save the model.
+Passing these arguments to the constructor will not save variables
+automatically for you.
+
+A training program that saves regularly looks like:
+
+```python
+...
+# Create a saver.
+saver = tf.compat.v1.train.Saver(...variables...)
+# Launch the graph and train, saving the model every 1,000 steps.
+sess = tf.compat.v1.Session()
+for step in xrange(1000000):
+ sess.run(..training_op..)
+ if step % 1000 == 0:
+ # Append the step number to the checkpoint name:
+ saver.save(sess, 'my-model', global_step=step)
+```
+
+In addition to checkpoint files, savers keep a protocol buffer on disk with
+the list of recent checkpoints. This is used to manage numbered checkpoint
+files and by `latest_checkpoint()`, which makes it easy to discover the path
+to the most recent checkpoint. That protocol buffer is stored in a file named
+'checkpoint' next to the checkpoint files.
+
+If you create several savers, you can specify a different filename for the
+protocol buffer file in the call to `save()`.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`var_list`
+ |
+
+A list of `Variable`/`SaveableObject`, or a dictionary mapping
+names to `SaveableObject`s. If `None`, defaults to the list of all
+saveable objects.
+ |
+
+|
+`reshape`
+ |
+
+If `True`, allows restoring parameters from a checkpoint where
+the variables have a different shape.
+ |
+
+|
+`sharded`
+ |
+
+If `True`, shard the checkpoints, one per device.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_to_keep`
+ |
+
+Maximum number of recent checkpoints to keep. Defaults to 5.
+ |
+
+|
+`keep_checkpoint_every_n_hours`
+ |
+
+How often to keep checkpoints. Defaults to
+10,000 hours.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+String. Optional name to use as a prefix when adding operations.
+ |
+
+|
+`restore_sequentially`
+ |
+
+A `Bool`, which if true, causes restore of different
+variables to happen sequentially within each device. This can lower
+memory usage when restoring very large models.
+ |
+
+|
+`saver_def`
+ |
+
+Optional `SaverDef` proto to use instead of running the
+builder. This is only useful for specialty code that wants to recreate a
+`Saver` object for a previously built `Graph` that had a `Saver`. The
+`saver_def` proto should be the one returned by the `as_saver_def()`
+call of the `Saver` that was created for that `Graph`.
+ |
+
+|
+`builder`
+ |
+
+Optional `SaverBuilder` to use if a `saver_def` was not provided.
+Defaults to `BulkSaverBuilder()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`defer_build`
+ |
+
+If `True`, defer adding the save and restore ops to the
+`build()` call. In that case `build()` should be called before
+finalizing the graph or using the saver.
+ |
+
+|
+`allow_empty`
+ |
+
+If `False` (default) raise an error if there are no variables
+in the graph. Otherwise, construct the saver anyway and make it a no-op.
+ |
+
+|
+`write_version`
+ |
+
+controls what format to use when saving checkpoints. It
+also affects certain filepath matching logic. The V2 format is the
+recommended choice: it is much more optimized than V1 in terms of memory
+required and latency incurred during restore. Regardless of this
+flag, the Saver is able to restore from both V2 and V1 checkpoints.
+ |
+
+|
+`pad_step_number`
+ |
+
+if True, pads the global step number in the checkpoint
+filepaths to some fixed width (8 by default). This is turned off by
+default.
+ |
+
+|
+`save_relative_paths`
+ |
+
+If `True`, will write relative paths to the
+checkpoint state file. This is needed if the user wants to copy the
+checkpoint directory and reload from the copied directory.
+ |
+
+|
+`filename`
+ |
+
+If known at graph construction time, filename used for variable
+loading/saving.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `var_list` is invalid.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If any of the keys or values in `var_list` are not unique.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If eager execution is enabled and`var_list` does not specify
+a list of variables to save.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`last_checkpoints`
+ |
+
+List of not-yet-deleted checkpoint filenames.
+
+You can pass any of the returned values to `restore()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+as_saver_def
+
+View source
+
+
+as_saver_def()
+
+
+Generates a `SaverDef` representation of this saver.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `SaverDef` proto.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+build
+
+View source
+
+
+build()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+View source
+
+
+export_meta_graph(
+ filename=None, collection_list=None, as_text=(False), export_scope=None,
+ clear_devices=(False), clear_extraneous_savers=(False),
+ strip_default_attrs=(False), save_debug_info=(False)
+)
+
+
+Writes `MetaGraphDef` to save_path/filename.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`filename`
+ |
+
+Optional meta_graph filename including the path.
+ |
+
+|
+`collection_list`
+ |
+
+List of string keys to collect.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+If `True`, writes the meta_graph as an ASCII proto.
+ |
+
+|
+`export_scope`
+ |
+
+Optional `string`. Name scope to remove.
+ |
+
+|
+`clear_devices`
+ |
+
+Whether or not to clear the device field for an `Operation`
+or `Tensor` during export.
+ |
+
+|
+`clear_extraneous_savers`
+ |
+
+Remove any Saver-related information from the
+graph (both Save/Restore ops and SaverDefs) that are not associated with
+this Saver.
+ |
+
+|
+`strip_default_attrs`
+ |
+
+Boolean. If `True`, default-valued attributes will be
+removed from the NodeDefs. For a detailed guide, see
+[Stripping Default-Valued
+Attributes](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/master/tensorflow/python/saved_model/README.md#stripping-default-valued-attributes).
+ |
+
+|
+`save_debug_info`
+ |
+
+If `True`, save the GraphDebugInfo to a separate file,
+which in the same directory of filename and with `_debug` added before
+the file extension.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `MetaGraphDef` proto.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+from_proto
+
+View source
+
+
+@staticmethod
+from_proto(
+ saver_def, import_scope=None
+)
+
+
+Returns a `Saver` object created from `saver_def`.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`saver_def`
+ |
+
+a `SaverDef` protocol buffer.
+ |
+
+|
+`import_scope`
+ |
+
+Optional `string`. Name scope to use.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Saver` built from saver_def.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+recover_last_checkpoints
+
+View source
+
+
+recover_last_checkpoints(
+ checkpoint_paths
+)
+
+
+Recovers the internal saver state after a crash.
+
+This method is useful for recovering the "self._last_checkpoints" state.
+
+Globs for the checkpoints pointed to by `checkpoint_paths`. If the files
+exist, use their mtime as the checkpoint timestamp.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`checkpoint_paths`
+ |
+
+a list of checkpoint paths.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+restore
+
+View source
+
+
+restore(
+ sess, save_path
+)
+
+
+Restores previously saved variables.
+
+This method runs the ops added by the constructor for restoring variables.
+It requires a session in which the graph was launched. The variables to
+restore do not have to have been initialized, as restoring is itself a way
+to initialize variables.
+
+The `save_path` argument is typically a value previously returned from a
+`save()` call, or a call to `latest_checkpoint()`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sess`
+ |
+
+A `Session` to use to restore the parameters. None in eager mode.
+ |
+
+|
+`save_path`
+ |
+
+Path where parameters were previously saved.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If save_path is None or not a valid checkpoint.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+save
+
+View source
+
+
+save(
+ sess, save_path, global_step=None, latest_filename=None,
+ meta_graph_suffix='meta', write_meta_graph=(True), write_state=(True),
+ strip_default_attrs=(False), save_debug_info=(False)
+)
+
+
+Saves variables.
+
+This method runs the ops added by the constructor for saving variables.
+It requires a session in which the graph was launched. The variables to
+save must also have been initialized.
+
+The method returns the path prefix of the newly created checkpoint files.
+This string can be passed directly to a call to `restore()`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sess`
+ |
+
+A Session to use to save the variables.
+ |
+
+|
+`save_path`
+ |
+
+String. Prefix of filenames created for the checkpoint.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+If provided the global step number is appended to `save_path`
+to create the checkpoint filenames. The optional argument can be a
+`Tensor`, a `Tensor` name or an integer.
+ |
+
+|
+`latest_filename`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the protocol buffer file that will
+contains the list of most recent checkpoints. That file, kept in the
+same directory as the checkpoint files, is automatically managed by the
+saver to keep track of recent checkpoints. Defaults to 'checkpoint'.
+ |
+
+|
+`meta_graph_suffix`
+ |
+
+Suffix for `MetaGraphDef` file. Defaults to 'meta'.
+ |
+
+|
+`write_meta_graph`
+ |
+
+`Boolean` indicating whether or not to write the meta
+graph file.
+ |
+
+|
+`write_state`
+ |
+
+`Boolean` indicating whether or not to write the
+`CheckpointStateProto`.
+ |
+
+|
+`strip_default_attrs`
+ |
+
+Boolean. If `True`, default-valued attributes will be
+removed from the NodeDefs. For a detailed guide, see
+[Stripping Default-Valued
+Attributes](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/master/tensorflow/python/saved_model/README.md#stripping-default-valued-attributes).
+ |
+
+|
+`save_debug_info`
+ |
+
+If `True`, save the GraphDebugInfo to a separate file,
+which in the same directory of save_path and with `_debug` added before
+the file extension. This is only enabled when `write_meta_graph` is
+`True`
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A string: path prefix used for the checkpoint files. If the saver is
+sharded, this string ends with: '-?????-of-nnnnn' where 'nnnnn'
+is the number of shards created.
+If the saver is empty, returns None.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `sess` is not a `Session`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `latest_filename` contains path components, or if it
+collides with `save_path`.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If save and restore ops weren't built.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+set_last_checkpoints
+
+View source
+
+
+set_last_checkpoints(
+ last_checkpoints
+)
+
+
+DEPRECATED: Use set_last_checkpoints_with_time.
+
+Sets the list of old checkpoint filenames.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`last_checkpoints`
+ |
+
+A list of checkpoint filenames.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`AssertionError`
+ |
+
+If last_checkpoints is not a list.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+set_last_checkpoints_with_time
+
+View source
+
+
+set_last_checkpoints_with_time(
+ last_checkpoints_with_time
+)
+
+
+Sets the list of old checkpoint filenames and timestamps.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`last_checkpoints_with_time`
+ |
+
+A list of tuples of checkpoint filenames and
+timestamps.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`AssertionError`
+ |
+
+If last_checkpoints_with_time is not a list.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+to_proto
+
+View source
+
+
+to_proto(
+ export_scope=None
+)
+
+
+Converts this `Saver` to a `SaverDef` protocol buffer.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`export_scope`
+ |
+
+Optional `string`. Name scope to remove.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `SaverDef` protocol buffer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/SaverDef.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/SaverDef.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..4e8d7fb6951
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/SaverDef.md
@@ -0,0 +1,98 @@
+description: A ProtocolMessage
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.SaverDef
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A ProtocolMessage
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`filename_tensor_name`
+ |
+
+`string filename_tensor_name`
+ |
+
+|
+`keep_checkpoint_every_n_hours`
+ |
+
+`float keep_checkpoint_every_n_hours`
+ |
+
+|
+`max_to_keep`
+ |
+
+`int32 max_to_keep`
+ |
+
+|
+`restore_op_name`
+ |
+
+`string restore_op_name`
+ |
+
+|
+`save_tensor_name`
+ |
+
+`string save_tensor_name`
+ |
+
+|
+`sharded`
+ |
+
+`bool sharded`
+ |
+
+|
+`version`
+ |
+
+`CheckpointFormatVersion version`
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `CheckpointFormatVersion`
+* `LEGACY = 0`
+* `V1 = 1`
+* `V2 = 2`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/Scaffold.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/Scaffold.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..79b27a6cdff
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/Scaffold.md
@@ -0,0 +1,319 @@
+description: Structure to create or gather pieces commonly needed to train a model.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.Scaffold
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Structure to create or gather pieces commonly needed to train a model.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.Scaffold(
+ init_op=None, init_feed_dict=None, init_fn=None, ready_op=None,
+ ready_for_local_init_op=None, local_init_op=None, summary_op=None, saver=None,
+ copy_from_scaffold=None, local_init_feed_dict=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+When you build a model for training you usually need ops to initialize
+variables, a `Saver` to checkpoint them, an op to collect summaries for
+the visualizer, and so on.
+
+Various libraries built on top of the core TensorFlow library take care of
+creating some or all of these pieces and storing them in well known
+collections in the graph. The `Scaffold` class helps pick these pieces from
+the graph collections, creating and adding them to the collections if needed.
+
+If you call the scaffold constructor without any arguments, it will pick
+pieces from the collections, creating default ones if needed when
+`scaffold.finalize()` is called. You can pass arguments to the constructor to
+provide your own pieces. Pieces that you pass to the constructor are not
+added to the graph collections.
+
+The following pieces are directly accessible as attributes of the `Scaffold`
+object:
+
+* `saver`: A tf.compat.v1.train.Saver object taking care of saving the
+variables.
+ Picked from and stored into the `SAVERS` collection in the graph by default.
+* `init_op`: An op to run to initialize the variables. Picked from and
+ stored into the `INIT_OP` collection in the graph by default.
+* `ready_op`: An op to verify that the variables are initialized. Picked
+ from and stored into the `READY_OP` collection in the graph by default.
+* `ready_for_local_init_op`: An op to verify that global state has been
+ initialized and it is alright to run `local_init_op`. Picked from and
+ stored into the `READY_FOR_LOCAL_INIT_OP` collection in the graph by
+ default. This is needed when the initialization of local variables depends
+ on the values of global variables.
+* `local_init_op`: An op to initialize the local variables. Picked
+ from and stored into the `LOCAL_INIT_OP` collection in the graph by default.
+* `summary_op`: An op to run and merge the summaries in the graph. Picked
+ from and stored into the `SUMMARY_OP` collection in the graph by default.
+
+You can also pass the following additional pieces to the constructor:
+
+* `init_feed_dict`: A session feed dictionary that should be used when
+ running the init op.
+* `init_fn`: A callable to run after the init op to perform additional
+ initializations. The callable will be called as
+ `init_fn(scaffold, session)`.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`init_op`
+ |
+
+Optional op for initializing variables.
+ |
+
+|
+`init_feed_dict`
+ |
+
+Optional session feed dictionary to use when running the
+init_op.
+ |
+
+|
+`init_fn`
+ |
+
+Optional function to use to initialize the model after running
+the init_op. Will be called as `init_fn(scaffold, session)`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ready_op`
+ |
+
+Optional op to verify that the variables are initialized. Must
+return an empty 1D string tensor when the variables are initialized, or
+a non-empty 1D string tensor listing the names of the non-initialized
+variables.
+ |
+
+|
+`ready_for_local_init_op`
+ |
+
+Optional op to verify that the global variables
+are initialized and `local_init_op` can be run. Must return an empty 1D
+string tensor when the global variables are initialized, or a non-empty
+1D string tensor listing the names of the non-initialized global
+variables.
+ |
+
+|
+`local_init_op`
+ |
+
+Optional op to initialize local variables.
+ |
+
+|
+`summary_op`
+ |
+
+Optional op to gather all summaries. Must return a scalar
+string tensor containing a serialized `Summary` proto.
+ |
+
+|
+`saver`
+ |
+
+Optional tf.compat.v1.train.Saver object to use to save and
+restore variables. May also be a tf.train.Checkpoint object, in which
+case object-based checkpoints are saved. This will also load some
+object-based checkpoints saved from elsewhere, but that loading may be
+fragile since it uses fixed keys rather than performing a full
+graph-based match. For example if a variable has two paths from the
+`Checkpoint` object because two `Model` objects share the `Layer` object
+that owns it, removing one `Model` may change the keys and break
+checkpoint loading through this API, whereas a graph-based match would
+match the variable through the other `Model`.
+ |
+
+|
+`copy_from_scaffold`
+ |
+
+Optional scaffold object to copy fields from. Its
+fields will be overwritten by the provided fields in this function.
+ |
+
+|
+`local_init_feed_dict`
+ |
+
+Optional session feed dictionary to use when running
+the local_init_op.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`init_feed_dict`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`init_fn`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`init_op`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`local_init_feed_dict`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`local_init_op`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`ready_for_local_init_op`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`ready_op`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`saver`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`summary_op`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+default_local_init_op
+
+View source
+
+
+@staticmethod
+default_local_init_op()
+
+
+Returns an op that groups the default local init ops.
+
+This op is used during session initialization when a Scaffold is
+initialized without specifying the local_init_op arg. It includes
+tf.compat.v1.local_variables_initializer,
+tf.compat.v1.tables_initializer, and also
+initializes local session resources.
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The default Scaffold local init op.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+finalize
+
+View source
+
+
+finalize()
+
+
+Creates operations if needed and finalizes the graph.
+
+
+get_or_default
+
+View source
+
+
+@staticmethod
+get_or_default(
+ arg_name, collection_key, default_constructor
+)
+
+
+Get from cache or create a default operation.
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/SessionCreator.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/SessionCreator.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..85446f89737
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/SessionCreator.md
@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
+description: A factory for tf.Session.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.SessionCreator
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A factory for tf.Session.
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+create_session
+
+View source
+
+
+@abc.abstractmethod
+create_session()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/SessionManager.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/SessionManager.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3415b39356d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/SessionManager.md
@@ -0,0 +1,516 @@
+description: Training helper that restores from checkpoint and creates session.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.SessionManager
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Training helper that restores from checkpoint and creates session.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.SessionManager(
+ local_init_op=None, ready_op=None, ready_for_local_init_op=None, graph=None,
+ recovery_wait_secs=30, local_init_run_options=None, local_init_feed_dict=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This class is a small wrapper that takes care of session creation and
+checkpoint recovery. It also provides functions that to facilitate
+coordination among multiple training threads or processes.
+
+* Checkpointing trained variables as the training progresses.
+* Initializing variables on startup, restoring them from the most recent
+ checkpoint after a crash, or wait for checkpoints to become available.
+
+### Usage:
+
+```python
+with tf.Graph().as_default():
+ ...add operations to the graph...
+ # Create a SessionManager that will checkpoint the model in '/tmp/mydir'.
+ sm = SessionManager()
+ sess = sm.prepare_session(master, init_op, saver, checkpoint_dir)
+ # Use the session to train the graph.
+ while True:
+ sess.run()
+```
+
+`prepare_session()` initializes or restores a model. It requires `init_op`
+and `saver` as an argument.
+
+A second process could wait for the model to be ready by doing the following:
+
+```python
+with tf.Graph().as_default():
+ ...add operations to the graph...
+ # Create a SessionManager that will wait for the model to become ready.
+ sm = SessionManager()
+ sess = sm.wait_for_session(master)
+ # Use the session to train the graph.
+ while True:
+ sess.run()
+```
+
+`wait_for_session()` waits for a model to be initialized by other processes.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`local_init_op`
+ |
+
+An `Operation` run immediately after session creation.
+Usually used to initialize tables and local variables.
+ |
+
+|
+`ready_op`
+ |
+
+An `Operation` to check if the model is initialized.
+ |
+
+|
+`ready_for_local_init_op`
+ |
+
+An `Operation` to check if the model is ready
+to run local_init_op.
+ |
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+The `Graph` that the model will use.
+ |
+
+|
+`recovery_wait_secs`
+ |
+
+Seconds between checks for the model to be ready.
+ |
+
+|
+`local_init_run_options`
+ |
+
+RunOptions to be passed to session.run when
+executing the local_init_op.
+ |
+
+|
+`local_init_feed_dict`
+ |
+
+Optional session feed dictionary to use when running
+the local_init_op.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If ready_for_local_init_op is not None but local_init_op is
+None
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+prepare_session
+
+View source
+
+
+prepare_session(
+ master, init_op=None, saver=None, checkpoint_dir=None,
+ checkpoint_filename_with_path=None, wait_for_checkpoint=(False),
+ max_wait_secs=7200, config=None, init_feed_dict=None, init_fn=None
+)
+
+
+Creates a `Session`. Makes sure the model is ready to be used.
+
+Creates a `Session` on 'master'. If a `saver` object is passed in, and
+`checkpoint_dir` points to a directory containing valid checkpoint
+files, then it will try to recover the model from checkpoint. If
+no checkpoint files are available, and `wait_for_checkpoint` is
+`True`, then the process would check every `recovery_wait_secs`,
+up to `max_wait_secs`, for recovery to succeed.
+
+If the model cannot be recovered successfully then it is initialized by
+running the `init_op` and calling `init_fn` if they are provided.
+The `local_init_op` is also run after init_op and init_fn, regardless of
+whether the model was recovered successfully, but only if
+`ready_for_local_init_op` passes.
+
+If the model is recovered from a checkpoint it is assumed that all
+global variables have been initialized, in particular neither `init_op`
+nor `init_fn` will be executed.
+
+It is an error if the model cannot be recovered and no `init_op`
+or `init_fn` or `local_init_op` are passed.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`master`
+ |
+
+`String` representation of the TensorFlow master to use.
+ |
+
+|
+`init_op`
+ |
+
+Optional `Operation` used to initialize the model.
+ |
+
+|
+`saver`
+ |
+
+A `Saver` object used to restore a model.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_dir`
+ |
+
+Path to the checkpoint files. The latest checkpoint in the
+dir will be used to restore.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_filename_with_path`
+ |
+
+Full file name path to the checkpoint file.
+ |
+
+|
+`wait_for_checkpoint`
+ |
+
+Whether to wait for checkpoint to become available.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_wait_secs`
+ |
+
+Maximum time to wait for checkpoints to become available.
+ |
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+Optional `ConfigProto` proto used to configure the session.
+ |
+
+|
+`init_feed_dict`
+ |
+
+Optional dictionary that maps `Tensor` objects to feed
+values. This feed dictionary is passed to the session `run()` call when
+running the init op.
+ |
+
+|
+`init_fn`
+ |
+
+Optional callable used to initialize the model. Called after the
+optional `init_op` is called. The callable must accept one argument,
+the session being initialized.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Session` object that can be used to drive the model.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If the model cannot be initialized or recovered.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If both checkpoint_dir and checkpoint_filename_with_path are
+set.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+recover_session
+
+View source
+
+
+recover_session(
+ master, saver=None, checkpoint_dir=None, checkpoint_filename_with_path=None,
+ wait_for_checkpoint=(False), max_wait_secs=7200, config=None
+)
+
+
+Creates a `Session`, recovering if possible.
+
+Creates a new session on 'master'. If the session is not initialized
+and can be recovered from a checkpoint, recover it.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`master`
+ |
+
+`String` representation of the TensorFlow master to use.
+ |
+
+|
+`saver`
+ |
+
+A `Saver` object used to restore a model.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_dir`
+ |
+
+Path to the checkpoint files. The latest checkpoint in the
+dir will be used to restore.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_filename_with_path`
+ |
+
+Full file name path to the checkpoint file.
+ |
+
+|
+`wait_for_checkpoint`
+ |
+
+Whether to wait for checkpoint to become available.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_wait_secs`
+ |
+
+Maximum time to wait for checkpoints to become available.
+ |
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+Optional `ConfigProto` proto used to configure the session.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A pair (sess, initialized) where 'initialized' is `True` if
+the session could be recovered and initialized, `False` otherwise.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If both checkpoint_dir and checkpoint_filename_with_path are
+set.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+wait_for_session
+
+View source
+
+
+wait_for_session(
+ master, config=None, max_wait_secs=float('Inf')
+)
+
+
+Creates a new `Session` and waits for model to be ready.
+
+Creates a new `Session` on 'master'. Waits for the model to be
+initialized or recovered from a checkpoint. It's expected that
+another thread or process will make the model ready, and that this
+is intended to be used by threads/processes that participate in a
+distributed training configuration where a different thread/process
+is responsible for initializing or recovering the model being trained.
+
+NB: The amount of time this method waits for the session is bounded
+by max_wait_secs. By default, this function will wait indefinitely.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`master`
+ |
+
+`String` representation of the TensorFlow master to use.
+ |
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+Optional ConfigProto proto used to configure the session.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_wait_secs`
+ |
+
+Maximum time to wait for the session to become available.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Session`. May be None if the operation exceeds the timeout
+specified by config.operation_timeout_in_ms.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`tf.DeadlineExceededError`
+ |
+
+if the session is not available after
+max_wait_secs.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/SingularMonitoredSession.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/SingularMonitoredSession.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..54721d47b7b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/SingularMonitoredSession.md
@@ -0,0 +1,401 @@
+description: Session-like object that handles initialization, restoring, and hooks.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.SingularMonitoredSession
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Session-like object that handles initialization, restoring, and hooks.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.SingularMonitoredSession(
+ hooks=None, scaffold=None, master='', config=None, checkpoint_dir=None,
+ stop_grace_period_secs=120, checkpoint_filename_with_path=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Please note that this utility is not recommended for distributed settings.
+For distributed settings, please use tf.compat.v1.train.MonitoredSession.
+The
+differences between `MonitoredSession` and `SingularMonitoredSession` are:
+
+* `MonitoredSession` handles `AbortedError` and `UnavailableError` for
+ distributed settings, but `SingularMonitoredSession` does not.
+* `MonitoredSession` can be created in `chief` or `worker` modes.
+ `SingularMonitoredSession` is always created as `chief`.
+* You can access the raw tf.compat.v1.Session object used by
+ `SingularMonitoredSession`, whereas in MonitoredSession the raw session is
+ private. This can be used:
+ - To `run` without hooks.
+ - To save and restore.
+* All other functionality is identical.
+
+#### Example usage:
+
+
+```python
+saver_hook = CheckpointSaverHook(...)
+summary_hook = SummarySaverHook(...)
+with SingularMonitoredSession(hooks=[saver_hook, summary_hook]) as sess:
+ while not sess.should_stop():
+ sess.run(train_op)
+```
+
+Initialization: At creation time the hooked session does following things
+in given order:
+
+* calls `hook.begin()` for each given hook
+* finalizes the graph via `scaffold.finalize()`
+* create session
+* initializes the model via initialization ops provided by `Scaffold`
+* restores variables if a checkpoint exists
+* launches queue runners
+
+Run: When `run()` is called, the hooked session does following things:
+
+* calls `hook.before_run()`
+* calls TensorFlow `session.run()` with merged fetches and feed_dict
+* calls `hook.after_run()`
+* returns result of `session.run()` asked by user
+
+Exit: At the `close()`, the hooked session does following things in order:
+
+* calls `hook.end()`
+* closes the queue runners and the session
+* suppresses `OutOfRange` error which indicates that all inputs have been
+ processed if the `SingularMonitoredSession` is used as a context.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`hooks`
+ |
+
+An iterable of `SessionRunHook' objects.
+ |
+
+|
+`scaffold`
+ |
+
+A `Scaffold` used for gathering or building supportive ops. If
+not specified a default one is created. It's used to finalize the graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`master`
+ |
+
+`String` representation of the TensorFlow master to use.
+ |
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+`ConfigProto` proto used to configure the session.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_dir`
+ |
+
+A string. Optional path to a directory where to restore
+variables.
+ |
+
+|
+`stop_grace_period_secs`
+ |
+
+Number of seconds given to threads to stop after
+`close()` has been called.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_filename_with_path`
+ |
+
+A string. Optional path to a checkpoint
+file from which to restore variables.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+The graph that was launched in this session.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Child Classes
+[`class StepContext`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/train/MonitoredSession/StepContext.md)
+
+## Methods
+
+close
+
+View source
+
+
+close()
+
+
+
+
+
+raw_session
+
+View source
+
+
+raw_session()
+
+
+Returns underlying `TensorFlow.Session` object.
+
+
+run
+
+View source
+
+
+run(
+ fetches, feed_dict=None, options=None, run_metadata=None
+)
+
+
+Run ops in the monitored session.
+
+This method is completely compatible with the `tf.Session.run()` method.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`fetches`
+ |
+
+Same as `tf.Session.run()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`feed_dict`
+ |
+
+Same as `tf.Session.run()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`options`
+ |
+
+Same as `tf.Session.run()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`run_metadata`
+ |
+
+Same as `tf.Session.run()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Same as `tf.Session.run()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+run_step_fn
+
+View source
+
+
+run_step_fn(
+ step_fn
+)
+
+
+Run ops using a step function.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`step_fn`
+ |
+
+A function or a method with a single argument of type
+`StepContext`. The function may use methods of the argument to perform
+computations with access to a raw session. The returned value of the
+`step_fn` will be returned from `run_step_fn`, unless a stop is
+requested. In that case, the next `should_stop` call will return True.
+Example usage:
+```python
+with tf.Graph().as_default():
+c = tf.compat.v1.placeholder(dtypes.float32)
+v = tf.add(c, 4.0)
+w = tf.add(c, 0.5)
+def step_fn(step_context):
+a = step_context.session.run(fetches=v, feed_dict={c: 0.5})
+if a <= 4.5:
+step_context.request_stop()
+return step_context.run_with_hooks(fetches=w,
+feed_dict={c: 0.1})
+
+with tf.MonitoredSession() as session:
+while not session.should_stop():
+a = session.run_step_fn(step_fn)
+```
+Hooks interact with the `run_with_hooks()` call inside the
+`step_fn` as they do with a `MonitoredSession.run` call.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Returns the returned value of `step_fn`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`StopIteration`
+ |
+
+if `step_fn` has called `request_stop()`. It may be
+caught by `with tf.MonitoredSession()` to close the session.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `step_fn` doesn't have a single argument called
+`step_context`. It may also optionally have `self` for cases when it
+belongs to an object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+should_stop
+
+View source
+
+
+should_stop()
+
+
+
+
+
+__enter__
+
+View source
+
+
+__enter__()
+
+
+
+
+
+__exit__
+
+View source
+
+
+__exit__(
+ exception_type, exception_value, traceback
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/Supervisor.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/Supervisor.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..8cae2271329
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/Supervisor.md
@@ -0,0 +1,1717 @@
+description: A training helper that checkpoints models and computes summaries.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.Supervisor
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A training helper that checkpoints models and computes summaries.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.Supervisor(
+ graph=None, ready_op=USE_DEFAULT, ready_for_local_init_op=USE_DEFAULT,
+ is_chief=(True), init_op=USE_DEFAULT, init_feed_dict=None,
+ local_init_op=USE_DEFAULT, logdir=None, summary_op=USE_DEFAULT,
+ saver=USE_DEFAULT, global_step=USE_DEFAULT, save_summaries_secs=120,
+ save_model_secs=600, recovery_wait_secs=30, stop_grace_secs=120,
+ checkpoint_basename='model.ckpt', session_manager=None,
+ summary_writer=USE_DEFAULT, init_fn=None, local_init_run_options=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This class is deprecated. Please use
+tf.compat.v1.train.MonitoredTrainingSession instead.
+
+The Supervisor is a small wrapper around a `Coordinator`, a `Saver`,
+and a `SessionManager` that takes care of common needs of TensorFlow
+training programs.
+
+#### Use for a single program
+
+```python
+with tf.Graph().as_default():
+ ...add operations to the graph...
+ # Create a Supervisor that will checkpoint the model in '/tmp/mydir'.
+ sv = Supervisor(logdir='/tmp/mydir')
+ # Get a TensorFlow session managed by the supervisor.
+ with sv.managed_session(FLAGS.master) as sess:
+ # Use the session to train the graph.
+ while not sv.should_stop():
+ sess.run()
+```
+
+Within the `with sv.managed_session()` block all variables in the graph have
+been initialized. In addition, a few services have been started to
+checkpoint the model and add summaries to the event log.
+
+If the program crashes and is restarted, the managed session automatically
+reinitialize variables from the most recent checkpoint.
+
+The supervisor is notified of any exception raised by one of the services.
+After an exception is raised, `should_stop()` returns `True`. In that case
+the training loop should also stop. This is why the training loop has to
+check for `sv.should_stop()`.
+
+Exceptions that indicate that the training inputs have been exhausted,
+tf.errors.OutOfRangeError, also cause `sv.should_stop()` to return `True`
+but are not re-raised from the `with` block: they indicate a normal
+termination.
+
+#### Use for multiple replicas
+
+To train with replicas you deploy the same program in a `Cluster`.
+One of the tasks must be identified as the *chief*: the task that handles
+initialization, checkpoints, summaries, and recovery. The other tasks
+depend on the *chief* for these services.
+
+The only change you have to do to the single program code is to indicate
+if the program is running as the *chief*.
+
+```python
+# Choose a task as the chief. This could be based on server_def.task_index,
+# or job_def.name, or job_def.tasks. It's entirely up to the end user.
+# But there can be only one *chief*.
+is_chief = (server_def.task_index == 0)
+server = tf.distribute.Server(server_def)
+
+with tf.Graph().as_default():
+ ...add operations to the graph...
+ # Create a Supervisor that uses log directory on a shared file system.
+ # Indicate if you are the 'chief'
+ sv = Supervisor(logdir='/shared_directory/...', is_chief=is_chief)
+ # Get a Session in a TensorFlow server on the cluster.
+ with sv.managed_session(server.target) as sess:
+ # Use the session to train the graph.
+ while not sv.should_stop():
+ sess.run()
+```
+
+In the *chief* task, the `Supervisor` works exactly as in the first example
+above. In the other tasks `sv.managed_session()` waits for the Model to have
+been initialized before returning a session to the training code. The
+non-chief tasks depend on the chief task for initializing the model.
+
+If one of the tasks crashes and restarts, `managed_session()`
+checks if the Model is initialized. If yes, it just creates a session and
+returns it to the training code that proceeds normally. If the model needs
+to be initialized, the chief task takes care of reinitializing it; the other
+tasks just wait for the model to have been initialized.
+
+NOTE: This modified program still works fine as a single program.
+The single program marks itself as the chief.
+
+#### What `master` string to use
+
+Whether you are running on your machine or in the cluster you can use the
+following values for the --master flag:
+
+* Specifying `''` requests an in-process session that does not use RPC.
+
+* Specifying `'local'` requests a session that uses the RPC-based
+ "Master interface" to run TensorFlow programs. See
+ `tf.train.Server.create_local_server` for
+ details.
+
+* Specifying `'grpc://hostname:port'` requests a session that uses
+ the RPC interface to a specific host, and also allows the in-process
+ master to access remote tensorflow workers. Often, it is
+ appropriate to pass `server.target` (for some tf.distribute.Server
+ named `server).
+
+#### Advanced use
+
+##### Launching additional services
+
+`managed_session()` launches the Checkpoint and Summary services (threads).
+If you need more services to run you can simply launch them in the block
+controlled by `managed_session()`.
+
+Example: Start a thread to print losses. We want this thread to run
+every 60 seconds, so we launch it with `sv.loop()`.
+
+```python
+...
+sv = Supervisor(logdir='/tmp/mydir')
+with sv.managed_session(FLAGS.master) as sess:
+ sv.loop(60, print_loss, (sess, ))
+ while not sv.should_stop():
+ sess.run(my_train_op)
+```
+
+##### Launching fewer services
+
+`managed_session()` launches the "summary" and "checkpoint" threads which use
+either the optionally `summary_op` and `saver` passed to the constructor, or
+default ones created automatically by the supervisor. If you want to run
+your own summary and checkpointing logic, disable these services by passing
+`None` to the `summary_op` and `saver` parameters.
+
+Example: Create summaries manually every 100 steps in the chief.
+
+```python
+# Create a Supervisor with no automatic summaries.
+sv = Supervisor(logdir='/tmp/mydir', is_chief=is_chief, summary_op=None)
+# As summary_op was None, managed_session() does not start the
+# summary thread.
+with sv.managed_session(FLAGS.master) as sess:
+ for step in xrange(1000000):
+ if sv.should_stop():
+ break
+ if is_chief and step % 100 == 0:
+ # Create the summary every 100 chief steps.
+ sv.summary_computed(sess, sess.run(my_summary_op))
+ else:
+ # Train normally
+ sess.run(my_train_op)
+```
+
+##### Custom model initialization
+
+`managed_session()` only supports initializing the model by running an
+`init_op` or restoring from the latest checkpoint. If you have special
+initialization needs, see how to specify a `local_init_op` when creating the
+supervisor. You can also use the `SessionManager` directly to create a
+session and check if it could be initialized automatically.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+A `Graph`. The graph that the model will use. Defaults to the
+default `Graph`. The supervisor may add operations to the graph before
+creating a session, but the graph should not be modified by the caller
+after passing it to the supervisor.
+ |
+
+|
+`ready_op`
+ |
+
+1-D string `Tensor`. This tensor is evaluated by supervisors in
+`prepare_or_wait_for_session()` to check if the model is ready to use.
+The model is considered ready if it returns an empty array. Defaults to
+the tensor returned from tf.compat.v1.report_uninitialized_variables()
+If `None`, the model is not checked for readiness.
+ |
+
+|
+`ready_for_local_init_op`
+ |
+
+1-D string `Tensor`. This tensor is evaluated by
+supervisors in `prepare_or_wait_for_session()` to check if the model is
+ready to run the local_init_op. The model is considered ready if it
+returns an empty array. Defaults to `None`. If `None`, the model is not
+checked for readiness before running local_init_op.
+ |
+
+|
+`is_chief`
+ |
+
+If True, create a chief supervisor in charge of initializing and
+restoring the model. If False, create a supervisor that relies on a
+chief supervisor for inits and restore.
+ |
+
+|
+`init_op`
+ |
+
+`Operation`. Used by chief supervisors to initialize the model
+when it can not be recovered. Defaults to an `Operation` that
+initializes all global variables. If `None`, no initialization is done
+automatically unless you pass a value for `init_fn`, see below.
+ |
+
+|
+`init_feed_dict`
+ |
+
+A dictionary that maps `Tensor` objects to feed values.
+This feed dictionary will be used when `init_op` is evaluated.
+ |
+
+|
+`local_init_op`
+ |
+
+`Operation`. Used by all supervisors to run initializations
+that should run for every new supervisor instance. By default these are
+table initializers and initializers for local variables. If `None`, no
+further per supervisor-instance initialization is done automatically.
+ |
+
+|
+`logdir`
+ |
+
+A string. Optional path to a directory where to checkpoint the
+model and log events for the visualizer. Used by chief supervisors. The
+directory will be created if it does not exist.
+ |
+
+|
+`summary_op`
+ |
+
+An `Operation` that returns a Summary for the event logs. Used
+by chief supervisors if a `logdir` was specified. Defaults to the
+operation returned from summary.merge_all(). If `None`, summaries are
+not computed automatically.
+ |
+
+|
+`saver`
+ |
+
+A Saver object. Used by chief supervisors if a `logdir` was
+specified. Defaults to the saved returned by Saver(). If `None`, the
+model is not saved automatically.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+An integer Tensor of size 1 that counts steps. The value
+from 'global_step' is used in summaries and checkpoint filenames.
+Default to the op named 'global_step' in the graph if it exists, is of
+rank 1, size 1, and of type tf.int32 or tf.int64. If `None` the global
+step is not recorded in summaries and checkpoint files. Used by chief
+supervisors if a `logdir` was specified.
+ |
+
+|
+`save_summaries_secs`
+ |
+
+Number of seconds between the computation of
+summaries for the event log. Defaults to 120 seconds. Pass 0 to
+disable summaries.
+ |
+
+|
+`save_model_secs`
+ |
+
+Number of seconds between the creation of model
+checkpoints. Defaults to 600 seconds. Pass 0 to disable checkpoints.
+ |
+
+|
+`recovery_wait_secs`
+ |
+
+Number of seconds between checks that the model is
+ready. Used by supervisors when waiting for a chief supervisor to
+initialize or restore the model. Defaults to 30 seconds.
+ |
+
+|
+`stop_grace_secs`
+ |
+
+Grace period, in seconds, given to running threads to
+stop when `stop()` is called. Defaults to 120 seconds.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_basename`
+ |
+
+The basename for checkpoint saving.
+ |
+
+|
+`session_manager`
+ |
+
+`SessionManager`, which manages Session creation and
+recovery. If it is `None`, a default `SessionManager` will be created
+with the set of arguments passed in for backwards compatibility.
+ |
+
+|
+`summary_writer`
+ |
+
+`SummaryWriter` to use or `USE_DEFAULT`. Can be `None` to
+indicate that no summaries should be written.
+ |
+
+|
+`init_fn`
+ |
+
+Optional callable used to initialize the model. Called after the
+optional `init_op` is called. The callable must accept one argument,
+the session being initialized.
+ |
+
+|
+`local_init_run_options`
+ |
+
+RunOptions to be passed as the SessionManager
+local_init_run_options parameter.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If called with eager execution enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`coord`
+ |
+
+Return the Coordinator used by the Supervisor.
+
+The Coordinator can be useful if you want to run multiple threads
+during your training.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Return the global_step Tensor used by the supervisor.
+ |
+
+|
+`init_feed_dict`
+ |
+
+Return the feed dictionary used when evaluating the `init_op`.
+ |
+
+|
+`init_op`
+ |
+
+Return the Init Op used by the supervisor.
+ |
+
+|
+`is_chief`
+ |
+
+Return True if this is a chief supervisor.
+ |
+
+|
+`ready_for_local_init_op`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`ready_op`
+ |
+
+Return the Ready Op used by the supervisor.
+ |
+
+|
+`save_model_secs`
+ |
+
+Return the delay between checkpoints.
+ |
+
+|
+`save_path`
+ |
+
+Return the save path used by the supervisor.
+ |
+
+|
+`save_summaries_secs`
+ |
+
+Return the delay between summary computations.
+ |
+
+|
+`saver`
+ |
+
+Return the Saver used by the supervisor.
+ |
+
+|
+`session_manager`
+ |
+
+Return the SessionManager used by the Supervisor.
+ |
+
+|
+`summary_op`
+ |
+
+Return the Summary Tensor used by the chief supervisor.
+ |
+
+|
+`summary_writer`
+ |
+
+Return the SummaryWriter used by the chief supervisor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+Loop
+
+View source
+
+
+Loop(
+ timer_interval_secs, target, args=None, kwargs=None
+)
+
+
+Start a LooperThread that calls a function periodically.
+
+If `timer_interval_secs` is None the thread calls `target(*args, **kwargs)`
+repeatedly. Otherwise it calls it every `timer_interval_secs`
+seconds. The thread terminates when a stop is requested.
+
+The started thread is added to the list of threads managed by the supervisor
+so it does not need to be passed to the `stop()` method.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`timer_interval_secs`
+ |
+
+Number. Time boundaries at which to call `target`.
+ |
+
+|
+`target`
+ |
+
+A callable object.
+ |
+
+|
+`args`
+ |
+
+Optional arguments to pass to `target` when calling it.
+ |
+
+|
+`kwargs`
+ |
+
+Optional keyword arguments to pass to `target` when calling it.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The started thread.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+PrepareSession
+
+View source
+
+
+PrepareSession(
+ master='', config=None, wait_for_checkpoint=(False), max_wait_secs=7200,
+ start_standard_services=(True)
+)
+
+
+Make sure the model is ready to be used.
+
+Create a session on 'master', recovering or initializing the model as
+needed, or wait for a session to be ready. If running as the chief
+and `start_standard_service` is set to True, also call the session
+manager to start the standard services.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`master`
+ |
+
+name of the TensorFlow master to use. See the
+tf.compat.v1.Session constructor for how this is interpreted.
+ |
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+Optional ConfigProto proto used to configure the session, which is
+passed as-is to create the session.
+ |
+
+|
+`wait_for_checkpoint`
+ |
+
+Whether we should wait for the availability of a
+checkpoint before creating Session. Defaults to False.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_wait_secs`
+ |
+
+Maximum time to wait for the session to become available.
+ |
+
+|
+`start_standard_services`
+ |
+
+Whether to start the standard services and the
+queue runners.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A Session object that can be used to drive the model.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+RequestStop
+
+View source
+
+
+RequestStop(
+ ex=None
+)
+
+
+Request that the coordinator stop the threads.
+
+See `Coordinator.request_stop()`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ex`
+ |
+
+Optional `Exception`, or Python `exc_info` tuple as returned by
+`sys.exc_info()`. If this is the first call to `request_stop()` the
+corresponding exception is recorded and re-raised from `join()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+ShouldStop
+
+View source
+
+
+ShouldStop()
+
+
+Check if the coordinator was told to stop.
+
+See `Coordinator.should_stop()`.
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+True if the coordinator was told to stop, False otherwise.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+StartQueueRunners
+
+View source
+
+
+StartQueueRunners(
+ sess, queue_runners=None
+)
+
+
+Start threads for `QueueRunners`.
+
+Note that the queue runners collected in the graph key `QUEUE_RUNNERS`
+are already started automatically when you create a session with the
+supervisor, so unless you have non-collected queue runners to start
+you do not need to call this explicitly.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sess`
+ |
+
+A `Session`.
+ |
+
+|
+`queue_runners`
+ |
+
+A list of `QueueRunners`. If not specified, we'll use the
+list of queue runners gathered in the graph under the key
+`GraphKeys.QUEUE_RUNNERS`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The list of threads started for the `QueueRunners`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If called with eager execution enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+Queues are not compatible with eager execution. To ingest data when eager
+execution is enabled, use the tf.data API.
+
+
+
+StartStandardServices
+
+View source
+
+
+StartStandardServices(
+ sess
+)
+
+
+Start the standard services for 'sess'.
+
+This starts services in the background. The services started depend
+on the parameters to the constructor and may include:
+
+ - A Summary thread computing summaries every save_summaries_secs.
+ - A Checkpoint thread saving the model every save_model_secs.
+ - A StepCounter thread measure step time.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sess`
+ |
+
+A Session.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+A list of threads that are running the standard services. You can use
+the Supervisor's Coordinator to join these threads with:
+sv.coord.Join()
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If called with a non-chief Supervisor.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If not `logdir` was passed to the constructor as the
+services need a log directory.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+Stop
+
+View source
+
+
+Stop(
+ threads=None, close_summary_writer=(True), ignore_live_threads=(False)
+)
+
+
+Stop the services and the coordinator.
+
+This does not close the session.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`threads`
+ |
+
+Optional list of threads to join with the coordinator. If
+`None`, defaults to the threads running the standard services, the
+threads started for `QueueRunners`, and the threads started by the
+`loop()` method. To wait on additional threads, pass the list in this
+parameter.
+ |
+
+|
+`close_summary_writer`
+ |
+
+Whether to close the `summary_writer`. Defaults to
+`True` if the summary writer was created by the supervisor, `False`
+otherwise.
+ |
+
+|
+`ignore_live_threads`
+ |
+
+If `True` ignores threads that remain running after a
+grace period when joining threads via the coordinator, instead of
+raising a RuntimeError.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+StopOnException
+
+View source
+
+
+StopOnException()
+
+
+Context handler to stop the supervisor when an exception is raised.
+
+See `Coordinator.stop_on_exception()`.
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A context handler.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+SummaryComputed
+
+View source
+
+
+SummaryComputed(
+ sess, summary, global_step=None
+)
+
+
+Indicate that a summary was computed.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sess`
+ |
+
+A `Session` object.
+ |
+
+|
+`summary`
+ |
+
+A Summary proto, or a string holding a serialized summary proto.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Int. global step this summary is associated with. If `None`,
+it will try to fetch the current step.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+if 'summary' is not a Summary proto or a string.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+if the Supervisor was created without a `logdir`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+WaitForStop
+
+View source
+
+
+WaitForStop()
+
+
+Block waiting for the coordinator to stop.
+
+
+loop
+
+View source
+
+
+loop(
+ timer_interval_secs, target, args=None, kwargs=None
+)
+
+
+Start a LooperThread that calls a function periodically.
+
+If `timer_interval_secs` is None the thread calls `target(*args, **kwargs)`
+repeatedly. Otherwise it calls it every `timer_interval_secs`
+seconds. The thread terminates when a stop is requested.
+
+The started thread is added to the list of threads managed by the supervisor
+so it does not need to be passed to the `stop()` method.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`timer_interval_secs`
+ |
+
+Number. Time boundaries at which to call `target`.
+ |
+
+|
+`target`
+ |
+
+A callable object.
+ |
+
+|
+`args`
+ |
+
+Optional arguments to pass to `target` when calling it.
+ |
+
+|
+`kwargs`
+ |
+
+Optional keyword arguments to pass to `target` when calling it.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The started thread.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+managed_session
+
+View source
+
+
+@contextlib.contextmanager
+managed_session(
+ master='', config=None, start_standard_services=(True),
+ close_summary_writer=(True)
+)
+
+
+Returns a context manager for a managed session.
+
+This context manager creates and automatically recovers a session. It
+optionally starts the standard services that handle checkpoints and
+summaries. It monitors exceptions raised from the `with` block or from the
+services and stops the supervisor as needed.
+
+The context manager is typically used as follows:
+
+```python
+def train():
+ sv = tf.compat.v1.train.Supervisor(...)
+ with sv.managed_session() as sess:
+ for step in xrange(..):
+ if sv.should_stop():
+ break
+ sess.run()
+ ...do other things needed at each training step...
+```
+
+An exception raised from the `with` block or one of the service threads is
+raised again when the block exits. This is done after stopping all threads
+and closing the session. For example, an `AbortedError` exception, raised
+in case of preemption of one of the workers in a distributed model, is
+raised again when the block exits.
+
+If you want to retry the training loop in case of preemption you can do it
+as follows:
+
+```python
+def main(...):
+ while True
+ try:
+ train()
+ except tf.errors.Aborted:
+ pass
+```
+
+As a special case, exceptions used for control flow, such as
+`OutOfRangeError` which reports that input queues are exhausted, are not
+raised again from the `with` block: they indicate a clean termination of
+the training loop and are considered normal termination.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`master`
+ |
+
+name of the TensorFlow master to use. See the
+tf.compat.v1.Session constructor for how this is interpreted.
+ |
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+Optional `ConfigProto` proto used to configure the session. Passed
+as-is to create the session.
+ |
+
+|
+`start_standard_services`
+ |
+
+Whether to start the standard services, such as
+checkpoint, summary and step counter.
+ |
+
+|
+`close_summary_writer`
+ |
+
+Whether to close the summary writer when closing the
+session. Defaults to True.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A context manager that yields a `Session` restored from the latest
+checkpoint or initialized from scratch if not checkpoint exists. The
+session is closed when the `with` block exits.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+prepare_or_wait_for_session
+
+View source
+
+
+prepare_or_wait_for_session(
+ master='', config=None, wait_for_checkpoint=(False), max_wait_secs=7200,
+ start_standard_services=(True)
+)
+
+
+Make sure the model is ready to be used.
+
+Create a session on 'master', recovering or initializing the model as
+needed, or wait for a session to be ready. If running as the chief
+and `start_standard_service` is set to True, also call the session
+manager to start the standard services.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`master`
+ |
+
+name of the TensorFlow master to use. See the
+tf.compat.v1.Session constructor for how this is interpreted.
+ |
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+Optional ConfigProto proto used to configure the session, which is
+passed as-is to create the session.
+ |
+
+|
+`wait_for_checkpoint`
+ |
+
+Whether we should wait for the availability of a
+checkpoint before creating Session. Defaults to False.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_wait_secs`
+ |
+
+Maximum time to wait for the session to become available.
+ |
+
+|
+`start_standard_services`
+ |
+
+Whether to start the standard services and the
+queue runners.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A Session object that can be used to drive the model.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+request_stop
+
+View source
+
+
+request_stop(
+ ex=None
+)
+
+
+Request that the coordinator stop the threads.
+
+See `Coordinator.request_stop()`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ex`
+ |
+
+Optional `Exception`, or Python `exc_info` tuple as returned by
+`sys.exc_info()`. If this is the first call to `request_stop()` the
+corresponding exception is recorded and re-raised from `join()`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+should_stop
+
+View source
+
+
+should_stop()
+
+
+Check if the coordinator was told to stop.
+
+See `Coordinator.should_stop()`.
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+True if the coordinator was told to stop, False otherwise.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+start_queue_runners
+
+View source
+
+
+start_queue_runners(
+ sess, queue_runners=None
+)
+
+
+Start threads for `QueueRunners`.
+
+Note that the queue runners collected in the graph key `QUEUE_RUNNERS`
+are already started automatically when you create a session with the
+supervisor, so unless you have non-collected queue runners to start
+you do not need to call this explicitly.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sess`
+ |
+
+A `Session`.
+ |
+
+|
+`queue_runners`
+ |
+
+A list of `QueueRunners`. If not specified, we'll use the
+list of queue runners gathered in the graph under the key
+`GraphKeys.QUEUE_RUNNERS`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The list of threads started for the `QueueRunners`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If called with eager execution enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+Queues are not compatible with eager execution. To ingest data when eager
+execution is enabled, use the tf.data API.
+
+
+
+start_standard_services
+
+View source
+
+
+start_standard_services(
+ sess
+)
+
+
+Start the standard services for 'sess'.
+
+This starts services in the background. The services started depend
+on the parameters to the constructor and may include:
+
+ - A Summary thread computing summaries every save_summaries_secs.
+ - A Checkpoint thread saving the model every save_model_secs.
+ - A StepCounter thread measure step time.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sess`
+ |
+
+A Session.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+A list of threads that are running the standard services. You can use
+the Supervisor's Coordinator to join these threads with:
+sv.coord.Join()
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If called with a non-chief Supervisor.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If not `logdir` was passed to the constructor as the
+services need a log directory.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+stop
+
+View source
+
+
+stop(
+ threads=None, close_summary_writer=(True), ignore_live_threads=(False)
+)
+
+
+Stop the services and the coordinator.
+
+This does not close the session.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`threads`
+ |
+
+Optional list of threads to join with the coordinator. If
+`None`, defaults to the threads running the standard services, the
+threads started for `QueueRunners`, and the threads started by the
+`loop()` method. To wait on additional threads, pass the list in this
+parameter.
+ |
+
+|
+`close_summary_writer`
+ |
+
+Whether to close the `summary_writer`. Defaults to
+`True` if the summary writer was created by the supervisor, `False`
+otherwise.
+ |
+
+|
+`ignore_live_threads`
+ |
+
+If `True` ignores threads that remain running after a
+grace period when joining threads via the coordinator, instead of
+raising a RuntimeError.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+stop_on_exception
+
+View source
+
+
+stop_on_exception()
+
+
+Context handler to stop the supervisor when an exception is raised.
+
+See `Coordinator.stop_on_exception()`.
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A context handler.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+summary_computed
+
+View source
+
+
+summary_computed(
+ sess, summary, global_step=None
+)
+
+
+Indicate that a summary was computed.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sess`
+ |
+
+A `Session` object.
+ |
+
+|
+`summary`
+ |
+
+A Summary proto, or a string holding a serialized summary proto.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Int. global step this summary is associated with. If `None`,
+it will try to fetch the current step.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+if 'summary' is not a Summary proto or a string.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+if the Supervisor was created without a `logdir`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+wait_for_stop
+
+View source
+
+
+wait_for_stop()
+
+
+Block waiting for the coordinator to stop.
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `USE_DEFAULT = 0`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/SyncReplicasOptimizer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/SyncReplicasOptimizer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..7c4bddb1615
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/SyncReplicasOptimizer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,788 @@
+description: Class to synchronize, aggregate gradients and pass them to the optimizer.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.SyncReplicasOptimizer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Class to synchronize, aggregate gradients and pass them to the optimizer.
+
+Inherits From: [`Optimizer`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/train/Optimizer.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.SyncReplicasOptimizer(
+ opt, replicas_to_aggregate, total_num_replicas=None, variable_averages=None,
+ variables_to_average=None, use_locking=(False), name='sync_replicas'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This class is deprecated. For synchronous training, please use [Distribution
+Strategies](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/tree/master/tensorflow/contrib/distribute).
+
+In a typical asynchronous training environment, it's common to have some
+stale gradients. For example, with a N-replica asynchronous training,
+gradients will be applied to the variables N times independently. Depending
+on each replica's training speed, some gradients might be calculated from
+copies of the variable from several steps back (N-1 steps on average). This
+optimizer avoids stale gradients by collecting gradients from all replicas,
+averaging them, then applying them to the variables in one shot, after
+which replicas can fetch the new variables and continue.
+
+The following accumulators/queue are created:
+
+* N `gradient accumulators`, one per variable to train. Gradients are pushed
+ to them and the chief worker will wait until enough gradients are collected
+ and then average them before applying to variables. The accumulator will
+ drop all stale gradients (more details in the accumulator op).
+* 1 `token` queue where the optimizer pushes the new global_step value after
+ all variables are updated.
+
+The following local variable is created:
+* `sync_rep_local_step`, one per replica. Compared against the global_step in
+ each accumulator to check for staleness of the gradients.
+
+The optimizer adds nodes to the graph to collect gradients and pause the
+trainers until variables are updated.
+For the Parameter Server job:
+
+1. An accumulator is created for each variable, and each replica pushes the
+ gradients into the accumulators instead of directly applying them to the
+ variables.
+2. Each accumulator averages once enough gradients (replicas_to_aggregate)
+ have been accumulated.
+3. Apply the averaged gradients to the variables.
+4. Only after all variables have been updated, increment the global step.
+5. Only after step 4, pushes `global_step` in the `token_queue`, once for
+ each worker replica. The workers can now fetch the global step, use it to
+ update its local_step variable and start the next batch. Please note that
+ some workers can consume multiple minibatches, while some may not consume
+ even one. This is because each worker fetches minibatches as long as
+ a token exists. If one worker is stuck for some reason and does not
+ consume a token, another worker can use it.
+
+#### For the replicas:
+
+
+
+1. Start a step: fetch variables and compute gradients.
+2. Once the gradients have been computed, push them into gradient
+ accumulators. Each accumulator will check the staleness and drop the stale.
+3. After pushing all the gradients, dequeue an updated value of global_step
+ from the token queue and record that step to its local_step variable. Note
+ that this is effectively a barrier.
+4. Start the next batch.
+
+### Usage
+
+```python
+# Create any optimizer to update the variables, say a simple SGD:
+opt = GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.1)
+
+# Wrap the optimizer with sync_replicas_optimizer with 50 replicas: at each
+# step the optimizer collects 50 gradients before applying to variables.
+# Note that if you want to have 2 backup replicas, you can change
+# total_num_replicas=52 and make sure this number matches how many physical
+# replicas you started in your job.
+opt = tf.compat.v1.train.SyncReplicasOptimizer(opt, replicas_to_aggregate=50,
+ total_num_replicas=50)
+
+# Some models have startup_delays to help stabilize the model but when using
+# sync_replicas training, set it to 0.
+
+# Now you can call `minimize()` or `compute_gradients()` and
+# `apply_gradients()` normally
+training_op = opt.minimize(total_loss, global_step=self.global_step)
+
+
+# You can create the hook which handles initialization and queues.
+sync_replicas_hook = opt.make_session_run_hook(is_chief)
+```
+
+In the training program, every worker will run the train_op as if not
+synchronized.
+
+```python
+with training.MonitoredTrainingSession(
+ master=workers[worker_id].target, is_chief=is_chief,
+ hooks=[sync_replicas_hook]) as mon_sess:
+ while not mon_sess.should_stop():
+ mon_sess.run(training_op)
+```
+
+To use SyncReplicasOptimizer with an `Estimator`, you need to send
+sync_replicas_hook while calling the fit.
+```python
+my_estimator = DNNClassifier(..., optimizer=opt)
+my_estimator.fit(..., hooks=[sync_replicas_hook])
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`opt`
+ |
+
+The actual optimizer that will be used to compute and apply the
+gradients. Must be one of the Optimizer classes.
+ |
+
+|
+`replicas_to_aggregate`
+ |
+
+number of replicas to aggregate for each variable
+update.
+ |
+
+|
+`total_num_replicas`
+ |
+
+Total number of tasks/workers/replicas, could be
+different from replicas_to_aggregate.
+If total_num_replicas > replicas_to_aggregate: it is backup_replicas +
+replicas_to_aggregate.
+If total_num_replicas < replicas_to_aggregate: Replicas compute
+multiple batches per update to variables.
+ |
+
+|
+`variable_averages`
+ |
+
+Optional `ExponentialMovingAverage` object, used to
+maintain moving averages for the variables passed in
+`variables_to_average`.
+ |
+
+|
+`variables_to_average`
+ |
+
+a list of variables that need to be averaged. Only
+needed if variable_averages is passed in.
+ |
+
+|
+`use_locking`
+ |
+
+If True use locks for update operation.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+string. Optional name of the returned operation.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+apply_gradients
+
+View source
+
+
+apply_gradients(
+ grads_and_vars, global_step=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+Apply gradients to variables.
+
+This contains most of the synchronization implementation and also wraps the
+apply_gradients() from the real optimizer.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`grads_and_vars`
+ |
+
+List of (gradient, variable) pairs as returned by
+compute_gradients().
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Optional Variable to increment by one after the
+variables have been updated.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the returned operation. Default to the
+name passed to the Optimizer constructor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`train_op`
+ |
+
+The op to dequeue a token so the replicas can exit this batch
+and start the next one. This is executed by each replica.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the grads_and_vars is empty.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If global step is not provided, the staleness cannot be
+checked.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+compute_gradients
+
+View source
+
+
+compute_gradients(
+ *args, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+Compute gradients of "loss" for the variables in "var_list".
+
+This simply wraps the compute_gradients() from the real optimizer. The
+gradients will be aggregated in the apply_gradients() so that user can
+modify the gradients like clipping with per replica global norm if needed.
+The global norm with aggregated gradients can be bad as one replica's huge
+gradients can hurt the gradients from other replicas.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`*args`
+ |
+
+Arguments for compute_gradients().
+ |
+
+|
+`**kwargs`
+ |
+
+Keyword arguments for compute_gradients().
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of (gradient, variable) pairs.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_chief_queue_runner
+
+View source
+
+
+get_chief_queue_runner()
+
+
+Returns the QueueRunner for the chief to execute.
+
+This includes the operations to synchronize replicas: aggregate gradients,
+apply to variables, increment global step, insert tokens to token queue.
+
+Note that this can only be called after calling apply_gradients() which
+actually generates this queuerunner.
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `QueueRunner` for chief to execute.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If this is called before apply_gradients().
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+get_init_tokens_op
+
+View source
+
+
+get_init_tokens_op(
+ num_tokens=-1
+)
+
+
+Returns the op to fill the sync_token_queue with the tokens.
+
+This is supposed to be executed in the beginning of the chief/sync thread
+so that even if the total_num_replicas is less than replicas_to_aggregate,
+the model can still proceed as the replicas can compute multiple steps per
+variable update. Make sure:
+`num_tokens >= replicas_to_aggregate - total_num_replicas`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`num_tokens`
+ |
+
+Number of tokens to add to the queue.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An op for the chief/sync replica to fill the token queue.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If this is called before apply_gradients().
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If num_tokens are smaller than replicas_to_aggregate -
+total_num_replicas.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+get_name
+
+View source
+
+
+get_name()
+
+
+
+
+
+get_slot
+
+View source
+
+
+get_slot(
+ *args, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+Return a slot named "name" created for "var" by the Optimizer.
+
+This simply wraps the get_slot() from the actual optimizer.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`*args`
+ |
+
+Arguments for get_slot().
+ |
+
+|
+`**kwargs`
+ |
+
+Keyword arguments for get_slot().
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The `Variable` for the slot if it was created, `None` otherwise.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_slot_names
+
+View source
+
+
+get_slot_names(
+ *args, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+Return a list of the names of slots created by the `Optimizer`.
+
+This simply wraps the get_slot_names() from the actual optimizer.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`*args`
+ |
+
+Arguments for get_slot().
+ |
+
+|
+`**kwargs`
+ |
+
+Keyword arguments for get_slot().
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of strings.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+make_session_run_hook
+
+View source
+
+
+make_session_run_hook(
+ is_chief, num_tokens=-1
+)
+
+
+Creates a hook to handle SyncReplicasHook ops such as initialization.
+
+
+minimize
+
+View source
+
+
+minimize(
+ loss, global_step=None, var_list=None, gate_gradients=GATE_OP,
+ aggregation_method=None, colocate_gradients_with_ops=(False), name=None,
+ grad_loss=None
+)
+
+
+Add operations to minimize `loss` by updating `var_list`.
+
+This method simply combines calls `compute_gradients()` and
+`apply_gradients()`. If you want to process the gradient before applying
+them call `compute_gradients()` and `apply_gradients()` explicitly instead
+of using this function.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`loss`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` containing the value to minimize.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Optional `Variable` to increment by one after the
+variables have been updated.
+ |
+
+|
+`var_list`
+ |
+
+Optional list or tuple of `Variable` objects to update to
+minimize `loss`. Defaults to the list of variables collected in
+the graph under the key `GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES`.
+ |
+
+|
+`gate_gradients`
+ |
+
+How to gate the computation of gradients. Can be
+`GATE_NONE`, `GATE_OP`, or `GATE_GRAPH`.
+ |
+
+|
+`aggregation_method`
+ |
+
+Specifies the method used to combine gradient terms.
+Valid values are defined in the class `AggregationMethod`.
+ |
+
+|
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops`
+ |
+
+If True, try colocating gradients with
+the corresponding op.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the returned operation.
+ |
+
+|
+`grad_loss`
+ |
+
+Optional. A `Tensor` holding the gradient computed for `loss`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Operation that updates the variables in `var_list`. If `global_step`
+was not `None`, that operation also increments `global_step`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If some of the variables are not `Variable` objects.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+When eager execution is enabled, `loss` should be a Python function that
+takes no arguments and computes the value to be minimized. Minimization (and
+gradient computation) is done with respect to the elements of `var_list` if
+not None, else with respect to any trainable variables created during the
+execution of the `loss` function. `gate_gradients`, `aggregation_method`,
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops` and `grad_loss` are ignored when eager
+execution is enabled.
+
+
+
+variables
+
+View source
+
+
+variables()
+
+
+Fetches a list of optimizer variables in the default graph.
+
+This wraps `variables()` from the actual optimizer. It does not include
+the `SyncReplicasOptimizer`'s local step.
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of variables.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `GATE_GRAPH = 2`
+* `GATE_NONE = 0`
+* `GATE_OP = 1`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/WorkerSessionCreator.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/WorkerSessionCreator.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e6c773827c3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/WorkerSessionCreator.md
@@ -0,0 +1,93 @@
+description: Creates a tf.compat.v1.Session for a worker.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.WorkerSessionCreator
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Creates a tf.compat.v1.Session for a worker.
+
+Inherits From: [`SessionCreator`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/train/SessionCreator.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.WorkerSessionCreator(
+ scaffold=None, master='', config=None, max_wait_secs=(30 * 60)
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`scaffold`
+ |
+
+A `Scaffold` used for gathering or building supportive ops. If
+not specified a default one is created. It's used to finalize the graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`master`
+ |
+
+`String` representation of the TensorFlow master to use.
+ |
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+`ConfigProto` proto used to configure the session.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_wait_secs`
+ |
+
+Maximum time to wait for the session to become available.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+create_session
+
+View source
+
+
+create_session()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/add_queue_runner.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/add_queue_runner.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..9a048981bc0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/add_queue_runner.md
@@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
+description: Adds a QueueRunner to a collection in the graph. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.add_queue_runner
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Adds a `QueueRunner` to a collection in the graph. (deprecated)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.train.queue_runner.add_queue_runner`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.add_queue_runner(
+ qr, collection=tf.GraphKeys.QUEUE_RUNNERS
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+To construct input pipelines, use the tf.data module.
+
+When building a complex model that uses many queues it is often difficult to
+gather all the queue runners that need to be run. This convenience function
+allows you to add a queue runner to a well known collection in the graph.
+
+The companion method `start_queue_runners()` can be used to start threads for
+all the collected queue runners.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`qr`
+ |
+
+A `QueueRunner`.
+ |
+
+|
+`collection`
+ |
+
+A `GraphKey` specifying the graph collection to add
+the queue runner to. Defaults to `GraphKeys.QUEUE_RUNNERS`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/assert_global_step.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/assert_global_step.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..1bb9c01a2a0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/assert_global_step.md
@@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
+description: Asserts global_step_tensor is a scalar int Variable or Tensor.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.assert_global_step
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Asserts `global_step_tensor` is a scalar int `Variable` or `Tensor`.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.assert_global_step(
+ global_step_tensor
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`global_step_tensor`
+ |
+
+`Tensor` to test.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/basic_train_loop.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/basic_train_loop.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..5b6dabf728f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/basic_train_loop.md
@@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
+description: Basic loop to train a model.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.basic_train_loop
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Basic loop to train a model.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.basic_train_loop(
+ supervisor, train_step_fn, args=None, kwargs=None, master=''
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Calls `train_step_fn` in a loop to train a model. The function is called as:
+
+```python
+train_step_fn(session, *args, **kwargs)
+```
+
+It is passed a tf.compat.v1.Session in addition to `args` and `kwargs`. The
+function
+typically runs one training step in the session.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`supervisor`
+ |
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.Supervisor to run the training services.
+ |
+
+|
+`train_step_fn`
+ |
+
+Callable to execute one training step. Called repeatedly as
+`train_step_fn(session, *args **kwargs)`.
+ |
+
+|
+`args`
+ |
+
+Optional positional arguments passed to `train_step_fn`.
+ |
+
+|
+`kwargs`
+ |
+
+Optional keyword arguments passed to `train_step_fn`.
+ |
+
+|
+`master`
+ |
+
+Master to use to create the training session. Defaults to `""`
+which causes the session to be created in the local process.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/batch.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/batch.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e798a9e2cba
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/batch.md
@@ -0,0 +1,208 @@
+description: Creates batches of tensors in tensors. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.batch
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Creates batches of tensors in `tensors`. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.batch(
+ tensors, batch_size, num_threads=1, capacity=32, enqueue_many=(False),
+ shapes=None, dynamic_pad=(False), allow_smaller_final_batch=(False),
+ shared_name=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Queue-based input pipelines have been replaced by tf.data. Use tf.data.Dataset.batch(batch_size) (or `padded_batch(...)` if `dynamic_pad=True`).
+
+The argument `tensors` can be a list or a dictionary of tensors.
+The value returned by the function will be of the same type
+as `tensors`.
+
+This function is implemented using a queue. A `QueueRunner` for the
+queue is added to the current `Graph`'s `QUEUE_RUNNER` collection.
+
+If `enqueue_many` is `False`, `tensors` is assumed to represent a single
+example. An input tensor with shape `[x, y, z]` will be output as a tensor
+with shape `[batch_size, x, y, z]`.
+
+If `enqueue_many` is `True`, `tensors` is assumed to represent a batch of
+examples, where the first dimension is indexed by example, and all members of
+`tensors` should have the same size in the first dimension. If an input
+tensor has shape `[*, x, y, z]`, the output will have shape `[batch_size, x,
+y, z]`. The `capacity` argument controls the how long the prefetching is
+allowed to grow the queues.
+
+The returned operation is a dequeue operation and will throw
+tf.errors.OutOfRangeError if the input queue is exhausted. If this
+operation is feeding another input queue, its queue runner will catch
+this exception, however, if this operation is used in your main thread
+you are responsible for catching this yourself.
+
+*N.B.:* If `dynamic_pad` is `False`, you must ensure that either
+(i) the `shapes` argument is passed, or (ii) all of the tensors in
+`tensors` must have fully-defined shapes. `ValueError` will be
+raised if neither of these conditions holds.
+
+If `dynamic_pad` is `True`, it is sufficient that the *rank* of the
+tensors is known, but individual dimensions may have shape `None`.
+In this case, for each enqueue the dimensions with value `None`
+may have a variable length; upon dequeue, the output tensors will be padded
+on the right to the maximum shape of the tensors in the current minibatch.
+For numbers, this padding takes value 0. For strings, this padding is
+the empty string. See `PaddingFIFOQueue` for more info.
+
+If `allow_smaller_final_batch` is `True`, a smaller batch value than
+`batch_size` is returned when the queue is closed and there are not enough
+elements to fill the batch, otherwise the pending elements are discarded.
+In addition, all output tensors' static shapes, as accessed via the
+`shape` property will have a first `Dimension` value of `None`, and
+operations that depend on fixed batch_size would fail.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`tensors`
+ |
+
+The list or dictionary of tensors to enqueue.
+ |
+
+|
+`batch_size`
+ |
+
+The new batch size pulled from the queue.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_threads`
+ |
+
+The number of threads enqueuing `tensors`. The batching will
+be nondeterministic if `num_threads > 1`.
+ |
+
+|
+`capacity`
+ |
+
+An integer. The maximum number of elements in the queue.
+ |
+
+|
+`enqueue_many`
+ |
+
+Whether each tensor in `tensors` is a single example.
+ |
+
+|
+`shapes`
+ |
+
+(Optional) The shapes for each example. Defaults to the
+inferred shapes for `tensors`.
+ |
+
+|
+`dynamic_pad`
+ |
+
+Boolean. Allow variable dimensions in input shapes.
+The given dimensions are padded upon dequeue so that tensors within a
+batch have the same shapes.
+ |
+
+|
+`allow_smaller_final_batch`
+ |
+
+(Optional) Boolean. If `True`, allow the final
+batch to be smaller if there are insufficient items left in the queue.
+ |
+
+|
+`shared_name`
+ |
+
+(Optional). If set, this queue will be shared under the given
+name across multiple sessions.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+(Optional) A name for the operations.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list or dictionary of tensors with the same types as `tensors` (except if
+the input is a list of one element, then it returns a tensor, not a list).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `shapes` are not specified, and cannot be
+inferred from the elements of `tensors`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+Input pipelines based on Queues are not supported when eager execution is
+enabled. Please use the tf.data API to ingest data under eager execution.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/batch_join.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/batch_join.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..dfc9dcf5890
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/batch_join.md
@@ -0,0 +1,214 @@
+description: Runs a list of tensors to fill a queue to create batches of examples. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.batch_join
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Runs a list of tensors to fill a queue to create batches of examples. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.batch_join(
+ tensors_list, batch_size, capacity=32, enqueue_many=(False), shapes=None,
+ dynamic_pad=(False), allow_smaller_final_batch=(False), shared_name=None,
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Queue-based input pipelines have been replaced by tf.data. Use `tf.data.Dataset.interleave(...).batch(batch_size)` (or `padded_batch(...)` if `dynamic_pad=True`).
+
+The `tensors_list` argument is a list of tuples of tensors, or a list of
+dictionaries of tensors. Each element in the list is treated similarly
+to the `tensors` argument of tf.compat.v1.train.batch().
+
+WARNING: This function is nondeterministic, since it starts a separate thread
+for each tensor.
+
+Enqueues a different list of tensors in different threads.
+Implemented using a queue -- a `QueueRunner` for the queue
+is added to the current `Graph`'s `QUEUE_RUNNER` collection.
+
+`len(tensors_list)` threads will be started,
+with thread `i` enqueuing the tensors from
+`tensors_list[i]`. `tensors_list[i1][j]` must match
+`tensors_list[i2][j]` in type and shape, except in the first
+dimension if `enqueue_many` is true.
+
+If `enqueue_many` is `False`, each `tensors_list[i]` is assumed
+to represent a single example. An input tensor `x` will be output as a
+tensor with shape `[batch_size] + x.shape`.
+
+If `enqueue_many` is `True`, `tensors_list[i]` is assumed to
+represent a batch of examples, where the first dimension is indexed
+by example, and all members of `tensors_list[i]` should have the
+same size in the first dimension. The slices of any input tensor
+`x` are treated as examples, and the output tensors will have shape
+`[batch_size] + x.shape[1:]`.
+
+The `capacity` argument controls the how long the prefetching is allowed to
+grow the queues.
+
+The returned operation is a dequeue operation and will throw
+tf.errors.OutOfRangeError if the input queue is exhausted. If this
+operation is feeding another input queue, its queue runner will catch
+this exception, however, if this operation is used in your main thread
+you are responsible for catching this yourself.
+
+*N.B.:* If `dynamic_pad` is `False`, you must ensure that either
+(i) the `shapes` argument is passed, or (ii) all of the tensors in
+`tensors_list` must have fully-defined shapes. `ValueError` will be
+raised if neither of these conditions holds.
+
+If `dynamic_pad` is `True`, it is sufficient that the *rank* of the
+tensors is known, but individual dimensions may have value `None`.
+In this case, for each enqueue the dimensions with value `None`
+may have a variable length; upon dequeue, the output tensors will be padded
+on the right to the maximum shape of the tensors in the current minibatch.
+For numbers, this padding takes value 0. For strings, this padding is
+the empty string. See `PaddingFIFOQueue` for more info.
+
+If `allow_smaller_final_batch` is `True`, a smaller batch value than
+`batch_size` is returned when the queue is closed and there are not enough
+elements to fill the batch, otherwise the pending elements are discarded.
+In addition, all output tensors' static shapes, as accessed via the
+`shape` property will have a first `Dimension` value of `None`, and
+operations that depend on fixed batch_size would fail.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`tensors_list`
+ |
+
+A list of tuples or dictionaries of tensors to enqueue.
+ |
+
+|
+`batch_size`
+ |
+
+An integer. The new batch size pulled from the queue.
+ |
+
+|
+`capacity`
+ |
+
+An integer. The maximum number of elements in the queue.
+ |
+
+|
+`enqueue_many`
+ |
+
+Whether each tensor in `tensor_list_list` is a single
+example.
+ |
+
+|
+`shapes`
+ |
+
+(Optional) The shapes for each example. Defaults to the
+inferred shapes for `tensor_list_list[i]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`dynamic_pad`
+ |
+
+Boolean. Allow variable dimensions in input shapes.
+The given dimensions are padded upon dequeue so that tensors within a
+batch have the same shapes.
+ |
+
+|
+`allow_smaller_final_batch`
+ |
+
+(Optional) Boolean. If `True`, allow the final
+batch to be smaller if there are insufficient items left in the queue.
+ |
+
+|
+`shared_name`
+ |
+
+(Optional) If set, this queue will be shared under the given
+name across multiple sessions.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+(Optional) A name for the operations.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list or dictionary of tensors with the same number and types as
+`tensors_list[i]`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `shapes` are not specified, and cannot be
+inferred from the elements of `tensor_list_list`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+Input pipelines based on Queues are not supported when eager execution is
+enabled. Please use the tf.data API to ingest data under eager execution.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/checkpoint_exists.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/checkpoint_exists.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..f39c286e9f9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/checkpoint_exists.md
@@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
+description: Checks whether a V1 or V2 checkpoint exists with the specified prefix. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.checkpoint_exists
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Checks whether a V1 or V2 checkpoint exists with the specified prefix. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.checkpoint_exists(
+ checkpoint_prefix
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use standard file APIs to check for files with this prefix.
+
+This is the recommended way to check if a checkpoint exists, since it takes
+into account the naming difference between V1 and V2 formats.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`checkpoint_prefix`
+ |
+
+the prefix of a V1 or V2 checkpoint, with V2 taking
+priority. Typically the result of `Saver.save()` or that of
+tf.train.latest_checkpoint(), regardless of sharded/non-sharded or
+V1/V2.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A bool, true if a checkpoint referred to by `checkpoint_prefix` exists.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/cosine_decay.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/cosine_decay.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..1a32af9281a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/cosine_decay.md
@@ -0,0 +1,152 @@
+description: Applies cosine decay to the learning rate.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.cosine_decay
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Applies cosine decay to the learning rate.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.cosine_decay(
+ learning_rate, global_step, decay_steps, alpha=0.0, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+When training a model, it is often recommended to lower the learning rate as
+the training progresses. This function applies a cosine decay function
+to a provided initial learning rate. It requires a `global_step` value to
+compute the decayed learning rate. You can just pass a TensorFlow variable
+that you increment at each training step.
+
+The function returns the decayed learning rate. It is computed as:
+```python
+global_step = min(global_step, decay_steps)
+cosine_decay = 0.5 * (1 + cos(pi * global_step / decay_steps))
+decayed = (1 - alpha) * cosine_decay + alpha
+decayed_learning_rate = learning_rate * decayed
+```
+
+#### Example usage:
+
+
+```python
+decay_steps = 1000
+lr_decayed = cosine_decay(learning_rate, global_step, decay_steps)
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`learning_rate`
+ |
+
+A scalar `float32` or `float64` Tensor or a Python number.
+The initial learning rate.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+A scalar `int32` or `int64` `Tensor` or a Python number. Global
+step to use for the decay computation.
+ |
+
+|
+`decay_steps`
+ |
+
+A scalar `int32` or `int64` `Tensor` or a Python number. Number
+of steps to decay over.
+ |
+
+|
+`alpha`
+ |
+
+A scalar `float32` or `float64` Tensor or a Python number. Minimum
+learning rate value as a fraction of learning_rate.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+String. Optional name of the operation. Defaults to 'CosineDecay'.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A scalar `Tensor` of the same type as `learning_rate`. The decayed
+learning rate.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `global_step` is not supplied.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### References:
+
+Stochastic Gradient Descent with Warm Restarts:
+ [Loshchilov et al., 2017]
+ (https://openreview.net/forum?id=Skq89Scxx¬eId=Skq89Scxx)
+ ([pdf](https://openreview.net/pdf?id=Skq89Scxx))
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+When eager execution is enabled, this function returns a function which in
+turn returns the decayed learning rate Tensor. This can be useful for changing
+the learning rate value across different invocations of optimizer functions.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/cosine_decay_restarts.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/cosine_decay_restarts.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..34161f060c6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/cosine_decay_restarts.md
@@ -0,0 +1,168 @@
+description: Applies cosine decay with restarts to the learning rate.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.cosine_decay_restarts
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Applies cosine decay with restarts to the learning rate.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.cosine_decay_restarts(
+ learning_rate, global_step, first_decay_steps, t_mul=2.0, m_mul=1.0, alpha=0.0,
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+When training a model, it is often recommended to lower the learning rate as
+the training progresses. This function applies a cosine decay function with
+restarts to a provided initial learning rate. It requires a `global_step`
+value to compute the decayed learning rate. You can just pass a TensorFlow
+variable that you increment at each training step.
+
+The function returns the decayed learning rate while taking into account
+possible warm restarts. The learning rate multiplier first decays
+from 1 to `alpha` for `first_decay_steps` steps. Then, a warm
+restart is performed. Each new warm restart runs for `t_mul` times more steps
+and with `m_mul` times smaller initial learning rate.
+
+#### Example usage:
+
+
+```python
+first_decay_steps = 1000
+lr_decayed = cosine_decay_restarts(learning_rate, global_step,
+ first_decay_steps)
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`learning_rate`
+ |
+
+A scalar `float32` or `float64` Tensor or a Python number.
+The initial learning rate.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+A scalar `int32` or `int64` `Tensor` or a Python number. Global
+step to use for the decay computation.
+ |
+
+|
+`first_decay_steps`
+ |
+
+A scalar `int32` or `int64` `Tensor` or a Python number.
+Number of steps to decay over.
+ |
+
+|
+`t_mul`
+ |
+
+A scalar `float32` or `float64` `Tensor` or a Python number. Used to
+derive the number of iterations in the i-th period
+ |
+
+|
+`m_mul`
+ |
+
+A scalar `float32` or `float64` `Tensor` or a Python number.
+Used to derive the initial learning rate of the i-th period:
+ |
+
+|
+`alpha`
+ |
+
+A scalar `float32` or `float64` Tensor or a Python number. Minimum
+learning rate value as a fraction of the learning_rate.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+String. Optional name of the operation. Defaults to 'SGDRDecay'.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A scalar `Tensor` of the same type as `learning_rate`. The decayed
+learning rate.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `global_step` is not supplied.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### References:
+
+Stochastic Gradient Descent with Warm Restarts:
+ [Loshchilov et al., 2017]
+ (https://openreview.net/forum?id=Skq89Scxx¬eId=Skq89Scxx)
+ ([pdf](https://openreview.net/pdf?id=Skq89Scxx))
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+When eager execution is enabled, this function returns a function which in
+turn returns the decayed learning rate Tensor. This can be useful for changing
+the learning rate value across different invocations of optimizer functions.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/create_global_step.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/create_global_step.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..55588ac7842
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/create_global_step.md
@@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
+description: Create global step tensor in graph.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.create_global_step
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Create global step tensor in graph.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.create_global_step(
+ graph=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+The graph in which to create the global step tensor. If missing, use
+default graph.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Global step tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if global step tensor is already defined.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/do_quantize_training_on_graphdef.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/do_quantize_training_on_graphdef.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..52a7b3b3d01
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/do_quantize_training_on_graphdef.md
@@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
+description: A general quantization scheme is being developed in tf.contrib.quantize. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.do_quantize_training_on_graphdef
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A general quantization scheme is being developed in `tf.contrib.quantize`. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.do_quantize_training_on_graphdef(
+ input_graph, num_bits
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+GraphDef quantized training rewriter is deprecated in the long term.
+
+Consider using that instead, though since it is in the tf.contrib namespace,
+it is not subject to backward compatibility guarantees.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_graph`
+ |
+
+A `GraphDef`.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_bits`
+ |
+
+The number of bits for quantize training.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The graph with quantize training done.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/experimental.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/experimental.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..91fdb852300
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/experimental.md
@@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
+description: Public API for tf.train.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.train.experimental
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.train.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class DynamicLossScale`](../../../../tf/mixed_precision/experimental/DynamicLossScale.md): Loss scale that dynamically adjusts itself.
+
+[`class FixedLossScale`](../../../../tf/mixed_precision/experimental/FixedLossScale.md): Loss scale with a fixed value.
+
+[`class LossScale`](../../../../tf/mixed_precision/experimental/LossScale.md): Base class for all loss scales.
+
+[`class MixedPrecisionLossScaleOptimizer`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/train/experimental/MixedPrecisionLossScaleOptimizer.md): An optimizer that applies loss scaling.
+
+[`class PythonState`](../../../../tf/train/experimental/PythonState.md): A mixin for putting Python state in an object-based checkpoint.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`disable_mixed_precision_graph_rewrite(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/train/experimental/disable_mixed_precision_graph_rewrite.md): Disables the mixed precision graph rewrite.
+
+[`enable_mixed_precision_graph_rewrite(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/train/experimental/enable_mixed_precision_graph_rewrite.md): Enable mixed precision via a graph rewrite.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/experimental/MixedPrecisionLossScaleOptimizer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/experimental/MixedPrecisionLossScaleOptimizer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..72c1cbc9277
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/experimental/MixedPrecisionLossScaleOptimizer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,555 @@
+description: An optimizer that applies loss scaling.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.experimental.MixedPrecisionLossScaleOptimizer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+An optimizer that applies loss scaling.
+
+Inherits From: [`Optimizer`](../../../../../tf/compat/v1/train/Optimizer.md)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.experimental.MixedPrecisionLossScaleOptimizer(
+ opt, loss_scale
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Loss scaling is a process that multiplies the loss by a multiplier called the
+loss scale, and divides each gradient by the same multiplier. The pseudocode
+for this process is:
+
+```
+loss = ...
+loss *= loss_scale
+grads = gradients(loss, vars)
+grads /= loss_scale
+```
+
+Mathematically, loss scaling has no effect, but can help avoid numerical
+underflow in intermediate gradients when float16 tensors are used for mixed
+precision training. By multiplying the loss, each intermediate gradient will
+have the same multiplier applied.
+
+The loss scale can either be a fixed constant, chosen by the user, or be
+dynamically determined. Dynamically determining the loss scale is convenient
+as a loss scale does not have to be explicitly chosen. However it reduces
+performance.
+
+This optimizer wraps another optimizer and applies loss scaling to it via a
+`LossScale`. Loss scaling is applied whenever gradients are
+computed, such as through `minimize()`.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`use_locking`
+ |
+
+Bool. If True apply use locks to prevent concurrent updates
+to variables.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A non-empty string. The name to use for accumulators created
+for the optimizer.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If name is malformed.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+apply_gradients
+
+View source
+
+
+apply_gradients(
+ grads_and_vars, global_step=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+Apply gradients to variables.
+
+This is the second part of `minimize()`. It returns an `Operation` that
+conditionally applies gradients if all gradient values are finite.
+Otherwise no update is performed (nor is `global_step` incremented).
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`grads_and_vars`
+ |
+
+List of (gradient, variable) pairs as returned by
+`compute_gradients()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Optional `Variable` to increment by one after the variables
+have been updated.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the returned operation. Default to the name
+passed to the `Optimizer` constructor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An `Operation` that conditionally applies the specified gradients. If
+`global_step` was not None, that operation also increments `global_step`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If you should use `_distributed_apply()` instead.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+compute_gradients
+
+View source
+
+
+compute_gradients(
+ loss, var_list=None, gate_gradients=optimizer.Optimizer.GATE_OP,
+ aggregation_method=None, colocate_gradients_with_ops=(False), grad_loss=None
+)
+
+
+Compute gradients of `loss` for the variables in `var_list`.
+
+This adjusts the dynamic range of the gradient evaluation by scaling up
+the `loss` value. The gradient values are then scaled back down by the
+reciprocal of the loss scale. This is useful in reduced precision training
+where small gradient values would otherwise underflow the representable
+range.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`loss`
+ |
+
+A Tensor containing the value to minimize or a callable taking no
+arguments which returns the value to minimize. When eager execution is
+enabled it must be a callable.
+ |
+
+|
+`var_list`
+ |
+
+Optional list or tuple of tf.Variable to update to minimize
+`loss`. Defaults to the list of variables collected in the graph under
+the key `GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES`.
+ |
+
+|
+`gate_gradients`
+ |
+
+How to gate the computation of gradients. Can be
+`GATE_NONE`, `GATE_OP`, or `GATE_GRAPH`.
+ |
+
+|
+`aggregation_method`
+ |
+
+Specifies the method used to combine gradient terms.
+Valid values are defined in the class `AggregationMethod`.
+ |
+
+|
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops`
+ |
+
+If True, try colocating gradients with the
+corresponding op.
+ |
+
+|
+`grad_loss`
+ |
+
+Optional. A `Tensor` holding the gradient computed for `loss`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of (gradient, variable) pairs. Variable is always present, but
+gradient can be `None`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_name
+
+View source
+
+
+get_name()
+
+
+
+
+
+get_slot
+
+View source
+
+
+get_slot(
+ var, name
+)
+
+
+Return a slot named `name` created for `var` by the Optimizer.
+
+Some `Optimizer` subclasses use additional variables. For example
+`Momentum` and `Adagrad` use variables to accumulate updates. This method
+gives access to these `Variable` objects if for some reason you need them.
+
+Use `get_slot_names()` to get the list of slot names created by the
+`Optimizer`.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`var`
+ |
+
+A variable passed to `minimize()` or `apply_gradients()`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The `Variable` for the slot if it was created, `None` otherwise.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_slot_names
+
+View source
+
+
+get_slot_names()
+
+
+Return a list of the names of slots created by the `Optimizer`.
+
+See `get_slot()`.
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of strings.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+minimize
+
+View source
+
+
+minimize(
+ loss, global_step=None, var_list=None, gate_gradients=GATE_OP,
+ aggregation_method=None, colocate_gradients_with_ops=(False), name=None,
+ grad_loss=None
+)
+
+
+Add operations to minimize `loss` by updating `var_list`.
+
+This method simply combines calls `compute_gradients()` and
+`apply_gradients()`. If you want to process the gradient before applying
+them call `compute_gradients()` and `apply_gradients()` explicitly instead
+of using this function.
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`loss`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` containing the value to minimize.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+Optional `Variable` to increment by one after the
+variables have been updated.
+ |
+
+|
+`var_list`
+ |
+
+Optional list or tuple of `Variable` objects to update to
+minimize `loss`. Defaults to the list of variables collected in
+the graph under the key `GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES`.
+ |
+
+|
+`gate_gradients`
+ |
+
+How to gate the computation of gradients. Can be
+`GATE_NONE`, `GATE_OP`, or `GATE_GRAPH`.
+ |
+
+|
+`aggregation_method`
+ |
+
+Specifies the method used to combine gradient terms.
+Valid values are defined in the class `AggregationMethod`.
+ |
+
+|
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops`
+ |
+
+If True, try colocating gradients with
+the corresponding op.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the returned operation.
+ |
+
+|
+`grad_loss`
+ |
+
+Optional. A `Tensor` holding the gradient computed for `loss`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Operation that updates the variables in `var_list`. If `global_step`
+was not `None`, that operation also increments `global_step`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If some of the variables are not `Variable` objects.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+When eager execution is enabled, `loss` should be a Python function that
+takes no arguments and computes the value to be minimized. Minimization (and
+gradient computation) is done with respect to the elements of `var_list` if
+not None, else with respect to any trainable variables created during the
+execution of the `loss` function. `gate_gradients`, `aggregation_method`,
+`colocate_gradients_with_ops` and `grad_loss` are ignored when eager
+execution is enabled.
+
+
+
+variables
+
+View source
+
+
+variables()
+
+
+A list of variables which encode the current state of `Optimizer`.
+
+Includes slot variables and additional global variables created by the
+optimizer in the current default graph.
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of variables.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `GATE_GRAPH = 2`
+* `GATE_NONE = 0`
+* `GATE_OP = 1`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/experimental/disable_mixed_precision_graph_rewrite.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/experimental/disable_mixed_precision_graph_rewrite.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..1160add5ee6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/experimental/disable_mixed_precision_graph_rewrite.md
@@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
+description: Disables the mixed precision graph rewrite.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.experimental.disable_mixed_precision_graph_rewrite
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Disables the mixed precision graph rewrite.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.experimental.disable_mixed_precision_graph_rewrite()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+After this is called, the mixed precision graph rewrite will no longer run for
+new Sessions, and so float32 operations will no longer be converted to float16
+in such Sessions. However, any existing Sessions will continue to have the
+graph rewrite enabled if they were created after
+`enable_mixed_precision_graph_rewrite` was called but before
+`disable_mixed_precision_graph_rewrite` was called.
+
+This does not undo the effects of loss scaling. Any optimizers wrapped with a
+LossScaleOptimizer will continue to do loss scaling, although this loss
+scaling will no longer be useful if the optimizer is used in new Sessions, as
+the graph rewrite no longer converts the graph to use float16.
+
+This function is useful for unit testing. A unit tests can test using the
+mixed precision graph rewrite, then disable it so future unit tests continue
+using float32. If this is done, unit tests should not share a single session,
+as `enable_mixed_precision_graph_rewrite` and
+`disable_mixed_precision_graph_rewrite` have no effect on existing sessions.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/experimental/enable_mixed_precision_graph_rewrite.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/experimental/enable_mixed_precision_graph_rewrite.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..c890522da69
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/experimental/enable_mixed_precision_graph_rewrite.md
@@ -0,0 +1,179 @@
+description: Enable mixed precision via a graph rewrite.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.experimental.enable_mixed_precision_graph_rewrite
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Enable mixed precision via a graph rewrite.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.experimental.enable_mixed_precision_graph_rewrite(
+ opt, loss_scale='dynamic'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Mixed precision is the use of both float32 and float16 data types when
+training a model to improve performance. This is achieved via a graph rewrite
+operation and a loss-scale optimizer.
+
+Performing arithmetic operations in float16 takes advantage of specialized
+processing units, such as NVIDIA Tensor Cores, for much higher arithmetic
+throughput. However, due to the smaller representable range, performing the
+entire training with float16 can result in gradient underflow, that is, small
+gradient values becoming zeroes. Instead, performing only select arithmetic
+operations in float16 results in higher throughput and decreased training
+time when using compatible hardware accelerators while also reducing memory
+usage, typically without sacrificing model accuracy.
+
+Note: While the mixed precision rewrite changes the datatype of various
+layers throughout the model, the same accuracy reached in float32 is
+expected. If a `NaN` gradient occurs with dynamic loss scaling, the model
+update for that batch is skipped. In this case, the global step count is not
+incremented, and the `LossScaleOptimizer` attempts to decrease the loss
+scaling value to avoid `NaN` values in subsequent iterations. This approach
+has been shown to achieve the same accuracy as float32 and, in most cases,
+better training throughput.
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
+ tf.keras.layers.Dense(64, activation='relu'),
+ tf.keras.layers.Dense(64, activation='softmax'),
+])
+
+opt = tf.keras.optimizers.SGD()
+opt = tf.train.experimental.enable_mixed_precision_graph_rewrite(opt)
+model.compile(loss="mse", optimizer=opt)
+
+x_train = np.random.random((1024, 64))
+y_train = np.random.random((1024, 64))
+model.fit(x_train, y_train)
+```
+
+Calling `enable_mixed_precision_graph_rewrite(opt)` enables the graph rewrite
+operation before computing gradients. The function additionally returns an
+`Optimizer` (`opt`) wrapped with a `LossScaleOptimizer`. This prevents
+underflow in the float16 tensors during the backward pass. An optimizer of
+type `tf.train.Optimizer` or tf.keras.optimizers.Optimizer must be passed
+to this function, which will then be wrapped to use loss scaling.
+
+The graph rewrite operation changes the `dtype` of certain operations in the
+graph from float32 to float16. There are several categories of operations
+that are either included or excluded by this rewrite operation. The following
+categories of Ops are defined inside corresponding functions under the class
+`AutoMixedPrecisionLists` in
+
+auto_mixed_precision_lists.h:
+
+* `ClearList`: Ops that do not have numerically significant adverse effects.
+E.g. `ArgMax` and `Floor`.
+* `WhiteList`: Ops that are considered numerically safe for execution in
+float16, and thus are always converted. E.g. `Conv2D`.
+* `BlackList`: Ops that are numerically unsafe to execute in float16 and
+can negatively affect downstream nodes. E.g. `Softmax`.
+* `GrayList`: Ops that are considered numerically safe for execution in
+float16 unless downstream from a BlackList Op. E.g. `Add` and `AvgPool`.
+
+When this function is used, gradients should only be computed and applied
+with the returned optimizer, either by calling `opt.minimize()` or
+`opt.compute_gradients()` followed by `opt.apply_gradients()`.
+Gradients should not be computed with tf.gradients or tf.GradientTape.
+This is because the returned optimizer will apply loss scaling, and
+tf.gradients or tf.GradientTape will not. If you do directly use
+tf.gradients or tf.GradientTape, your model may not converge due to
+float16 underflow problems.
+
+When eager execution is enabled, the mixed precision graph rewrite is only
+enabled within tf.functions, as outside tf.functions, there is no graph.
+
+For NVIDIA GPUs with Tensor cores, as a general performance guide, dimensions
+(such as batch size, input size, output size, and channel counts)
+should be powers of two if under 256, or otherwise divisible by 8 if above
+256. For more information, check out the
+[NVIDIA Deep Learning Performance Guide](
+https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/sdk/dl-performance-guide/index.html).
+
+Currently, mixed precision is only enabled on NVIDIA Tensor Core GPUs with
+Compute Capability 7.0 and above (Volta, Turing, or newer architectures). The
+parts of the graph on CPUs and TPUs are untouched by the graph rewrite.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`opt`
+ |
+
+An instance of a tf.keras.optimizers.Optimizer or a
+`tf.train.Optimizer`.
+ |
+
+|
+`loss_scale`
+ |
+
+Either an int/float, the string `"dynamic"`, or an instance of
+a tf.mixed_precision.experimental.LossScale. The loss scale to use. It
+is recommended to keep this as its default value of `"dynamic"`, which
+will adjust the scaling automatically to prevent `Inf` or `NaN` values.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A version of `opt` that will use loss scaling to prevent underflow.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/exponential_decay.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/exponential_decay.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..2430c40b698
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/exponential_decay.md
@@ -0,0 +1,162 @@
+description: Applies exponential decay to the learning rate.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.exponential_decay
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Applies exponential decay to the learning rate.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.exponential_decay(
+ learning_rate, global_step, decay_steps, decay_rate, staircase=(False),
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+When training a model, it is often recommended to lower the learning rate as
+the training progresses. This function applies an exponential decay function
+to a provided initial learning rate. It requires a `global_step` value to
+compute the decayed learning rate. You can just pass a TensorFlow variable
+that you increment at each training step.
+
+The function returns the decayed learning rate. It is computed as:
+
+```python
+decayed_learning_rate = learning_rate *
+ decay_rate ^ (global_step / decay_steps)
+```
+
+If the argument `staircase` is `True`, then `global_step / decay_steps` is an
+integer division and the decayed learning rate follows a staircase function.
+
+Example: decay every 100000 steps with a base of 0.96:
+
+```python
+...
+global_step = tf.Variable(0, trainable=False)
+starter_learning_rate = 0.1
+learning_rate = tf.compat.v1.train.exponential_decay(starter_learning_rate,
+global_step,
+ 100000, 0.96, staircase=True)
+# Passing global_step to minimize() will increment it at each step.
+learning_step = (
+ tf.compat.v1.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate)
+ .minimize(...my loss..., global_step=global_step)
+)
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`learning_rate`
+ |
+
+A scalar `float32` or `float64` `Tensor` or a Python number.
+The initial learning rate.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+A scalar `int32` or `int64` `Tensor` or a Python number. Global
+step to use for the decay computation. Must not be negative.
+ |
+
+|
+`decay_steps`
+ |
+
+A scalar `int32` or `int64` `Tensor` or a Python number. Must
+be positive. See the decay computation above.
+ |
+
+|
+`decay_rate`
+ |
+
+A scalar `float32` or `float64` `Tensor` or a Python number.
+The decay rate.
+ |
+
+|
+`staircase`
+ |
+
+Boolean. If `True` decay the learning rate at discrete intervals
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+String. Optional name of the operation. Defaults to
+'ExponentialDecay'.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A scalar `Tensor` of the same type as `learning_rate`. The decayed
+learning rate.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `global_step` is not supplied.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+When eager execution is enabled, this function returns a function which in
+turn returns the decayed learning rate Tensor. This can be useful for changing
+the learning rate value across different invocations of optimizer functions.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/export_meta_graph.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/export_meta_graph.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..84e7462d9c1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/export_meta_graph.md
@@ -0,0 +1,199 @@
+description: Returns MetaGraphDef proto.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.export_meta_graph
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns `MetaGraphDef` proto.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.export_meta_graph(
+ filename=None, meta_info_def=None, graph_def=None, saver_def=None,
+ collection_list=None, as_text=(False), graph=None, export_scope=None,
+ clear_devices=(False), clear_extraneous_savers=(False),
+ strip_default_attrs=(False), save_debug_info=(False), **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Optionally writes it to filename.
+
+This function exports the graph, saver, and collection objects into
+`MetaGraphDef` protocol buffer with the intention of it being imported
+at a later time or location to restart training, run inference, or be
+a subgraph.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`filename`
+ |
+
+Optional filename including the path for writing the generated
+`MetaGraphDef` protocol buffer.
+ |
+
+|
+`meta_info_def`
+ |
+
+`MetaInfoDef` protocol buffer.
+ |
+
+|
+`graph_def`
+ |
+
+`GraphDef` protocol buffer.
+ |
+
+|
+`saver_def`
+ |
+
+`SaverDef` protocol buffer.
+ |
+
+|
+`collection_list`
+ |
+
+List of string keys to collect.
+ |
+
+|
+`as_text`
+ |
+
+If `True`, writes the `MetaGraphDef` as an ASCII proto.
+ |
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+The `Graph` to export. If `None`, use the default graph.
+ |
+
+|
+`export_scope`
+ |
+
+Optional `string`. Name scope under which to extract the
+subgraph. The scope name will be striped from the node definitions for
+easy import later into new name scopes. If `None`, the whole graph is
+exported. graph_def and export_scope cannot both be specified.
+ |
+
+|
+`clear_devices`
+ |
+
+Whether or not to clear the device field for an `Operation`
+or `Tensor` during export.
+ |
+
+|
+`clear_extraneous_savers`
+ |
+
+Remove any Saver-related information from the graph
+(both Save/Restore ops and SaverDefs) that are not associated with the
+provided SaverDef.
+ |
+
+|
+`strip_default_attrs`
+ |
+
+Boolean. If `True`, default-valued attributes will be
+removed from the NodeDefs. For a detailed guide, see
+[Stripping Default-Valued Attributes](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/master/tensorflow/python/saved_model/README.md#stripping-default-valued-attributes).
+ |
+
+|
+`save_debug_info`
+ |
+
+If `True`, save the GraphDebugInfo to a separate file,
+which in the same directory of filename and with `_debug` added before the
+file extend.
+ |
+
+|
+`**kwargs`
+ |
+
+Optional keyed arguments.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `MetaGraphDef` proto.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+When the `GraphDef` is larger than 2GB.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If called with eager execution enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+Exporting/importing meta graphs is not supported unless both `graph_def` and
+`graph` are provided. No graph exists when eager execution is enabled.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/generate_checkpoint_state_proto.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/generate_checkpoint_state_proto.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..78ed79255bb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/generate_checkpoint_state_proto.md
@@ -0,0 +1,120 @@
+description: Generates a checkpoint state proto.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.generate_checkpoint_state_proto
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Generates a checkpoint state proto.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.generate_checkpoint_state_proto(
+ save_dir, model_checkpoint_path, all_model_checkpoint_paths=None,
+ all_model_checkpoint_timestamps=None, last_preserved_timestamp=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`save_dir`
+ |
+
+Directory where the model was saved.
+ |
+
+|
+`model_checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint file.
+ |
+
+|
+`all_model_checkpoint_paths`
+ |
+
+List of strings. Paths to all not-yet-deleted
+checkpoints, sorted from oldest to newest. If this is a non-empty list,
+the last element must be equal to model_checkpoint_path. These paths
+are also saved in the CheckpointState proto.
+ |
+
+|
+`all_model_checkpoint_timestamps`
+ |
+
+A list of floats, indicating the number of
+seconds since the Epoch when each checkpoint was generated.
+ |
+
+|
+`last_preserved_timestamp`
+ |
+
+A float, indicating the number of seconds since
+the Epoch when the last preserved checkpoint was written, e.g. due to a
+`keep_checkpoint_every_n_hours` parameter (see
+tf.train.CheckpointManager for an implementation).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+CheckpointState proto with model_checkpoint_path and
+all_model_checkpoint_paths updated to either absolute paths or
+relative paths to the current save_dir.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `all_model_checkpoint_timestamps` was provided but its length
+does not match `all_model_checkpoint_paths`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/get_checkpoint_mtimes.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/get_checkpoint_mtimes.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..9f9bd319f58
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/get_checkpoint_mtimes.md
@@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
+description: Returns the mtimes (modification timestamps) of the checkpoints. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.get_checkpoint_mtimes
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns the mtimes (modification timestamps) of the checkpoints. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.get_checkpoint_mtimes(
+ checkpoint_prefixes
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use standard file utilities to get mtimes.
+
+Globs for the checkpoints pointed to by `checkpoint_prefixes`. If the files
+exist, collect their mtime. Both V2 and V1 checkpoints are considered, in
+that priority.
+
+This is the recommended way to get the mtimes, since it takes into account
+the naming difference between V1 and V2 formats.
+
+Note: If not all checkpoints exist, the length of the returned mtimes list
+will be smaller than the length of `checkpoint_prefixes` list, so mapping
+checkpoints to corresponding mtimes will not be possible.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`checkpoint_prefixes`
+ |
+
+a list of checkpoint paths, typically the results of
+`Saver.save()` or those of tf.train.latest_checkpoint(), regardless of
+sharded/non-sharded or V1/V2.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of mtimes (in microseconds) of the found checkpoints.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/get_global_step.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/get_global_step.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..162cd41c556
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/get_global_step.md
@@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
+description: Get the global step tensor.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.get_global_step
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Get the global step tensor.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.get_global_step(
+ graph=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The global step tensor must be an integer variable. We first try to find it
+in the collection `GLOBAL_STEP`, or by name `global_step:0`.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+The graph to find the global step in. If missing, use default graph.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The global step variable, or `None` if none was found.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If the global step tensor has a non-integer type, or if it is not
+a `Variable`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/get_or_create_global_step.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/get_or_create_global_step.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..46096225cb0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/get_or_create_global_step.md
@@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
+description: Returns and create (if necessary) the global step tensor.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.get_or_create_global_step
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns and create (if necessary) the global step tensor.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.get_or_create_global_step(
+ graph=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`graph`
+ |
+
+The graph in which to create the global step tensor. If missing, use
+default graph.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The global step tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/global_step.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/global_step.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..39e9b71e6f1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/global_step.md
@@ -0,0 +1,85 @@
+description: Small helper to get the global step.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.global_step
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Small helper to get the global step.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.global_step(
+ sess, global_step_tensor
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+```python
+# Create a variable to hold the global_step.
+global_step_tensor = tf.Variable(10, trainable=False, name='global_step')
+# Create a session.
+sess = tf.compat.v1.Session()
+# Initialize the variable
+sess.run(global_step_tensor.initializer)
+# Get the variable value.
+print('global_step: %s' % tf.compat.v1.train.global_step(sess,
+global_step_tensor))
+
+global_step: 10
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sess`
+ |
+
+A TensorFlow `Session` object.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step_tensor`
+ |
+
+`Tensor` or the `name` of the operation that contains
+the global step.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The global step value.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/import_meta_graph.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/import_meta_graph.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..c5f00f6fc4d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/import_meta_graph.md
@@ -0,0 +1,196 @@
+description: Recreates a Graph saved in a MetaGraphDef proto.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.import_meta_graph
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Recreates a Graph saved in a `MetaGraphDef` proto.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.import_meta_graph(
+ meta_graph_or_file, clear_devices=(False), import_scope=None, **kwargs
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This function takes a `MetaGraphDef` protocol buffer as input. If
+the argument is a file containing a `MetaGraphDef` protocol buffer ,
+it constructs a protocol buffer from the file content. The function
+then adds all the nodes from the `graph_def` field to the
+current graph, recreates all the collections, and returns a saver
+constructed from the `saver_def` field.
+
+In combination with `export_meta_graph()`, this function can be used to
+
+* Serialize a graph along with other Python objects such as `QueueRunner`,
+ `Variable` into a `MetaGraphDef`.
+
+* Restart training from a saved graph and checkpoints.
+
+* Run inference from a saved graph and checkpoints.
+
+```Python
+...
+# Create a saver.
+saver = tf.compat.v1.train.Saver(...variables...)
+# Remember the training_op we want to run by adding it to a collection.
+tf.compat.v1.add_to_collection('train_op', train_op)
+sess = tf.compat.v1.Session()
+for step in xrange(1000000):
+ sess.run(train_op)
+ if step % 1000 == 0:
+ # Saves checkpoint, which by default also exports a meta_graph
+ # named 'my-model-global_step.meta'.
+ saver.save(sess, 'my-model', global_step=step)
+```
+
+Later we can continue training from this saved `meta_graph` without building
+the model from scratch.
+
+```Python
+with tf.Session() as sess:
+ new_saver =
+ tf.train.import_meta_graph('my-save-dir/my-model-10000.meta')
+ new_saver.restore(sess, 'my-save-dir/my-model-10000')
+ # tf.get_collection() returns a list. In this example we only want
+ # the first one.
+ train_op = tf.get_collection('train_op')[0]
+ for step in xrange(1000000):
+ sess.run(train_op)
+```
+
+NOTE: Restarting training from saved `meta_graph` only works if the
+device assignments have not changed.
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+Variables, placeholders, and independent operations can also be stored, as
+shown in the following example.
+
+```Python
+# Saving contents and operations.
+v1 = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, name="v1")
+v2 = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, name="v2")
+v3 = tf.math.multiply(v1, v2)
+vx = tf.Variable(10.0, name="vx")
+v4 = tf.add(v3, vx, name="v4")
+saver = tf.train.Saver([vx])
+sess = tf.Session()
+sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
+sess.run(vx.assign(tf.add(vx, vx)))
+result = sess.run(v4, feed_dict={v1:12.0, v2:3.3})
+print(result)
+saver.save(sess, "./model_ex1")
+```
+
+Later this model can be restored and contents loaded.
+
+```Python
+# Restoring variables and running operations.
+saver = tf.train.import_meta_graph("./model_ex1.meta")
+sess = tf.Session()
+saver.restore(sess, "./model_ex1")
+result = sess.run("v4:0", feed_dict={"v1:0": 12.0, "v2:0": 3.3})
+print(result)
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`meta_graph_or_file`
+ |
+
+`MetaGraphDef` protocol buffer or filename (including
+the path) containing a `MetaGraphDef`.
+ |
+
+|
+`clear_devices`
+ |
+
+Whether or not to clear the device field for an `Operation`
+or `Tensor` during import.
+ |
+
+|
+`import_scope`
+ |
+
+Optional `string`. Name scope to add. Only used when
+initializing from protocol buffer.
+ |
+
+|
+`**kwargs`
+ |
+
+Optional keyed arguments.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A saver constructed from `saver_def` in `MetaGraphDef` or None.
+
+A None value is returned if no variables exist in the `MetaGraphDef`
+(i.e., there are no variables to restore).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If called with eager execution enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+Exporting/importing meta graphs is not supported. No graph exists when eager
+execution is enabled.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/init_from_checkpoint.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/init_from_checkpoint.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..82dd4877ca4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/init_from_checkpoint.md
@@ -0,0 +1,146 @@
+description: Replaces tf.Variable initializers so they load from a checkpoint file.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.init_from_checkpoint
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Replaces tf.Variable initializers so they load from a checkpoint file.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.init_from_checkpoint(
+ ckpt_dir_or_file, assignment_map
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Values are not loaded immediately, but when the initializer is run
+(typically by running a tf.compat.v1.global_variables_initializer op).
+
+Note: This overrides default initialization ops of specified variables and
+redefines dtype.
+
+Assignment map supports following syntax:
+
+* `'checkpoint_scope_name/': 'scope_name/'` - will load all variables in
+ current `scope_name` from `checkpoint_scope_name` with matching tensor
+ names.
+* `'checkpoint_scope_name/some_other_variable': 'scope_name/variable_name'` -
+ will initialize `scope_name/variable_name` variable
+ from `checkpoint_scope_name/some_other_variable`.
+* `'scope_variable_name': variable` - will initialize given tf.Variable
+ object with tensor 'scope_variable_name' from the checkpoint.
+* `'scope_variable_name': list(variable)` - will initialize list of
+ partitioned variables with tensor 'scope_variable_name' from the checkpoint.
+* `'/': 'scope_name/'` - will load all variables in current `scope_name` from
+ checkpoint's root (e.g. no scope).
+
+Supports loading into partitioned variables, which are represented as
+`'/part_'`.
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+
+# Say, '/tmp/model.ckpt' has the following tensors:
+# -- name='old_scope_1/var1', shape=[20, 2]
+# -- name='old_scope_1/var2', shape=[50, 4]
+# -- name='old_scope_2/var3', shape=[100, 100]
+
+# Create new model's variables
+with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope('new_scope_1'):
+ var1 = tf.compat.v1.get_variable('var1', shape=[20, 2],
+ initializer=tf.compat.v1.zeros_initializer())
+with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope('new_scope_2'):
+ var2 = tf.compat.v1.get_variable('var2', shape=[50, 4],
+ initializer=tf.compat.v1.zeros_initializer())
+ # Partition into 5 variables along the first axis.
+ var3 = tf.compat.v1.get_variable(name='var3', shape=[100, 100],
+ initializer=tf.compat.v1.zeros_initializer(),
+ partitioner=lambda shape, dtype: [5, 1])
+
+# Initialize all variables in `new_scope_1` from `old_scope_1`.
+init_from_checkpoint('/tmp/model.ckpt', {'old_scope_1/': 'new_scope_1'})
+
+# Use names to specify which variables to initialize from checkpoint.
+init_from_checkpoint('/tmp/model.ckpt',
+ {'old_scope_1/var1': 'new_scope_1/var1',
+ 'old_scope_1/var2': 'new_scope_2/var2'})
+
+# Or use tf.Variable objects to identify what to initialize.
+init_from_checkpoint('/tmp/model.ckpt',
+ {'old_scope_1/var1': var1,
+ 'old_scope_1/var2': var2})
+
+# Initialize partitioned variables using variable's name
+init_from_checkpoint('/tmp/model.ckpt',
+ {'old_scope_2/var3': 'new_scope_2/var3'})
+
+# Or specify the list of tf.Variable objects.
+init_from_checkpoint('/tmp/model.ckpt',
+ {'old_scope_2/var3': var3._get_variable_list()})
+
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ckpt_dir_or_file`
+ |
+
+Directory with checkpoints file or path to checkpoint.
+ |
+
+|
+`assignment_map`
+ |
+
+Dict, where keys are names of the variables in the
+checkpoint and values are current variables or names of current variables
+(in default graph).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If missing variables in current graph, or if missing
+checkpoints or tensors in checkpoints.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/input_producer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/input_producer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..4f3f1ef0f36
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/input_producer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,177 @@
+description: Output the rows of input_tensor to a queue for an input pipeline. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.input_producer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Output the rows of `input_tensor` to a queue for an input pipeline. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.input_producer(
+ input_tensor, element_shape=None, num_epochs=None, shuffle=(True), seed=None,
+ capacity=32, shared_name=None, summary_name=None, name=None, cancel_op=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Queue-based input pipelines have been replaced by tf.data. Use `tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(input_tensor).shuffle(tf.shape(input_tensor, out_type=tf.int64)[0]).repeat(num_epochs)`. If `shuffle=False`, omit the `.shuffle(...)`.
+
+Note: if `num_epochs` is not `None`, this function creates local counter
+`epochs`. Use `local_variables_initializer()` to initialize local variables.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input_tensor`
+ |
+
+A tensor with the rows to produce. Must be at least
+one-dimensional. Must either have a fully-defined shape, or
+`element_shape` must be defined.
+ |
+
+|
+`element_shape`
+ |
+
+(Optional.) A `TensorShape` representing the shape of a
+row of `input_tensor`, if it cannot be inferred.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_epochs`
+ |
+
+(Optional.) An integer. If specified `input_producer` produces
+each row of `input_tensor` `num_epochs` times before generating an
+`OutOfRange` error. If not specified, `input_producer` can cycle through
+the rows of `input_tensor` an unlimited number of times.
+ |
+
+|
+`shuffle`
+ |
+
+(Optional.) A boolean. If true, the rows are randomly shuffled
+within each epoch.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+(Optional.) An integer. The seed to use if `shuffle` is true.
+ |
+
+|
+`capacity`
+ |
+
+(Optional.) The capacity of the queue to be used for buffering
+the input.
+ |
+
+|
+`shared_name`
+ |
+
+(Optional.) If set, this queue will be shared under the given
+name across multiple sessions.
+ |
+
+|
+`summary_name`
+ |
+
+(Optional.) If set, a scalar summary for the current queue
+size will be generated, using this name as part of the tag.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+(Optional.) A name for queue.
+ |
+
+|
+`cancel_op`
+ |
+
+(Optional.) Cancel op for the queue
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A queue with the output rows. A `QueueRunner` for the queue is
+added to the current `QUEUE_RUNNER` collection of the current
+graph.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the shape of the input cannot be inferred from the arguments.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If called with eager execution enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+Input pipelines based on Queues are not supported when eager execution is
+enabled. Please use the tf.data API to ingest data under eager execution.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/inverse_time_decay.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/inverse_time_decay.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..ad558b45805
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/inverse_time_decay.md
@@ -0,0 +1,168 @@
+description: Applies inverse time decay to the initial learning rate.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.inverse_time_decay
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Applies inverse time decay to the initial learning rate.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.inverse_time_decay(
+ learning_rate, global_step, decay_steps, decay_rate, staircase=(False),
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+When training a model, it is often recommended to lower the learning rate as
+the training progresses. This function applies an inverse decay function
+to a provided initial learning rate. It requires an `global_step` value to
+compute the decayed learning rate. You can just pass a TensorFlow variable
+that you increment at each training step.
+
+The function returns the decayed learning rate. It is computed as:
+
+```python
+decayed_learning_rate = learning_rate / (1 + decay_rate * global_step /
+decay_step)
+```
+
+or, if `staircase` is `True`, as:
+
+```python
+decayed_learning_rate = learning_rate / (1 + decay_rate * floor(global_step /
+decay_step))
+```
+
+Example: decay 1/t with a rate of 0.5:
+
+```python
+...
+global_step = tf.Variable(0, trainable=False)
+learning_rate = 0.1
+decay_steps = 1.0
+decay_rate = 0.5
+learning_rate = tf.compat.v1.train.inverse_time_decay(learning_rate,
+global_step,
+decay_steps, decay_rate)
+
+# Passing global_step to minimize() will increment it at each step.
+learning_step = (
+ tf.compat.v1.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate)
+ .minimize(...my loss..., global_step=global_step)
+)
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`learning_rate`
+ |
+
+A scalar `float32` or `float64` `Tensor` or a Python number.
+The initial learning rate.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+A Python number. Global step to use for the decay computation.
+Must not be negative.
+ |
+
+|
+`decay_steps`
+ |
+
+How often to apply decay.
+ |
+
+|
+`decay_rate`
+ |
+
+A Python number. The decay rate.
+ |
+
+|
+`staircase`
+ |
+
+Whether to apply decay in a discrete staircase, as opposed to
+continuous, fashion.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+String. Optional name of the operation. Defaults to
+'InverseTimeDecay'.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A scalar `Tensor` of the same type as `learning_rate`. The decayed
+learning rate.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `global_step` is not supplied.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+When eager execution is enabled, this function returns a function which in
+turn returns the decayed learning rate Tensor. This can be useful for changing
+the learning rate value across different invocations of optimizer functions.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/limit_epochs.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/limit_epochs.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a4af3cd2756
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/limit_epochs.md
@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
+description: Returns tensor num_epochs times and then raises an OutOfRange error. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.limit_epochs
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns tensor `num_epochs` times and then raises an `OutOfRange` error. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.limit_epochs(
+ tensor, num_epochs=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Queue-based input pipelines have been replaced by tf.data. Use `tf.data.Dataset.from_tensors(tensor).repeat(num_epochs)`.
+
+Note: creates local counter `epochs`. Use `local_variables_initializer()` to
+initialize local variables.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`tensor`
+ |
+
+Any `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_epochs`
+ |
+
+A positive integer (optional). If specified, limits the number
+of steps the output tensor may be evaluated.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operations (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+tensor or `OutOfRange`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `num_epochs` is invalid.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/linear_cosine_decay.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/linear_cosine_decay.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..9af8af8e446
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/linear_cosine_decay.md
@@ -0,0 +1,176 @@
+description: Applies linear cosine decay to the learning rate.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.linear_cosine_decay
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Applies linear cosine decay to the learning rate.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.linear_cosine_decay(
+ learning_rate, global_step, decay_steps, num_periods=0.5, alpha=0.0, beta=0.001,
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Note that linear cosine decay is more aggressive than cosine decay and
+larger initial learning rates can typically be used.
+
+When training a model, it is often recommended to lower the learning rate as
+the training progresses. This function applies a linear cosine decay function
+to a provided initial learning rate. It requires a `global_step` value to
+compute the decayed learning rate. You can just pass a TensorFlow variable
+that you increment at each training step.
+
+The function returns the decayed learning rate. It is computed as:
+```python
+global_step = min(global_step, decay_steps)
+linear_decay = (decay_steps - global_step) / decay_steps)
+cosine_decay = 0.5 * (
+ 1 + cos(pi * 2 * num_periods * global_step / decay_steps))
+decayed = (alpha + linear_decay) * cosine_decay + beta
+decayed_learning_rate = learning_rate * decayed
+```
+
+#### Example usage:
+
+
+```python
+decay_steps = 1000
+lr_decayed = linear_cosine_decay(learning_rate, global_step, decay_steps)
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`learning_rate`
+ |
+
+A scalar `float32` or `float64` Tensor or a Python number.
+The initial learning rate.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+A scalar `int32` or `int64` `Tensor` or a Python number. Global
+step to use for the decay computation.
+ |
+
+|
+`decay_steps`
+ |
+
+A scalar `int32` or `int64` `Tensor` or a Python number. Number
+of steps to decay over.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_periods`
+ |
+
+Number of periods in the cosine part of the decay. See
+computation above.
+ |
+
+|
+`alpha`
+ |
+
+See computation above.
+ |
+
+|
+`beta`
+ |
+
+See computation above.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+String. Optional name of the operation. Defaults to
+'LinearCosineDecay'.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A scalar `Tensor` of the same type as `learning_rate`. The decayed
+learning rate.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `global_step` is not supplied.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### References:
+
+Neural Optimizer Search with Reinforcement Learning:
+ [Bello et al., 2017](http://proceedings.mlr.press/v70/bello17a.html)
+ ([pdf](http://proceedings.mlr.press/v70/bello17a/bello17a.pdf))
+Stochastic Gradient Descent with Warm Restarts:
+ [Loshchilov et al., 2017]
+ (https://openreview.net/forum?id=Skq89Scxx¬eId=Skq89Scxx)
+ ([pdf](https://openreview.net/pdf?id=Skq89Scxx))
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+When eager execution is enabled, this function returns a function which in
+turn returns the decayed learning rate Tensor. This can be useful for changing
+the learning rate value across different invocations of optimizer functions.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/maybe_batch.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/maybe_batch.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..cf1387d7f24
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/maybe_batch.md
@@ -0,0 +1,170 @@
+description: Conditionally creates batches of tensors based on keep_input. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.maybe_batch
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Conditionally creates batches of tensors based on `keep_input`. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.maybe_batch(
+ tensors, keep_input, batch_size, num_threads=1, capacity=32,
+ enqueue_many=(False), shapes=None, dynamic_pad=(False),
+ allow_smaller_final_batch=(False), shared_name=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Queue-based input pipelines have been replaced by tf.data. Use `tf.data.Dataset.filter(...).batch(batch_size)` (or `padded_batch(...)` if `dynamic_pad=True`).
+
+See docstring in `batch` for more details.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`tensors`
+ |
+
+The list or dictionary of tensors to enqueue.
+ |
+
+|
+`keep_input`
+ |
+
+A `bool` Tensor. This tensor controls whether the input is
+added to the queue or not. If it is a scalar and evaluates `True`, then
+`tensors` are all added to the queue. If it is a vector and `enqueue_many`
+is `True`, then each example is added to the queue only if the
+corresponding value in `keep_input` is `True`. This tensor essentially
+acts as a filtering mechanism.
+ |
+
+|
+`batch_size`
+ |
+
+The new batch size pulled from the queue.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_threads`
+ |
+
+The number of threads enqueuing `tensors`. The batching will
+be nondeterministic if `num_threads > 1`.
+ |
+
+|
+`capacity`
+ |
+
+An integer. The maximum number of elements in the queue.
+ |
+
+|
+`enqueue_many`
+ |
+
+Whether each tensor in `tensors` is a single example.
+ |
+
+|
+`shapes`
+ |
+
+(Optional) The shapes for each example. Defaults to the
+inferred shapes for `tensors`.
+ |
+
+|
+`dynamic_pad`
+ |
+
+Boolean. Allow variable dimensions in input shapes.
+The given dimensions are padded upon dequeue so that tensors within a
+batch have the same shapes.
+ |
+
+|
+`allow_smaller_final_batch`
+ |
+
+(Optional) Boolean. If `True`, allow the final
+batch to be smaller if there are insufficient items left in the queue.
+ |
+
+|
+`shared_name`
+ |
+
+(Optional). If set, this queue will be shared under the given
+name across multiple sessions.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+(Optional) A name for the operations.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list or dictionary of tensors with the same types as `tensors`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `shapes` are not specified, and cannot be
+inferred from the elements of `tensors`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/maybe_batch_join.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/maybe_batch_join.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..b27670e7c2b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/maybe_batch_join.md
@@ -0,0 +1,164 @@
+description: Runs a list of tensors to conditionally fill a queue to create batches. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.maybe_batch_join
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Runs a list of tensors to conditionally fill a queue to create batches. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.maybe_batch_join(
+ tensors_list, keep_input, batch_size, capacity=32, enqueue_many=(False),
+ shapes=None, dynamic_pad=(False), allow_smaller_final_batch=(False),
+ shared_name=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Queue-based input pipelines have been replaced by tf.data. Use `tf.data.Dataset.interleave(...).filter(...).batch(batch_size)` (or `padded_batch(...)` if `dynamic_pad=True`).
+
+See docstring in `batch_join` for more details.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`tensors_list`
+ |
+
+A list of tuples or dictionaries of tensors to enqueue.
+ |
+
+|
+`keep_input`
+ |
+
+A `bool` Tensor. This tensor controls whether the input is
+added to the queue or not. If it is a scalar and evaluates `True`, then
+`tensors` are all added to the queue. If it is a vector and `enqueue_many`
+is `True`, then each example is added to the queue only if the
+corresponding value in `keep_input` is `True`. This tensor essentially
+acts as a filtering mechanism.
+ |
+
+|
+`batch_size`
+ |
+
+An integer. The new batch size pulled from the queue.
+ |
+
+|
+`capacity`
+ |
+
+An integer. The maximum number of elements in the queue.
+ |
+
+|
+`enqueue_many`
+ |
+
+Whether each tensor in `tensor_list_list` is a single
+example.
+ |
+
+|
+`shapes`
+ |
+
+(Optional) The shapes for each example. Defaults to the
+inferred shapes for `tensor_list_list[i]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`dynamic_pad`
+ |
+
+Boolean. Allow variable dimensions in input shapes.
+The given dimensions are padded upon dequeue so that tensors within a
+batch have the same shapes.
+ |
+
+|
+`allow_smaller_final_batch`
+ |
+
+(Optional) Boolean. If `True`, allow the final
+batch to be smaller if there are insufficient items left in the queue.
+ |
+
+|
+`shared_name`
+ |
+
+(Optional) If set, this queue will be shared under the given
+name across multiple sessions.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+(Optional) A name for the operations.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list or dictionary of tensors with the same number and types as
+`tensors_list[i]`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `shapes` are not specified, and cannot be
+inferred from the elements of `tensor_list_list`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/maybe_shuffle_batch.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/maybe_shuffle_batch.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..1861c9aec23
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/maybe_shuffle_batch.md
@@ -0,0 +1,182 @@
+description: Creates batches by randomly shuffling conditionally-enqueued tensors. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.maybe_shuffle_batch
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Creates batches by randomly shuffling conditionally-enqueued tensors. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.maybe_shuffle_batch(
+ tensors, batch_size, capacity, min_after_dequeue, keep_input, num_threads=1,
+ seed=None, enqueue_many=(False), shapes=None, allow_smaller_final_batch=(False),
+ shared_name=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Queue-based input pipelines have been replaced by tf.data. Use `tf.data.Dataset.filter(...).shuffle(min_after_dequeue).batch(batch_size)`.
+
+See docstring in `shuffle_batch` for more details.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`tensors`
+ |
+
+The list or dictionary of tensors to enqueue.
+ |
+
+|
+`batch_size`
+ |
+
+The new batch size pulled from the queue.
+ |
+
+|
+`capacity`
+ |
+
+An integer. The maximum number of elements in the queue.
+ |
+
+|
+`min_after_dequeue`
+ |
+
+Minimum number elements in the queue after a
+dequeue, used to ensure a level of mixing of elements.
+ |
+
+|
+`keep_input`
+ |
+
+A `bool` Tensor. This tensor controls whether the input is
+added to the queue or not. If it is a scalar and evaluates `True`, then
+`tensors` are all added to the queue. If it is a vector and `enqueue_many`
+is `True`, then each example is added to the queue only if the
+corresponding value in `keep_input` is `True`. This tensor essentially
+acts as a filtering mechanism.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_threads`
+ |
+
+The number of threads enqueuing `tensor_list`.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+Seed for the random shuffling within the queue.
+ |
+
+|
+`enqueue_many`
+ |
+
+Whether each tensor in `tensor_list` is a single example.
+ |
+
+|
+`shapes`
+ |
+
+(Optional) The shapes for each example. Defaults to the
+inferred shapes for `tensor_list`.
+ |
+
+|
+`allow_smaller_final_batch`
+ |
+
+(Optional) Boolean. If `True`, allow the final
+batch to be smaller if there are insufficient items left in the queue.
+ |
+
+|
+`shared_name`
+ |
+
+(Optional) If set, this queue will be shared under the given
+name across multiple sessions.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+(Optional) A name for the operations.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list or dictionary of tensors with the types as `tensors`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `shapes` are not specified, and cannot be
+inferred from the elements of `tensors`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+Input pipelines based on Queues are not supported when eager execution is
+enabled. Please use the tf.data API to ingest data under eager execution.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/maybe_shuffle_batch_join.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/maybe_shuffle_batch_join.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..be3057047c0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/maybe_shuffle_batch_join.md
@@ -0,0 +1,177 @@
+description: Create batches by randomly shuffling conditionally-enqueued tensors. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.maybe_shuffle_batch_join
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Create batches by randomly shuffling conditionally-enqueued tensors. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.maybe_shuffle_batch_join(
+ tensors_list, batch_size, capacity, min_after_dequeue, keep_input, seed=None,
+ enqueue_many=(False), shapes=None, allow_smaller_final_batch=(False),
+ shared_name=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Queue-based input pipelines have been replaced by tf.data. Use `tf.data.Dataset.interleave(...).filter(...).shuffle(min_after_dequeue).batch(batch_size)`.
+
+See docstring in `shuffle_batch_join` for more details.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`tensors_list`
+ |
+
+A list of tuples or dictionaries of tensors to enqueue.
+ |
+
+|
+`batch_size`
+ |
+
+An integer. The new batch size pulled from the queue.
+ |
+
+|
+`capacity`
+ |
+
+An integer. The maximum number of elements in the queue.
+ |
+
+|
+`min_after_dequeue`
+ |
+
+Minimum number elements in the queue after a
+dequeue, used to ensure a level of mixing of elements.
+ |
+
+|
+`keep_input`
+ |
+
+A `bool` Tensor. This tensor controls whether the input is
+added to the queue or not. If it is a scalar and evaluates `True`, then
+`tensors` are all added to the queue. If it is a vector and `enqueue_many`
+is `True`, then each example is added to the queue only if the
+corresponding value in `keep_input` is `True`. This tensor essentially
+acts as a filtering mechanism.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+Seed for the random shuffling within the queue.
+ |
+
+|
+`enqueue_many`
+ |
+
+Whether each tensor in `tensor_list_list` is a single
+example.
+ |
+
+|
+`shapes`
+ |
+
+(Optional) The shapes for each example. Defaults to the
+inferred shapes for `tensors_list[i]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`allow_smaller_final_batch`
+ |
+
+(Optional) Boolean. If `True`, allow the final
+batch to be smaller if there are insufficient items left in the queue.
+ |
+
+|
+`shared_name`
+ |
+
+(optional). If set, this queue will be shared under the given
+name across multiple sessions.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+(Optional) A name for the operations.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list or dictionary of tensors with the same number and types as
+`tensors_list[i]`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `shapes` are not specified, and cannot be
+inferred from the elements of `tensors_list`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+Input pipelines based on Queues are not supported when eager execution is
+enabled. Please use the tf.data API to ingest data under eager execution.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/natural_exp_decay.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/natural_exp_decay.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..9ed69929a14
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/natural_exp_decay.md
@@ -0,0 +1,168 @@
+description: Applies natural exponential decay to the initial learning rate.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.natural_exp_decay
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Applies natural exponential decay to the initial learning rate.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.natural_exp_decay(
+ learning_rate, global_step, decay_steps, decay_rate, staircase=(False),
+ name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+When training a model, it is often recommended to lower the learning rate as
+the training progresses. This function applies an exponential decay function
+to a provided initial learning rate. It requires an `global_step` value to
+compute the decayed learning rate. You can just pass a TensorFlow variable
+that you increment at each training step.
+
+The function returns the decayed learning rate. It is computed as:
+
+```python
+decayed_learning_rate = learning_rate * exp(-decay_rate * global_step /
+decay_step)
+```
+
+or, if `staircase` is `True`, as:
+
+```python
+decayed_learning_rate = learning_rate * exp(-decay_rate * floor(global_step /
+decay_step))
+```
+
+Example: decay exponentially with a base of 0.96:
+
+```python
+...
+global_step = tf.Variable(0, trainable=False)
+learning_rate = 0.1
+decay_steps = 5
+k = 0.5
+learning_rate = tf.compat.v1.train.natural_exp_decay(learning_rate,
+global_step,
+ decay_steps, k)
+
+# Passing global_step to minimize() will increment it at each step.
+learning_step = (
+ tf.compat.v1.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate)
+ .minimize(...my loss..., global_step=global_step)
+)
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`learning_rate`
+ |
+
+A scalar `float32` or `float64` `Tensor` or a Python number.
+The initial learning rate.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+A Python number. Global step to use for the decay computation.
+Must not be negative.
+ |
+
+|
+`decay_steps`
+ |
+
+How often to apply decay.
+ |
+
+|
+`decay_rate`
+ |
+
+A Python number. The decay rate.
+ |
+
+|
+`staircase`
+ |
+
+Whether to apply decay in a discrete staircase, as opposed to
+continuous, fashion.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+String. Optional name of the operation. Defaults to
+'ExponentialTimeDecay'.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A scalar `Tensor` of the same type as `learning_rate`. The decayed
+learning rate.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `global_step` is not supplied.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+When eager execution is enabled, this function returns a function which in
+turn returns the decayed learning rate Tensor. This can be useful for changing
+the learning rate value across different invocations of optimizer functions.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/noisy_linear_cosine_decay.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/noisy_linear_cosine_decay.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3e9786e2b8d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/noisy_linear_cosine_decay.md
@@ -0,0 +1,194 @@
+description: Applies noisy linear cosine decay to the learning rate.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.noisy_linear_cosine_decay
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Applies noisy linear cosine decay to the learning rate.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.noisy_linear_cosine_decay(
+ learning_rate, global_step, decay_steps, initial_variance=1.0,
+ variance_decay=0.55, num_periods=0.5, alpha=0.0, beta=0.001, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Note that linear cosine decay is more aggressive than cosine decay and
+larger initial learning rates can typically be used.
+
+When training a model, it is often recommended to lower the learning rate as
+the training progresses. This function applies a noisy linear
+cosine decay function to a provided initial learning rate.
+It requires a `global_step` value to compute the decayed learning rate.
+You can just pass a TensorFlow variable that you increment at each
+training step.
+
+The function returns the decayed learning rate. It is computed as:
+```python
+global_step = min(global_step, decay_steps)
+linear_decay = (decay_steps - global_step) / decay_steps)
+cosine_decay = 0.5 * (
+ 1 + cos(pi * 2 * num_periods * global_step / decay_steps))
+decayed = (alpha + linear_decay + eps_t) * cosine_decay + beta
+decayed_learning_rate = learning_rate * decayed
+```
+where eps_t is 0-centered gaussian noise with variance
+initial_variance / (1 + global_step) ** variance_decay
+
+#### Example usage:
+
+
+```python
+decay_steps = 1000
+lr_decayed = noisy_linear_cosine_decay(
+ learning_rate, global_step, decay_steps)
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`learning_rate`
+ |
+
+A scalar `float32` or `float64` Tensor or a Python number.
+The initial learning rate.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+A scalar `int32` or `int64` `Tensor` or a Python number. Global
+step to use for the decay computation.
+ |
+
+|
+`decay_steps`
+ |
+
+A scalar `int32` or `int64` `Tensor` or a Python number. Number
+of steps to decay over.
+ |
+
+|
+`initial_variance`
+ |
+
+initial variance for the noise. See computation above.
+ |
+
+|
+`variance_decay`
+ |
+
+decay for the noise's variance. See computation above.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_periods`
+ |
+
+Number of periods in the cosine part of the decay. See
+computation above.
+ |
+
+|
+`alpha`
+ |
+
+See computation above.
+ |
+
+|
+`beta`
+ |
+
+See computation above.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+String. Optional name of the operation. Defaults to
+'NoisyLinearCosineDecay'.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A scalar `Tensor` of the same type as `learning_rate`. The decayed
+learning rate.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `global_step` is not supplied.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### References:
+
+Neural Optimizer Search with Reinforcement Learning:
+ [Bello et al., 2017](http://proceedings.mlr.press/v70/bello17a.html)
+ ([pdf](http://proceedings.mlr.press/v70/bello17a/bello17a.pdf))
+Stochastic Gradient Descent with Warm Restarts:
+ [Loshchilov et al., 2017]
+ (https://openreview.net/forum?id=Skq89Scxx¬eId=Skq89Scxx)
+ ([pdf](https://openreview.net/pdf?id=Skq89Scxx))
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+When eager execution is enabled, this function returns a function which in
+turn returns the decayed learning rate Tensor. This can be useful for changing
+the learning rate value across different invocations of optimizer functions.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/piecewise_constant.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/piecewise_constant.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..d583d2ca9ab
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/piecewise_constant.md
@@ -0,0 +1,142 @@
+description: Piecewise constant from boundaries and interval values.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.piecewise_constant
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Piecewise constant from boundaries and interval values.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.train.piecewise_constant_decay`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.piecewise_constant(
+ x, boundaries, values, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Example: use a learning rate that's 1.0 for the first 100001 steps, 0.5
+ for the next 10000 steps, and 0.1 for any additional steps.
+
+```python
+global_step = tf.Variable(0, trainable=False)
+boundaries = [100000, 110000]
+values = [1.0, 0.5, 0.1]
+learning_rate = tf.compat.v1.train.piecewise_constant(global_step, boundaries,
+values)
+
+# Later, whenever we perform an optimization step, we increment global_step.
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`x`
+ |
+
+A 0-D scalar `Tensor`. Must be one of the following types: `float32`,
+`float64`, `uint8`, `int8`, `int16`, `int32`, `int64`.
+ |
+
+|
+`boundaries`
+ |
+
+A list of `Tensor`s or `int`s or `float`s with strictly
+increasing entries, and with all elements having the same type as `x`.
+ |
+
+|
+`values`
+ |
+
+A list of `Tensor`s or `float`s or `int`s that specifies the values
+for the intervals defined by `boundaries`. It should have one more element
+than `boundaries`, and all elements should have the same type.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A string. Optional name of the operation. Defaults to
+'PiecewiseConstant'.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A 0-D Tensor. Its value is `values[0]` when `x <= boundaries[0]`,
+`values[1]` when `x > boundaries[0]` and `x <= boundaries[1]`, ...,
+and values[-1] when `x > boundaries[-1]`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if types of `x` and `boundaries` do not match, or types of all
+`values` do not match or
+the number of elements in the lists does not match.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+When eager execution is enabled, this function returns a function which in
+turn returns the decayed learning rate Tensor. This can be useful for changing
+the learning rate value across different invocations of optimizer functions.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/polynomial_decay.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/polynomial_decay.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..8a4cfa57e7b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/polynomial_decay.md
@@ -0,0 +1,186 @@
+description: Applies a polynomial decay to the learning rate.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.polynomial_decay
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Applies a polynomial decay to the learning rate.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.polynomial_decay(
+ learning_rate, global_step, decay_steps, end_learning_rate=0.0001, power=1.0,
+ cycle=(False), name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+It is commonly observed that a monotonically decreasing learning rate, whose
+degree of change is carefully chosen, results in a better performing model.
+This function applies a polynomial decay function to a provided initial
+`learning_rate` to reach an `end_learning_rate` in the given `decay_steps`.
+
+It requires a `global_step` value to compute the decayed learning rate. You
+can just pass a TensorFlow variable that you increment at each training step.
+
+The function returns the decayed learning rate. It is computed as:
+
+```python
+global_step = min(global_step, decay_steps)
+decayed_learning_rate = (learning_rate - end_learning_rate) *
+ (1 - global_step / decay_steps) ^ (power) +
+ end_learning_rate
+
+```
+
+If `cycle` is True then a multiple of `decay_steps` is used, the first one
+that is bigger than `global_steps`.
+
+```python
+decay_steps = decay_steps * ceil(global_step / decay_steps)
+decayed_learning_rate = (learning_rate - end_learning_rate) *
+ (1 - global_step / decay_steps) ^ (power) +
+ end_learning_rate
+
+```
+
+Example: decay from 0.1 to 0.01 in 10000 steps using sqrt (i.e. power=0.5):
+
+```python
+...
+global_step = tf.Variable(0, trainable=False)
+starter_learning_rate = 0.1
+end_learning_rate = 0.01
+decay_steps = 10000
+learning_rate = tf.compat.v1.train.polynomial_decay(starter_learning_rate,
+global_step,
+ decay_steps, end_learning_rate,
+ power=0.5)
+# Passing global_step to minimize() will increment it at each step.
+learning_step = (
+ tf.compat.v1.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate)
+ .minimize(...my loss..., global_step=global_step)
+)
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`learning_rate`
+ |
+
+A scalar `float32` or `float64` `Tensor` or a Python number.
+The initial learning rate.
+ |
+
+|
+`global_step`
+ |
+
+A scalar `int32` or `int64` `Tensor` or a Python number. Global
+step to use for the decay computation. Must not be negative.
+ |
+
+|
+`decay_steps`
+ |
+
+A scalar `int32` or `int64` `Tensor` or a Python number. Must
+be positive. See the decay computation above.
+ |
+
+|
+`end_learning_rate`
+ |
+
+A scalar `float32` or `float64` `Tensor` or a Python
+number. The minimal end learning rate.
+ |
+
+|
+`power`
+ |
+
+A scalar `float32` or `float64` `Tensor` or a Python number. The
+power of the polynomial. Defaults to linear, 1.0.
+ |
+
+|
+`cycle`
+ |
+
+A boolean, whether or not it should cycle beyond decay_steps.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+String. Optional name of the operation. Defaults to
+'PolynomialDecay'.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A scalar `Tensor` of the same type as `learning_rate`. The decayed
+learning rate.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `global_step` is not supplied.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+When eager execution is enabled, this function returns a function which in
+turn returns the decayed learning rate Tensor. This can be useful for changing
+the learning rate value across different invocations of optimizer functions.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/queue_runner.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/queue_runner.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..35f4413d610
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/queue_runner.md
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+description: Public API for tf.train.queue_runner namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.train.queue_runner
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.train.queue_runner namespace.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class QueueRunner`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/train/QueueRunner.md): Holds a list of enqueue operations for a queue, each to be run in a thread.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`add_queue_runner(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/train/add_queue_runner.md): Adds a `QueueRunner` to a collection in the graph. (deprecated)
+
+[`start_queue_runners(...)`](../../../../tf/compat/v1/train/start_queue_runners.md): Starts all queue runners collected in the graph. (deprecated)
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/range_input_producer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/range_input_producer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..ae3991bc181
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/range_input_producer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,126 @@
+description: Produces the integers from 0 to limit-1 in a queue. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.range_input_producer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Produces the integers from 0 to limit-1 in a queue. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.range_input_producer(
+ limit, num_epochs=None, shuffle=(True), seed=None, capacity=32,
+ shared_name=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Queue-based input pipelines have been replaced by tf.data. Use `tf.data.Dataset.range(limit).shuffle(limit).repeat(num_epochs)`. If `shuffle=False`, omit the `.shuffle(...)`.
+
+Note: if `num_epochs` is not `None`, this function creates local counter
+`epochs`. Use `local_variables_initializer()` to initialize local variables.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`limit`
+ |
+
+An int32 scalar tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_epochs`
+ |
+
+An integer (optional). If specified, `range_input_producer`
+produces each integer `num_epochs` times before generating an
+OutOfRange error. If not specified, `range_input_producer` can cycle
+through the integers an unlimited number of times.
+ |
+
+|
+`shuffle`
+ |
+
+Boolean. If true, the integers are randomly shuffled within each
+epoch.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+An integer (optional). Seed used if shuffle == True.
+ |
+
+|
+`capacity`
+ |
+
+An integer. Sets the queue capacity.
+ |
+
+|
+`shared_name`
+ |
+
+(optional). If set, this queue will be shared under the given
+name across multiple sessions.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operations (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A Queue with the output integers. A `QueueRunner` for the Queue
+is added to the current `Graph`'s `QUEUE_RUNNER` collection.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+Input pipelines based on Queues are not supported when eager execution is
+enabled. Please use the tf.data API to ingest data under eager execution.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/remove_checkpoint.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/remove_checkpoint.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..1d259d1b718
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/remove_checkpoint.md
@@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
+description: Removes a checkpoint given by checkpoint_prefix. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.remove_checkpoint
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Removes a checkpoint given by `checkpoint_prefix`. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.remove_checkpoint(
+ checkpoint_prefix, checkpoint_format_version=tf.train.SaverDef.V2,
+ meta_graph_suffix='meta'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use standard file APIs to delete files with this prefix.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`checkpoint_prefix`
+ |
+
+The prefix of a V1 or V2 checkpoint. Typically the result
+of `Saver.save()` or that of tf.train.latest_checkpoint(), regardless of
+sharded/non-sharded or V1/V2.
+ |
+
+|
+`checkpoint_format_version`
+ |
+
+`SaverDef.CheckpointFormatVersion`, defaults to
+`SaverDef.V2`.
+ |
+
+|
+`meta_graph_suffix`
+ |
+
+Suffix for `MetaGraphDef` file. Defaults to 'meta'.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/replica_device_setter.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/replica_device_setter.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..dbdc00b2fdd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/replica_device_setter.md
@@ -0,0 +1,161 @@
+description: Return a device function to use when building a Graph for replicas.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.replica_device_setter
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Return a `device function` to use when building a Graph for replicas.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.replica_device_setter(
+ ps_tasks=0, ps_device='/job:ps', worker_device='/job:worker',
+ merge_devices=(True), cluster=None, ps_ops=None, ps_strategy=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Device Functions are used in `with tf.device(device_function):` statement to
+automatically assign devices to `Operation` objects as they are constructed,
+Device constraints are added from the inner-most context first, working
+outwards. The merging behavior adds constraints to fields that are yet unset
+by a more inner context. Currently the fields are (job, task, cpu/gpu).
+
+If `cluster` is `None`, and `ps_tasks` is 0, the returned function is a no-op.
+Otherwise, the value of `ps_tasks` is derived from `cluster`.
+
+By default, only Variable ops are placed on ps tasks, and the placement
+strategy is round-robin over all ps tasks. A custom `ps_strategy` may be used
+to do more intelligent placement, such as
+`tf.contrib.training.GreedyLoadBalancingStrategy`.
+
+For example,
+
+```python
+# To build a cluster with two ps jobs on hosts ps0 and ps1, and 3 worker
+# jobs on hosts worker0, worker1 and worker2.
+cluster_spec = {
+ "ps": ["ps0:2222", "ps1:2222"],
+ "worker": ["worker0:2222", "worker1:2222", "worker2:2222"]}
+with
+tf.device(tf.compat.v1.train.replica_device_setter(cluster=cluster_spec)):
+ # Build your graph
+ v1 = tf.Variable(...) # assigned to /job:ps/task:0
+ v2 = tf.Variable(...) # assigned to /job:ps/task:1
+ v3 = tf.Variable(...) # assigned to /job:ps/task:0
+# Run compute
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ps_tasks`
+ |
+
+Number of tasks in the `ps` job. Ignored if `cluster` is
+provided.
+ |
+
+|
+`ps_device`
+ |
+
+String. Device of the `ps` job. If empty no `ps` job is used.
+Defaults to `ps`.
+ |
+
+|
+`worker_device`
+ |
+
+String. Device of the `worker` job. If empty no `worker`
+job is used.
+ |
+
+|
+`merge_devices`
+ |
+
+`Boolean`. If `True`, merges or only sets a device if the
+device constraint is completely unset. merges device specification rather
+than overriding them.
+ |
+
+|
+`cluster`
+ |
+
+`ClusterDef` proto or `ClusterSpec`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ps_ops`
+ |
+
+List of strings representing `Operation` types that need to be
+placed on `ps` devices. If `None`, defaults to `STANDARD_PS_OPS`.
+ |
+
+|
+`ps_strategy`
+ |
+
+A callable invoked for every ps `Operation` (i.e. matched by
+`ps_ops`), that takes the `Operation` and returns the ps task index to
+use. If `None`, defaults to a round-robin strategy across all `ps`
+devices.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+
+A function to pass to tf.device().
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+|
+TypeError if `cluster` is not a dictionary or `ClusterDef` protocol buffer,
+or if `ps_strategy` is provided but not a callable.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/sdca_fprint.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/sdca_fprint.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3ecc1f15780
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/sdca_fprint.md
@@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
+description: Computes fingerprints of the input strings.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.sdca_fprint
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Computes fingerprints of the input strings.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.sdca_fprint(
+ input, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`input`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `string`.
+vector of strings to compute fingerprints on.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` of type `int64`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/sdca_optimizer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/sdca_optimizer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..42fa39aaad1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/sdca_optimizer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,234 @@
+description: Distributed version of Stochastic Dual Coordinate Ascent (SDCA) optimizer for
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.sdca_optimizer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Distributed version of Stochastic Dual Coordinate Ascent (SDCA) optimizer for
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.sdca_optimizer(
+ sparse_example_indices, sparse_feature_indices, sparse_feature_values,
+ dense_features, example_weights, example_labels, sparse_indices, sparse_weights,
+ dense_weights, example_state_data, loss_type, l1, l2, num_loss_partitions,
+ num_inner_iterations, adaptative=(True), name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+linear models with L1 + L2 regularization. As global optimization objective is
+strongly-convex, the optimizer optimizes the dual objective at each step. The
+optimizer applies each update one example at a time. Examples are sampled
+uniformly, and the optimizer is learning rate free and enjoys linear convergence
+rate.
+
+[Proximal Stochastic Dual Coordinate Ascent](http://arxiv.org/pdf/1211.2717v1.pdf).
+Shai Shalev-Shwartz, Tong Zhang. 2012
+
+$$Loss Objective = \sum f_{i} (wx_{i}) + (l2 / 2) * |w|^2 + l1 * |w|$$
+
+[Adding vs. Averaging in Distributed Primal-Dual Optimization](http://arxiv.org/abs/1502.03508).
+Chenxin Ma, Virginia Smith, Martin Jaggi, Michael I. Jordan,
+Peter Richtarik, Martin Takac. 2015
+
+[Stochastic Dual Coordinate Ascent with Adaptive Probabilities](https://arxiv.org/abs/1502.08053).
+Dominik Csiba, Zheng Qu, Peter Richtarik. 2015
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sparse_example_indices`
+ |
+
+A list of `Tensor` objects with type `int64`.
+a list of vectors which contain example indices.
+ |
+
+|
+`sparse_feature_indices`
+ |
+
+A list with the same length as `sparse_example_indices` of `Tensor` objects with type `int64`.
+a list of vectors which contain feature indices.
+ |
+
+|
+`sparse_feature_values`
+ |
+
+A list of `Tensor` objects with type `float32`.
+a list of vectors which contains feature value
+associated with each feature group.
+ |
+
+|
+`dense_features`
+ |
+
+A list of `Tensor` objects with type `float32`.
+a list of matrices which contains the dense feature values.
+ |
+
+|
+`example_weights`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `float32`.
+a vector which contains the weight associated with each
+example.
+ |
+
+|
+`example_labels`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `float32`.
+a vector which contains the label/target associated with each
+example.
+ |
+
+|
+`sparse_indices`
+ |
+
+A list with the same length as `sparse_example_indices` of `Tensor` objects with type `int64`.
+a list of vectors where each value is the indices which has
+corresponding weights in sparse_weights. This field maybe omitted for the
+dense approach.
+ |
+
+|
+`sparse_weights`
+ |
+
+A list with the same length as `sparse_example_indices` of `Tensor` objects with type `float32`.
+a list of vectors where each value is the weight associated with
+a sparse feature group.
+ |
+
+|
+`dense_weights`
+ |
+
+A list with the same length as `dense_features` of `Tensor` objects with type `float32`.
+a list of vectors where the values are the weights associated
+with a dense feature group.
+ |
+
+|
+`example_state_data`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `float32`.
+a list of vectors containing the example state data.
+ |
+
+|
+`loss_type`
+ |
+
+A `string` from: `"logistic_loss", "squared_loss", "hinge_loss", "smooth_hinge_loss", "poisson_loss"`.
+Type of the primal loss. Currently SdcaSolver supports logistic,
+squared and hinge losses.
+ |
+
+|
+`l1`
+ |
+
+A `float`. Symmetric l1 regularization strength.
+ |
+
+|
+`l2`
+ |
+
+A `float`. Symmetric l2 regularization strength.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_loss_partitions`
+ |
+
+An `int` that is `>= 1`.
+Number of partitions of the global loss function.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_inner_iterations`
+ |
+
+An `int` that is `>= 1`.
+Number of iterations per mini-batch.
+ |
+
+|
+`adaptative`
+ |
+
+An optional `bool`. Defaults to `True`.
+Whether to use Adaptive SDCA for the inner loop.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A tuple of `Tensor` objects (out_example_state_data, out_delta_sparse_weights, out_delta_dense_weights).
+ |
+
+
+|
+`out_example_state_data`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `float32`.
+ |
+
+|
+`out_delta_sparse_weights`
+ |
+
+A list with the same length as `sparse_example_indices` of `Tensor` objects with type `float32`.
+ |
+
+|
+`out_delta_dense_weights`
+ |
+
+A list with the same length as `dense_features` of `Tensor` objects with type `float32`.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/sdca_shrink_l1.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/sdca_shrink_l1.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..72b5bba4893
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/sdca_shrink_l1.md
@@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
+description: Applies L1 regularization shrink step on the parameters.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.sdca_shrink_l1
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Applies L1 regularization shrink step on the parameters.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.sdca_shrink_l1(
+ weights, l1, l2, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`weights`
+ |
+
+A list of `Tensor` objects with type mutable `float32`.
+a list of vectors where each value is the weight associated with a
+feature group.
+ |
+
+|
+`l1`
+ |
+
+A `float`. Symmetric l1 regularization strength.
+ |
+
+|
+`l2`
+ |
+
+A `float`.
+Symmetric l2 regularization strength. Should be a positive float.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The created Operation.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/shuffle_batch.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/shuffle_batch.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..2221a1f93f7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/shuffle_batch.md
@@ -0,0 +1,220 @@
+description: Creates batches by randomly shuffling tensors. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.shuffle_batch
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Creates batches by randomly shuffling tensors. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.shuffle_batch(
+ tensors, batch_size, capacity, min_after_dequeue, num_threads=1, seed=None,
+ enqueue_many=(False), shapes=None, allow_smaller_final_batch=(False),
+ shared_name=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Queue-based input pipelines have been replaced by tf.data. Use `tf.data.Dataset.shuffle(min_after_dequeue).batch(batch_size)`.
+
+This function adds the following to the current `Graph`:
+
+* A shuffling queue into which tensors from `tensors` are enqueued.
+* A `dequeue_many` operation to create batches from the queue.
+* A `QueueRunner` to `QUEUE_RUNNER` collection, to enqueue the tensors
+ from `tensors`.
+
+If `enqueue_many` is `False`, `tensors` is assumed to represent a
+single example. An input tensor with shape `[x, y, z]` will be output
+as a tensor with shape `[batch_size, x, y, z]`.
+
+If `enqueue_many` is `True`, `tensors` is assumed to represent a
+batch of examples, where the first dimension is indexed by example,
+and all members of `tensors` should have the same size in the
+first dimension. If an input tensor has shape `[*, x, y, z]`, the
+output will have shape `[batch_size, x, y, z]`.
+
+The `capacity` argument controls the how long the prefetching is allowed to
+grow the queues.
+
+The returned operation is a dequeue operation and will throw
+tf.errors.OutOfRangeError if the input queue is exhausted. If this
+operation is feeding another input queue, its queue runner will catch
+this exception, however, if this operation is used in your main thread
+you are responsible for catching this yourself.
+
+#### For example:
+
+
+
+```python
+# Creates batches of 32 images and 32 labels.
+image_batch, label_batch = tf.compat.v1.train.shuffle_batch(
+ [single_image, single_label],
+ batch_size=32,
+ num_threads=4,
+ capacity=50000,
+ min_after_dequeue=10000)
+```
+
+*N.B.:* You must ensure that either (i) the `shapes` argument is
+passed, or (ii) all of the tensors in `tensors` must have
+fully-defined shapes. `ValueError` will be raised if neither of
+these conditions holds.
+
+If `allow_smaller_final_batch` is `True`, a smaller batch value than
+`batch_size` is returned when the queue is closed and there are not enough
+elements to fill the batch, otherwise the pending elements are discarded.
+In addition, all output tensors' static shapes, as accessed via the
+`shape` property will have a first `Dimension` value of `None`, and
+operations that depend on fixed batch_size would fail.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`tensors`
+ |
+
+The list or dictionary of tensors to enqueue.
+ |
+
+|
+`batch_size`
+ |
+
+The new batch size pulled from the queue.
+ |
+
+|
+`capacity`
+ |
+
+An integer. The maximum number of elements in the queue.
+ |
+
+|
+`min_after_dequeue`
+ |
+
+Minimum number elements in the queue after a
+dequeue, used to ensure a level of mixing of elements.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_threads`
+ |
+
+The number of threads enqueuing `tensor_list`.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+Seed for the random shuffling within the queue.
+ |
+
+|
+`enqueue_many`
+ |
+
+Whether each tensor in `tensor_list` is a single example.
+ |
+
+|
+`shapes`
+ |
+
+(Optional) The shapes for each example. Defaults to the
+inferred shapes for `tensor_list`.
+ |
+
+|
+`allow_smaller_final_batch`
+ |
+
+(Optional) Boolean. If `True`, allow the final
+batch to be smaller if there are insufficient items left in the queue.
+ |
+
+|
+`shared_name`
+ |
+
+(Optional) If set, this queue will be shared under the given
+name across multiple sessions.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+(Optional) A name for the operations.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list or dictionary of tensors with the types as `tensors`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `shapes` are not specified, and cannot be
+inferred from the elements of `tensors`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+Input pipelines based on Queues are not supported when eager execution is
+enabled. Please use the tf.data API to ingest data under eager execution.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/shuffle_batch_join.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/shuffle_batch_join.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a2e4868105f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/shuffle_batch_join.md
@@ -0,0 +1,206 @@
+description: Create batches by randomly shuffling tensors. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.shuffle_batch_join
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Create batches by randomly shuffling tensors. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.shuffle_batch_join(
+ tensors_list, batch_size, capacity, min_after_dequeue, seed=None,
+ enqueue_many=(False), shapes=None, allow_smaller_final_batch=(False),
+ shared_name=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Queue-based input pipelines have been replaced by tf.data. Use `tf.data.Dataset.interleave(...).shuffle(min_after_dequeue).batch(batch_size)`.
+
+The `tensors_list` argument is a list of tuples of tensors, or a list of
+dictionaries of tensors. Each element in the list is treated similarly
+to the `tensors` argument of tf.compat.v1.train.shuffle_batch().
+
+This version enqueues a different list of tensors in different threads.
+It adds the following to the current `Graph`:
+
+* A shuffling queue into which tensors from `tensors_list` are enqueued.
+* A `dequeue_many` operation to create batches from the queue.
+* A `QueueRunner` to `QUEUE_RUNNER` collection, to enqueue the tensors
+ from `tensors_list`.
+
+`len(tensors_list)` threads will be started, with thread `i` enqueuing
+the tensors from `tensors_list[i]`. `tensors_list[i1][j]` must match
+`tensors_list[i2][j]` in type and shape, except in the first dimension if
+`enqueue_many` is true.
+
+If `enqueue_many` is `False`, each `tensors_list[i]` is assumed
+to represent a single example. An input tensor with shape `[x, y, z]`
+will be output as a tensor with shape `[batch_size, x, y, z]`.
+
+If `enqueue_many` is `True`, `tensors_list[i]` is assumed to
+represent a batch of examples, where the first dimension is indexed
+by example, and all members of `tensors_list[i]` should have the
+same size in the first dimension. If an input tensor has shape `[*, x,
+y, z]`, the output will have shape `[batch_size, x, y, z]`.
+
+The `capacity` argument controls the how long the prefetching is allowed to
+grow the queues.
+
+The returned operation is a dequeue operation and will throw
+tf.errors.OutOfRangeError if the input queue is exhausted. If this
+operation is feeding another input queue, its queue runner will catch
+this exception, however, if this operation is used in your main thread
+you are responsible for catching this yourself.
+
+If `allow_smaller_final_batch` is `True`, a smaller batch value than
+`batch_size` is returned when the queue is closed and there are not enough
+elements to fill the batch, otherwise the pending elements are discarded.
+In addition, all output tensors' static shapes, as accessed via the
+`shape` property will have a first `Dimension` value of `None`, and
+operations that depend on fixed batch_size would fail.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`tensors_list`
+ |
+
+A list of tuples or dictionaries of tensors to enqueue.
+ |
+
+|
+`batch_size`
+ |
+
+An integer. The new batch size pulled from the queue.
+ |
+
+|
+`capacity`
+ |
+
+An integer. The maximum number of elements in the queue.
+ |
+
+|
+`min_after_dequeue`
+ |
+
+Minimum number elements in the queue after a
+dequeue, used to ensure a level of mixing of elements.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+Seed for the random shuffling within the queue.
+ |
+
+|
+`enqueue_many`
+ |
+
+Whether each tensor in `tensor_list_list` is a single
+example.
+ |
+
+|
+`shapes`
+ |
+
+(Optional) The shapes for each example. Defaults to the
+inferred shapes for `tensors_list[i]`.
+ |
+
+|
+`allow_smaller_final_batch`
+ |
+
+(Optional) Boolean. If `True`, allow the final
+batch to be smaller if there are insufficient items left in the queue.
+ |
+
+|
+`shared_name`
+ |
+
+(optional). If set, this queue will be shared under the given
+name across multiple sessions.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+(Optional) A name for the operations.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list or dictionary of tensors with the same number and types as
+`tensors_list[i]`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the `shapes` are not specified, and cannot be
+inferred from the elements of `tensors_list`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+Input pipelines based on Queues are not supported when eager execution is
+enabled. Please use the tf.data API to ingest data under eager execution.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/slice_input_producer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/slice_input_producer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..1e41bd1b875
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/slice_input_producer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,145 @@
+description: Produces a slice of each Tensor in tensor_list. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.slice_input_producer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Produces a slice of each `Tensor` in `tensor_list`. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.slice_input_producer(
+ tensor_list, num_epochs=None, shuffle=(True), seed=None, capacity=32,
+ shared_name=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Queue-based input pipelines have been replaced by tf.data. Use `tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(tuple(tensor_list)).shuffle(tf.shape(input_tensor, out_type=tf.int64)[0]).repeat(num_epochs)`. If `shuffle=False`, omit the `.shuffle(...)`.
+
+Implemented using a Queue -- a `QueueRunner` for the Queue
+is added to the current `Graph`'s `QUEUE_RUNNER` collection.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`tensor_list`
+ |
+
+A list of `Tensor` objects. Every `Tensor` in
+`tensor_list` must have the same size in the first dimension.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_epochs`
+ |
+
+An integer (optional). If specified, `slice_input_producer`
+produces each slice `num_epochs` times before generating
+an `OutOfRange` error. If not specified, `slice_input_producer` can cycle
+through the slices an unlimited number of times.
+ |
+
+|
+`shuffle`
+ |
+
+Boolean. If true, the integers are randomly shuffled within each
+epoch.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+An integer (optional). Seed used if shuffle == True.
+ |
+
+|
+`capacity`
+ |
+
+An integer. Sets the queue capacity.
+ |
+
+|
+`shared_name`
+ |
+
+(optional). If set, this queue will be shared under the given
+name across multiple sessions.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operations (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of tensors, one for each element of `tensor_list`. If the tensor
+in `tensor_list` has shape `[N, a, b, .., z]`, then the corresponding output
+tensor will have shape `[a, b, ..., z]`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `slice_input_producer` produces nothing from `tensor_list`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+Input pipelines based on Queues are not supported when eager execution is
+enabled. Please use the tf.data API to ingest data under eager execution.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/start_queue_runners.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/start_queue_runners.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..93edd9d1ed1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/start_queue_runners.md
@@ -0,0 +1,169 @@
+description: Starts all queue runners collected in the graph. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.start_queue_runners
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Starts all queue runners collected in the graph. (deprecated)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.train.queue_runner.start_queue_runners`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.start_queue_runners(
+ sess=None, coord=None, daemon=(True), start=(True),
+ collection=tf.GraphKeys.QUEUE_RUNNERS
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+To construct input pipelines, use the tf.data module.
+
+This is a companion method to `add_queue_runner()`. It just starts
+threads for all queue runners collected in the graph. It returns
+the list of all threads.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`sess`
+ |
+
+`Session` used to run the queue ops. Defaults to the
+default session.
+ |
+
+|
+`coord`
+ |
+
+Optional `Coordinator` for coordinating the started threads.
+ |
+
+|
+`daemon`
+ |
+
+Whether the threads should be marked as `daemons`, meaning
+they don't block program exit.
+ |
+
+|
+`start`
+ |
+
+Set to `False` to only create the threads, not start them.
+ |
+
+|
+`collection`
+ |
+
+A `GraphKey` specifying the graph collection to
+get the queue runners from. Defaults to `GraphKeys.QUEUE_RUNNERS`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `sess` is None and there isn't any default session.
+ |
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+if `sess` is not a tf.compat.v1.Session object.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of threads.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If called with eager execution enabled.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If called without a default tf.compat.v1.Session registered.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+Not compatible with eager execution. To ingest data under eager execution,
+use the tf.data API instead.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/string_input_producer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/string_input_producer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..0b1188b1985
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/string_input_producer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,155 @@
+description: Output strings (e.g. filenames) to a queue for an input pipeline. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.string_input_producer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Output strings (e.g. filenames) to a queue for an input pipeline. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.string_input_producer(
+ string_tensor, num_epochs=None, shuffle=(True), seed=None, capacity=32,
+ shared_name=None, name=None, cancel_op=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Queue-based input pipelines have been replaced by tf.data. Use `tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(string_tensor).shuffle(tf.shape(input_tensor, out_type=tf.int64)[0]).repeat(num_epochs)`. If `shuffle=False`, omit the `.shuffle(...)`.
+
+Note: if `num_epochs` is not `None`, this function creates local counter
+`epochs`. Use `local_variables_initializer()` to initialize local variables.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`string_tensor`
+ |
+
+A 1-D string tensor with the strings to produce.
+ |
+
+|
+`num_epochs`
+ |
+
+An integer (optional). If specified, `string_input_producer`
+produces each string from `string_tensor` `num_epochs` times before
+generating an `OutOfRange` error. If not specified,
+`string_input_producer` can cycle through the strings in `string_tensor`
+an unlimited number of times.
+ |
+
+|
+`shuffle`
+ |
+
+Boolean. If true, the strings are randomly shuffled within each
+epoch.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+An integer (optional). Seed used if shuffle == True.
+ |
+
+|
+`capacity`
+ |
+
+An integer. Sets the queue capacity.
+ |
+
+|
+`shared_name`
+ |
+
+(optional). If set, this queue will be shared under the given
+name across multiple sessions. All sessions open to the device which has
+this queue will be able to access it via the shared_name. Using this in
+a distributed setting means each name will only be seen by one of the
+sessions which has access to this operation.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operations (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`cancel_op`
+ |
+
+Cancel op for the queue (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A queue with the output strings. A `QueueRunner` for the Queue
+is added to the current `Graph`'s `QUEUE_RUNNER` collection.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the string_tensor is a null Python list. At runtime,
+will fail with an assertion if string_tensor becomes a null tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Eager Compatibility
+Input pipelines based on Queues are not supported when eager execution is
+enabled. Please use the tf.data API to ingest data under eager execution.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/summary_iterator.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/summary_iterator.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..55a0d01c533
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/summary_iterator.md
@@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
+description: An iterator for reading Event protocol buffers from an event file.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.summary_iterator
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+An iterator for reading `Event` protocol buffers from an event file.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.summary_iterator(
+ path
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+You can use this function to read events written to an event file. It returns
+a Python iterator that yields `Event` protocol buffers.
+
+Example: Print the contents of an events file.
+
+```python
+for e in tf.compat.v1.train.summary_iterator(path to events file):
+ print(e)
+```
+
+Example: Print selected summary values.
+
+```python
+# This example supposes that the events file contains summaries with a
+# summary value tag 'loss'. These could have been added by calling
+# `add_summary()`, passing the output of a scalar summary op created with
+# with: `tf.compat.v1.summary.scalar('loss', loss_tensor)`.
+for e in tf.compat.v1.train.summary_iterator(path to events file):
+ for v in e.summary.value:
+ if v.tag == 'loss':
+ print(v.simple_value)
+```
+
+See the protocol buffer definitions of
+[Event](https://www.tensorflow.org/code/tensorflow/core/util/event.proto)
+and
+[Summary](https://www.tensorflow.org/code/tensorflow/core/framework/summary.proto)
+for more information about their attributes.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`path`
+ |
+
+The path to an event file created by a `SummaryWriter`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Yields:
+
+`Event` protocol buffers.
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/update_checkpoint_state.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/update_checkpoint_state.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..357daa89afe
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/update_checkpoint_state.md
@@ -0,0 +1,120 @@
+description: Updates the content of the 'checkpoint' file. (deprecated)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.update_checkpoint_state
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Updates the content of the 'checkpoint' file. (deprecated)
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.update_checkpoint_state(
+ save_dir, model_checkpoint_path, all_model_checkpoint_paths=None,
+ latest_filename=None, all_model_checkpoint_timestamps=None,
+ last_preserved_timestamp=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warning: THIS FUNCTION IS DEPRECATED. It will be removed in a future version.
+Instructions for updating:
+Use tf.train.CheckpointManager to manage checkpoints rather than manually editing the Checkpoint proto.
+
+This updates the checkpoint file containing a CheckpointState
+proto.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`save_dir`
+ |
+
+Directory where the model was saved.
+ |
+
+|
+`model_checkpoint_path`
+ |
+
+The checkpoint file.
+ |
+
+|
+`all_model_checkpoint_paths`
+ |
+
+List of strings. Paths to all not-yet-deleted
+checkpoints, sorted from oldest to newest. If this is a non-empty list,
+the last element must be equal to model_checkpoint_path. These paths
+are also saved in the CheckpointState proto.
+ |
+
+|
+`latest_filename`
+ |
+
+Optional name of the checkpoint file. Default to
+'checkpoint'.
+ |
+
+|
+`all_model_checkpoint_timestamps`
+ |
+
+Optional list of timestamps (floats,
+seconds since the Epoch) indicating when the checkpoints in
+`all_model_checkpoint_paths` were created.
+ |
+
+|
+`last_preserved_timestamp`
+ |
+
+A float, indicating the number of seconds since
+the Epoch when the last preserved checkpoint was written, e.g. due to a
+`keep_checkpoint_every_n_hours` parameter (see
+tf.train.CheckpointManager for an implementation).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+If any of the model checkpoint paths conflict with the file
+containing CheckpointSate.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/warm_start.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/warm_start.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..16e7a6086ae
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/train/warm_start.md
@@ -0,0 +1,123 @@
+description: Warm-starts a model using the given settings.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.train.warm_start
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Warm-starts a model using the given settings.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.train.warm_start(
+ ckpt_to_initialize_from, vars_to_warm_start='.*', var_name_to_vocab_info=None,
+ var_name_to_prev_var_name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+If you are using a tf.estimator.Estimator, this will automatically be called
+during training.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ckpt_to_initialize_from`
+ |
+
+[Required] A string specifying the directory with
+checkpoint file(s) or path to checkpoint from which to warm-start the
+model parameters.
+ |
+
+|
+`vars_to_warm_start`
+ |
+
+[Optional] One of the following:
+
+- A regular expression (string) that captures which variables to
+warm-start (see tf.compat.v1.get_collection). This expression will only
+consider variables in the TRAINABLE_VARIABLES collection -- if you need
+to warm-start non_TRAINABLE vars (such as optimizer accumulators or
+batch norm statistics), please use the below option.
+- A list of strings, each a regex scope provided to
+tf.compat.v1.get_collection with GLOBAL_VARIABLES (please see
+tf.compat.v1.get_collection). For backwards compatibility reasons,
+this is separate from the single-string argument type.
+- A list of Variables to warm-start. If you do not have access to the
+`Variable` objects at the call site, please use the above option.
+- `None`, in which case only TRAINABLE variables specified in
+`var_name_to_vocab_info` will be warm-started.
+
+Defaults to `'.*'`, which warm-starts all variables in the
+TRAINABLE_VARIABLES collection. Note that this excludes variables such
+as accumulators and moving statistics from batch norm.
+ |
+
+|
+`var_name_to_vocab_info`
+ |
+
+[Optional] Dict of variable names (strings) to
+tf.estimator.VocabInfo. The variable names should be "full" variables,
+not the names of the partitions. If not explicitly provided, the variable
+is assumed to have no (changes to) vocabulary.
+ |
+
+|
+`var_name_to_prev_var_name`
+ |
+
+[Optional] Dict of variable names (strings) to
+name of the previously-trained variable in `ckpt_to_initialize_from`. If
+not explicitly provided, the name of the variable is assumed to be same
+between previous checkpoint and current model. Note that this has no
+effect on the set of variables that is warm-started, and only controls
+name mapping (use `vars_to_warm_start` for controlling what variables to
+warm-start).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If the WarmStartSettings contains prev_var_name or VocabInfo
+configuration for variable names that are not used. This is to ensure
+a stronger check for variable configuration than relying on users to
+examine the logs.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/trainable_variables.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/trainable_variables.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3d50f45f074
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/trainable_variables.md
@@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
+description: Returns all variables created with trainable=True.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.trainable_variables
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns all variables created with `trainable=True`.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.trainable_variables(
+ scope=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+When passed `trainable=True`, the `Variable()` constructor automatically
+adds new variables to the graph collection
+`GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES`. This convenience function returns the
+contents of that collection.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`scope`
+ |
+
+(Optional.) A string. If supplied, the resulting list is filtered to
+include only items whose `name` attribute matches `scope` using
+`re.match`. Items without a `name` attribute are never returned if a scope
+is supplied. The choice of `re.match` means that a `scope` without special
+tokens filters by prefix.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A list of Variable objects.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/transpose.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/transpose.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..f37f5fff5a3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/transpose.md
@@ -0,0 +1,143 @@
+description: Transposes a.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.transpose
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Transposes `a`.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.transpose(
+ a, perm=None, name='transpose', conjugate=(False)
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Permutes the dimensions according to `perm`.
+
+The returned tensor's dimension i will correspond to the input dimension
+`perm[i]`. If `perm` is not given, it is set to (n-1...0), where n is
+the rank of the input tensor. Hence by default, this operation performs a
+regular matrix transpose on 2-D input Tensors. If conjugate is True and
+`a.dtype` is either `complex64` or `complex128` then the values of `a`
+are conjugated and transposed.
+
+
+
+#### For example:
+
+
+
+```python
+x = tf.constant([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
+tf.transpose(x) # [[1, 4]
+ # [2, 5]
+ # [3, 6]]
+
+# Equivalently
+tf.transpose(x, perm=[1, 0]) # [[1, 4]
+ # [2, 5]
+ # [3, 6]]
+
+# If x is complex, setting conjugate=True gives the conjugate transpose
+x = tf.constant([[1 + 1j, 2 + 2j, 3 + 3j],
+ [4 + 4j, 5 + 5j, 6 + 6j]])
+tf.transpose(x, conjugate=True) # [[1 - 1j, 4 - 4j],
+ # [2 - 2j, 5 - 5j],
+ # [3 - 3j, 6 - 6j]]
+
+# 'perm' is more useful for n-dimensional tensors, for n > 2
+x = tf.constant([[[ 1, 2, 3],
+ [ 4, 5, 6]],
+ [[ 7, 8, 9],
+ [10, 11, 12]]])
+
+# Take the transpose of the matrices in dimension-0
+# (this common operation has a shorthand `linalg.matrix_transpose`)
+tf.transpose(x, perm=[0, 2, 1]) # [[[1, 4],
+ # [2, 5],
+ # [3, 6]],
+ # [[7, 10],
+ # [8, 11],
+ # [9, 12]]]
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`a`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`perm`
+ |
+
+A permutation of the dimensions of `a`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`conjugate`
+ |
+
+Optional bool. Setting it to `True` is mathematically equivalent
+to tf.math.conj(tf.transpose(input)).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A transposed `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Numpy Compatibility
+In `numpy` transposes are memory-efficient constant time operations as they
+simply return a new view of the same data with adjusted `strides`.
+
+TensorFlow does not support strides, so `transpose` returns a new tensor with
+the items permuted.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/truncated_normal_initializer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/truncated_normal_initializer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..129de6258db
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/truncated_normal_initializer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,229 @@
+description: Initializer that generates a truncated normal distribution.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.truncated_normal_initializer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Initializer that generates a truncated normal distribution.
+
+Inherits From: [`Initializer`](../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Initializer.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.initializers.truncated_normal`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.truncated_normal_initializer(
+ mean=0.0, stddev=1.0, seed=None, dtype=tf.dtypes.float32
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+These values are similar to values from a `random_normal_initializer`
+except that values more than two standard deviations from the mean
+are discarded and re-drawn. This is the recommended initializer for
+neural network weights and filters.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`mean`
+ |
+
+a python scalar or a scalar tensor. Mean of the random values to
+generate.
+ |
+
+|
+`stddev`
+ |
+
+a python scalar or a scalar tensor. Standard deviation of the random
+values to generate.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+A Python integer. Used to create random seeds. See
+tf.compat.v1.set_random_seed for behavior.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+Default data type, used if no `dtype` argument is provided when
+calling the initializer. Only floating point types are supported.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+from_config
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+from_config(
+ config
+)
+
+
+Instantiates an initializer from a configuration dictionary.
+
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+initializer = RandomUniform(-1, 1)
+config = initializer.get_config()
+initializer = RandomUniform.from_config(config)
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+A Python dictionary. It will typically be the output of
+`get_config`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Initializer instance.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_config
+
+View source
+
+
+get_config()
+
+
+Returns the configuration of the initializer as a JSON-serializable dict.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A JSON-serializable Python dict.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+__call__
+
+View source
+
+
+__call__(
+ shape, dtype=None, partition_info=None
+)
+
+
+Returns a tensor object initialized as specified by the initializer.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of the tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+Optional dtype of the tensor. If not provided use the initializer
+dtype.
+ |
+
+|
+`partition_info`
+ |
+
+Optional information about the possible partitioning of a
+tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tuple.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tuple.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a45ee9bf731
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/tuple.md
@@ -0,0 +1,117 @@
+description: Group tensors together.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.tuple
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Group tensors together.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.tuple(
+ tensors, name=None, control_inputs=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This creates a tuple of tensors with the same values as the `tensors`
+argument, except that the value of each tensor is only returned after the
+values of all tensors have been computed.
+
+`control_inputs` contains additional ops that have to finish before this op
+finishes, but whose outputs are not returned.
+
+This can be used as a "join" mechanism for parallel computations: all the
+argument tensors can be computed in parallel, but the values of any tensor
+returned by `tuple` are only available after all the parallel computations
+are done.
+
+See also tf.group and
+tf.control_dependencies.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`tensors`
+ |
+
+A list of `Tensor`s or `IndexedSlices`, some entries can be `None`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+(optional) A name to use as a `name_scope` for the operation.
+ |
+
+|
+`control_inputs`
+ |
+
+List of additional ops to finish before returning.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Same as `tensors`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If `tensors` does not contain any `Tensor` or `IndexedSlices`.
+ |
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+If `control_inputs` is not a list of `Operation` or `Tensor`
+objects.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/uniform_unit_scaling_initializer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/uniform_unit_scaling_initializer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..4bc53720808
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/uniform_unit_scaling_initializer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,236 @@
+description: Initializer that generates tensors without scaling variance.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.uniform_unit_scaling_initializer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Initializer that generates tensors without scaling variance.
+
+Inherits From: [`Initializer`](../../../tf/compat/v1/keras/initializers/Initializer.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.initializers.uniform_unit_scaling`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.uniform_unit_scaling_initializer(
+ factor=1.0, seed=None, dtype=tf.dtypes.float32
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+When initializing a deep network, it is in principle advantageous to keep
+the scale of the input variance constant, so it does not explode or diminish
+by reaching the final layer. If the input is `x` and the operation `x * W`,
+and we want to initialize `W` uniformly at random, we need to pick `W` from
+
+ [-sqrt(3) / sqrt(dim), sqrt(3) / sqrt(dim)]
+
+to keep the scale intact, where `dim = W.shape[0]` (the size of the input).
+A similar calculation for convolutional networks gives an analogous result
+with `dim` equal to the product of the first 3 dimensions. When
+nonlinearities are present, we need to multiply this by a constant `factor`.
+See (Sussillo et al., 2014) for deeper motivation, experiments
+and the calculation of constants. In section 2.3 there, the constants were
+numerically computed: for a linear layer it's 1.0, relu: ~1.43, tanh: ~1.15.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`factor`
+ |
+
+Float. A multiplicative factor by which the values will be scaled.
+ |
+
+|
+`seed`
+ |
+
+A Python integer. Used to create random seeds. See
+tf.compat.v1.set_random_seed for behavior.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+Default data type, used if no `dtype` argument is provided when
+calling the initializer. Only floating point types are supported.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### References:
+
+[Sussillo et al., 2014](https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6558)
+([pdf](http://arxiv.org/pdf/1412.6558.pdf))
+
+
+## Methods
+
+from_config
+
+View source
+
+
+@classmethod
+from_config(
+ config
+)
+
+
+Instantiates an initializer from a configuration dictionary.
+
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+initializer = RandomUniform(-1, 1)
+config = initializer.get_config()
+initializer = RandomUniform.from_config(config)
+```
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`config`
+ |
+
+A Python dictionary. It will typically be the output of
+`get_config`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Initializer instance.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+get_config
+
+View source
+
+
+get_config()
+
+
+Returns the configuration of the initializer as a JSON-serializable dict.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A JSON-serializable Python dict.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+__call__
+
+View source
+
+
+__call__(
+ shape, dtype=None, partition_info=None
+)
+
+
+Returns a tensor object initialized as specified by the initializer.
+
+
+
+
+
+| Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`shape`
+ |
+
+Shape of the tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+Optional dtype of the tensor. If not provided use the initializer
+dtype.
+ |
+
+|
+`partition_info`
+ |
+
+Optional information about the possible partitioning of a
+tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/user_ops.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/user_ops.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..4e236a4e440
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/user_ops.md
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+description: Public API for tf.user_ops namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.user_ops
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.user_ops namespace.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`my_fact(...)`](../../../tf/compat/v1/user_ops/my_fact.md): Example of overriding the generated code for an Op.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/user_ops/my_fact.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/user_ops/my_fact.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..04e7c1cd4e9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/user_ops/my_fact.md
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+description: Example of overriding the generated code for an Op.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.user_ops.my_fact
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Example of overriding the generated code for an Op.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.user_ops.my_fact()
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/variable_axis_size_partitioner.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/variable_axis_size_partitioner.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e288ebe5dcd
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/variable_axis_size_partitioner.md
@@ -0,0 +1,117 @@
+description: Get a partitioner for VariableScope to keep shards below max_shard_bytes.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.variable_axis_size_partitioner
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Get a partitioner for VariableScope to keep shards below `max_shard_bytes`.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.variable_axis_size_partitioner(
+ max_shard_bytes, axis=0, bytes_per_string_element=16, max_shards=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This partitioner will shard a Variable along one axis, attempting to keep
+the maximum shard size below `max_shard_bytes`. In practice, this is not
+always possible when sharding along only one axis. When this happens,
+this axis is sharded as much as possible (i.e., every dimension becomes
+a separate shard).
+
+If the partitioner hits the `max_shards` limit, then each shard may end up
+larger than `max_shard_bytes`. By default `max_shards` equals `None` and no
+limit on the number of shards is enforced.
+
+One reasonable value for `max_shard_bytes` is `(64 << 20) - 1`, or almost
+`64MB`, to keep below the protobuf byte limit.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`max_shard_bytes`
+ |
+
+The maximum size any given shard is allowed to be.
+ |
+
+|
+`axis`
+ |
+
+The axis to partition along. Default: outermost axis.
+ |
+
+|
+`bytes_per_string_element`
+ |
+
+If the `Variable` is of type string, this provides
+an estimate of how large each scalar in the `Variable` is.
+ |
+
+|
+`max_shards`
+ |
+
+The maximum number of shards in int created taking precedence
+over `max_shard_bytes`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A partition function usable as the `partitioner` argument to
+`variable_scope` and `get_variable`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If any of the byte counts are non-positive.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/variable_creator_scope.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/variable_creator_scope.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..1f7fde0bd38
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/variable_creator_scope.md
@@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
+description: Scope which defines a variable creation function to be used by variable().
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.variable_creator_scope
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Scope which defines a variable creation function to be used by variable().
+
+
+@tf_contextlib.contextmanager
+tf.compat.v1.variable_creator_scope(
+ variable_creator
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+variable_creator is expected to be a function with the following signature:
+
+```
+ def variable_creator(next_creator, **kwargs)
+```
+
+The creator is supposed to eventually call the next_creator to create a
+variable if it does want to create a variable and not call Variable or
+ResourceVariable directly. This helps make creators composable. A creator may
+choose to create multiple variables, return already existing variables, or
+simply register that a variable was created and defer to the next creators in
+line. Creators can also modify the keyword arguments seen by the next
+creators.
+
+Custom getters in the variable scope will eventually resolve down to these
+custom creators when they do create variables.
+
+The valid keyword arguments in kwds are:
+
+ * initial_value: A `Tensor`, or Python object convertible to a `Tensor`,
+ which is the initial value for the Variable. The initial value must have
+ a shape specified unless `validate_shape` is set to False. Can also be a
+ callable with no argument that returns the initial value when called. In
+ that case, `dtype` must be specified. (Note that initializer functions
+ from init_ops.py must first be bound to a shape before being used here.)
+ * trainable: If `True`, the default, also adds the variable to the graph
+ collection `GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES`. This collection is used as
+ the default list of variables to use by the `Optimizer` classes.
+ `trainable` defaults to `True`, unless `synchronization` is
+ set to `ON_READ`, in which case it defaults to `False`.
+ * collections: List of graph collections keys. The new variable is added to
+ these collections. Defaults to `[GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES]`.
+ * validate_shape: If `False`, allows the variable to be initialized with a
+ value of unknown shape. If `True`, the default, the shape of
+ `initial_value` must be known.
+ * caching_device: Optional device string describing where the Variable
+ should be cached for reading. Defaults to the Variable's device.
+ If not `None`, caches on another device. Typical use is to cache
+ on the device where the Ops using the Variable reside, to deduplicate
+ copying through `Switch` and other conditional statements.
+ * name: Optional name for the variable. Defaults to `'Variable'` and gets
+ uniquified automatically.
+ * dtype: If set, initial_value will be converted to the given type.
+ If `None`, either the datatype will be kept (if `initial_value` is
+ a Tensor), or `convert_to_tensor` will decide.
+ * constraint: A constraint function to be applied to the variable after
+ updates by some algorithms.
+ * use_resource: if True, a ResourceVariable is always created.
+ * synchronization: Indicates when a distributed a variable will be
+ aggregated. Accepted values are constants defined in the class
+ tf.VariableSynchronization. By default the synchronization is set to
+ `AUTO` and the current `DistributionStrategy` chooses
+ when to synchronize.
+ * aggregation: Indicates how a distributed variable will be aggregated.
+ Accepted values are constants defined in the class
+ tf.VariableAggregation.
+
+This set may grow over time, so it's important the signature of creators is as
+mentioned above.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`variable_creator`
+ |
+
+the passed creator
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Yields:
+
+A scope in which the creator is active
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/variable_op_scope.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/variable_op_scope.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..6c5ea3efaf0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/variable_op_scope.md
@@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
+description: Deprecated: context manager for defining an op that creates variables.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.variable_op_scope
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Deprecated: context manager for defining an op that creates variables.
+
+
+@tf_contextlib.contextmanager
+tf.compat.v1.variable_op_scope(
+ values, name_or_scope, default_name=None, initializer=None, regularizer=None,
+ caching_device=None, partitioner=None, custom_getter=None, reuse=None,
+ dtype=None, use_resource=None, constraint=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/variable_scope.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/variable_scope.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a36bec48ca5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/variable_scope.md
@@ -0,0 +1,367 @@
+description: A context manager for defining ops that creates variables (layers).
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.variable_scope
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A context manager for defining ops that creates variables (layers).
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.variable_scope(
+ name_or_scope, default_name=None, values=None, initializer=None,
+ regularizer=None, caching_device=None, partitioner=None, custom_getter=None,
+ reuse=None, dtype=None, use_resource=None, constraint=None,
+ auxiliary_name_scope=(True)
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+This context manager validates that the (optional) `values` are from the same
+graph, ensures that graph is the default graph, and pushes a name scope and a
+variable scope.
+
+If `name_or_scope` is not None, it is used as is. If `name_or_scope` is None,
+then `default_name` is used. In that case, if the same name has been
+previously used in the same scope, it will be made unique by appending `_N`
+to it.
+
+Variable scope allows you to create new variables and to share already created
+ones while providing checks to not create or share by accident. For details,
+see the [Variable Scope How To](https://tensorflow.org/guide/variables), here
+we present only a few basic examples.
+
+Simple example of how to create a new variable:
+
+```python
+with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope("foo"):
+ with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope("bar"):
+ v = tf.compat.v1.get_variable("v", [1])
+ assert v.name == "foo/bar/v:0"
+```
+
+Simple example of how to reenter a premade variable scope safely:
+
+```python
+with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope("foo") as vs:
+ pass
+
+# Re-enter the variable scope.
+with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope(vs,
+ auxiliary_name_scope=False) as vs1:
+ # Restore the original name_scope.
+ with tf.name_scope(vs1.original_name_scope):
+ v = tf.compat.v1.get_variable("v", [1])
+ assert v.name == "foo/v:0"
+ c = tf.constant([1], name="c")
+ assert c.name == "foo/c:0"
+```
+
+Keep in mind that the counters for `default_name` are discarded once the
+parent scope is exited. Therefore when the code re-enters the scope (for
+instance by saving it), all nested default_name counters will be restarted.
+
+#### For instance:
+
+
+
+```python
+with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope("foo") as vs:
+ with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope(None, default_name="bar"):
+ v = tf.compat.v1.get_variable("a", [1])
+ assert v.name == "foo/bar/a:0", v.name
+ with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope(None, default_name="bar"):
+ v = tf.compat.v1.get_variable("b", [1])
+ assert v.name == "foo/bar_1/b:0"
+
+with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope(vs):
+ with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope(None, default_name="bar"):
+ v = tf.compat.v1.get_variable("c", [1])
+ assert v.name == "foo/bar/c:0" # Uses bar instead of bar_2!
+```
+
+Basic example of sharing a variable AUTO_REUSE:
+
+```python
+def foo():
+ with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope("foo", reuse=tf.compat.v1.AUTO_REUSE):
+ v = tf.compat.v1.get_variable("v", [1])
+ return v
+
+v1 = foo() # Creates v.
+v2 = foo() # Gets the same, existing v.
+assert v1 == v2
+```
+
+Basic example of sharing a variable with reuse=True:
+
+```python
+with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope("foo"):
+ v = tf.compat.v1.get_variable("v", [1])
+with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope("foo", reuse=True):
+ v1 = tf.compat.v1.get_variable("v", [1])
+assert v1 == v
+```
+
+Sharing a variable by capturing a scope and setting reuse:
+
+```python
+with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope("foo") as scope:
+ v = tf.compat.v1.get_variable("v", [1])
+ scope.reuse_variables()
+ v1 = tf.compat.v1.get_variable("v", [1])
+assert v1 == v
+```
+
+To prevent accidental sharing of variables, we raise an exception when getting
+an existing variable in a non-reusing scope.
+
+```python
+with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope("foo"):
+ v = tf.compat.v1.get_variable("v", [1])
+ v1 = tf.compat.v1.get_variable("v", [1])
+ # Raises ValueError("... v already exists ...").
+```
+
+Similarly, we raise an exception when trying to get a variable that does not
+exist in reuse mode.
+
+```python
+with tf.compat.v1.variable_scope("foo", reuse=True):
+ v = tf.compat.v1.get_variable("v", [1])
+ # Raises ValueError("... v does not exists ...").
+```
+
+Note that the `reuse` flag is inherited: if we open a reusing scope, then all
+its sub-scopes become reusing as well.
+
+A note about name scoping: Setting `reuse` does not impact the naming of other
+ops such as mult. See related discussion on
+[github#6189](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/issues/6189)
+
+Note that up to and including version 1.0, it was allowed (though explicitly
+discouraged) to pass False to the reuse argument, yielding undocumented
+behaviour slightly different from None. Starting at 1.1.0 passing None and
+False as reuse has exactly the same effect.
+
+A note about using variable scopes in multi-threaded environment: Variable
+scopes are thread local, so one thread will not see another thread's current
+scope. Also, when using `default_name`, unique scopes names are also generated
+only on a per thread basis. If the same name was used within a different
+thread, that doesn't prevent a new thread from creating the same scope.
+However, the underlying variable store is shared across threads (within the
+same graph). As such, if another thread tries to create a new variable with
+the same name as a variable created by a previous thread, it will fail unless
+reuse is True.
+
+Further, each thread starts with an empty variable scope. So if you wish to
+preserve name prefixes from a scope from the main thread, you should capture
+the main thread's scope and re-enter it in each thread. For e.g.
+
+```
+main_thread_scope = variable_scope.get_variable_scope()
+
+# Thread's target function:
+def thread_target_fn(captured_scope):
+ with variable_scope.variable_scope(captured_scope):
+ # .... regular code for this thread
+
+
+thread = threading.Thread(target=thread_target_fn, args=(main_thread_scope,))
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name_or_scope`
+ |
+
+`string` or `VariableScope`: the scope to open.
+ |
+
+|
+`default_name`
+ |
+
+The default name to use if the `name_or_scope` argument is
+`None`, this name will be uniquified. If name_or_scope is provided it
+won't be used and therefore it is not required and can be None.
+ |
+
+|
+`values`
+ |
+
+The list of `Tensor` arguments that are passed to the op function.
+ |
+
+|
+`initializer`
+ |
+
+default initializer for variables within this scope.
+ |
+
+|
+`regularizer`
+ |
+
+default regularizer for variables within this scope.
+ |
+
+|
+`caching_device`
+ |
+
+default caching device for variables within this scope.
+ |
+
+|
+`partitioner`
+ |
+
+default partitioner for variables within this scope.
+ |
+
+|
+`custom_getter`
+ |
+
+default custom getter for variables within this scope.
+ |
+
+|
+`reuse`
+ |
+
+`True`, None, or tf.compat.v1.AUTO_REUSE; if `True`, we go into
+reuse mode for this scope as well as all sub-scopes; if
+tf.compat.v1.AUTO_REUSE, we create variables if they do not exist, and
+return them otherwise; if None, we inherit the parent scope's reuse
+flag. When eager execution is enabled, new variables are always created
+unless an EagerVariableStore or template is currently active.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+type of variables created in this scope (defaults to the type in
+the passed scope, or inherited from parent scope).
+ |
+
+|
+`use_resource`
+ |
+
+If False, all variables will be regular Variables. If True,
+experimental ResourceVariables with well-defined semantics will be used
+instead. Defaults to False (will later change to True). When eager
+execution is enabled this argument is always forced to be True.
+ |
+
+|
+`constraint`
+ |
+
+An optional projection function to be applied to the variable
+after being updated by an `Optimizer` (e.g. used to implement norm
+constraints or value constraints for layer weights). The function must
+take as input the unprojected Tensor representing the value of the
+variable and return the Tensor for the projected value (which must have
+the same shape). Constraints are not safe to use when doing asynchronous
+distributed training.
+ |
+
+|
+`auxiliary_name_scope`
+ |
+
+If `True`, we create an auxiliary name scope with
+the scope. If `False`, we don't create it. Note that the argument is not
+inherited, and it only takes effect for once when creating. You should
+only use it for re-entering a premade variable scope.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+when trying to reuse within a create scope, or create within
+a reuse scope.
+ |
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+when the types of some arguments are not appropriate.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Methods
+
+__enter__
+
+View source
+
+
+__enter__()
+
+
+
+
+
+__exit__
+
+View source
+
+
+__exit__(
+ type_arg, value_arg, traceback_arg
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/variables_initializer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/variables_initializer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..5e4d1ce54f1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/variables_initializer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,91 @@
+description: Returns an Op that initializes a list of variables.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.variables_initializer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns an Op that initializes a list of variables.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.initializers.variables`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.variables_initializer(
+ var_list, name='init'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+After you launch the graph in a session, you can run the returned Op to
+initialize all the variables in `var_list`. This Op runs all the
+initializers of the variables in `var_list` in parallel.
+
+Calling `initialize_variables()` is equivalent to passing the list of
+initializers to `Group()`.
+
+If `var_list` is empty, however, the function still returns an Op that can
+be run. That Op just has no effect.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`var_list`
+ |
+
+List of `Variable` objects to initialize.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the returned operation.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+An Op that run the initializers of all the specified variables.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/verify_tensor_all_finite.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/verify_tensor_all_finite.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..27e4a2b8bf2
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/verify_tensor_all_finite.md
@@ -0,0 +1,103 @@
+description: Assert that the tensor does not contain any NaN's or Inf's.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.verify_tensor_all_finite
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Assert that the tensor does not contain any NaN's or Inf's.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.debugging.assert_all_finite`
+
+
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.verify_tensor_all_finite(
+ t=None, msg=None, name=None, x=None, message=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`t`
+ |
+
+Tensor to check.
+ |
+
+|
+`msg`
+ |
+
+Message to log on failure.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for this operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`x`
+ |
+
+Alias for t.
+ |
+
+|
+`message`
+ |
+
+Alias for msg.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Same tensor as `t`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/version.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/version.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..b7247ff9297
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/version.md
@@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
+description: Public API for tf.version namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.version
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.version namespace.
+
+
+
+## Other Members
+
+* `COMPILER_VERSION = '7.3.1 20180303'`
+* `GIT_VERSION = 'v2.2.0-rc4-8-g2b96f3662b'`
+* `GRAPH_DEF_VERSION = 175`
+* `GRAPH_DEF_VERSION_MIN_CONSUMER = 0`
+* `GRAPH_DEF_VERSION_MIN_PRODUCER = 0`
+* `VERSION = '2.2.0'`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/where.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/where.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..b5f40ad267d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/where.md
@@ -0,0 +1,127 @@
+description: Return the elements, either from x or y, depending on the condition.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.where
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Return the elements, either from `x` or `y`, depending on the `condition`.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.where(
+ condition, x=None, y=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+If both `x` and `y` are None, then this operation returns the coordinates of
+true elements of `condition`. The coordinates are returned in a 2-D tensor
+where the first dimension (rows) represents the number of true elements, and
+the second dimension (columns) represents the coordinates of the true
+elements. Keep in mind, the shape of the output tensor can vary depending on
+how many true values there are in input. Indices are output in row-major
+order.
+
+If both non-None, `x` and `y` must have the same shape.
+The `condition` tensor must be a scalar if `x` and `y` are scalar.
+If `x` and `y` are tensors of higher rank, then `condition` must be either a
+vector with size matching the first dimension of `x`, or must have the same
+shape as `x`.
+
+The `condition` tensor acts as a mask that chooses, based on the value at each
+element, whether the corresponding element / row in the output should be taken
+from `x` (if true) or `y` (if false).
+
+If `condition` is a vector and `x` and `y` are higher rank matrices, then it
+chooses which row (outer dimension) to copy from `x` and `y`. If `condition`
+has the same shape as `x` and `y`, then it chooses which element to copy from
+`x` and `y`.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`condition`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor` of type `bool`
+ |
+
+|
+`x`
+ |
+
+A Tensor which may have the same shape as `condition`. If `condition` is
+rank 1, `x` may have higher rank, but its first dimension must match the
+size of `condition`.
+ |
+
+|
+`y`
+ |
+
+A `tensor` with the same shape and type as `x`.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name of the operation (optional)
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` with the same type and shape as `x`, `y` if they are non-None.
+Otherwise, a `Tensor` with shape `(num_true, rank(condition))`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+When exactly one of `x` or `y` is non-None.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/while_loop.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/while_loop.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..37b230a7ad6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/while_loop.md
@@ -0,0 +1,295 @@
+description: Repeat body while the condition cond is true.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.while_loop
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Repeat `body` while the condition `cond` is true.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.while_loop(
+ cond, body, loop_vars, shape_invariants=None, parallel_iterations=10,
+ back_prop=(True), swap_memory=(False), name=None, maximum_iterations=None,
+ return_same_structure=(False)
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+`cond` is a callable returning a boolean scalar tensor. `body` is a callable
+returning a (possibly nested) tuple, namedtuple or list of tensors of the same
+arity (length and structure) and types as `loop_vars`. `loop_vars` is a
+(possibly nested) tuple, namedtuple or list of tensors that is passed to both
+`cond` and `body`. `cond` and `body` both take as many arguments as there are
+`loop_vars`.
+
+In addition to regular Tensors or IndexedSlices, the body may accept and
+return TensorArray objects. The flows of the TensorArray objects will
+be appropriately forwarded between loops and during gradient calculations.
+
+Note that `while_loop` calls `cond` and `body` *exactly once* (inside the
+call to `while_loop`, and not at all during `Session.run()`). `while_loop`
+stitches together the graph fragments created during the `cond` and `body`
+calls with some additional graph nodes to create the graph flow that
+repeats `body` until `cond` returns false.
+
+For correctness, tf.while_loop() strictly enforces shape invariants for
+the loop variables. A shape invariant is a (possibly partial) shape that
+is unchanged across the iterations of the loop. An error will be raised
+if the shape of a loop variable after an iteration is determined to be more
+general than or incompatible with its shape invariant. For example, a shape
+of [11, None] is more general than a shape of [11, 17], and [11, 21] is not
+compatible with [11, 17]. By default (if the argument `shape_invariants` is
+not specified), it is assumed that the initial shape of each tensor in
+`loop_vars` is the same in every iteration. The `shape_invariants` argument
+allows the caller to specify a less specific shape invariant for each loop
+variable, which is needed if the shape varies between iterations. The
+tf.Tensor.set_shape
+function may also be used in the `body` function to indicate that
+the output loop variable has a particular shape. The shape invariant for
+SparseTensor and IndexedSlices are treated specially as follows:
+
+a) If a loop variable is a SparseTensor, the shape invariant must be
+TensorShape([r]) where r is the rank of the dense tensor represented
+by the sparse tensor. It means the shapes of the three tensors of the
+SparseTensor are ([None], [None, r], [r]). NOTE: The shape invariant here
+is the shape of the SparseTensor.dense_shape property. It must be the shape of
+a vector.
+
+b) If a loop variable is an IndexedSlices, the shape invariant must be
+a shape invariant of the values tensor of the IndexedSlices. It means
+the shapes of the three tensors of the IndexedSlices are (shape, [shape[0]],
+[shape.ndims]).
+
+`while_loop` implements non-strict semantics, enabling multiple iterations
+to run in parallel. The maximum number of parallel iterations can be
+controlled by `parallel_iterations`, which gives users some control over
+memory consumption and execution order. For correct programs, `while_loop`
+should return the same result for any parallel_iterations > 0.
+
+For training, TensorFlow stores the tensors that are produced in the
+forward inference and are needed in back propagation. These tensors are a
+main source of memory consumption and often cause OOM errors when training
+on GPUs. When the flag swap_memory is true, we swap out these tensors from
+GPU to CPU. This for example allows us to train RNN models with very long
+sequences and large batches.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cond`
+ |
+
+A callable that represents the termination condition of the loop.
+ |
+
+|
+`body`
+ |
+
+A callable that represents the loop body.
+ |
+
+|
+`loop_vars`
+ |
+
+A (possibly nested) tuple, namedtuple or list of numpy array,
+`Tensor`, and `TensorArray` objects.
+ |
+
+|
+`shape_invariants`
+ |
+
+The shape invariants for the loop variables.
+ |
+
+|
+`parallel_iterations`
+ |
+
+The number of iterations allowed to run in parallel. It
+must be a positive integer.
+ |
+
+|
+`back_prop`
+ |
+
+Whether backprop is enabled for this while loop.
+ |
+
+|
+`swap_memory`
+ |
+
+Whether GPU-CPU memory swap is enabled for this loop.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name prefix for the returned tensors.
+ |
+
+|
+`maximum_iterations`
+ |
+
+Optional maximum number of iterations of the while loop
+to run. If provided, the `cond` output is AND-ed with an additional
+condition ensuring the number of iterations executed is no greater than
+`maximum_iterations`.
+ |
+
+|
+`return_same_structure`
+ |
+
+If True, output has same structure as `loop_vars`. If
+eager execution is enabled, this is ignored (and always treated as True).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+The output tensors for the loop variables after the loop.
+If `return_same_structure` is True, the return value has the same
+structure as `loop_vars`.
+If `return_same_structure` is False, the return value is a Tensor,
+TensorArray or IndexedSlice if the length of `loop_vars` is 1, or a list
+otherwise.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+if `cond` or `body` is not callable.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `loop_vars` is empty.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+i = tf.constant(0)
+c = lambda i: tf.less(i, 10)
+b = lambda i: tf.add(i, 1)
+r = tf.while_loop(c, b, [i])
+```
+
+Example with nesting and a namedtuple:
+
+```python
+import collections
+Pair = collections.namedtuple('Pair', 'j, k')
+ijk_0 = (tf.constant(0), Pair(tf.constant(1), tf.constant(2)))
+c = lambda i, p: i < 10
+b = lambda i, p: (i + 1, Pair((p.j + p.k), (p.j - p.k)))
+ijk_final = tf.while_loop(c, b, ijk_0)
+```
+
+Example using shape_invariants:
+
+```python
+i0 = tf.constant(0)
+m0 = tf.ones([2, 2])
+c = lambda i, m: i < 10
+b = lambda i, m: [i+1, tf.concat([m, m], axis=0)]
+tf.while_loop(
+ c, b, loop_vars=[i0, m0],
+ shape_invariants=[i0.get_shape(), tf.TensorShape([None, 2])])
+```
+
+Example which demonstrates non-strict semantics: In the following
+example, the final value of the counter `i` does not depend on `x`. So
+the `while_loop` can increment the counter parallel to updates of `x`.
+However, because the loop counter at one loop iteration depends
+on the value at the previous iteration, the loop counter itself cannot
+be incremented in parallel. Hence if we just want the final value of the
+counter (which we print on the line `print(sess.run(i))`), then
+`x` will never be incremented, but the counter will be updated on a
+single thread. Conversely, if we want the value of the output (which we
+print on the line `print(sess.run(out).shape)`), then the counter may be
+incremented on its own thread, while `x` can be incremented in
+parallel on a separate thread. In the extreme case, it is conceivable
+that the thread incrementing the counter runs until completion before
+`x` is incremented even a single time. The only thing that can never
+happen is that the thread updating `x` can never get ahead of the
+counter thread because the thread incrementing `x` depends on the value
+of the counter.
+
+```python
+import tensorflow as tf
+
+n = 10000
+x = tf.constant(list(range(n)))
+c = lambda i, x: i < n
+b = lambda i, x: (tf.compat.v1.Print(i + 1, [i]), tf.compat.v1.Print(x + 1,
+[i], "x:"))
+i, out = tf.while_loop(c, b, (0, x))
+with tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess:
+ print(sess.run(i)) # prints [0] ... [9999]
+
+ # The following line may increment the counter and x in parallel.
+ # The counter thread may get ahead of the other thread, but not the
+ # other way around. So you may see things like
+ # [9996] x:[9987]
+ # meaning that the counter thread is on iteration 9996,
+ # while the other thread is on iteration 9987
+ print(sess.run(out).shape)
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/wrap_function.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/wrap_function.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..ddcbef70ad3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/wrap_function.md
@@ -0,0 +1,122 @@
+description: Wraps the TF 1.x function fn into a graph function.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.wrap_function
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Wraps the TF 1.x function fn into a graph function.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.wrap_function(
+ fn, signature, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The python function `fn` will be called once with symbolic arguments specified
+in the `signature`, traced, and turned into a graph function. Any variables
+created by `fn` will be owned by the object returned by `wrap_function`. The
+resulting graph function can be called with tensors which match the
+signature.
+
+```python
+def f(x, do_add):
+ v = tf.Variable(5.0)
+ if do_add:
+ op = v.assign_add(x)
+ else:
+ op = v.assign_sub(x)
+ with tf.control_dependencies([op]):
+ return v.read_value()
+
+f_add = tf.compat.v1.wrap_function(f, [tf.TensorSpec((), tf.float32), True])
+
+assert float(f_add(1.0)) == 6.0
+assert float(f_add(1.0)) == 7.0
+
+# Can call tf.compat.v1.wrap_function again to get a new trace, a new set
+# of variables, and possibly different non-template arguments.
+f_sub= tf.compat.v1.wrap_function(f, [tf.TensorSpec((), tf.float32), False])
+
+assert float(f_sub(1.0)) == 4.0
+assert float(f_sub(1.0)) == 3.0
+```
+
+Both tf.compat.v1.wrap_function and tf.function create a callable
+TensorFlow graph. But while tf.function runs all stateful operations
+(e.g. tf.print) and sequences operations to provide the same semantics as
+eager execution, `wrap_function` is closer to the behavior of `session.run` in
+TensorFlow 1.x. It will not run any operations unless they are required to
+compute the function's outputs, either through a data dependency or a control
+dependency. Nor will it sequence operations.
+
+Unlike tf.function, `wrap_function` will only trace the Python function
+once. As with placeholders in TF 1.x, shapes and dtypes must be provided to
+`wrap_function`'s `signature` argument.
+
+Since it is only traced once, variables and state may be created inside the
+function and owned by the function wrapper object.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`fn`
+ |
+
+python function to be wrapped
+ |
+
+|
+`signature`
+ |
+
+the placeholder and python arguments to be passed to the wrapped
+function
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional. The name of the function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+the wrapped graph function.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/xla.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/xla.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..c7c2611d881
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/xla.md
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
+description: Public API for tf.xla namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.xla
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.xla namespace.
+
+
+
+## Modules
+
+[`experimental`](../../../tf/compat/v1/xla/experimental.md) module: Public API for tf.xla.experimental namespace.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/xla/experimental.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/xla/experimental.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e1d38e284a8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/xla/experimental.md
@@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
+description: Public API for tf.xla.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.compat.v1.xla.experimental
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.xla.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`compile(...)`](../../../../tf/xla/experimental/compile.md): Builds an operator that compiles and runs `computation` with XLA.
+
+[`jit_scope(...)`](../../../../tf/xla/experimental/jit_scope.md): Enable or disable JIT compilation of operators within the scope.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/zeros_like.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/zeros_like.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..b9361cab329
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/compat/v1/zeros_like.md
@@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
+description: Creates a tensor with all elements set to zero.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.compat.v1.zeros_like
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Creates a tensor with all elements set to zero.
+
+
+tf.compat.v1.zeros_like(
+ tensor, dtype=None, name=None, optimize=(True)
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+See also tf.zeros.
+
+Given a single tensor (`tensor`), this operation returns a tensor of the
+same type and shape as `tensor` with all elements set to zero. Optionally,
+you can use `dtype` to specify a new type for the returned tensor.
+
+#### Examples:
+
+
+```
+>>> tensor = tf.constant([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
+>>> tf.zeros_like(tensor)
+
+```
+
+```
+>>> tf.zeros_like(tensor, dtype=tf.float32)
+
+```
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`tensor`
+ |
+
+A `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+A type for the returned `Tensor`. Must be `float16`, `float32`,
+`float64`, `int8`, `uint8`, `int16`, `uint16`, `int32`, `int64`,
+`complex64`, `complex128`, `bool` or `string`. (optional)
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+|
+`optimize`
+ |
+
+if `True`, attempt to statically determine the shape of `tensor`
+and encode it as a constant. (optional, defaults to `True`)
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` with all elements set to zero.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/concat.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/concat.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..680541b1ea1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/concat.md
@@ -0,0 +1,164 @@
+description: Concatenates tensors along one dimension.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.concat
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Concatenates tensors along one dimension.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.concat`
+
+
+
+
+tf.concat(
+ values, axis, name='concat'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+See also tf.tile, tf.stack, tf.repeat.
+
+Concatenates the list of tensors `values` along dimension `axis`. If
+`values[i].shape = [D0, D1, ... Daxis(i), ...Dn]`, the concatenated
+result has shape
+
+ [D0, D1, ... Raxis, ...Dn]
+
+where
+
+ Raxis = sum(Daxis(i))
+
+That is, the data from the input tensors is joined along the `axis`
+dimension.
+
+The number of dimensions of the input tensors must match, and all dimensions
+except `axis` must be equal.
+
+#### For example:
+
+
+
+```
+>>> t1 = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]
+>>> t2 = [[7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 12]]
+>>> concat([t1, t2], 0)
+
+```
+
+```
+>>> concat([t1, t2], 1)
+
+```
+
+As in Python, the `axis` could also be negative numbers. Negative `axis`
+are interpreted as counting from the end of the rank, i.e.,
+ `axis + rank(values)`-th dimension.
+
+#### For example:
+
+
+
+```
+>>> t1 = [[[1, 2], [2, 3]], [[4, 4], [5, 3]]]
+>>> t2 = [[[7, 4], [8, 4]], [[2, 10], [15, 11]]]
+>>> tf.concat([t1, t2], -1)
+
+```
+
+Note: If you are concatenating along a new axis consider using stack.
+E.g.
+
+```python
+tf.concat([tf.expand_dims(t, axis) for t in tensors], axis)
+```
+
+can be rewritten as
+
+```python
+tf.stack(tensors, axis=axis)
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`values`
+ |
+
+A list of `Tensor` objects or a single `Tensor`.
+ |
+
+|
+`axis`
+ |
+
+0-D `int32` `Tensor`. Dimension along which to concatenate. Must be
+in the range `[-rank(values), rank(values))`. As in Python, indexing for
+axis is 0-based. Positive axis in the rage of `[0, rank(values))` refers
+to `axis`-th dimension. And negative axis refers to `axis +
+rank(values)`-th dimension.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+A name for the operation (optional).
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A `Tensor` resulting from concatenation of the input tensors.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/cond.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/cond.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..b926545931f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/cond.md
@@ -0,0 +1,164 @@
+description: Return true_fn() if the predicate pred is true else false_fn().
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.cond
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Return `true_fn()` if the predicate `pred` is true else `false_fn()`.
+
+
+tf.cond(
+ pred, true_fn=None, false_fn=None, name=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+`true_fn` and `false_fn` both return lists of output tensors. `true_fn` and
+`false_fn` must have the same non-zero number and type of outputs.
+
+**WARNING**: Any Tensors or Operations created outside of `true_fn` and
+`false_fn` will be executed regardless of which branch is selected at runtime.
+
+Although this behavior is consistent with the dataflow model of TensorFlow,
+it has frequently surprised users who expected a lazier semantics.
+Consider the following simple program:
+
+```python
+z = tf.multiply(a, b)
+result = tf.cond(x < y, lambda: tf.add(x, z), lambda: tf.square(y))
+```
+
+If `x < y`, the `tf.add` operation will be executed and `tf.square`
+operation will not be executed. Since `z` is needed for at least one
+branch of the `cond`, the tf.multiply operation is always executed,
+unconditionally.
+
+Note that `cond` calls `true_fn` and `false_fn` *exactly once* (inside the
+call to `cond`, and not at all during `Session.run()`). `cond`
+stitches together the graph fragments created during the `true_fn` and
+`false_fn` calls with some additional graph nodes to ensure that the right
+branch gets executed depending on the value of `pred`.
+
+tf.cond supports nested structures as implemented in
+`tensorflow.python.util.nest`. Both `true_fn` and `false_fn` must return the
+same (possibly nested) value structure of lists, tuples, and/or named tuples.
+Singleton lists and tuples form the only exceptions to this: when returned by
+`true_fn` and/or `false_fn`, they are implicitly unpacked to single values.
+
+Note: It is illegal to "directly" use tensors created inside a cond branch
+outside it, e.g. by storing a reference to a branch tensor in the python
+state. If you need to use a tensor created in a branch function you should
+return it as an output of the branch function and use the output from
+tf.cond instead.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`pred`
+ |
+
+A scalar determining whether to return the result of `true_fn` or
+`false_fn`.
+ |
+
+|
+`true_fn`
+ |
+
+The callable to be performed if pred is true.
+ |
+
+|
+`false_fn`
+ |
+
+The callable to be performed if pred is false.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name prefix for the returned tensors.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Tensors returned by the call to either `true_fn` or `false_fn`. If the
+callables return a singleton list, the element is extracted from the list.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+if `true_fn` or `false_fn` is not callable.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if `true_fn` and `false_fn` do not return the same number of
+tensors, or return tensors of different types.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+#### Example:
+
+
+
+```python
+x = tf.constant(2)
+y = tf.constant(5)
+def f1(): return tf.multiply(x, 17)
+def f2(): return tf.add(y, 23)
+r = tf.cond(tf.less(x, y), f1, f2)
+# r is set to f1().
+# Operations in f2 (e.g., tf.add) are not executed.
+```
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..361898d4d65
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config.md
@@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
+description: Public API for tf.config namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.config
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.config namespace.
+
+
+
+## Modules
+
+[`experimental`](../tf/config/experimental.md) module: Public API for tf.config.experimental namespace.
+
+[`optimizer`](../tf/config/optimizer.md) module: Public API for tf.config.optimizer namespace.
+
+[`threading`](../tf/config/threading.md) module: Public API for tf.config.threading namespace.
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class LogicalDevice`](../tf/config/LogicalDevice.md): Abstraction for a logical device initialized by the runtime.
+
+[`class LogicalDeviceConfiguration`](../tf/config/LogicalDeviceConfiguration.md): Configuration class for a logical devices.
+
+[`class PhysicalDevice`](../tf/config/PhysicalDevice.md): Abstraction for a locally visible physical device.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`experimental_connect_to_cluster(...)`](../tf/config/experimental_connect_to_cluster.md): Connects to the given cluster.
+
+[`experimental_connect_to_host(...)`](../tf/config/experimental_connect_to_host.md): Connects to a single machine to enable remote execution on it.
+
+[`experimental_functions_run_eagerly(...)`](../tf/config/experimental_functions_run_eagerly.md): Returns the value of the `experimental_run_functions_eagerly` setting.
+
+[`experimental_run_functions_eagerly(...)`](../tf/config/experimental_run_functions_eagerly.md): Enables / disables eager execution of tf.functions.
+
+[`get_logical_device_configuration(...)`](../tf/config/get_logical_device_configuration.md): Get the virtual device configuration for a tf.config.PhysicalDevice.
+
+[`get_soft_device_placement(...)`](../tf/config/get_soft_device_placement.md): Get if soft device placement is enabled.
+
+[`get_visible_devices(...)`](../tf/config/get_visible_devices.md): Get the list of visible physical devices.
+
+[`list_logical_devices(...)`](../tf/config/list_logical_devices.md): Return a list of logical devices created by runtime.
+
+[`list_physical_devices(...)`](../tf/config/list_physical_devices.md): Return a list of physical devices visible to the host runtime.
+
+[`set_logical_device_configuration(...)`](../tf/config/set_logical_device_configuration.md): Set the logical device configuration for a tf.config.PhysicalDevice.
+
+[`set_soft_device_placement(...)`](../tf/config/set_soft_device_placement.md): Set if soft device placement is enabled.
+
+[`set_visible_devices(...)`](../tf/config/set_visible_devices.md): Set the list of visible devices.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/LogicalDevice.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/LogicalDevice.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..ef1a6b7a9d0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/LogicalDevice.md
@@ -0,0 +1,91 @@
+description: Abstraction for a logical device initialized by the runtime.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.config.LogicalDevice
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Abstraction for a logical device initialized by the runtime.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.config.LogicalDevice`
+
+
+
+
+tf.config.LogicalDevice(
+ name, device_type
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A tf.config.LogicalDevice corresponds to an initialized logical device on a
+tf.config.PhysicalDevice or a remote device visible to the cluster. Tensors
+and operations can be placed on a specific logical device by calling
+tf.device with a specified tf.config.LogicalDevice.
+
+#### Fields:
+
+
+* `name`: The fully qualified name of the device. Can be used for Op or function
+ placement.
+* `device_type`: String declaring the type of device such as "CPU" or "GPU".
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`device_type`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `device_type`
+* `name`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/LogicalDeviceConfiguration.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/LogicalDeviceConfiguration.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..51151b4b59c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/LogicalDeviceConfiguration.md
@@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
+description: Configuration class for a logical devices.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.config.LogicalDeviceConfiguration
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Configuration class for a logical devices.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Main aliases
+
`tf.config.experimental.VirtualDeviceConfiguration`
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.config.LogicalDeviceConfiguration`, `tf.compat.v1.config.experimental.VirtualDeviceConfiguration`
+
+
+
+
+tf.config.LogicalDeviceConfiguration(
+ memory_limit=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The class specifies the parameters to configure a tf.config.PhysicalDevice
+as it is initialized to a tf.config.LogicalDevice during runtime
+initialization. Not all fields are valid for all device types.
+
+See tf.config.get_logical_device_configuration and
+tf.config.set_logical_device_configuration for usage examples.
+
+#### Fields:
+
+
+* `memory_limit`: (optional) Maximum memory (in MB) to allocate on the virtual
+ device. Currently only supported for GPUs.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`memory_limit`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `memory_limit`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/PhysicalDevice.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/PhysicalDevice.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..9ee4a8038d8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/PhysicalDevice.md
@@ -0,0 +1,98 @@
+description: Abstraction for a locally visible physical device.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.config.PhysicalDevice
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Abstraction for a locally visible physical device.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.config.PhysicalDevice`
+
+
+
+
+tf.config.PhysicalDevice(
+ name, device_type
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+TensorFlow can utilize various devices such as the CPU or multiple GPUs
+for computation. Before initializing a local device for use, the user can
+customize certain properties of the device such as it's visibility or memory
+configuration.
+
+Once a visible tf.config.PhysicalDevice is initialized one or more
+tf.config.LogicalDevice objects are created. Use
+tf.config.set_visible_devices to configure the visibility of a physical
+device and tf.config.set_logical_device_configuration to configure multiple
+tf.config.LogicalDevice objects for a tf.config.PhysicalDevice. This is
+useful when separation between models is needed or to simulate a multi-device
+environment.
+
+#### Fields:
+
+
+* `name`: Unique identifier for device.
+* `device_type`: String declaring the type of device such as "CPU" or "GPU".
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Attributes |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+|
+`device_type`
+ |
+
+
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+## Class Variables
+
+* `device_type`
+* `name`
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..8c6fde8e57b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental.md
@@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
+description: Public API for tf.config.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.config.experimental
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.config.experimental namespace.
+
+
+
+## Classes
+
+[`class ClusterDeviceFilters`](../../tf/config/experimental/ClusterDeviceFilters.md): Represent a collection of device filters for the remote workers in cluster.
+
+[`class VirtualDeviceConfiguration`](../../tf/config/LogicalDeviceConfiguration.md): Configuration class for a logical devices.
+
+## Functions
+
+[`disable_mlir_bridge(...)`](../../tf/config/experimental/disable_mlir_bridge.md): Disables experimental MLIR-Based TensorFlow Compiler Bridge.
+
+[`enable_mlir_bridge(...)`](../../tf/config/experimental/enable_mlir_bridge.md): Enables experimental MLIR-Based TensorFlow Compiler Bridge.
+
+[`get_device_policy(...)`](../../tf/config/experimental/get_device_policy.md): Gets the current device policy.
+
+[`get_memory_growth(...)`](../../tf/config/experimental/get_memory_growth.md): Get if memory growth is enabled for a `PhysicalDevice`.
+
+[`get_synchronous_execution(...)`](../../tf/config/experimental/get_synchronous_execution.md): Gets whether operations are executed synchronously or asynchronously.
+
+[`get_virtual_device_configuration(...)`](../../tf/config/get_logical_device_configuration.md): Get the virtual device configuration for a tf.config.PhysicalDevice.
+
+[`get_visible_devices(...)`](../../tf/config/get_visible_devices.md): Get the list of visible physical devices.
+
+[`list_logical_devices(...)`](../../tf/config/list_logical_devices.md): Return a list of logical devices created by runtime.
+
+[`list_physical_devices(...)`](../../tf/config/list_physical_devices.md): Return a list of physical devices visible to the host runtime.
+
+[`set_device_policy(...)`](../../tf/config/experimental/set_device_policy.md): Sets the current thread device policy.
+
+[`set_memory_growth(...)`](../../tf/config/experimental/set_memory_growth.md): Set if memory growth should be enabled for a `PhysicalDevice`.
+
+[`set_synchronous_execution(...)`](../../tf/config/experimental/set_synchronous_execution.md): Specifies whether operations are executed synchronously or asynchronously.
+
+[`set_virtual_device_configuration(...)`](../../tf/config/set_logical_device_configuration.md): Set the logical device configuration for a tf.config.PhysicalDevice.
+
+[`set_visible_devices(...)`](../../tf/config/set_visible_devices.md): Set the list of visible devices.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental/ClusterDeviceFilters.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental/ClusterDeviceFilters.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..f7bd7b1f414
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental/ClusterDeviceFilters.md
@@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
+description: Represent a collection of device filters for the remote workers in cluster.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.config.experimental.ClusterDeviceFilters
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Represent a collection of device filters for the remote workers in cluster.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.config.experimental.ClusterDeviceFilters`
+
+
+
+
+tf.config.experimental.ClusterDeviceFilters()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+NOTE: this is an experimental API and subject to changes.
+
+Set device filters for selective jobs and tasks. For each remote worker, the
+device filters are a list of strings. When any filters are present, the remote
+worker will ignore all devices which do not match any of its filters. Each
+filter can be partially specified, e.g. "/job:ps", "/job:worker/replica:3",
+etc. Note that a device is always visible to the worker it is located on.
+
+For example, to set the device filters for a parameter server cluster:
+
+```python
+cdf = tf.config.experimental.ClusterDeviceFilters()
+for i in range(num_workers):
+ cdf.set_device_filters('worker', i, ['/job:ps'])
+for i in range(num_ps):
+ cdf.set_device_filters('ps', i, ['/job:worker'])
+
+tf.config.experimental_connect_to_cluster(cluster_def,
+ cluster_device_filters=cdf)
+```
+
+The device filters can be partically specified. For remote tasks that do not
+have device filters specified, all devices will be visible to them.
+
+## Methods
+
+set_device_filters
+
+View source
+
+
+set_device_filters(
+ job_name, task_index, device_filters
+)
+
+
+Set the device filters for given job name and task id.
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental/disable_mlir_bridge.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental/disable_mlir_bridge.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..2e272dd73f6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental/disable_mlir_bridge.md
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
+description: Disables experimental MLIR-Based TensorFlow Compiler Bridge.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.config.experimental.disable_mlir_bridge
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Disables experimental MLIR-Based TensorFlow Compiler Bridge.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.config.experimental.disable_mlir_bridge`
+
+
+
+
+tf.config.experimental.disable_mlir_bridge()
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental/enable_mlir_bridge.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental/enable_mlir_bridge.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..0da6ae72c29
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental/enable_mlir_bridge.md
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
+description: Enables experimental MLIR-Based TensorFlow Compiler Bridge.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.config.experimental.enable_mlir_bridge
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Enables experimental MLIR-Based TensorFlow Compiler Bridge.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.config.experimental.enable_mlir_bridge`
+
+
+
+
+tf.config.experimental.enable_mlir_bridge()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+DO NOT USE, DEV AND TESTING ONLY AT THE MOMENT.
+
+NOTE: MLIR-Based TensorFlow Compiler is under active development and has
+missing features, please refrain from using. This API exists for development
+and testing only.
+
+TensorFlow Compiler Bridge (TF Bridge) is responsible for translating parts
+of TensorFlow graph into a form that can be accepted as an input by a backend
+compiler such as XLA.
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental/get_device_policy.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental/get_device_policy.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..1d2c18fbea5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental/get_device_policy.md
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
+description: Gets the current device policy.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.config.experimental.get_device_policy
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Gets the current device policy.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.config.experimental.get_device_policy`
+
+
+
+
+tf.config.experimental.get_device_policy()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The device policy controls how operations requiring inputs on a specific
+device (e.g., on GPU:0) handle inputs on a different device (e.g. GPU:1).
+
+This function only gets the device policy for the current thread. Any
+subsequently started thread will again use the default policy.
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Current thread device policy
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental/get_memory_growth.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental/get_memory_growth.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..54648cca40b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental/get_memory_growth.md
@@ -0,0 +1,108 @@
+description: Get if memory growth is enabled for a PhysicalDevice.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.config.experimental.get_memory_growth
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Get if memory growth is enabled for a `PhysicalDevice`.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.config.experimental.get_memory_growth`
+
+
+
+
+tf.config.experimental.get_memory_growth(
+ device
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+If memory growth is enabled for a `PhysicalDevice`, the runtime initialization
+will not allocate all memory on the device.
+
+#### For example:
+
+
+
+```
+>>> physical_devices = tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU')
+>>> try:
+... tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(physical_devices[0], True)
+... assert tf.config.experimental.get_memory_growth(physical_devices[0])
+... except:
+... # Invalid device or cannot modify virtual devices once initialized.
+... pass
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`device`
+ |
+
+`PhysicalDevice` to query
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A boolean indicating the memory growth setting for the `PhysicalDevice`.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+Invalid `PhysicalDevice` specified.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental/get_synchronous_execution.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental/get_synchronous_execution.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..497eff87d38
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental/get_synchronous_execution.md
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
+description: Gets whether operations are executed synchronously or asynchronously.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.config.experimental.get_synchronous_execution
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Gets whether operations are executed synchronously or asynchronously.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.config.experimental.get_synchronous_execution`
+
+
+
+
+tf.config.experimental.get_synchronous_execution()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+TensorFlow can execute operations synchronously or asynchronously. If
+asynchronous execution is enabled, operations may return "non-ready" handles.
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Current thread execution mode
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental/set_device_policy.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental/set_device_policy.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..65ad0727956
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental/set_device_policy.md
@@ -0,0 +1,96 @@
+description: Sets the current thread device policy.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.config.experimental.set_device_policy
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Sets the current thread device policy.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.config.experimental.set_device_policy`
+
+
+
+
+tf.config.experimental.set_device_policy(
+ device_policy
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+The device policy controls how operations requiring inputs on a specific
+device (e.g., on GPU:0) handle inputs on a different device (e.g. GPU:1).
+
+When using the default, an appropriate policy will be picked automatically.
+The default policy may change over time.
+
+This function only sets the device policy for the current thread. Any
+subsequently started thread will again use the default policy.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`device_policy`
+ |
+
+A device policy.
+Valid values:
+- None: Switch to a system default.
+- 'warn': Copies the tensors which are not on the right device and logs
+a warning.
+- 'explicit': Raises an error if the placement is not as required.
+- 'silent': Silently copies the tensors. Note that this may hide
+performance problems as there is no notification provided when
+operations are blocked on the tensor being copied between devices.
+- 'silent_for_int32': silently copies `int32` tensors, raising errors on
+the other ones.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If an invalid `device_policy` is passed.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental/set_memory_growth.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental/set_memory_growth.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..b3f9b8a75e3
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental/set_memory_growth.md
@@ -0,0 +1,108 @@
+description: Set if memory growth should be enabled for a PhysicalDevice.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Set if memory growth should be enabled for a `PhysicalDevice`.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.config.experimental.set_memory_growth`
+
+
+
+
+tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(
+ device, enable
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+If memory growth is enabled for a `PhysicalDevice`, the runtime initialization
+will not allocate all memory on the device. Memory growth cannot be configured
+on a `PhysicalDevice` with virtual devices configured.
+
+#### For example:
+
+
+
+```
+>>> physical_devices = tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU')
+>>> try:
+... tf.config.experimental.set_memory_growth(physical_devices[0], True)
+... except:
+... # Invalid device or cannot modify virtual devices once initialized.
+... pass
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`device`
+ |
+
+`PhysicalDevice` to configure
+ |
+
+|
+`enable`
+ |
+
+(Boolean) Whether to enable or disable memory growth
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+Invalid `PhysicalDevice` specified.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+Runtime is already initialized.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental/set_synchronous_execution.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental/set_synchronous_execution.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..0ba95c68e8b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental/set_synchronous_execution.md
@@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
+description: Specifies whether operations are executed synchronously or asynchronously.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.config.experimental.set_synchronous_execution
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Specifies whether operations are executed synchronously or asynchronously.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.config.experimental.set_synchronous_execution`
+
+
+
+
+tf.config.experimental.set_synchronous_execution(
+ enable
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+TensorFlow can execute operations synchronously or asynchronously. If
+asynchronous execution is enabled, operations may return "non-ready" handles.
+
+When `enable` is set to None, an appropriate value will be picked
+automatically. The value picked may change between TensorFlow releases.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`enable`
+ |
+
+Whether operations should be dispatched synchronously.
+Valid values:
+- None: sets the system default.
+- True: executes each operation synchronously.
+- False: executes each operation asynchronously.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental_connect_to_cluster.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental_connect_to_cluster.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3708e5d1924
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental_connect_to_cluster.md
@@ -0,0 +1,135 @@
+description: Connects to the given cluster.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.config.experimental_connect_to_cluster
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Connects to the given cluster.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.config.experimental_connect_to_cluster`
+
+
+
+
+tf.config.experimental_connect_to_cluster(
+ cluster_spec_or_resolver, job_name='localhost', task_index=0, protocol=None,
+ make_master_device_default=(True), cluster_device_filters=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Will make devices on the cluster available to use. Note that calling this more
+than once will work, but will invalidate any tensor handles on the old remote
+devices.
+
+If the given local job name is not present in the cluster specification, it
+will be automatically added, using an unused port on the localhost.
+
+Device filters can be specified to isolate groups of remote tasks to avoid
+undesired accesses between workers. Workers accessing resources or launching
+ops / functions on filtered remote devices will result in errors (unknown
+devices). For any remote task, if no device filter is present, all cluster
+devices will be visible; if any device filter is specified, it can only
+see devices matching at least one filter. Devices on the task itself are
+always visible. Device filters can be particially specified.
+
+For example, for a cluster set up for parameter server training, the following
+device filters might be specified:
+
+```python
+cdf = tf.config.experimental.ClusterDeviceFilters()
+# For any worker, only the devices on PS nodes and itself are visible
+for i in range(num_workers):
+ cdf.set_device_filters('worker', i, ['/job:ps'])
+# Similarly for any ps, only the devices on workers and itself are visible
+for i in range(num_ps):
+ cdf.set_device_filters('ps', i, ['/job:worker'])
+
+tf.config.experimental_connect_to_cluster(cluster_def,
+ cluster_device_filters=cdf)
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`cluster_spec_or_resolver`
+ |
+
+A `ClusterSpec` or `ClusterResolver` describing
+the cluster.
+ |
+
+|
+`job_name`
+ |
+
+The name of the local job.
+ |
+
+|
+`task_index`
+ |
+
+The local task index.
+ |
+
+|
+`protocol`
+ |
+
+The communication protocol, such as `"grpc"`. If unspecified, will
+use the default from `python/platform/remote_utils.py`.
+ |
+
+|
+`make_master_device_default`
+ |
+
+If True and a cluster resolver is passed, will
+automatically enter the master task device scope, which indicates the
+master becomes the default device to run ops. It won't do anything if
+a cluster spec is passed. Will throw an error if the caller is currently
+already in some device scope.
+ |
+
+|
+`cluster_device_filters`
+ |
+
+an instance of
+`tf.train.experimental/ClusterDeviceFilters` that specify device filters
+to the remote tasks in cluster.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental_connect_to_host.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental_connect_to_host.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a29cba3738e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental_connect_to_host.md
@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
+description: Connects to a single machine to enable remote execution on it.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.config.experimental_connect_to_host
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Connects to a single machine to enable remote execution on it.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.config.experimental_connect_to_host`
+
+
+
+
+tf.config.experimental_connect_to_host(
+ remote_host=None, job_name='worker'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Will make devices on the remote host available to use. Note that calling this
+more than once will work, but will invalidate any tensor handles on the old
+remote devices.
+
+Using the default job_name of worker, you can schedule ops to run remotely as
+follows:
+```python
+# When eager execution is enabled, connect to the remote host.
+tf.config.experimental_connect_to_host("exampleaddr.com:9876")
+
+with ops.device("job:worker/replica:0/task:1/device:CPU:0"):
+ # The following tensors should be resident on the remote device, and the op
+ # will also execute remotely.
+ x1 = array_ops.ones([2, 2])
+ x2 = array_ops.ones([2, 2])
+ y = math_ops.matmul(x1, x2)
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`remote_host`
+ |
+
+a single or a list the remote server addr in host-port format.
+ |
+
+|
+`job_name`
+ |
+
+The job name under which the new server will be accessible.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if remote_host is None.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental_functions_run_eagerly.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental_functions_run_eagerly.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..df1f15a2604
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental_functions_run_eagerly.md
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
+description: Returns the value of the experimental_run_functions_eagerly setting.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.config.experimental_functions_run_eagerly
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns the value of the `experimental_run_functions_eagerly` setting.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.config.experimental_functions_run_eagerly`
+
+
+
+
+tf.config.experimental_functions_run_eagerly()
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental_run_functions_eagerly.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental_run_functions_eagerly.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e029cf5dc5a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/experimental_run_functions_eagerly.md
@@ -0,0 +1,98 @@
+description: Enables / disables eager execution of tf.functions.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.config.experimental_run_functions_eagerly
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Enables / disables eager execution of tf.functions.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.config.experimental_run_functions_eagerly`
+
+
+
+
+tf.config.experimental_run_functions_eagerly(
+ run_eagerly
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Calling tf.config.experimental_run_functions_eagerly(True) will make all
+invocations of tf.function run eagerly instead of running as a traced graph
+function.
+
+This can be useful for debugging or profiling. For example, let's say you
+implemented a simple iterative sqrt function, and you want to collect the
+intermediate values and plot the convergence. Appending the values to a list
+in `@tf.function` normally wouldn't work since it will just record the Tensors
+being traced, not the values. Instead, you can do the following.
+
+```
+>>> ys = []
+>>>
+>>> @tf.function
+... def sqrt(x):
+... y = x / 2
+... d = y
+... for _ in range(10):
+... d /= 2
+... if y * y < x:
+... y += d
+... else:
+... y -= d
+... ys.append(y.numpy())
+... return y
+>>>
+>>> tf.config.experimental_run_functions_eagerly(True)
+>>> sqrt(tf.constant(2.))
+
+>>> ys
+[1.5, 1.25, 1.375, 1.4375, 1.40625, 1.421875, 1.4140625, 1.4179688, 1.4160156,
+1.4150391]
+>>> tf.config.experimental_run_functions_eagerly(False)
+```
+
+Calling tf.config.experimental_run_functions_eagerly(False) will undo this
+behavior.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`run_eagerly`
+ |
+
+Boolean. Whether to run functions eagerly.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/get_logical_device_configuration.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/get_logical_device_configuration.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..ee22181b23e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/get_logical_device_configuration.md
@@ -0,0 +1,106 @@
+description: Get the virtual device configuration for a tf.config.PhysicalDevice.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.config.get_logical_device_configuration
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Get the virtual device configuration for a tf.config.PhysicalDevice.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Main aliases
+
`tf.config.experimental.get_virtual_device_configuration`
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.config.experimental.get_virtual_device_configuration`, `tf.compat.v1.config.get_logical_device_configuration`
+
+
+
+
+tf.config.get_logical_device_configuration(
+ device
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns the list of tf.config.LogicalDeviceConfiguration
+objects previously configured by a call to
+tf.config.set_logical_device_configuration.
+
+#### For example:
+
+
+
+```
+>>> physical_devices = tf.config.list_physical_devices('CPU')
+>>> assert len(physical_devices) == 1, "No CPUs found"
+>>> configs = tf.config.get_logical_device_configuration(
+... physical_devices[0])
+>>> try:
+... assert configs is None
+... tf.config.set_logical_device_configuration(
+... physical_devices[0],
+... [tf.config.LogicalDeviceConfiguration(),
+... tf.config.LogicalDeviceConfiguration()])
+... configs = tf.config.get_logical_device_configuration(
+... physical_devices[0])
+... assert len(configs) == 2
+... except:
+... # Cannot modify virtual devices once initialized.
+... pass
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`device`
+ |
+
+`PhysicalDevice` to query
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/get_soft_device_placement.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/get_soft_device_placement.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a81cd39259a
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/get_soft_device_placement.md
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+description: Get if soft device placement is enabled.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.config.get_soft_device_placement
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Get if soft device placement is enabled.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.config.get_soft_device_placement`
+
+
+
+
+tf.config.get_soft_device_placement()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+If enabled, an op will be placed on CPU if any of the following are true
+ 1. there's no GPU implementation for the OP
+ 2. no GPU devices are known or registered
+ 3. need to co-locate with reftype input(s) which are from CPU
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+If soft placement is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/get_visible_devices.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/get_visible_devices.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..e3109b0a523
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/get_visible_devices.md
@@ -0,0 +1,97 @@
+description: Get the list of visible physical devices.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.config.get_visible_devices
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Get the list of visible physical devices.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Main aliases
+
`tf.config.experimental.get_visible_devices`
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.config.experimental.get_visible_devices`, `tf.compat.v1.config.get_visible_devices`
+
+
+
+
+tf.config.get_visible_devices(
+ device_type=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns the list of `PhysicalDevice`s currently marked as visible to the
+runtime. A visible device will have at least one `LogicalDevice` associated
+with it once the runtime is initialized.
+
+The following example verifies all visible GPUs have been disabled:
+
+```
+>>> physical_devices = tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU')
+>>> try:
+... # Disable all GPUS
+... tf.config.set_visible_devices([], 'GPU')
+... visible_devices = tf.config.get_visible_devices()
+... for device in visible_devices:
+... assert device.device_type != 'GPU'
+... except:
+... # Invalid device or cannot modify virtual devices once initialized.
+... pass
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`device_type`
+ |
+
+(optional string) Only include devices matching this device
+type. For example "CPU" or "GPU".
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+List of visible `PhysicalDevice`s
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/list_logical_devices.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/list_logical_devices.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..79c664dfb35
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/list_logical_devices.md
@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
+description: Return a list of logical devices created by runtime.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.config.list_logical_devices
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Return a list of logical devices created by runtime.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Main aliases
+
`tf.config.experimental.list_logical_devices`
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.config.experimental.list_logical_devices`, `tf.compat.v1.config.list_logical_devices`
+
+
+
+
+tf.config.list_logical_devices(
+ device_type=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Logical devices may correspond to physical devices or remote devices in the
+cluster. Operations and tensors may be placed on these devices by using the
+`name` of the tf.config.LogicalDevice.
+
+Calling tf.config.list_logical_devices triggers the runtime to configure any
+tf.config.PhysicalDevice visible to the runtime, thereby preventing
+further configuration. To avoid runtime initialization, call
+tf.config.list_physical_devices instead.
+
+#### For example:
+
+
+
+```
+>>> logical_devices = tf.config.list_logical_devices('GPU')
+>>> if len(logical_devices) > 0:
+... # Allocate on GPU:0
+... with tf.device(logical_devices[0].name):
+... one = tf.constant(1)
+... # Allocate on GPU:1
+... with tf.device(logical_devices[1].name):
+... two = tf.constant(2)
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`device_type`
+ |
+
+(optional string) Only include devices matching this device
+type. For example "CPU" or "GPU".
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+List of initialized `LogicalDevice`s
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/list_physical_devices.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/list_physical_devices.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..2d91651ce99
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/list_physical_devices.md
@@ -0,0 +1,98 @@
+description: Return a list of physical devices visible to the host runtime.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.config.list_physical_devices
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Return a list of physical devices visible to the host runtime.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Main aliases
+
`tf.config.experimental.list_physical_devices`
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.config.experimental.list_physical_devices`, `tf.compat.v1.config.list_physical_devices`
+
+
+
+
+tf.config.list_physical_devices(
+ device_type=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Physical devices are hardware devices present on the host machine. By default
+all discovered CPU and GPU devices are considered visible.
+
+This API allows querying the physical hardware resources prior to runtime
+initialization. Thus, giving an opportunity to call any additional
+configuration APIs. This is in contrast to tf.config.list_logical_devices,
+which triggers runtime initialization in order to list the configured devices.
+
+The following example lists the number of visible GPUs on the host.
+
+```
+>>> physical_devices = tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU')
+>>> print("Num GPUs:", len(physical_devices))
+Num GPUs: ...
+```
+
+However, the number of GPUs available to the runtime may change during runtime
+initialization due to marking certain devices as not visible or configuring
+multiple logical devices.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`device_type`
+ |
+
+(optional string) Only include devices matching this device
+type. For example "CPU" or "GPU".
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/optimizer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/optimizer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..bc08d93909d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/optimizer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+description: Public API for tf.config.optimizer namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.config.optimizer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.config.optimizer namespace.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`get_experimental_options(...)`](../../tf/config/optimizer/get_experimental_options.md): Get experimental optimizer options.
+
+[`get_jit(...)`](../../tf/config/optimizer/get_jit.md): Get if JIT compilation is enabled.
+
+[`set_experimental_options(...)`](../../tf/config/optimizer/set_experimental_options.md): Set experimental optimizer options.
+
+[`set_jit(...)`](../../tf/config/optimizer/set_jit.md): Set if JIT compilation is enabled.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/optimizer/get_experimental_options.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/optimizer/get_experimental_options.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..a7ab62734f0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/optimizer/get_experimental_options.md
@@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
+description: Get experimental optimizer options.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.config.optimizer.get_experimental_options
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Get experimental optimizer options.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.config.optimizer.get_experimental_options`
+
+
+
+
+tf.config.optimizer.get_experimental_options()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Refer to tf.config.optimizer.set_experimental_options for a list of current
+options.
+
+Note that optimizations are only applied in graph mode, (within tf.function).
+In addition, as these are experimental options, the list is subject to change.
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Dictionary of configured experimental optimizer options
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/optimizer/get_jit.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/optimizer/get_jit.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..391faed9000
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/optimizer/get_jit.md
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
+description: Get if JIT compilation is enabled.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.config.optimizer.get_jit
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Get if JIT compilation is enabled.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.config.optimizer.get_jit`
+
+
+
+
+tf.config.optimizer.get_jit()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Note that optimizations are only applied to code that is compiled into a
+graph. In eager mode, which is the TF2 API default, that means only code that
+is defined under a tf.function decorator.
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+If JIT compilation is enabled.
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/optimizer/set_experimental_options.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/optimizer/set_experimental_options.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..aefafe31cb7
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/optimizer/set_experimental_options.md
@@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
+description: Set experimental optimizer options.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.config.optimizer.set_experimental_options
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Set experimental optimizer options.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.config.optimizer.set_experimental_options`
+
+
+
+
+tf.config.optimizer.set_experimental_options(
+ options
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Note that optimizations are only applied in graph mode, (within tf.function).
+In addition, as these are experimental options, the list is subject to change.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`options`
+ |
+
+Dictionary of experimental optimizer options to configure.
+Valid keys:
+- layout_optimizer: Optimize tensor layouts
+e.g. This will try to use NCHW layout on GPU which is faster.
+- constant_folding: Fold constants
+Statically infer the value of tensors when possible, and materialize the
+result using constants.
+- shape_optimization: Simplify computations made on shapes.
+- remapping: Remap subgraphs onto more efficient implementations.
+- arithmetic_optimization: Simplify arithmetic ops with common
+sub-expression elimination and arithmetic simplification.
+- dependency_optimization: Control dependency optimizations. Remove
+redundant control dependencies, which may enable other optimization.
+This optimizer is also essential for pruning Identity and NoOp nodes.
+- loop_optimization: Loop optimizations.
+- function_optimization: Function optimizations and inlining.
+- debug_stripper: Strips debug-related nodes from the graph.
+- disable_model_pruning: Disable removal of unnecessary ops from the graph
+- scoped_allocator_optimization: Try to allocate some independent Op
+outputs contiguously in order to merge or eliminate downstream Ops.
+- pin_to_host_optimization: Force small ops onto the CPU.
+- implementation_selector: Enable the swap of kernel implementations based
+on the device placement.
+- auto_mixed_precision: Change certain float32 ops to float16 on Volta
+GPUs and above. Without the use of loss scaling, this can cause
+numerical underflow (see
+keras.mixed_precision.experimental.LossScaleOptimizer).
+- disable_meta_optimizer: Disable the entire meta optimizer.
+- min_graph_nodes: The minimum number of nodes in a graph to optimizer.
+For smaller graphs, optimization is skipped.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/optimizer/set_jit.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/optimizer/set_jit.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..8ab62332feb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/optimizer/set_jit.md
@@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
+description: Set if JIT compilation is enabled.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.config.optimizer.set_jit
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Set if JIT compilation is enabled.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.config.optimizer.set_jit`
+
+
+
+
+tf.config.optimizer.set_jit(
+ enabled
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Note that optimizations are only applied to code that is compiled into a
+graph. In eager mode, which is the TF2 API default, that means only code that
+is defined under a tf.function decorator.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`enabled`
+ |
+
+Whether to enable JIT compilation.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/set_logical_device_configuration.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/set_logical_device_configuration.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..89fb8f6c5a1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/set_logical_device_configuration.md
@@ -0,0 +1,148 @@
+description: Set the logical device configuration for a tf.config.PhysicalDevice.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.config.set_logical_device_configuration
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Set the logical device configuration for a tf.config.PhysicalDevice.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Main aliases
+
`tf.config.experimental.set_virtual_device_configuration`
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.config.experimental.set_virtual_device_configuration`, `tf.compat.v1.config.set_logical_device_configuration`
+
+
+
+
+tf.config.set_logical_device_configuration(
+ device, logical_devices
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+A visible tf.config.PhysicalDevice will by default have a single
+tf.config.LogicalDevice associated with it once the runtime is initialized.
+Specifying a list of tf.config.LogicalDeviceConfiguration objects allows
+multiple devices to be created on the same tf.config.PhysicalDevice.
+
+The following example splits the CPU into 2 logical devices:
+
+```
+>>> physical_devices = tf.config.list_physical_devices('CPU')
+>>> assert len(physical_devices) == 1, "No CPUs found"
+>>> # Specify 2 virtual CPUs. Note currently memory limit is not supported.
+>>> try:
+... tf.config.set_logical_device_configuration(
+... physical_devices[0],
+... [tf.config.LogicalDeviceConfiguration(),
+... tf.config.LogicalDeviceConfiguration()])
+... logical_devices = tf.config.list_logical_devices('CPU')
+... assert len(logical_devices) == 2
+...
+... tf.config.set_logical_device_configuration(
+... physical_devices[0],
+... [tf.config.LogicalDeviceConfiguration(),
+... tf.config.LogicalDeviceConfiguration(),
+... tf.config.LogicalDeviceConfiguration(),
+... tf.config.LogicalDeviceConfiguration()])
+... except:
+... # Cannot modify logical devices once initialized.
+... pass
+```
+
+The following example splits the GPU into 2 logical devices with 100 MB each:
+
+```
+>>> physical_devices = tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU')
+>>> try:
+... tf.config.set_logical_device_configuration(
+... physical_devices[0],
+... [tf.config.LogicalDeviceConfiguration(memory_limit=100),
+... tf.config.LogicalDeviceConfiguration(memory_limit=100)])
+...
+... logical_devices = tf.config.list_logical_devices('GPU')
+... assert len(logical_devices) == len(physical_devices) + 1
+...
+... tf.config.set_logical_device_configuration(
+... physical_devices[0],
+... [tf.config.LogicalDeviceConfiguration(memory_limit=10),
+... tf.config.LogicalDeviceConfiguration(memory_limit=10)])
+... except:
+... # Invalid device or cannot modify logical devices once initialized.
+... pass
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`device`
+ |
+
+The `PhysicalDevice` to configure.
+ |
+
+|
+`logical_devices`
+ |
+
+(optional) List of tf.config.LogicalDeviceConfiguration
+objects to allocate for the specified `PhysicalDevice`. If None, the
+default configuration will be used.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If argument validation fails.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+Runtime is already initialized.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/set_soft_device_placement.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/set_soft_device_placement.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..37df414d779
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/set_soft_device_placement.md
@@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
+description: Set if soft device placement is enabled.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.config.set_soft_device_placement
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Set if soft device placement is enabled.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.config.set_soft_device_placement`
+
+
+
+
+tf.config.set_soft_device_placement(
+ enabled
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+If enabled, an op will be placed on CPU if any of the following are true
+ 1. there's no GPU implementation for the OP
+ 2. no GPU devices are known or registered
+ 3. need to co-locate with reftype input(s) which are from CPU
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`enabled`
+ |
+
+Whether to enable soft placement.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/set_visible_devices.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/set_visible_devices.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..af6b08b2a96
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/set_visible_devices.md
@@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
+description: Set the list of visible devices.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.config.set_visible_devices
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Set the list of visible devices.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Main aliases
+
`tf.config.experimental.set_visible_devices`
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.config.experimental.set_visible_devices`, `tf.compat.v1.config.set_visible_devices`
+
+
+
+
+tf.config.set_visible_devices(
+ devices, device_type=None
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Specifies which `PhysicalDevice` objects are visible to the runtime.
+TensorFlow will only allocate memory and place operations on visible
+physical devices, as otherwise no `LogicalDevice` will be created on them.
+By default all discovered devices are marked as visible.
+
+The following example demonstrates disabling the first GPU on the machine.
+
+```
+>>> physical_devices = tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU')
+>>> try:
+... # Disable first GPU
+... tf.config.set_visible_devices(physical_devices[1:], 'GPU')
+... logical_devices = tf.config.list_logical_devices('GPU')
+... # Logical device was not created for first GPU
+... assert len(logical_devices) == len(physical_devices) - 1
+... except:
+... # Invalid device or cannot modify virtual devices once initialized.
+... pass
+```
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`devices`
+ |
+
+List of `PhysicalDevice`s to make visible
+ |
+
+|
+`device_type`
+ |
+
+(optional) Only configure devices matching this device type.
+For example "CPU" or "GPU". Other devices will be left unaltered.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+If argument validation fails.
+ |
+
+|
+`RuntimeError`
+ |
+
+Runtime is already initialized.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/threading.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/threading.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..0d82ae5e36c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/threading.md
@@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
+description: Public API for tf.config.threading namespace.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# Module: tf.config.threading
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Public API for tf.config.threading namespace.
+
+
+
+## Functions
+
+[`get_inter_op_parallelism_threads(...)`](../../tf/config/threading/get_inter_op_parallelism_threads.md): Get number of threads used for parallelism between independent operations.
+
+[`get_intra_op_parallelism_threads(...)`](../../tf/config/threading/get_intra_op_parallelism_threads.md): Get number of threads used within an individual op for parallelism.
+
+[`set_inter_op_parallelism_threads(...)`](../../tf/config/threading/set_inter_op_parallelism_threads.md): Set number of threads used for parallelism between independent operations.
+
+[`set_intra_op_parallelism_threads(...)`](../../tf/config/threading/set_intra_op_parallelism_threads.md): Set number of threads used within an individual op for parallelism.
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/threading/get_inter_op_parallelism_threads.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/threading/get_inter_op_parallelism_threads.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..59b049866b9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/threading/get_inter_op_parallelism_threads.md
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
+description: Get number of threads used for parallelism between independent operations.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.config.threading.get_inter_op_parallelism_threads
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Get number of threads used for parallelism between independent operations.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.config.threading.get_inter_op_parallelism_threads`
+
+
+
+
+tf.config.threading.get_inter_op_parallelism_threads()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Determines the number of threads used by independent non-blocking operations.
+0 means the system picks an appropriate number.
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Number of parallel threads
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/threading/get_intra_op_parallelism_threads.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/threading/get_intra_op_parallelism_threads.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..b83381db814
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/threading/get_intra_op_parallelism_threads.md
@@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
+description: Get number of threads used within an individual op for parallelism.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.config.threading.get_intra_op_parallelism_threads
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Get number of threads used within an individual op for parallelism.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.config.threading.get_intra_op_parallelism_threads`
+
+
+
+
+tf.config.threading.get_intra_op_parallelism_threads()
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Certain operations like matrix multiplication and reductions can utilize
+parallel threads for speed ups. A value of 0 means the system picks an
+appropriate number.
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+Number of parallel threads
+ |
+
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/threading/set_inter_op_parallelism_threads.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/threading/set_inter_op_parallelism_threads.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..ef7d7e54004
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/threading/set_inter_op_parallelism_threads.md
@@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
+description: Set number of threads used for parallelism between independent operations.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.config.threading.set_inter_op_parallelism_threads
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Set number of threads used for parallelism between independent operations.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.config.threading.set_inter_op_parallelism_threads`
+
+
+
+
+tf.config.threading.set_inter_op_parallelism_threads(
+ num_threads
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Determines the number of threads used by independent non-blocking operations.
+0 means the system picks an appropriate number.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`num_threads`
+ |
+
+Number of parallel threads
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/threading/set_intra_op_parallelism_threads.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/threading/set_intra_op_parallelism_threads.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..bbcfc8f28de
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/config/threading/set_intra_op_parallelism_threads.md
@@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
+description: Set number of threads used within an individual op for parallelism.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.config.threading.set_intra_op_parallelism_threads
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Set number of threads used within an individual op for parallelism.
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Compat aliases for migration
+
See
+Migration guide for
+more details.
+`tf.compat.v1.config.threading.set_intra_op_parallelism_threads`
+
+
+
+
+tf.config.threading.set_intra_op_parallelism_threads(
+ num_threads
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Certain operations like matrix multiplication and reductions can utilize
+parallel threads for speed ups. A value of 0 means the system picks an
+appropriate number.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`num_threads`
+ |
+
+Number of parallel threads
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/constant.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/constant.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..0999c1e1bc8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/constant.md
@@ -0,0 +1,202 @@
+description: Creates a constant tensor from a tensor-like object.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.constant
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Creates a constant tensor from a tensor-like object.
+
+
+tf.constant(
+ value, dtype=None, shape=None, name='Const'
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Note: All eager tf.Tensor values are immutable (in contrast to
+tf.Variable). There is nothing especially _constant_ about the value
+returned from tf.constant. This function it is not fundamentally different
+from tf.convert_to_tensor. The name tf.constant comes from the symbolic
+APIs (like tf.data or keras functional models) where the `value` is embeded
+in a `Const` node in the tf.Graph. tf.constant is useful for asserting
+that the value can be embedded that way.
+
+If the argument `dtype` is not specified, then the type is inferred from
+the type of `value`.
+
+```
+>>> # Constant 1-D Tensor from a python list.
+>>> tf.constant([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
+
+>>> # Or a numpy array
+>>> a = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
+>>> tf.constant(a)
+
+```
+
+If `dtype` is specified the resulting tensor values are cast to the requested
+`dtype`.
+
+```
+>>> tf.constant([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6], dtype=tf.float64)
+
+```
+
+If `shape` is set, the `value` is reshaped to match. Scalars are expanded to
+fill the `shape`:
+
+```
+>>> tf.constant(0, shape=(2, 3))
+
+>>> tf.constant([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6], shape=[2, 3])
+
+```
+
+tf.constant has no effect if an eager Tensor is passed as the `value`, it
+even transmits gradients:
+
+```
+>>> v = tf.Variable([0.0])
+>>> with tf.GradientTape() as g:
+... loss = tf.constant(v + v)
+>>> g.gradient(loss, v).numpy()
+array([2.], dtype=float32)
+```
+
+But, since tf.constant embeds the value in the tf.Graph this fails for
+symbolic tensors:
+
+```
+>>> i = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=[None, None])
+>>> t = tf.constant(i)
+Traceback (most recent call last):
+...
+NotImplementedError: ...
+```
+
+tf.constant will _always_ create CPU (host) tensors. In order to create
+tensors on other devices, use tf.identity. (If the `value` is an eager
+Tensor, however, the tensor will be returned unmodified as mentioned above.)
+
+#### Related Ops:
+
+
+
+* tf.convert_to_tensor is similar but:
+ * It has no `shape` argument.
+ * Symbolic tensors are allowed to pass through.
+
+ ```
+ >>> i = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=[None, None])
+ >>> t = tf.convert_to_tensor(i)
+ ```
+
+* tf.fill: differs in a few ways:
+ * tf.constant supports arbitrary constants, not just uniform scalar
+ Tensors like tf.fill.
+ * tf.fill creates an Op in the graph that is expanded at runtime, so it
+ can efficiently represent large tensors.
+ * Since tf.fill does not embed the value, it can produce dynamically
+ sized outputs.
+
+
+
+
+Args |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`value`
+ |
+
+A constant value (or list) of output type `dtype`.
+ |
+
+|
+`dtype`
+ |
+
+The type of the elements of the resulting tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`shape`
+ |
+
+Optional dimensions of resulting tensor.
+ |
+
+|
+`name`
+ |
+
+Optional name for the tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Returns |
|---|
+
+|
+A Constant Tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Raises |
|---|
+
+
+|
+`TypeError`
+ |
+
+if shape is incorrectly specified or unsupported.
+ |
+
+|
+`ValueError`
+ |
+
+if called on a symbolic tensor.
+ |
+
+
+
diff --git a/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/constant_initializer.md b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/constant_initializer.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..ed18cdae3bf
--- /dev/null
+++ b/site/en/api_docs/python/tf/constant_initializer.md
@@ -0,0 +1,282 @@
+description: Initializer that generates tensors with constant values.
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+# tf.constant_initializer
+
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Initializer that generates tensors with constant values.
+
+Inherits From: [`Initializer`](../tf/keras/initializers/Initializer.md)
+
+
+ View aliases
+
+Main aliases
+
`tf.initializers.Constant`, `tf.initializers.constant`, `tf.keras.initializers.Constant`, `tf.keras.initializers.constant`
+
+
+
+
+tf.constant_initializer(
+ value=0
+)
+
+
+
+
+
+
+Initializers allow you to pre-specify an initialization strategy, encoded in
+the Initializer object, without knowing the shape and dtype of the variable
+being initialized.
+
+tf.constant_initializer returns an object which when called returns a tensor
+populated with the `value` specified in the constructor. This `value` must be
+convertible to the requested `dtype`.
+
+The argument `value` can be a scalar constant value, or a list of
+values. Scalars broadcast to whichever shape is requested from the
+initializer.
+
+If `value` is a list, then the length of the list must be equal to the number
+of elements implied by the desired shape of the tensor. If the total number of
+elements in `value` is not equal to the number of elements required by the
+tensor shape, the initializer will raise a `TypeError`.
+
+#### Examples:
+
+
+
+```
+>>> def make_variables(k, initializer):
+... return (tf.Variable(initializer(shape=[k], dtype=tf.float32)),
+... tf.Variable(initializer(shape=[k, k], dtype=tf.float32)))
+>>> v1, v2 = make_variables(3, tf.constant_initializer(2.))
+>>> v1
+
+>>> v2
+
+>>> make_variables(4, tf.random_uniform_initializer(minval=-1., maxval=1.))
+(, >> value = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
+>>> init = tf.constant_initializer(value)
+>>> # Fitting shape
+>>> tf.Variable(init(shape=[2, 4], dtype=tf.float32))
+
 + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ +
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ +
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ +
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+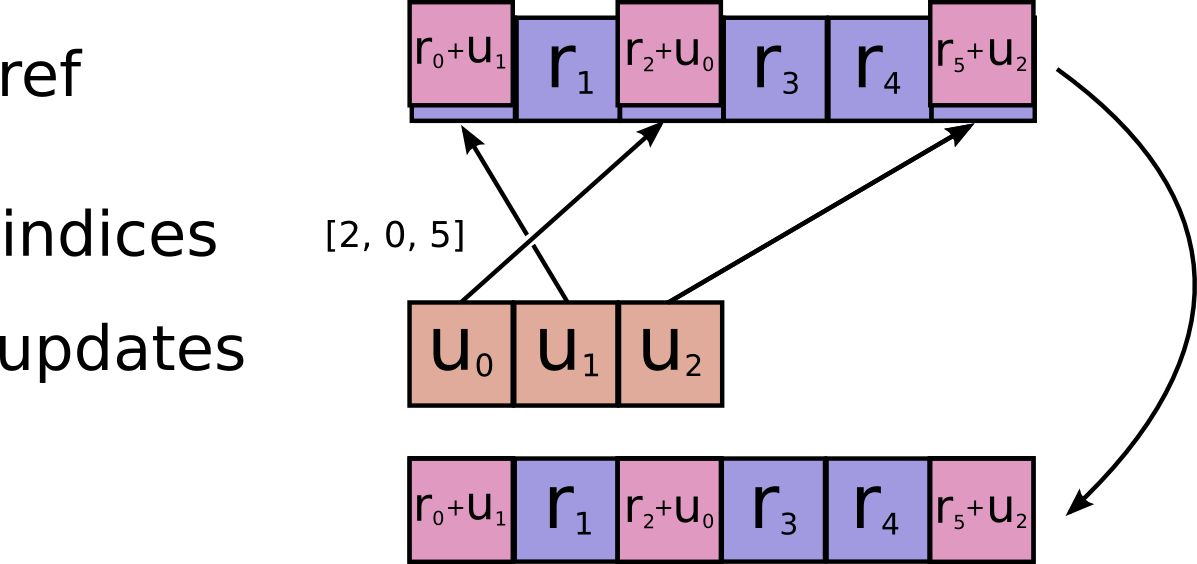 +
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+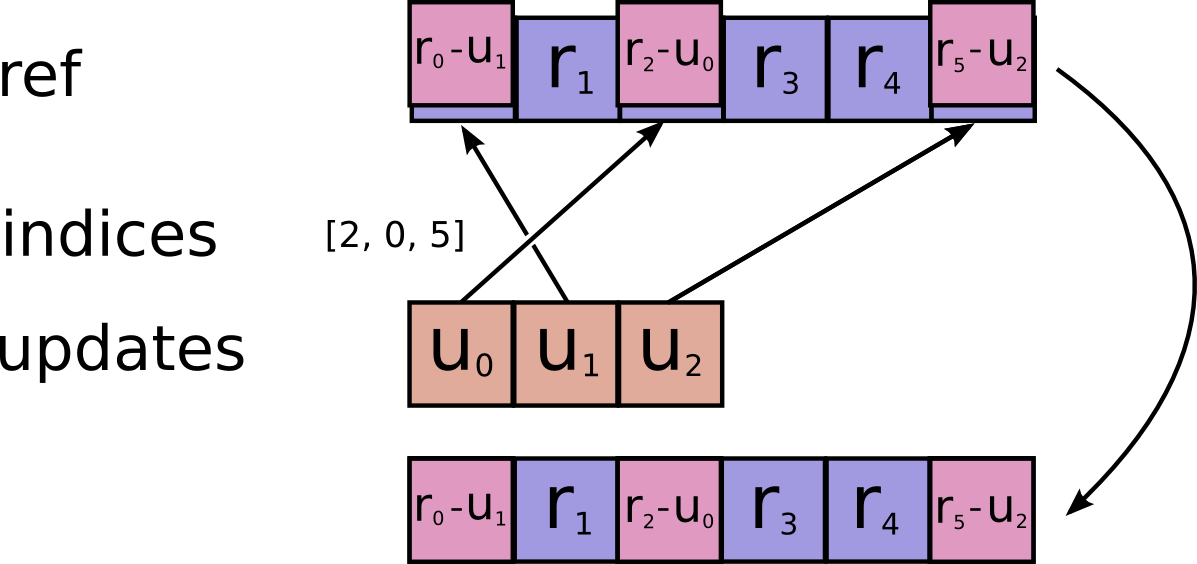 +
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ +
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+ + View source on GitHub
+
+
+ View source on GitHub
+
+